Phase Evolution History of Deep-Seated Hydrocarbon Fluids in the Western Junggar Basin: Insights from Geochemistry, PVT, and Basin Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting
3. Samples and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. Oil Density
3.2.2. Fluid Composition Testing and Constant Mass Expansion Experiment
3.2.3. GC and GC-MS
3.2.4. Carbon Isotope Analysis
3.2.5. Fluid Inclusion Test
3.2.6. Basin Modeling
3.2.7. PVT Simulation
4. Results
4.1. Physical Properties and Bulk Composition
4.2. Constant Mass Expansion
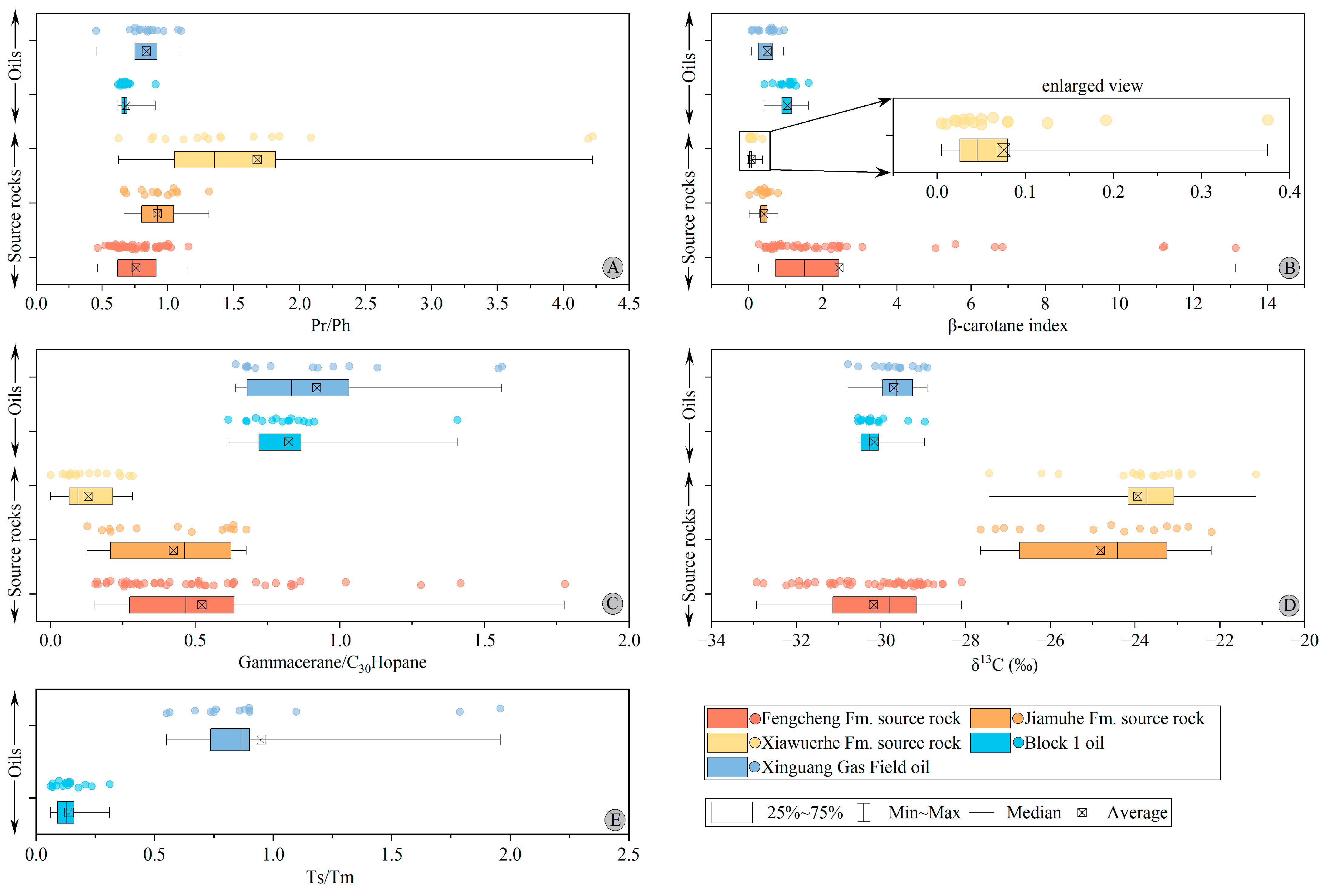
4.3. GC-MS and Carbon Isotopes
4.3.1. Alkanes
4.3.2. Hopanes
4.3.3. Carbon Isotope
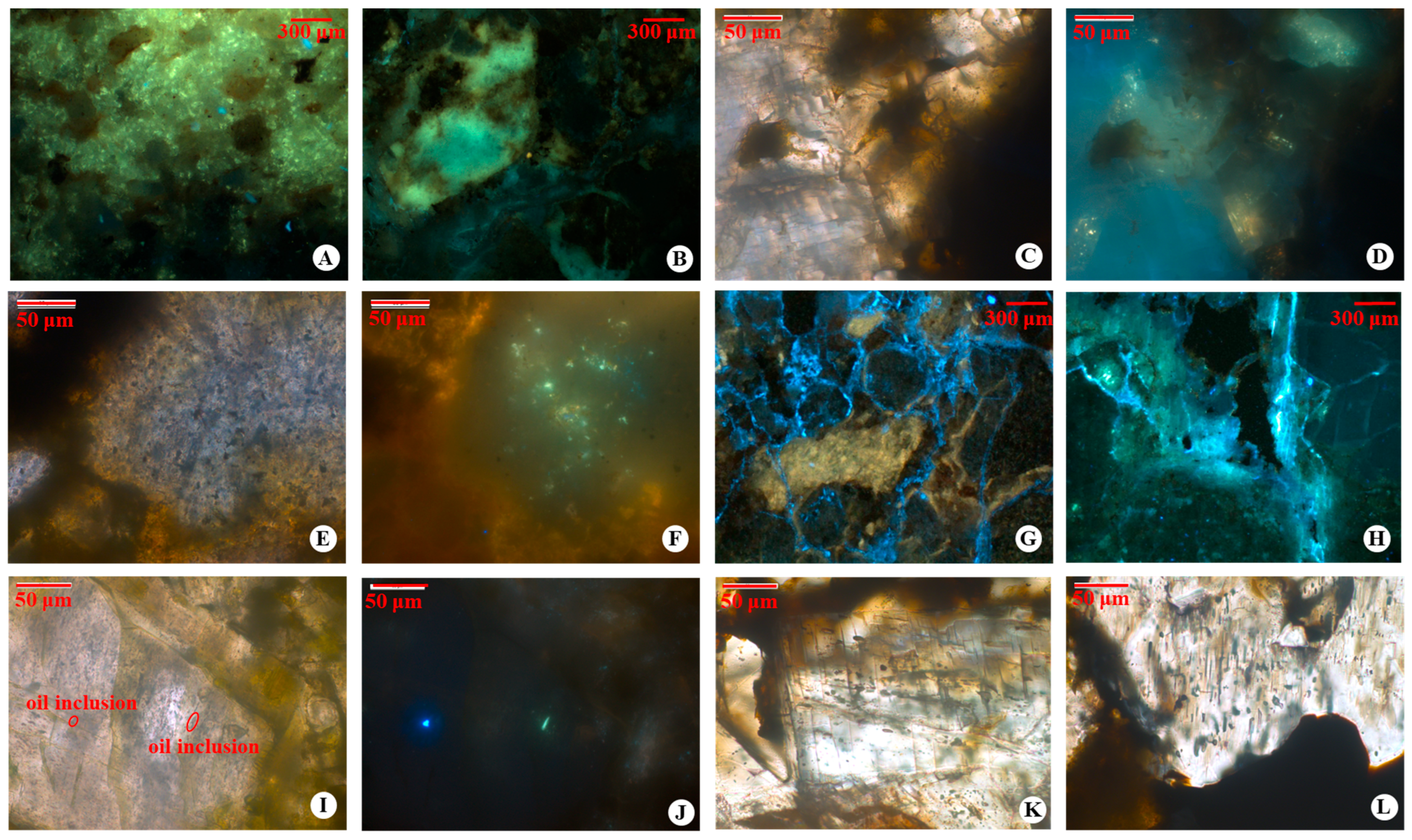
4.4. Fluid Inclusion Analysis
4.4.1. Organic Micropetrological Characteristics
4.4.2. Microthermometry Analysis
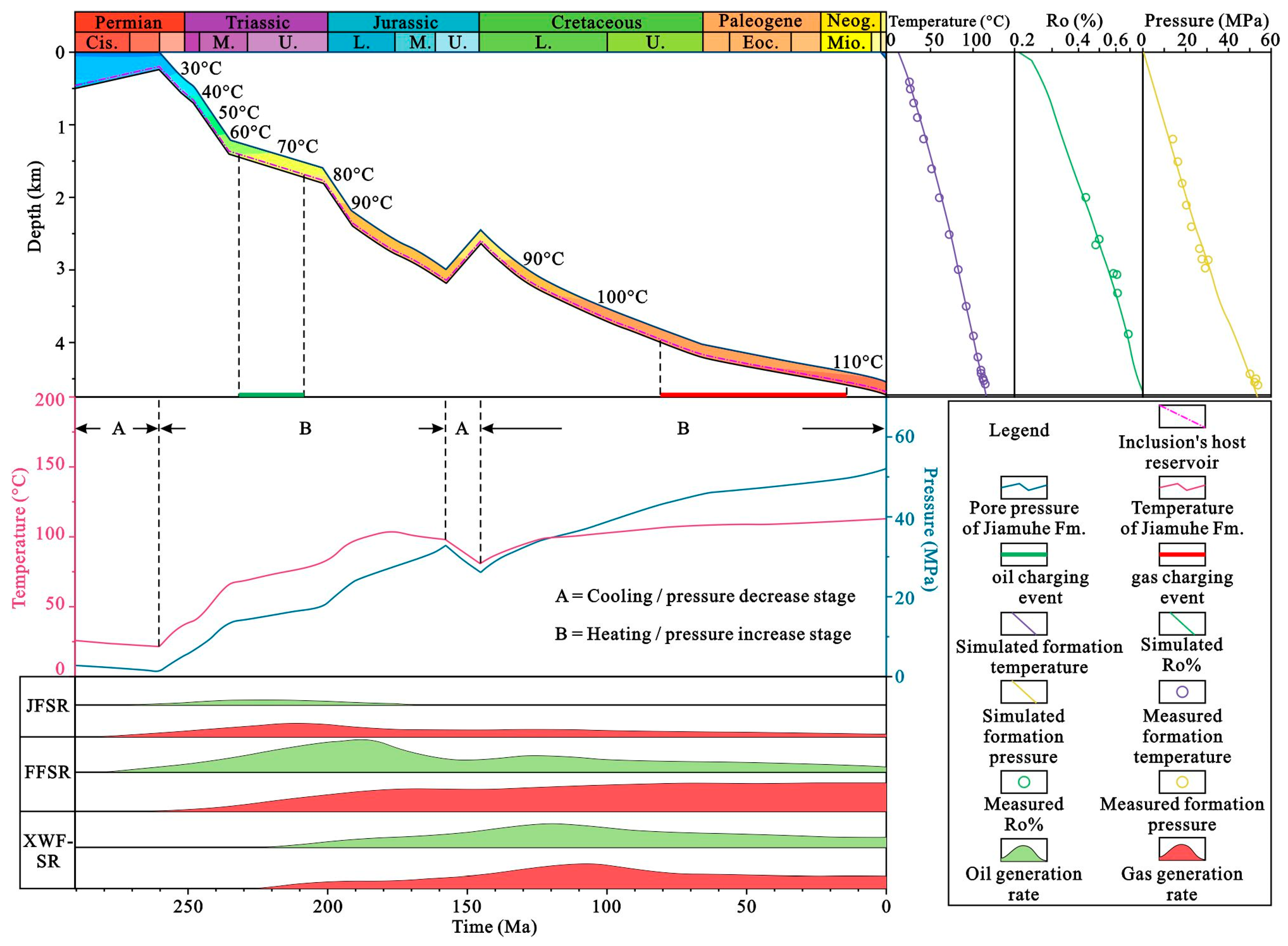
4.5. Burial, Thermal, and Pressure Histories of Reservoir
5. Discussion
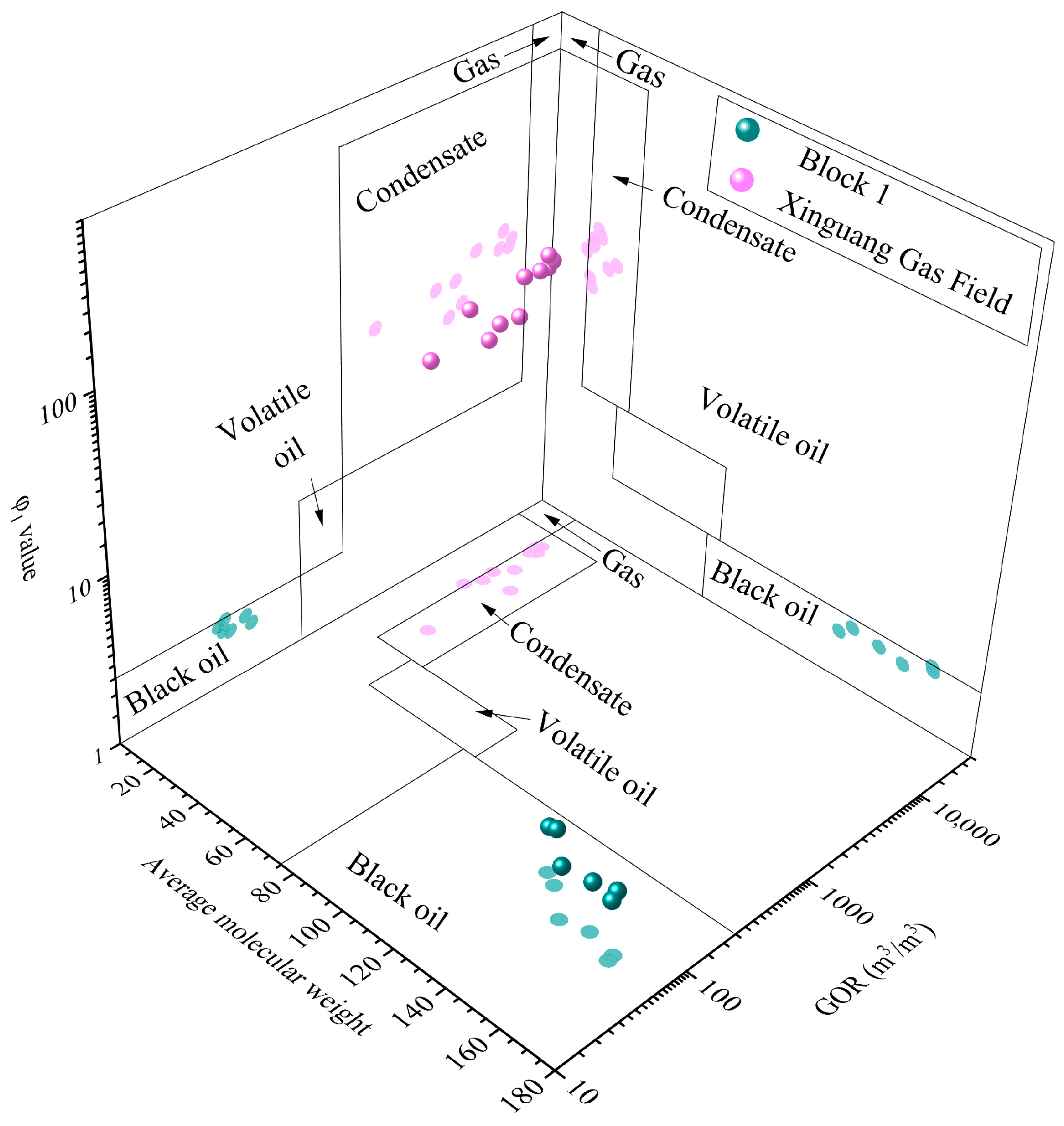
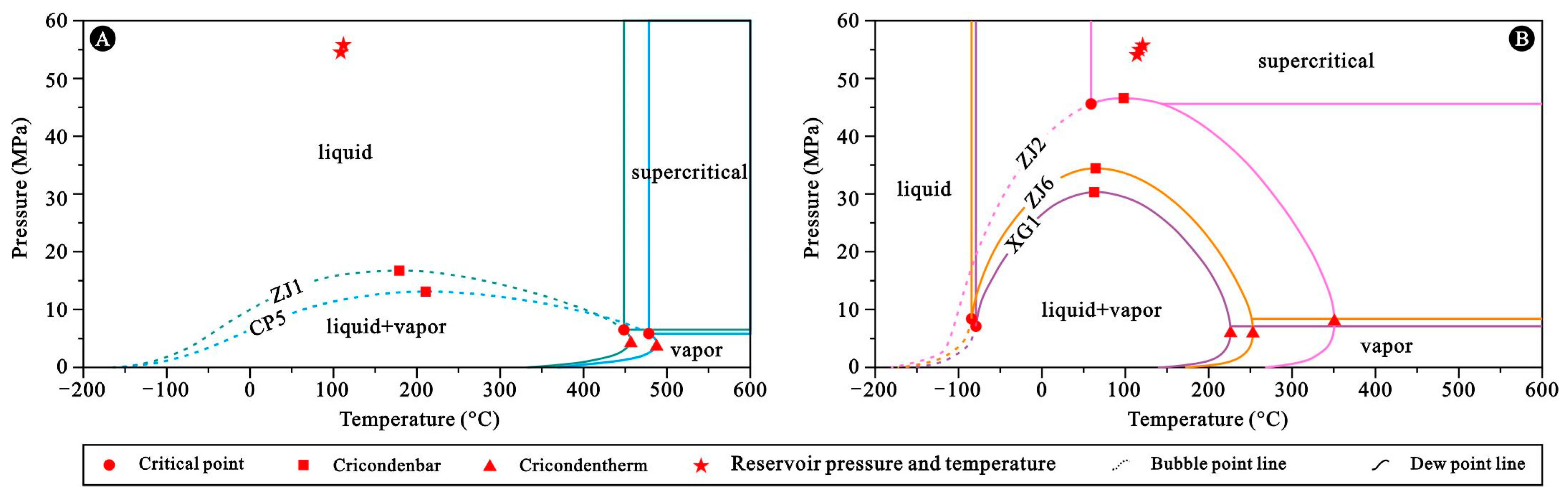
5.1. Phase State of Reservoir Fluid
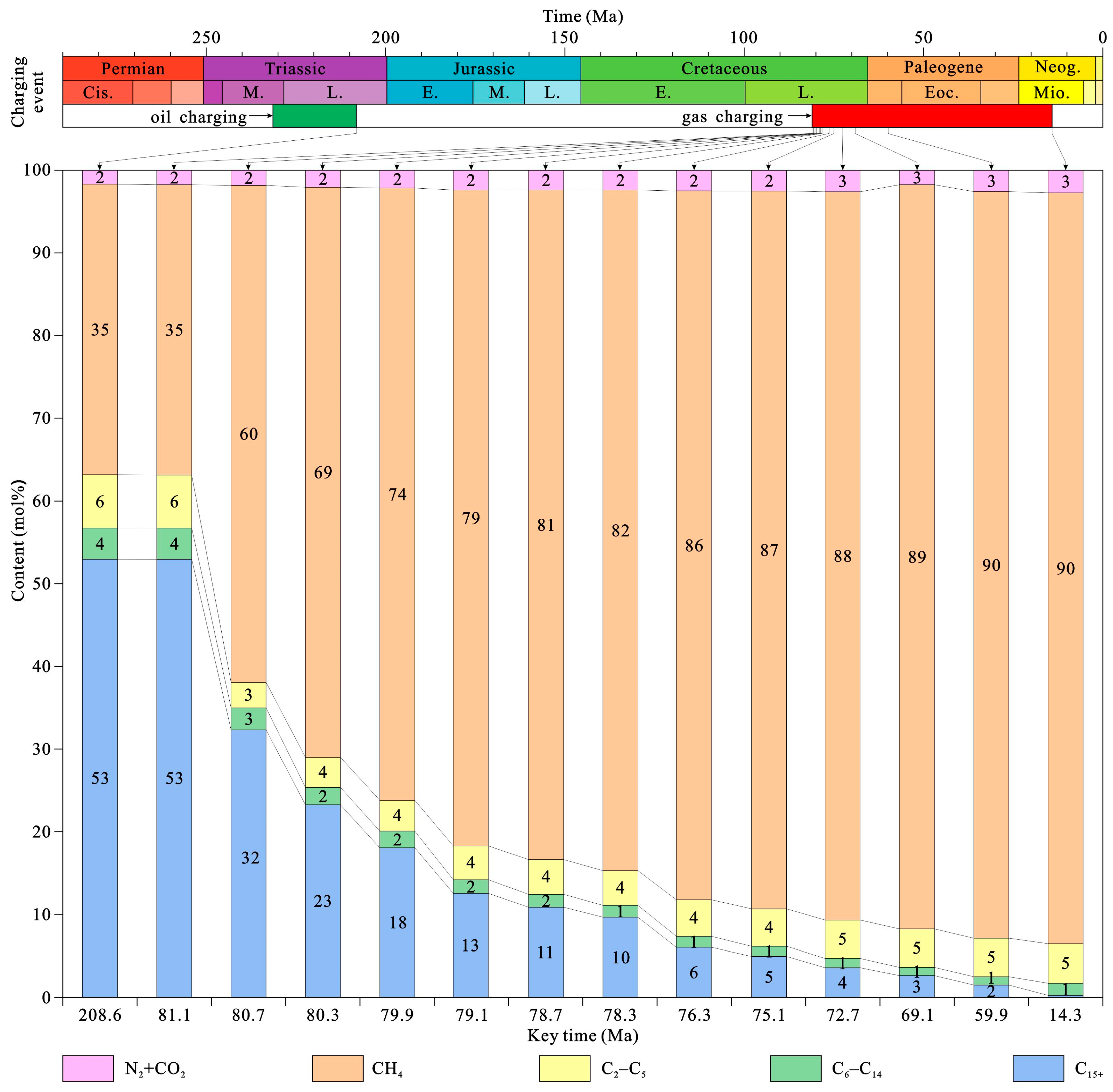
5.2. Charging Period and Time of Hydrocarbon Fluids
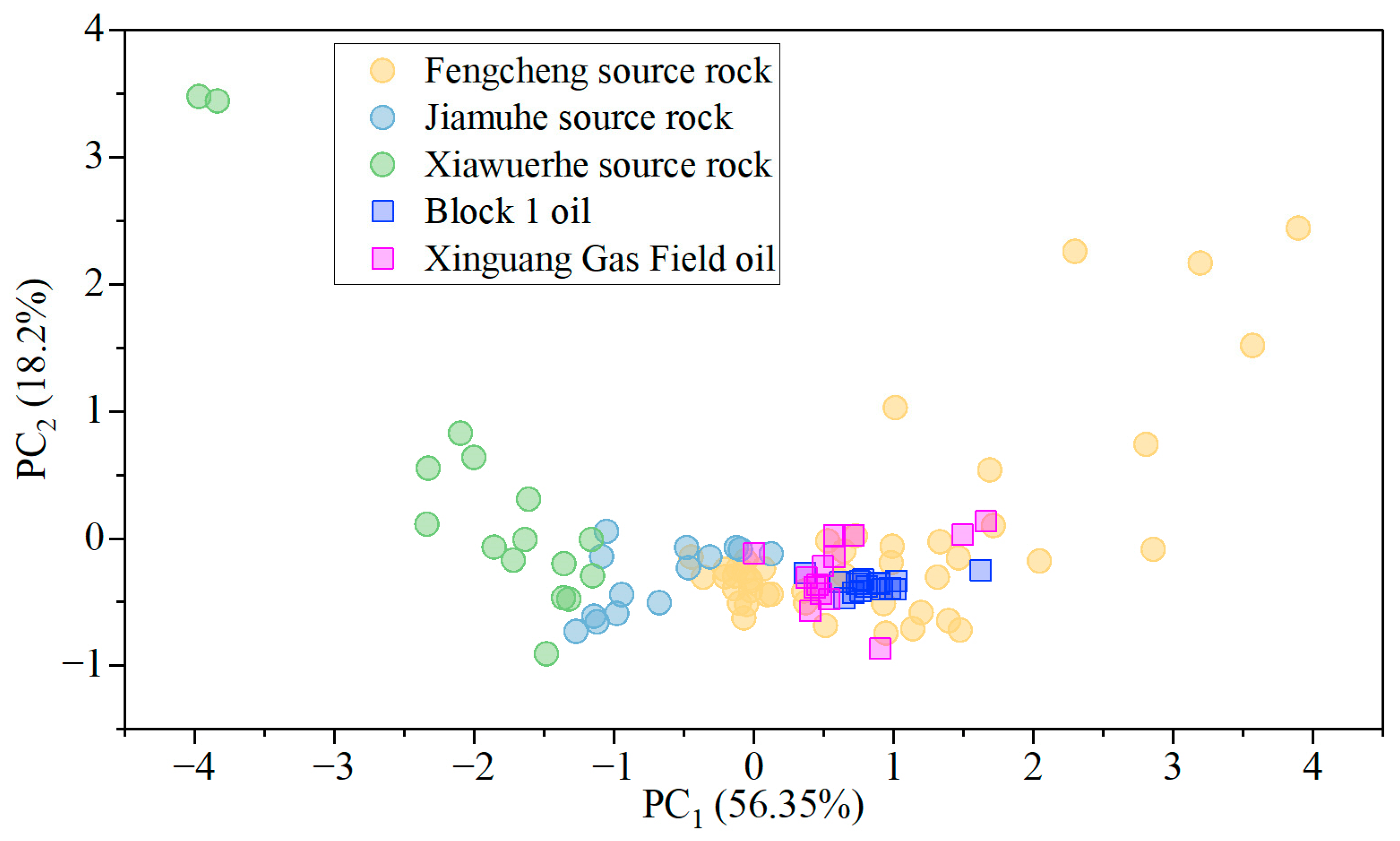
5.3. Oil and Gas Source
5.4. Evolution of Reservoir Hydrocarbon Fluid Composition and Temperature–Pressure Conditions
5.4.1. Composition Evolution of Reservoir Hydrocarbon Fluid
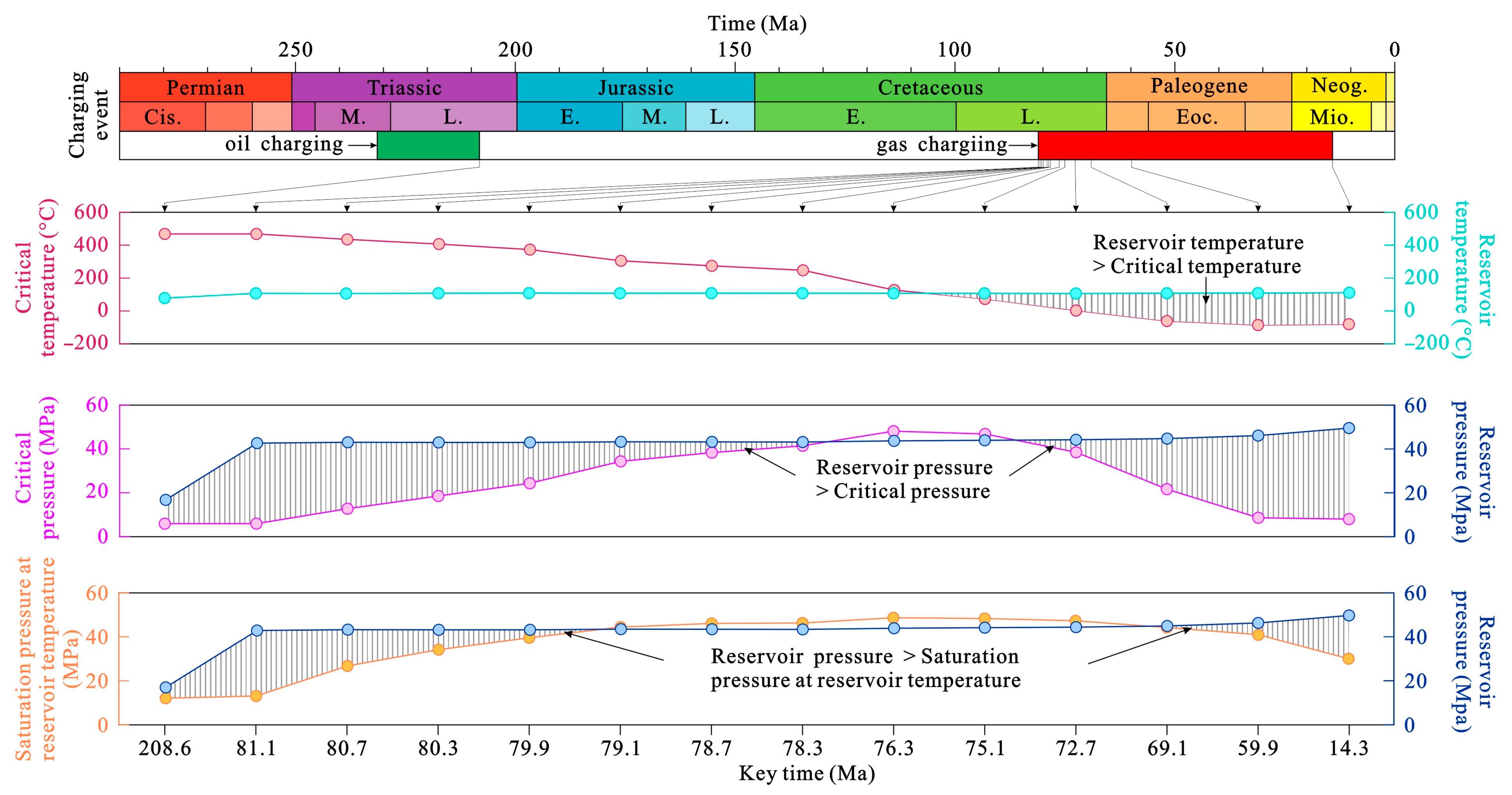
5.4.2. Evolution of Reservoir Temperature, Pressure, and Fluid Property Parameters
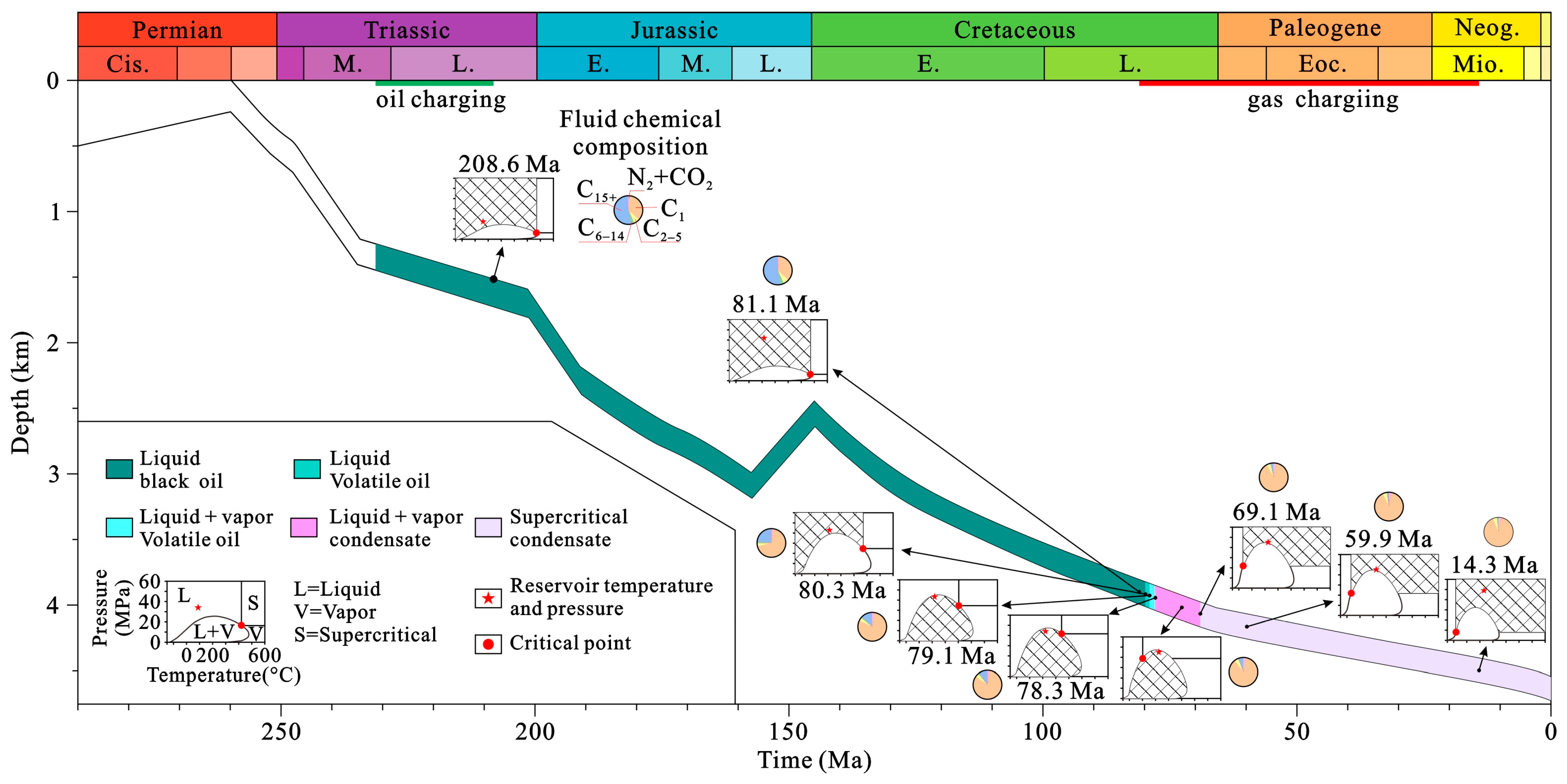
5.5. Evolution Process of Hydrocarbon Fluid Phase Behavior
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations and Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Z.L.; Cui, J.P.; Qi, K.; Yang, G.L.; Chen, Z.J.; Yang, P.; Wang, K. Control effects of temperature and thermal evolution history of deep and ultra-deep layers on hydrocarbon phase state and hydrocarbon generation history. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2020, 7, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatampour, A.; Schaffie, M.; Jafari, S. Hydraulic flow units, depositional facies and pore type of Kangan and Dalan Formations, South Pars Gas Field, Iran. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zeng, J.; Yu, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, D.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Origin, migration, and characterization of petroleum in the Perdido Fold Belt, Gulf of Mexico basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuni, R.A. Petroleum systems and hydrocarbon potential of the Ruvuma Basin, Tanzania. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 223, 211588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Cai, X.Y.; Yun, L.; Li, Z.J.; Li, H.L.; Deng, S.; Zhao, P.R. Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra-deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, F. Predicting petroleum gravity with basin modeling: New kinetic models. AAPG Bull. 2019, 103, 1811–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.G.; Zha, M.; Ding, X.J.; Yin, H.; Bian, B.L.; Liu, H.L.; Jiang, Z.F. Source and accumulation process of Jurassic biodegraded oil in the Eastern Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Graas, G.W.; Elin Gilje, A.; Isom, T.P.; Aase Tau, L. The effects of phase fractionation on the composition of oils, condensates and gases. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losh, S.; Cathles, L.; Meulbroek, P. Gas washing of oil along a regional transect, offshore Louisiana. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z.C.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.H. Origin of deep oil accumulations in carbonate reservoirs within the north Tarim Basin: Insights from molecular and isotopic compositions. Org. Geochem. 2020, 139, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, B.P.; Welte, D.H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence, 2nd ed.; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar, A.Y. Petroleum Reservoir Rock and Fluid Properties, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.S.; Wang, Y.P.; Beagle, J.R.; Liao, L.L.; Shi, S.Y.; Deng, R. Reconstruction of the evolution of deep fluids in light oil reservoirs in the Central Tarim Basin by using PVT simulation and basin modeling. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 107, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjabin, N.; Banik, S.C. An integrated study of phase behavior in natural gas reservoirs through experimental and simulation approach: A case study. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 6631–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhu, G.Y.; Chi, L.X.; Wang, P.J.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.F.; Wu, Z.H. Discovery of the high-yield well GT1 in the deep strata of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin, China: Implications for liquid petroleum potential in deep assemblage. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 191, 107178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.G.; Luo, Z.Y.; Zou, H.L.; Li, Y.P.; Hu, Z.Z.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.; Han, M.M.; Zhao, L.P.; Lin, Z.H. Geochemical characteristics, origin, and mechanism of differential accumulation of natural gas in the carboniferous kelameili gas field in Junggar basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Cao, Y.C.; Ma, Z.J.; Zhen, Y.S. Geochemistry and origins of natural gases in the Zhongguai area of Junggar Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 119, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L. Tight sandstone gas genetic type and gas source in the Jiamuhe Formation of Zhongguai Area, Junggar Basin. Xinjiang OilGas 2017, 13, 6–10, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, E.; Jin, J.; Cao, J.; Ma, W.Y.; Mi, J.L.; Ren, J.L. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of natural gas in Jiamuhe Formation in Xinguang area, Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Yang, H.; Fei, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Bao, H. Comprehensive analysis of tight sandstone gas resource potential in the favorable area of Jiamuhe Formation in Xinguang area, Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2018, 29, 370–381. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Qiu, L.; Sun, B.; Tang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhu, S. Characteristics of Fluid Inclusion and Charging Events of NaturalGas in Permian Jiamuhe Formation of Zhongguai Area, Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2013, 24, 931–939. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Li, S.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J. Hydrocarbon Phase State Evolution and Accumulation Process of Ultradeep Permian Reservoirs in Shawan Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 12762–12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.F.; Chen, X.F.; Kuang, J.; Zhou, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, D.G. Development and Genetic Mechanism of Chepaizi-Mosuowan Uplift in Junggar Basin, China. Earth Sci. Front. 2008, 15, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, J.G.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.J.; He, Q.B. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks and gas exploration direction in Shawan Sag, Junggar Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 8, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.M.; Song, Y.; Zheng, M.L.; Qin, Z.J.; Gong, D.Y. Genetic types, origins, and accumulation process of natural gas from the southwestern Junggar Basin: New implications for natural gas exploration potential. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 123, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.G.; Qu, J.X.; Zha, M.; Swennen, R.; Ding, X.J.; Imin, A.; Liu, H.L.; Bian, B.L. Significant contribution of haloalkaliphilic cyanobacteria to organic matter in an ancient alkaline lacustrine source rock: A case study from the Permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 138, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5002-13; Standard Test Method for Density and Relative Density of Crude Oils by Digital Density Analyzer. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- SY/T5542-2009; Test Methods for Reservoir Fluid Physical Properties. National Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 26981-2011; Test Method for Reservoir Fluid Physical Properties. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- SY/T6010-2011; Test Method for Fluid Inclusion in Sedimentary Basins by Microthermometry. National Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, J.; Lei, D.; He, D.F.; Tang, Y.; Shi, X.P.; Pang, L.; Yang, Z. Recovery of eroded thickness of the Jurassic of Chemo palaeouplift in Junggar Basin. J. Palaeogeogr. 2007, 9, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, N.S.; Zha, M.; Wang, X.L.; Yang, H.B. Tectono-thermal evolution of the Junggar Basin, NW China: Constraints from Ro and apatite fission track modelling. Pet. Geosci. 2005, 11, 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, K.E.; Walters, C.C.; Moldowan, J.M. The biomarker guide. In Biomarkers & Isotopes in Petroleum Systems & Earth History; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stasiuk, L.; Snowdon, L. Fluorescence micro-spectrometry of synthetic and natural hydrocarbon fluid inclusions: Crude oil chemistry, density and application to petroleum migration. Appl. Geochem. 1997, 12, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.D. Methods for determining the type of different oil and gas reservoirs fluid. Pertroleum Explor. Dev. 1996, 1, 69–75+106, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Aali, J.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Kamali, M.R. Geochemistry and origin of the world’s largest gas field from Persian Gulf, Iran. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2006, 50, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.Z.; Chen, Z.H. Petroleum phase evolution at high temperature: A combined study of oil cracking experiment and deep oil in Dongying Depression, eastern China. Fuel 2022, 326, 124978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.G.; Zha, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.L.; Ding, X.J. Significant Control of Gas Invasion to the Phase Behavior of Deep-Seated Hydrocarbon Fluids in Western Junggar Basin, NW China. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 22285–22295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Wang, Z.M.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Xiao, X.M. Kinetic Simulation of Crude Oil Cracking into Gas and Its Significance. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Su, J.; Wang, X.M.; Zhu, G.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Liu, K.Y.; Li, Z.X. Geochemistry of Palaeozoic marine petroleum from the Tarim Basin, NW China: Part 3. Thermal cracking of liquid hydrocarbons and gas washing as the major mechanisms for deep gas condensate accumulations. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 1394–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, D.B.; Zarra, L.; Meyer, D. The Lower Tertiary Wilcox Trend in the Deepwater Gulf of Mexico. In Proceedings of the AAPG 2007 Annual Convention, Long Beach, CA, USA, 1–4 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Di Primio, R.; Neumann, V. HPHT reservoir evolution: A case study from Jade and Judy fields, Central Graben, UK North Sea. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2008, 97, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
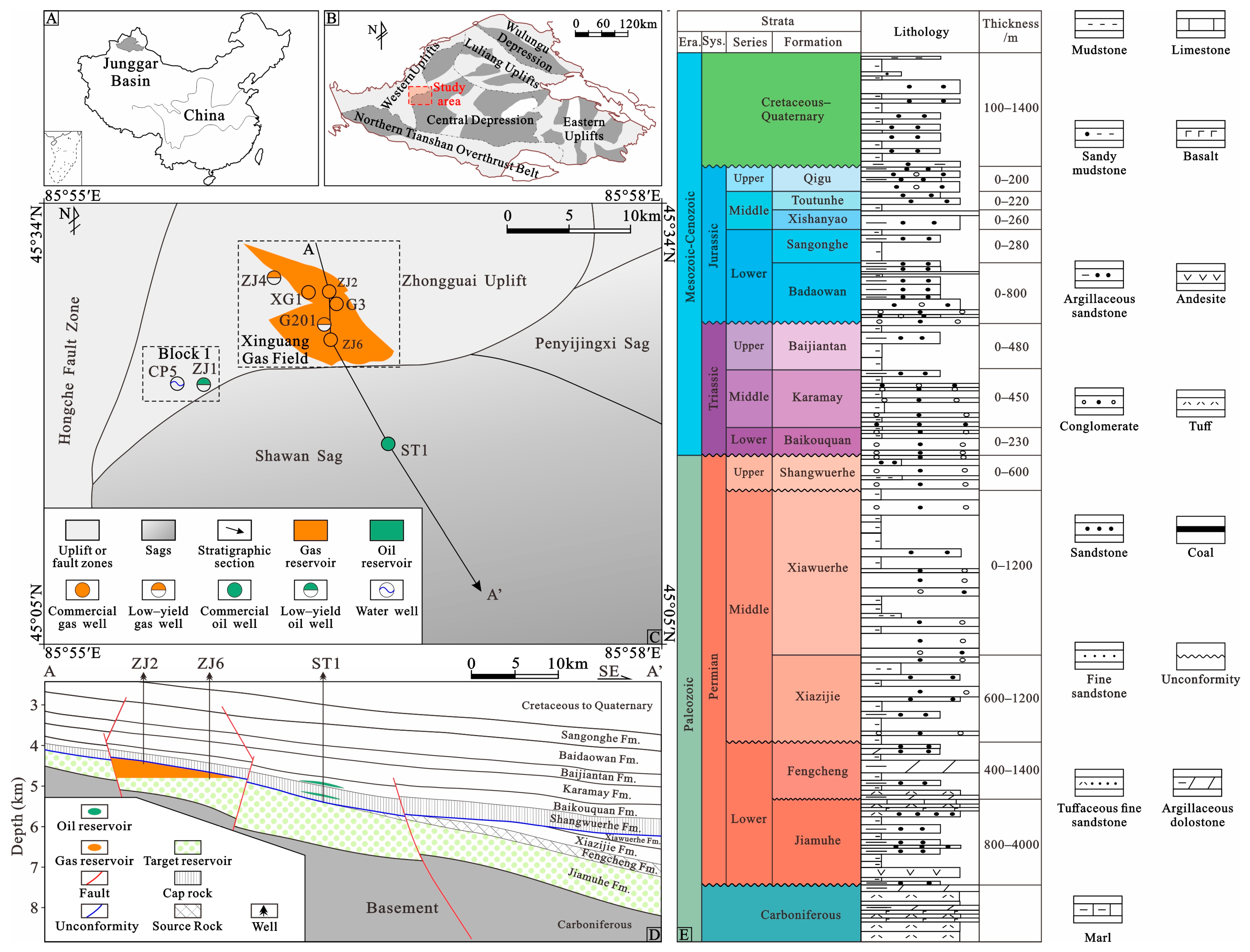
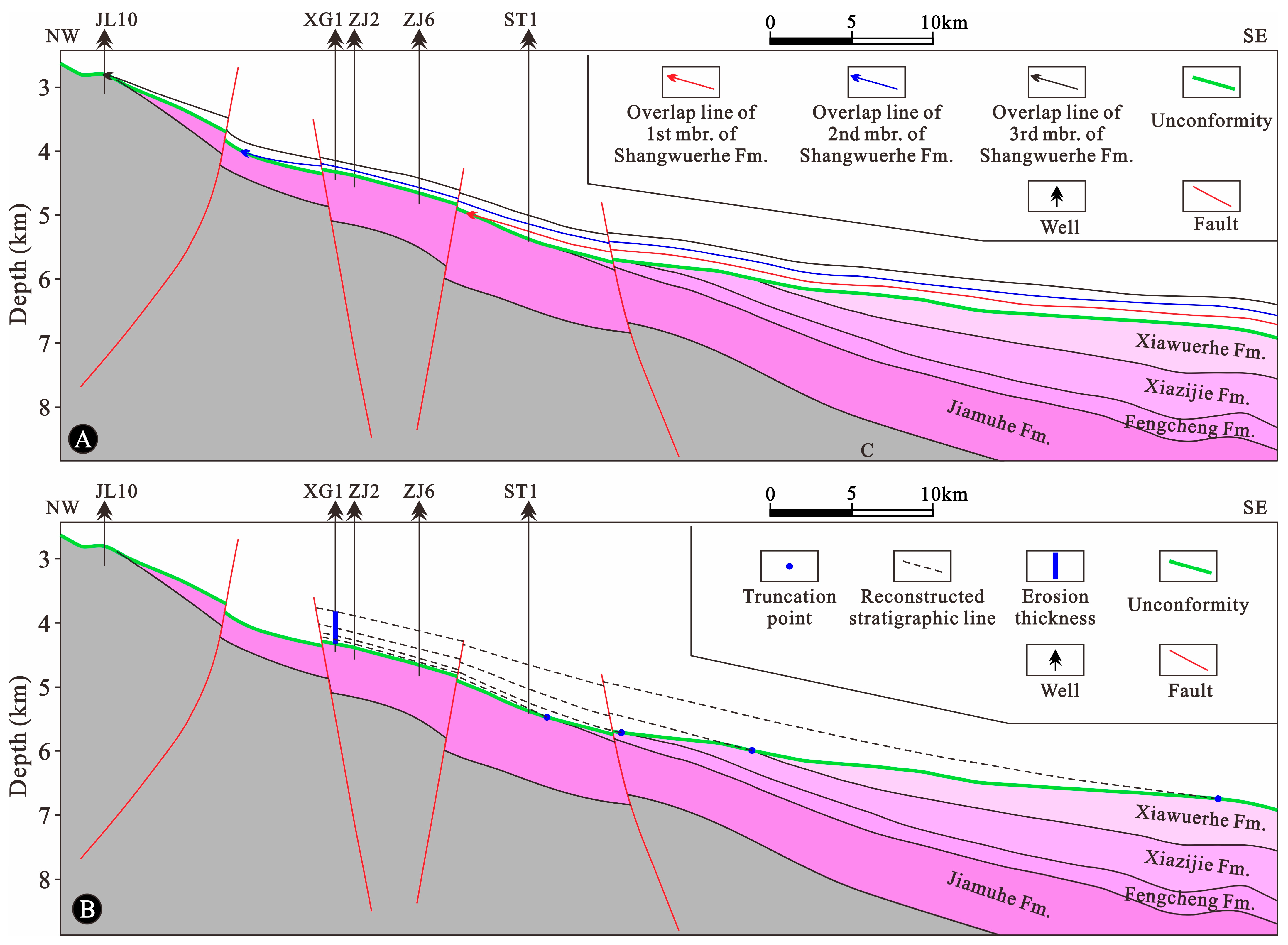
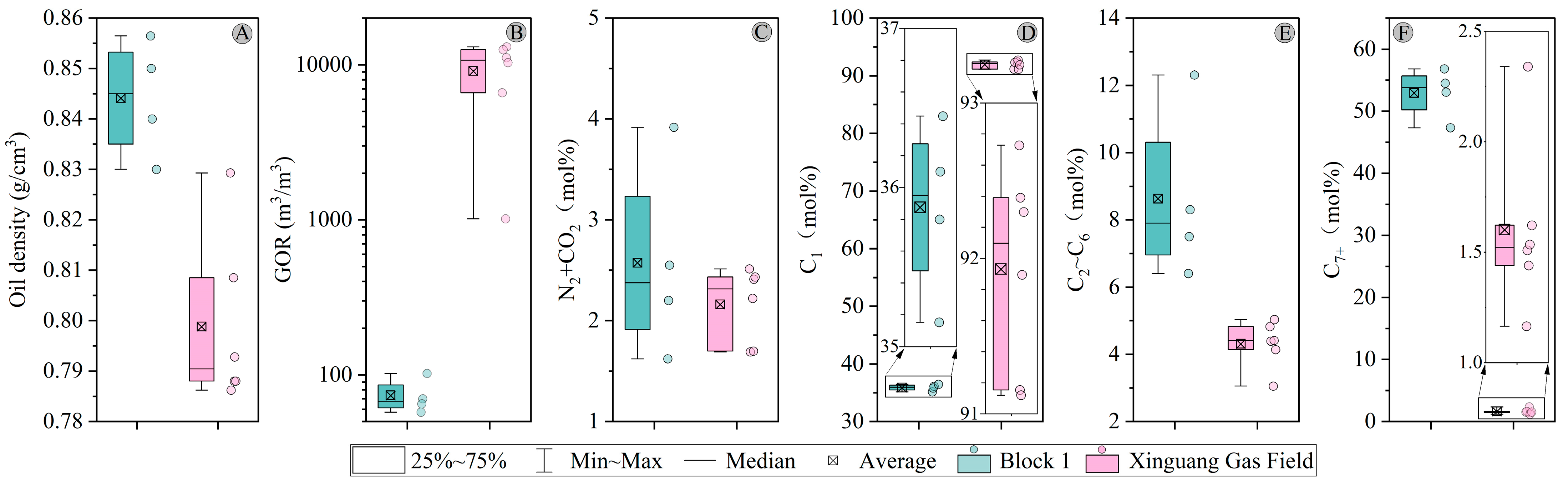
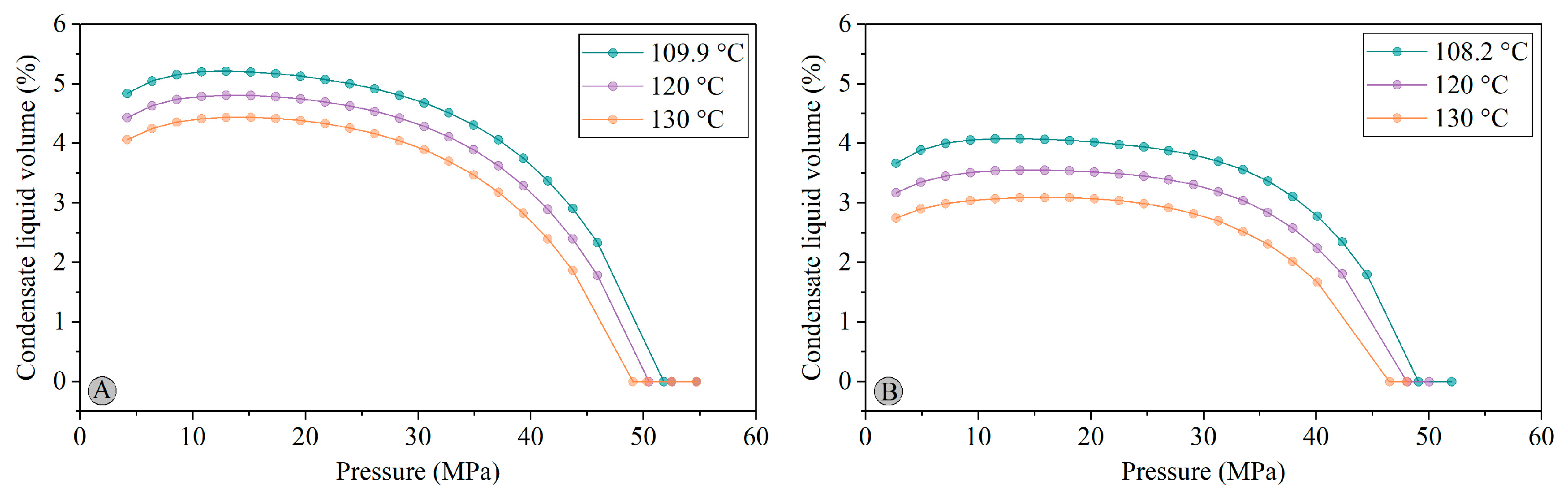

| Strata/ Erosion | Top Depth (m) | Bottom Depth (m) | Strata/Erosion Thickness (m) | Event Type | Deposited/Eroded from (Ma) | Deposited/Eroded to (Ma) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quaternary-Paleogene | 0 | 913 | 913 | Deposition | 66 | 0 |
| Cretaceous | 913 | 2413 | 1500 | Deposition | 145 | 66 |
| Erosion 2 | / | / | 205 | Erosion | 157.3 | 145 |
| Xishanyao | 2413 | 2530 | 117 | Deposition | 174.1 | 157.3 |
| Sangonghe | 2530 | 2900 | 370 | Deposition | 190.8 | 174.1 |
| Badaowan | 2900 | 3484 | 584 | Deposition | 201.3 | 190.8 |
| Baokouquan | 3483.5 | 3799 | 315.5 | Deposition | 235 | 201.3 |
| Karamay | 3799 | 4250 | 451 | Deposition | 247.2 | 235 |
| Baijiantan | 4250 | 4390 | 140 | Deposition | 251.9 | 247.2 |
| Shangwuerhe | 4390 | 4548 | 158 | Deposition | 259.9 | 251.9 |
| Erosion 1 | / | / | 505 | Erosion | 290.1 | 259.9 |
| Jiamuhe | 4548 | 4730 | 182 | Deposition | 298.9 | 290.1 |
| Strata | Lithological Proportion (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mud Stone | Silty Mudstone | Sandy Mudstone | Argillaceous Siltstone | Siltstone | Fine Sandstone | Conglomerate | Coal | |
| Quaternary-Cretaceous | 53.48 | 17.04 | 2.61 | 15.21 | 0.84 | 5.85 | 4.97 | / |
| Xishanyao | 8.55 | / | / | / | / | 91.45 | / | / |
| Sangonghe | 64.38 | 13.04 | / | 8.60 | / | 12.37 | 1.61 | / |
| Badaowan | 38.35 | 8.60 | / | 11.34 | 3.44 | 25.54 | 9.63 | 3.10 |
| Baokouquan | 45.94 | 26.07 | / | 24.17 | 1.91 | 1.91 | / | / |
| Karamay | 34.15 | 31.93 | / | 17.96 | 7.54 | 3.99 | 2.66 | 1.77 |
| Baijiantan | / | 7.22 | / | 20.94 | / | / | 71.84 | / |
| Shangwuerhe | 50.46 | 33.54 | / | 3.69 | / | / | 12.31 | / |
| Jiamuhe | / | / | 6.67 | / | / | / | 93.33 | / |
| Time (Ma) | GOR (m3/m3) | Type | Source | Non-Hydrocarbon Gas Content (%) | Hydrocarbon Content (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | CO2 | CH4 | C2H6 | C3H8 | i-C4H10 | n-C4H10 | i-C5H12 | n-C5H12 | C6+ | ||||
| 0 | / | Gas | MSWX | 2.51 | 0.13 | 91.69 | 2.56 | 0.98 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.91 |
| 81.1 | 57.38 | Fluid | SP | 1.60 | 0.02 | 35.15 | 2.99 | 1.60 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 56.83 |
| 80.7 | 139.11 | Fluid | SP | 1.65 | 0.08 | 60.15 | 1.68 | 0.64 | 0.23 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 35.01 |
| 80.3 | 220.63 | Fluid | SP | 1.89 | 0.10 | 69.01 | 1.93 | 0.73 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 25.42 |
| 79.9 | 301.16 | Fluid | SP | 2.03 | 0.10 | 73.99 | 2.07 | 0.79 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 20.04 |
| 79.1 | 460.95 | Fluid | SP | 2.17 | 0.11 | 79.39 | 2.22 | 0.85 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 14.21 |
| 78.7 | 541.46 | Fluid | SP | 2.22 | 0.11 | 81.01 | 2.26 | 0.86 | 0.31 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 12.47 |
| 78.3 | 621.01 | Fluid | SP | 2.25 | 0.12 | 82.26 | 2.30 | 0.88 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 11.10 |
| 76.3 | 1016.59 | Fluid | SP | 2.35 | 0.12 | 85.74 | 2.39 | 0.91 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 7.35 |
| 75.1 | 1252.49 | Fluid | SP | 2.38 | 0.12 | 86.82 | 2.42 | 0.92 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 6.18 |
| 72.7 | 1725.36 | Fluid | SP | 2.41 | 0.12 | 88.12 | 2.46 | 0.94 | 0.34 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 4.79 |
| 69.1 | 2430.74 | Fluid | SP | 2.44 | 0.13 | 89.14 | 2.49 | 0.95 | 0.35 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 3.67 |
| 59.9 | 4215.46 | Fluid | SP | 2.47 | 0.13 | 90.22 | 2.52 | 0.96 | 0.35 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 2.50 |
| 14.3 | 13504.78 | Fluid | SP | 2.49 | 0.13 | 90.92 | 2.54 | 0.97 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 1.75 |
| Block | Well | Depth (m) | Non-Hydrocarbon Gas Content (%) | Hydrocarbon Gas Content (%) | Dryness Coefficient | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | CO2 | CH4 | C2H6 | C3H8 | i-C4H10 | n-C4H10 | i-C5H12 | n-C5H12 | C6+ | ||||
| 1 | ZJ1 | 4875 | 10.99 | 0.1 | 71.56 | 5.24 | 4.59 | 2.3 | 1.97 | 1 | 0.77 | 1.48 | 0.82 |
| Xinguang Gas Field | ZJ2 | 4840.7 | 1.91 | 0.48 | 94.03 | 1.94 | 0.7 | 0.23 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.97 |
| ZJ2 | 4855 | 3.11 | 0.69 | 92.55 | 1.93 | 0.77 | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.96 | |
| ZJ2 | 4872 | 3.24 | 0.45 | 92.89 | 1.93 | 0.66 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.97 | |
| ZJ2 | 4936 | 2.05 | 0.22 | 94.24 | 1.96 | 0.69 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.1 | 0.13 | 0.97 | |
| ZJ2 | 5300.5 | 2.17 | 0.11 | 94.62 | 1.88 | 0.52 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.97 | |
| ZJ6 | 4875 | 2.26 | 0.19 | 92.61 | 2.13 | 0.87 | 0.3 | 0.41 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.77 | 0.96 | |
| ZJ6 | 4990 | 1.52 | 0.19 | 93.39 | 2.3 | 0.93 | 0.32 | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.46 | 0.95 | |
| G3 | 4610 | 2.21 | 0.07 | 93.82 | 1.93 | 0.72 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.96 | |
| G3 | 4615 | 1.71 | 0.09 | 95.58 | 1.71 | 0.48 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.97 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, M.; Ding, X.; Chu, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Jiang, W.; Zha, M.; Yue, G.; Liu, K. Phase Evolution History of Deep-Seated Hydrocarbon Fluids in the Western Junggar Basin: Insights from Geochemistry, PVT, and Basin Modeling. Processes 2025, 13, 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082667
Hou M, Ding X, Chu C, Wang J, Huang J, Liu H, Jiang W, Zha M, Yue G, Liu K. Phase Evolution History of Deep-Seated Hydrocarbon Fluids in the Western Junggar Basin: Insights from Geochemistry, PVT, and Basin Modeling. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082667
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Maoguo, Xiujian Ding, Chenglin Chu, Jie Wang, Jiwen Huang, Hailei Liu, Wenlong Jiang, Ming Zha, Gang Yue, and Keshun Liu. 2025. "Phase Evolution History of Deep-Seated Hydrocarbon Fluids in the Western Junggar Basin: Insights from Geochemistry, PVT, and Basin Modeling" Processes 13, no. 8: 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082667
APA StyleHou, M., Ding, X., Chu, C., Wang, J., Huang, J., Liu, H., Jiang, W., Zha, M., Yue, G., & Liu, K. (2025). Phase Evolution History of Deep-Seated Hydrocarbon Fluids in the Western Junggar Basin: Insights from Geochemistry, PVT, and Basin Modeling. Processes, 13(8), 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082667







