Large Eddy Simulation of Leakage Flow in a Stepped Labyrinth Seal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Method and Verification
Computational Domain and Boundary Conditions
3. Results
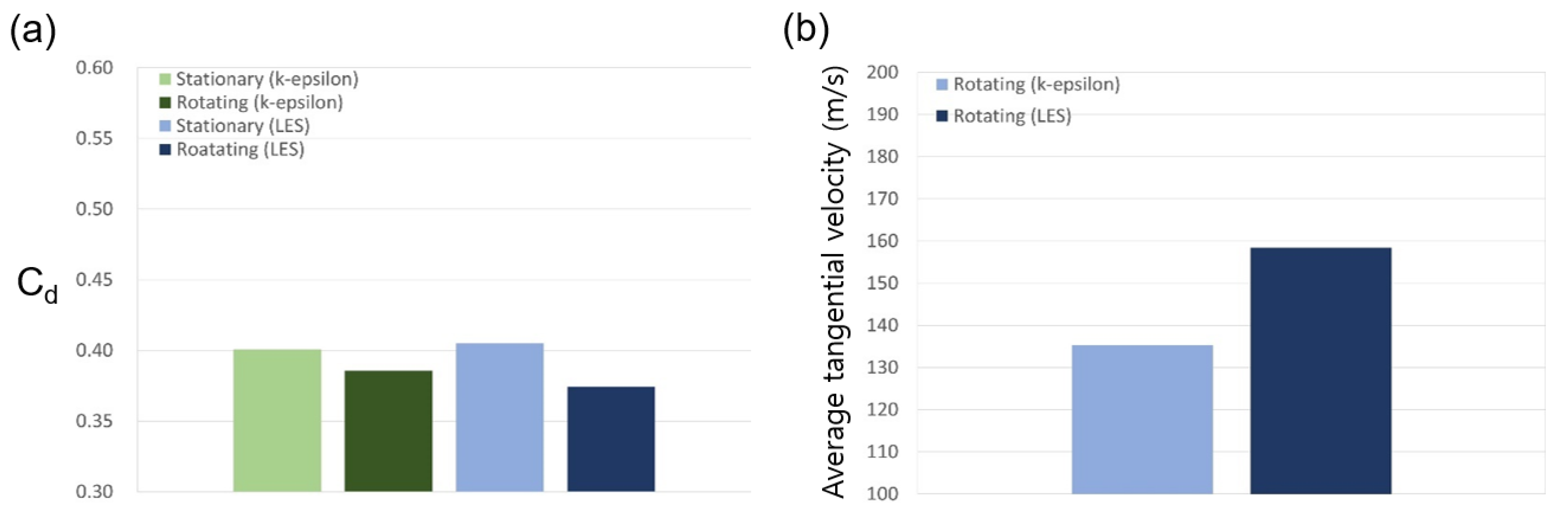
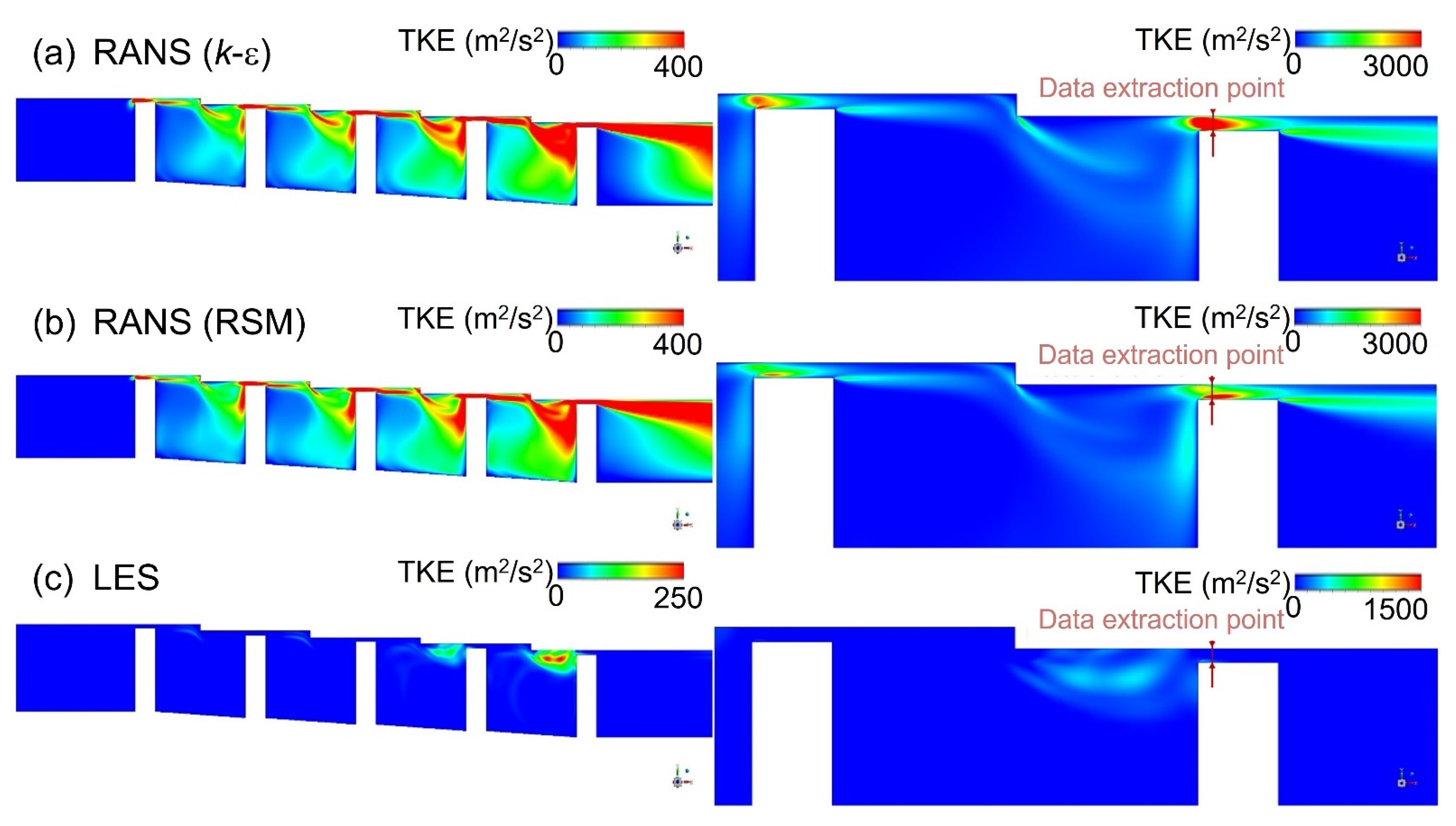
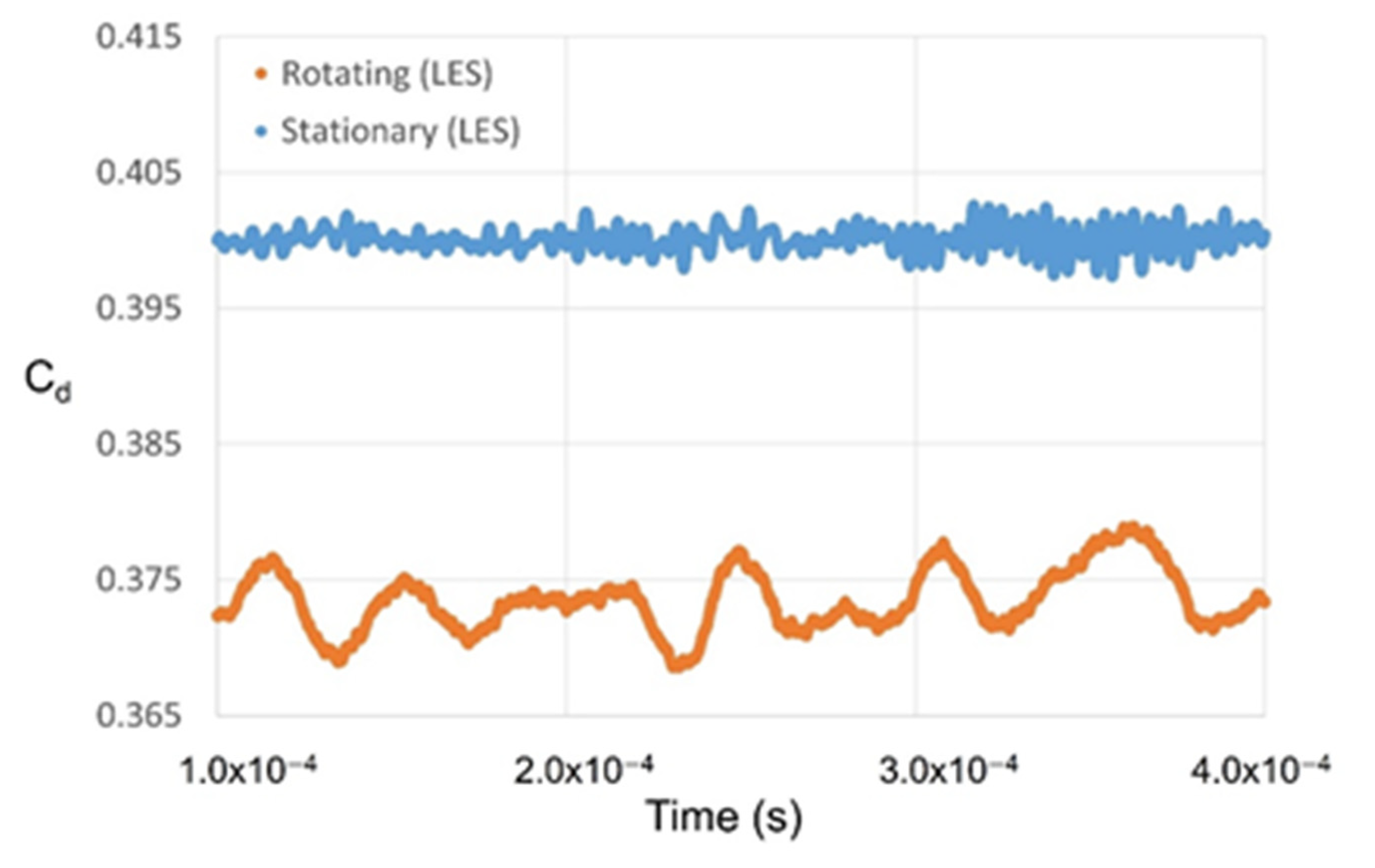
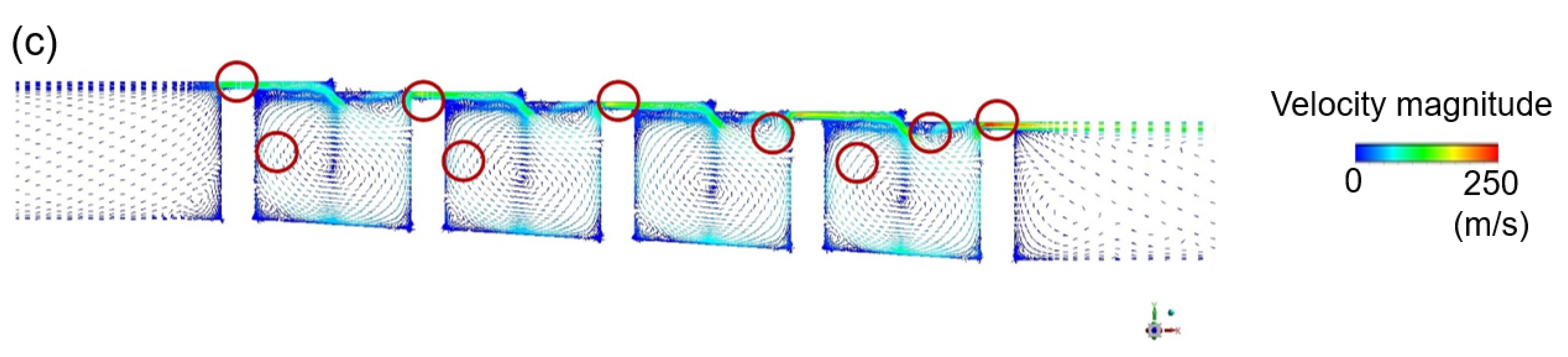
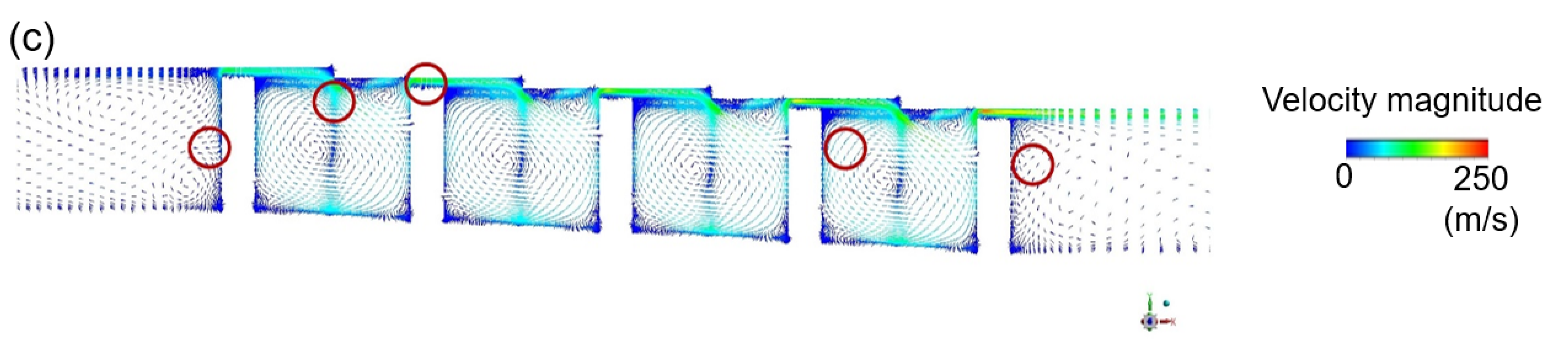
3.1. Discharge Coefficient and Flow Structure
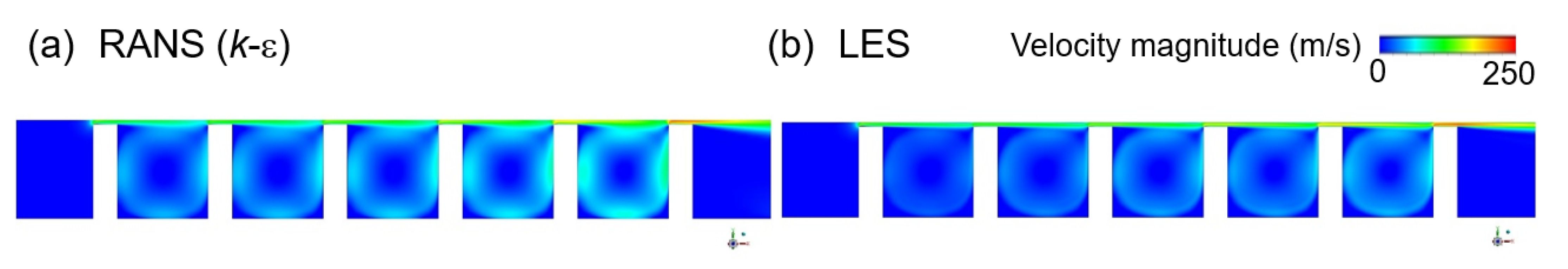
3.1.1. Straight-Through Seal
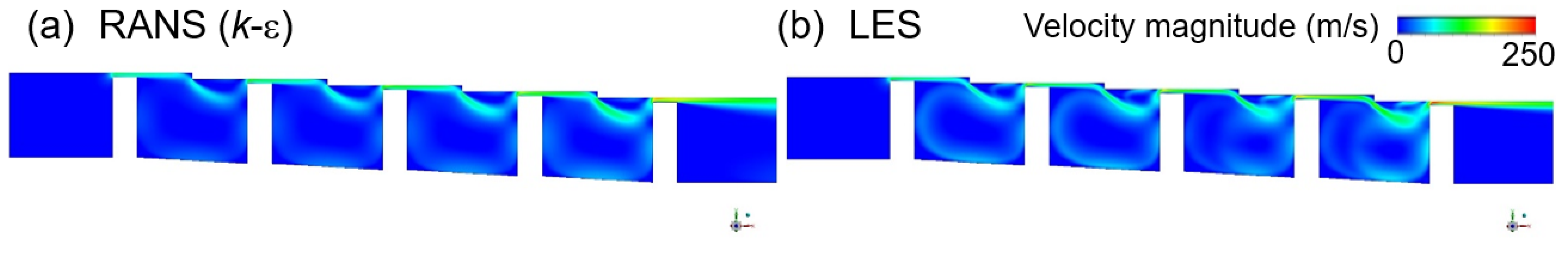
3.1.2. Stationary Stepped Seal
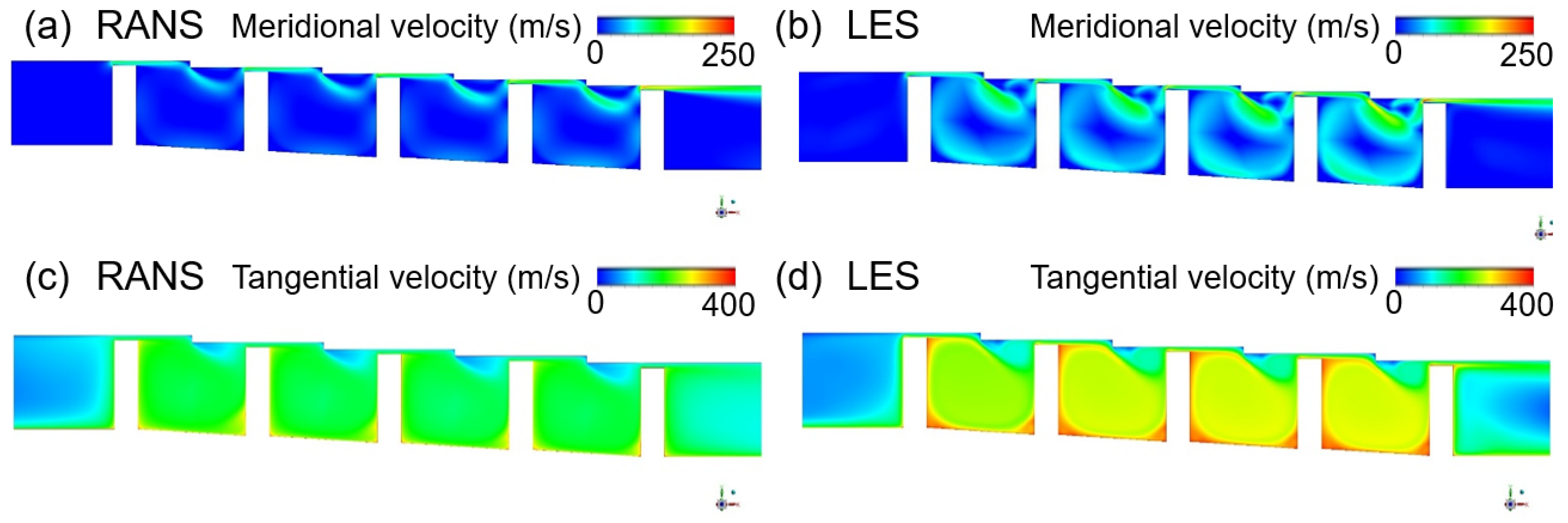
3.1.3. Rotating Stepped Seal
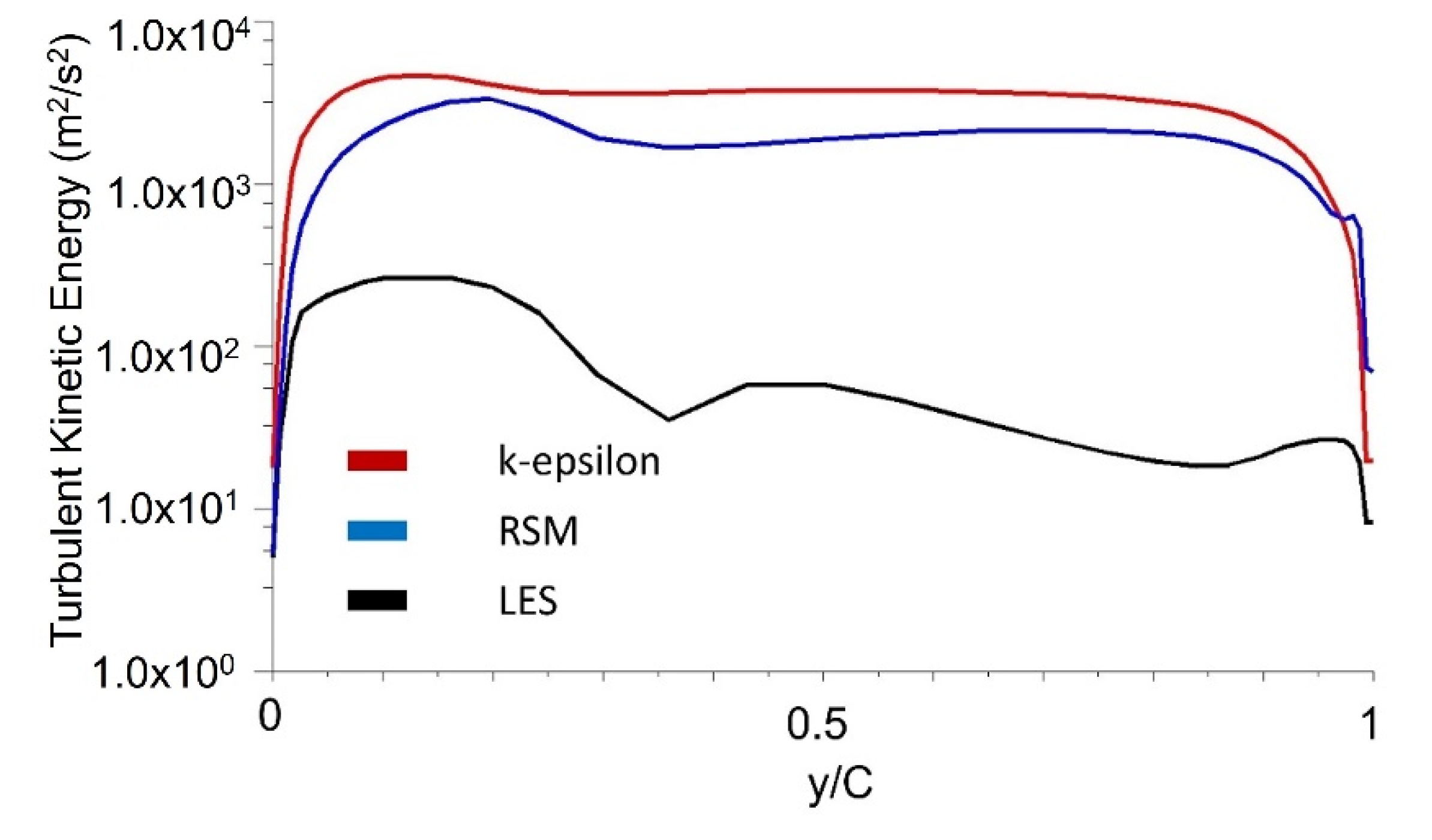
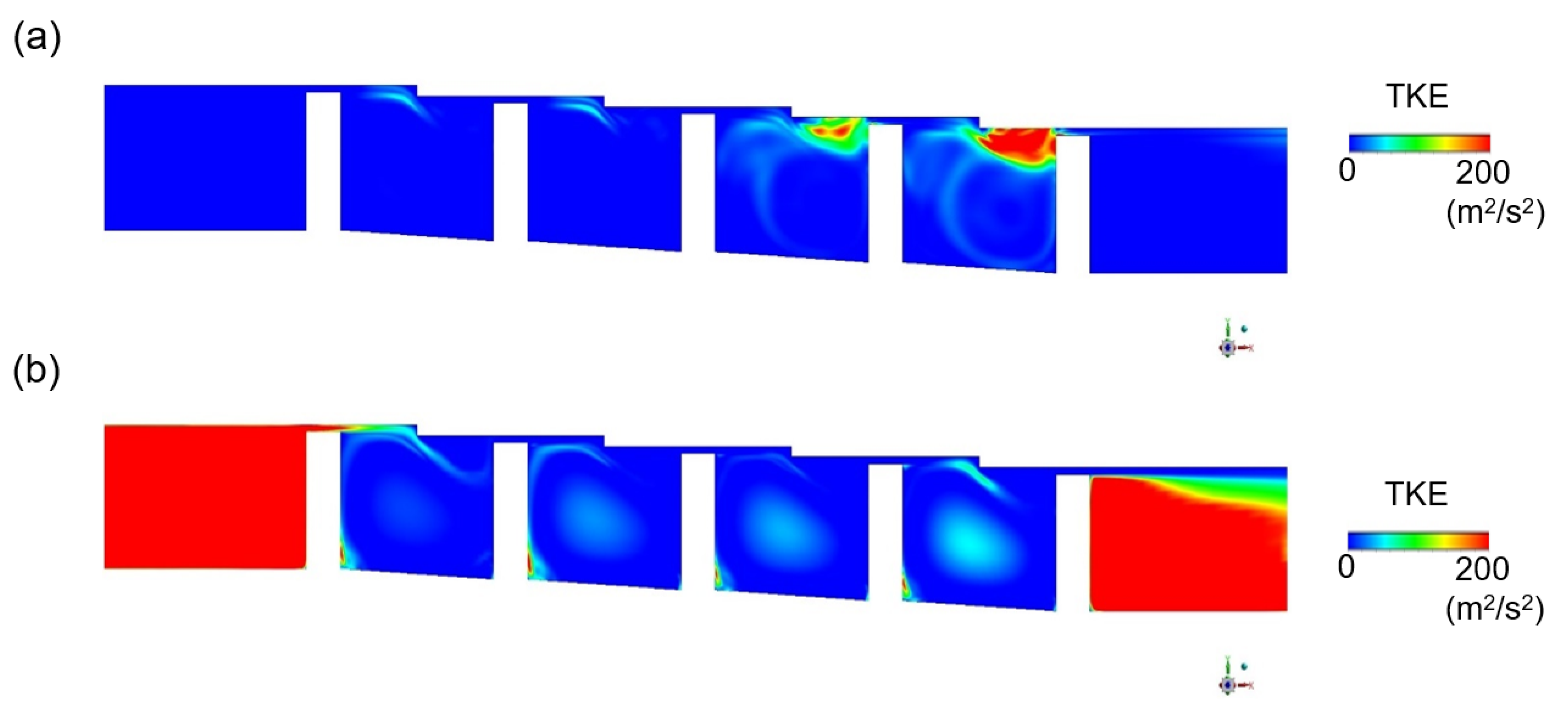
3.2. Turbulence Kinetic Energy Estimation
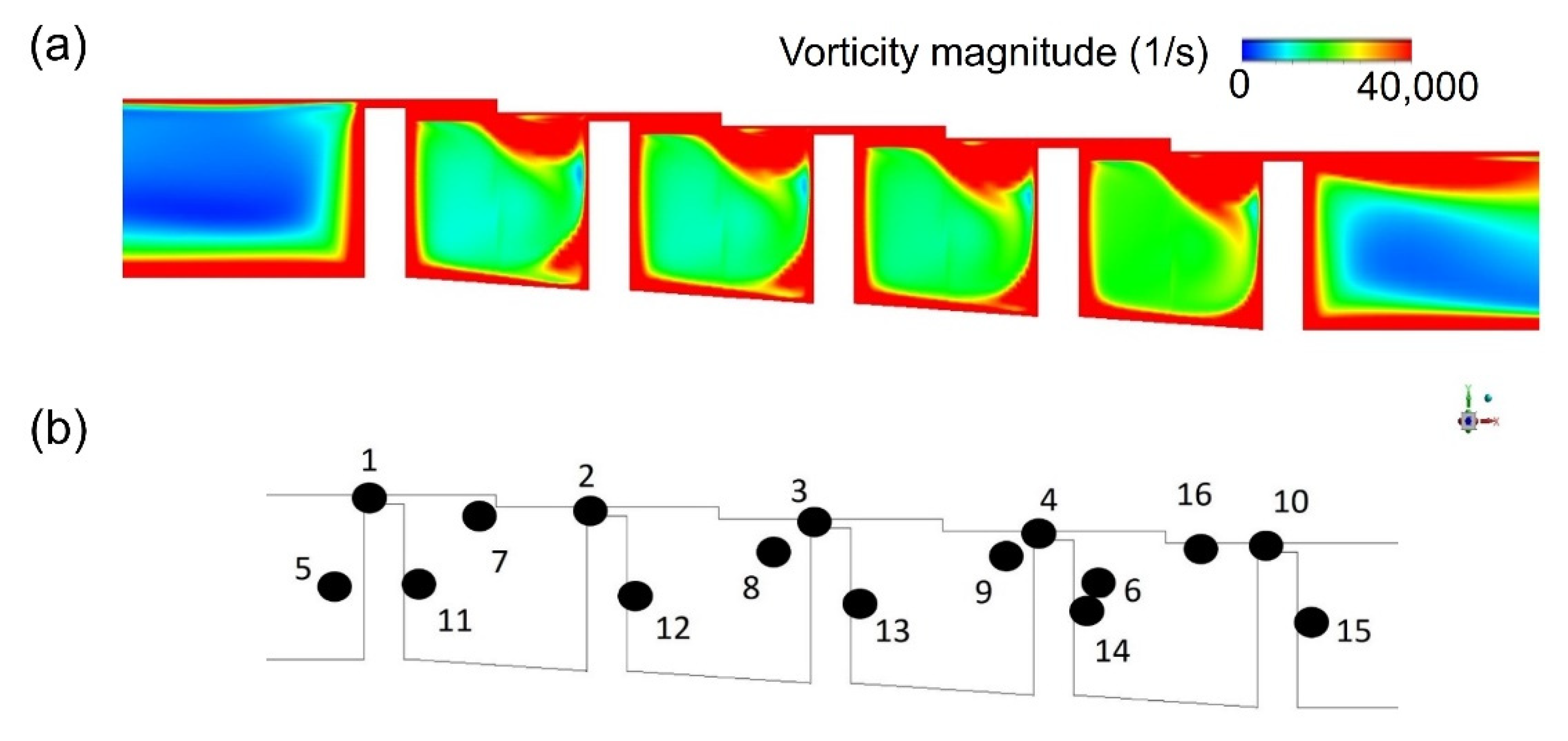
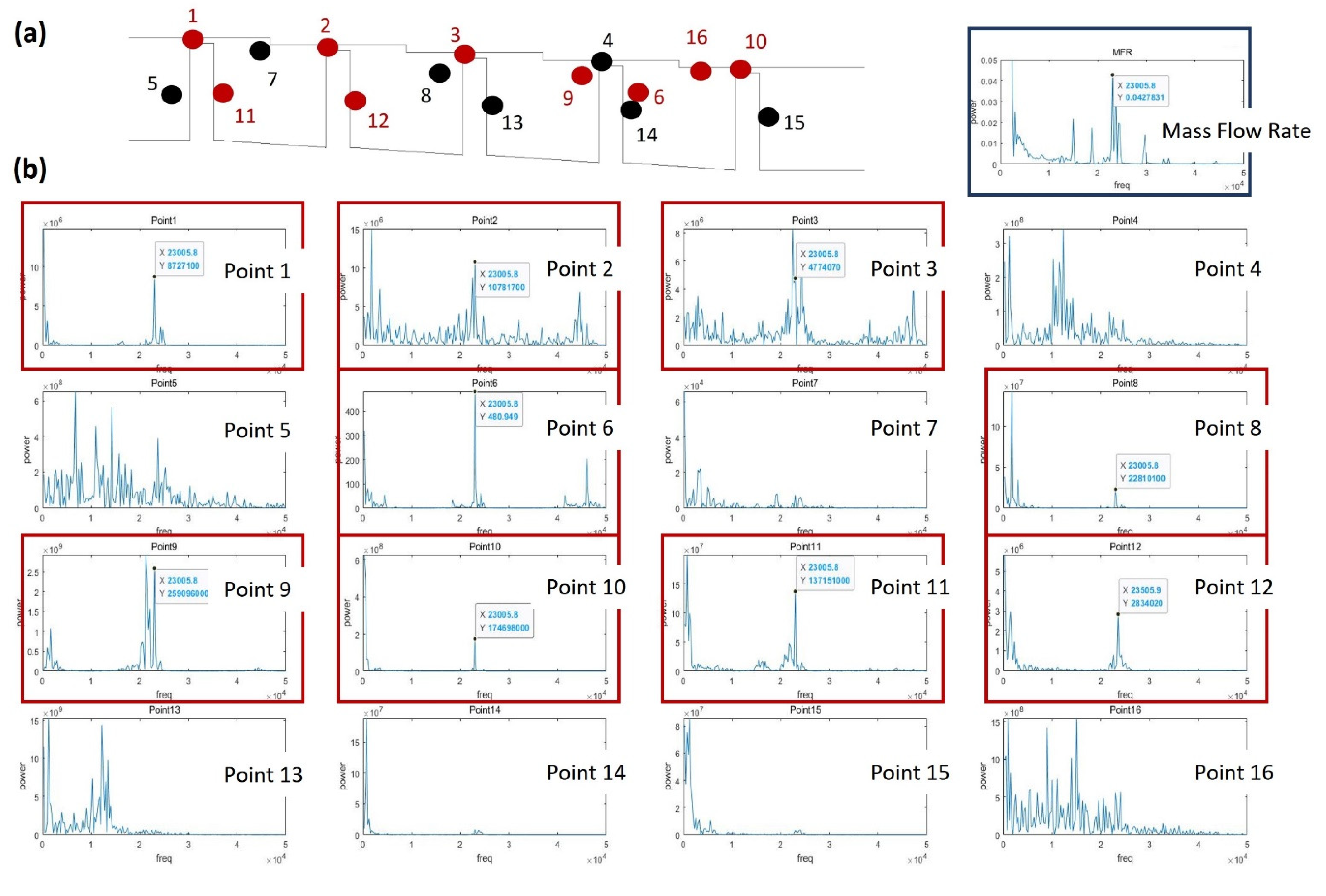
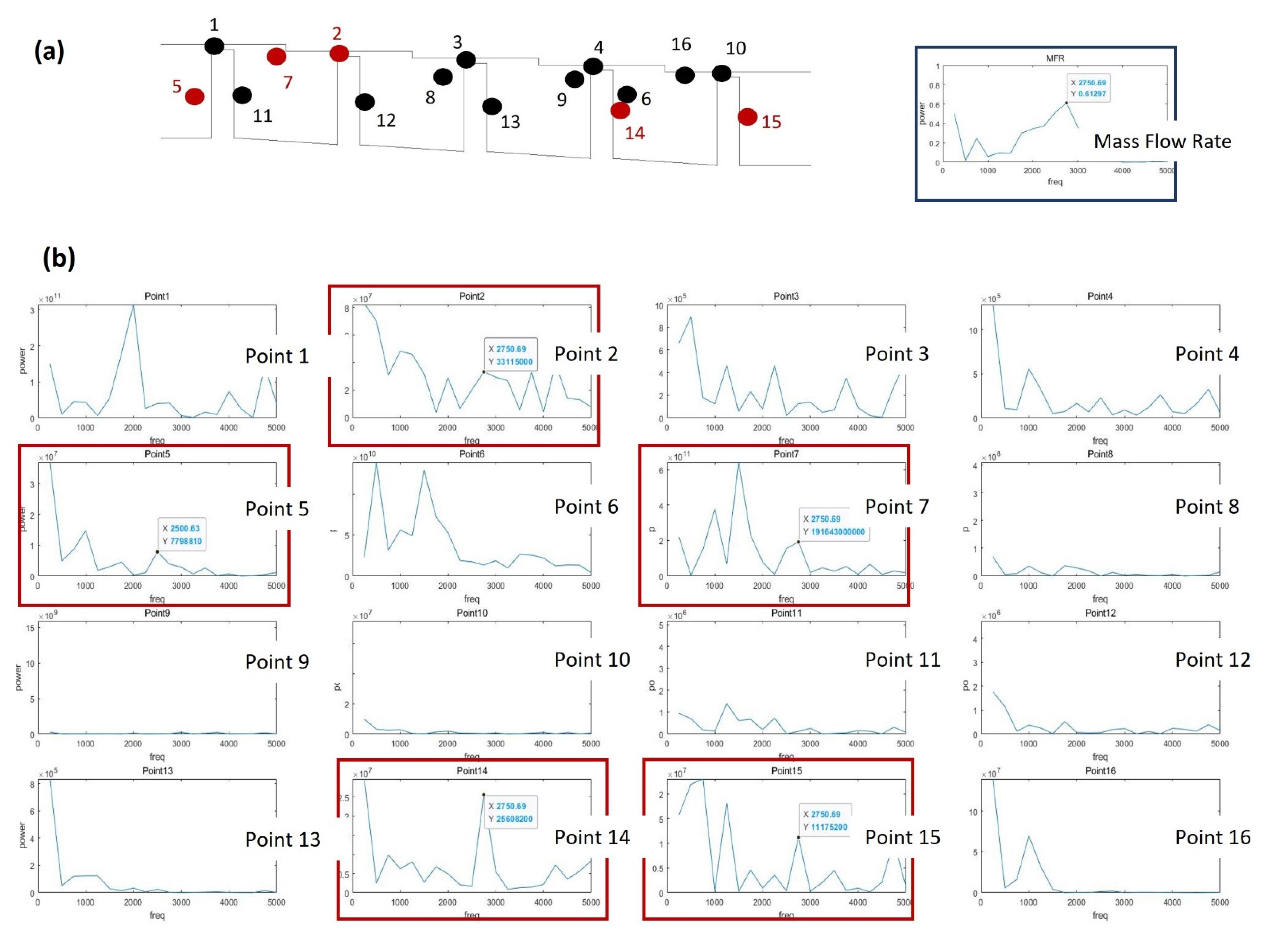
3.3. Flow Structure Effects on Mass Flow Rate Oscillation
3.3.1. Stationary Condition
3.3.2. Rotating Condition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Ac | Cross sectional area of labyrinth seal [m2] |
| Cd | Discharge coefficient |
| Cp | Specific heat |
| k | Turbulence kinetic energy [m2/s2] |
| Ls | Mixing length for sub-grid scales |
| T | Temperature [K] |
| U | x Velocity component [m/s] |
| u | Flow velocity [m/s] |
| u’ | RMS of the turbulent velocity fluctuations [m/s] |
| P | Pressure [Pa] |
| R | Specific gas constant |
| t | Time [s] |
| ṁ | Mass flow rate [kg/s] |
| V | y velocity Component [m/s] |
| x | coordinate |
| Greek Symbols | |
| ρ | Density [kg/m3] |
| Turbulence stress | |
| ε | Turbulence kinetic energy dissipation [m2/s3] |
| ν | Kinematic viscosity [m2/s] |
| γ | Specific heat ratio |
| μ | Dynamic Viscosity [kg/m∙s] |
| μt | Turbulence viscosity |
| Subscripts | |
| id | ideal |
| in | inlet |
| out | outlet |
References
- Lakshminarayana, B. Fluid Dynamics and Heat Transfer of Turbomachinery; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 155–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Song, J.C.; Lee, J.S. Fully Coupled Large Eddy Simulation of Conjugate Heat Transfer in a Ribbed Channel with a 0.1 Blockage Ratio. Energies 2021, 14, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.J.; Eckert, E.R.G.; Ramsey, J.W. Film Cooling with Injection through Holes: Adiabatic Wall Temperatures Downstream of a Circular Hole. J. Eng. Power. 1968, 90, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls-Royce Ltd. The Jet Engine; Rolls-Royce plc: Derby, UK, 2005; pp. 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, C. Influence of tilting rotor on characteristics of fluid-induced vibration for labyrinth seals. J. Vibroeng. 2016, 18, 5416–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schramm, V.; Willenborg, K.; Kim, S.; Wittig, S. Influence of a Honeycomb Facing on the Flow Through a Stepped Labyrinth Seal. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power. 2000, 124, 140–146. Available online: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/gasturbinespower/article/124/1/140/461748/Influence-of-a-Honeycomb-Facing-on-the-Flow (accessed on 25 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Wittig, S.; Schelling, U.; Kim, S.; Jacobsen, K. Numerical Predictions and Measurements of Discharge Coefficients in Labyrinth Seals. In Proceedings of the ASME 1987 International Gas Turbine Conference and Exhibition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 31 May–4 June 1987; Available online: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/GT/proceedings/GT1987/79238/V001T01A064/237847 (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Denecke, J.; Dullenkopf, K.; Wittig, S.; Bauer, H.-J. Experimental Investigation of the Total Temperature Increase and Swirl Development in Rotating Labyrinth Seals. ASME J. Turbomach. 2005, 3, 1161–1171. Available online: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/GT/proceedings-abstract/GT2005/47268/1161/312940 (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Szymanski, A.; Dykas, S.; Wroblewski, W.; Fraczek, D. Experimental and Numerical Validation Study of the Labyrinth Seal Configurations. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics & Thermodynamics ETC12, Stockholm, Sweden, 3–7 April 2017; Available online: https://www.euroturbo.eu/publications/proceedings-papers/etc2017-340/ (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Zimmermann, H.; Wolff, K.H. Comparison Between Empirical and Numerical Labyrinth Flow Correlations. In Proceedings of the ASME 1987 International Gas Turbine Conference and Exhibition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 31 May–4 June 1987; V001T01A028. ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. Available online: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/GT/proceedings/GT1987/79238/V001T01A028/237848 (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Zimmermann, H.; Wolff, K.H. Air system correlations part 1: Labyrinth seals. Proc. ASME Turbo Expo 1998, 4, 1–8. Available online: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/GT/proceedings/GT1998/78651/V004T09A048/248910 (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Kaszonwski, P.; Dzida, M. CFD analysis of fluid flow through the labyrinth seal. Trans. Inst. Fluid-Flow Mach. 2015, 130, 71–82. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/323847858_CFD_analysis_of_fluid_flow_through_the_labyrinth_seal (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Baek, S.I.; Ahn, J. Optimizing the Geometric Parameters of a Straight-Through Labyrinth Seal to Minimize the Leakage Flow Rate and the Discharge Coefficient. Energies 2021, 14, 705. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1073/14/3/705 (accessed on 25 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Eser, D.; Kazakia, J.Y. Air flow in cavities of labyrinth seals. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1995, 33, 2309–2326. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0020722595000726 (accessed on 25 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Wein, L.; Kluge, T.; Seume, J.R.; Hain, R.; Fuchs, T.; Kähler, C.; Schmierer, R.; Herbst, F. Validation of RANS Turbulence Models for Labyrinth Seal Flows by Means of Particle Image Velocimetry. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo/ Expo, Virtual, Online, 21–25 September 2020; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 10A. V10AT25A015. Available online: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/GT/proceedings-abstract/GT2020/84218/V10AT25A015/1095264 (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Gao, F.; Chew, J.W.; Beard, P.F.; Amirante, D.; Hills, N.J. Numerical Studies of Turbine Rim Sealing Flows on a Chute Seal Configuration. In Proc ETC 12; Rolls-Royce plc: Derby, UK, 2017; ETC2017-284; Available online: https://www.euroturbo.eu/publications/proceedings-papers/etc2017-284/ (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Tyacke, J.C.; Dai, Y.; Watson, R.; Tucker, P.G. Design Optimisation of Labyrinth Seals Using LES. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2021, 2, 1–23. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/347638823_Design_Optimisation_of_Labyrinth_Seals_using_LES (accessed on 25 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.M. Labyrinth Packings. Engineer 1908, 85, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vermes, G. A Fluid Mechanics Approach to the Labyrinth Seal Leakage Problem. ASME J. Eng. Power 1961, 83, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, A. The Leakage of Steam Through Labyrinth Seals. Trans. ASME 1935, 57, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Hodkinson, B. Estimation of the Leakage Through a Labyrinth Gland. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1939, 141, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, A.D.; Meganathan, A.J.; Michaud, M.; Radhakrishnan, S. An Experimental and Numerical Study of Labyrinth Seal Flow. In Proceedings of the Turbo Expo 2005, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 June 2005; pp. 1121–1128. Available online: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/GT/proceedings-abstract/GT2005/47268/1121/312900 (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Szymański, A.; Wróblewski, W.; Bochon, K.; Majkut, M.; Strozik, M.; Marugi, K. Experimental validation of optimised straight-through labyrinth seals with various land structures. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 158, 119930. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0017931020302957 (accessed on 25 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Loizou, P.A. Laminarization of three-dimensional accelerating boundary layers in a curved rectangular-sectioned duct. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 1992, 13, 124–131. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Laminarization-of-three-dimensional-accelerating-in-Launder-Loizou/78be90a8044caa0888d28c17084fcdd8d8f719cd (accessed on 25 November 2021). [CrossRef]
- MATLAB Documentation. Available online: https://mathworks.com/help/index.html (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- ANSYS Fluent v19.1 Theory Guide. Available online: https://ansyshelp.ansys.com/account/secured?returnurl=/Views/Secured/corp/v193/flu_th/flu_th.html (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- ANSYS ICEM CFD Help Manual. Available online: https://ansyshelp.ansys.com/account/secured?returnurl=/Views/Secured/corp/v193/icm_help/icm_help.html (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Potter, M.C.; Wiggert, D.C.; Ramadan, B.H. Mechanics of Fluids, 4th ed.; CENGAGE Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 192–221. [Google Scholar]
- Boussinesq, J.V. Théorie de l’écoulement Tourbillonnant et Tumultueux des Liquides dans les Lits Rectilignes a Grande Section; Quai Des Grands-Augustins, 55; Gauthier-Villars et fils: Paris, France, 1897; pp. 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD; DCW Industries: La Cañada Flintridge, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 377–398. [Google Scholar]
- Saffman, P.G. Vortex Dynamics. In Cambridge Monographs on Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 1–19. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/vortex-dynamics/2F33335617172249253B949EA3406F89 (accessed on 25 November 2021). [CrossRef]

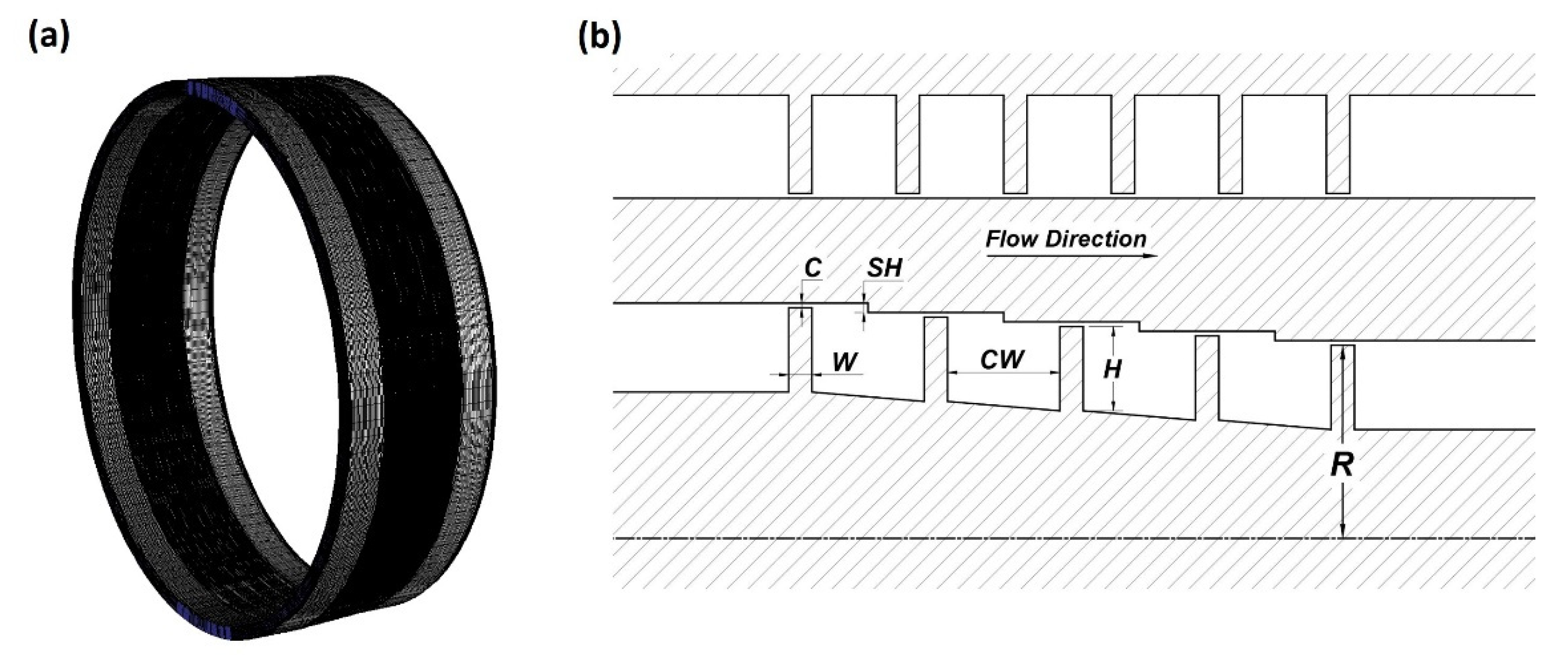
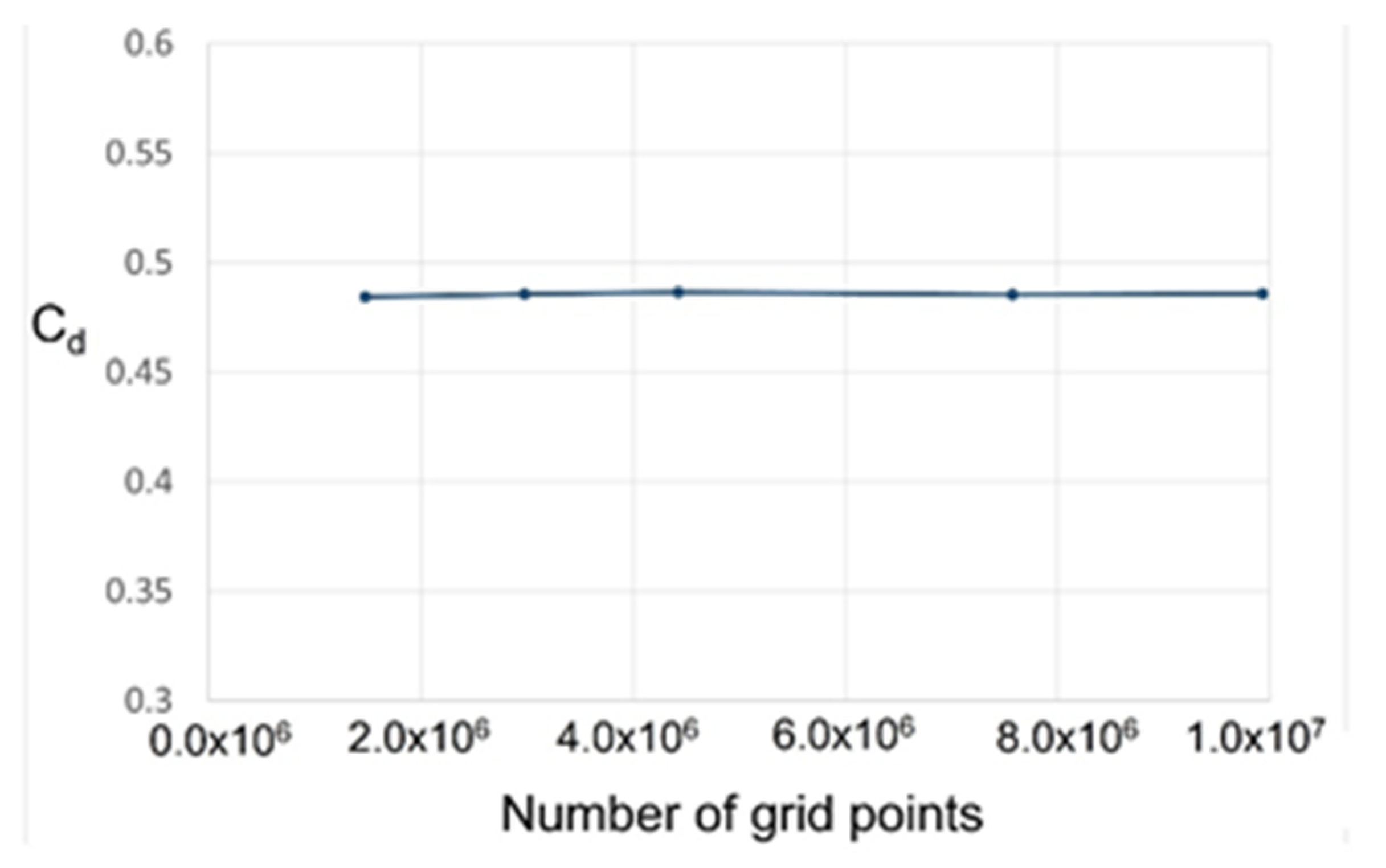
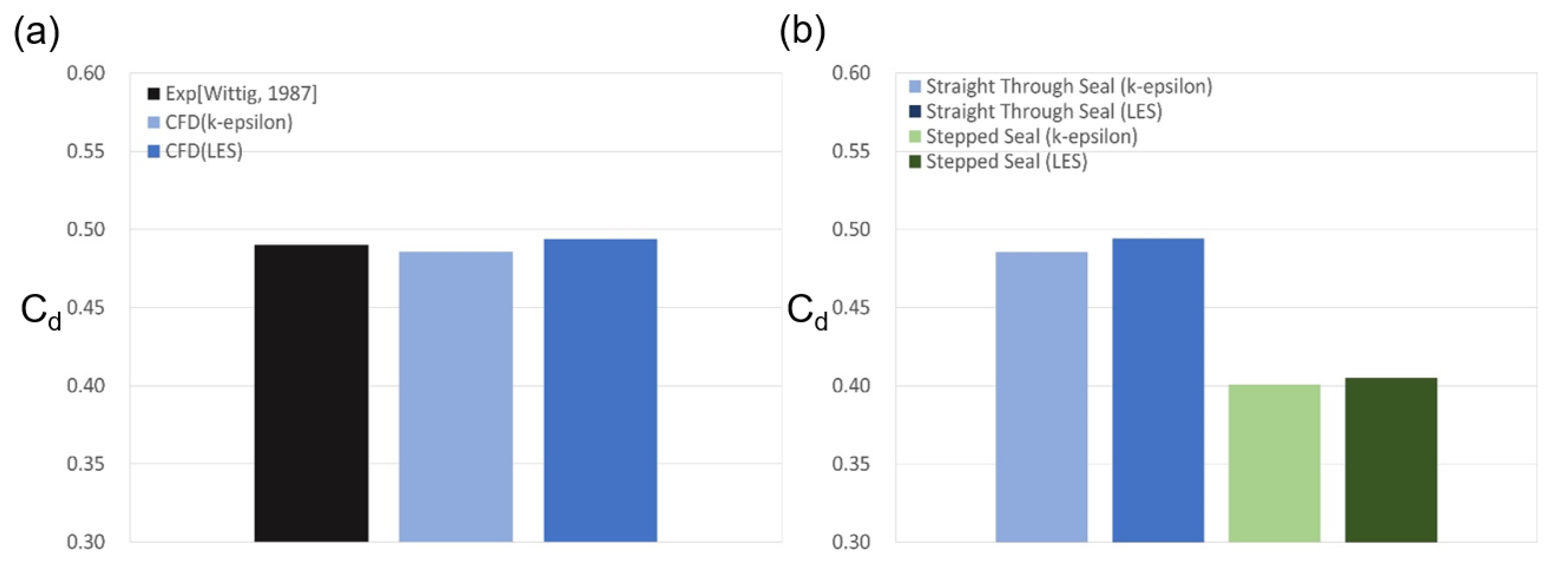
| Geometrical Parameter | Straight-Through Seal | Stepped Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Clearance (C) | 0.5 mm | 0.5 mm |
| Cavity width (CW) | 9 mm | 11.5 mm |
| Tooth width (W) | 2.5 mm | 2.5 mm |
| Tooth height (H) | 10.5 mm | 9 mm |
| Minimum radius (R) | 200 mm | 200 mm |
| Number of teeth (N) | 6 | 5 |
| Step height (SH) | - | 0.7 mm |
| Surface | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|
| Inlet | Absolute Total Pressure = 202,650 Pa |
| Outlet | Absolute Total Pressure = 101,325 Pa |
| Shaft | 0 RPM, 20,000 RPM, Adiabatic wall |
| Casing | 0 RPM, Adiabatic wall |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-H.; Ahn, J. Large Eddy Simulation of Leakage Flow in a Stepped Labyrinth Seal. Processes 2021, 9, 2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9122179
Kim J-H, Ahn J. Large Eddy Simulation of Leakage Flow in a Stepped Labyrinth Seal. Processes. 2021; 9(12):2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9122179
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ji-Hwan, and Joon Ahn. 2021. "Large Eddy Simulation of Leakage Flow in a Stepped Labyrinth Seal" Processes 9, no. 12: 2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9122179
APA StyleKim, J.-H., & Ahn, J. (2021). Large Eddy Simulation of Leakage Flow in a Stepped Labyrinth Seal. Processes, 9(12), 2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9122179







