Influence of Ultrasound Frequency as a Preliminary Treatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Fried Native Potato Chips
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Evaluate, for the first time, the effect of two fixed ultrasound frequencies (28 and 40 kHz) on the quality of native potato chips from the Sempal and Agustina varieties.
- Analyze changes in physicochemical, structural, and sensory properties induced by the pretreatment before frying.
- Discuss the balance between technological improvements and potential losses of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity at higher frequencies.
- Propose ultrasound as a sustainable alternative for the valorization of Andean native potatoes in the snack industry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Obtaining Fried Chips from Native Potatoes
2.3. Preparation of Methanolic Extract
2.4. Total Phenolic Compounds
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity by DPPH
2.6. Reducing Sugars
2.7. Water Activity (Aw)
2.8. Color Analysis
2.9. Proximate Composition
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis (FTIR)
2.11. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.12. Sensory Evaluation
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Total Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Capacity by DPPH, Reducing Sugars, and Water Activity
3.2. Color Analysis
3.3. Proximate Composition
3.4. FTIR Analysis
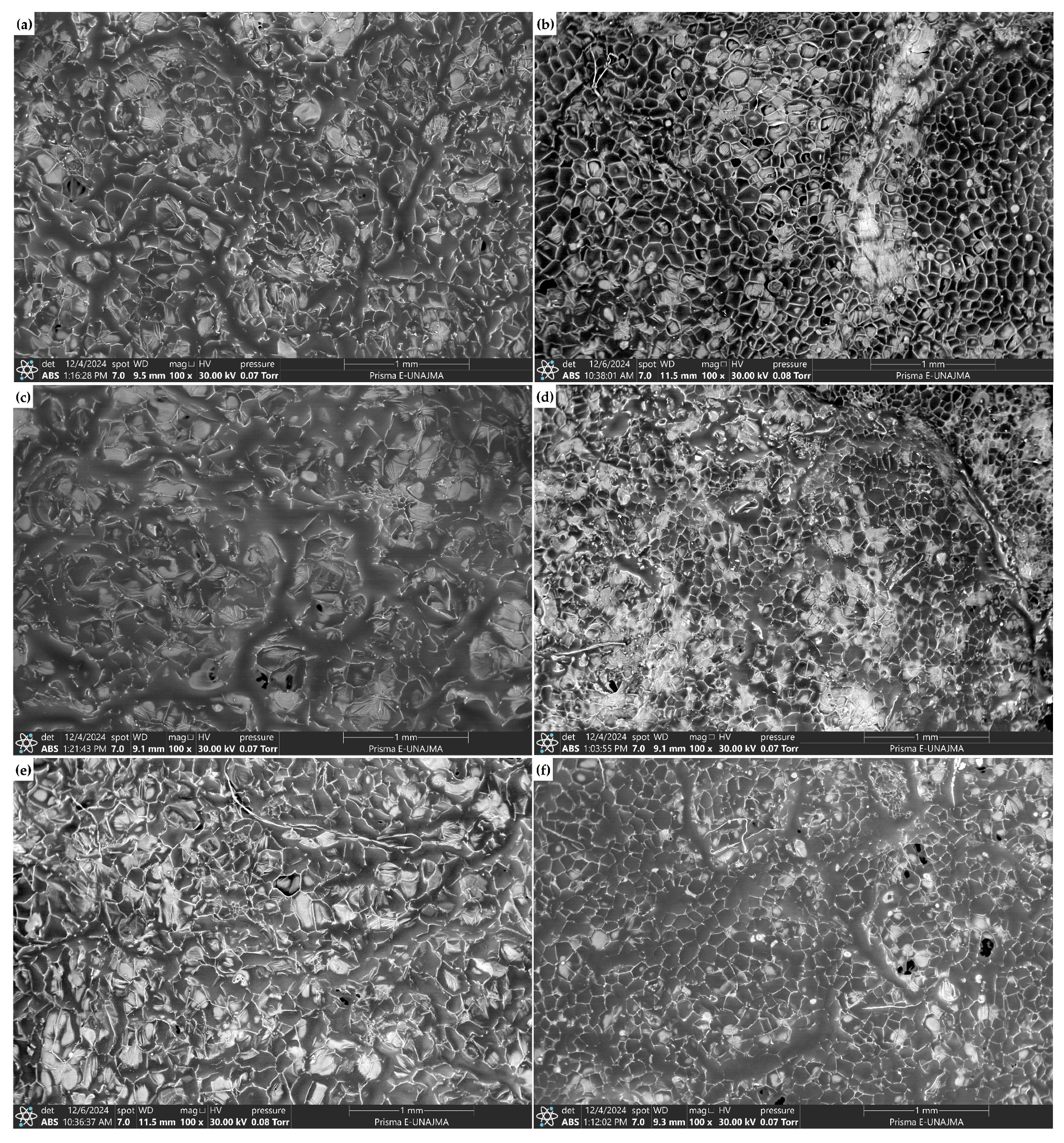
3.5. SEM Analysis
3.6. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhutto, R.A.; Bhutto, N.u.a.H.B.; Khanal, S.; Wang, M.; Iqbal, S.; Fan, Y.; Yi, J. Potato protein as an emerging high-quality: Source, extraction, purification, properties (functional, nutritional, physicochemical, and processing), applications, and challenges using potato protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereje, B.; Chibuzo, N. Nutritional composition and biochemical properties of Solanum tuberosum. In Solanum Tuberosum—A Promising Crop for Starvation Problem; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadu, T.; Abdullahi, A.; Ahmad, K.; Ahmadu, T.; Abdullahi, A.; Ahmad, K. The role of crop protection in sustainable potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) production to alleviate global starvation problem: An overview. In Solanum Tuberosum—A Promising Crop for Starvation Problem; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 19–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, D.; Bates, R.; Brennan, M.; Gill, T. Peru potato potential: Biodiversity conservation and value chain development. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2018, 33, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligarda-Samanez, C.A.; Palomino-Rincón, H.; Choque-Quispe, D.; Moscoso-Moscoso, E.; Arévalo-Quijano, J.C.; Huamán-Carrión, M.L.; Quispe-Quezada, U.R.; Muñoz-Saenz, J.C.; Gutiérrez-Gómez, E.; Cabel-Moscoso, D.J.; et al. Bioactive Compounds and Sensory Quality in Chips of Native Potato Clones (Solanum tuberosum spp. andigena) Grown in the High Andean Region of PERU. Foods 2023, 12, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, A.; Kołodziejczyk, M.; Michalska-Ciechanowska, A.; Brzezowska, J.; Wicha-Komsta, K.; Turski, W. The Effect of Thermal Treatment on Selected Properties and Content of Biologically Active Compounds in Potato Crisps. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomide, A.I.; Monteiro, R.L.; Carciofi, B.A.; Laurindo, J.B. The Effect of Pretreatments on the Physical Properties and Starch Structure of Potato Chips Dried by Microwaves under Vacuum. Foods 2022, 11, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomide, A.I.; Monteiro, R.L.; Laurindo, J.B. Impact of the power density on the physical properties, starch structure, and acceptability of oil-free potato chips dehydrated by microwave vacuum drying. LWT 2022, 155, 112917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Torres, S.M.; Chire-Fajardo, G.C.; Repo-Carrasco, R.; Ureña-Peralta, M.O. Efecto de la fritura sobre los componentes bioactivos de la papa nativa (Solanum tuberosum sp.) Puka Ambrosio. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2022, 49, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, P.; Peña, F.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Núñez-Santiago, C.; Yee-Madeira, H.; Velezmoro, C. Physicochemical, functional and morphological characterization of starches isolated from three native potatoes of the Andean region. Food Chem. X 2019, 2, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, C.A.; Dudenhoefer, D.; Polar, V.; Scurrah, M.; Ccanto, R.C.; Heider, B. Gender Roles and Native Potato Diversity Management in Highland Communities of Peru. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, A.; Bąkowska-Barczak, A.; Hamouz, K.; Kułakowska, K.; Lisińska, G. The effect of frying on anthocyanin stability and antioxidant activity of crisps from red- and purple-fleshed potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 32, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, L. Effects of preliminary treatment by ultrasonic and convective air drying on the properties and oil absorption of potato chips. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 74, 105548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska-Turak, E.; Sitkiewicz, I.; Janowicz, M. Influence of Ultrasound on the Rheological Properties, Color, Carotenoid Content, and Other Physical Characteristics of Carrot Puree. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Fan, L.; Sun, Y. Effects of ultrasound treatment on the starch properties and oil absorption of potato chips. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 70, 105347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Bhandari, B. Effects of ultrasound pretreatments on the quality of fried sweet potato (Ipomea batatas) chips during microwave-assisted vacuum frying. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, F.; Incedayi, B.; Turkmen Erol, N.; Akpinar, P.; Copur, O.U. Impact of Ohmic Heating and Ultrasound Pretreatments on Oil Absorption and Other Quality Parameters of Fried Potato. Potato Res. 2024, 68, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lv, M.; Du, H.; Deng, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Li, B. Effect of Preliminary Treatment by Pulsed Electric Fields and Blanching on the Quality of Fried Sweet Potato Chips. Foods 2023, 12, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onacik-Gür, S.; Ptasznik, S.; Zbikowska, A.; Marciniak-Lukasiak, K. Acrylamide Contamination, Shelf-Life and Sensory Properties of Puffed Potato Starch Chips Deep-Fried in Rapeseed Oil-Based Oleogels. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Wang, T.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T. Comprehensive Analysis of Physicochemical Properties and Sensory Attributes of Original-Cut Potato Chips in the Chinese Market. Foods 2024, 13, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 299, pp. 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, D.B.; Bocourt, E.C.; Maqueira, Y.D. Determinación de azúcares reductores totales en jugos mezclados de caña de azúcar utilizando el método del ácido 3, 5 dinitrosalicílico. ICIDCA. Sobre Los Deriv. La Caña Azúcar 2006, 40, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Pacheco, B.S.; Ligarda-Samanez, C.A.; Choque-Quispe, D.; Choque-Quispe, Y.; Solano-Reynoso, A.M.; Choque-Quispe, K.; Palomino-Rincón, H.; Taipe-Pardo, F.; Peralta-Guevara, D.E.; Moscoso-Moscoso, E.; et al. Study of the Physical–Chemical, Thermal, Structural, and Rheological Properties of Four High Andean Varieties of Germinated Chenopodium quinoa. Polymers 2025, 17, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligarda-Samanez, C.A.; Villano-Limache, E.; Pichihua-Oscco, W.; Choque-Quispe, D.; Sucari-León, R.; Calderón Huamaní, D.F.; Cruz, G.D.; Luciano-Alipio, R.; Calsina Ponce, W.C.; Aroquipa-Durán, Y.; et al. Physicochemical and Sensory Evaluation of Gummy Candies Fortified with Microcapsules of Guinea Pig (Cavia porcellus) Blood Erythrocytes and Tumbo (Passiflora tarminiana) Juice. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. Volume I, Agricultural Chemicals, Contaminants. Drugs 2000, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ligarda-Samanez, C.A.; Choque-Quispe, D.; Palomino-Rincón, H.; Moscoso-Moscoso, E.; Guzmán Gutiérrez, R.J.; Banda Mozo, I. Microencapsulation of Propolis by Complex Coacervation with Chia Mucilage and Gelatin: Antioxidant Stability and Functional Potential. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; Zill e, H.; Khan, M.K. Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golmohamadi, A.; Möller, G.; Powers, J.; Nindo, C. Effect of ultrasound frequency on antioxidant activity, total phenolic and anthocyanin content of red raspberry puree. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2013, 20, 1316–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, H.S.; Silva, E.K.; Pereira, G.A.; Angolini, C.F.F.; Eberlin, M.N.; Meireles, M.A.A.; Pastore, G.M. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound process parameters on the phenolic compounds recovery from araticum peel. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 50, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lučić, M.; Potkonjak, N.; Sredović Ignjatović, I.; Lević, S.; Dajić-Stevanović, Z.; Kolašinac, S.; Belović, M.; Torbica, A.; Zlatanović, I.; Pavlović, V.; et al. Influence of Ultrasonic and Chemical Pretreatments on Quality Attributes of Dried Pepper (Capsicum annuum). Foods 2023, 12, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, S.; Jafari, S.M. The Influence of Ohmic Heating on Degradation of Food Bioactive Ingredients. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Donsì, F.; Yildiz, S.; Candoğan, K.; Pokhrel, P.R.; Guadarrama-Lezama, A.Y. Nonthermal Processing Technologies for Stabilization and Enhancement of Bioactive Compounds in Foods. Food Eng. Rev. 2022, 14, 63–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajner-Czopek, A.; Kita, A.; Rytel, E. Characteristics of French Fries and Potato Chips in Aspect of Acrylamide Content—Methods of Reducing the Toxic Compound Content in Ready Potato Snacks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, V.; Navarro, C.; Ronco, A.M. Acrilamida en los alimentos: Valores de referencia, recomendaciones y acciones de mitigación. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2021, 48, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, N.; Mor, R.S.; Kumar, K.; Sharanagat, V.S. Advances in application of ultrasound in food processing: A review. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2021, 70, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Sun, D.-W. Enhancement of Food Processes by Ultrasound: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 570–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduh, S.B.; Leong, S.Y.; Zhao, C.; Baldwin, S.; Burritt, D.J.; Agyei, D.; Oey, I. Kinetics of Colour Development during Frying of Potato Pre-Treated with Pulsed Electric Fields and Blanching: Effect of Cultivar. Foods 2021, 10, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, D.; Rohm, H.; Struck, S. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Protein from Pumpkin Seed Press Cake: Impact on Protein Yield and Techno-Functionality. Foods 2022, 11, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Lamsal, B.P. Ultrasound-assisted extraction and modification of plant-based proteins: Impact on physicochemical, functional, and nutritional properties. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2021, 20, 1457–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes-Rohling, A.; Ciudad-Hidalgo, S.; Mir-Bel, J.; Raso, J.; Cebrián, G.; Álvarez, I. Ultrasound as a pretreatment to reduce acrylamide formation in fried potatoes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 49, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreschi, F.; Ferrera, A.; Bunger, A.; Alvarez, F.; Huamán-Castilla, N.L.; Mariotti-Celis, M.S. Ultrasonic-assisted leaching of glucose and fructose as an alternative mitigation technology of acrylamide and 5- hydroxymethylfurfural in potato chips. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 73, 102752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, A. Factors affecting potato chips texture during storage. Acta Agrophysica 2002, 77, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, A.M.M.N.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Samad, A.; Joo, S.-T. Meat Quality Traits Using Gelatin–Green Tea Extract Hybrid Electrospun Nanofiber Active Packaging. Foods 2025, 14, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Frequency | Sempal | Agustina | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Phenolic Compounds (mg AGE/g) | |||||||||
| ± | s | * | ± | s | * | ||||
| Control | 5.47 | ± | 0.01 | a | 2.01 | ± | 0.07 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 2.22 | ± | 0.01 | b | 1.78 | ± | 0.02 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 2.19 | ± | 0.02 | c | 1.53 | ± | 0.02 | c | |
| Antioxidant Capacity by DPPH (µmol ET/g) | |||||||||
| Control | 33.70 | ± | 0.08 | a | 19.49 | ± | 1.61 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 30.90 | ± | 0.06 | b | 14.09 | ± | 0.88 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 24.81 | ± | 0.09 | c | 9.78 | ± | 0.63 | c | |
| Reducing Sugars (mg/100 g) | |||||||||
| Control | 33.92 | ± | 0.05 | a | 83.86 | ± | 0.18 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 30.79 | ± | 1.16 | b | 60.28 | ± | 1.11 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 25.68 | ± | 1.71 | c | 59.28 | ± | 0.47 | b | |
| Water activity (Aw) | |||||||||
| Control | 0.62 | ± | 0.01 | a | 0.37 | ± | 0.01 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 0.55 | ± | 0.02 | b | 0.33 | ± | 0.02 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 0.36 | ± | 0.02 | c | 0.32 | ± | 0.01 | b | |
| Frequency | Sempal | Agustina | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lightness L* | |||||||||
| ± | s | * | ± | s | * | ||||
| Control | 30.51 | ± | 0.51 | a | 41.15 | ± | 0.29 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 31.76 | ± | 0.55 | b | 42.49 | ± | 0.34 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 32.31 | ± | 0.37 | b | 44.04 | ± | 0.41 | c | |
| Chroma a* | |||||||||
| Control | 1.66 | ± | 0.05 | a | 8.84 | ± | 0.23 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 1.73 | ± | 0.05 | a | 9.12 | ± | 0.08 | a | |
| 40 kHz | 1.82 | ± | 0.03 | b | 12.33 | ± | 0.15 | b | |
| Chroma b* | |||||||||
| Control | −3.36 | ± | 0.10 | a | 11.41 | ± | 0.11 | a | |
| 28 kHz | −3.00 | ± | 0.06 | b | 10.05 | ± | 0.05 | b | |
| 40 kHz | −2.78 | ± | 0.09 | c | 8.70 | ± | 0.17 | c | |
| Frequency | Sempal | Agustina | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat (%) | |||||||||
| ± | s | * | ± | s | * | ||||
| Control | 33.49 | ± | 0.15 | a | 22.84 | ± | 0.12 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 33.47 | ± | 0.09 | a | 22.50 | ± | 0.02 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 33.14 | ± | 0.04 | b | 22.07 | ± | 0.10 | c | |
| Protein (%) | |||||||||
| Control | 5.50 | ± | 0.10 | a | 5.52 | ± | 0.13 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 5.93 | ± | 0.13 | b | 6.36 | ± | 0.14 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 5.99 | ± | 0.12 | b | 6.86 | ± | 0.11 | c | |
| Carbohydrates (%) | |||||||||
| Control | 55.93 | ± | 0.04 | a | 66.72 | ± | 0.23 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 55.72 | ± | 0.10 | b | 66.24 | ± | 0.11 | b | |
| 40 kHz | 55.69 | ± | 0.03 | b | 66.17 | ± | 0.15 | b | |
| Moisture (%) | |||||||||
| Control | 2.54 | ± | 0.03 | a | 2.98 | ± | 0.04 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 2.53 | ± | 0.05 | a | 2.91 | ± | 0.02 | a | |
| 40 kHz | 2.52 | ± | 0.04 | a | 2.90 | ± | 0.15 | a | |
| Ash (%) | |||||||||
| Control | 2.53 | ± | 0.15 | ab | 1.94 | ± | 0.11 | a | |
| 28 kHz | 2.36 | ± | 0.11 | a | 1.99 | ± | 0.13 | a | |
| 40 kHz | 2.66 | ± | 0.14 | b | 2.00 | ± | 0.12 | a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palomino-Rincón, H.; Ramos-Pacheco, B.S.; Buleje Campos, D.; Guzmán Gutiérrez, R.J.; Yauris-Navez, E.M.; Alarcón-Quispe, E. Influence of Ultrasound Frequency as a Preliminary Treatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Fried Native Potato Chips. Processes 2025, 13, 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082668
Palomino-Rincón H, Ramos-Pacheco BS, Buleje Campos D, Guzmán Gutiérrez RJ, Yauris-Navez EM, Alarcón-Quispe E. Influence of Ultrasound Frequency as a Preliminary Treatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Fried Native Potato Chips. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082668
Chicago/Turabian StylePalomino-Rincón, Henry, Betsy S. Ramos-Pacheco, Dianeth Buleje Campos, Rodrigo J. Guzmán Gutiérrez, Evelin M. Yauris-Navez, and Elizabeth Alarcón-Quispe. 2025. "Influence of Ultrasound Frequency as a Preliminary Treatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Fried Native Potato Chips" Processes 13, no. 8: 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082668
APA StylePalomino-Rincón, H., Ramos-Pacheco, B. S., Buleje Campos, D., Guzmán Gutiérrez, R. J., Yauris-Navez, E. M., & Alarcón-Quispe, E. (2025). Influence of Ultrasound Frequency as a Preliminary Treatment on the Physicochemical, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Fried Native Potato Chips. Processes, 13(8), 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082668










