Preparation of Fe3O4-Reduced Graphene-Activated Carbon from Wastepaper in the Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction and UHPLC-PDA Determination of Antibiotics in Human Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Reagents
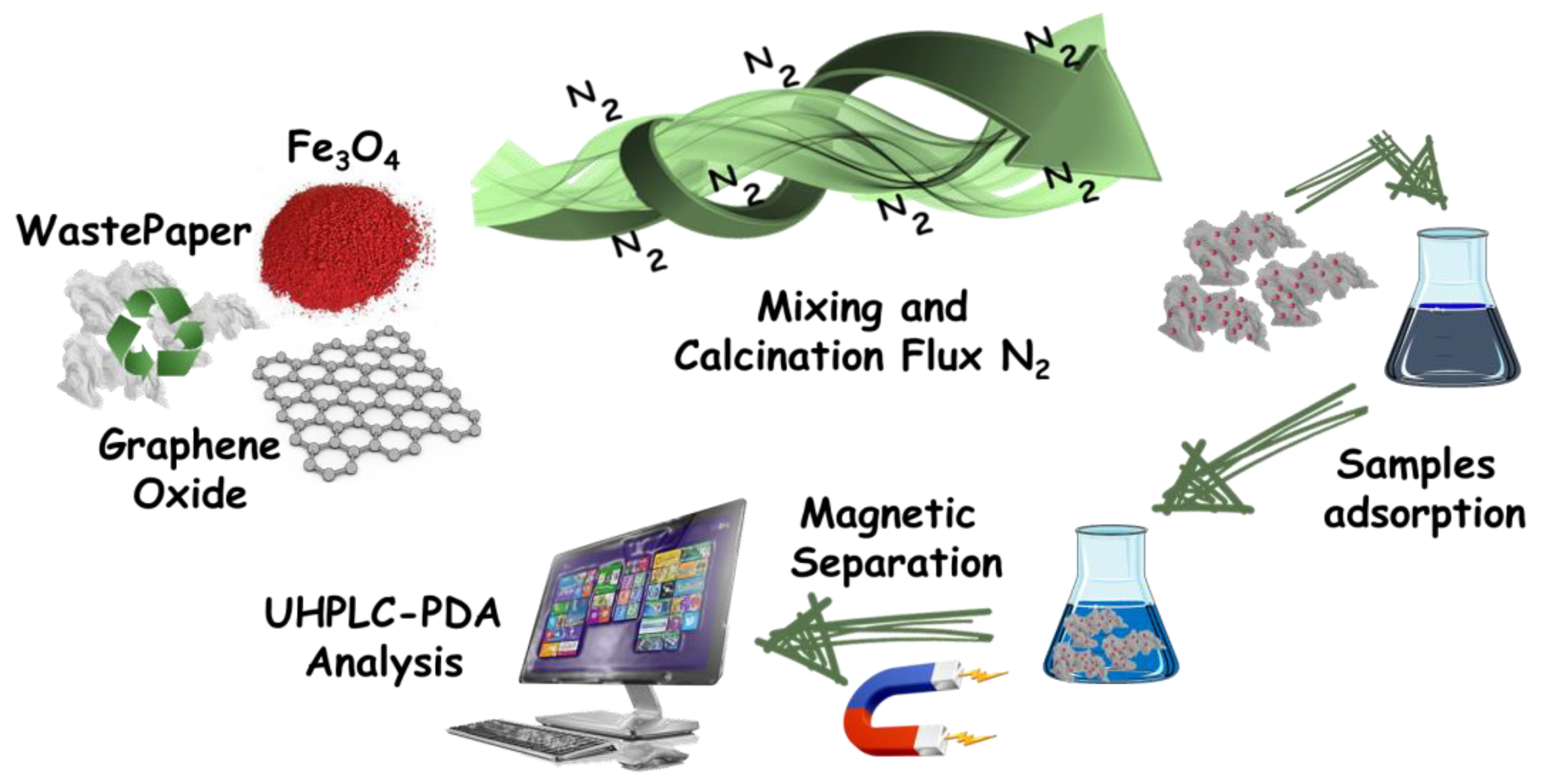
2.2. Preparation of “Fe3O4-rG-Activated Carbon” Sorbent
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Dispersive Solid Phase Extraction Procedure
2.5. Chromatographic Conditions
3. Results and Discussions
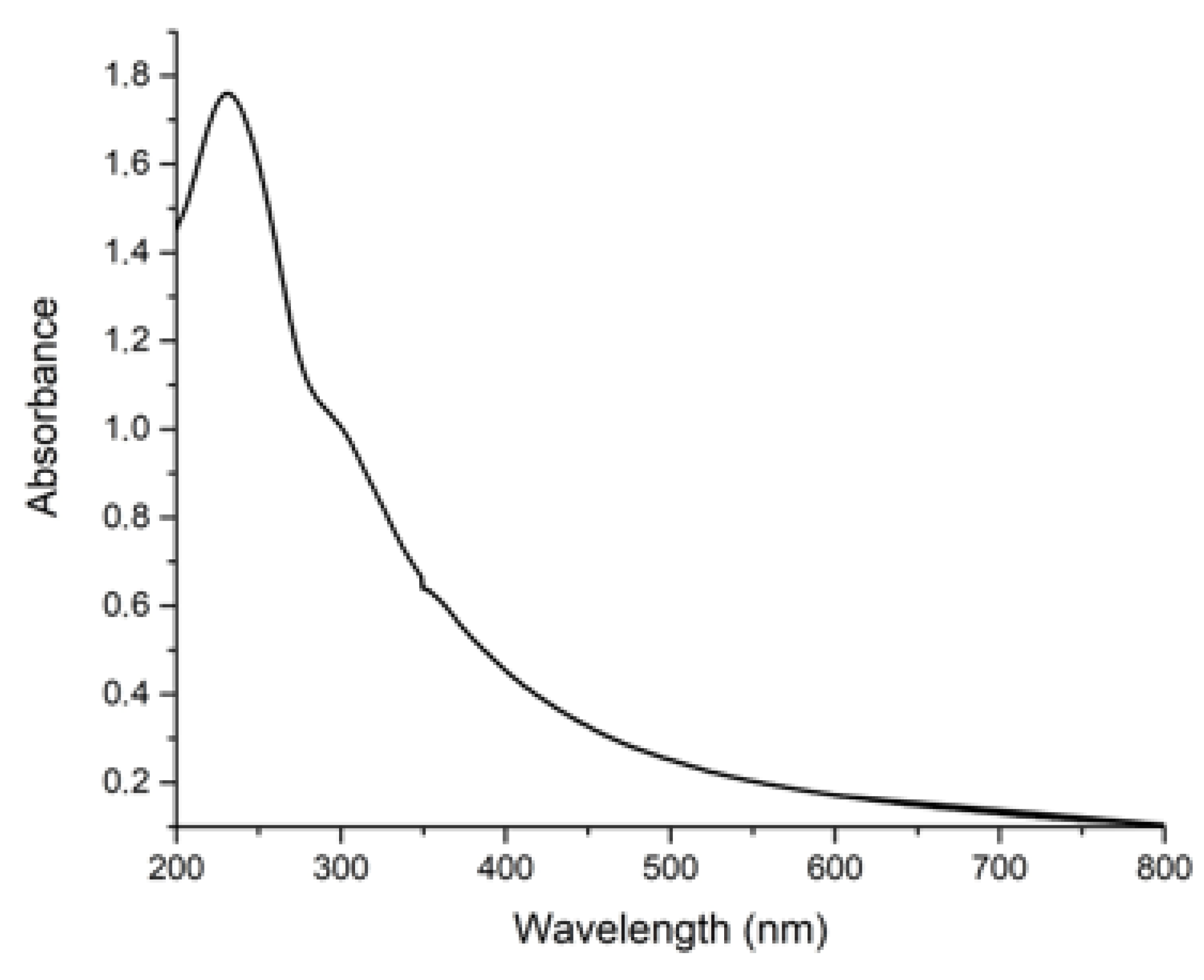
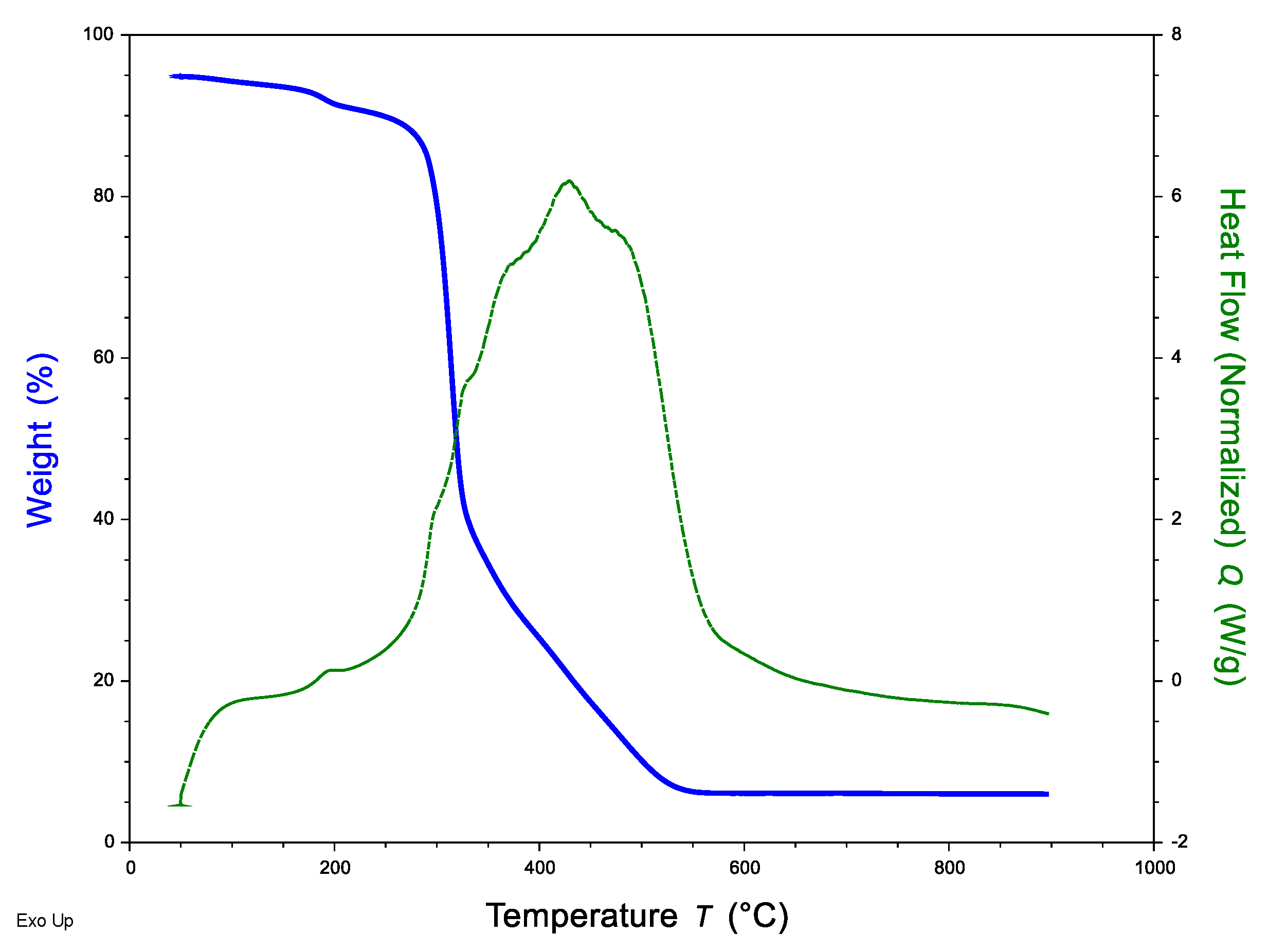
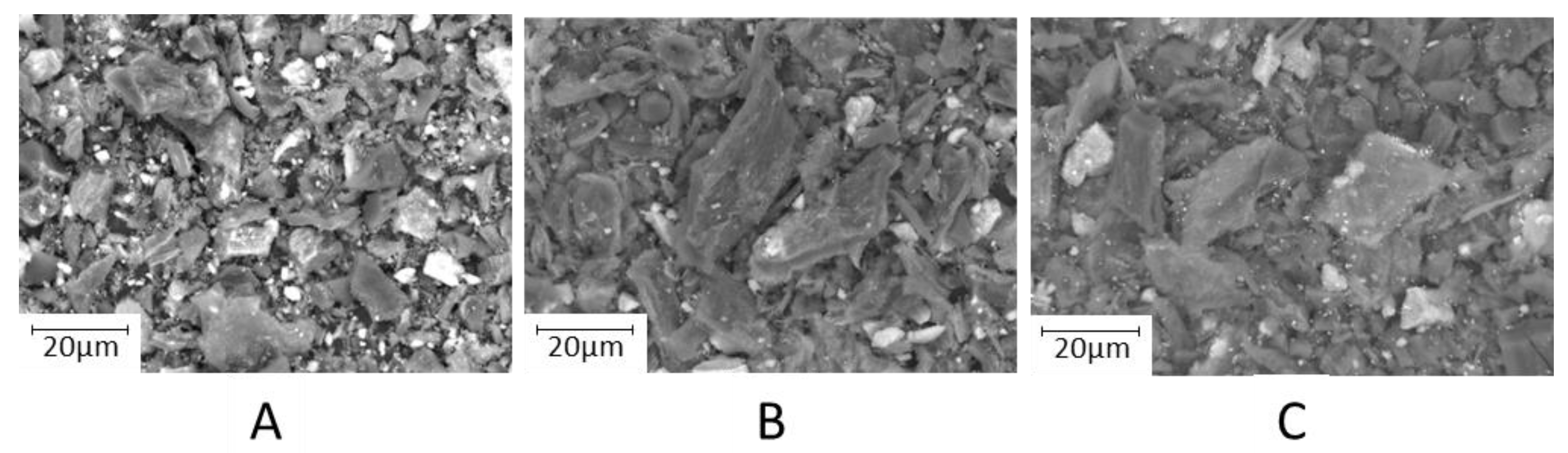
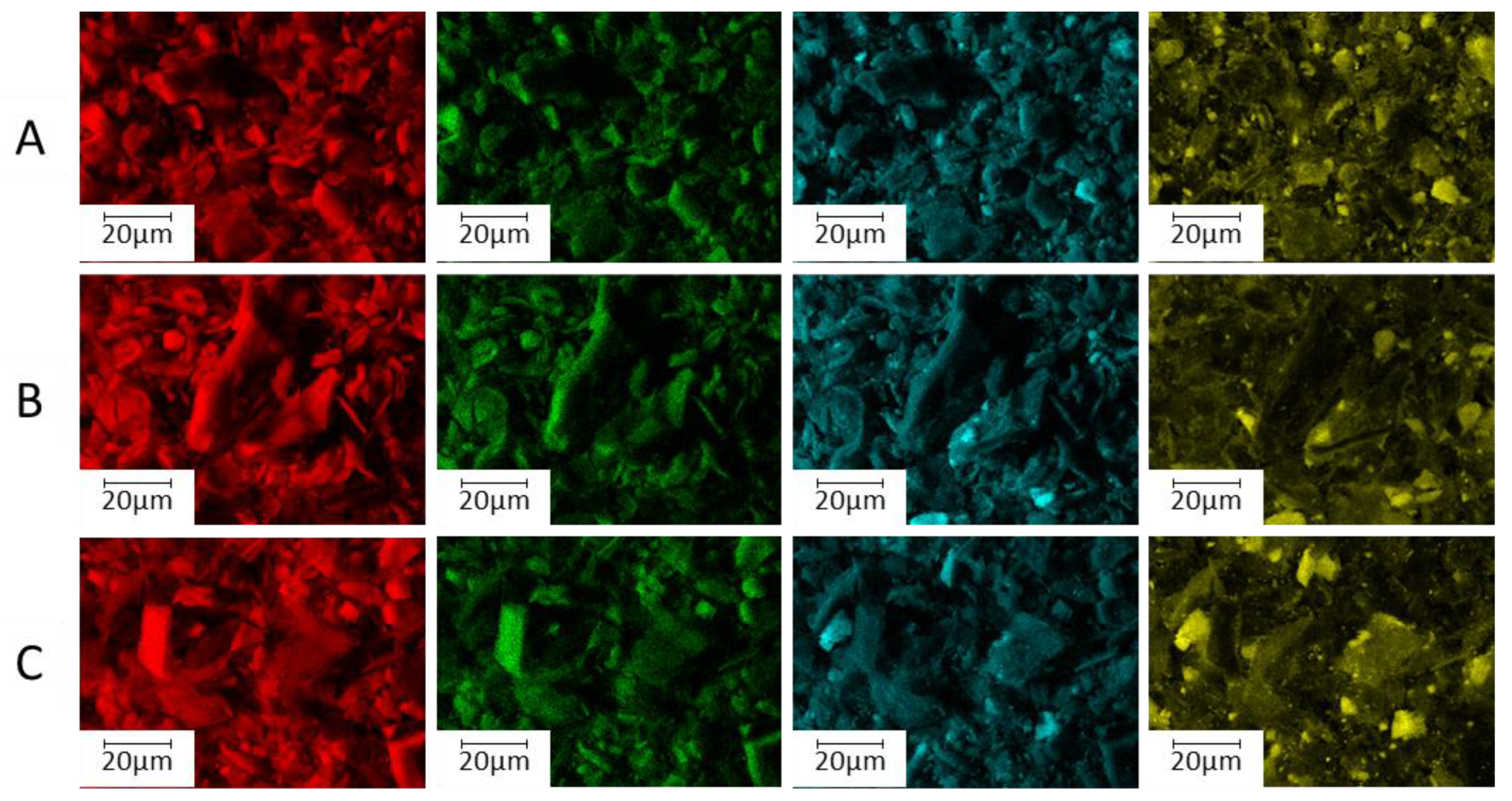
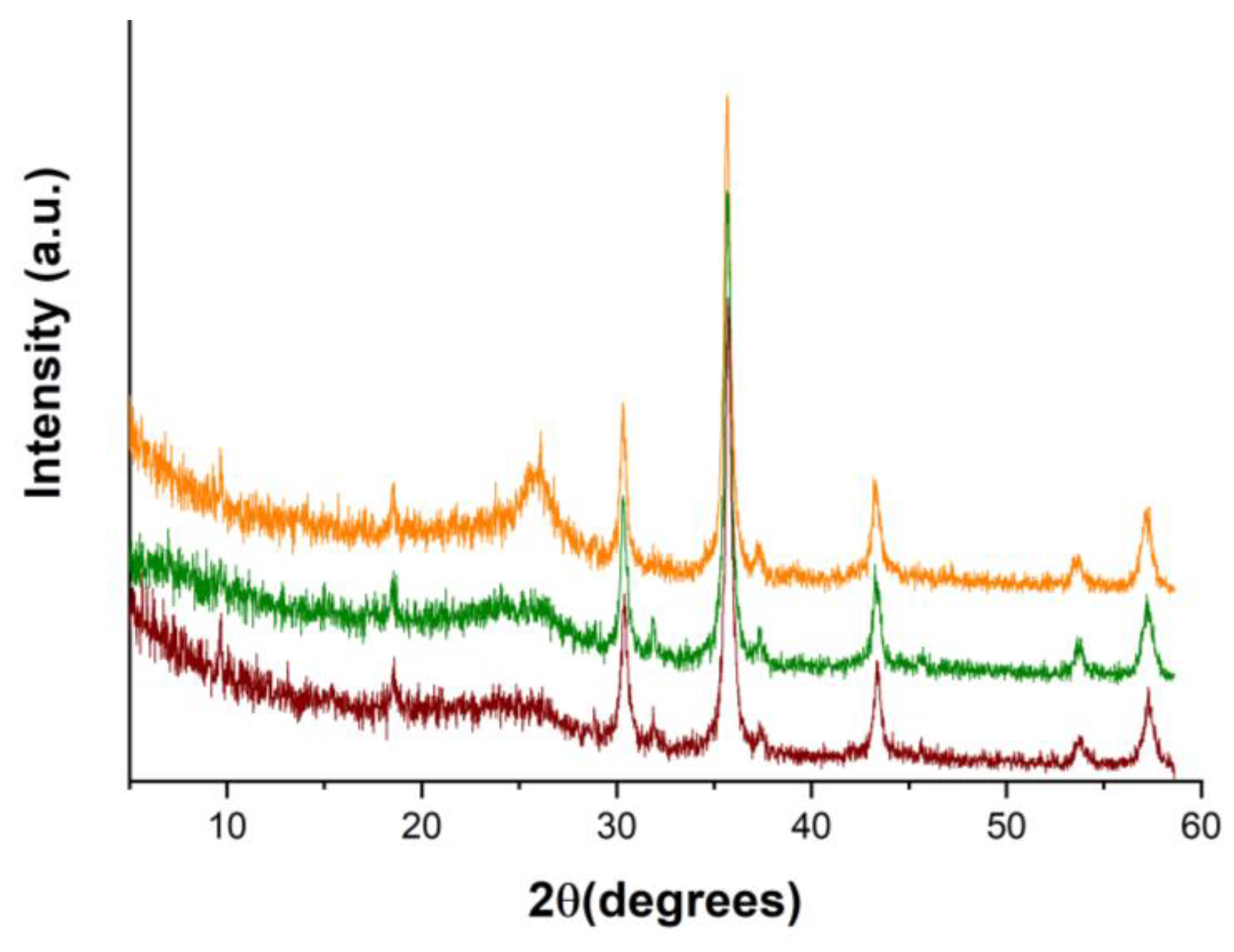
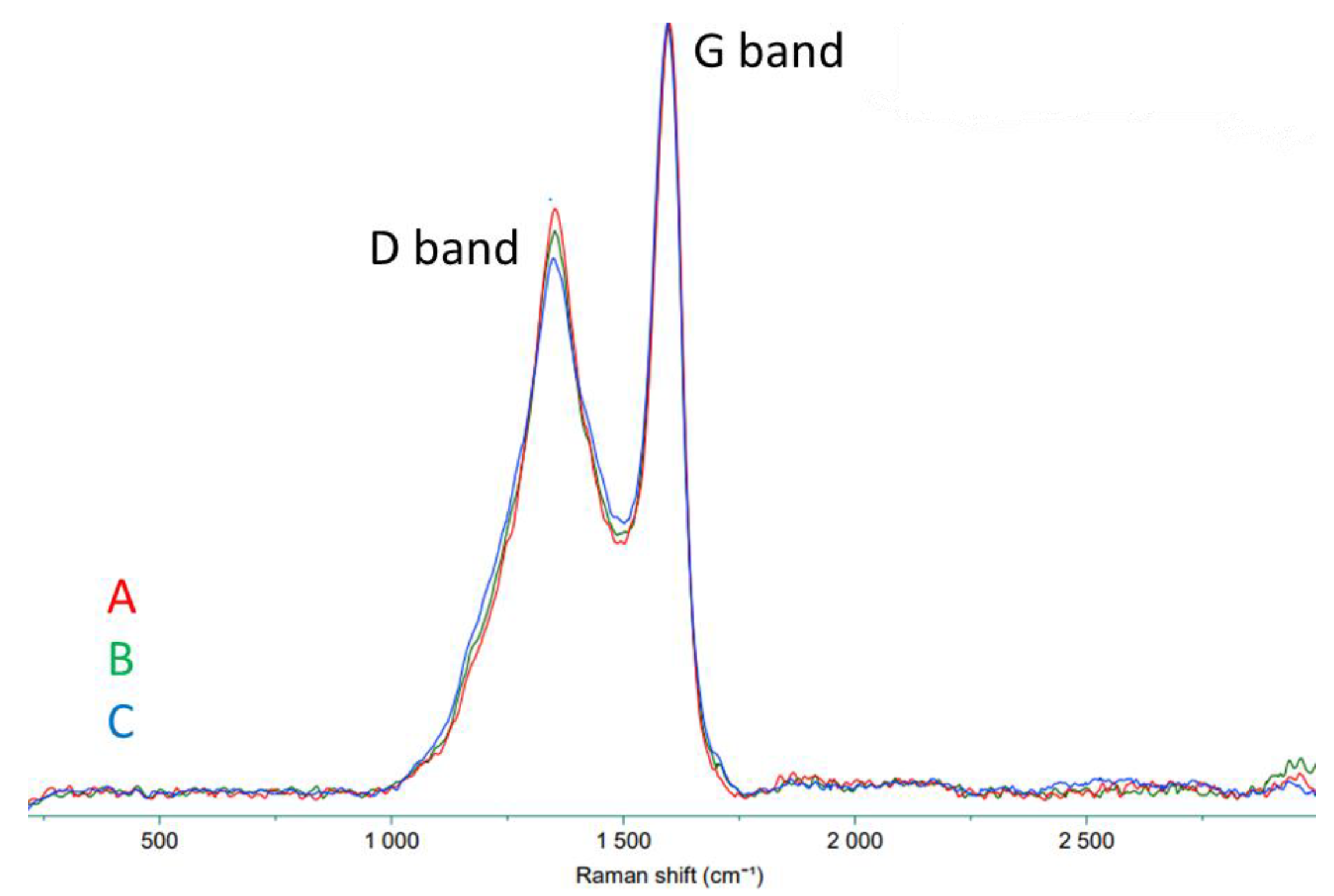
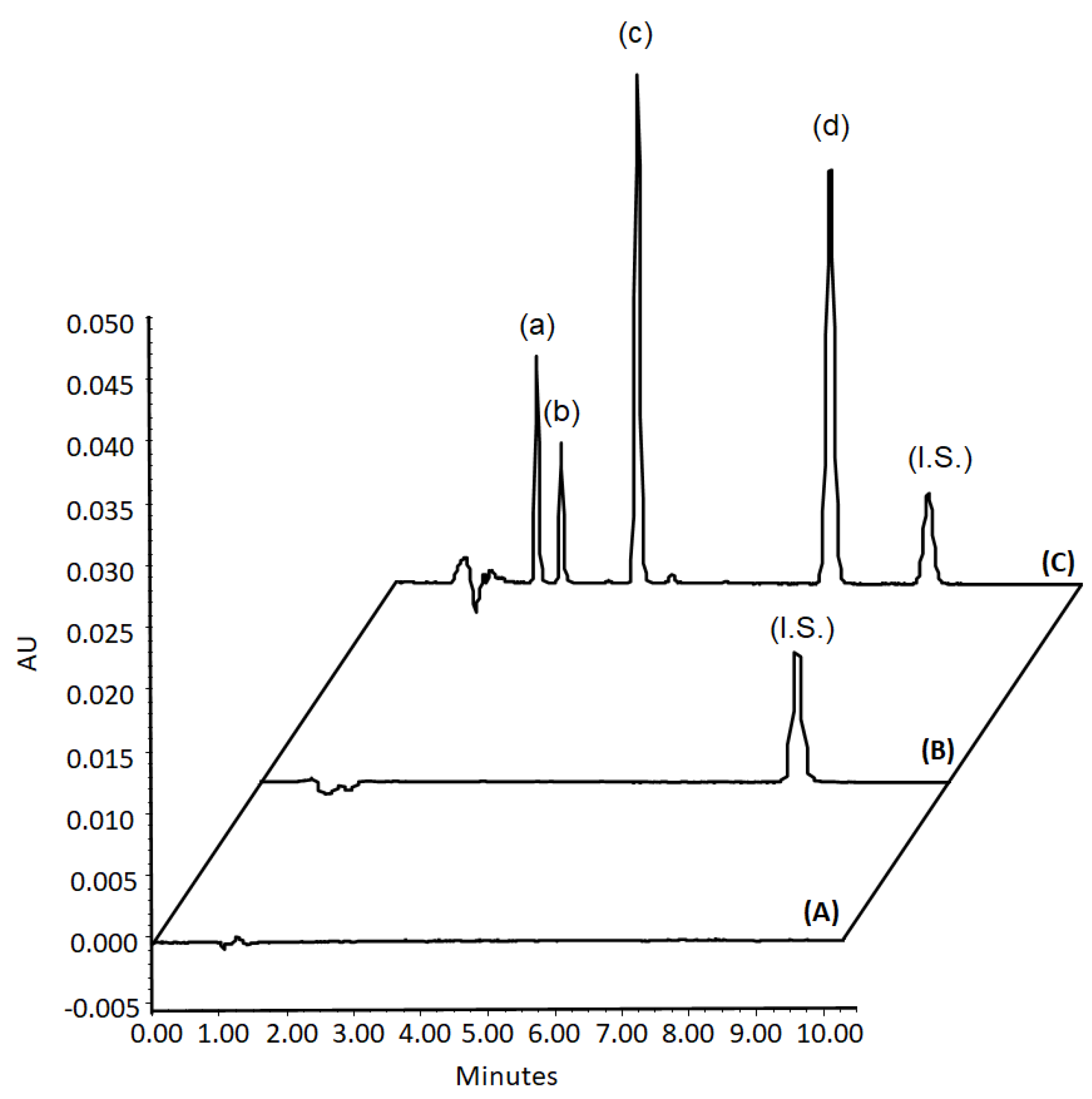
3.1. Characterization of the Sorbent
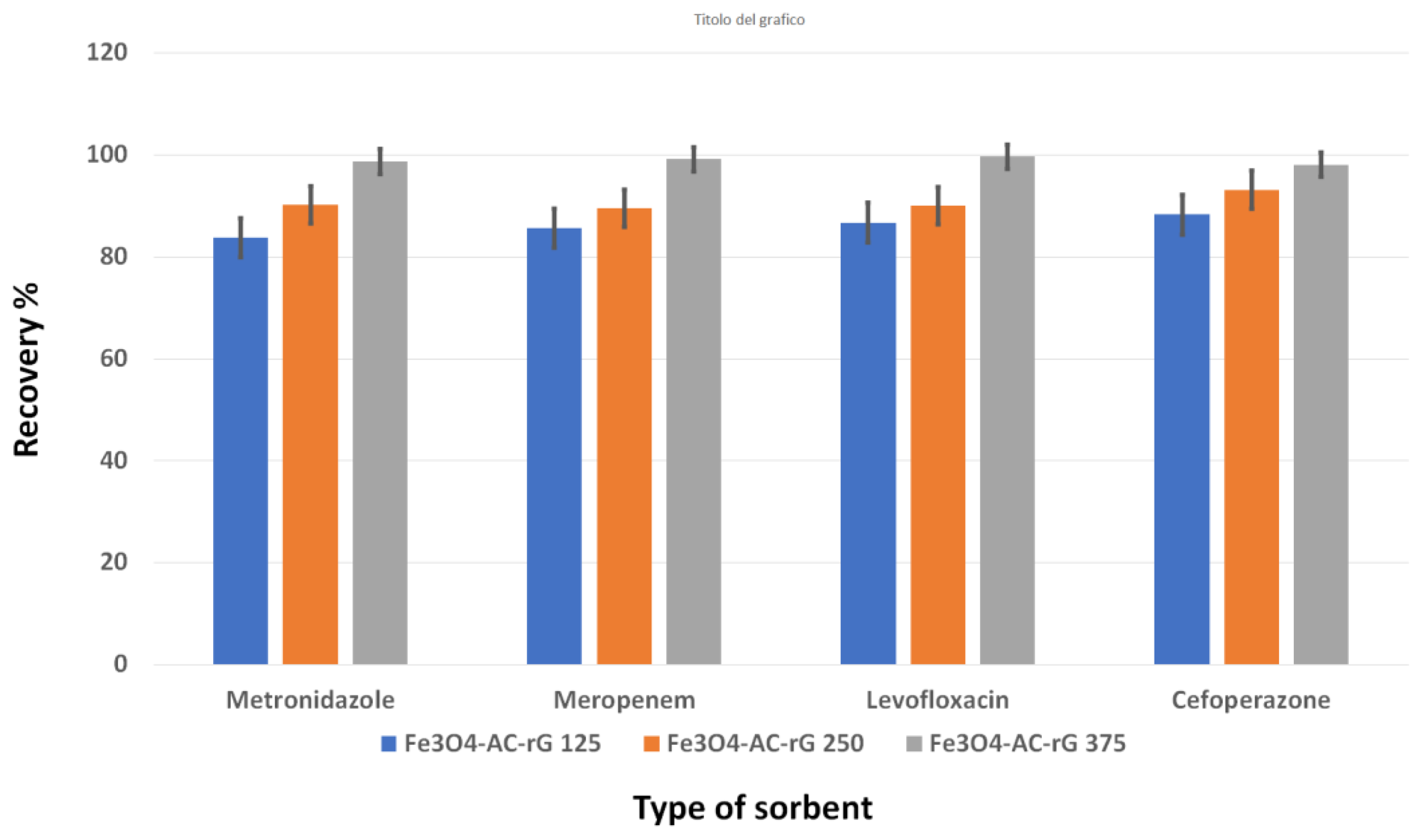
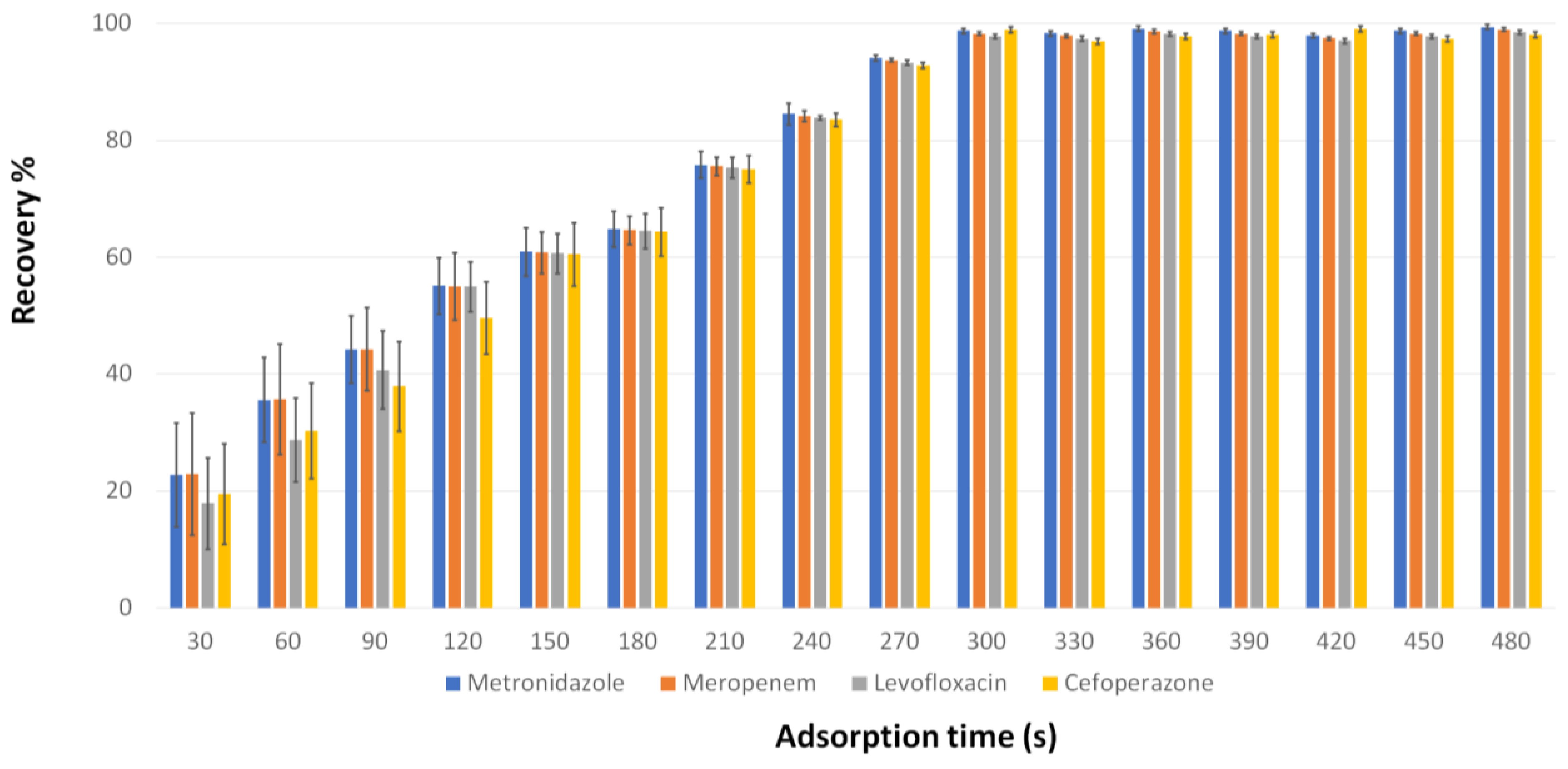
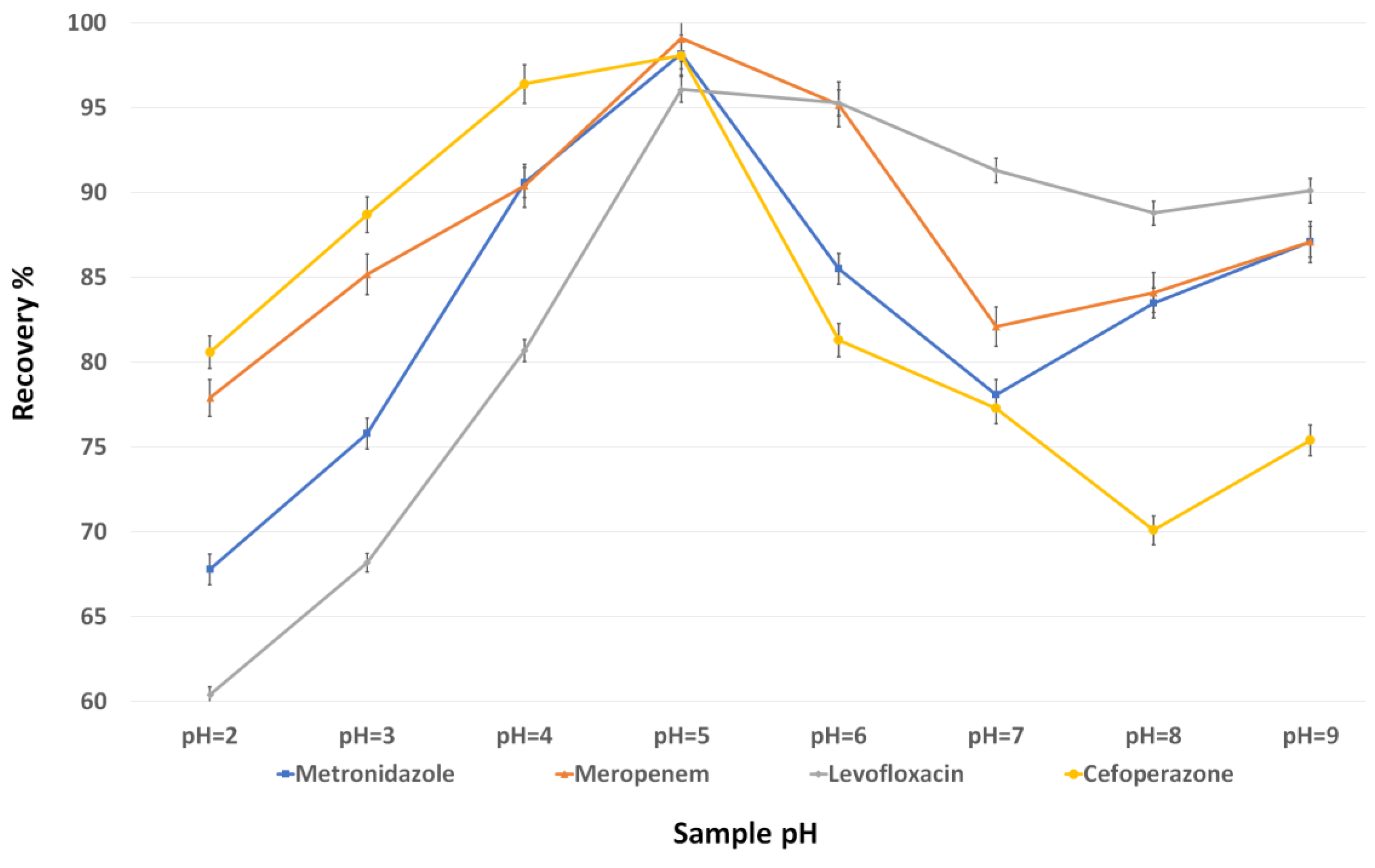
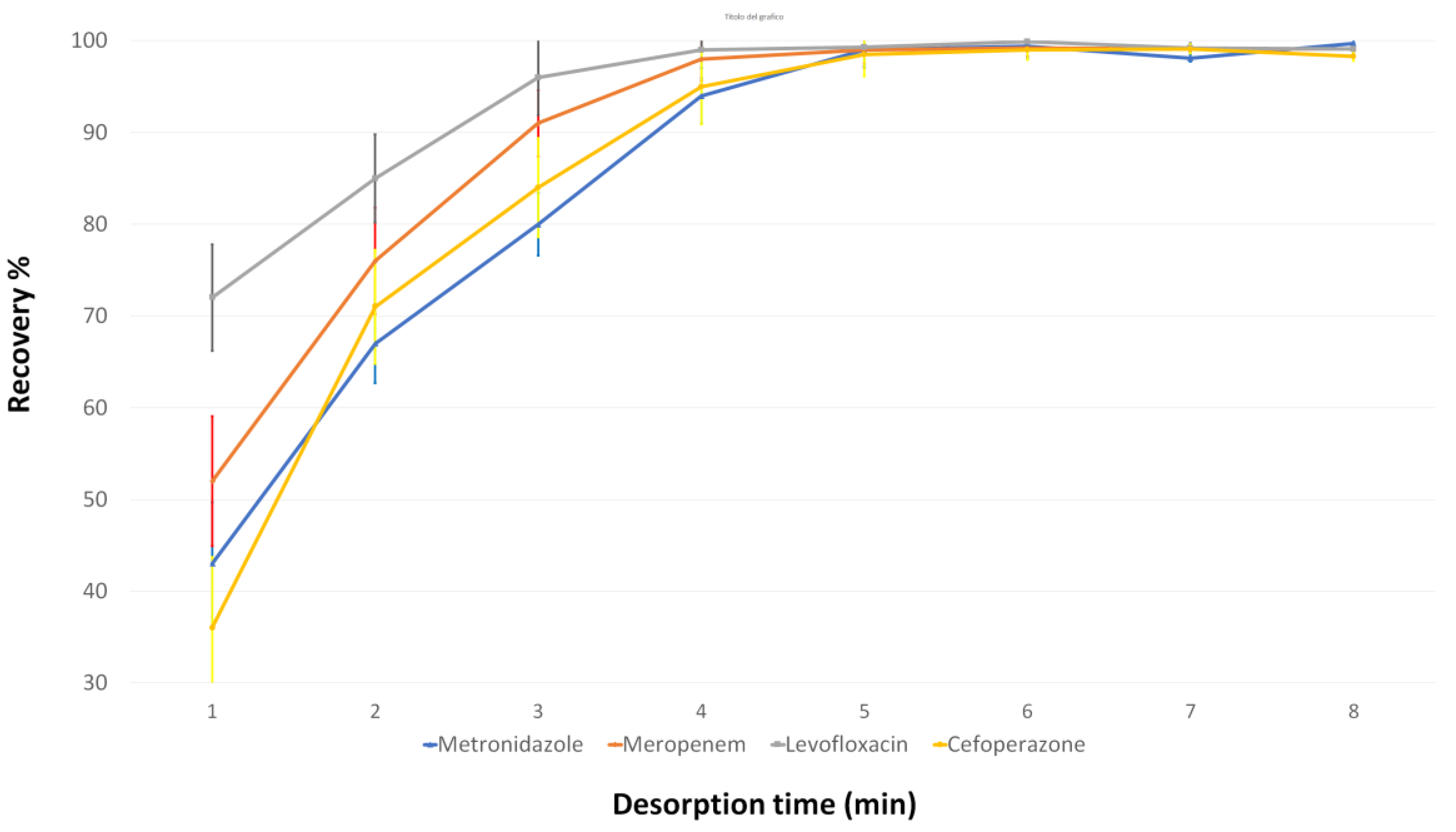
3.2. Evaluation of the d-MSPE Conditions
3.3. Method Validation
3.4. Comparison with Existing Methods in the Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Economides, D.G.; Vlyssides, A.G.; Simonetis, S.I.; Philippakopoulou, T.L. Reuse of effluent from a wastepaper wash-deinking process. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 103, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiaani, P.; Kuppens, T.; Van Dael, M.; Azadi, H.; Lebailly, P.; Van Passel, S. Social sustainability assessments in the biobased economy: Towards a systemic approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 82, 1839–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A. Current research on the blends of natural and synthetic polymers as new biomaterials: Review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1254–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummartyotin, S.; Manuspiya, H. A critical review on cellulose: From fundamental to an approach on sensor technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Du, H.; Kuai, L.; Huang, K.; Xia, Y.; Geng, B. Scalable Dry Production Process of a Superior 3D Net-Like Car-bon-Based Iron Oxide Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12649–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, S.; Chen, P.; Zhu, G.-T.; Jiang, X.; Di, S. Eco-friendly and facile one-step synthesis of a three dimensional net-like magnetic mesoporous carbon derived from wastepaper as a renewable adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12419–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, T.; Hossain, M.S.; Dhar, P.K.; Rahman, S.; Hossain, A.; Ahmed, M.B. Efficacies of Carbon-Based Adsorbents for Carbon Dioxide Capture. Processes 2020, 8, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madima, N.; Mishra, S.B.; Inamuddin, I.; Mishra, A.K. Carbon-based nanomaterials for remediation of organic and inorganic pollutants from wastewater. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1169–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Kaur, G.; Sharma, V.; Nagraik, R.; Shandilya, M. Increasing the efficiency of reduced graphene oxide obtained via high temperature electrospun calcination process for the electrochemical detection of dopamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 904, 115904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Feng, J.; Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Feng, Y.; Sun, M. Carbon aerogels derived from waste paper for pipette-tip solid-phase extraction of triazole fungicides in tomato, apple and pear. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.Y.; Meng, J.R.; Deng, C.H. Enrichment and detection of small molecules using magnetic graphene as an adsorbent and a novel matrix of MALDI-TOFMS. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2418–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shi, J.B.; Sun, J.T.; Wang, T.; Zeng, L.X.; Jiang, G.B. Graphene and graphene oxide sheets supported on silica as versatile and high-performance adsorbents for solid-phase extraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 123, 5913–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitko, R.; Zawisza, B.; Malicka, E. Graphene as a new sorbent in analytical chemistry. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2013, 51, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, V.; Carlucci, M.; Ettorre, V.; Cotellese, R.; Palumbo, P.; Fontana, A.; Siani, G.; Carlucci, G. Dispersive magnetic solid phase extraction exploiting magnetic graphene nanocomposite coupled with UHPLC-PDA for simultaneous determination of NSAIDs in human plasma and urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 161, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, V.; Todaro, S.; Carlucci, M.; Fontana, A.; Ventrella, A.; Carlucci, G.; Milanetti, E. Optimization by response surface methodology of a dispersive magnetic solid phase extraction exploiting magnetic graphene nanocomposite coupled with UHPLC-PDA for simultaneous determination of new oral anticoagulants (NAOs) in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 179, 112992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.H.; Kim, M.W.; Zhang, W.L.; Moon, I.J.; Choi, H.J. Fabrication of smart magnetite/reduced graphene oxide composite nanoparticles and their magnetic stimuli-response. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 481, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Prakash, A.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Agarrwal, A.; Bahadur, D. Superparamagnetic iron oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid-a vehicle for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia treatment of cancer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 448, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Hur, S.H.; Kim, E.J.; Rajagopalan, B.; Babu, K.F.; Senthilkumar, V.; Chung, J.S.; Choi, W.M.; Kim, Y.S. Highly-ordered maghemite/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for high-performance photoelectrochemical water splitting. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29159–29166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jiang, H.-L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhao, R.-S.; Lin, J.-M. Recent advances in graphene-based magnetic composites for magnetic solid-phase extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sun, M.; Sun, M.; Feng, J.; Sun, H.; Feng, J. Extraction performance-structure relationship of polyamidoamine dendrimers on silica for online solid-phase extraction of organic pollutants. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1673, 463132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-F.; You, N.; Fan, H.-T. A hybrid sorbent of α-iron oxide/reduced graphene oxide: Studies for adsorptive removal of tetracycline antibiotics. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 863, 158475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamian, R.; Behnejad, H. A comprehensive adsorption study and modeling of antibiotics as a pharmaceutical waste by graphene oxide nanosheets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yin, R.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, M. A review of graphene-based nanomaterials for removal of antibiotics from aqueous environments. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrone, V.; Bruni, P.; Canale, V.; Sbrascini, L.; Nobili, F.; Carlucci, G.; Ferrari, S. Simple synthesis of Fe3O4@activated carbon from wastepaper for dispersive magnetic solid-phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and their UHPLC-PDA determination in human plasma. Fibers 2022, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L. Green construction of Fe3O4@GC submicrocubes for highly sensitive magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction of five phthalate esters in beverages and plastic bottles. Food Chem. 2018, 277, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuepfer, D.B.; Badaczewski, F.; Guerra-Castro, J.M.; Hofmann, D.M.; Heiliger, C.; Smarsly, B.; Klar, P.J. Assessing the structural properties of graphitic and non-graphitic carbons by Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 2020, 161, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, T.; Yamauchi, S.; Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kurimoto, Y.; Takayama, T.; Sakai, Y. Mössbauer and Raman spectroscopic characterization of iron and carbon in iron-loaded Japanese cypress charcoal. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereshti, H.; Bakhtiari, S. Three-dimensional graphene/Fe3O4-based magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 75757–75765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappacosta, R.; Di Giulio, M.; Ettorre, V.; Bosco, D.; Hadad, C.; Siani, G.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; Cataldi, A.; Cellini, L.; Fontana, A. Liposome induced exfoliation of graphite to few layer graphene dispersion with antibacterial activity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6520–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.P.; Ren, X.C.; Wang, P.; Yu, S.H. Macroscopic Multifunctional Graphene-Based Hydrogels and Aerogels by a Metal Ion Induced Self-Assembly Process. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation 2011 EMEA/CHMP/EWP/192217/2009. 2011. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/bioanalytical-method-validation-scientific-guideline (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Cohen-Wolkowiez, M.; White, N.R.; Bridges, A.; Beanjamin, D.K., Jr.; Kashube, A.D.M. Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay of six antimicrobials in plasma for pharmacokinetic studies in premature infants. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrone, V.; Cotellese, R.; Di Marco, L.; Bacchi, S.; Carlucci, M.; Cichella, A.; Raimondi, P.; Carlucci, G. Meropenem, levofloxacin and linezolid in human plasma of critical care patients: A fast semi-automated micro-extraction by packed sorbent UHPLC-PDA method for their simultaneous determination. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 140, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairoli, S.; Simeoli, R.; Tarchi, M.; Dionisi, M.; Vitale, A.; Perioli, L.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Goffredo, B.M. A new HPLC–DAD method for contemporary quantificationof 10 antibiotics for therapeutic drug monitoring of critically ill pediatric patients. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34, e4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, S. An UPLC-PDA assay for simultaneous determination of seven antibiotics in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 210, 114558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Dang, Z.-L.; Bin Li, B.; Zhu, L.; Qin, H.-Y.; Wu, X.-A.; Wei, Y.-H. Determination of Total and Unbound Meropenem, Imipenem/Cilastatin, and Cefoperazone/Sulbactam in Human Plasma: Application for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Critically Ill Patients. Ther. Drug Monit. 2020, 42, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Analyte | Amount Added (µg mL–1) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (BIAS%) | Precision (RSD%) | Accuracy (BIAS%) | Precision (RSD%) | ||
| Metronidazole | 0.0010 | 3.13 | 2.81 | 1.79 | 5.27 |
| 0.0025 | −4.01 | 4.27 | −4.63 | 6.98 | |
| 0.50 | 3.12 | 3.88 | 3.88 | 6.53 | |
| 10.0 | 5.03 | 5.05 | 6.16 | 7.90 | |
| Meropenem | 0.0010 | −2.76 | 3.50 | −3.14 | 6.08 |
| 0.0025 | 0.43 | 2.23 | 0.67 | 4.60 | |
| 0.50 | 0.76 | 2.43 | 1.06 | 4.84 | |
| 10.0 | −1.54 | 2.75 | −1.68 | 5.21 | |
| Levofloxacin | 0.0010 | 2.74 | 3.65 | 3.43 | 6.26 |
| 0.0025 | 0.89 | 2.51 | 1.22 | 4.93 | |
| 0.50 | −0.40 | 2.05 | −0.32 | 4.39 | |
| 10.0 | −0.18 | 1.92 | −0.06 | 4.24 | |
| Cefoperazone | 0.0010 | 2.42 | 3.45 | 3.04 | 6.03 |
| 0.0025 | −3.12 | 3.72 | −3.57 | 6.34 | |
| 0.50 | −4.86 | 4.79 | −5.65 | 7.59 | |
| 10.0 | −0.82 | 2.31 | −0.82 | 4.69 | |
| Analytes | Sample Preparation | Instrumentation | Run Time (min) | LOQ (µg/mL) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MET, MER, | P.P.1 | HPLC-MS/MS | 5 | 0.01 | [32] |
| MER, LEV | MEPS 2 | UHPLC-PDA | 5 | 0.01 | [33] |
| MER, LEV | P.P. | HPLC-PDA | 20 | 1 | [34] |
| MER, CEF | P.P. | UHPLC-PDA | 5 | 0.3–0.6 | [35] |
| MER-CEF | P.P. | HPLC-MS | 5 | 0.05 | [36] |
| MET, MER, LEV, CEF | d-MSPE | UHPLC-PDA | 10 | 0.001 | This method |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruni, P.; Avino, P.; Ferrone, V.; Pilato, S.; Barbacane, N.; Canale, V.; Carlucci, G.; Ferrari, S. Preparation of Fe3O4-Reduced Graphene-Activated Carbon from Wastepaper in the Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction and UHPLC-PDA Determination of Antibiotics in Human Plasma. Separations 2023, 10, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020115
Bruni P, Avino P, Ferrone V, Pilato S, Barbacane N, Canale V, Carlucci G, Ferrari S. Preparation of Fe3O4-Reduced Graphene-Activated Carbon from Wastepaper in the Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction and UHPLC-PDA Determination of Antibiotics in Human Plasma. Separations. 2023; 10(2):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020115
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruni, Pantaleone, Pasquale Avino, Vincenzo Ferrone, Serena Pilato, Nadia Barbacane, Valentino Canale, Giuseppe Carlucci, and Stefania Ferrari. 2023. "Preparation of Fe3O4-Reduced Graphene-Activated Carbon from Wastepaper in the Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction and UHPLC-PDA Determination of Antibiotics in Human Plasma" Separations 10, no. 2: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020115
APA StyleBruni, P., Avino, P., Ferrone, V., Pilato, S., Barbacane, N., Canale, V., Carlucci, G., & Ferrari, S. (2023). Preparation of Fe3O4-Reduced Graphene-Activated Carbon from Wastepaper in the Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction and UHPLC-PDA Determination of Antibiotics in Human Plasma. Separations, 10(2), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020115








