An Overview of Recent Advances in State-of-the-Art Techniques in the Demulsification of Crude Oil Emulsions
Abstract
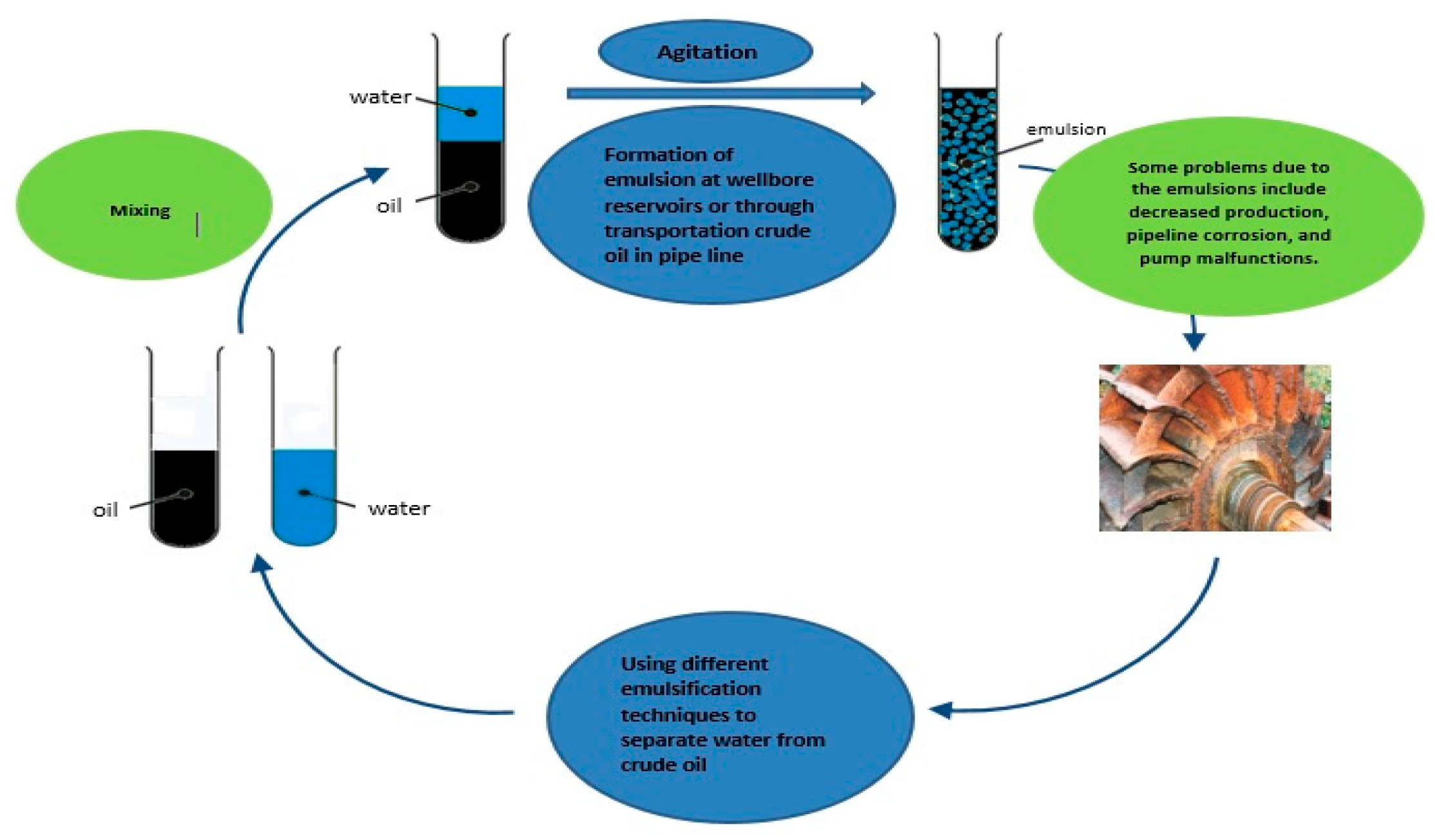
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Emulsions
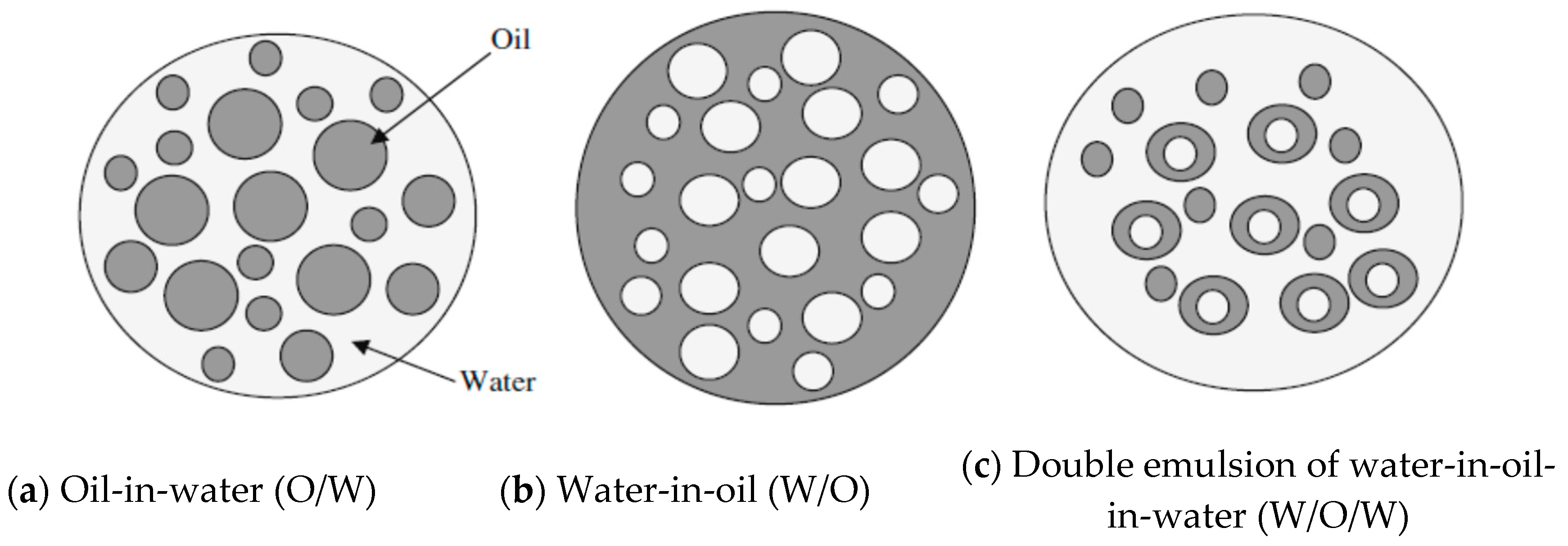
3.1. Types and Structure of Crude Oil Emulsions
3.1.1. Oil-in-Water Emulsions (O/W)
3.1.2. Water-in-Oil Emulsion (W/O)
3.1.3. Multiple Emulsions
3.2. Emulsion Formation
3.3. Stability of the Emulsions
3.4. Emulsification Methods
3.4.1. Gel-Emulsification Method
3.4.2. Direct Mechanical Method
3.4.3. Emulsification by Ultrasound
3.5. Parameters Used for the Emulsification Formation Process
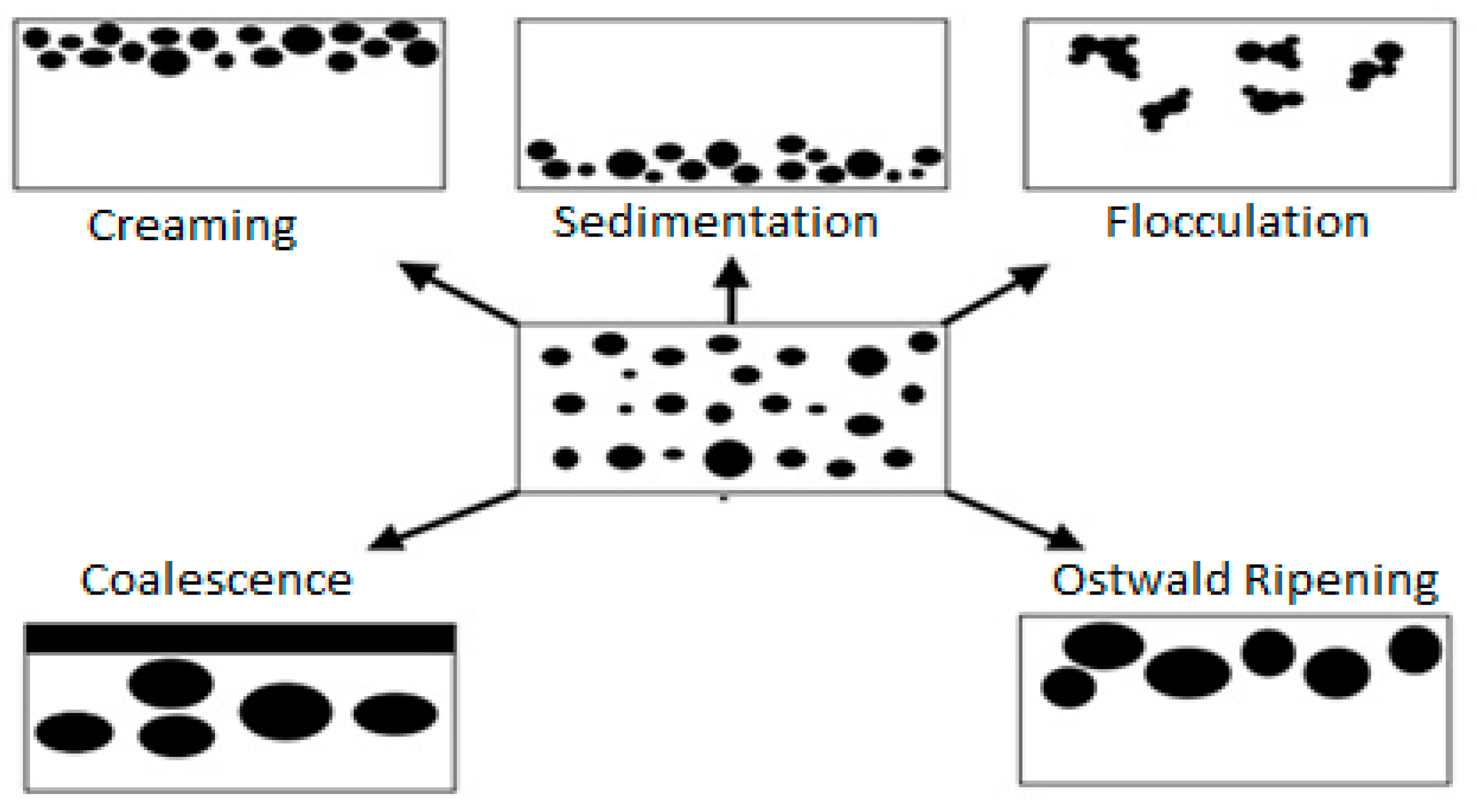
4. Demulsification Mechanism
4.1. Creaming and Sedimentation
4.2. Flocculation
4.3. Ostwald Ripening
4.4. Coalescence
5. Crude Oil Demulsification and Different Demulsification Techniques
5.1. Chemical Demulsification
5.2. Biological Demulsification
5.3. Mechanical Demulsification
5.4. Thermal (Convectional and Microwave) Demulsification
5.5. Electrical Demulsification
5.6. Ultrasonic Demulsification
5.7. Membrane Demulsification
6. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Some Demulsification Techniques
7. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Issaka, S.A.; Nour, A.H.; Yunus, R.M. Review on the fundamental aspects of petroleum oil emulsions and techniques of demulsification. J. Pet. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, R.; Fakhru’l-Razi, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Elnashaie, S.S.E.H.; Pendashteh, A. Demulsification techniques of water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsions in petroleum industry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 377–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Mohammed, M.S. The application of microwave technology in demulsification of water-in-oil emulsion for missan oil fields. Iraqi J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2013, 14, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dejam, M.; Hassanzadeh, H.; Chen, Z. A reduced-order model for chemical species transport in a tube with a constant wall concentration. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel-David, D.; Le Follotec, A.; Pezron, I.; Dalmazzone, C.; Noik, C.; Barre, L.; Komunjer, L. Destabilisation of water-in-crude oil emulsions by silicone copolymer demulsifiers. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. L’IFP 2008, 63, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Paul, V.; Kumar, V.; Mishra, I.M. Formulation development, modeling and optimization of emulsification process using evolving RSM coupled hybrid ANN-GA framework. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 104, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Palou, R.; Reyes, J.; Cerón-Camacho, R.; Ramírez-de-Santiago, M.; Villanueva, D.; Vallejo, A.A.; Aburto, J. Study of the formation and breaking of extra-heavy-crude-oil-in-water emulsions—A proposed strategy for transporting extra heavy crude oils. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 98, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laosiripojana, N.; Sutthisripok, W.; Assabumrungrat, S. Synthesis gas production from dry reforming of methane over CeO2 doped Ni/Al2O3: Influence of the doping ceria on the resistance toward carbon formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 112, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.; Aditya, S.; Yang, H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, S.O.; Ko, S. Co-delivery of hydrophobic curcumin and hydrophilic catechin by a water-in-oil-in-water double emulsion. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Lim, J.; Dol, S. Crude oil emulsion: A review on formation, classification and stability of water-in-oil emulsions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejam, M.; Hassanzadeh, H.; Chen, Z. Shear dispersion in combined pressure-driven and electro-osmotic flows in a capillary tube with a porous wall. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 3981–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulredha, M.M. Overview on petroleum emulsions, formation, influence and demulsification treatment techniques. Arab. J. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokal, S.L. Crude oil emulsions: A state-of-the-art review. SPE Prod. Facil. 2005, 20, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Jia, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, S. Demulsification of crude oil-in-water emulsions driven by graphene oxide nanosheets. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 4644–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, K.; Alade, A.; Arinkoola, A.; Opawale, A. Improving the demulsification process of heavy crude oil emulsion through blending with diluent. J. Pet. Eng. 2013, 2013, 793101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Yin, X.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Hou, X.; Sarsenbekuly, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; et al. Demulsification performance, behavior and mechanism of different demulsifiers on the light crude oil emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 545, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Jia, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, S. Recyclable magnetic graphene oxide for rapid and efficient demulsification of crude oil-in-water emulsion. Fuel 2017, 189, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Huang, J.; Wang, L. Research on Crude Oil Demulsification Using the Combined Method of Ultrasound and Chemical Demulsifier. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 9147926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, G.F.; Silva, R.C.; Barbosa, L.L.; Freitas, J.C.; Sad, C.M.; Tose, L.V.; Vaz, B.G.; Romão, W.; de Castro, E.V.; Neto, A.C. Characterisation and selection of demulsifiers for water-in-crude oil emulsions using low-field 1H NMR and ESI–FT-ICR MS. Fuel 2015, 140, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, S.; Simon, S.; Sjöblom, J.; Xu, Z. Demulsifier assisted film thinning and coalescence in crude oil emulsions under DC electric fields. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 134, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennela, N.; Mondal, S.; De, S.; Bhattacharjee, S. Sherwood number in flow through parallel porous plates (Microchannel) due to pressure and electroosmotic flow. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Lyu, R.; Gao, X.; Liang, C.; Wang, C. MPEG grafted quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan for demulsification of crude oil emulsions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Qi, A. A Comparative Research of Microwave, Conventional-Heating, and Microwave/Chemical Demulsification of Tahe Heavy-Oil-in-Water Emulsion. SPE Prod. Oper. 2018, 33, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Cheng, H.; Lu, L.J.; Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Guan, W.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X.F. Analysis of biological demulsification process of water-in-oil emulsion by Alcaligenes sp. S-XJ-1. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8315–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah, M.; Tohidian, T.; Rahimpour, M.R.; Jahanmiri, A. Efficient demulsification of water-in-oil emulsion by a novel nano-titania modified chemical demulsifier. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 94, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zaman, W.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q. Interfacially active and magnetically responsive composite nanoparticles with raspberry like structure; synthesis and its applications for heavy crude oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 472, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, M.; Rahimpour, M.R.; Jahanmiri, A.; Azad, F. Effect of a different formulation of demulsifiers on the efficiency of chemical demulsification of heavy crude oil. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binner, E.R.; Robinson, J.P.; Silvester, S.A.; Kingman, S.W.; Lester, E.H. Investigation into the mechanisms by which microwave heating enhances separation of water-in-oil emulsions. Fuel 2014, 116, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennela, N.; Bhattacharjee, S.; De, S. Sherwood number in porous microtube due to combined pressure and electroosmotically driven flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 6515–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, A.K.; Ricardez-Sandoval, L.A.; Elkamel, A. Designing and Testing a Chemical Demulsifier Dosage Controller in a Crude Oil Desalting Plant: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Network Approach. Chem. Eng. Technol. Ind. Chem. Plant Equip. Process Eng. Biotechnol. 2010, 33, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejam, M.; Hassanzadeh, H.; Chen, Z. Shear dispersion in combined pressure-driven and electro-osmotic flows in a channel with porous walls. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 137, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Palou, R.; Cerón-Camacho, R.; Chávez, B.; Vallejo, A.A.; Villanueva-Negrete, D.; Castellanos, J.; Karamath, J.; Reyes, J.; Aburto, J. Demulsification of heavy crude oil-in-water emulsions: A comparative study between microwave and thermal heating. Fuel 2013, 113, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G. Rapid and efficient separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsions using a Janus cotton fabric. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.H.; Masliyah, J.H.; Bhattacharjee, S. Simulations of a dielectrophoretic membrane filtration process for removal of water droplets from water-in-oil emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 287, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, J.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Jara, A.M.A.T.; Brasileiro, P.P.F.; Sarubbo, L.A. Environmental applications of the biosurfactant produced by Candida sphaerica cultivated in low-cost substrates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 480, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenoble, Z.; Trabelsi, S. Mechanisms, performance optimization and new developments in demulsification processes for oil and gas applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 260, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Rajiah, P.; Middlebrooks, E.H.; Baruah, D.; Carter, B.W.; Burton, K.R.; Chatterjee, A.R.; Miller, M.M. Systematic Review of the Literature: Best Practices. Acad. Radiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzing, A.-W.; Alakangas, S. Google Scholar, Scopus and the Web of Science: A longitudinal and cross-disciplinary comparison. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.K.; Saha, U.K.; Sahoo, N. A comprehensive review on the application of emulsions as an alternative fuel for diesel engines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, D.; Poteau, S.; Hénaut, I.; Argillier, J. Crude oil emulsion properties and their application to heavy oil transportation. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2004, 59, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.A.; Saaid, I.B.M.; Sulaimon, A.A.; Pilus, R.B.M. A review of petroleum emulsions and recent progress on water-in-crude oil emulsions stabilized by natural surfactants and solids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 165, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, D.R. Asphalt Emulsion Technology; TRC E-102; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, A. A review of technologies for transporting heavy crude oil and bitumen via pipelines. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2014, 4, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, D.; Kantzas, A.; Bryant, S.L. Nanoparticle stabilized oil in water emulsions: A critical review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 163, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurahman, N.; Rosli, Y.; Azhari, N.; Hayder, B. Pipeline transportation of viscous crudes as concentrated oil-in-water emulsions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 90, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, L.L. Preparation, inhibition, and destruction of dispersions. Emuls. Foam. Suspens. Fundam. Appl. 2005, 1, 201–221. [Google Scholar]
- Schramm, L.L. Emulsions: Fundamentals and applications in the Petroleum Industry. Adv. Chem. Ser. 1992, 321, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Roshan, N.; Ghader, S.; Rahimpour, M.R. Application of the response surface methodology for modeling demulsification of crude oil emulsion using a demulsifier. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, B.J.; Kilpatrick, P.K. Molecular characterization of wax isolated from a variety of crude oils. Energy Fuels 1998, 12, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.F. Agents which promote and stabilize water-in-oil emulsions. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 1999, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat, H.; Samsuri, A.; Rahman, W.A.; Aizan, W.; Othman, N.; Chieng, Y.Y.; Jong, S.C.; Zulkania, A. Study on Demulsifier Formulation for Treating Malaysian Crude Oil Emulsion; Project Report; Universiti Teknologi Malaysia: Skudai, Malaysia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Biniaz, P.; Farsi, M.; Rahimpour, M.R. Demulsification of water in oil emulsion using ionic liquids: Statistical modeling and optimization. Fuel 2016, 184, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Linares, J.G.; Pereira, J.C.; Rondón, M.; Bullón, J.; Salager, J.-L. Breaking of water-in-crude oil emulsions. 6. Estimating the demulsifier performance at optimum formulation from both the required dose and the attained instability. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5483–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, F.; Hussein, I.A.; Kamal, M.S.; Ahmad, W.; Sultan, A.S.; Nasser, M.S. Polymeric surfactants and emerging alternatives used in the demulsification of produced water: A review. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 63–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, F.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-energy formation of edible nanoemulsions: Factors influencing droplet size produced by emulsion phase inversion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 388, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, W.-A.C.; Fischlechner, M.; Abell, C.; Huck, W.T. Hydrophilic PDMS microchannels for high-throughput formation of oil-in-water microdroplets and water-in-oil-in-water double emulsions. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; Solé, I. Nano-emulsions: Formation by low-energy methods. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, D.; Hyman, A.A.; Juelicher, F. Suppression of Ostwald ripening in active emulsions. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 012317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, N.N.; Carbonell, R.G.; Kilpatrick, P.K. A novel process for demulsification of water-in-crude oil emulsions by dense carbon dioxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 6661–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pensini, E.; Harbottle, D.; Yang, F.; Tchoukov, P.; Li, Z.; Kailey, I.; Behles, J.; Masliyah, J.; Xu, Z. Demulsification mechanism of asphaltene-stabilized water-in-oil emulsions by a polymeric ethylene oxide–propylene oxide demulsifier. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 6760–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, P.K. Water-in-crude oil emulsion stabilization: Review and unanswered questions. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4017–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Simon, S.; Sjöblom, J. Interfacial shear rheology of asphaltenes at oil–water interface and its relation to emulsion stability: Influence of concentration, solvent aromaticity and nonionic surfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 366, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, T.; Hascakir, B. The role of resins, asphaltenes, and water in water–oil emulsion breaking with microwave heating. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Mishra, I.; Bhattacharya, S.; Joshi, J. Removal of oil from oil-in-water emulsion using a packed bed of commercial resin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 389, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.-M.; Fan, W.-Y.; Nan, G.-Z.; Li, S.-P.; Yu, B.-S. Influence of interaction between heavy oil components and petroleum sulfonate on the oil–water interfacial tension. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraho, T.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Impact of free fatty acid concentration and structure on lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Correlations between emulsification behaviors of crude oil-water systems and crude oil compositions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, Z.; Shariaty Niassar, M.; Rashidi, A.M. Application of Box Behnken Design to Optimize the Parameters to Synthesis Graphene by CVD Process. J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2015, 49, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Anisa, A.; Nour, A.H. Affect of Viscosity and Droplet Diameter on water-in-oil (w/o) Emulsions: An Experimental Study. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 4, 2–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fallah, F.; Khorasani, M.; Ebrahimi, M. Factors affecting the properties of nitrocellulose emulsions: A comparative study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, F.; Khorasani, M.; Ebrahimi, M. Comparative study of gel emulsification and direct mechanical emulsification methods. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 492, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao-Sáinz, C.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Wood, D.F.; Williams, T.G.; McHugh, T.H. Nanoemulsions prepared by a low-energy emulsification method applied to edible films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11932–11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Murray, B.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I. Comparison of batch and continuous ultrasonic emulsification processes. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucheval, A.; Chow, R. A study on the emulsification of oil by power ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, T.; Wooster, T.; Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Minimising oil droplet size using ultrasonic emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mahto, V. Emulsification of Indian heavy crude oil using a novel surfactant for pipeline transportation. Pet. Sci. 2017, 14, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, M.; Tayebi, L.; Dezfouli, H. Investigation of factors affecting on viscosity reduction of sludge from Iranian crude oil storage tanks. Pet. Sci. 2018, 15, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, S.; Kamran, M. Emulsification of heavy crude oil in water for pipeline transportation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 71, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.W.; Ghannam, M.T.; Esmail, N. Heavy crude oil viscosity reduction and rheology for pipeline transportation. Fuel 2010, 89, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.G.; Bannwart, A.C.; Briceño, M.I.; Loh, W. Physico-chemical properties of heavy crude oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by mixtures of ionic and non-ionic ethoxylated nonylphenol surfactants and medium chain alcohols. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, S.; Motaee, E.; Hoshyargar, V. Emulsification of heavy crude oil in water by natural surfactants. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 86, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurahman, N.; Azhari, N.; Yunus, Y. Formulation and evaluation of water-continuous emulsion of heavy crude oil prepared for pipeline transportation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Innov. Technol. 2013, 2, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Rodionova, G.; Pettersen, B.; Kelesoğlu, S.; Sjöblom, J. Preparation and characterization of reference fluid mimicking behavior of North Sea heavy crude oil. Fuel 2014, 135, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajivand, P.; Vaziri, A. Optimization of demulsifier formulation for separation of water from crude oil emulsions. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; ElSaeed, S.M. Application of new amphiphilic ionic liquid based on ethoxylated octadecylammonium tosylate as demulsifier and petroleum crude oil spill dispersant. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 33, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Noah, N.F.M.; Shu, L.Y.; Ooi, Z.-Y.; Jusoh, N.; Idroas, M.; Goto, M. Easy removing of phenol from wastewater using vegetable oil-based organic solvent in emulsion liquid membrane process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippmann, S.; Ahmed, S.S.; Fröhlich, P.; Bertau, M. Demulsification of water/crude oil emulsion using natural rock Alginite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 553, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. Emulsion Science and Technology: A General Introduction; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Roques-Carmes, T.; Monnier, H.; Portha, J.-F.; Marchal, P.; Falk, L. Influence of the plate-type continuous micro-separator dimensions on the efficiency of demulsification of oil-in-water emulsion. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Koizumi, N.; Kondo, Y. Active demulsification of photoresponsive emulsions using cationic-anionic surfactant mixtures. Langmuir 2016, 32, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eow, J.S.; Ghadiri, M. Electrostatic enhancement of coalescence of water droplets in oil: A review of the technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 85, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.H.; Ghadiri, M.; Buckley, M. Electro-coalescence of water drops in oils under pulsatile electric fields. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 120, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalık, P.; Çalık, G.; Özdamar, T.H. Oxygen-transfer strategy and its regulation effects in serine alkaline protease production by Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 69, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiabudi, H.D.; Chong, C.C.; Abed, S.; Teh, L.; Chin, S. Comparative study of Ni-Ce loading method: Beneficial effect of ultrasonic-assisted impregnation method in CO2 reforming of CH4 over Ni-Ce/SBA-15. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.; Elsharaky, E.; El-Tabey, A.E. Demulsification performance and the relative solubility number (RSN) of modified poly (maleic anhydride-alt-1-dodecene) on naturally asphaltenic crude oil emulsion. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, P.K. Evaluation of calcium chloride for synergistic demulsification of super heavy oil wastewater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 419, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.A.; Flores, E.A.; Hernández, E.; Castro, L.V.; García, A.; Alvarez, F.; Vázquez, F.S. Anion and cation effects of ionic liquids and ammonium salts evaluated as dehydrating agents for super-heavy crude oil: Experimental and theoretical points of view. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 196, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazbekuly, Y.; Boiko, G.I.; Lubchenko, N.P.; Dergunov, S.A. Novel high-molecular multifunctional reagent for the improvement of crude oil properties. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 128, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Ma, Y.; Fang, S.; Shi, P.; Zhang, J.; Jing, B. Treatment of wastewater produced from polymer flooding using polyoxyalkylated polyethyleneimine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilbekova, A.O.; Omarova, K.I.; Karakulova, A.; Musabekov, K.B. Nonionic surfactants based on polyoxyalkylated copolymers used as demulsifying agents. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 480, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Geng, H.; Wang, X.; Jing, B.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y. Noval tannic acid-based polyether as an effective demulsifier for water-in-aging crude oil emulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Shah, K. Treatment of oil-contaminated water by modified polysilicate aluminum ferric sulfate. Processes 2018, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmawgoud, H.; Elshiekh, T.; Khalil, S.; Alsabagh, A.; Tawfik, M. Modeling of hydrogen sulfide removal from Petroleum production facilities using H2S scavenger. Egypt. J. Pet. 2015, 24, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, W.; Ren, S.; Wang, J. Novel and recyclable demulsifier of expanded perlite grafted by magnetic nanoparticles for oil separation from emulsified oil wastewaters. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Du, N.; Song, S.; Hou, W. Magnetic demulsification of diluted crude oil-in-water nanoemulsions using oleic acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zaman, W.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Q. Novel Janus magnetic micro particle synthesis and its applications as a demulsifier for breaking heavy crude oil and water emulsion. Fuel 2015, 141, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, B.; Lu, L.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Q.; Jia, Y. Treatment of produced water from polymer flooding in oil production by the combined method of hydrolysis acidification-dynamic membrane bioreactor–coagulation process. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 74, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Fu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Screening and Optimization of Demulsifiers and Flocculants Based on ASP Flooding-Produced Water. Processes 2019, 7, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Nasser, N.M.; Abd El-Hamid, T.M. Investigation of Kinetic and Rheological Properties for the Demulsification Process. Egypt. J. Pet. 2013, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabagh, A.M.; Hassan, M.E.; Desouky, S.E.M.; Nasser, N.M.; Elsharaky, E.A.; Abdelhamid, M.M. Demulsification of W/O emulsion at petroleum field and reservoir conditions using some demulsifiers based on polyethylene and propylene oxides. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lin, F.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Sui, H. Enhancing heavy oil liberation from solid surfaces using biodegradable demulsifiers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodbari, N.H.; Badiei, A.; Soleimani, E.; Khaniani, Y. Tweens demulsification effects on heavy crude oil/water emulsion. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S806–S811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Chen, B.; Chen, T.; Duan, M.; Xiong, Y.; Shi, P. An innovative method to introduce magnetism into demulsifier. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ying, H.; Yan, S.; Zhan, N.; Guo, Y.; Fang, W. Hyperbranched poly(amido amine) demulsifiers with ethylenediamine/1,3-propanediamine as an initiator for oil-in-water emulsions with microdroplets. Fuel 2018, 226, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.-F.; Lu, L.-J.; Xu, J.-C.; Wen, Y.; Yang, D.-H.; Zhou, Q. Comparison between waste frying oil and paraffin as carbon source in the production of biodemulsifier by Dietzia sp. S-JS-1. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6481–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, K.; Huang, X.; Lu, L.; Cheng, H.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Deng, H. Application of waste frying oils in the biosynthesis of biodemulsifier by a demulsifying strain Alcaligenes sp. S-XJ-1. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Peng, K.; Feng, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, L. Separation and characterization of effective demulsifying substances from surface of Alcaligenes sp. S-XJ-1 and its application in water-in-kerosene emulsion. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Yin, W.; Lu, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, K. Demulsification of a new magnetically responsive bacterial demulsifier for water-in-oil emulsions. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5190–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, J.O.; Silva, M.P.; Moraes, P.M.; Monteiro, A.S.; Barcelos, J.C.; Siqueira, E.P.; Santos, V.L. Demulsifying properties of extracellular products and cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MSJ isolated from petroleum-contaminated soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Zhang, G.; Shen, C.; Sun, G.; Wang, R.; Yin, L.; Meng, Q. Application of rhamnolipid as a novel biodemulsifier for destabilizing waste crude oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roostaie, T.; Farsi, M.; Rahimpour, M.R.; Biniaz, P. Performance of biodegradable cellulose based agents for demulsification of crude oil: Dehydration capacity and rate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Pal, N.; Dey, S.; Mandal, A. Characterizations of surfactant synthesized from palm oil and its application in enhanced oil recovery. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 81, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Kang, W.; Bai, B. Application of alpha-amylase as a novel biodemulsifier for destabilizing amphiphilic polymer-flooding produced liquid treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, N.; Biria, D. Investigation of the activity of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus biodemulsifier to break stable water in oil emulsions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4144–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, T.; Schroën, C.; Boom, R. Separation kinetics of an oil-in-water emulsion under enhanced gravity. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 71, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Bai, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. Removal of oil from electric desalting wastewater using centrifugal contactors. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 111, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schie, L. Oil/water separation: Suparator meets the oil/water challenge. Filtr. Sep. 2013, 50, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lee, H.K. Low-density solvent-based solvent demulsification dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the fast determination of trace levels of sixteen priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5040–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; da Rocha, E.C.; Santos, R.L.; Cancelas, A.J.; Franceschi, E.; Santos, A.F.; Fortuny, M.; Dariva, C. Demulsification of water-in-crude oil emulsions using single mode and multimode microwave irradiation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Nour, A.; Jamari, S.; Rajabi, A. Demulsification of water-in-crude oil emulsion via conventional heating and microwave heating technology in their optimum conditions. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 10, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.E. Thermal destabilisation of bitumen-in-water emulsions—A spinning drop tensiometry study. Fuel 2011, 90, 3028–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Nasser, N.M.; Khamis, E.A.; Abd-El-Raouf, M. Resolution of water in crude oil emulsion by some novel aromatic amine polyesters. Egypt. J. Pet. 2015, 24, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bukosky, S.C.; Ristenpart, W.D. Low-Voltage Electrical Demulsification of Oily Wastewater. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 8341–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Less, S.; Hannisdal, A.; Bjørklund, E.; Sjöblom, J. Electrostatic destabilization of water-in-crude oil emulsions: Application to a real case and evaluation of the Aibel VIEC technology. Fuel 2008, 87, 2572–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian Kakhki, N.; Farsi, M.; Rahimpour, M.R. Effect of current frequency on crude oil dehydration in an industrial electrostatic coalescer. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Less, S.; Vilagines, R. The electrocoalescers’ technology: Advances, strengths and limitations for crude oil separation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 81, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, L.; Ghadiri, M.; Hassanpour, A. Effect of surfactants on the deformation and break-up of an aqueous drop in oils under high electric field strengths. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 125, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, S.; Thaokar, R. Electrocoalescence in non-uniform electric fields: An experimental study. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 96, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, T.-H.; Lu, G.; Yan, W.-M. Electro-coalescence of two charged droplets under constant and pulsed DC electric fields. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 98, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, A.; Hiraguchi, Y.; Kinugawa, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Tokumoto, H. Effects of organic solvent and ionic strength on continuous demulsification using an alternating electric field. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, E.; Taju Ariffin, T.S.; Azdarpour, A.; Hamidi, H.; Yusof, S.; Sabet, M.; Yahya, E. Demulsification of Light Malaysian Crude Oil Emulsions Using an Electric Field Method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13247–13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Check, G.R.; Mowla, D. Theoretical and experimental investigation of desalting and dehydration of crude oil by assistance of ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Check, G.R. Two-stage ultrasonic irradiation for dehydration and desalting of crude oil: A novel method. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2014, 81, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antes, F.G.; Diehl, L.O.; Pereira, J.S.; Guimaraes, R.C.; Guarnieri, R.A.; Ferreira, B.M.; Dressler, V.L.; Flores, E.M. Feasibility of low frequency ultrasound for water removal from crude oil emulsions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 25, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajehesamedini, A.; Sadatshojaie, A.; Parvasi, P.; Reza Rahimpour, M.; Mehdi Naserimojarad, M. Experimental and theoretical study of crude oil pretreatment using low-frequency ultrasonic waves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 48, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, R.; Lu, X. Pulsed ultrasound assisted dehydration of waste oil. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 26, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antes, F.G.; Diehl, L.O.; Pereira, J.S.; Guimaraes, R.C.; Guarnieri, R.A.; Ferreira, B.M.; Flores, E.M. Effect of ultrasonic frequency on separation of water from heavy crude oil emulsion using ultrasonic baths. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrotti, M.F.; Enders, M.S.P.; Pereira, L.S.F.; Mesko, M.F.; Flores, E.M.M.; Bizzi, C.A. Intensification of ultrasonic-assisted crude oil demulsification based on acoustic field distribution data. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wei, W.; Li, S.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, F.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J. The effect of membrane surface charges on demulsification and fouling resistance during emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y.; Feng, L. Fabrication of silica nanospheres coated membranes: Towards the effective separation of oil-in-water emulsion in extremely acidic and concentrated salty environments. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic nanofibrous membrane with hierarchical structured skin for effective oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Palou, R. Química en Microondas; CEM Publishing: Mattews, NC, USA, 2006; pp. 131–154. [Google Scholar]
- Auflem, I.H. Influence of Asphaltene Aggregation and Pressure on Crude Oil Emulsion Stability. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Perles, C.E.; Volpe, P.L.O.; Bombard, A.J.F. Study of the cation and salinity effect on electrocoalescence of water/crude oil emulsions. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6914–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-M.; Sams, G.W.; Wagner, J. Power consumption measurements for ac and pulsed dc for electrostatic coalescence of water-in-oil emulsions. J. Electrost. 2001, 53, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavichoubeh, M.; Shariaty-Niassar, M.; Ghadiri, M. The effect of interfacial tension on secondary drop formation in electro-coalescence of water droplets in oil. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 5330–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisa, A.I.; Nour, A.H.; Nour, A.H. Heating Technology: An Optimization Study. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 2898–2906. [Google Scholar]
- Alinezhad, K.; Hosseini, M.; Movagarnejad, K.; Salehi, M. Experimental and modeling approach to study separation of water in crude oil emulsion under non-uniform electrical field. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, N. Efficient demulsification of diesel-in-water emulsions by different structural dendrimer-based demulsifiers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, L.L. Surfactants: Fundamentals and Applications in the Petroleum Industry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, М.; Basimova, R. Research of Properties of Known (RS-N) and Developed Demulsifiers for Dewatering and Desalting of Oil-Water Emulsions. Электронный научный журнал Нефтегазовое дело 2010, 2, 20. [Google Scholar]
| Emulsion Description | Type of Emulsion | Desirable | Undesirable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy oil pipeline emulsions | O/W | √ | |
| Oil flotation process emulsions | O/W | √ | |
| Emulsion drilling fluid: oil-emulsion mud | O/W | √ | |
| Oil-base mud | W/O | √ | |
| Asphalt emulsion | O/W | √ | |
| Enhance oil recovery from in situ emulsions | O/W | √ | |
| Fuel oil emulsion (70% heavy oil) | O/W | √ | |
| Wellhead emulsions | W/O | √ | |
| Fuel oil emulsions | W/O | √ | |
| Oil flotation process froth emulsions | W/O or O/W | √ | |
| Oil flotation process diluted froth emulsions | O/W/O | √ | |
| Oil spills mousse emulsions | W/O | √ |
| Type of Emulsion | Oil/Water Content (v/v) | Mixing Time (min) | Mixing Speed (rpm) | Type of Emulsifier | Emulsifier Concentration | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W/O | Oil content 40 wt%–80 wt% | 5–40 | 1000–15,000 | Triton X-100 | 0.5 wt%–4 wt% | 2010 | [80] |
| O/W | 60 | Triton X-100 | 0.1% | 2010 | [81] | ||
| O/W | 50/50 | 0.5–1 | 1000 | Ethoxylated nonylphenol family (RENEX) with an ethoxylated amine (Ultramina, five EO groups) | N/R | 2011 | [82] |
| O/W | 60/30 | 10 | 6000 | Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) | 500–15,000 (ppm) | 2012 | [83] |
| O/W | 69 vol%, 72 vol%, and 66 vol% | 5–15 | 1000–2000 | Triton X-100 | 0.3 wt%–2.5 wt% | 2013 | [84] |
| W/O | 15 | 2000 | SPAN 83 | 2014 | [85] | ||
| W/O | 4/1 | 5 | 10,000 | n-Heptane (analytical grade) and toluene | N/R | 2015 | [86] |
| O/W | 90/10, 70/30, and 50/50 | 30 | 9000 | 2016 | [87] | ||
| W/O | 70/30 | 5 | 1300 | SPAN 80 | 3% | 2017 | [88] |
| W/O | 50/50 | 30 | 15,000 | 2018 | [89] |
| Type of Emulsion | Type of Demulsification | Emulsifier/Demulsifier Concentration | Ratio and Effect of Demulsifier on Separation | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W/O | Polymer | The efficiency of water separation increases as the molecular weight increases. | 2013 | [111] | |
| Heavy oil wastewater | CaCl2 with cationic poly(dimethylamine-co-epichlorohydrin) and cationic polyacrylamine | 20:600:1.2 (m/m) | Removal rates for mineral oil (98.04%). | 2013 | [98] |
| Super-heavy crude oil | Ionic liquids | 1000–1500 ppm | Water removal efficiency of 95–100%. | 2014 | [99] |
| W/O | Nonionic surfactant | 180, 120, and 80 ppm | A high demulsifying activity 97%. | 2014 | [100] |
| Oily wastewater produced from polymer flooding | Non-ionic demulsifiers | 250 mg/L | The demulsifiers were mainly affected by temperature. | 2014 | [101] |
| W/O | Non-ionic block copolymers | The dewatering was conducted at 80 °C and equal to 51.95%. | 2015 | [102] | |
| W/O | Janus magnetic submicron particles | 600 ppm | More than 95% of emulsifier was separated within 2 h at 60 °C. | 2015 | [108] |
| O/W | Ionic demulsifier | 900 mg/L | Dewatering efficiency of 89.5%. | 2015 | [7] |
| O/W | Oleic acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4@OA) | 0.10–1.00 g of Fe3O4@OA | Demulsification efficiency of 97% at a higher dosage. | 2015 | [107] |
| W/O | Polymer molecules of alkene oxides diesters | 100–600 ppm | Maximum demulsification efficiency was 76%. | 2016 | [112] |
| O/W | Ethylcellulose (EC) and EO/PO polymers | 200–300 ppm | Addition of 300 ppm of demulsifiers improved the bitumen liberation rate. | 2016 | [113] |
| W/O | Tweens (nonionic polymers) | 300–1000 ppm | Better demulsification at a dosage lower than 700 ppm. | 2016 | [114] |
| W/O | Magnetic demulsifier | 0.625 g/L | The dewatering efficiency reached 95%. | 2017 | [115] |
| O/W | Hyperbranched poly(amidoamine) | 0–40 mg/L | Oil removal ratio reached 92% with a small dosage (<40 mg/L) within 30 min. | 2018 | [116] |
| Oily wastewater | Magnetic demulsifier | 500 mg/L | The demulsifier had a good demulsification efficiency. | 2018 | [106] |
| Type of Emulsion | Name of Biodemulsifier | Demulsifier Concentration | Ratio and Effect of Demulsifier on Separation | Year of Study | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W/O | S-XJ-1 | 2550, 100, and 500 mg/L | Emulsion breaking ratio of 81.3% within 24 h. | 2010 | [25] |
| W/O | Alcaligenes sp. S-XJ-1 | 1000 mg/L | The highest demulsification ratio reached 84.5%. | 2011 | [118] |
| O/W | Rhamnolipid | 1000–2000 mg/L | The dewatering efficiency of the waste crude oil reached over 90%. | 2013 | [122] |
| O/W | Rhamnolipid | 300–1000 mg/L | The water separation reached 50–80%. | 2013 | [122] |
| W/O | Candida sphaerica UCP 0995 | The demulsification values reached around 40%. | 2015 | [36] | |
| W/O | Cellulose-based compounds | 100–1500 ppm | The ethylcellulose is efficient at breaking the emulsion, but a low dehydration rate is the main disadvantage of this agent. | 2017 | [123] |
| Enhanced oil recovery process | Alpha sulfonated ethyl ester (α-SEE) | The surfactant shows good wetting characteristics. | 2017 | [124] | |
| O/W | α-Amylase | 0–6000 mg/L | The results show that α-amylase is an efficient biodemulsifier. | 2018 | [125] |
| W/O | Biodemulsifier | Biodemulsifier breaks 95% of the emulsion. | 2018 | [126] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saad, M.A.; Kamil, M.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Yunus, R.M.; Awad, O.I. An Overview of Recent Advances in State-of-the-Art Techniques in the Demulsification of Crude Oil Emulsions. Processes 2019, 7, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7070470
Saad MA, Kamil M, Abdurahman NH, Yunus RM, Awad OI. An Overview of Recent Advances in State-of-the-Art Techniques in the Demulsification of Crude Oil Emulsions. Processes. 2019; 7(7):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7070470
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaad, M. A., Mohammed Kamil, N. H. Abdurahman, Rosli Mohd Yunus, and Omar I. Awad. 2019. "An Overview of Recent Advances in State-of-the-Art Techniques in the Demulsification of Crude Oil Emulsions" Processes 7, no. 7: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7070470
APA StyleSaad, M. A., Kamil, M., Abdurahman, N. H., Yunus, R. M., & Awad, O. I. (2019). An Overview of Recent Advances in State-of-the-Art Techniques in the Demulsification of Crude Oil Emulsions. Processes, 7(7), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7070470




