Abstract
The application of circulating fluidized bed technology in calcium looping (CaL) requires that CaO-based sorbents should be manufactured in the form of spherical pellets. However, the pelletization of powdered sorbents is always hampered by the problem that the mechanical strength of sorbents is improved at the cost of loss in CO2 sorption performance. To promote both the CO2 sorption and anti-attrition performance, in this work, four kinds of pore-forming materials were screened and utilized to prepare sorbent pellets via the extrusion-spheronization process. In addition, impacts of the additional content of pore-forming material and their particle sizes were also investigated comprehensively. It was found that the addition of 5 wt.% polyethylene possesses the highest CO2 capture capacity (0.155 g-CO2/g-sorbent in the 25th cycle) and mechanical performance of 4.0 N after high-temperature calcination, which were about 14% higher and 25% improved, compared to pure calcium hydrate pellets. The smaller particle size of pore-forming material was observed to lead to a better performance in CO2 sorption, while for mechanical performance, there was an optimal size for the pore-former used.
1. Introduction
Greenhouse gases, such as CO2 which is mainly produced from fossil fuel combustion, are believed to be the major contributors to the rise of global temperatures [1]. It is predicted that the total emission amount of CO2 will increase to 40.2 Gt by 2030 [2]. Therefore, many researchers around the world focus their studies on various technologies to reduce the emission of CO2, and the capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) of CO2 has been considered as the most effective way to solve the problem [3,4,5,6]. Capture is the key process in CCUS, and among different capture technologies, calcium looping (CaL) has been demonstrated as having good potential in achieving high-efficiency CO2 separation with affordable cost [7]. With the development of CaL, some pilot plant projects have already been put into large-scale testing [8,9,10].
Calcium looping is based on the reversible chemical reaction of . Generally, CO2 is captured in a carbonator at around 650 °C by CaO-based sorbents and released subsequently in a calciner above 900 °C. In this way, CO2 in the flue gas can be separated and collected in high purity. Though CaL has the significant advantages of low cost and high CO2 uptake capacity, there are still some obstacles in the commercialization of calcium looping. Firstly, all the natural sorbents will face a severe problem of loss-in-capacity due to sintering at a high temperature [11,12]. Another problem is attrition and fragmentation of sorbents due to its cyclic operation in fluidized bed systems [13,14,15]. As a result, partial sorbent will be lost and cannot be used repeatedly and economically. Although tremendous efforts have been made in improving the capacity and stability of sorbents [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30], these materials still face the problem that powders are too small and must be produced in the form of pellets before they can be practically applied in CaL [14,31].
Pelletization is a good way to solve the problem by shaping powdered sorbent to the desired size with suitable anti-attrition property for industrial application. However, pelletization process usually causes the loss of CO2 uptake capacity of sorbent due to the destruction of the original porous structure, so pore-forming materials are needed in the process to obtain sorbent pellets with balanced mechanical and chemical performance. Sun et al. [27] found that carbide sorbent doped with microcrystalline via extrusion-spheronization could get a carbonation conversion of 52.64% in the 25th cycle on the premise of sacrificing mechanical strength. Firas et al. [32] reported that biomass-derived materials could increase the porosity of pellets and achieve a CO2 capture capacity of around 30% higher than biomass-free pellets. Therefore, it is important to find suitable pore-forming candidates to improve chemical sorption and minimize the negative impact on mechanical performance.
In order to obtain sorbent pellets with balanced mechanical and chemical performance, in this work, the pore-forming materials, widely used in industry, including polyethylene, polystyrene, graphite, and microcrystalline cellulose were screened and tested by the fabrication of CaO-based sorbent pellets using an extrusion-spheronization method. The effects of different pore-forming materials, their size, and doping ratio were comprehensively investigated and evaluated, and the roles of pore-forming materials in the preparation of sorbent pellets were well understood.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Calcium hydroxide (CH) powder (>95%) with a particle diameter of 30–50 μm was used as the precursor of CaO. Four types of pore-forming materials including: polyethylene (denoted as PE, >99%), polystyrene (PS, >99%), graphite powder (C, >99%), and microcrystalline cellulose (MC, >99%) were screened and tested. For the specific test, PE powder with four different sizes of 6 μm, 12 μm, 30 μm, and 150 μm were utilized in the work.
2.2. Sorbent Pellets Preparation
Sorbent pellets were manufactured using an extrusion-spheronization method. For each sorbent, first, weighted calcium hydroxide and pore-forming material were vigorously dry-blended for 20 min and wet-mixed for 5 min in a stainless steel basin to get the homogeneous mixtures. Then, the wet mixtures were extruded into cylinders with a diameter of 1 mm by a mini-extruder (LEAP E-26, Chongqing, China). After that, the cylinders were cut off and rounded in a spheronizer (LEAP R-120, Chongqing, China) with a rotational speed of 3000 rpm for 25 min. Finally, pellets with a diameter of 0.75–1.25 mm were obtained through sieving and one-day air drying (called fresh pellets). A part of the pellets was calcined in a muffle furnace at 900 °C for 10 min (called pre-calcination). For simplicity, sorbent pellets were named as CH-PMX-Y, where PM refers to the pore-forming material, and X and Y are its initial mass content and particle size, respectively. For example, CH-PE10-12 means the pellet was doped with 10 wt. % PE whose particle size is 12 μm in preparation. The pellets consisting of pure calcium hydroxide is denoted as CH.
2.3. Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis
The CO2 capture capacity and CaO conversion of the samples were tested in a thermo-gravimetric analyzer (NETZSCH TG209 F3, Selb, Germany). Approximately 15 mg of the sample was placed on a corundum crucible in TGA and heated to 900 °C at a rate of 30 °C/min under a N2 flow of 85 mL/min, and the temperature was kept for 5 min to remove the moisture completely. Then, the sample was cooled down to 650 °C at a rate of −30 °C/min. Once the temperature was reached, a CO2 flow of 15 mL/min was added immediately, and the CO2 sorption condition was kept for 20 min. The aforementioned process of carbonation and calcination was repeated totally 25 times to investigate the cyclic CO2 capture performance. Based on the mass data recorded, CaO carbonation conversion (Xn, %) and CO2 sorption capacity (Cn, g-CO2/g-sorbent) of the samples were calculated using the following formulas:
where m is the maximum mass of CaO-based sorbents in sorption stage and m0 is minimum mass in calcination stage, φ is the mass content of CaO in the CaO-based sorbent, and are the molar mass of CaO and CO2, respectively. The CO2 sortion capacity uncertainty is around ±0.002 g-CO2/g-sorbent based on repeated tests.
2.4. Pellets Impact Crushing Test
Impact crushing of the pellet was carried out using an apparatus built by ourselves, as shown in Figure 1, according to the literature [33,34,35]. A high-pressure air bottle with a volumetric flow meter was used to control the velocity of air flow, and two valves were used to feed samples without the escaping of gas and particles. Particles were accelerated in an educator (1.2 m in length and 10 mm in I.D) by air at a speed of 18 m/s and impacted a stainless target (inclined by 60° with respect to the vertical direction) in the collection chamber. To filter the entrained fine particle (<12 μm), a sintered porous metal plate was installed on the top of the chamber.
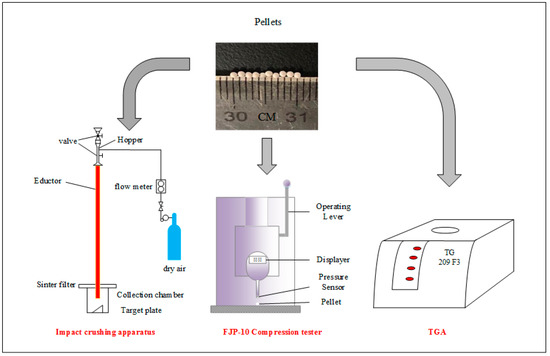
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of experimental devices.
In each test, 0.5 g samples were loaded, and after impact crushing residual particles were collected and screened through sieving into 7 size ranges: 750~1250 μm, 500~750 μm, 375~500 μm, 187.5~375 μm, 75~187.5 μm, 12~75 μm, and <12 μm. In the work, particles with a diameter smaller than 187.5 μm are regarded as completely crushed particles.
2.5. Compressive Strength Test
The compressive strength of pellets was tested using a precision digital compression tester (SHIMPO FGP-10, Kyoto, Japan), and each sample was tested for 10 times. The maximum crushing force was obtained by slowly increasing the pressure until the particle was crushed. Compression strength was evaluated by the average crushing force and the error bar was calculated.
2.6. Characterization of Sorbents
Surface morphology of sorbents was captured using a field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, SU8020, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). To determine the specific Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface, Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) pore volume and pore size distribution of selected samples, N2 adsorption/desorption analysis was measured at approximately −196 °C using a Micromeritics TriStar II 3020 instrument after outgassing under vacuum for 18 h at 200 °C.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Decomposition of Pore-Forming Materials
To understand thermal properties of pore-forming materials, they were first tested in the TGA at a constant ramping rate of 30 °C/min to 900 °C followed by isothermal calcination for 5 min, and the results are shown in Figure 2. It was seen that under the atmosphere of N2, MC, PS, and PE started to pyrolyze at 300–400 °C with a quick weight loss until they were completely decomposed. In contrast, there was almost no decomposition of C in N2 flow. When the atmosphere was switched to a flow containing 15 vol. % O2 balanced with N2, C was observed to start burning at 600 °C until it was burnt out at around 900 °C. Based on the decomposition characteristics, it can be concluded that all pore-forming materials would be burnt into gases to create pores without any solid residues left in the prepared sorbent pellets.
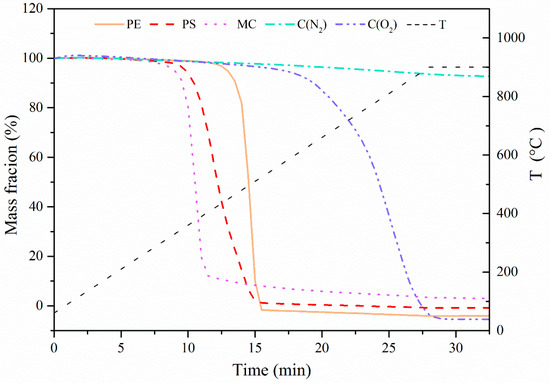
Figure 2.
Decomposition property of pore-forming materials at a constant ramping rate of 30 °C/min to 900 °C under the atmosphere of N2 or N2/O2.
3.2. Characterization of Sorbent Pellets
To see the effect of pore-forming materials on the structure of sorbent pellets, cross-sectional images were captured of the calcined CH and CH-PE5 using the field emission scanning electron microscopy, and the results are depicted in Figure 3. It is very clear that grains and pores in CH-PE5 are much smaller and their distributions are more uniform than those in the sample of CH. These differences can be attributed to the positive pore-forming effect of PE on sorbents microstructure during its decomposition to gaseous phases. The roles of pore-formers could be further understood from the results of the N2 adsorption/desorption test. Table 1 summarizes the specific surface area, BJH average pore width, and pore volume of CH and CH-PE5. It is seen that CH-PE5 pellets have a BET surface area of 11.66 m2/g, BJH cumulative pore volume of 0.0436 cm3/g, and an average pore diameter of 15.2 nm, which are all superior to those of CH. Figure 4 indicates that the higher pore volume of CH-PE5 is mainly correlated to pores of size in the range of 2–40 nm, which also contributed to the higher specific surface area in comparison with CH. Based on these results, it is reasonable to predict that the better microstructure of CH-PE5 would lead to an easier diffusion of CO2 within the sorbent and the following carbonation reaction.
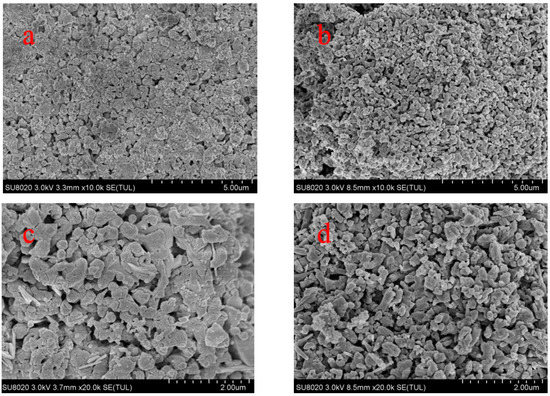
Figure 3.
Cross-sectional images of calcined (a,c) CH (Ca(OH)2), and (b,d) CH-PE5 (Ca(OH)2 doped with 5 wt. % PE).

Table 1.
Microstructures of sorbent pellets after calcination at 900 °C.
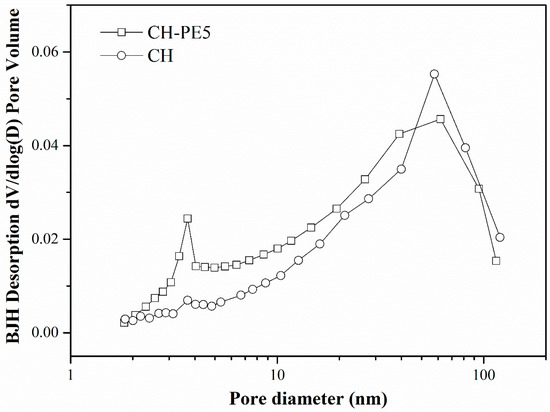
Figure 4.
Pore size distribution of CH-PE5 and CH pellets.
3.3. Effect of Various Pore-Forming Materials
To understand the impact of different pore-forming materials, CO2 sorption/desorption performance, compressive strength, and anti-impact crushing capacity of prepared sorbent pellets were tested and evaluated in this section. Pore-forming materials with a particle size of 12 μm were used, and their contents were kept at the same of 5 wt. %.
3.3.1. Sorption/Desorption Performance
Cyclic CO2 uptake capacity and CaO conversion of sorbent pellets prepared with different pore-formers were presented in Figure 5. It shows that CH possesses a CO2 capture around 0.556 g-CO2/g-sorbents initially, but the value quickly decreased to 0.136 g-CO2/g-sorbent after 25 cycles. For sorbent pellets with the addition of pore-forming materials in preparation, CH-PE5 shows the highest CO2 capture capacity of 0.574 g-CO2/g-sorbent in the first cycle and 0.155 g-CO2/g-sorbent after 25 cycles, which are both higher than those of CH. This is in accordance with the aforementioned characterization results, demonstrating that CH-PE5 modified inner structure of sorbents during the pyrolysis of PE, resulted in a shifting of pores to smaller sizes of 2–40 nm (see Figure 4), and an increase of surface area and pore volume (see Table 1). It is well known that a bigger pore volume means a smaller CO2 transfer resistance, and a higher specific surface area could supply more available sites in pellets to react with CO2 [32,34]. Thus, CO2 sorption performance of CH-PE5 was improved. The CH-C5 shows a similar CO2 uptake capacity, which is only slightly lower than CH-PE5 but higher than CH. For CH-PS5 and CH-MC5, no improvement in sorption performance was observed compared to CH. The CaO conversion, the other aspect of sorption property, shares the same trend with the CO2 uptake capacity.
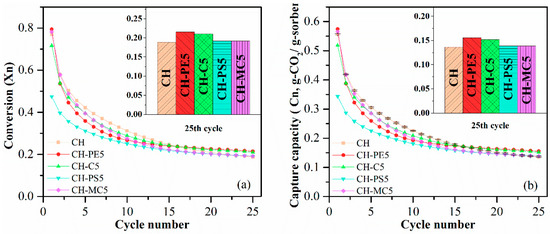
Figure 5.
(a) Carbonation conversion and (b) CO2 capture capacity of sorbent pellets prepared with different pore-forming materials. Testing conditions: calcination at 900 °C for 5 min in N2, and carbonation at 650 °C for 20 min in 15 vol. % CO2.
3.3.2. Mechanical Performance
Figure 6 plots the compressive strength of sorbent pellets (with/without calcination) prepared from different pore-forming materials. Without the calcination, CH pellets show a compressive strength of 6.7 N, while CH-PE5 possesses a value of 7.6 N, the highest among all fresh pellets. After calcination, the mechanical strength of all pellets experiences a significant decline. Among them, CH shows the lowest compressive strength of 3.2 N, almost a half loss comparing to that without calcination. By contrast, the addition of PS leads to about 30% improvement of the compressive strength to 4.2 N, and calcined pellets of CH-PE5, CH-C5, and CH-MC5 demonstrated a compressive strength of 4.0 N, 4.0 N, and 3.2 N, respectively. Since the compressive strength of calcined pellets is more meaningful in CaL application, it is concluded that the addition of pore-formers PE, PS, and C could modify pore structure of sorbents in the way that benefits the mechanical strength of pellets.
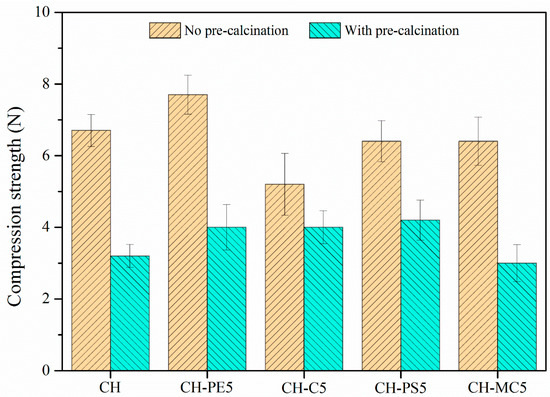
Figure 6.
Compressive strength of sorbent pellets (at a mean diameter of 1 mm) with different pore-forming materials.
The results of impact crushing test are shown in Figure 7. By comparing particle size distribution after impact crushing, attrition resistance of diverse sorbent pellets could be evaluated. Obviously, the anti-attrition ability of fresh pellets is much better than calcined pellets, which, however, is more meaningful in the practical CaL application. That is our focus in the following work. It is seen that when particles smaller than 187.5 μm are regarded as completely crushed materials, the mass loss fraction of CH pellets reach to nearly 24.4% from the cumulative percentage results. In contrast, the value for CH-PE5% and CH-C5 was only around 5.9% and 5.2%, respectively. Meanwhile, the mass fraction of residual particles within a diameter range of 750–1250 μm is 11.2% for CH-PE5 from the mass fraction results, which is the highest. These results indicate that the addition of a small amount pore-formers enhances the mechanical strength of sorbent pellets. It is possible that the pores formed during the pyrolysis of pore-formers at a relatively low temperature are able to act as channels for the release of CO2 in the decomposition of CaCO3, avoiding the formation of additional cracks, and is beneficial for keeping the mechanical strength.
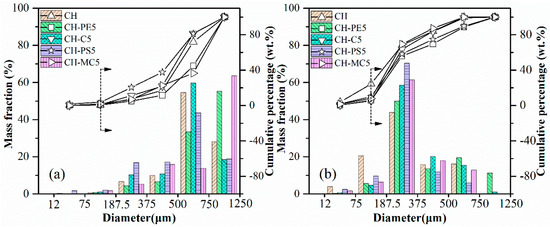
Figure 7.
Impact crushing resulted in particle size distribution of sorbent pellets with different pore-forming materials: (a) fresh, (b) after calcination at 900 °C.
3.4. Effect of Addition Content of PE
The above results indicate that the addition of PE resulted in the best improvement in both the CO2 sorption and the mechanical performance among all pore-formers, thus we optimized its addition content from 2.5% to 20% in this part, while keeping the particle size of PE at 12 μm.
3.4.1. Sorption/Desorption Performance
Figure 8 shows that CO2 sorption capacity of all CH-PE samples were improved under the conditions studied. A tendency of first-increase-then-decrease was observed with the increasing addition of PE, and the peak appears when 5 wt. % PE was utilized. Theoretically, with the increasing addition of pore-forming materials, CO2 sorption performance should keep going up. However, it never happened in our experiment. The reason could be that the most suitable pore size range for long cyclic CO2 capture is 20–50 nm [35]. However, the addition of too much PE would result in pores that are out of the aforementioned optimum range and lead to a loss in CO2 capacity in a long cycle.
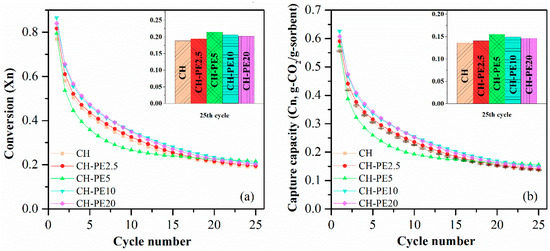
Figure 8.
(a) Carbonation conversion and (b) CO2 capture capacity of sorbent pellets with different addition of PE. Testing conditions: calcination at 900 °C for 5 min in N2, and carbonation at 650 °C for 20 min in 15 vol. % CO2.
3.4.2. Mechanical Performance
The compressive strength of pellets with different addition of PE is illustrated in Figure 9. Similar to the variation of chemical sorption, the compressive strength of calcined CH-PE goes up with the increasing addition of PE, especially for 2.5 wt. % and 5 wt. %, and then slightly declines. It is also clear that pellets without calcination have a much better mechanical strength. The results of impact crushing test for different CH-PE sorbent pellets are summarized in Figure 10. It shows that calcined CH-PE2.5 and CH-PE5 pellets have a much better attrition resistance, whose complete mass loss is 6.9% and 5.9%, respectively, from the cumulative percentage results. In contrast, the value for CH-PE10 and CH-PE20 pellets is 22.1% and 31.1%, which are similar to CH. In addition, CH-PE5% has the biggest mass fraction of residual particle whose size ranges in 750–1250 μm. So, it could be concluded that, within a small addition of PE, the mechanical strength could be significantly enhanced. However, when further increasing the amount of PE, the cavities and gases released in PE pyrolysis are too much to hold a favorable structure for the good mechanical strength of sorbent pellets.
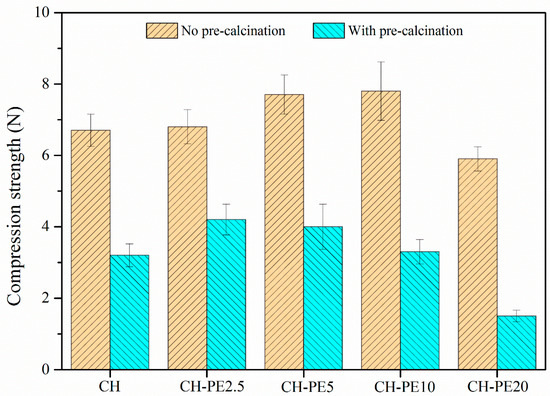
Figure 9.
Compressive strength of synthetic sorbent pellets (a mean diameter of 1 mm) with different addition of PE.
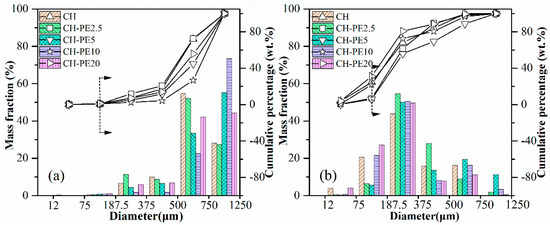
Figure 10.
Impact crushing resulted in particle size distribution of sorbent pellets with different additions of PE: (a) fresh, (b) after calcination at 900 °C.
3.5. Effect of Pore-Former Particle Size
Particle size of the pore-forming material could possibly change the performance of sorbent pellets. However, few experiments were reported in this field deeply. Here, PE with varying particle sizes from 6 μm to 150 μm were selected and tested while its addition content was kept at 5%.
3.5.1. Sorption/Desorption Performance
The CO2 sorption performance of sorbent pellets with different particle sizes of PE are presented in Figure 11. It is evident that sorbent pellets with a smaller particle size of PE have a better performance in CO2 capturing. The CH-PE5-6 pellet had the highest CO2 uptake capacity of 0.157 g-CO2/g-sorbent which was 6.8% higher than CH-PE5-150 pellets, followed by CH-PE5-12 and CH-PE5-50. It can be concluded that the chemical performance was inversely proportional to the particle size of pore-former utilized. It is very likely that with the same content of PE added, the smaller particle size could lead to the formation of a more uniform distribution of smaller pores, in other words, a bigger specific surface area, and bigger pore volume. Thus, there is more “activated space” for the CO2 to react with CaO.
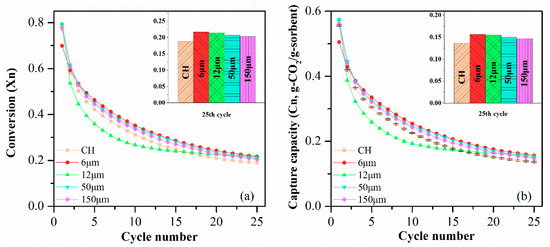
Figure 11.
(a) Carbonation conversion and (b) CO2 capture capacity of synthetic pellets with different particle sizes of PE. Testing conditions: calcination at 900 °C for 5 min in N2, and carbonation at 650 °C for 20 min in 15 vol. % CO2.
3.5.2. Mechanical Performance
Compressive strength of synthetic sorbent pellets with different particle sizes of PE are shown in Figure 12. A tendency of first-increase-then-decrease compressive strength was observed with the increasing particle size of PE, for both fresh and calcined pellets. The CH-PE5-12 possessed the biggest compressive strength among all calcined pellets while CH-PE5-150 was the worst. The ratio of the mechanical strength value for pellets after calcination to fresh pellet was also calculated in order to understand the influence of different particle sizes. The value is 55.9%, 51.9%, 23.9%, and 18.9% for CH-PE5-6, CH-PE5-12, CH-PE5-50, and CH-PE5-150, respectively, showing that bigger particle size of the pore-former has a negative effect in maintaining the compressive strength of pellets during high-temperature calcination.
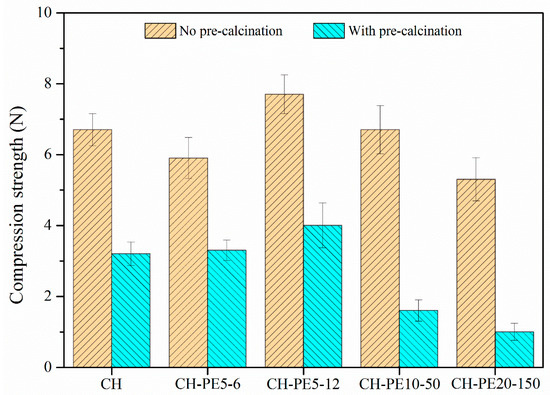
Figure 12.
Compressive strength of synthetic sorbent pellets (a mean diameter of 1 mm) with different particle size of PE.
Figure 13 summarizes impacting test results for sorbent pellets with different particle sizes of PE. For the various fresh pellets, their particle distribution after impacting test is very similar, and the complete mass loss is around 1% from the cumulative percentage results. For calcined ones, due to the significant loss in mechanical strength of pellets added with bigger PE (50 μm, 150 μm), lots of them broke up during the pre-calcination process. Thus, we did not present results in the diagram. But conclusion can also be reached that with the smaller particle size of pore-former added, the better mechanical strength sorbent pellets have, which is also consistent with the conclusion obtained in the compression test.
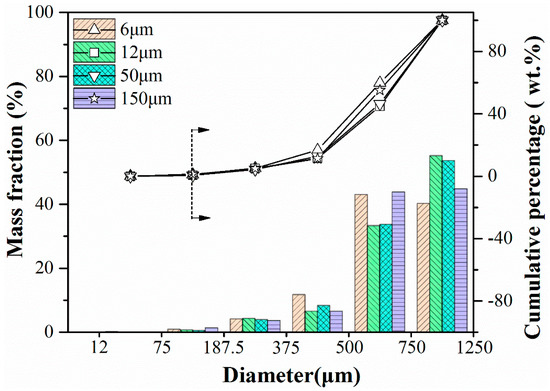
Figure 13.
Impact crushing resulted in particle size distribution of fresh sorbent pellets with different particle size of PE.
4. Conclusions
This work studied CO2 uptake and anti-attrition performance of CaO-based pellets synthesized via extrusion-spheronization with the addition of a small amount of pore-forming materials. Four kinds of pore-forming materials with varying additional content and particle size were investigated in this work. It was found that the addition of PE had a positive effect on enhancing the CO2 sorption capacity meanwhile maintaining a relatively high mechanical strength, compared to pure Ca(OH)2 pellets. The reason is micro-structures (i.e., pore distribution, surface area, and pore volume) of synthetic sorbents were modified in a way promoting the diffusion and subsequent CO2 reaction with sorbents. After 25 typical cycles, pellets with 5% PE captured 14% more CO2 and possessed 25% higher mechanical strength than pure Ca(OH)2 pellets. The lesser or greater addition of PE did not bring further performance enhancement. The particle size of pore-formers was also observed to affect the performance of prepared sorbent pellets, and the smaller ones led to a better chemical performance in CO2 sorption. In contrast, there was an optimal size of PE (12 μm) for the mechanical strength of sorbent pellets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Q. and Z.Z.; investigation, Z.Z.; resources, C.Q.; data curation, S.P. and D.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z.; writing—review and editing, C.Q.; supervision, C.Q. and J.R..; project administration, C.Q and J.R.; funding acquisition, C.Q. and J.R.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2017YFB0603300; National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51606018; Chongqing Basic Science and Advanced Technology Research Program, grant number cstc2017jcyjAX0324; the Innovation Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees, grant number cx2017021; Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, grant number 2018CDJDDL0005; Key Industrial Generic Technology Innovation Project of Chongqing, grant number cstc2016zdcy-ztzx20006.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFB0603300), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51606018), Chongqing Basic Science and Advanced Technology Research Program (No. cstc2017jcyjAX0324), the Innovation Program for Chongqing Overseas Returnees (No. cx2017021), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2018CDJDDL0005), and Key Industrial Generic Technology Innovation Project of Chongqing (No. cstc2016zdcy-ztzx20006).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pachauri, K.; Meyer, A. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Environ. Policy Collect. 2014, 27, 408. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.Q.; An, H.; Qin, C.L.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, G.X.; Feng, B.; Xu, M.H. Performance Enhancement of Calcium Oxide Sorbents for Cyclic CO2 Capture—A Review. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2751–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, Z. Energy and Material Balance of CO2 Capture from Ambient Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7558–7563. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Soltanian, M.R.; Olabi, A.G. Effectiveness of amino acid salt solutions in capturing CO2: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 98, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, J.; Chen, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Qi, W. Progress in enhancement of CO2 absorption by nanofluids: A mini review of mechanisms and current status. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; He, D.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, L.; Ran, J. The consecutive calcination sulfation in calcium looping for CO2 capture Particle modeling and behaviour investigation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Rodríguez, N.; González, B.; Grasa, G.; Murillo, R.; Abanades, J.C. Carbon dioxide capture from combustion flue gases with a calcium oxide chemical loop. Experimental results and process development. Int J Grennh Gas Con. 2010, 4, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.Y.; Hughes, R.W.; Anthony, E.J. Ca-based sorbent looping combustion for CO2 capture in pilot-scale dual fluidized beds. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströhle, J.; Junk, M.; Kremer, J.; Galloy, A.; Epple, B. Carbonate looping experiments in a 1 MW th pilot plant and model validation. Fuel 2014, 127, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yin, J.; Feng, B.; Ran, J.; Li, Z.; Manovic, V. Modelling of the calcination behaviour of a uniformly-distributed CuO/CaCO3 particle in Ca–Cu chemical looping. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Bo, F.; Yin, J.; Ran, J.; Li, Z.; Manovic, V. Matching of kinetics of CaCO3 decomposition and CuO reduction with CH4 in Ca–Cu chemical looping. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materic, V.; Hyland, M.; Jones, M.I.; Holt, R. Investigation of the friability of Ca looping sorbents during and after hydration based reactivation. Fuel 2014, 127, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, F.; Salatino, P.; Boerefijn, R.; Ghadiri, M. Attrition of sorbents during fluidized bed calcination and sulphation. Powder Technol. 2000, 107, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. Enhancement of attrition resistance and cyclic CO2 capture of calcium-based sorbent pellets. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 116, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Low, N.W.; Feng, B.; Wang, G.; Diniz da Costa, J.C. Calcium precursors for the production of CaO sorbents for multicycle CO2 capture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martavaltzi, C.S.; Lemonidou, A.A. Development of new CaO based sorbent materials for CO2 removal at high temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 110, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, S. A new nano CaO-based CO2 adsorbent prepared using an adsorption phase technique. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, C.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, L. Natural Calcium-Based Sorbents Doped with Sea Salt for Cyclic CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jeboori, M.J.; Fennell, P.S.; Nguyen, M.; Ke, F. Effects of Different Dopants and Doping Procedures on the Reactivity of CaO-based Sorbents for CO2 Capture. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 6584–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Fennell, P.S.; Al-Jeboori, M.J.; Anthony, E.J. Steam-Enhanced Calcium Looping Cycles with Calcium Aluminate Pellets Doped with Bromides. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 7677–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Suzuki, Y. Limestone Calcination with CO2 Capture (II): Decomposition in CO2 /Steam and CO2 /N2 Atmospheres. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Duan, L.; Su, C.; Li, Y.; Anthony, E.J. Effect of steam hydration on reactivity and strength of cement-supported calcium sorbents for CO2 capture. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Labiano, F.; Abad, A.; De Diego, L.; Gayan, P.; Adanez, J. Calcination of calcium-based sorbents at pressure in a broad range of CO2 concentrations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 2381–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, P.S.; Pacciani, R.; Dennis, J.S.; Davidson, J.F.; Hayhurst, A.N. The Effects of Repeated Cycles of Calcination and Carbonation on a Variety of Different Limestones, as Measured in a Hot Fluidized Bed of Sand. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Smirniotis, P.G.; Ernst, F.O.; Pratsinis, S.E. Nanostructured Ca-based sorbents with high CO2 uptake efficiency. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, M. Enhanced performance of extruded–spheronized carbide slag pellets for high temperature CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Qin, C.; Manovic, V.; Ran, J.; Bo, F. Study on the interaction between CaO-based sorbents and coal ash in calcium looping process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 156, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, C.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, H.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Characteristics and performance of CaO-based high temperature CO2 sorbents derived from sol-gel process with different supports. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 79285–79296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, H.; Luo, C.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, C.; Zhang, L. Porous spherical calcium-based sorbents prepared by a bamboo templating method for cyclic CO2 capture. Fuel 2018, 219, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Wu, Y.H.; He, I.; Anthony, E.J. Spray Water Reactivation/Pelletization of Spent CaO-based Sorbent from Calcium Looping Cycles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12720–12725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, F.N.; Wu, Y.; Manovic, V.; Macchi, A.; Anthony, E.J. Enhanced CO2 capture by biomass-templated Ca(OH)2-based pellets. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 274, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yu, Z.; Erans, M.; Li, Y.; Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. Attrition study of cement-supported biomass-activated calcium sorbents for CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9476–9484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, F.; Montagnaro, F.; Salatino, P. Attrition of Limestone by Impact Loading in Fluidized Beds. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 2566–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, F.; Salatino, P. Flue gas desulfurization under simulated oxyfiring fluidized bed combustion conditions: The influence of limestone attrition and fragmentation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).