Abstract
The green biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (GBS ZnO NPs) using Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract assisted by ultrasonic irradiation was reported in this research work. The green biosynthesized ZnO NPs were characterized using different techniques and the results revealed the synthesis of hexagonal wurtzite crystal of GBS ZnO nanoparticles; per the XRD measurement, with average practice size of 90 ± 10 nm; based on both SEM and TEM images, and with specific surface area of 14.23 m2/g; per the nitrogen gas adsorption/desorption isotherms. The antibacterial activity of the prepared GBS ZnO NPs was explored against S. aureus and E. coli bacteria using different evaluation methods; disc diffusion, column (filter), and aqueous solution, and the results showed the effective antibacterial activities against S. aureus and E. coli bacteria, as the inhibition zones were 15 mm and 11 mm for the E. coli and S. aureus, respectively. Moreover, the anticancer activity of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs was evaluated on two different cancer cells; human colon cancer cell lines (HCT-116) and the human liver cancer (HepG2) cells, and the experiments showed that GBS ZnO NPs had an outstanding cytotoxic effect on both cancer cell lines, as well as dose-dependent behavior, as the viability of the cancer cells decreased by using GBS ZnO NPs at concentrations of 10 and 20 µg/mL. Cell lines (HCT-116) and the human liver cancer (HepG2) cells, and the experiments showed that GBS ZnO NPs had an outstanding cytotoxic effect on both cancer cell lines, as the GBS ZnO NPs enhanced the cytotoxicity mechanism by generating ROS as the nanoparticles interact with cells, lower its cellular defense mechanism, and accordingly cause apoptosis to the cell.
1. Introduction
Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles have become increasingly important in many of the nanotechnology and biological applications such as antibacterial, anticancer, cell imaging, drug delivery and biosensing [1,2]. Among the metal oxide nanoparticles used, zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were found to be easily fabricated, environmentally friendly, and non-toxic [3,4], but most of the traditional methods used for ZnO NPs preparation is mostly based on the wet chemical routes which involve the use of various hazardous chemicals through tedious and long multistep processes associated with the production of huge quantities of hazardous byproducts, and accordingly harmful chemical waste [5]. Recently, the application of more eco-friendly methods for the preparation brought more attention to replacing the hazardous traditional chemicals with more green and eco-friendly extracts of different natural materials such as plants, fungus, bacteria, and algae, in order to prepare ZnO NPs, which showed comparable, and higher activities compared with the traditional ones. For example, various plants part extracts have been used for the green biosynthesis of ZnO NPs, such as Abelmoschus esculentus (okra) mucilage [6], Azadirachta indica (Neem) leaf [7], Cuminum cyminum (cumin) [8], Mangifera indica (mango) leaves [9], Calotropis gigantea leaves [10], Aloe socotrina leaf [11], Cyanometra ramiflora leaves [12], Ganoderma lucidum [13], and Ziziphus jujube (Sidr or Nabq) [14,15,16], where the plant extracts are employed as stabilizing and capping agents to prevent the agglomeration of the nanoparticles and to stabilize the formed nanoparticles [17]. Moreover, eco-friendly prepared zinc oxide nanoparticles were used for biomedical applications [18,19], antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer purposes [20,21,22], in addition to drug delivery [11]. Furthermore, it is noteworthy to mention that Ziziphus jujube is one of the very common plants in the region and is characterized by its different medicinal features [23,24,25,26], and the existence of different long chains of natural compounds which could act as capping and stabilizing agents, and prevent the agglomeration of the nanoparticles [15,16,27,28].
Additionally, the ultrasonic-assisted route for nanoparticle preparation was the focus of the scientific community attributable to the outstanding preparation rate due to the tremendous heating effect with high pressure, resulting from the collapse of the acoustic cavitation [29]. For instance, ZnO NPs prepared through ultrasonic-assisted methods exhibited exceptional characteristics and activities [30,31,32,33]. It is hypothesized that the combination of the fast-heating effect, application of ultrasonic, and the use of a green and eco-friendly route for the ZnO NPs preparation could result in nanoparticles with extraordinary biological activity compared to the ZnO NPs prepared through traditional routes.
Herein, a facile and efficient strategy for the eco-friendly and robust preparation of ZnO nanoparticles using Ziziphus jujuba leaf extract and ultrasonic-assisted with high purity was explored. The morphological and structural characteristics of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs were investigated, and additionally, the antibacterial efficacy of ZnO NPs against two pathogenic bacteria; gram-positive S. aureus and gram-negative E. coli were explored. The green biosynthesized ZnO NPs were also explored for anticancer activity on HepG2 (liver cancer) and HCT-116 (colon cancer) cells as liver and colon cancer are major health problems worldwide.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The leaves of Ziziphus jujuba were collected from Jeddah in October 2019. Zinc acetate was procured from Sigma-Aldrich(Oakville, ON, Canada). Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC, 25923), and Escherichia coli (ATCC, 25922) was obtained from King Abdulaziz University, King Fahd center for medical research, Jeddah City. The human colon cancer cell lines (HCT-116) and the human liver cancer (HepG2) were obtained from the King Fahd Center for Medical Research, King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia, which was originally provided from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Cell viability was measured by a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8, Lot. No. LE612, Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Rockville, MD 20850, United States). Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM, Biosera, Nuaillé, France), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, South America origin, FB-1001/100) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Biosera).
2.2. Preparation of Ziziphus jujuba Leaf and Green Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs
The leaves of Ziziphus jujuba were washed with tap water, followed by deionized water, and then were later dried in air. The cleaned dried leaves were cut into small pieces and then ground, and 5.0 g was placed in a beaker containing 100.0 mL of deionized water, and the mixture was then boiled for 20.0 min, cooled to room temperature, and was centrifuged at 3600 rpm for 30 min twice to achieve a clear extract. The filtrate was stored at 277 K until required for further analysis. For Ziziphus jujuba leaf extract mediated green biosynthesis of ZnO NPs, 250 mL of 0.2 M (CH3CO2)2Zn solution and 250 mL of 0.5 M sodium hydroxide solution were prepared using the Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract. The sodium hydroxide solution was then added drop-wise using a burette to the (CH3CO2)2Zn solution at room temperature under stirring, followed by a probe sonication using Sonicator Ultrasonic Processor Part No. S-4000, ½” Horn, 5” L x1.5” Dia. (12.7 cm x 3.8 cm), Titanium Alloy (Misonix, Inc.). The ultrasound amplitude was set at 75% and ZnO samples were obtained at 20 min, and the colloidal zinc oxide precipitate was formed. The colloidal precipitate of zinc oxide was separated by centrifugation at 3900 rpm for 30 min and washed three times with distilled water, followed by ethanol, and then was air dried at 333 K for 24 h.
2.3. Characterization of ZnO NPs
Philips X-pert pro diffractometer was used for the x-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements of the ZnO NPs patterns, and the crystal size was estimated using Scherrer equation [34]. The FT-IR spectra were recorded using FTIR spectrophotometer (Spectrum 100, Perkin Elmer, Shelton, CT, USA). The zeta potential was obtained through measurement of the electrophoretic mobility of the particles using a Zeta sizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments GmbH, Malvern WR14 1XZ United Kingdom). The sample holder temperature was maintained at 298 K. LYRA3, Tescan (Kohoutovice, Czech Republic) scanning electron microscopy (SEM) operated at 20 kV, and JEOL JEM-1011 high-resolution transmission electron microscope (TEM) was used to explore the morphological and topographical features of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs. NOVA3200e (Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL USA) was used to measure the texture properties of the green biosynthesis ZnO NPs using the nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms at 77 K.
2.4. Antibacterial Activity
The antibacterial activity of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs towards two different well-known human pathogens; gram-positive S. aureus and gram-negative E. coli were studied by different methods: disc diffusion, column, and aqueous solution.
2.4.1. Antibacterial Activity by Disc Diffusion Method
The antibacterial activity of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs for two different well-known human pathogens; gram-positive S. aureus and gram-negative E. coli, was tested by the disc diffusion method as per the following: 2.8 g of nutrient agar was dissolved in 100.0 mL of sterile distilled water and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 7.2, then autoclaved at 394 K for 15 min, then 20 mL of molten agar was poured into the sterile Petri plate and allowed to solidify. Some 6 mm discs were prepared using a Whatman No:1 filter paper by punching and putting in vials and sterilizing at 423 K for 15 min, then the antibacterial activity was evaluated by measuring the inhibition zone. Preculture of each selected bacterial strain was prepared using 5 mL 0.9% normal saline in a test tube and a single colony from the bacteria agar plate. The bacterial strains were swabbed on nutrient agar plates. 1An amount of 100 mg of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs samples per 1 mL deionized water was sonicated for 60 min to form a suspension, and then the discs were impregnated with (50 µL/disc) of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs, where deionized water was used as a control, all the filter paper discs were allowed to dry for 60 min in a sterile environment. All the filter paper discs were placed on nutrient agar plates and left for 15 min, then incubated at 300 K for 24 h, and finally, the antibacterial activity was evaluated by measuring the diameter of the inhibition zone (IZ) around the disc.
2.4.2. Antibacterial Activity by Column (Filter) Method
The effect of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs on the bacteria at aqueous solutions was investigated by using the column method, as the solid green biosynthesized ZnO NPs put in a small glass pipette and used as a (column) filter with glass wool, then the 20.0 mL of E. coli bacteria solution was filtered using the above-mentioned glass pipette, and the presence of the bacteria was measured at the filtrate by measuring the optical density at 600 nm [35,36].
2.4.3. Antibacterial Activity by Aqueous Solution Method
The effect of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs on the bacteria E. coli in a liquid medium was investigated by examining the growth of bacterial cells in the presence of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs as the following: 20 mL of nutrient broth was inoculated with fresh growing bacteria colonies on agar plates. The culture broth was incubated in a shaking incubator for 24 h at 300 K, and subsequently, an aliquot was transferred to Erlenmeyer flasks that contain 20 mL nutrient broth amended with different concentrations of zinc oxide nanoparticles. All the flasks were then incubated in a shaker at 300 K, and at 200 rpm. The control experiment was performed using nutrient broth without zinc oxide nanoparticles. The growth of the bacteria was examined by measuring the optical density at 600 nm after 24 h [35,36].
2.5. Cytotoxicity Studies of ZnO NPs
The human colon cancer cell lines (HCT-116) and the human liver cancer (HepG2) cells were used to determine the cell viability against ZnO NPs exposure. HCT-116 and HepG2 cells were cultured in DMEM in the presence of Fetal Bovine Serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin antibiotics. The cells were grown in a CO2 incubator containing at 300 K, 5% CO2 and 95% air. The cells were subcultured at the 3–4-day interval, then were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 104 cells/well, and the cell viability was measured by a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8). After one day exposure of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs, the 5-μL kit-8 solution was added and incubated for 70.0 min. By a microplate reader (BioTek, USA), the cell viabilities were measured at 450 nm. The percentage (%) viability is calculated according to the following equation:
where OD is the optical densities.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticles Formation
The mechanism of the green biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract assisted by ultrasonic irradiation could be explained as the following. It is well known that Ziziphus jujube plant contains high concentrations of phytochemicals such as saponins, tannins, phenolic compounds, alpha-tocopherol beta-carotene, terpenoids, alkaloids, sterols, flavonoids, and fatty acids which act as both reducing agents as well as capping agents, and prevent the agglomeration of the ZnO NPs due to the existence of long-chain natural products in the plant extract [28,29]. These compounds may reduce the zinc ions (Zn2+) to the metallic zero valence zinc (Zn0) and upon the heating process, the metallic zinc could be oxidized to ZnO NPs. Additionally, a complexation could occur between the zinc ions present in the solution and any Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract phytochemicals such as polyphenols, followed by the formation of zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)2) through the hydrolysis process and upon heating, the complex decomposes and forms stable ZnO NPs [15,16,17,37].
Also, the application of the ultrasonic as a source of heating after the precipitation of the Zn(OH)2 could assist in the formation of a homogenized solution, which enhanced the dehydration of Zn(OH)2 and the fast nucleation of ZnO as well as promoting defects in ZnO crystals under the influence of intense mechanical action caused by the ultrasonic cavitation, as the nanoparticles are exposed not only to the action of electromagnetic fields, but also to shock waves during the collapse of cavitation bubbles, and the ultrasonic energy could be released into the reactive solution via high-energy jets and provide extreme turbulent flows as well as high extensive mixing, which prevents the agglomeration to form clusters or large structures of zinc oxide [38,39]. This directly leads to and facilitates the formation of the crystalline structure of ZnO NPs without using calcination.
3.2. Nanoparticles Characterization
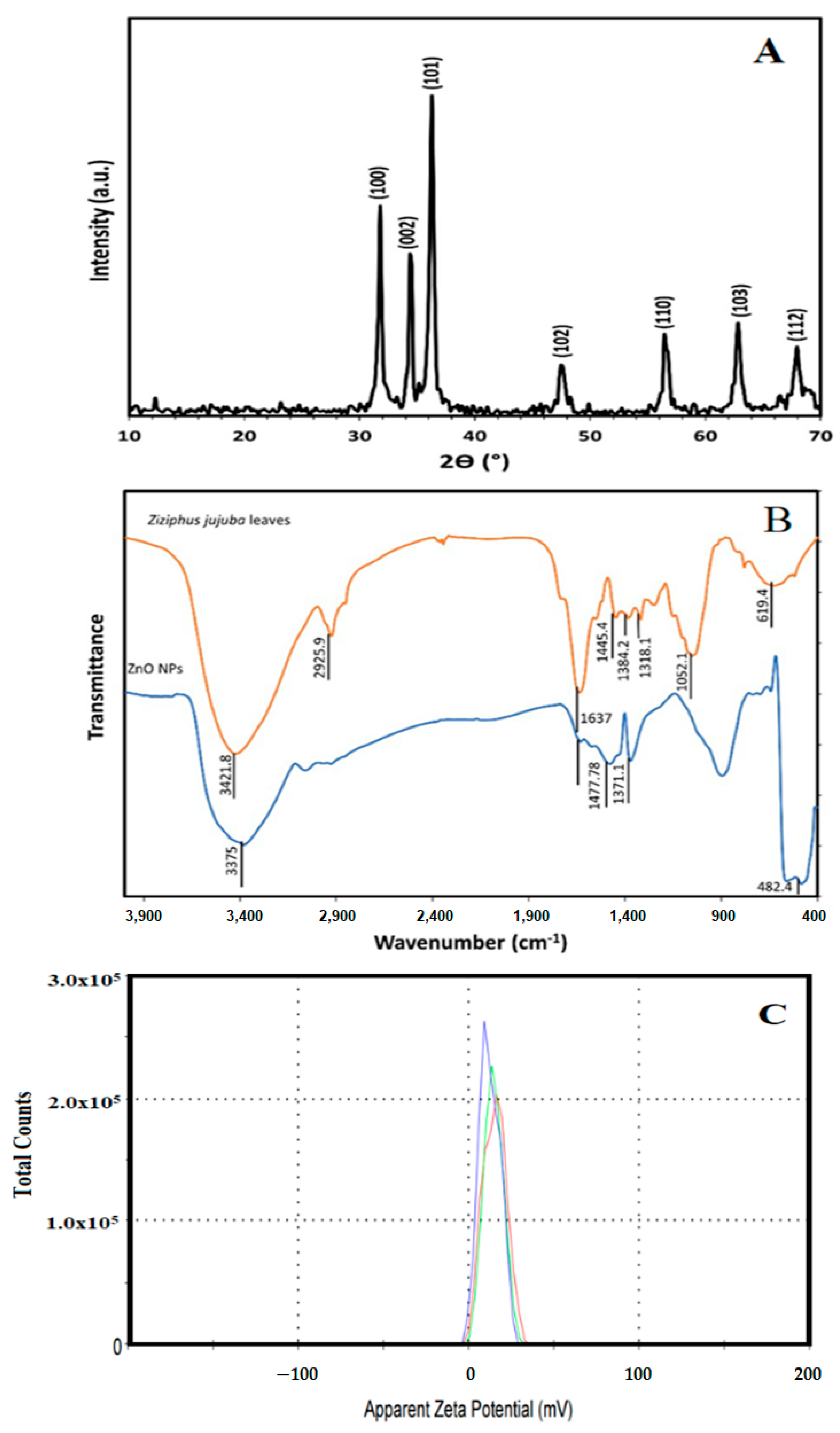
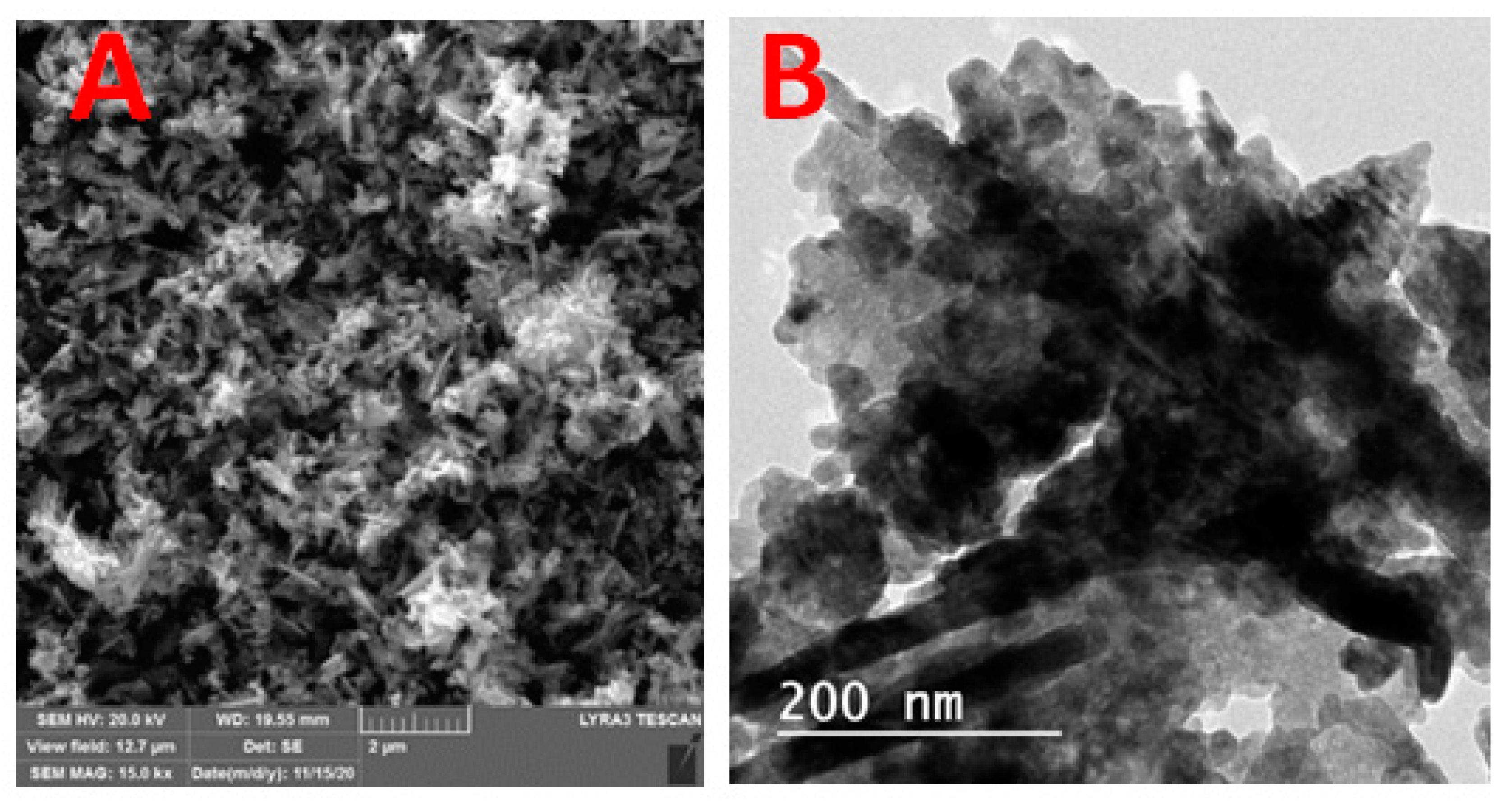
Figure 1A illustrates the XRD patterns of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs where the characteristic peaks of hexagonal wurtzite ZnO (JCPDS file no.36-1451) were identified by the three main diffraction peaks related to the (100), (002), and (101) crystal planes at 2θ = 31.73°, 34.38°, and 36.20°. Using the Scherer equation, the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs calculated crystallite size was 25.1 nm. Figure 1B showed the FT-IR spectra of the Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract and green biosynthesized ZnO NPs, where many different absorption peaks were present. For the Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract FT-IR spectrum, at 3421 cm−l, a strong absorption peak resulted from O–H groups stretching attributed to the presence of phenols, alcohols, carbohydrates, etc., within the Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract [40]. Another two peaks at 2925 cm−1 and 1637 cm−1 attributed to the ν (=C–H) and ν (C=C) stretching vibration. Additionally, another absorption peak appeared at 1637 cm−1, most likely due to the surface-adsorbed water molecule. Moreover, C–S, R–C–CH3 stretching for sulfur compounds or δ(C–H) bending vibration were presented at 619 cm−1. Similarly, the stretching vibration of in-plane bending vibration of ν (O–H), and δ (O–H) bands at 1384 cm−1 and 3421 cm−4, respectively were present. Moreover, the skeletal C–O and C–C vibration bands of the pyrinoid ring and glycosidic at 1052 cm−1 were pronounced [41]. Meanwhile, the FT-IR spectrum of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs was analyzed to confirm the purity and phase transformation of the ZnO (Figure 1B). The green biosynthesized ZnO NPs FT-IR spectrum showed the presence of surface hydroxyl groups due to the presence of a trace amount of water at 3400 cm−1 was present. Also, asymmetric and symmetric C=O stretching modes bands centered at about 1640, 1480 and 1370 were present. Moreover, the presence of peaks in the region between 600 and 450 cm−1 are assigned to metal oxygen vibration (Zn–O) of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs [42]. The surface charge of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs was determined by Zeta Potential analysis (Figure 1C). The ZnO NPs showed a mean Zeta Potential of +11.9 mV indicating that they are moderately stable. A large positive value of Zeta Potential indicates better physical colloidal stability due to the electrostatic repulsions between the individual particles. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs are presented in Figure 2, which showed the irregular shape and size of the synthesized nanoparticles which may be attributed to the tremendous heating effect with high-pressure, resulting from the collapse of the acoustic cavitation [30]. The average diameter of the particle size was 90 ± 10 nm, based on both SEM (Figure 2A) and TEM (Figure 2B) images. The average diameter of the nanoparticles was estimated manually by measuring the diameters of 12 particles, eliminating the highest and lowest values, then determining the average using the other 10 readings, and the results revealed the average diameter of 90 ± 10 nm. The nitrogen gas adsorption/desorption isotherms at 77 K were used to determine the specific surface area of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs by applying the BET equation [43], and were found to be 14.23 m2/g, with average pore volume, and pore diameter of 0.000463 cm3/g and 281.547 Å, respectively.
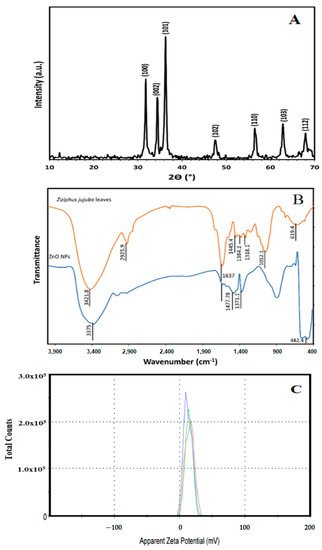
Figure 1.
X-ray diffraction pattern of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs (A), FT-IR spectra of Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract and green biosynthesized ZnO NPs (B), and the zeta potential measurement of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs (C).
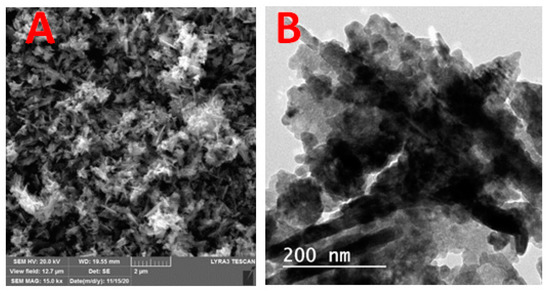
Figure 2.
Scanning Electron Microscope (A) and transmission Electron Microscope (B) micrographs of ZnO NPs.
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of Green Biosynthesized ZnO NPs
The antibacterial activity of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs to gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria was investigated by different methods; disc diffusion, column, and aqueous solution. According to the previous study of ZnO NPs antibacterial activity [44], it was found that the antibacterial activity of ZnO NPs enhanced with increasing interaction time, and increasing powder concentration, as well as decreasing particle size, in addition to the bacteria type (gram-positive or gram-negative). Generally, bacteria are characterized by a cytoplasm, cell wall, and cell membrane. It is well known that the gram-negative bacteria wall is composed of two cell membranes; an outer membrane and a plasma membrane with a thin layer of peptidoglycan with a thickness of 7–8 nm, whereas the gram-positive bacteria contain one cytoplasmic membrane with a multilayer of peptidoglycan polymer, and a thicker cell wall of 20–80 nm [45]. The advantages of ZnO NPs as an antibacterial agent are their greater effectiveness on bacteria pathogens, lower toxicity and heat resistance. ZnO NPs were described by various studies as non-toxic; this aspect enhanced their applications as an antibacterial agent and pernicious to the microorganisms [46,47].
3.3.1. Disc Diffusion Method
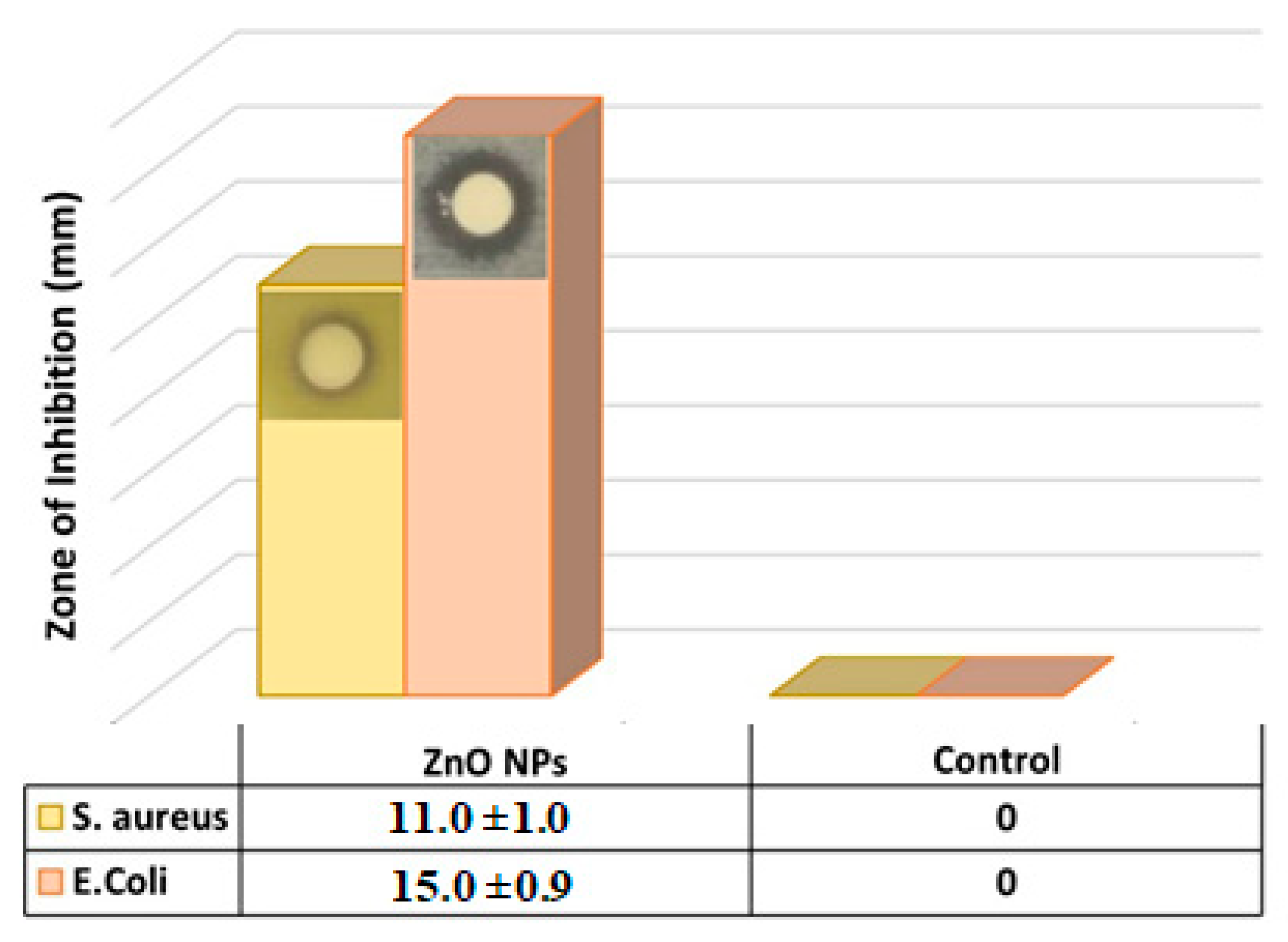
The antibacterial activity of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs against two different human pathogens was tested by the disc diffusion method and deionized water as control, and the antibacterial activity was evaluated by measuring the inhibition zones. Figure 3 revealed that E. coli showed a greater significant inhibition zone of 15.0 ± 0.9 mm in the presence of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs, whereas S. aureus showed a less significant inhibition zone of 11.0 ± 1.0 mm, which clearly indicated the antibacterial effect of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs. Due to the high antibacterial activity and efficiency of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs on the E. coli compared to the S. aureus, the rest of the experiments exploring the antibacterial activities were conducted on the E. coli only.
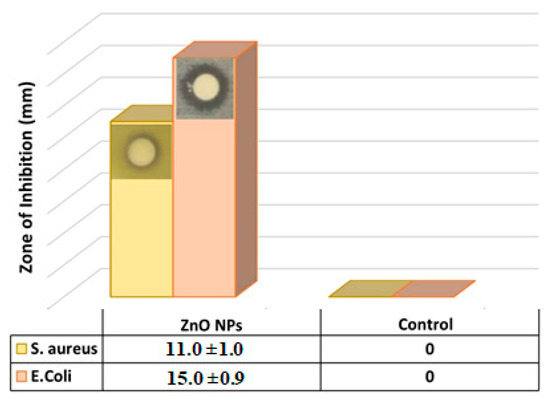
Figure 3.
Inhibition Zone produced by green biosynthesized ZnO NPs against S. aureus and E. coli bacteria (the reported values are average and based on four measurements).
3.3.2. Column (Filter) Method
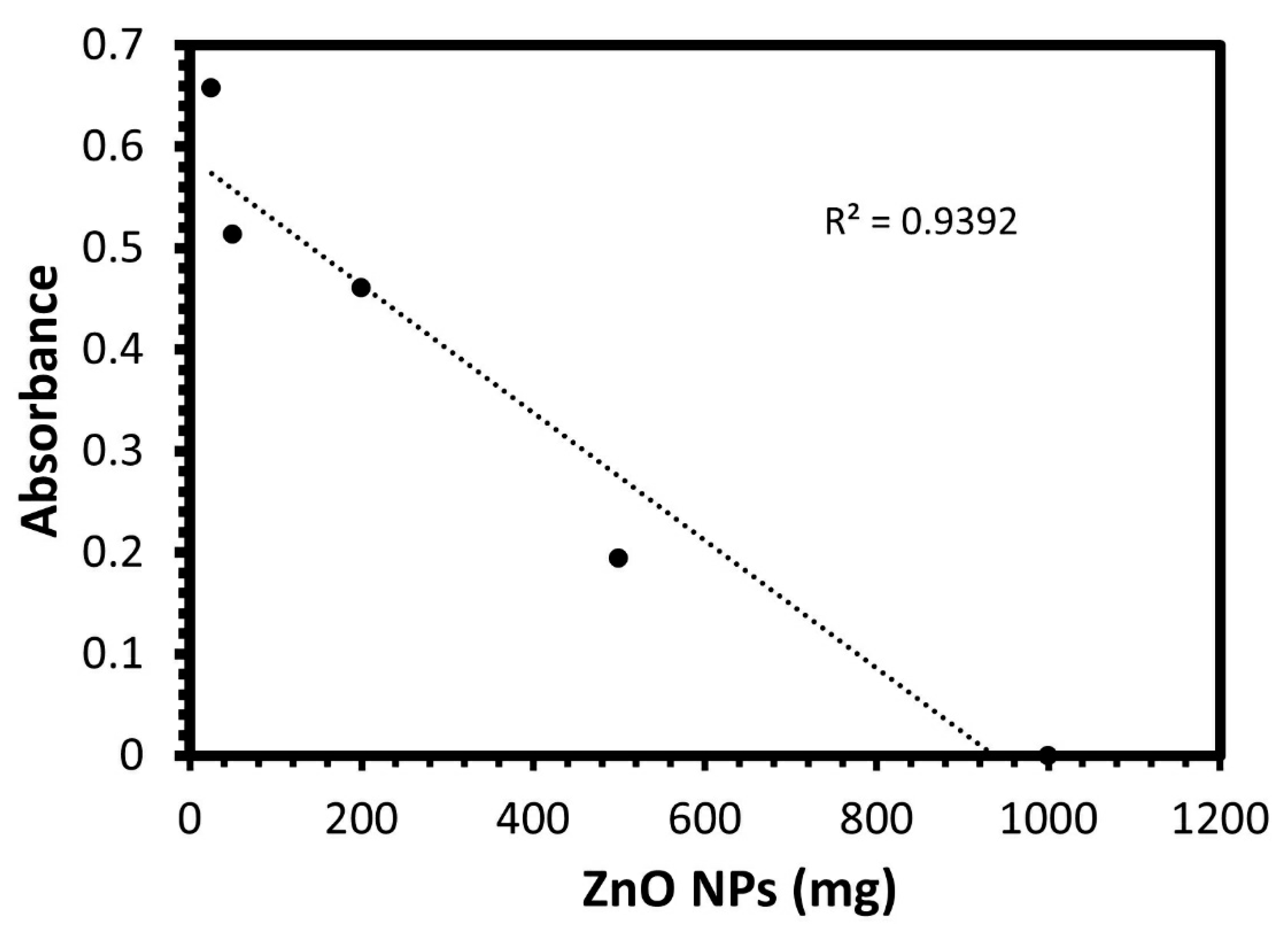
The column method was performed to explore the inhibition efficacy of the ZnO NPs to the bacteria in water, as the disc diffusion method gives the antibacterial effect only based on the inhibition zone, but most importantly is to examine this inhibition effect in real samples containing the bacteria such as water. Accordingly, the effect of the weight of ZnO NPs on bacteria at aqueous solutions by using the column method was investigated. The antibacterial activity was studied at different dosages of ZnO NPs:(1, 0.5, 0.02, 0.05, 0.025) g, and the optical density of E. coli was measured at 600 nm and recorded in Table 1 and Figure 4. It was observed that the bacteria were mostly purified with the ZnO NPs filter when the weight of zinc oxide was 1 g, indicating the ability of the ZnO NPs to retain the bacteria and produce pure water, with no sign of bacteria.

Table 1.
The value of absorbance for E. coli bacteria in various dosages of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs.
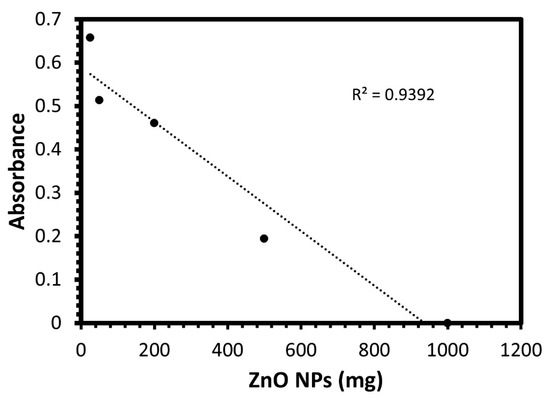
Figure 4.
The optical density at 600 nm for E. coli bacteria in various dosages of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs.
3.3.3. Aqueous Solution Method
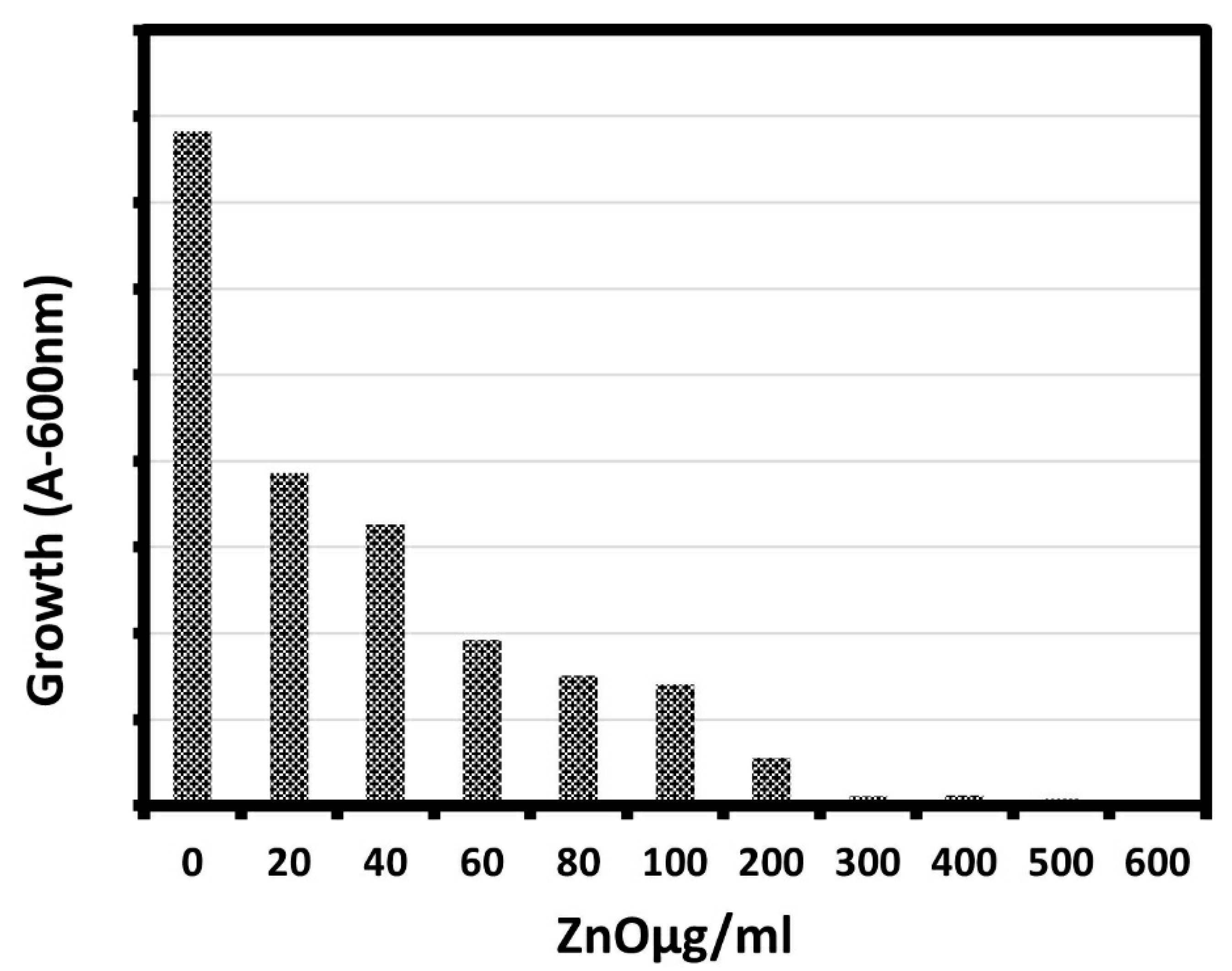
The effect of different concentrations of biosynthesized ZnO NPs against E. coli was studied using the shake flask method as a function of ZnO concentration as shown in Figure 5 and Table 2. It is clear from the figure and the table that the growth of the bacterial cells in presence of ZnO NPs was lower than that of cells in the control, indicating that ZnO NPs could inhibit the growth of bacterial cells. The percentage of bacterial growth decreased to 0.32% for the E. coli with increasing the ZnO NPs concentration, as the growth of E. coli bacterial cells significantly inhibited with the increase of ZnO NP concentration from 20 μg/mL to 600 μg/mL, and the maximum reduction in bacterial growth was observed at 600 μg/mL. Moreover, there was a sharp reduction in the growth of E. coli with an increase in the concentration of ZnO NPs, which agreed well with previous study [48].
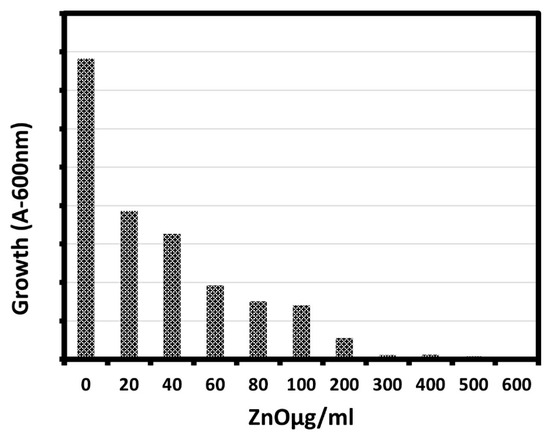
Figure 5.
Growth of bacteria (E. coli) exposed to various concentrations of ZnO NPs (20–600 μg/mL).

Table 2.
Antibacterial activity of ZnO NPs aqueous solution method (using nutrient broth shake flask test).
The above results, which showed the efficient inhibition of the bacterial activity of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs, especially in the case of the gram-negative bacteria E. coli, could be attributed to different reasons. E. coli is a gram-negative bacterium; the cell wall is composed of a single layer of peptidoglycan enclosed by the outer membrane, which facilitates the interaction with NPs and eases its destruction. In contrast, S. aureus is a gram-positive bacterium, and it is very difficult to destroy the thick cell wall as it consists of many layers of peptidoglycan. The inhibition mechanism of the ZnO NPs could be attributed to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), OH− (hydroxyl radicals), and O2 −2 (peroxide), as the ROS could cause damage to the cell as a result of the ZnO NPs localized interaction. This interaction usually enhances the membrane permeability, and the internalization of ZnO NPs due to the loss of proton motive force, as well as the uptake of toxic dissolved zinc ions. These actions may lead to the weakness of the mitochondria, lower the intracellular outflow, and release gene expression of oxidative stress which causes eventual cell growth inhibition and cell death [49,50]. Also, the enhancement in the antibacterial activity can be attributed to surface defects on the ZnO abrasive surface texture, which could be produced in this study, due to the application of the ultrasonic treatment during the preparation process [39,40]. In addition, the bacterial inhibition in the presence of the green biosynthesized ZnO NPs may be due to the enhancement in the bacterial membrane permeability for the entry of abrasive texture ZnO NPs, and ultimately causes disorganization of the membrane and changes at the protein level occurs, which leads to the inhibition of cellular metabolism causing the bacterial cell death [50]. Moreover, the toxicity of green biosynthesized ZnO NPs against the E. coli is intensified as a result of the persistent contact between the bacterial cellular membrane and the nanoparticles [51]. The zeta potential measurement showed that green biosynthesized ZnO NPs were positively charged, which could bind more tightly to negatively charged bacterial surfaces (E. coli) and show higher antimicrobial effects [52,53]. Moreover, it was reported that the toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles on the bacterial cell may be attributed to the creation of a positive zeta potential that is completely different from the other biological sources employed for the preparation of the nanoparticle [54]. The ZnO NPs penetration into the bacterial membrane usually leads to the respiratory enzymes’ deactivation and outflow of cytoplasmic contents enhancement, which causes membrane damage and leads to the death of the bacteria [7].
3.4. Cytotoxicity Studies of Synthesized ZnO NPs
The cytotoxicity of ZnO was studied on two kinds of human cell cancer, human colon cancer (HCT-116) and human liver cancer (HepG2), and the cell viability was measured by a cell counting kit-8.
3.4.1. The Human Colon Cancer (HCT-116) Cell Viability
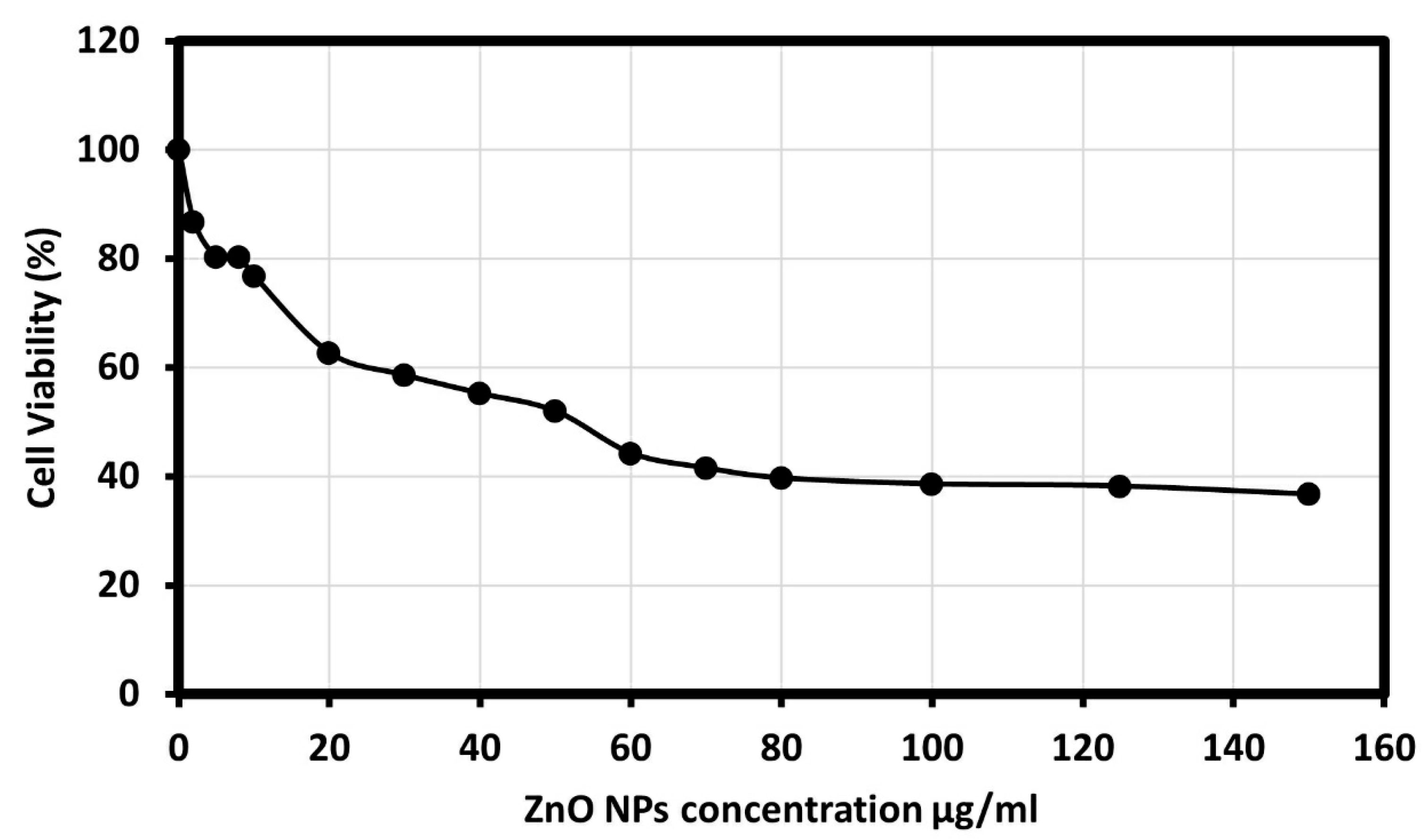
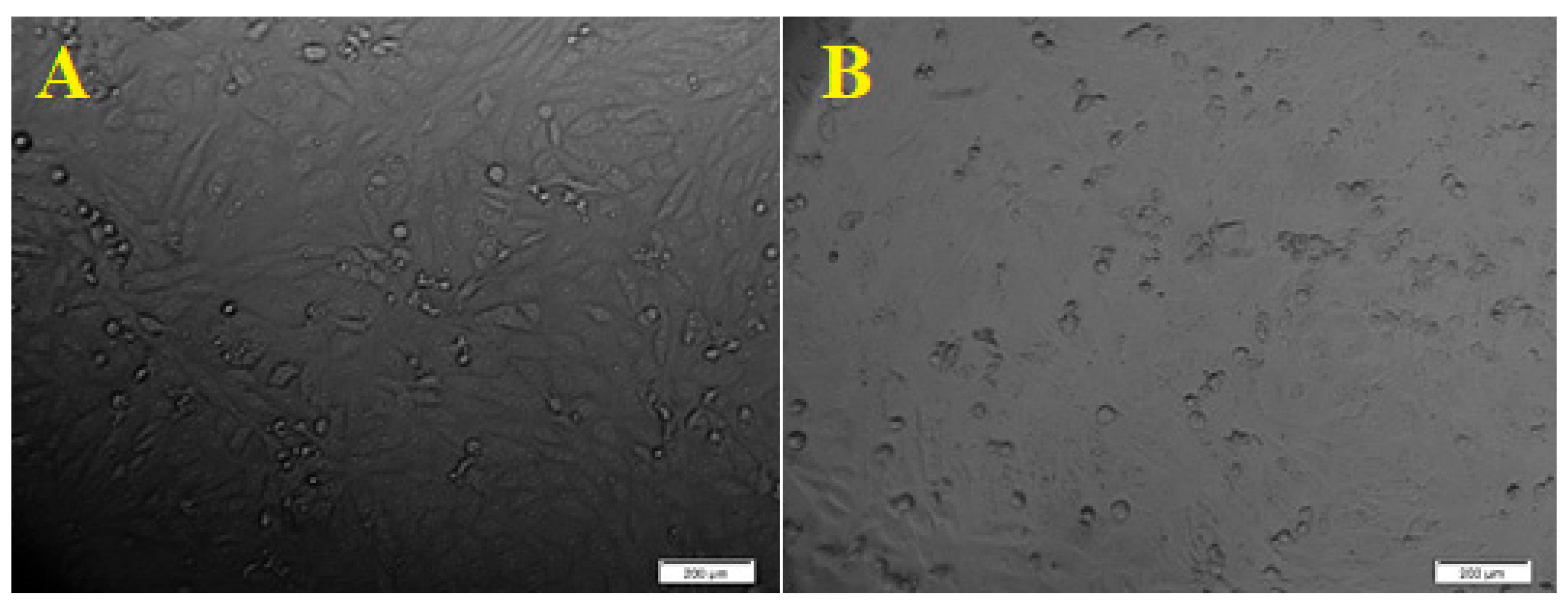
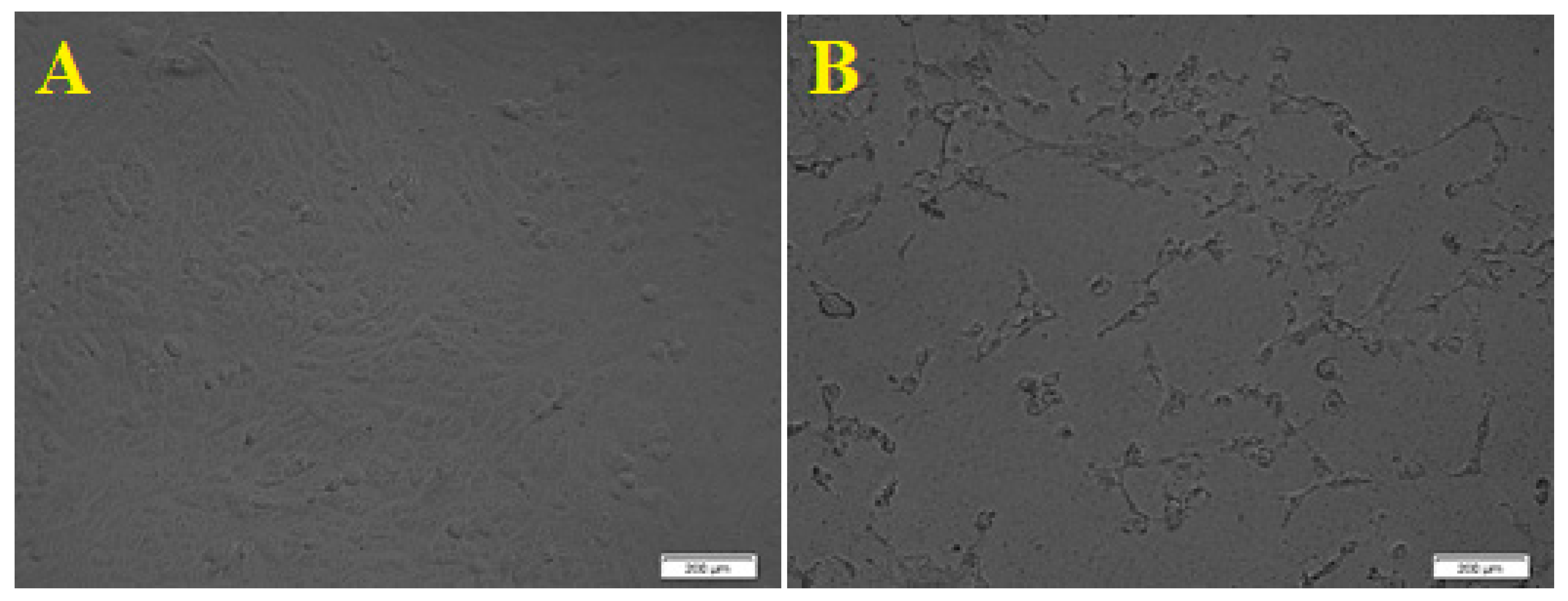
The human colon cancer cell viability was studied in the presence of ZnO NPs, and the results showed that synthesized ZnO NPS showed an outstanding cytotoxic effect on the HCT-116 cell line, as morphological changes of the HCT-116 cells were observed as it is presented in Figure 6. Additionally, the results showed dose-dependent behavior using different concentrations of ZnO NPs; 2, 5, 8, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 100, 125, and 150 μg/mL, and an IC50 value of 50 μg/mL on cancer cells was observed. The results described a significant reduction in cell viability subsequent treatment with 70 to 150 µg/mL. Although significant differences in cell viability were observed between 10 and 70 µg/mL, a remarkable difference was observed only between 10 and 20 µg/mL. Figure 7 showed the graphical representation and the morphological changes due to the effect of ZnO NPs on the HCT- 116 cancer cells.
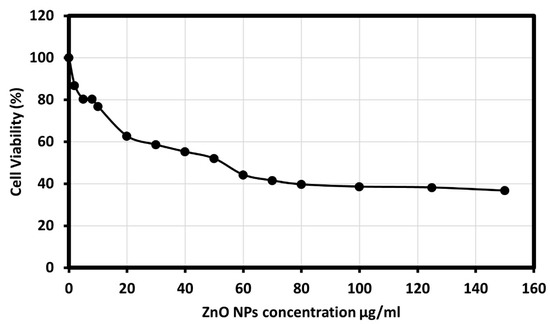
Figure 6.
Cancer cell viability percentage on HCT-116 cell line at various concentrations of ZnO NPs.
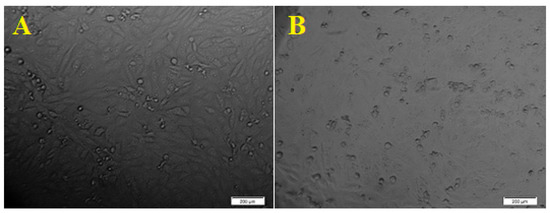
Figure 7.
Morphological changes of HCT- 116 cell line due to the cytotoxicity effect of ZnO NPs. ((A). Control. (B). Morphological changes in the cell after 24 h. scale bars = 200 µm).
3.4.2. The Human Liver Cancer (HepG2) Cell Viability
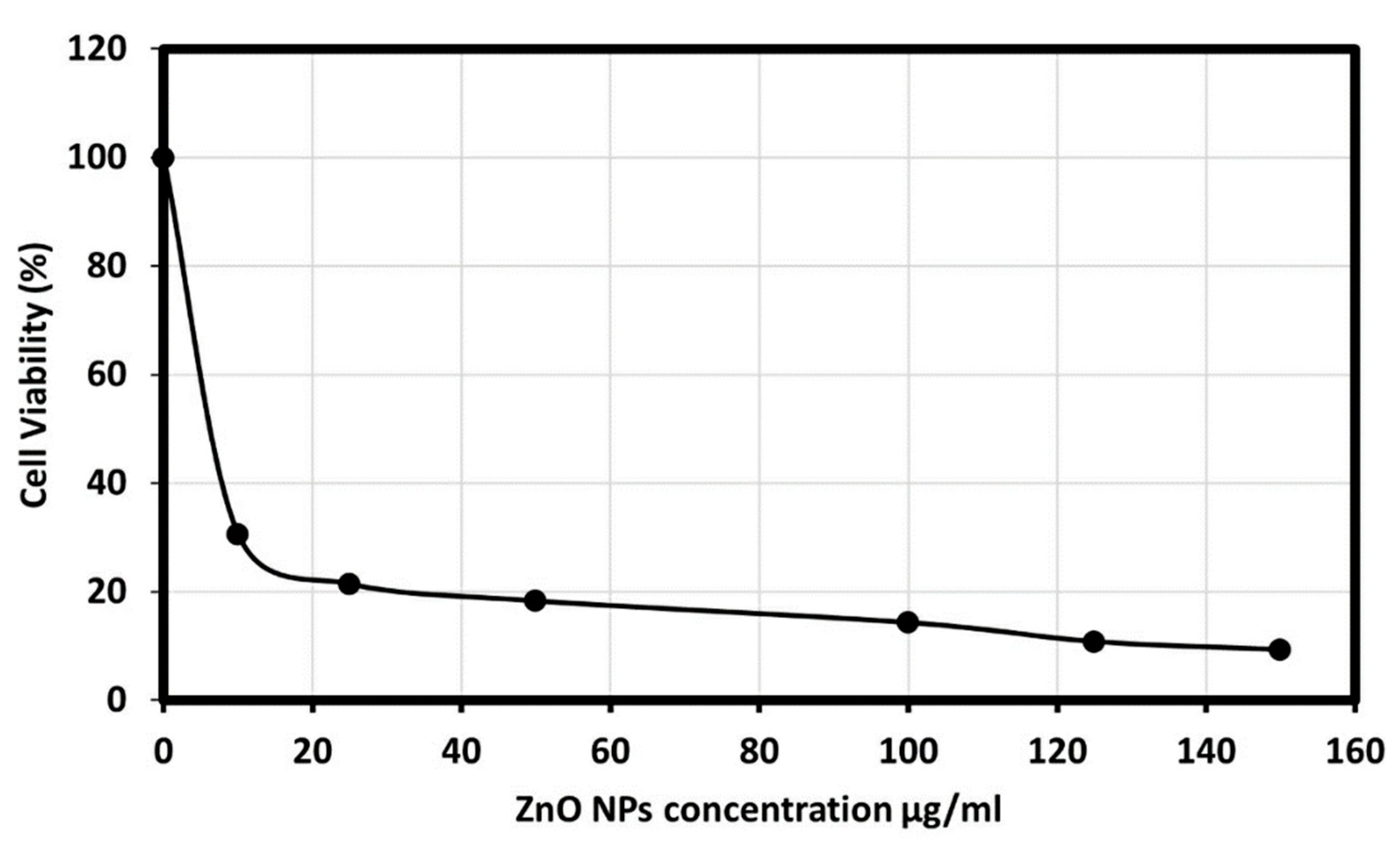
The cytotoxicity effect of ZnO nanoparticles on the HepG2 (human liver cancer) cells was explored; as liver cancer is a significant health problem worldwide [55]. Viability and apoptosis of the cell in the presence of NPs were analyzed by using a cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay. The biosynthesized ZnO NPs showed an excellent cytotoxic effect on the HepG2 cell line, as the morphology of the HepG2 cells was changed. Figure 8 presents the dose-dependent behavior by using different concentrations of ZnO NPs from 10, 25, 50, 100, 125, and 150 μg/mL. The results showed a significant reduction in cell viability subsequent treatment with 10 to 50 µg/mL. However, significant differences in cell viability were observed between 100 and 125 µg/mL, and Figure 9 showed the graphical representation of the morphological changes due to the effect of ZnO nanoparticles on cancer cells. It is noteworthy to mention that the cytotoxicity of ZnO NPs was high on HepG2 cells compared with HCT-116 cells.
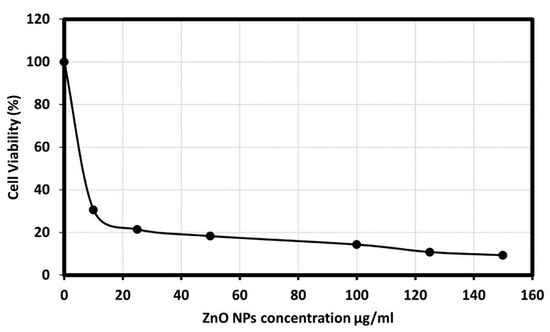
Figure 8.
Cancer cell viability percentage on Hep-G2 cell line at various concentrations of ZnO NPs.
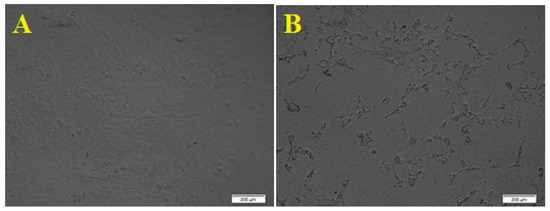
Figure 9.
Morphological changes of HepG2 cell line due to the cytotoxicity effect of ZnO NPs. (A). Control. (B). Morphological changes in the cell after 24 h. Scale bars = 200 µm.
The cytotoxicity mechanism of ZnO NPs has not been completely investigated, but the major component is the ROS that is generated in most interactions, as the nanoparticles interact with cells, lower its cellular defense mechanism, and accordingly cause apoptosis to the cell. However, when ROS production is more than the antioxidative defensive capacity of the cell, it will lead to the oxidative stress of the biomolecules, leading to cell death [56]. Additionally, ZnO NPs could release their Zn2+ ions under the physiological conditions. Therefore, the dissolution of nanoparticles, which triggers the release of Zn2+, and the ROS are generated because of the internalization of the nanoparticles, which may lead to higher cytotoxicity of the cancer cells. Furthermore, the released Zn2+ can trigger the formation of intracellular ROS, which may be the main factor for oxidative stress and cell damage [57,58,59].
Our results confirm that synthesized ZnO NPs using Ziziphus jujuba leaves aqueous extract assisted with ultrasonic irradiation showed preferential apoptosis to cancer cell HCT-116 and HepG2. ZnO NPs could be used as a promising cure for colon and liver cancer, although the internal mechanism needs to be discovered in the future.
4. Conclusions
The green biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles from the Ziziphus jujuba leaves aqueous extract assisted with ultrasonic irradiation were prepared and the XRD and TEM measurements confirm the synthesis of ZnO NPs with an average particle size of ~25 nm. The green biosynthesized ZnO NPs were evaluated biologically for their antibacterial efficacy against S. aureus and E. coli. The bacterial cells’ growth was significantly inhibited in the presence of the nanoparticles and enhanced more with increasing the ZnO NP concentrations, and this attributed to the bacterial membrane permeability enhancement for the entry of the abrasive texture nanoparticles, which ultimately leads to the cellular metabolism inhibition leading to bacterial death. Additionally, the cytotoxicity of ZnO was studied on two kinds of human cell cancer, human colon cancer (HCT-116) and human liver cancer (HepG2). The cytotoxicity mechanisms of ZnO NPs are not completely investigated, but the major component is the reactive oxygen species (ROS) that was generated in most interactions, as the ZnO nanoparticles interact with cells, lower its cellular defense mechanisms, and accordingly, cause the apoptosis to the cell.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.S. and I.I.; Data curation, M.N.A. and M.A.S., methodology; M.A.S. and I.I.; investigation, M.N.A., I.I. and M.A.S.; validation, M.A.S., M.J. and S.B.; supervision, M.A.S. and I.I.; formal analysis, M.A.S., S.E.M.A.-A. and M.J.; visualization, M.N.A. and M.A.S.; resources, M.A.S., M.J. and S.E.M.A.-A.; writing—original draft, M.N.A. and M.A.S.; writing—review and editing, M.A.S., M.J. and M.N.A.; funding acquisition M.A.S.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia under grant no. (KEP-PhD-2-130-40) and the APC was funded by KAUST.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia under grant no. (KEP-PhD-2-130-40). The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR technical and financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chavali, M.S.; Nikolova, M.P. Metal oxide nanoparticles and their applications in nanotechnology. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhong, Y.; He, T.; Peng, S.; Yang, L. A Codispersed Nanosystem of Silver-anchored MoS2 Enhances Antibacterial and Antitumor Properties of Selective Laser Sintered Scaffolds. Int. J. Bioprinting 2022, 8, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Mishra, H.; Ekielski, A.; Talegaonkar, S.; Vaidya, B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: A promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-belely, E.F.; Farag, M.M.S.; Said, H.A.; Amin, A.S.; Azab, E.; Gobouri, A.A.; Fouda, A. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) Using Arthrospira platensis (Class: Cyanophyceae) and Evaluation of their Biomedical Activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide-from synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.R.; Garvasis, J.; Oruvil, S.K.; Joseph, A. Bio-inspired green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Abelmoschus esculentus mucilage and selective degradation of cationic dye pollutants. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 127, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, T.; Mishra, K.; Khanuja, M.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Azadirachta indica for antibacterial and photocatalytic applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 32, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, E.; Pourseyedi, S.; Khatami, M.; Darezereshki, E. Simple biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using nature’s source, and it’s in vitro bio-activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1146, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Kumar, S.V.; Ramaiah, A.; Agarwal, H.; Roopan, T.L.S.M. Enzyme and Microbial Technology Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Mangifera indica leaves and evaluation of their antioxidant and cytotoxic properties in lung cancer (A549) cells. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2018, 117, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, S.K.; Malodia, L. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea: Characterization and its evaluation on tree seedling growth in nursery stage. Appl. Nanosci. 2017, 7, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimmunisha, B.A.; Ishwarya, R.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Govindarajan, M.; Vaseeharan, B. Green fabrication, characterization and antibacterial potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Aloe socotrina leaf extract: A novel drug delivery approach. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadavenkatesan, T.; Lyubchik, E.; Pai, S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Vinayagam, R.; Selvaraj, R. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B by zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the leaf extract of Cyanometra ramiflora. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 199, 111621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedefoglu, N.; Zalaoglu, Y.; Bozok, F. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using Ganoderma lucidum: Characterization and In Vitro Nanofertilizer effects. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, M.; Honarmand, M.; Ghanbari, S. A green approach to synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using jujube fruit extract and their application in photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 229, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, M.N.; Ismail, I.; Bellucci, S.; Khdary, N.H.; Abdel Salam, M. Biosynthesis microwave-assisted of zinc oxide nanoparticles with Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract: Characterization and photocatalytic application. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, M.N.; Ismail, I.; Bellucci, S.; Abdel Salam, M. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Ziziphus jujuba leaves extract: Environmental application, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 158, 110237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Chanu, T.I.; Samanta, D.; Chatterjee, S. A review on bio-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts as reductants and stabilizing agents. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 183, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cui, L.; Chang, X.; Guan, D. Biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Artemisia annua and investigate their effect on proliferation, osteogenic differentiation and mineralization in human osteoblast-like MG-63 Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 202, 111652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Jeevithan, E.; Hu, X.; Chelliah, R.; Oh, D.; Wang, M. Enhanced anti-lung carcinoma and anti-biofilm activity of fungal molecules mediated biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles conjugated with β-D-glucan from barley. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 203, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Irshad, R.; Li, B.; Tahir, K.; Ahmad, A.; Shakeel, M.; Khan, N.U.; Khan, Z.U.H. Synthesis and characterization of phytochemical fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles with enhanced antibacterial and catalytic applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 183, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Nakara, A.; Menon, S.; Shanmugam, V.K. Eco-friendly synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cinnamomum Tamala leaf extract and its promising effect towards the antibacterial activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, G.; Thirumarimurugan, M.; Muthukumaran, C. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Tecoma castanifolia leaf extract: Characterization and evaluation of its antioxidant, bactericidal and anticancer activities. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Ji, X. The Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) Fruit: A Review of Current Knowledge of Fruit Composition and Health Benefits, Chinese Dates, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; Yosri, N.; Khatib, A.; Chen, L.; Saeed, A.; Efferth, T.; Verpoorte, R. Review Plants mentioned in the Islamic Scriptures (Holy Qur’ân and Ahadith): Traditional uses and medicinal importance in contemporary times. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 243, 112007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, M.I.H. Plants of the Qur’an; Sidrah Publishers: Lucknow, India, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tahergorabi, Z.; Abedini, M.R.; Mitra, M.; Fard, M.H.; Beydokhti, H. “Ziziphus jujuba”: A red fruit with promising anticancer activities. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halawani, E.M. Rapid Biosynthesis Method and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Zizyphus spina christi Leaf Extract and Their Antibacterial Efficacy in Therapeutic Application. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 8, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabali, A.A.A.; Akkam, Y.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Al-Batayneh, K.M.; Al-Trad, B.; Alrob, O.A.; Alkilany, A.M.; Benamara, M.; Evans, D.J. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of ziziphus zizyphus and their antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.H.; Doraiswamy, L.K. Sonochemistry: Science and Engineering. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 1215–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Y.M.A.; Attia, Y.A. The influence of ultrasonic irradiation on catalytic performance of ZnO nanoparticles toward the synthesis of chiral 1-substituted-1H-tetrazolederivatives from α-amino acid ethyl esters. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhu, M.; Guo, M.; Lian, Z.; Tong, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wei, W. Ultrasonic-Assisted Dispersion of ZnO Nanoparticles and Its Inhibition Activity to Trichoderma viride. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Darvishzadeh, M. Nanocomposite materials based on poly(vinyl chloride) and bovine serum albumin modified ZnO through ultrasonic irradiation as a green technique: Optical, thermal, mechanical and morphological properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Dhavan, P.P.; Ratna, D.; Shimpi, N.G. Ultrasonic-assisted biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Sonneratia alba leaf extract and investigation of its photocatalytic and biological activities. J. Clust. Sci. 2022, 33, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Göttinger Nachrichten Gesell. A. L. Patterson. Phys. Rev. 1918, 2, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, S.; Krishnan, D.; Barman, G.; Ghosh, S.K.; Laha, J.K. Antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Lycopersicon esculentum extract. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabary, M.K.; Emam, A.N. Antibiofilm, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of extracellular green-synthesized silver nanoparticles by two marine-derived actinomycete. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10361–10367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, N.; Saha, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Maiti, M.; Das, S.; Basu, R.; Nandy, P. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus subdariffa leaf extract: Effect of temperature on synthesis, anti-bacterial activity and anti-diabetic activity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 4993–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, N.N.; Thuy, V.T.T.; Thang, N.H.; Thuy, N.T.; Quynh, L.T.; Khoi, T.T.; Van Thanh, D. Facile one-step synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by ultrasonic-assisted precipitation method and its application for H2S adsorption in air. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 132, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulychev, N.A.; Kazaryan, M.A. Optical properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized in plasma discharge in liquid under ultrasonic cavitation. In Proceedings of the XIV International Conference on Pulsed Lasers and Laser Applications, Tomsk, Russia, 11 December 2019; SPIE: 2019. Volume 11322, pp. 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- College, S.C. Antibacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle by Sonochemical Method and Green Method Using Zingiber. Green Chem. Technol. Lett. 2016, 2, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.G.; Huo, C.; Gui, B.; Liu, J.F.; Chen, Y.S. Facile phyto-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Chinese winter jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv. Dongzao) extract and their antibacterial/catalytic properties. IET Nanobiotechnology 2017, 11, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: Structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, D.H.; Piva, R.H.; Rocha, M.C.; Dias, J.A.; Montedo, O.R.K.; Malavazi, I.; Morellia, M.R. Antibacterial and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles from Zn(OH)2 dehydrated by azeotropic distillation, freeze drying, and ethanol washing. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Experts, D. 10 in One Study Package for CBSE Biology Class 11 with 3 Sample Papers; Disha Publications: Delhi, India, 2017; p. 520. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gendy, A.O.; Nawaf, K.; Ahmed, E.; Samir, A.; Hamblin, M.R.; Hassan, M.; Mohamed, T. Preparation of zinc oxide nanoparticles using laser-ablation technique: Retinal epithelial cell (ARPE-19) biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity when activated with femtosecond laser. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2022, 234, 112540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononenko, V.; Repar, N.; Marušič, N.; Drašler, B.; Romih, T.; Hočevar, S.; Drobne, D. Comparative in vitro genotoxicity study of ZnO nanoparticles, ZnO macroparticles and ZnCl2 to MDCK kidney cells: Size matters. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 40, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Ur Rahman, A.; Tajuddin; Husen, A. Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Activity Against Microbes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.-H.; Ke, W.-J.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Lin, K.-S.; Tzou, D.-Y.; Chiang, C.-L. ZnO Nanoparticles Affect Bacillus subtilis Cell Growth and Biofilm Formation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairyte, K.; Kadys, A.; Luksiene, Z. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of photoactivated ZnO nanoparticles in suspension. J Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 128, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, M.; Gurkok, S. Recent advances in nanoparticles as antibacterial agent. ADMET DMPK. 2022, 10, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Ruan, J.; Zhuang, X. Using Positively Charged Magnetic Nanoparticles to Capture Bacteria at Ultralow Concentration. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Rajput, J.; Kaith, B.S.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, S. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and study of their antibacterial and antifungal properties. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 519, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, R.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Saquib, Q.; Dwivedi, S.; Ahmad, J.; Musarrat, J.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Shin, H.-S. ZnO nanoparticles induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cells and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, G.K.; Prashanth, P.A.; Ramani, M.; Ananda, S.; Nagabhushana, B.M.; Krishnaiah, G.M.; Nagendra, H.G.; Sathyananda, H.M.; Mutthuraju, M.; Rajendra Singh, C. Comparison of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of ZnO Nanoparticles Prepared by Lemon Juice and Citric Acid Fueled Solution Combustion Synthesis. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 799–812. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Shu, X.; Zhu, D.; Liang, S.; Hasan, M.; Gong, S. Lipid-coated ZnO nanoparticles synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity studies in cancer cell. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Nenavathu, B.; Gangishetty, M.; Reddy, A. Studies on antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles by ROS induced lipid peroxidation. Colloid Surf. B 2012, 94, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, X. Silica nanoparticles induce reversible damage of spermatogenic cells via RIPK1 signal pathways in C57 mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2251. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).