Abstract
A multiple heart-cutting (mLC-LC) two-dimensional HPLC-UV achiral–chiral method for the direct analysis of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) in food supplements under environmentally friendly conditions was developed to cope with the very well-known limited chemoselectivity of chromatographic media for enantioselective analysis. Both achiral and chiral methods were developed in compliance with the main principles of green chromatography. The achiral analysis was performed isocratically with an optimized ion-pair reversed-phase (IP-RP) method based on a water/EtOH (95:5, v/v) mobile phase containing heptafluorobutyric acid (7 mM) as the IP agent. The achiral method was characterized by a very appreciable performance and was validated before the analysis of the real sample. High recovery values for all compounds (from 97% to 101%) were found in the interday evaluation. Additionally, low RSD% values in the long-term period were measured, in the range between 1.1% and 4.8%. Still, an LOQ value of 0.06 mg/mL was established for all compounds. The quantitative analysis of a commercial food supplement revealed that BCAAs were present in amounts very close to those declared by the producer. The enantioselective analysis was carried out through the application of the chiral ligand-exchange chromatography (CLEC) approach, using O-benzyl-(S)-serine ((S)-OBS, 0.5 mM) as the chiral selector and Cu(II) nitrate (0.25 mM) as the metal source in the eluent. Resolution and separation factor values up to 2.31 and 1.43, respectively, were obtained. The two chromatographic systems were connected through a six-port switching valve, and the developed two-dimensional mLC-LC method confirmed the absence of D-enantiomers of BCAAs in the food supplement, as reported in the manufacturer’s label.
1. Introduction
Green chromatography [1,2,3,4,5] is a specific branch of green chemistry [6,7,8] that originates from the very well-known “twelve principles” of Anastas, intended to minimize the impact of chromatographic processes on the environment and human health. Along this line, several research efforts have been and are still being conducted to address green separation processes in liquid chromatography (LC) through the replacement of toxic solvents and mobile phase eluents with more benign ones, while simultaneously reducing the analysis time [1,2,3,4,5]. Other primary goals of such practices are to make analysis faster and more energy-efficient, without compromising the performance characteristics of the original methods. This latter goal is often the bottleneck in converting existing methods to more environmentally friendly alternatives. Typical aqueous eluents for reversed-phase applications in liquid chromatography (RP-LC) contain acetonitrile (ACN) and/or methanol (MeOH) as elution strength modulators. Both of these organic modifiers are toxic, but MeOH has lower disposal costs, which should lead operators to use it preferentially over ACN [1,9,10,11].
In the last two decades, and especially since the ACN shortage in 2009, ethanol (EtOH) has increasingly been regarded as an environmentally friendly solvent that is particularly desirable for RP applications [9,10,11,12]. EtOH is indeed less volatile, less toxic, and has a very modest disposal cost compared with ACN and MeOH. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that EtOH can preserve fair-to-good chemoselective performances and provide reproducible analyses when used in place of ACN for RP-LC applications.
Another important green aspect of chromatographic methods is the presence or absence of sample preparation steps, including derivatization reagents, which are frequently highly polluting and toxic [1,2,3,4,5]. Therefore, from a green analytical chemistry perspective, it is highly advantageous to rely upon direct chromatographic procedures whenever possible.
Making a chromatographic process green also means, for a given sample, obtaining as much information as possible with a single analysis. This can be made possible through the application of multidimensional (mostly two-dimensional) methods [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. In this context, the application of multiple heart-cutting (mLC-LC) [15,20,21,22]—a two-dimensional LC method—is attracting increasing attention due to the reduced complexity of the required equipment. In mLC-LC applications, fractions from different peaks in the first dimension (first column) are selectively transferred one at a time to the second dimension (second column), where they undergo an additional separation process. In most cases, two HPLC systems are connected with a switch valve that allows the aforementioned selective transfer. Very profitably, the two separation processes (that is, the first and second dimensions) can be performed in series, resulting in reduced solvent consumption and waste generation, combined with shorter analysis time.
mLC-LC analysis is particularly advantageous when an achiral column is connected to a chiral one, to cope with the intrinsically limited chemoselectivity of the commercially available enantioselective materials [23,24,25,26,27]. Indeed, mixtures containing enantiomers of different compounds could not be analyzed in one run, due to the occurrence of overlapping peaks.
For the achiral–chiral analysis of amino acid (AA) mixtures, several mLC-LC methods have been developed to date [16,25,26,27,28]. The common aspect of almost all of the studies found in the literature is the pre-column derivatization of the target molecules with achiral chromophores or fluorophores to improve the detection sensitivity and separation.
The main objective of this work was the development of an mLC-LC method for the direct HPLC achiral–chiral analysis of three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)—valine (Val), isoleucine (Ile), and leucine (Leu)—contained in commercial food supplements, according to the main principles of green chemistry [1,29]. In the following sections, the development of the methods for the achiral–chiral analysis is described in detail. The achiral analysis was performed by relying on an optimized ion-pair (IP)-RP-HPLC method [30,31,32,33], while the enantioselective analysis was carried out through a chiral ligand-exchange chromatography (CLEC) approach [34,35,36].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Analytical-grade ethanol (EtOH), acetic acid (AcOH), heptafluorobutyric acid (HFBA), nonafluoropentanoic acid (NFPA), tridecafluoroheptanoic acid (TDFHA), O-benzyl-(S)-serine ((S)-OBS), copper(II) nitrate pentahemihydrate (Cu(NO3)2 × 2.5 H2O), all of the standard branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) (i.e., valine (Val), leucine (Leu), and isoleucine (Ile) (both as racemates and in their enantiomerically pure forms)), and sodium nitrite (used as an unretained marker) were purchased from Merck Life Science (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). A commercial dietary supplement labeled as containing only L-AAs was obtained from a local drug store. Water for HPLC analysis was purified with a New Human Power I Scholar water purification system (Human Corporation, Seoul, Korea) and a Millipore Milli-Q water purification system (Milan, Italy). The mobile phases were degassed via 10 min of sonication before use.
2.2. Extraction of the AA Pool from the Food Supplement
Five tablets of the commercial food supplement were weighed and accurately ground in a mortar to obtain a homogeneous fine powder. About 200 mg of the powder was weighed, transferred into a volumetric flask, and solubilized with a water/EtOH (95:5, v/v) solution to obtain a final 1.5 mg/mL concentration. The resulting suspension was sonicated for 5 min to facilitate the extraction of all three BCAAs, and then 5 mL was filtered through a 0.45 µm nylon filter. The filtered solution was used for the achiral IP-RP-HPLC analysis. This procedure was repeated thrice, and each solution was subjected to chromatographic analysis. In the context of the extraction process, both plain water and other EtOH contents higher than 5% (v/v) were comparatively tested. The presence of a minor amount of EtOH made it necessary to favor the extraction of the three rather hydrophobic AAs, while amounts higher than 5% (v/v) did not further improve the extraction extent, which was rather quantitative (>98%).
2.3. Achiral–Chiral HPLC Analysis
The achiral HPLC analysis was conducted on a Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan) LC-20A Prominence equipped with a CBM-20A communication bus module, two LC-20AD dual-piston pumps, and an SPD-M20A photodiode array detector with a 20 µL stainless steel loop. A Prevail RP18 column (Grace, Sedriano, Italy, 250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm, 110 Å pore size) was used as the analytical column for all of the IP-RP-HPLC analyses. Unless otherwise stated, the eluent flow rate was 1.2 mL/min, while the column temperature was set to 25 °C. The optimized mobile phase composition was water/EtOH (95:5, v/v) with 7 mM heptafluorobutyric acid (HFBA). In addition, a fully aqueous solution containing HFBA (7 mM) was used in the study. In the context of the optimization method for the achiral analysis, two additional but less high-performing volatile perfluoroalkyl acids were also comparatively tested in an effort to ameliorate the extent of chemoselectivity between the structurally similar Ile and Leu: nonafluoropentanoic acid (NFPA), and tridecafluoroheptanoic acid (TDFHA). In all cases, the chromatographic runs were observed with a UV–Vis detector at 220 nm.
The enantioselective analysis was performed on a Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan) LC-Workstation Class LC-10 equipped with a CBM-10A system controller, two LC-10AD high-pressure binary gradient delivery systems, an SPD-10A variable-wavelength UV–Vis detector, and a Rheodyne 7725i injector (Rheodyne Inc., Cotati, CA, USA) with a 20 µL stainless steel loop. For the chiral analysis, a GraceSmart RP18 column (Grace, Sedriano, Italy, 250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d. 5 µm, 120 Å pore size) was used. In the optimized conditions, an aqueous 0.5 mM (S)-OBS and 0.25 mM Cu(II) solution was used as the mobile phase for the CLEC system, and the analysis was performed at a 1.0 mL/min flow rate. The column temperature was fixed at 25 °C with a Grace heather/chiller (Model 7956R) thermostat. A 254 nm detection wavelength was selected for the CLEC analyses.
Sodium nitrite was selected as the unretained marker to evaluate both the IP-RP-HPLC and CLEC performances (that is, for the calculation of the following chromatographic parameters: retention factor, k; separation factor, α; resolution factor, RS; number of theoretical plates, N).
For the mLC-LC applications, a manual two-position six-port switching valve assembled in our laboratory for a previous study focused on the achiral–chiral analysis of an AA pool in a complex food matrix [27] was efficiently used. This system was very similar to that employed by other authors for similar applications [22,23], and it included a 100 μL stainless steel loop. For both the achiral and chiral analyses, the chromatograms were obtained and handled with the LC Solution Software (Version 1.22 SP1) from Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development of the Achiral IP-RP-HPLC Method
In order to maximize the chemoselectivity of the IP-RP method representing the first dimension of the mLC-LC system, the effects of the following variables were iteratively scrutinized: (i) concentration of organic modifier (EtOH); (ii) type and concentration of IP agent; (iii) eluent flow rate. Based on some successful IP-RP-HPLC studies on the analysis of AA mixtures in food matrices [30,32,37,38], we decided to test a similar chromatographic method by simply replacing the commonly used acetonitrile (ACN) with the greener and less toxic EtOH.
Based on the satisfactory results recently obtained in our laboratory [33], a water/EtOH—95/5 (v/v; 7mM of HFBA) mobile phase was initially tested. With a 7 mM HFBA concentration, the baseline separation of the three BCAAs was achieved, and the AAs were eluted in direct relation to their lipophilicity [37,38]. The elution order in the EtOH-based system was exactly the same as obtained with water/ACN mobile phases [37,38] (Val < Ile < Leu), even though EtOH produced lower elution efficiencies than ACN as a result of its slower mass transfer kinetics.
According to the IP-RP mechanism, the analysis time increases with the increase in the concentration of the IP reagent [39]. This retention trend could be conveniently accompanied by improved selectivity. For this reason, the effect of HFBA concentration on the overall chromatographic performance was evaluated, trying to enhance the “critical chemoselectivity” of the system towards the pair Ile–Leu. As shown in Table 1 (entries a and b), by increasing the concentration of the IP reagent up to 15 mM, the residence time of the analytes in the columns was prolonged, with only a marginal effect on critical selectivity; accordingly, the lower tested HFBA concentration (7 mM) was preferred to enhance the lifespan of the LC column.

Table 1.
IP-RP-HPLC performance obtained under the tested experimental conditions (details are reported as footnotes and in Section 2.3); k: retention factor; α: separation factor; RS: resolution factor. All of the analyses were observed at 220 nm. F.r.: eluent flow rate. Separation and resolution factor values refer to two consecutive peaks in the chromatogram.
Owing to its advantageous low viscosity, full miscibility with water, and low UV absorption, ACN has been and remains the most widespread organic modifier for IP- RP-HPLC applications. However, in spite of all of these favorable characteristics, ACN is well recognized as having some toxic effects (mostly of dermal and oral character), in addition to being highly flammable and volatile. All of these characteristics justify its inclusion in the list of hazardous air pollutants [40]. On the other hand, compared to ACN, EtOH exhibits lower toxicity, reduced cost, is easier to dispose of, and has been demonstrated to provide comparable or even superior characteristics for the separation of biomolecules under IP-RP conditions [9,41]. There is currently only one published paper that applies the IP-RP-HPLC approach to the analysis of underivatized proteinogenic AAs using EtOH as an organic modifier of the aqueous mobile phase [33].
Two other perfluorinated carboxylic acids with different side-chain lengths were screened using the same water/EtOH ratio. Accordingly, nonafluoropentanoic acid (NFPA) and tridecafluoroheptanoic acid (TDFHA) were considered for comparative evaluation. Flowing a mobile phase with 7 mM NFPA resulted in unprofitably long retention (Table 1, entry a vs. entries e and f), even with a 1.5 mL/min flow rate. Following the IP-RP principles [30,39], a lower concentration of NFBA was tested as well. Accordingly, maintaining a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, a concentration of 3.85 mM of NFPA was employed. Nevertheless, even if all compounds were satisfactorily eluted within 40 min, the eluent carrying 7 mM HFBA still remained the best option (Table 1, entry a vs. g) considering the lower column equilibration times required compared to NFPA [30,32,39].
The last perfluoroalkyl acid tested was TDFHA, which is able to produce peculiar chromatographic performances, as demonstrated by several authors [30,30,32]. Generally, this IP agent is used at lower concentrations than those of HFBA [39,42]; therefore, a 0.5 mM concentration was tested. Nevertheless, under these conditions, extremely long and unprofitable retention times were observed (i.e., for Val the retention time was about 60 min; data not shown), thereby excluding the use of this IP agent. Therefore, HFBA was used in the subsequent optimization steps.
In order to further improve the sustainability of the IP-RP-HPLC system, half the percentage of EtOH (from 5% down to 2.5%, v/v) in the eluent was scrutinized under isocratic elution conditions, keeping the HFBA content at 7 mM. An increase in the water percentage produced an increase in the residence time of the analytes in the column, with favorable improvements of the separation (α) and resolution (RS) values (Table 1, entry a vs. entry c). Interestingly, the profitable use of a fully aqueous mobile phase was also tested by increasing the temperature to 45 °C, which reduced the otherwise very long retention times. Decreasing the EtOH content in the eluent produced lower elution efficiencies for the “critical pair” Ile–Leu, as a result of the reduced mass transfer kinetics (Table 1, entry a vs. entry c). Consistent with a conventional RP retention mechanism [42], an increase in retention was observed for almost all compounds. On the basis of the above, the best compromise was found to be the eluent containing 5% (v/v) EtOH. Based on the eluent composition, the method was in evident adherence to the main principles of green chemistry [1]; therefore, it was applied to the analysis of the real sample.
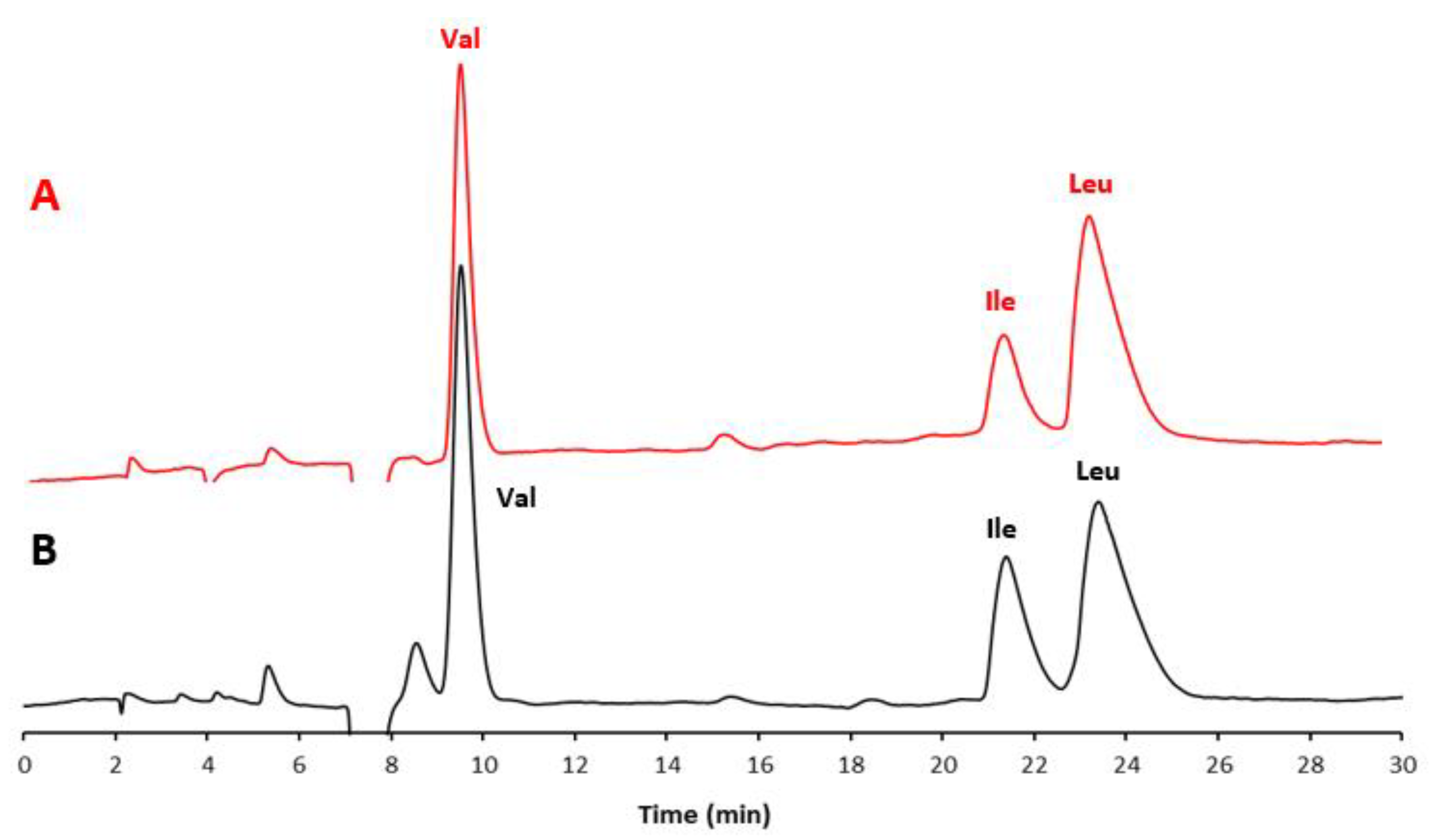
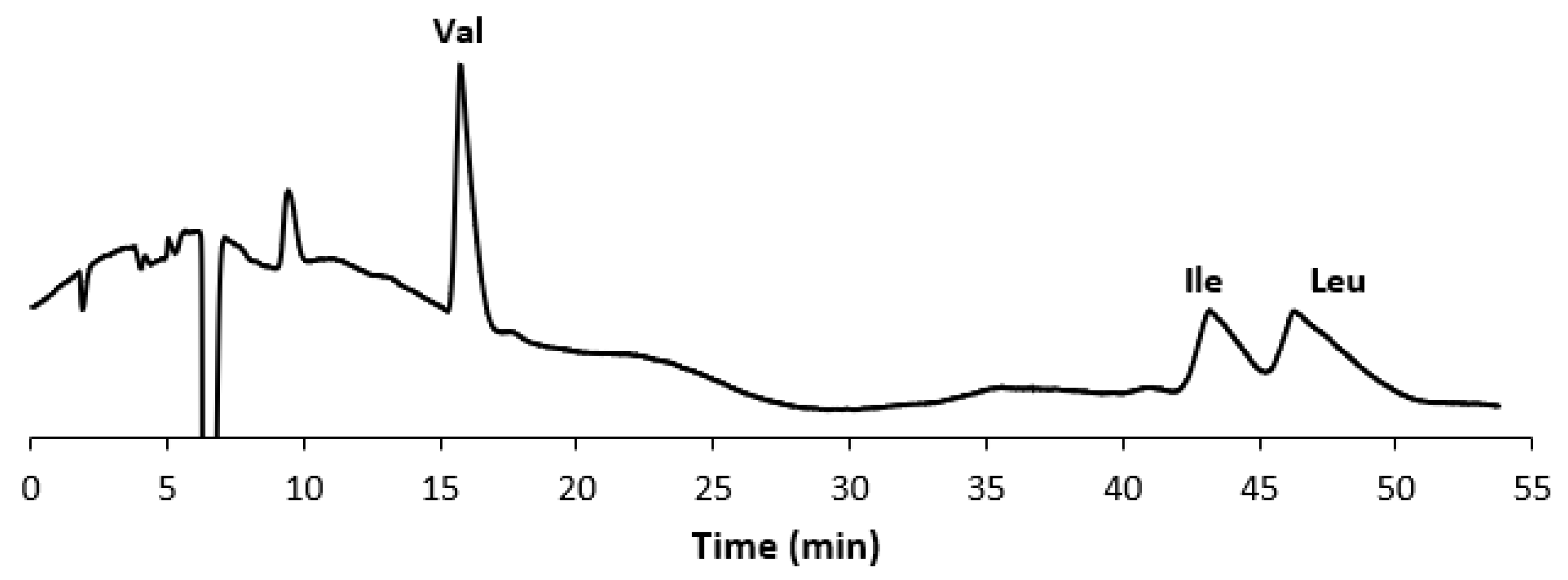
In Figure 1A, the chromatogram of a standard mixture of the three BCAAs is shown, while Figure 1B displays the chromatogram of the extract from the commercial food supplement. In Figure 2, the chromatogram of the extract of the food supplement obtained with a fully aqueous mobile phase carrying HFBA (7 mM) is also presented.
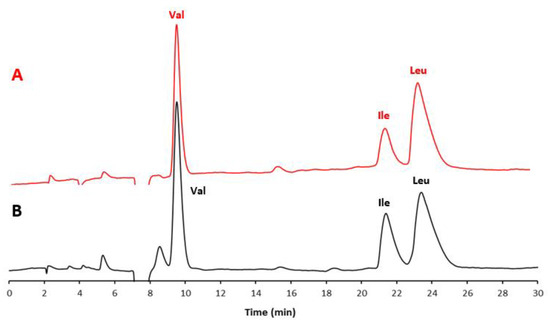
Figure 1.
Chromatograms of (A) the mixture of three AA standards (red line) and (B) the extract from the selected food supplement (black line). Experimental conditions: column, Prevail RP18 (Grace, Sedriano, Italy) (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm, 110 Å pore size); mobile phase, water/EtOH/HFBA (95:5:0.1, v/v/v; HFBA concentration corresponding to 7 mM); column temperature, 25 °C; flow rate, 1.0 mL/min; UV @ 220 nm.
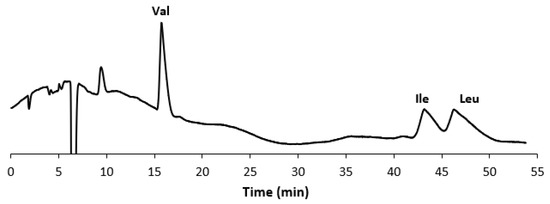
Figure 2.
Chromatogram of the extract from the selected food supplement. Experimental conditions: column, Prevail RP18 (Grace, Sedriano, Italy) (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm, 110 Å pore size); mobile phase, water with 0.1% (v/v) HFBA (7 mM); column temperature, 45 °C; flow rate, 1.2 mL/min; UV @ 220 nm.
3.2. Validation of the Optimized Achiral IP-RP-HPLC Method and Quantitative Analysis of the AAs in the Food Supplement
A preliminary validation study of the developed IP-RP-HPLC method was performed on all three BCAAs. The following parameters were considered: selectivity, linearity, precision (in the short- and long-term), accuracy (in the short- and long-term), and limit of quantification (LOQ).
For each AA, the quantitative analysis was performed using calibration curves that were properly constructed by plotting the concentrations of five calibration standard solutions versus the corresponding peak areas. The tested linearity concentration range was 0.125–0.75 mg/mL for the three BCAAs, while the coefficient of determination (R2) was higher than 0.9991. In this respect, a range of concentrations between 50 and 150% of the expected/theoretical AA concentration was used.
The method’s selectivity was evaluated by injecting 20 μL of a blank (mobile phase). No system or interference peaks were detected at the retention time of the three BCAAs. To evaluate the accuracy and precision of the developed IP-RP-HPLC method, an external set of two control solutions was considered: for Val (from 0.25 to 0.7 mg/mL), and for Ile and Leu (from 0.16 to 0.7 mg/mL). These solutions were injected in triplicate on the same day and on three consecutive days (Table 2). The system’s precision was determined as the relative standard deviation (RSD%) among the concentration values obtained from consecutive injections, within the short- and long-term periods. The same experimental protocol was also applied to measure the accuracy of the method, expressed as recovery (%). The data in Table 2 represent three replicates of each external test solution within one day and for three consecutive days.

Table 2.
Intraday and interday RSD% and recovery% values.
As evident from the data in Table 2, good recovery (%) values (97−101%) and RSD values (<5%) were found in the long-term (interday) evaluation. The LOQ was measured considering the lowest concentration at which the RSD% of the peak area values from five consecutive injections was lower than 5.0%. Accordingly, an LOQ value of 0.06 mg/mL was established for all compounds. The results obtained in the validation study were consistent with those reported by other authors [43,44,45] in the analysis of food matrices, thereby confirming the good quality of the developed method. Therefore, the optimized IP-RP-HPLC method was applied for quantitative analysis of the three BCAAs contained in the tablets under investigations injecting the extract solutions in triplicate.
After some preliminary experiments, a 1.5 mg/mL concentration of the food supplement was found to be optimal for the quantitative analysis, since at this concentration the peaks of the three BCAAs were in the tested linearity range (Table 2).
The results showed that the BCAAs were present in amounts very close (from 92% up to 99%) to those declared by the producer: 457.0 ± 2.6 mg of Leu/tablet, 239 ± 4 mg of Val/tablet, and 248.0 ± 3.6 mg of Ile/tablet (means of three replicates). The amounts determined were compliant with those labeled, i.e., 500 mg of Leu/tablet, 250 mg of Val/tablet, and 250 mg of Ile/tablet, since in the official control a lower tolerance of 20% is admitted (https://food.ec.europa.eu/safety/labelling-and-nutrition/addition-vitamins-and-minerals_en; accessed on 6 January 2023).
3.3. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions for the CLEC Analysis
For the enantioseparation of the three underivatized BCAA enantiomeric couples, a system operating according to the CLEC strategy, with a chiral mobile phase (CMP) system for the presence of O-benzyl-(S)-serine [(S)-OBS] [46] as a chiral selector, was used.
The selection of a CMP-CLEC system was due to its intrinsic green features and cost-effectiveness. Indeed, CLEC systems operating under CMP conditions allow the use of conventional and relatively inexpensive RP columns (usually C18 stationary phases) coupled with commercially available and low-cost chiral selectors, without the need for pre-chromatographic derivatization procedures [34].
Unlike other chiral selectors for CMP-CLEC applications [47,48], (S)-OBS contains a free underivatized amino group, with the only hydrophobic region being represented by the benzyl residue. This CMP-CLEC system was successfully applied by the group of Natalini and co-workers for the efficient enantioseparation of natural and synthetic AAs [46,49,50].
In the setting of the optimization study, a preliminary comparison between two Cu(II) salts (i.e., sulfate and nitrate) was performed, since the type of counterion influences the CLEC process when (S)-OBS is used as a chiral additive [49]. As expected, nitrate provided better elution efficiency (i.e., higher N and RS values) than sulfate; therefore, the subsequent experiments were performed using (S)-OBS and Cu(II) nitrate in the mobile phase in order to test (i) chiral selector and copper salt concentrations, and (ii) the presence/absence of ethanol as an organic modifier.
Based on previous studies by Davankov and co-workers [34,51], the optimal 2:1 (S)-OBS/Cu(II) concentration ratio was maintained in this study [46,49,50]. Natalini and co-workers observed that when keeping both the eluent pH (4.00) and the chiral selector/Cu(II) ion concentration ratio (2:1) constant, an increase in the metal concentration from 0.25 mM to 0.87 mM resulted in significantly shortened retention times and reduced RS values, along with negligible changes in terms of enantioselectivity [46]. Indeed, according to CLEC theory [35,51,52], the Cu(II) concentration influences the mobile phase’s strength and affects the ligand-exchange mechanism; higher Cu(II) ion concentrations, favoring the location of the diastereomeric ternary complexes in the mobile phase, produce lower retention times. The pH of the mobile phase is another crucial parameter that determines the behavior of all CLEC systems [35,46,48]. In order to be coordinated as a bidentate ligand to Cu(II), the AA has to release one proton from its NH3+ group. As a result, the formation of Cu(II) complexes tends to be favored when eluent’s pH is progressively increased; accordingly, the retention of AA enantiomers also almost always increases when raising the mobile phase’s pH [35]. While retention trends are almost always the same upon changing the two above mobile phase variables, this is not always the case as far as α and RS values are concerned [35,46,47,52,53].
In the present work, the eluent’s pH was not fixed at a specific value. Therefore, it exclusively depended upon the composition of the mobile phase. In this context, the eluent’s pH was found to increase upon decreasing the concentrations of (S)-OBS and Cu(NO3)2. The concentration of the chiral selector was evaluated at three different values—that is, 0.25 mM, 0.5 mM, and 1.0 mM—and, accordingly, the Cu(NO3)2 concentration was set to 0.125 mM, 0.25 mM, and 0.5 mM, respectively. The pH values of these mobile phases were measured to be 4.3, 4.0, and 3.8, respectively (from the most diluted to the most concentrated). As expected, reducing the additive concentration involved an increase in the retention of the three AAs, which was also accompanied by an equal trend of enantioseparation and RS factors (Table 3, entries a–c). This behavior can be mostly ascribed to the variation in both the pH and the Cu(II) concentration. Only Leu showed a maximum in terms of resolution in correspondence with the intermediate concentration tested.

Table 3.
Chromatographic performances obtained in the sole enantioselective LC system for the three BCAAs when varying the concentrations of the eluent additives. Mobile phase compositions are reported as footnotes to the table, while other experimental conditions are detailed in Section 2.3. The enantiomer elution order was the same in all of the analyses: D < L; k2 is the retention factor of the second eluted enantiomer of each enantiomeric pair.
The use of EtOH was also evaluated, since in CLEC applications the presence of an organic modifier in the mobile phase—even at a low percentage—can have a remarkable effect on the overall chromatographic performance, leading to significant decreases in analyte retention and, on the other hand, to a dramatic loss in column selectivity [46,47,54]. Indeed, the organic modifier strongly affects the hydrophobic interactions involved in controlling both the retention and enantioselectivity of hydrophobic AAs, and it can be useful to reduce the run time of the most retained analytes. However, this parameter should be used with special care, because the column’s stability could be compromised when C-CSPs are used, while simultaneously leading to an increase in the eluent cutoff. Natalini and co-workers [46] noticed that, compared to other more hydrophobic selectors for CMP-CLEC applications, the use of (S)-OBS required lower percentages of organic modifier to achieve the elution of particularly hydrophobic AAs in acceptable run times. Indeed, for the same compounds, the retention factor values provided by (S)-OBS were found to be generally lower than those obtained with other chiral additives for CMP-CLEC, such as the widely employed N,N-dimethyl-(S)-phenylalanine. This behavior can be tentatively ascribed to the reduced hydrophobicity of the diastereomeric ternary complexes containing (S)-OBS, as a consequence of the absence of other alkyl or arylalkyl groups on the amino-acidic nitrogen atom.
In the present work, the effect of low percentages (0–5%, v/v) of EtOH was evaluated, mostly to reduce the retention time of Ile and Leu, in an effort to keep the chromatographic performance unchanged. The obtained results were consistent with the literature [47]: increasing concentrations of organic modifier led to decreases in the retention, selectivity, and resolution factors. Most importantly, with 5% (v/v) EtOH, L- and D-Val were unresolved, while a general deterioration of the chromatographic performances was observed for the other two compounds (data not shown). This behavior can be explained by considering that the CLEC mechanism implies the superimposition of complexation events and hydrophobic interactions with the C18 layer [35,52,55]. Excessive reduction in the hydrophobic interactions led to an overall deterioration of the chromatographic performances. A D < L enantiomer elution order (EEO) was defined in all of the experimental conditions, by injecting pure enantiomeric standards. At the end of this optimization step, the best conditions identified for the analysis of the real sample were as follows: fully aqueous solution with 0.5 mM (S)-OBS + 0.25 mM Cu(II) nitrate, pH 4.0; 1.0 mL/min flow rate; wavelength of detection fixed at 254 nm; column temperature fixed at 25 °C.
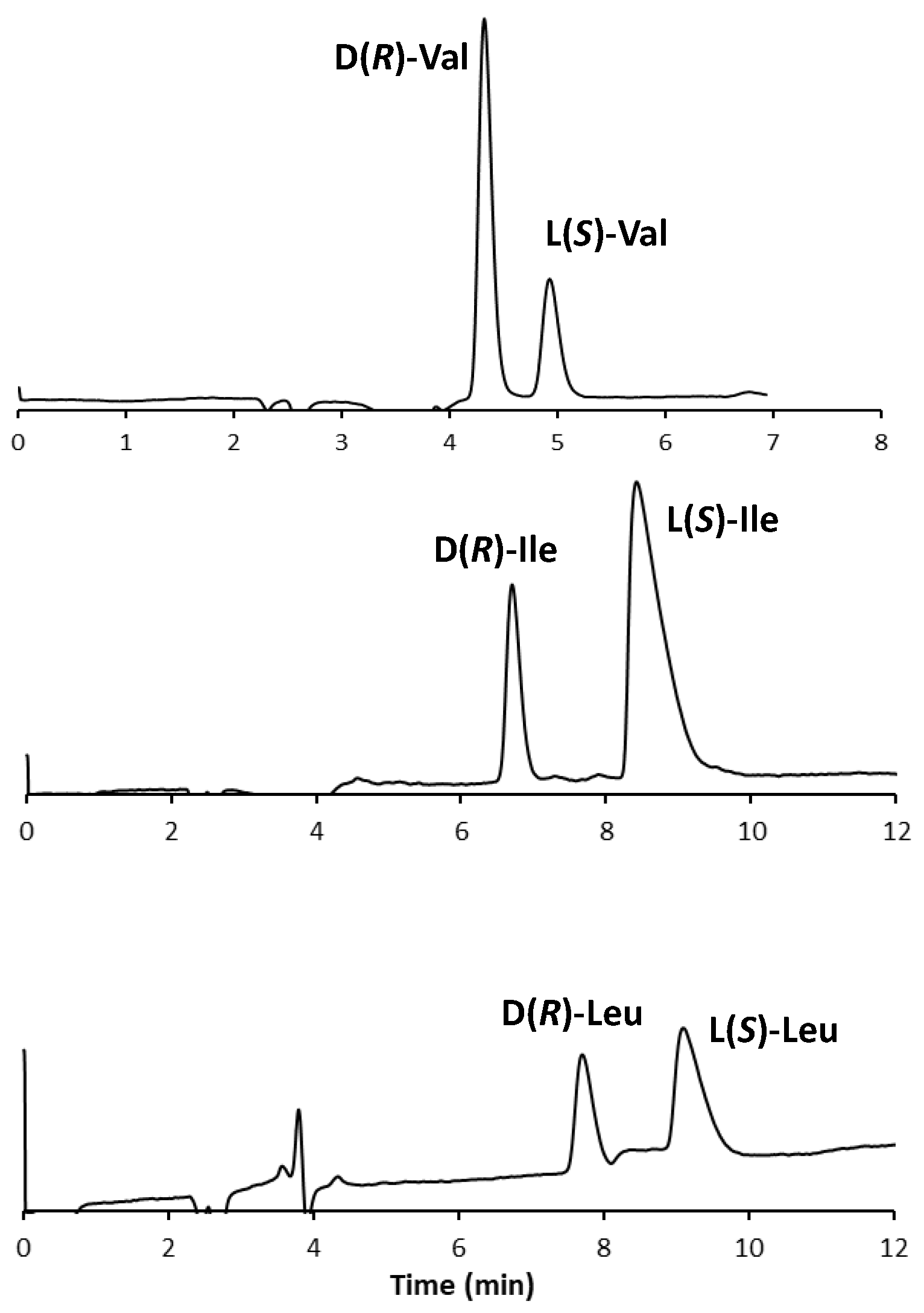
The chromatograms of the three standard enantiomeric mixtures are shown in Figure 3.
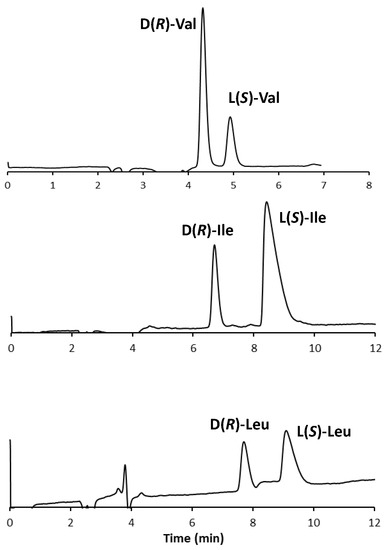
Figure 3.
Chromatogram of three standard enantiomeric mixtures. Experimental conditions: column, Prevail RP18 (Grace, Sedriano, Italy) (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm, 110 Å pore size); mobile phase, fully aqueous solution with 0.5 mM (S)-OBS and 0.25 mM Cu(NO3)2; column temperature, 25 °C; flow rate, 1.0 mL/min; UV @ 254 nm.
3.4. mLC-LC Achiral–Chiral Analysis of BCAAs in Food Supplements
Chiral LC methods are often inadequate to separate complex mixtures with different analytes. A possible solution is the implementation of a two-dimensional (2D) analytical platform, combining a non-enantioselective (achiral) column that should provide sufficient target chemoselectivity with a chiral column that achieves enantioseparation.
Among the most common “off-line” or “on-line” approaches applied for the coupling of two chromatographic systems, the former avoid the use of a special interface between the two systems and are free of limitations in terms of flow and eluent mismatches. This strategy implies the collection of the eluent from the first-dimension column (which can be performed either manually or with a fraction collector), the removal of the mobile phase with a drying step, and the re-dissolution of the dried sample in a second solvent for the enantioselective analysis in the second dimension. In spite of some evident advantages (such as the simplicity of the process), there are also some drawbacks to this method, such as time, difficulty of automation, scarce run-to-run reproducibility, and high risk of contamination. On the other hand, on-line methods always require specific interfaces and well-trained operators, but once optimized they are labor-saving, with a minimal risk of contamination, and in most cases can be completely automated [14].
The method developed in this work falls within the domain of the multiple heart-cutting (mLC-LC) approach, manually operated with a laboratory-made switch valve. Each AA from the first dimension was singularly heart-cut and transferred to the second column. The extract from the food supplement tablets was solubilized in the mobile phase system optimized for the 1D analysis. The optimization of the valve-switching time demonstrated that the best results were achieved by switching the valve in correspondence with the apex of the 1D peak and maintaining it in the “load” position for about 10 s before switching it again to ensure that the loop was adequately filled.
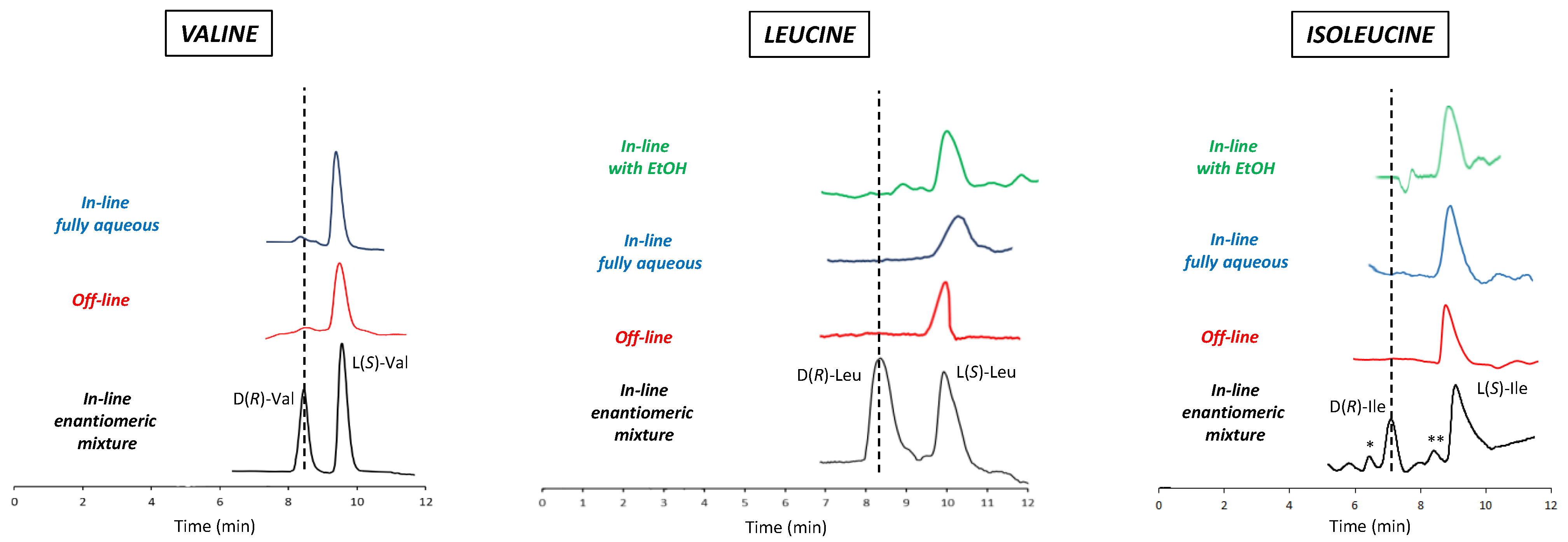
To verify the reliability of the developed mLC-LC method, the off-line 2D chiral analysis of the three peaks obtained from the 1D achiral analysis of the food supplement was included in the study. For this purpose, each peak from the first dimension was individually collected, dried under N2, and then injected into the second column. The results of both the on-line and off-line analyses were evaluated by considering the retention times of the two enantiomers obtained through an in-line LC-LC analysis of the enantiomeric mixture of each standard. The chromatograms of the in-line analyses (with and without ethanol in the 1D mobile phase), off-line analysis, and in-line spiking analysis are shown in Figure 4.
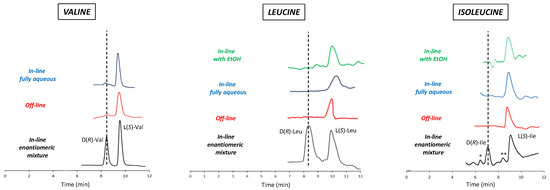
Figure 4.
Chromatograms obtained for all three BCAAs in various types of analyses. From the bottom to the top: chromatogram of the artificial enantiomeric mixture analyzed in-line with the implemented LC-LC system (under fully aqueous condition in the achiral separation, black line); chromatogram of the fraction collected during the achiral separation (first dimension) and then reinjected into the chiral column (second dimension) after drying under vacuum and re-solubilized in the chiral selector/Cu(II)-containing eluent (off-line mode; red line); chromatogram of the fraction switched from the first (achiral) to the second (chiral) column, using the fully aqueous mobile phase in the first dimension (blue line); chromatogram of the fraction switched from the first (achiral) to the second (chiral) column, using the water/EtOH-containing mobile phase in the first dimension (green line). Chromatograms with red, blue, and green lines refer to the analysis of real samples (that is, the extract from the food supplement). Experimental conditions: column, Prevail RP18 (Grace, Sedriano, Italy) (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm, 110 Å pore size); mobile phase, fully aqueous solution with 0.5 mM (S)-OBS and 0.25 mM Cu(NO3)2; column temperature, 25 °C; flow rate, 1.0 mL/min for Ile and Leu, 0.5 mL/min for Val; UV @ 254 nm.
The satisfactory results (Figure 4) obtained in strict adherence to the main paradigms of green chemistry clearly demonstrate the applicability of the implemented mLC-LC system [1,6,56] for the characterization of BCAAs in commercial food supplements. Apart from the use of environmentally sustainable eluents, another strength of this method is its limited cost.
In spite of the advantageous features of the developed mLC-LC system, some issues should nevertheless be highlighted. First of all, the presence of EtOH in the mobile phase of the first dimension caused some interference with the retention times of the Val enantiomers in the second dimension. As a result, it readily emerged that it was impossible to adequately analyze Val enantiomers in this way. This problem did not disturb the enantioselective 2D heart-cutting analysis of the more-retained Ile and Leu. This drawback requires the development of different elution conditions for the 1D analysis, avoiding the use of EtOH. A fully aqueous mobile phase was therefore employed (Figure 2) and, in order to reduce the extremely high retention time, the temperature was increased to 45 °C. As expected, the absence of EtOH in the 1D mobile phase almost completely eliminated the interference occurring in the corresponding retention of the 2D Val enantiomers. This finding led to the hypothesis that the increase in temperature (45 °C) applied for enantioselective 1D analysis was also beneficial with respect to the noise effect derived from HFBA, probably due to the high volatility of this additive, which evaporated at the inlet of the second column. Finally, the analysis of the commercial food supplement (Figure 4) confirmed the exclusive presence of L-enantiomers in accordance with the producer’s declaration. This result was readily evident from both off-line and in-line analyses.
4. Conclusions
In this work, an achiral–chiral two-dimensional mLC-LC method was developed and successfully applied for the analysis of a commercial food supplement containing BCAAs.
For the 1D achiral separation, an IP-RP-HPLC method was optimized with UV detection, eluting analytes with a water/EtOH (95:5, v/v) mixture containing 7 mM HFBA. The validation study demonstrated satisfactory performance characteristics of this developed procedure, which was then applied for the quantitative analysis of the food supplement. The obtained results revealed that the concentrations of the three BCAAs were consistent with those declared by the producer. For the 2D chiral analysis, a CLEC system operating with (S)-OBS (0.5 mM) as a CMP additive and Cu(II) nitrate was optimized. The mLC-LC method was finally applied for the analysis of the same food supplement, also confirming the absence of D-enantiomers of BCAAs, consistent with the producer’s declaration.
This study clearly demonstrates that environmentally sustainable chromatographic methods can be conveniently applied for the overall characterization of AA-based food supplements, which have seen widespread production and use in the last decade.
Author Contributions
I.V.: investigation, validation, formal analysis, data curation. S.M.: investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation. F.I.: validation, data curation, supervision. C.B.: data curation, writing—review and editing. G.W.A.A.: data curation. A.C.: investigation, data curation. L.C.: conceptualization, methodology, supervision. R.G.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation; R.S.: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the authors.
Acknowledgments
Dedicated to Benedetto Natalini to celebrate his 75th birthday.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Płotka, J.; Tobiszewski, M.; Sulej, A.M.; Kupska, M.; Górecki, T.; Namieśnik, J. Green chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1307, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, F.R.P.; Nóbrega, J.A.; Filho, O.F. Flow analysis strategies to greener analytical chemistry. An overview. Green Chem. 2001, 3, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, L.H.; Gron, L.U.; Young, J.L. Green Analytical Methodologies. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2695–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.; David, F.; Vanhoenacker, G.; Sandra, K.; Sandra, P. Green Chromatography (Part 1): Introduction and Liquid Chromatography. LCGC Eur. 2010, 23, 242–259. [Google Scholar]
- Shaaban, H. New insights into liquid chromatography for more eco-friendly analysis of pharmaceuticals. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6929–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastas, P.; Eghbali, N. Green Chemistry: Principles and Practice. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, I.T.; Anastas, P.T. Innovations and Green Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2169–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabré, M.; Ferey, L.; Somé, I.T.; Gaudin, K. Greening Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography Methods Using Alternative Solvents for Pharmaceutical Analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.; Eylem, C.C.; Akduman, N.E.B. Application of green methodology to pharmaceutical analysis using eco-friendly ethanol-water mobile phases. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, B.; van Beek, T.A. Alternative solvents can make preparative liquid chromatography greener. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4073–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, A.B.; Ismaiel, O.A.; Hassan, W.E.; Shalaby, A.A. Green analytical chemistry: Opportunities for pharmaceutical quality control. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 71, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, D.R.; Carr, P.W. Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography: A State of the Art Tutorial. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-González, M.E.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; Perez-Arribas, L.V.; Guillén-Casla, V. Two-dimensional liquid chromatography for direct chiral separations: A review. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Tsang, M.; Chetwyn, N.P. Analysis of pharmaceutical impurities using multi-heartcutting 2D LC coupled with UV-charged aerosol MS detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karongo, R.; Ge, M.; Geibel, C.; Horak, J.; Lämmerhofer, M. Enantioselective multiple heart cutting online two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of all proteinogenic amino acids with second dimension chiral separations in one-minute time scales on a chiral tandem column. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1180, 338858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woiwode, U.; Reischl, R.J.; Buckenmaier, S.; Lindner, W.; Lämmerhofer, M. Imaging Peptide and Protein Chirality via Amino Acid Analysis by Chiral × Chiral Two-Dimensional Correlation Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7963–7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A. Multidimensional Chromatography Edited by Luigi Mondello (Universita Degli Studi Di Messina), Alastair C. Lewis, and Keith D. Bartle (University of Leeds). J. Wiley & Sons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13959–13960. [Google Scholar]
- Blahová, E.; Jandera, P.; Cacciola, F.; Mondello, L. Two-dimensional and serial column reversed-phase separation of phenolic antioxidants on octadecyl-, polyethyleneglycol-, and pentafluorophenylpropyl-silica columns. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Rong, Y.; Song, Y.; Shi, L.; Chen, B.; Yang, X.; Xu, N.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zhang, Z. Profiling Analysis of Low Molecular Weight Heparins by Multiple Heart-Cutting Two Dimensional Chromatography with Quadruple Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8957–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursch, M.; Buckenmaier, S. Loop-Based Multiple Heart-Cutting Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography for Target Analysis in Complex Matrices. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5310–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piendl, S.K.; Geissler, D.; Weigelt, L.; Belder, D. Multiple Heart-Cutting Two-Dimensional Chip-HPLC Combined with Deep-UV Fluorescence and Mass Spectrometric Detection. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3795–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamase, K.; Homma, H.; Takigawa, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Santa, T.; Imai, K. Regional distribution and postnatal changes of d-amino acids in rat brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1334, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamase, K.; Inoue, T.; Morikawa, A.; Konno, R.; Zaitsu, K. Determination of free d-proline and d-leucine in the brains of mutant mice lacking d-amino acid oxidase activity. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 298, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, T.; Schmidtkunz, C.; Müller, B.; Meier, F.; Chlup, M.; Köhne, A.; Lämmerhofer, M.; Lindner, W. A comprehensive chemoselective and enantioselective 2D-HPLC set-up for fast enantiomer analysis of a multicomponent mixture of derivatized amino acids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamase, K.; Morikawa, A.; Ohgusu, T.; Lindner, W.; Zaitsu, K. Comprehensive analysis of branched aliphatic d-amino acids in mammals using an integrated multi-loop two-dimensional column-switching high-performance liquid chromatographic system combining reversed-phase and enantioselective columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1143, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianni, F.; Sardella, R.; Lisanti, A.; Gioiello, A.; Goga, B.T.C.; Lindner, W.; Natalini, B. Achiral–chiral two-dimensional chromatography of free amino acids in milk: A promising tool for detecting different levels of mastitis in cows. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 116, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woiwode, U.; Neubauer, S.; Lindner, W.; Buckenmaier, S.; Lämmerhofer, M. Enantioselective multiple heartcut two-dimensional ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography method with a Coreshell chiral stationary phase in the second dimension for analysis of all proteinogenic amino acids in a single run. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1562, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano-Tabares, P.I.; Negrín-Santamaría, I.; Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Pino, V. Recent efforts to increase greenness in chromatography. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 32, 100536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petritis, K.; Chaimbault, P.; Elfakir, C.; Dreux, M. Ion-pair reversed-phase liquid chromatography for determination of polar underivatized amino acids using perfluorinated carboxylic acids as ion pairing agent. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 833, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.D.; McCroskey, M.C. Perfluorinated acid alternatives to trifluoroacetic acid for reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 746, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petritis, K.; De Person, M.; Elfakir, C.; Dreux, M. Validation of an Ion-Interaction Chromatography Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids in Commercial Preparation Using Evaporative Light Scattering Detection. Chromatographia 2004, 60, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfaj, I.; Carotti, A.; Mangiapelo, L.; Cossignani, L.; Taticchi, A.; Macchiarulo, A.; Ianni, F.; Sardella, R. Environmentally Sustainable Achiral and Chiral Chromatographic Analysis of Amino Acids in Food Supplements. Molecules 2022, 27, 7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davankov, V.A.; Kurganov, A.A.; Ponomareva, T.M. Enantioselectivity of complex formation in ligand-exchange chromatographic systems with chiral stationary and/or chiral mobile phases. J. Chromatogr. A 1988, 452, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davankov, V.A.; Bochkov, A.S.; Kurganov, A.A.; Roumeliotis, P.; Unger, K.K. Separation of unmodified α-amino acid enantiomers by reverse phase HPLC. Chromatographia 1980, 13, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davankov, V.A.; Kurganov, A.A. The role of achiral sorbent matrix in chiral recognition of amino acid enantiomers in ligand-exchange chromatography. Chromatographia 1983, 17, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianni, F.; Lisanti, A.; Marinozzi, M.; Camaioni, E.; Pucciarini, L.; Massoli, A.; Sardella, R.; Concezzi, L.; Natalini, B. Hydrophobic Amino Acid Content in Onions as Potential Fingerprints of Geographical Origin: The Case of Rossa da Inverno sel. Rojo Duro. Molecules 2018, 23, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianni, F.; Sechi, P.; La Mantia, A.; Pucciarini, L.; Camaioni, E.; Cenci Goga, B.T.; Sardella, R.; Natalini, B. The Relationships between Somatic Cells and Isoleucine, Leucine and Tyrosine Content in Cow Milk. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaimbault, P.; Petritis, K.; Elfakir, C.; Dreux, M. Ion-pair chromatography on a porous graphitic carbon stationary phase for the analysis of twenty underivatized protein amino acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 870, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.D. Research and Evaluation of Organic Hazardous Air Pollutant Source Emission Test Methods. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1996, 46, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, F.; Jankowski, V.; Günthner, T.; Salem, S.; Nierhaus, M.; Schulz, A.; Zidek, W.; Jankowski, J. Replacement of acetonitrile by ethanol as solvent in reversed phase chromatography of biomolecules. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, M.; Mant, C.; Hodges, R. Effect of anionic ion-pairing reagent hydrophobicity on selectivity of peptide separations by reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1080, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, S.M.; Farag, M.A.; Bawazeer, S. Underivatized Amino Acid Chromatographic Separation: Optimized Conditions for HPLC-UV Simultaneous Quantification of Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Threonine, Histidine, Valine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, and Tyrosine in Dietary Supplements. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 31106–31114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, C.; Aldana Mejía, J.A.; Pena Ribeiro, V.; Gambeta Borges, C.H.; Gomes Martins, C.H.; Sola Veneziani, R.C.; Ambrósio, S.R.; Bastos, J.K. Occurrence, chemical composition, biological activities and analytical methods on Copaifera genus—A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, H.; Talebpour, Z.; Haghighi, F. Development, validation, and uncertainty measurement of HPLC-DAD method for determination of some free amino acids in infant formula and medical food products for inborn errors of metabolism. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natalini, B.; Sardella, R.; Pellicciari, R. O-Benzyl-(S)-Serine, a New Chiral Selector for Ligand-Exchange Chromatography of Amino Acids. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2005, 1, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, R. Separation of Underivatised Amino Acid Enantiomers by Means of a Chiral Solvent-Generated Phase. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1985, 23, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S. Resolution of D- and L-Amino Acids by HPLC using Copper Complexes of N,N-Dialkyl-α-amino Acids as Novel Chiral Additives. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. Engl. 1982, 21, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardella, R.; Macchiarulo, A.; Carotti, A.; Ianni, F.; Rubiño, M.E.G.; Natalini, B. Chiral mobile phase in ligand-exchange chromatography of amino acids: Exploring the copper(II) salt anion effect with a computational approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1269, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianni, F.; Sardella, R.; Lisanti, A.; Giacchè, N.; Conti, P.; Pinto, A.; Tamborini, L.; Natalini, B. Use of an o-Benzyl-(S)-Serine Containing Eluent for the Efficient Ligand-Exchange Chromatography-Based Enantioseparation of Constrained Glutamate Receptor Ligands. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davankov, V.A. Chiral selectors with chelating properties in liquid chromatography: Fundamental reflections and selective review of recent developments. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 666, 55–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remelli, M.; Fornasari, P.; Pulidori, F. Study of retention, efficiency and selectivity in chiral ligand-exchange chromatography with a dynamically coated stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 761, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remelli, M.; Pozzati, G.; Conato, C. Direct chiral resolution of underivatized amino acids on a stationary phase dynamically modified with the ion-exchanger Nτ-decyl-L-spinacine. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaverna, G.; Pantò, F.; Dossena, A.; Marchelli, R.; Bigi, F. Chiral Separation of Unmodified α-Hydroxy Acids by Ligand Exchange HPLC Using Chiral Copper(II) Complexes of (S)-Phenylalaninamide as Additives to the Eluent. Chirality 1995, 7, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, M.H.; Han, S.C.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, Y.K. Preparation and application of a new ligand exchange chiral stationary phase for the liquid chromatographic resolution of α-amino acid enantiomers. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 950, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Marć, M.; Gałuszka, A.; Namieśnik, J. Green Chemistry Metrics with Special Reference to Green Analytical Chemistry. Molecules 2015, 20, 10928–10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).