CFD Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer of V-Shaped Wavy Microchannels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. V-Shaped Wavy Microchannel Heat Sink
3. Simulation Methods
3.1. Controlling Equations and Boundary Conditions
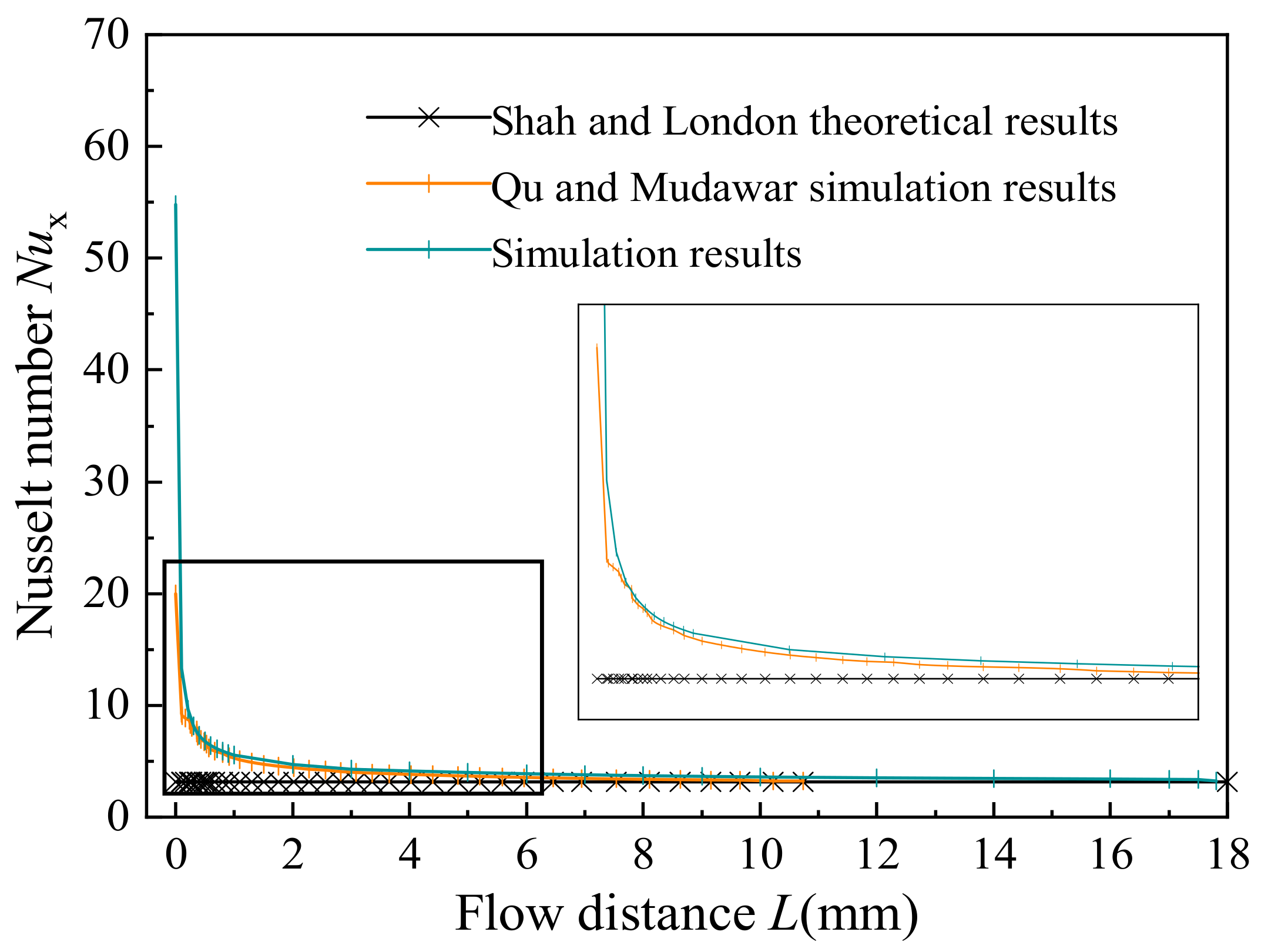
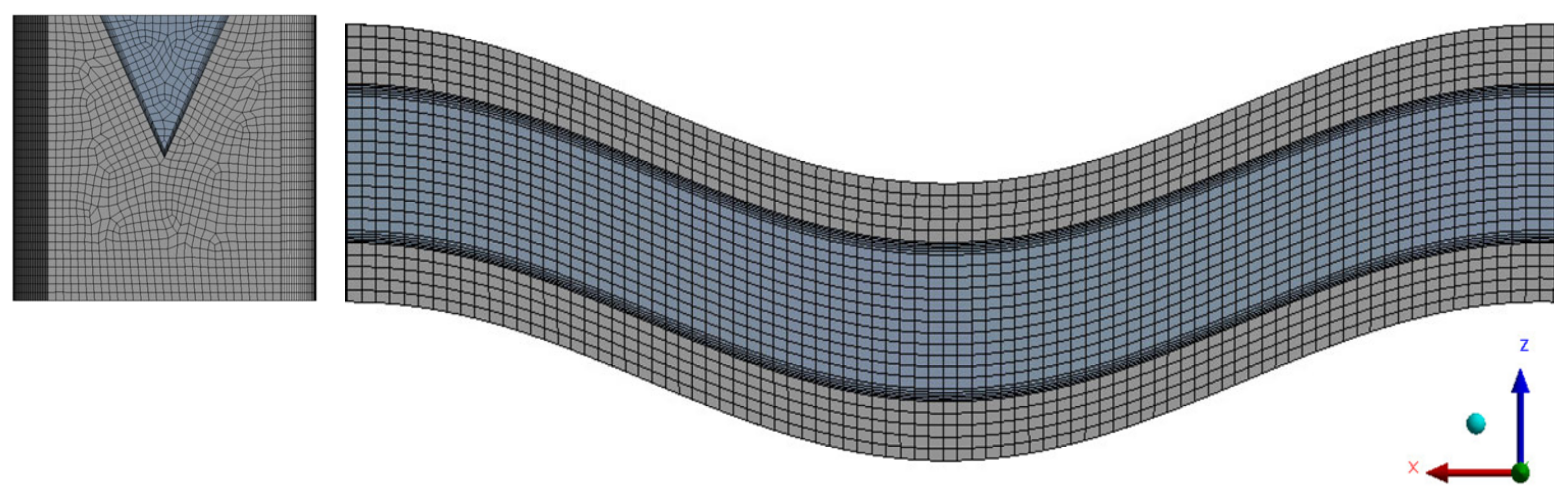
3.2. Mesh Division and Model Validation
3.3. Evaluation Variables
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Influence of Several Variables
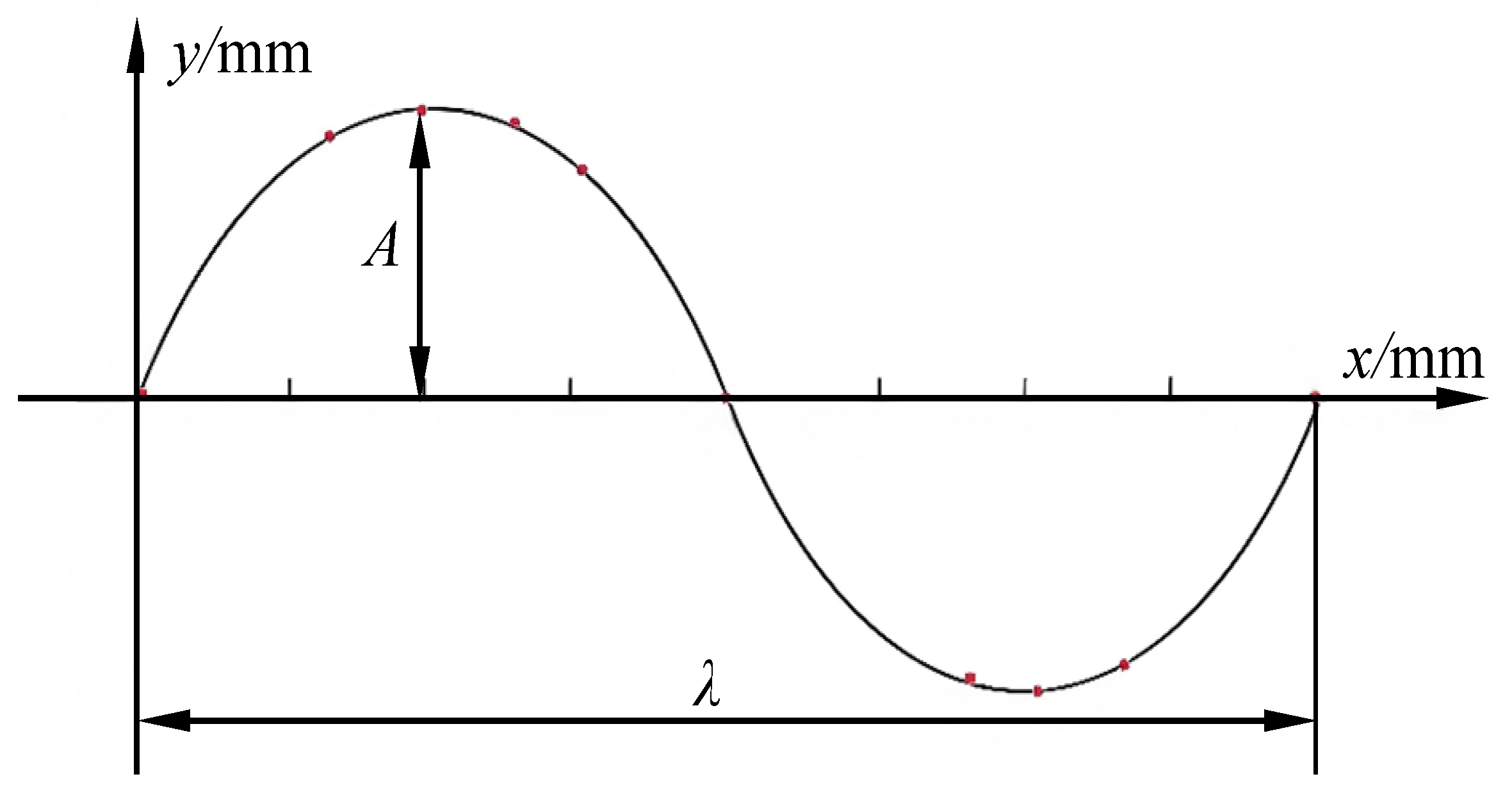
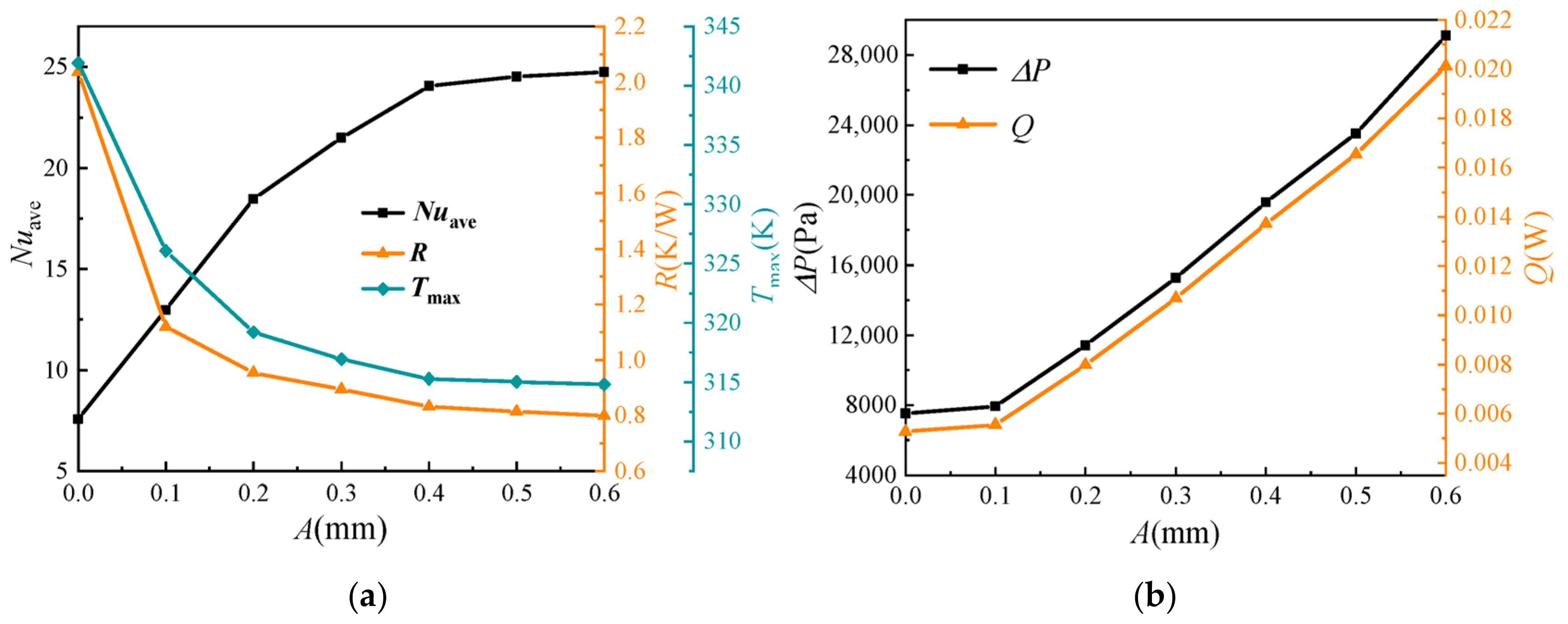
4.1.1. Influence of Wave Amplitude A
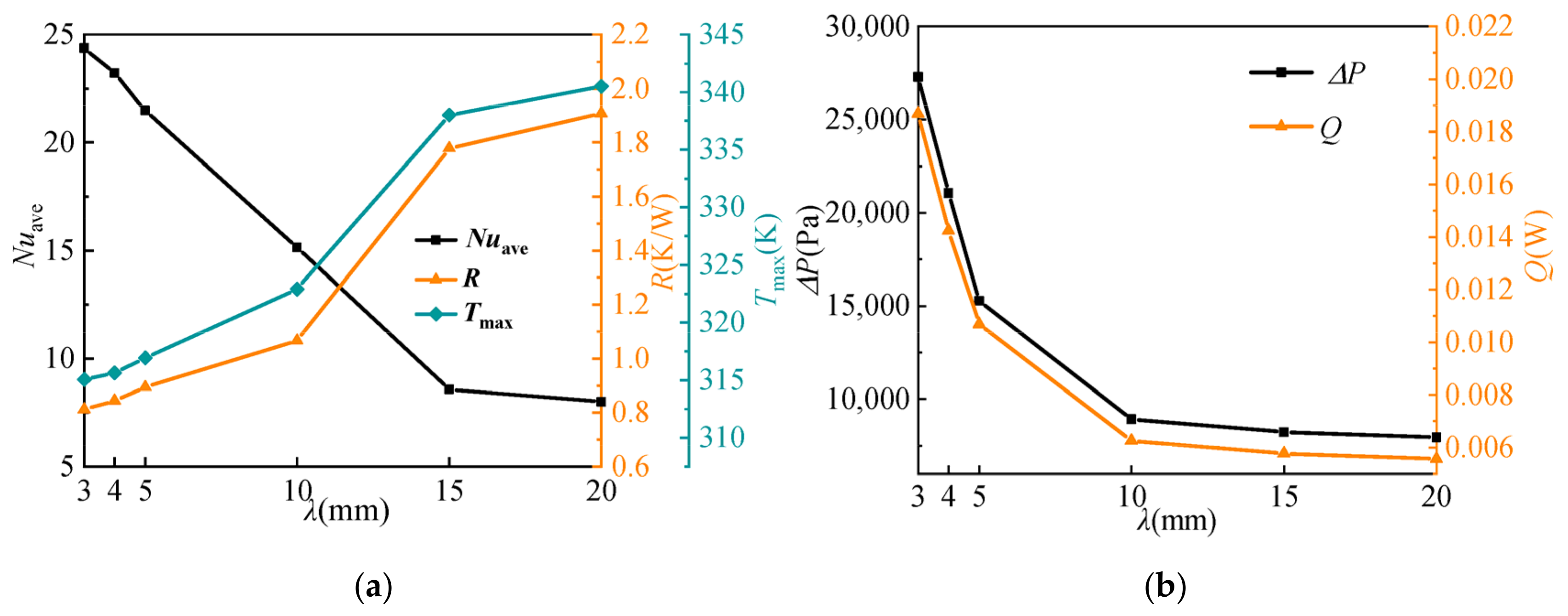
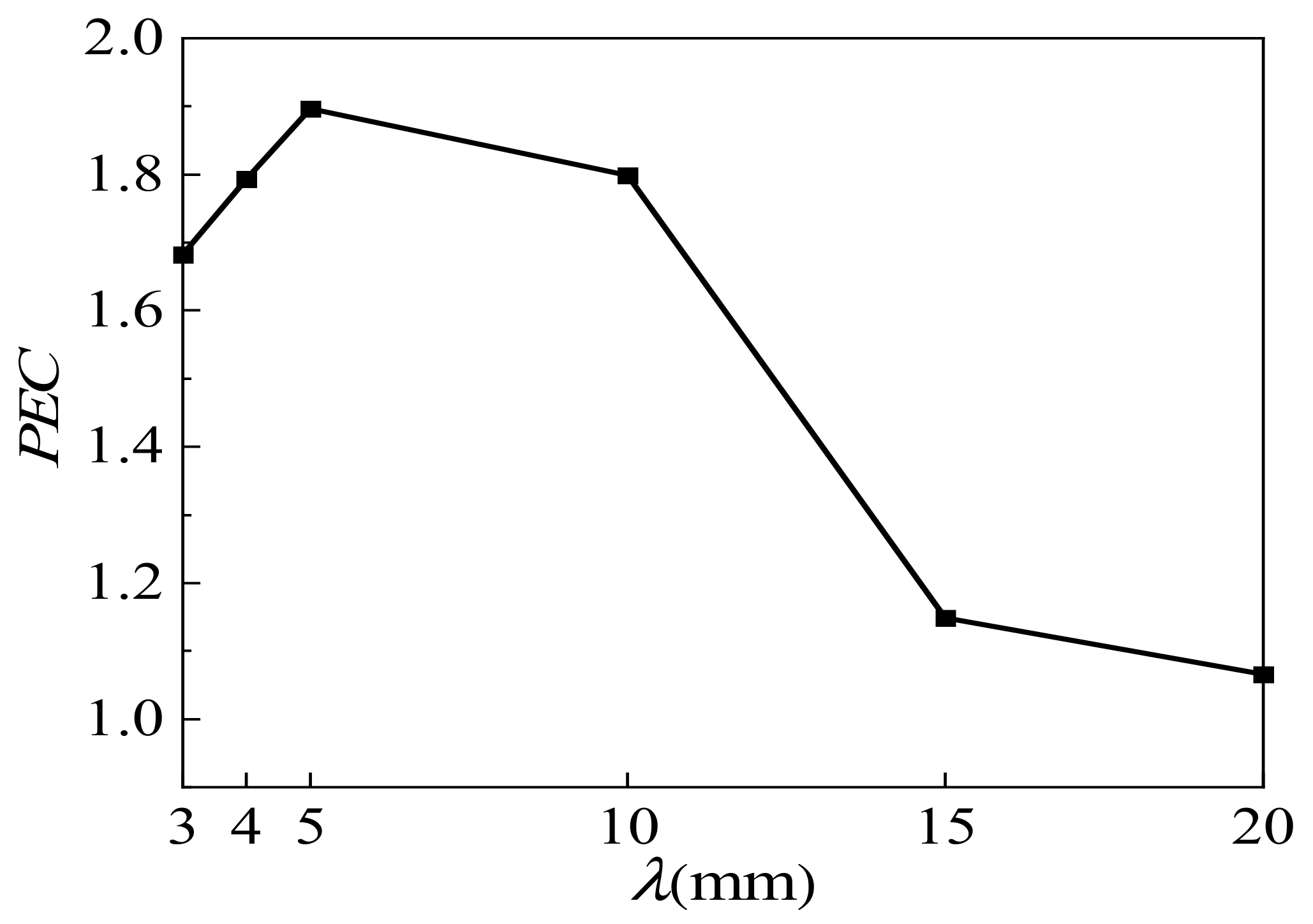
4.1.2. Influence of Wave Length λ
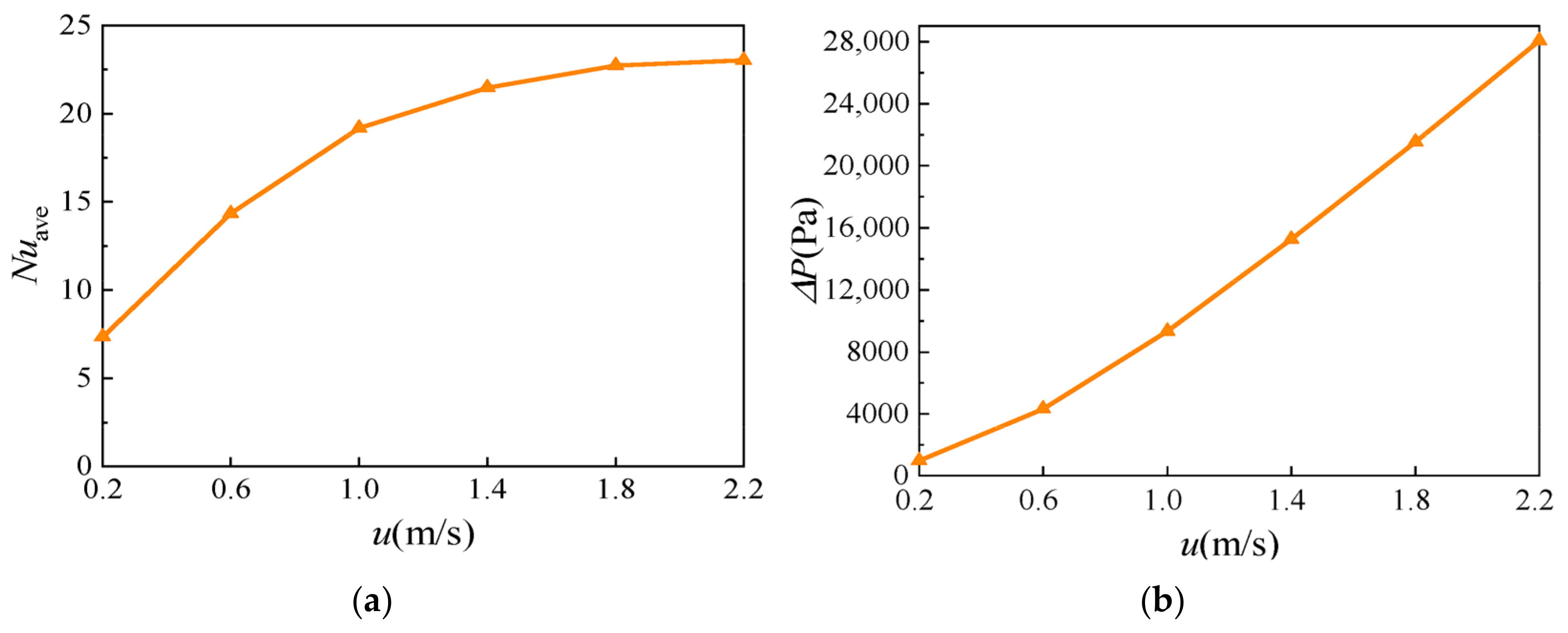
4.1.3. Influence of Inlet Velocity u
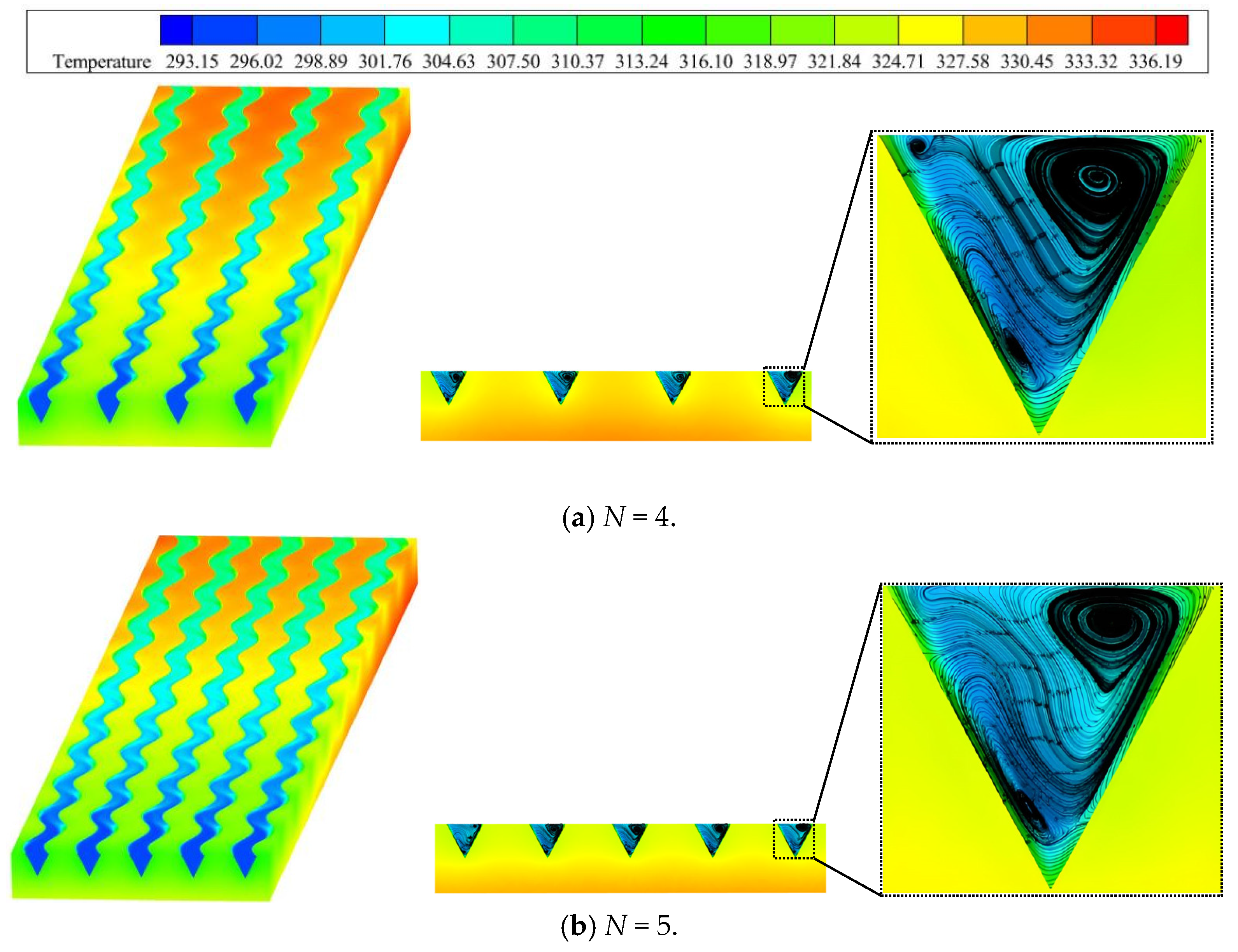
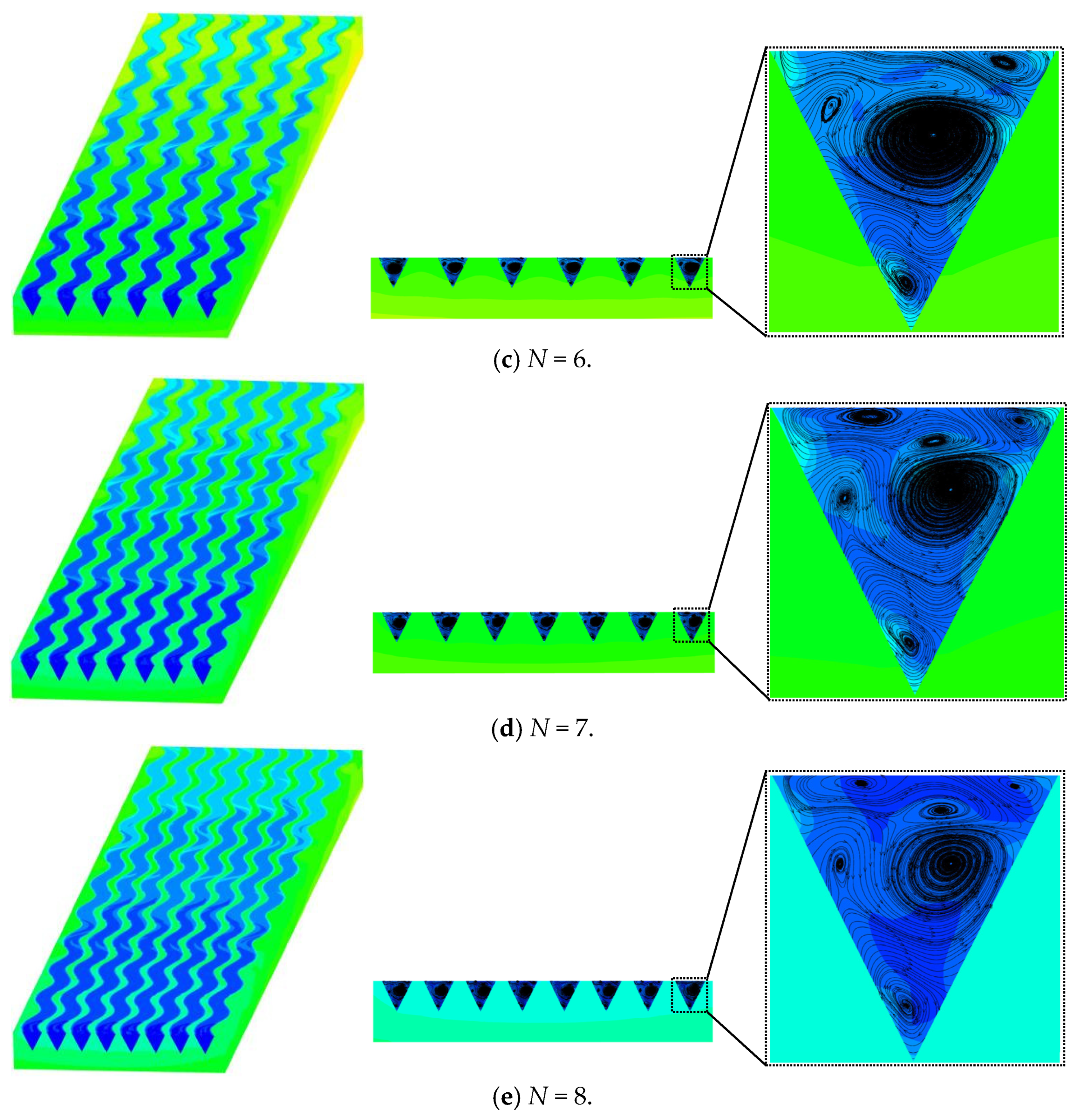
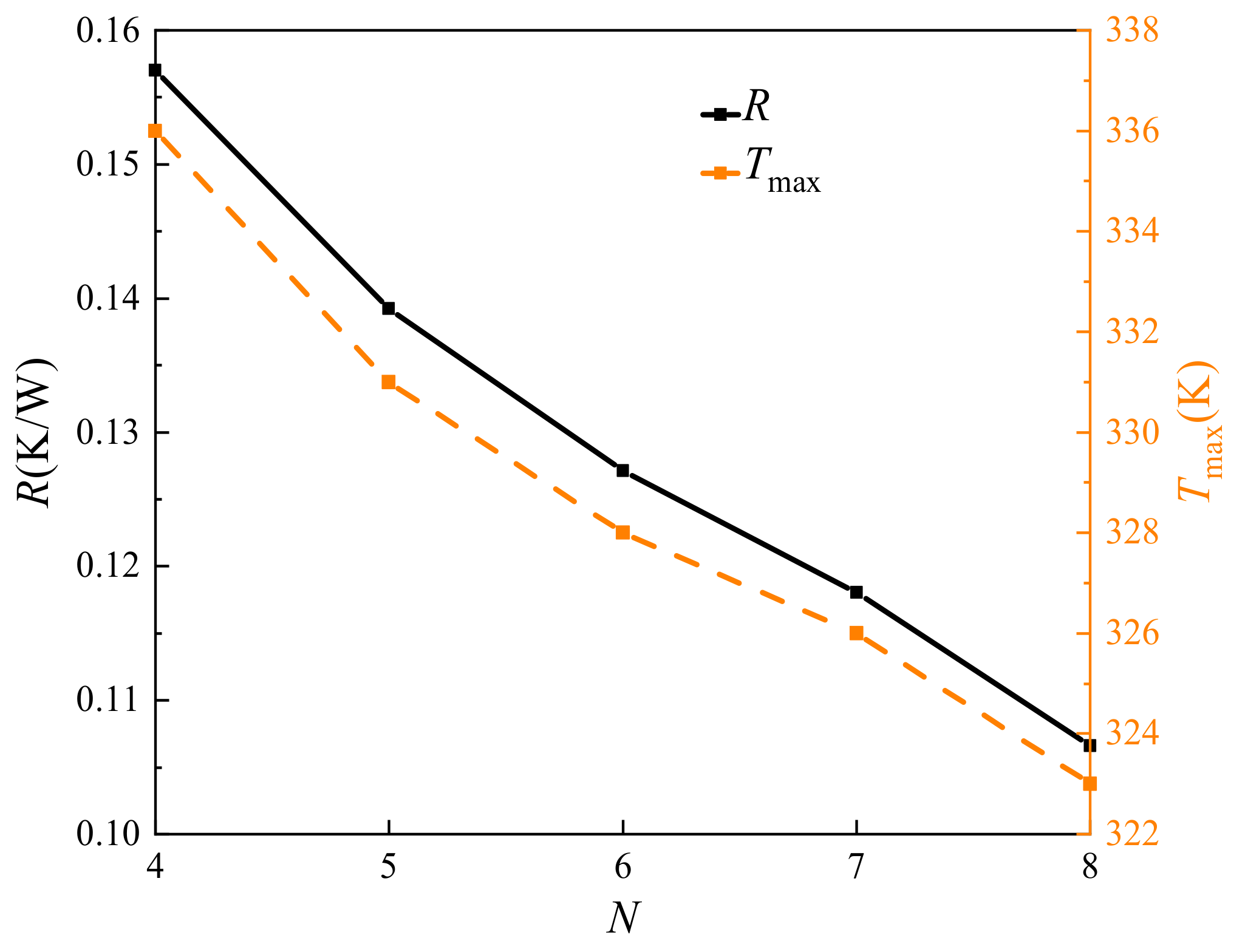
4.1.4. Influence of Microchannel Number N
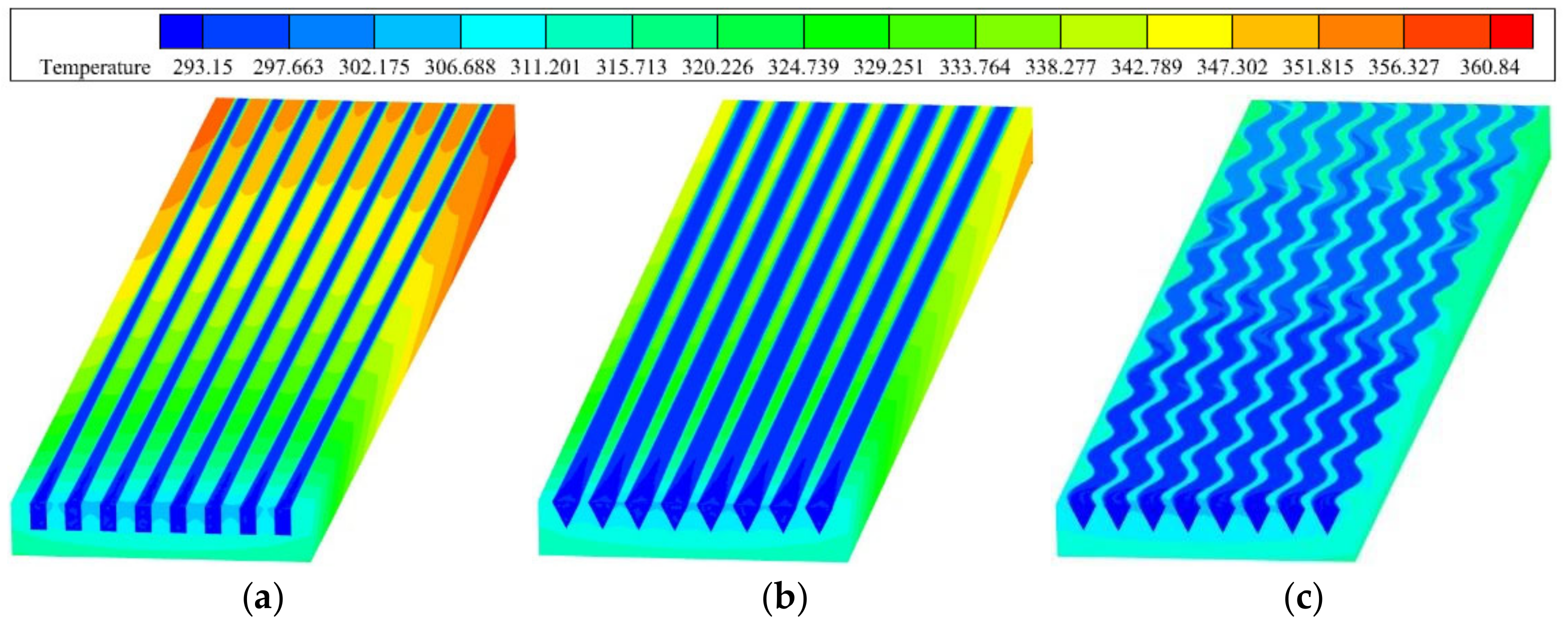
4.2. Comparison of Three Kinds of Microchannels
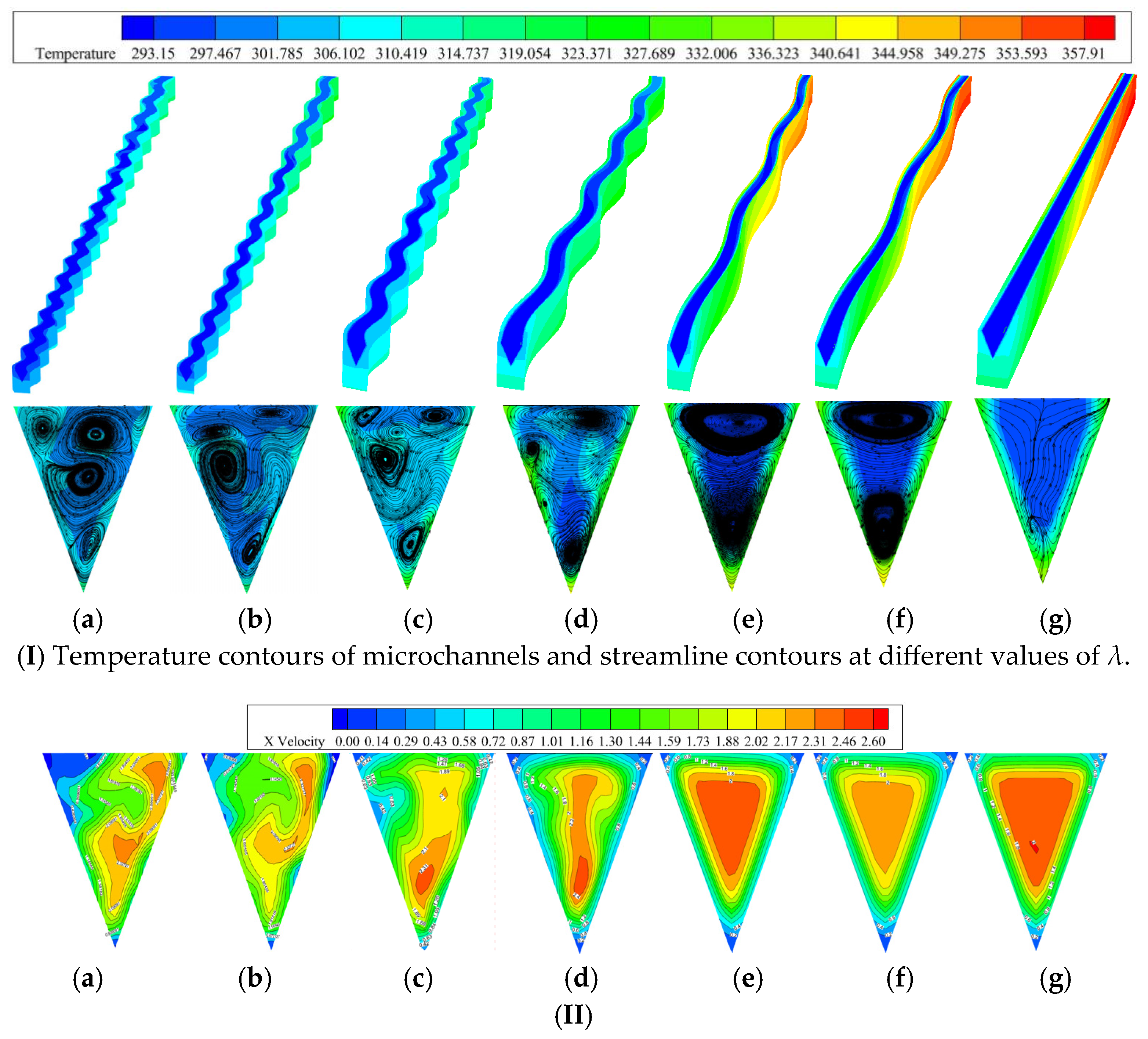
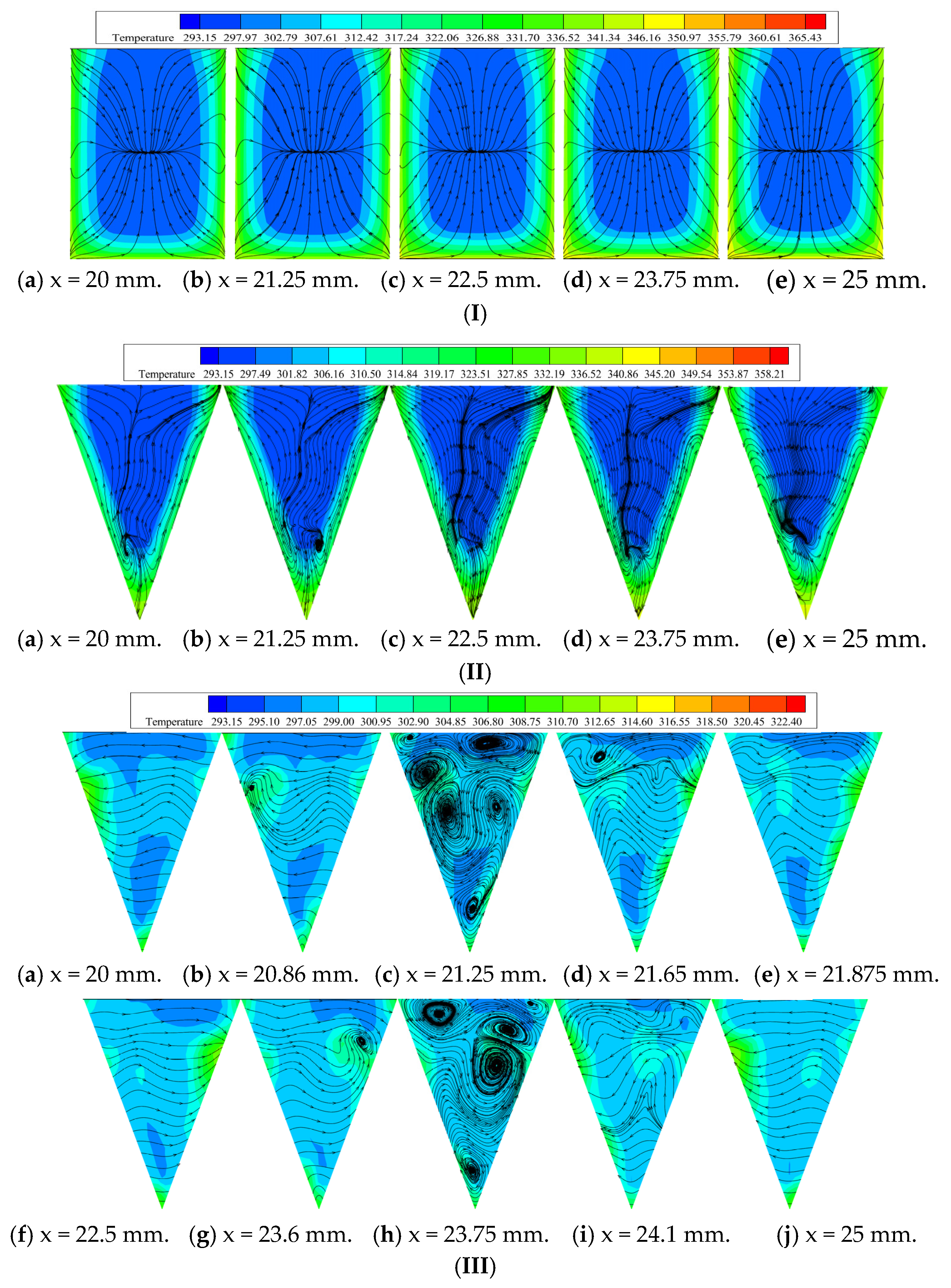
4.2.1. Comparison of Development of Dean Vortexes
4.2.2. Comparison of Heat Transfer Property
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeed, M.; Kim, M.H. Heat transfer enhancement using nanofluids (Al2O3-H2O) in mini-channel heatsinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 120, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ding, S.; Cui, B.; Shentu, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Finite Element Analysis of Heat Transfer and the Dean Vortexes of Rectangular Wavy Microchannel. Heat Transf. Res. 2024, 55, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islami, B.; Dastvareh, S.; Gharraei, R. An investigation on the hydrodynamic and heat transfer of nanofluid flow, with non-Newtonian base fluid, in micromixers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 78, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhammati, S.; Hossainpour, S. Improving the hydrothermal characteristics of wavy microchannel heat sink by modification of wave length and wave wave amplitude. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 130, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.E.; Ahmed, M.I. Optimal thermal design of triangular, trapezoidal and rectangular-shaped grooved microchannel heat sinks. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 66, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Kim, K.Y. Evaluation of Various Channel Shapes of a Microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Air-Cond. Refrig. 2016, 24, 1650018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, Z.Q. Numerical Study of Condensation Heat Transfer in Curved Triangle Microchannels. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, Z. Numerical Study of Condensation Heat Transfer in Curved Square and Triangle Microchannels. Heat Transf. Eng. 2019, 41, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, J.; Yu, X.; Jia, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Miao, J.; Li, C. Surface treatment of an applied novel all-diamond microchannel heat sink for heat transfer property enhancement. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 177, 13594311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shi, M.; Wu, J. Three-dimensional numerical simulation of heat and fluid flow in noncircular microchannel heat sinks. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 36, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J. Influence of geometric parameters on flow and heat transfer property of micro-channel heat sinks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monavari, A.; Jamaati, J.; Bahiraei, M. Thermohydraulic performance of a nanofluid in a microchannel heat sink: Use of different microchannels for change in process severity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 125, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonov, R.; Sorvari, J. Numerical study on the influence of section orientation on fluid flow and heat transfer in a periodic serpentine triangular microchannel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 125, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Duan, Z.; Ning, X.; Su, L. Numerical investigation on heat transfer behavior of thermally developing flow inside rectangular-shaped microchannels. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 24, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, W.; Fang, K.; Wong, C.N. Heat transfer property of a fractal silicon microchannel heat sink subjected to pulsation flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 81, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, M.; Al-Abdeli, Y.M.; Khiadani, M. Nozzle exit conditions and the heat transfer in non-swirling and weakly swirling turbulent impinging jets. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 56, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.K.; London, A.L. Laminar Flow Forced Convection in Ducts; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1978; pp. 196–246. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.L.; Mudawar, I. Analysis of three-dimensional heat transfer in microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 3973–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Huang, K. Numerical analysis of overall performance of heat sink in sinusoidal bottom microchannel. Chem. Eng. 2020, 48, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
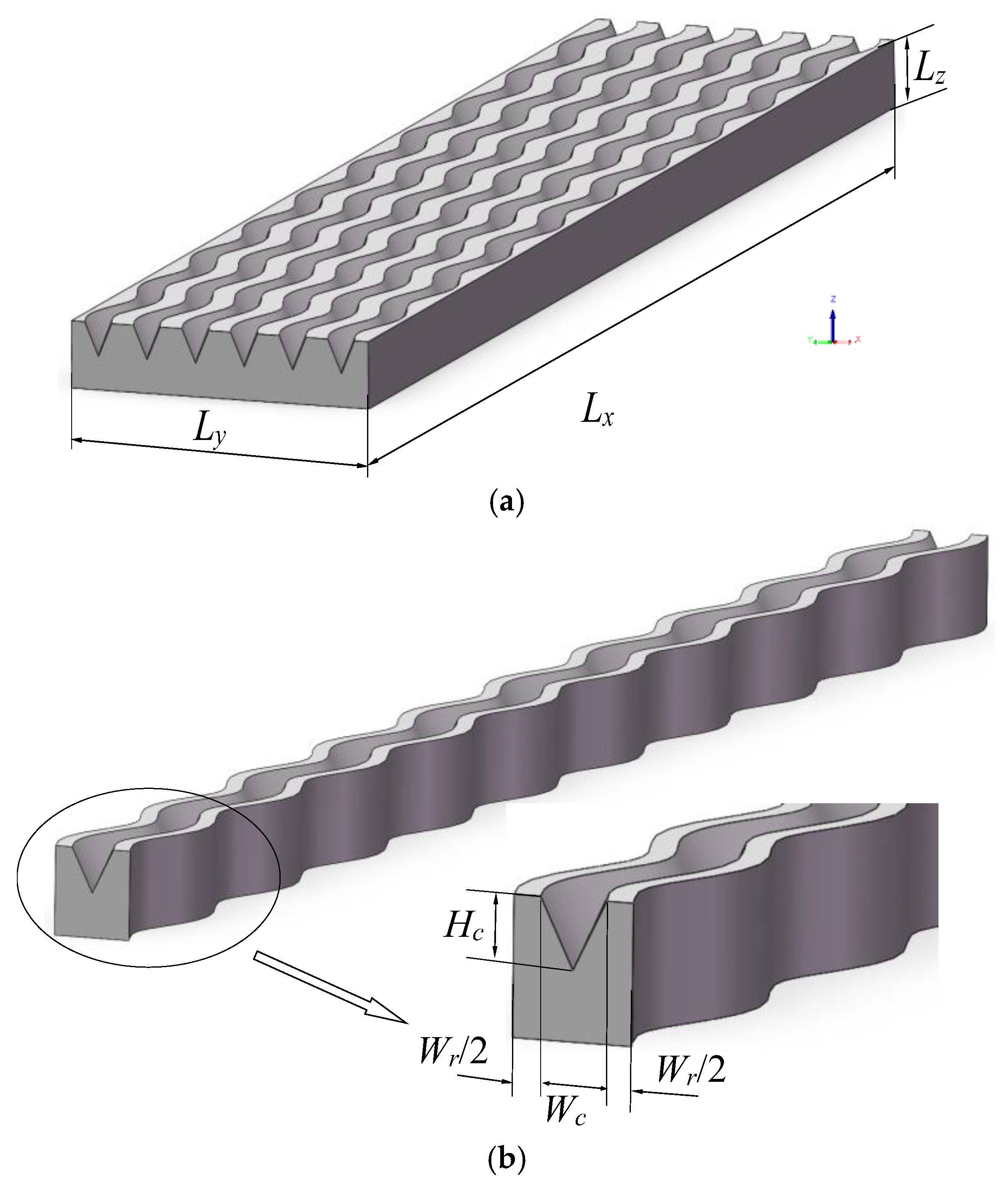




| Lx (mm) | Ly (mm) | Lz (mm) | Wr (mm) | Wc (mm) | Hc (mm) | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 11 | 2 | 0.445 | 1 | 1 | 4/5/6/8 |
| Material | Density ρ (kg·m−3) | Pressure Specific Heat Capacity cp (J·kg−1·K−1) | Thermal Conductivity k (W·m−1·k−1) | Dynamic Viscosity μ (kg·m−1·s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling liquid | water | 998.2 | 4182 | 0.6 | 0.001003 |
| Solid substrate | silicon | 2328.3 | 703 | 148 | - |
| Type | GRID | Mesh Size | Nuave | Relative Error | fave | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0.1–λ5 mm | Ultrafine | 0.03 mm | 13.02 | 0 | 0.025052 | 0 |
| Fine | 0.04 mm | 12.97 | 0.37% | 0.025017 | 0.17% | |
| Medium | 0.06 mm | 12.75 | 2.12% | 0.024721 | 1.34% | |
| Coarse | 0.08 mm | 12.54 | 3.86% | 0.024427 | 2.56% | |
| A0.3–λ5 mm | Ultrafine | 0.03 mm | 21.59 | 0 | 0.048238 | 0 |
| Fine | 0.04 mm | 21.48 | 0.47% | 0.048137 | 0.21% | |
| Medium | 0.06 mm | 21.07 | 2.47% | 0.047446 | 1.67% | |
| Coarse | 0.08 mm | 20.76 | 4.02% | 0.046820 | 3.22% | |
| A0.3–λ10 mm | Ultrafine | 0.03 mm | 15.21 | 0 | 0.028205 | 0 |
| Fine | 0.04 mm | 15.15 | 0.41% | 0.028143 | 0.22% | |
| Medium | 0.06 mm | 14.80 | 2.75% | 0.027778 | 1.54% | |
| Coarse | 0.08 mm | 14.63 | 3.98% | 0.027338 | 3.17% |
| RSM | VSM | VWM | Increase or Decrease in VWM Compared to VSM and RSM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSM | RSM | ||||
| Heat transfer area (m2) | 1.04 × 10−3 | 8.944 × 10−4 | 9.144 × 10−4 | 2.23% | −12.08% |
| Temperature rise (K) | 67.96 | 59.32 | 29.39 | −29.93 K | −38.03 K |
| R (K/W) | 0.247 | 0.216 | 0.107 | −50.46% | −56.68% |
| have (W·m−2·K−1) | 8593.65 | 8560.70 | 21,951.60 | 156.42% | 155.43% |
| ΔP (Pa) | 4987.85 | 7522.49 | 15,264.04 | 102.91% | 206.05% |
| PEC | 1.027 | 1.0 | 2.37 | 137% | 130.78% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mi, S.; Chen, M.; Li, T.; Yang, L. CFD Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer of V-Shaped Wavy Microchannels. Processes 2025, 13, 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092865
Mi S, Chen M, Li T, Yang L. CFD Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer of V-Shaped Wavy Microchannels. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092865
Chicago/Turabian StyleMi, Shuzhen, Mengting Chen, Tianyu Li, and Lin Yang. 2025. "CFD Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer of V-Shaped Wavy Microchannels" Processes 13, no. 9: 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092865
APA StyleMi, S., Chen, M., Li, T., & Yang, L. (2025). CFD Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer of V-Shaped Wavy Microchannels. Processes, 13(9), 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092865