Solar Photo-Fenton: An Effective Method for MCPA Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
| AOP | Catalyst | Operating Conditions | Results | Observations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozonation | - | [MCPA]0: 80 mg/L, T: 20 °C, Qg: 0.06 m3/h, [TBA]0: 5 mM | XMCPA: 100% | Experiments were conducted in the presence of tert-BuOH as hydroxyl scavenger. | [9] |
| UV/H2O2 | - | [MCPA]0: 50 mg/L, [H2O2]0: 68 mg/L, T: 20 °C | XMCPA: 100% | Synergic effects of O3 and hydroxyl radicals. | [10] |
| O3/H2O2 | - | XMCPA: 100% | |||
| Photocatalytic ozonation | B-doped TiO2 | [MCPA]0: 5 mg/L, [cat]: 0.33 g/L, [O3 g inlet]: 5 mg/L pH0: 6.5, T: 25–40 °C, t: 120 min | XMCPA: 100% XTOC: 75% | The catalytic activity was maintained after 3 consecutive runs with no boron leaching detected. | [11] |
| UV/Sulfite reduction | - | [MCPA]0: 50–200 mg/L MCPA:Sulfite ratio 3:1, pH0: 11, t: 30 min | XMCPA: 100% XTOC: 100% | Effluent toxicity: very low after treatment (Kirby-Bauer disc method). | [12] |
| Fenton | Fe2+ | [MCPA]0: 10 mg/L and 1.5 µg/L, Fe (II): 2.5 mg/L, H2O2: 1.53 mg/L, pH0: 3–6.5, t: 120 min | XMCPA: >90% | Study in relevant pollutant concentrations (1.5 µg/L) and surface water. | [18] |
| Electro-Fenton | Fe2+ | [MCPA]0: 380 mg/L, [Fe2+]: 5 mg/L, pH0: 3, T: 35 °C, t: 360 min | XMCPA: 100% XTOC: 70–75% | H2O2 electrogenerated on the cathode. | [19] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactants
2.2. Typical Procedure for Oxidation Experiments
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Toxicity Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Process Evaluation for MCPA Oxidation
3.2. Parametric Study
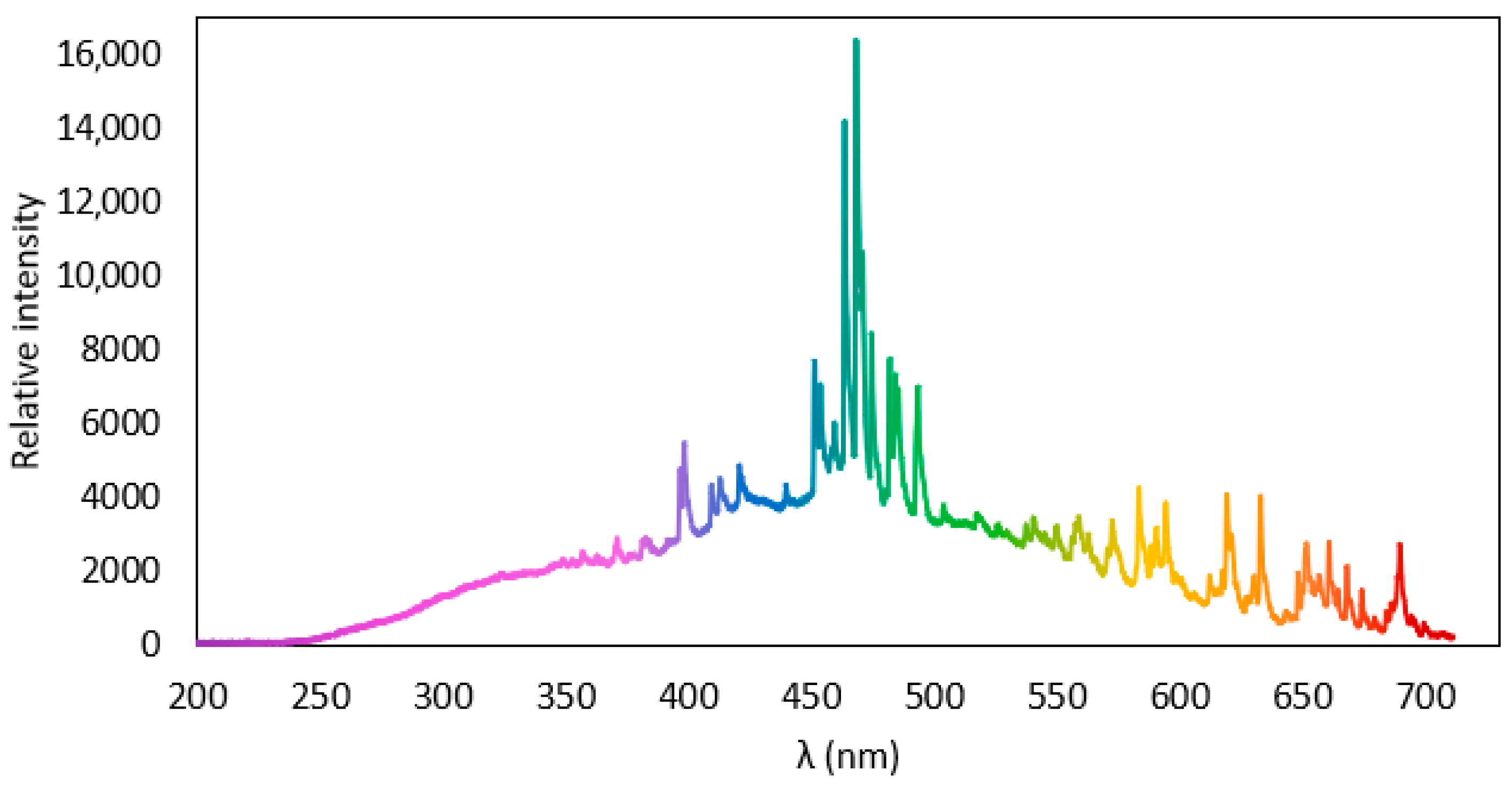
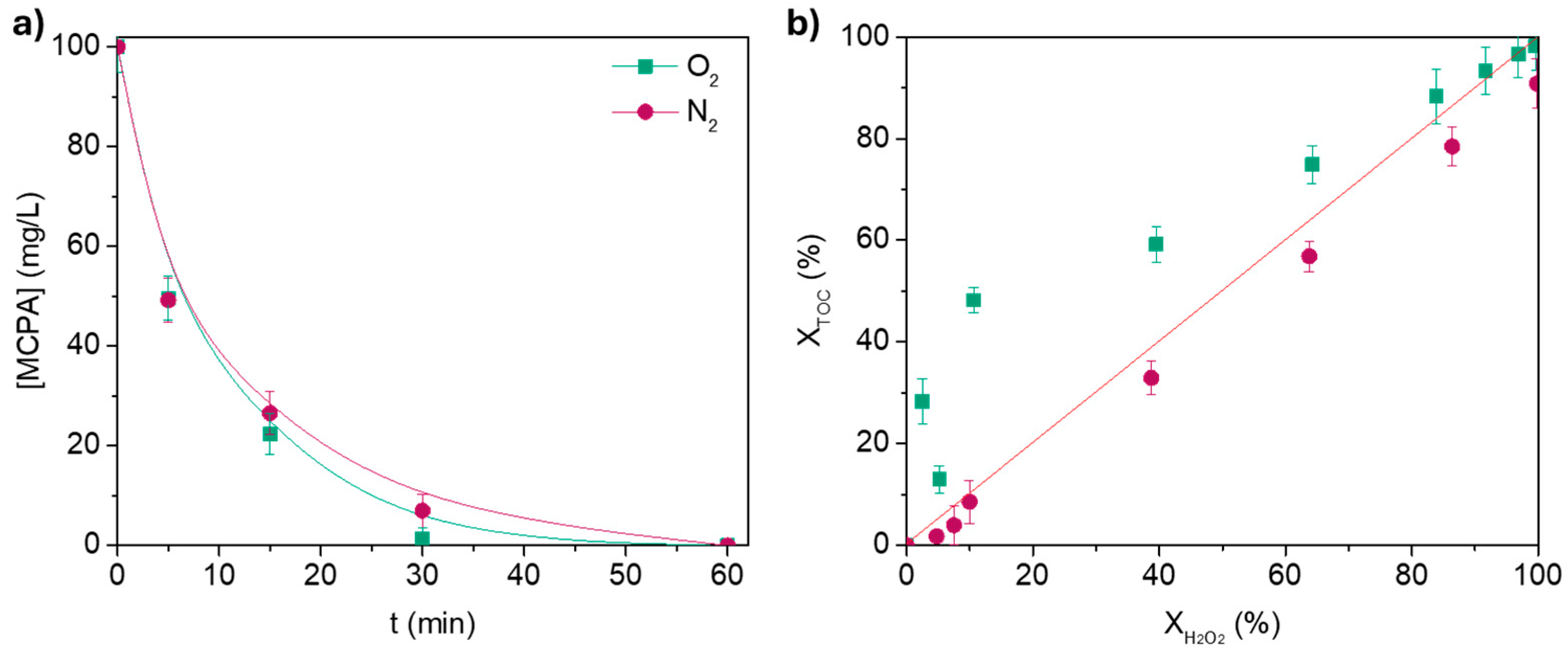
3.2.1. Effect of Dissolved O2
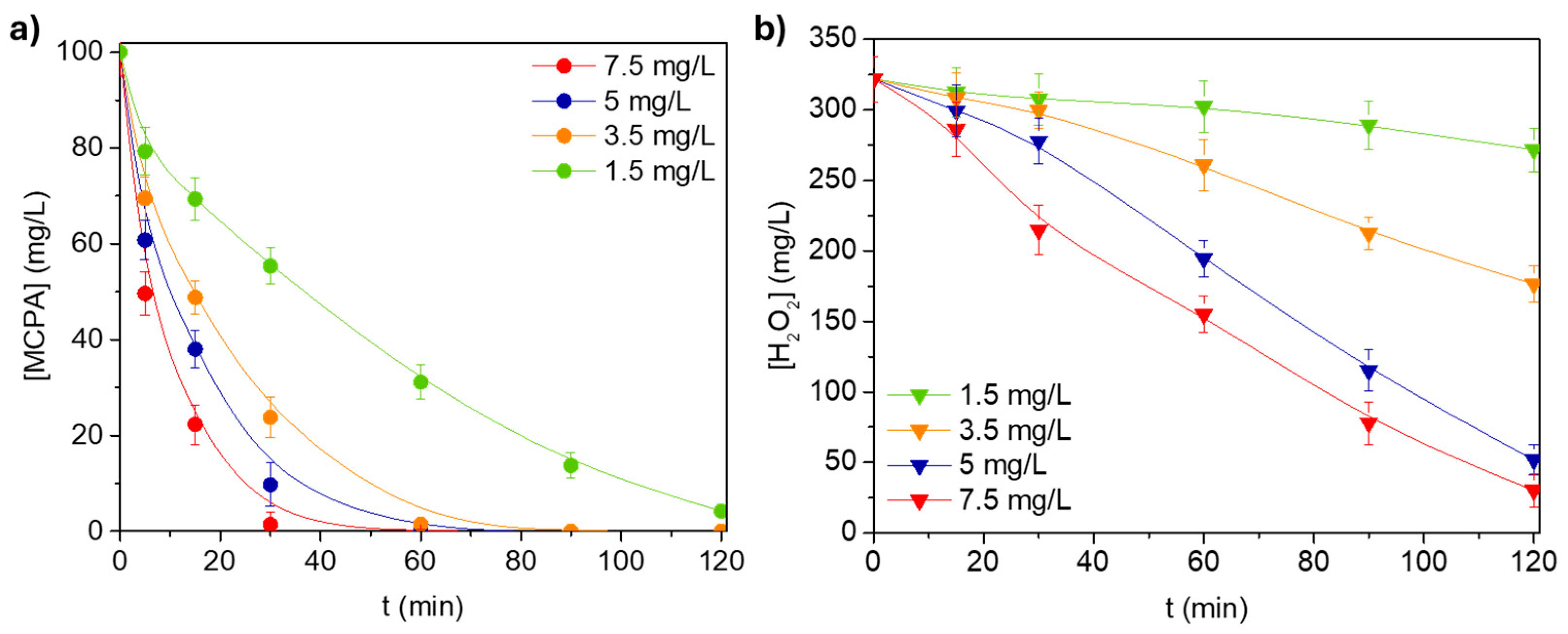
3.2.2. Catalyst Concentration
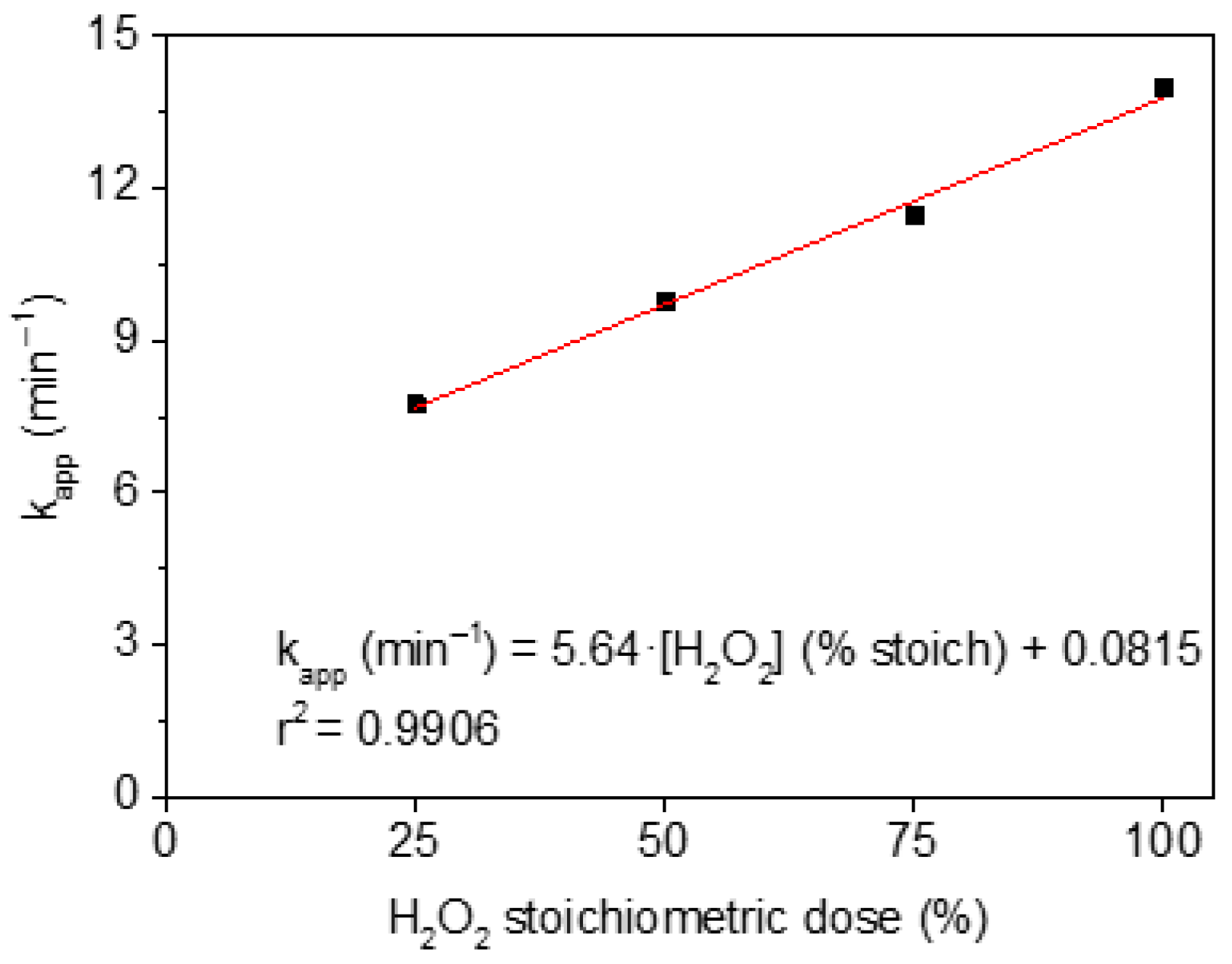
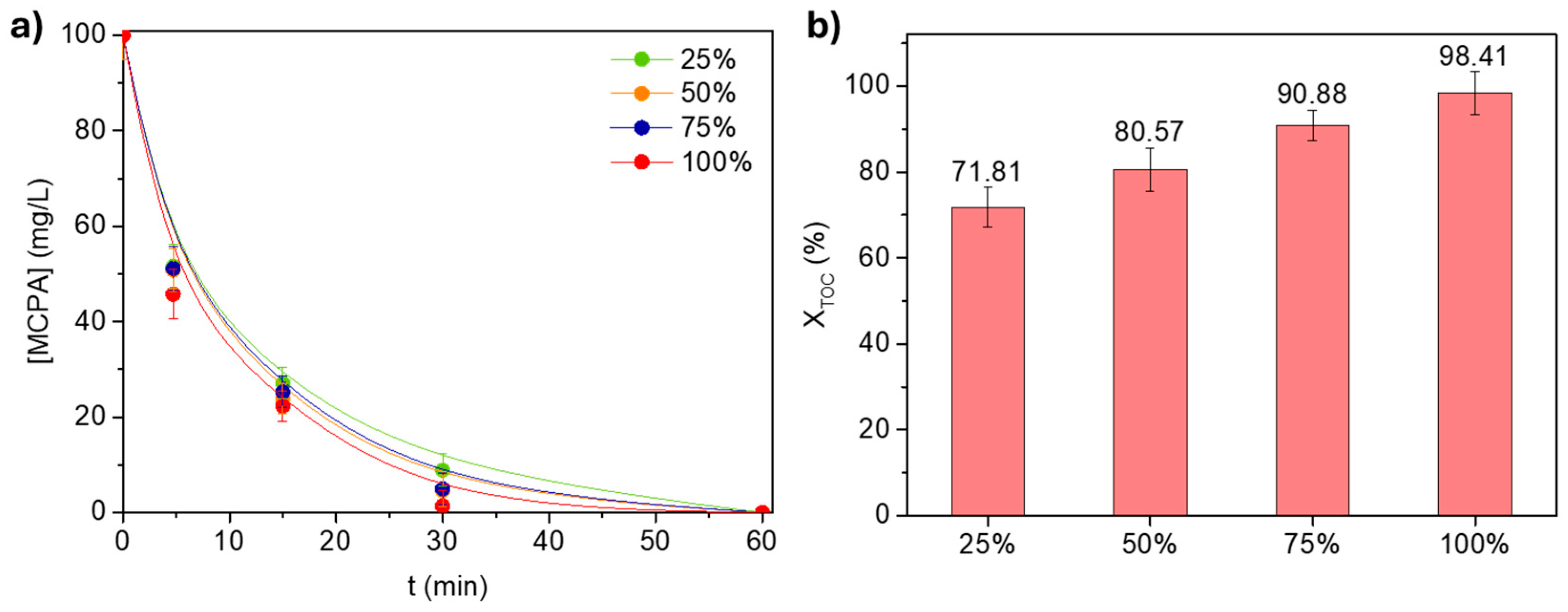
3.2.3. H2O2 Dosage
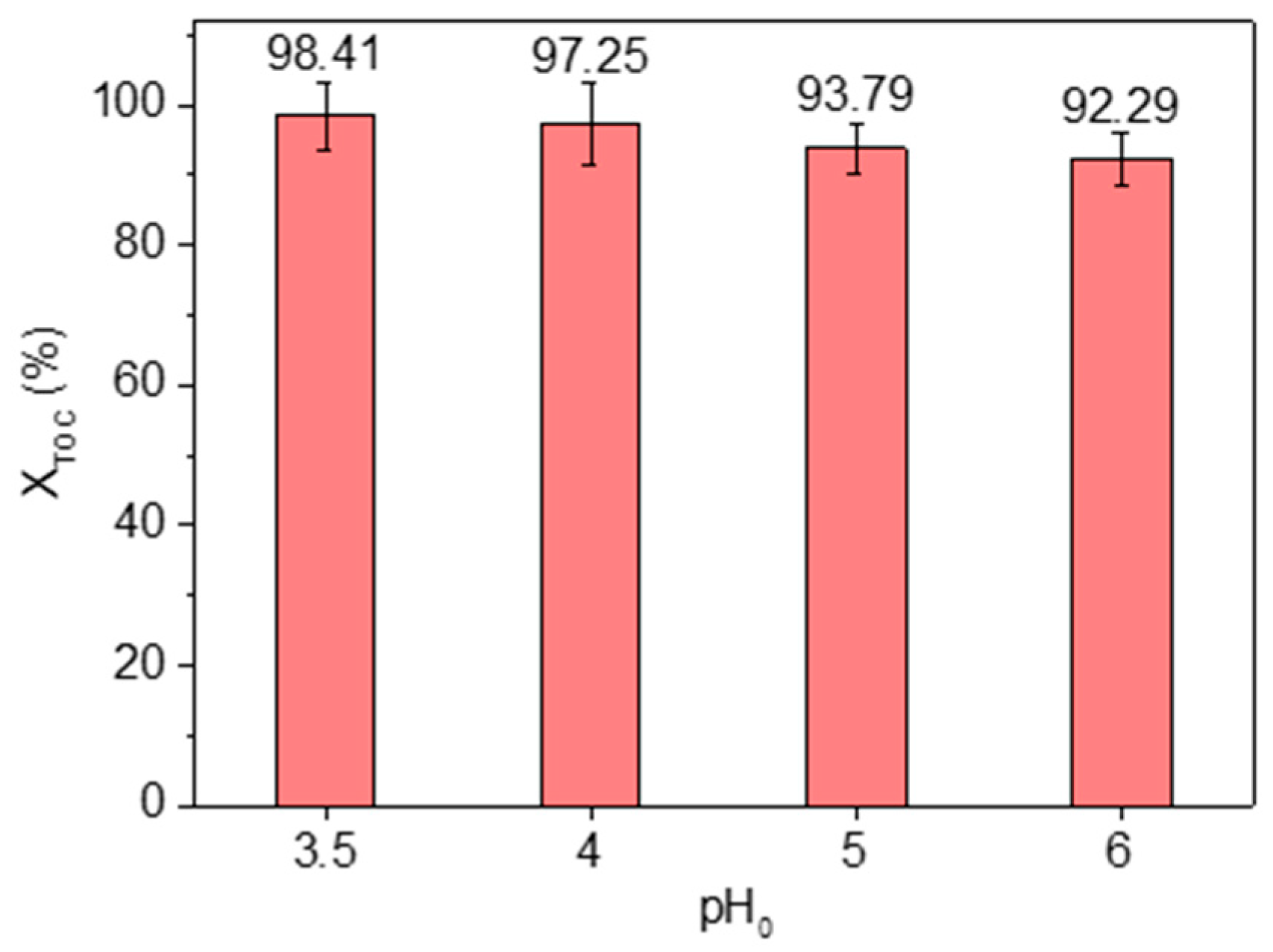
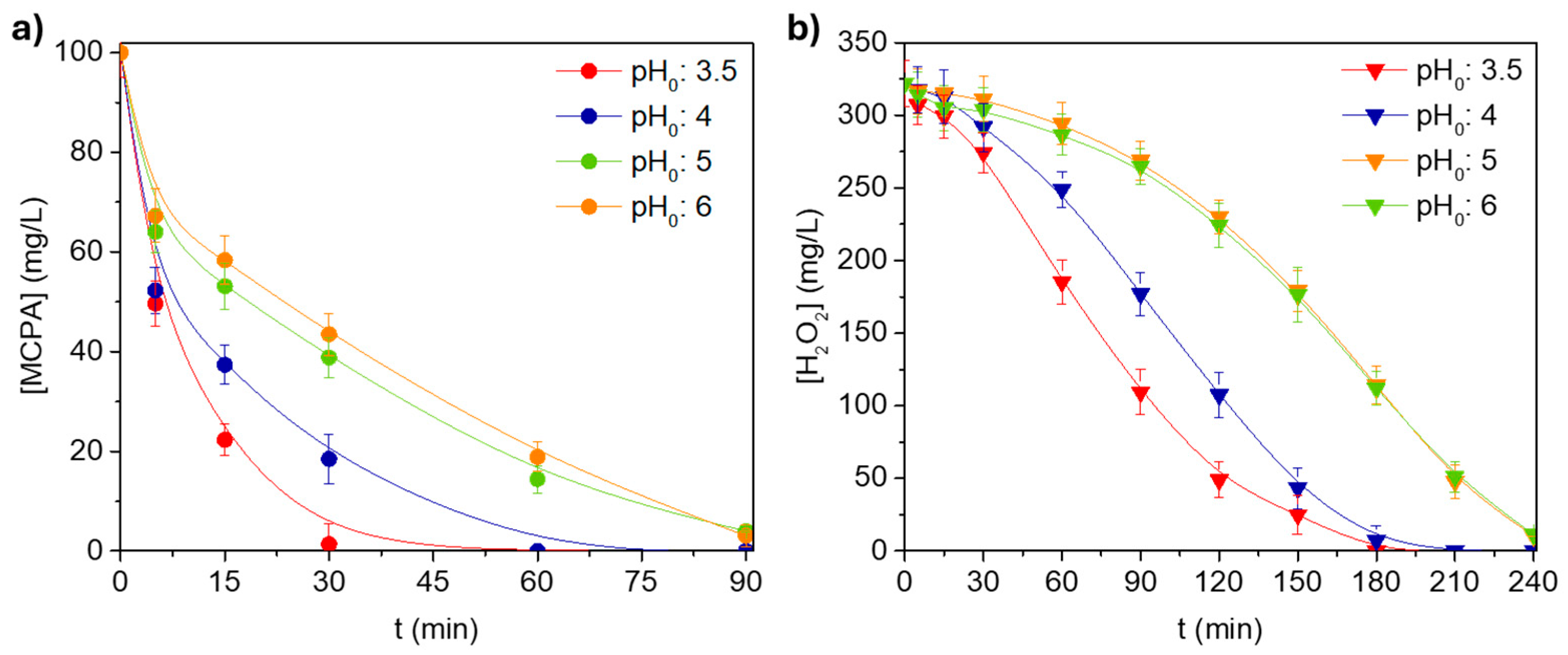
3.2.4. pH0
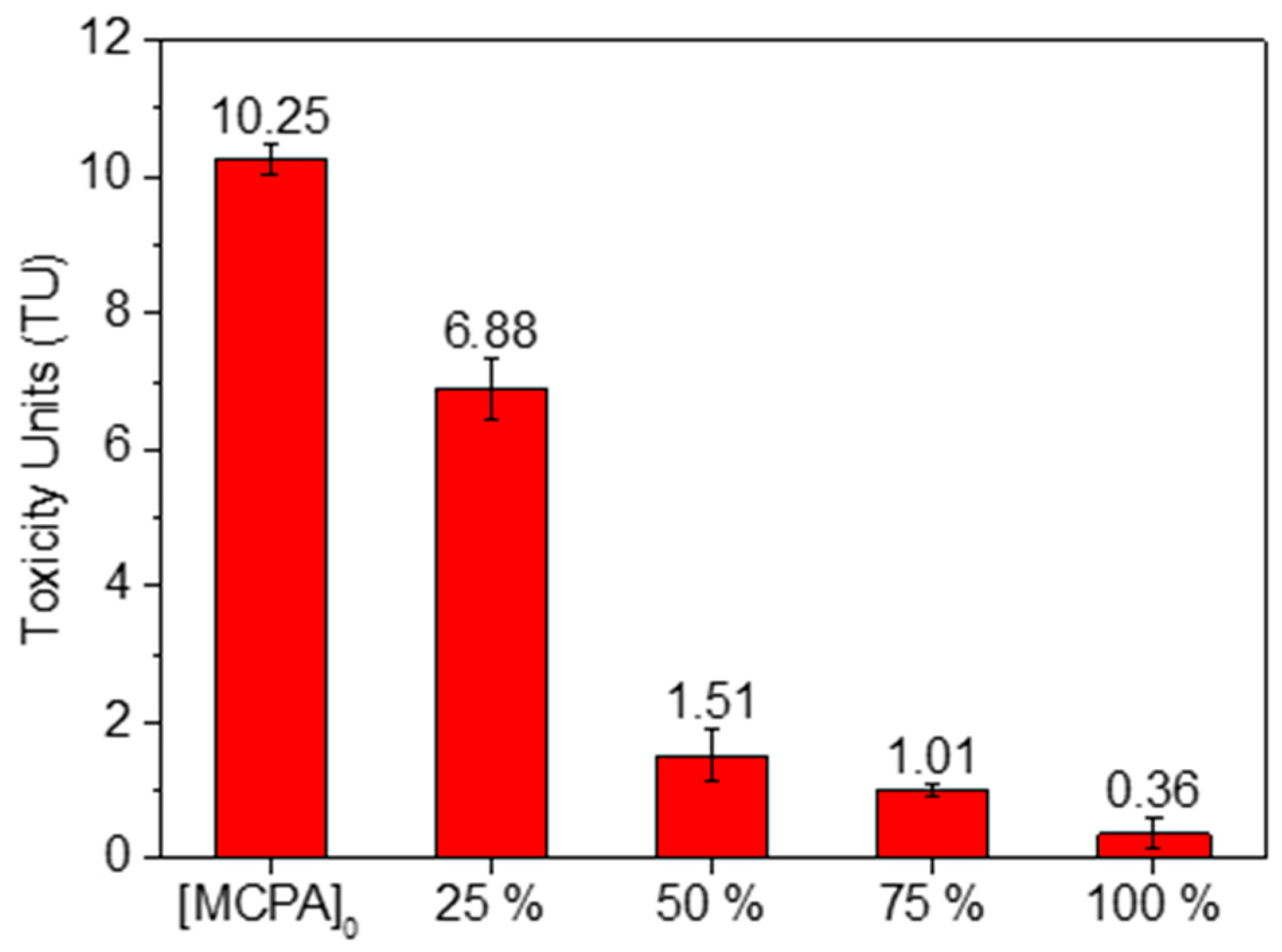
3.3. Reaction Intermediates and Toxicity Assessment
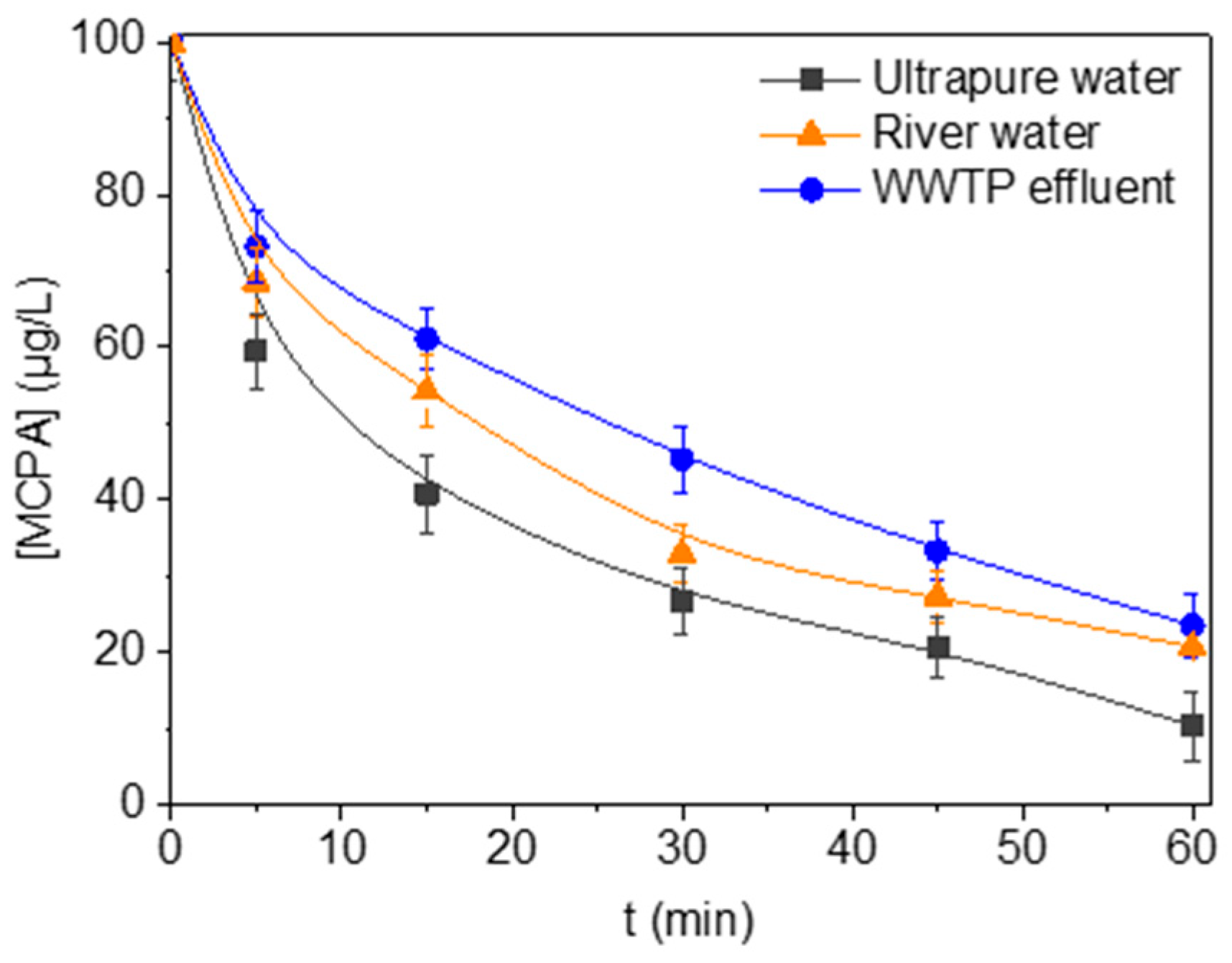
3.4. Water Matrices Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



| River Water | WWTP Effluent | |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.11 | 7.24 |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 322 | 599 |
| TOC (mg/L) | 0.2 | 8.55 |
| IC (mg/L) | 42.38 | 14.36 |
| F− (mg/L) | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 16.09 | 87.72 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 31.35 | 46.89 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 11.30 | 34.79 |
References
- Khan, B.A.; Nadeem, M.A.; Nawaz, H.; Amin, M.M.; Abbasi, G.H.; Nadeem, M.; Ali, M.; Ameen, M.; Javaid, M.M.; Maqbool, R.; et al. Pesticides: Impacts on Agriculture Productivity, Environment, and Management Strategies. In Emerging Contaminants and Associated Treatment Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Zouari, N.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Removal of pesticides from water and wastewater: Chemical, physical and biological treatment approaches. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, P.A.; Fennell, C.; Cassidy, R.; Doody, D.; Fenton, O.; Mellander, P.; Jordan, P. A review of the pesticide MCPA in the land-water environment and emerging research needs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 7, e1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Gao, C.; Ji, S.; Xing, Y. Efficient degradation of MCPA in water by light/MIL-88A/H2O2 system: Mechanism, degradation pathways and toxicity assessment. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico. Informe de Resultados de la Campaña de Muestreo 2023: Red de Detección del Riesgo por Plaguicidas; Dirección General del Agua: Madrid, Spain, 2024. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/ (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B. A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment I: Oxidation technologies at ambient conditions. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 8, 501–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment—A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, M.A.; Aaron, J. Advanced Oxidation Processes in Water/Wastewater Treatment: Principles and Applications. A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2577–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Zhao, P.; Chen, L. Kinetics of ozonation of 4-Chloro-2-Methyl phenoxyacetic acid in aqueous solution. Proc. Int. Conf. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 43, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, F.J.; Acero, J.L.; Real, F.J.; Roman, S. Oxidation of MCPA and 2,4-D by UV Radiation, Ozone, and the Combinations UV/H2O2 and O3/H2O2. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2004, 39, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, D.; Rey, A.; Álvarez, P.; Beltrán, F.; Puma, G.L. Boron doped TiO2 catalysts for photocatalytic ozonation of aqueous mixtures of common pesticides: Diuron, o-phenylphenol, MCPA and terbuthylazine. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 178, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarpira, H.; Rasolevandi, T.; Mahvi, A.H. 4-Chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid decomposition by production of reduction species in sulfite excitation through photolysis. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1316, 138927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munter, R. Advanced oxidation processes—Current status and prospects. Proc. Estonian Acad. Sci. Chem. 2001, 50, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.D.; Azevedo, E.B. Degradation of NSAIDs by optimized photo-Fenton process using UV-LEDs at near-neutral pH. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Galvez, J.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Malato-Rodríguez, S. Solar Photocatalytic Detoxification and Disinfection of Water: Recent Overview. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2006, 129, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAdam, J.; Parsons, S.A. An investigation into advanced oxidation of three chlorophenoxy pesticides in surface water. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Boye, B.; Dieng, M.M. General and UV-Assisted Cathodic Fenton Treatments for the Mineralization of Herbicide MCPA. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, E583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, M.; Liberatore, L.; D’Alessandro, N.; Tonucci, L.; Belli, C.; Ranalli, G. Improved Combined Chemical and Biological Treatments of Olive Oil Mill Wastewaters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Fernández-Ibáñez, P.; Maldonado, M.; Blanco, J.; Gernjak, W. Decontamination and disinfection of water by solar photocatalysis: Recent overview and trends. Catal. Today 2009, 147, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, A.; Vercher, R.; Santos-Juanes, L.; Simón, P.; Lardín, C.; Martínez, M.; Vicente, J.; González, R.; Llosá, C.; Arques, A.; et al. Solar photocatalysis as a tertiary treatment to remove emerging pollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Catal. Today 2010, 161, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Recent Progress in TiO2-Mediated Solar Photocatalysis for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 607954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Mata, A.G.; Velazquez-Martínez, S.; Álvarez-Gallegos, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Hernández-Pérez, J.A.; Ghanbari, F.; Silva-Martínez, S. Recent Overview of Solar Photocatalysis and Solar Photo-Fenton Processes for Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Photoenergy 2017, 2017, 8528063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.; Fallmann, H. The Photo-Fenton Oxidation—A Cheap and Efficient Wastewater Treatment Method. Res. Chem. Intermed. 1997, 23, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, G. Colorimetric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1943, 15, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 18763:2016; Soil Quality—Determination of the Toxic Effects of Pollutants on Germination and Early Growth of Higher Plants. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 11348-3; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio fischeri (Luminescent bacteria Test)—Part 3: Method Using Freeze-Dried Bacteria. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Hao, O.J.; Lin, C.F.; Jeng, F.T.; Shih, C.J. A review of Microtox test and its applications. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 1995, 52, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo, J.A.; Casas, J.A.; Molina, C.B.; Quintanilla, A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Evolution of Ecotoxicity upon Fenton’s Oxidation of Phenol in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7164–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olak-Kucharczyk, M.; Ledakowicz, S. Advanced oxidation of preservative agents in H2O2/UVC system—Kinetics study, transformation products and toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Costa, A.L.; Lopez-Perela, L.; Pliego, G.; Zazo, J.A.; Casas, J.A. Effective degradation of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid by visible LED driven photo-Fenton. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 9, 100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sonntag, C.; Dowideit, P.; Fang, X.; Mertens, R.; Pan, X.; Schuchmann, M.N.; Schuchmann, H. The fate of peroxyl radicals in aqueous solution. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, M.; Fernández-Castro, P.; Román, M.F.S.; Ortiz, I. Assessment of PCDD/Fs formation in the Fenton oxidation of 2-chlorophenol: Influence of the iron dose applied. Chemosphere 2015, 137, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Marques, C.C.; Portugal, I.; Nunes, M.I. Fenton processes for AOX removal from a kraft pulp bleaching industrial wastewater: Optimisation of operating conditions and cost assessment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; De Pedro, Z.M.; Pliego, G.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Chlorinated Byproducts from the Fenton-like Oxidation of Polychlorinated Phenols. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13092–13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, F.J.; Roth, J.A. Oxidation of Chlorinated Phenols Using Fenton’s Reagent. Hazard. Waste Hazard. Mater. 1993, 10, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, O.; Sans, C.; Esplugas, S. Sulfamethoxazole abatement by photo-Fenton: Toxicity, inhibition and biodegradability assessment of intermediates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarizia, L.; Russo, D.; Di Somma, I.; Marotta, R.; Andreozzi, R. Homogeneous photo-Fenton processes at near neutral pH: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 209, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulich, A.A. A practical and reliable method for monitoring the toxicity of aquatic samples. Process Biochem. 1982, 17, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Neamţu, M.; Grandjean, D.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Le Faucheur, S.; Slaveykova, V.; Velez Colmenares, J.J.; Pulgarin, C.; de Alencastro, L.F. Degradation of eight relevant micropollutants in different water matrices by neutral photo-Fenton process under UV254 and simulated solar light irradiation—A comparative study. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 158–159, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liang, L.; Ye, J.; Li, N.; Yan, B.; Chen, G. Influence and mechanism of water matrices on H2O2-based Fenton-like oxidation processes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautitz, I.R.; Nogueira, R.F.P. Degradation of tetracycline by photo-Fenton process—Solar irradiation and matrix effects. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2006, 187, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebel, J.E.; Pignatello, J.J.; Mitch, W.A. Effect of Halide Ions and Carbonates on Organic Contaminant Degradation by Hydroxyl Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes in Saline Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6822–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Meng, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wacławek, S.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zeng, W.; Hu, W. The overlooked carbonate radical in micropollutant degradation: An insight into hydration interaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
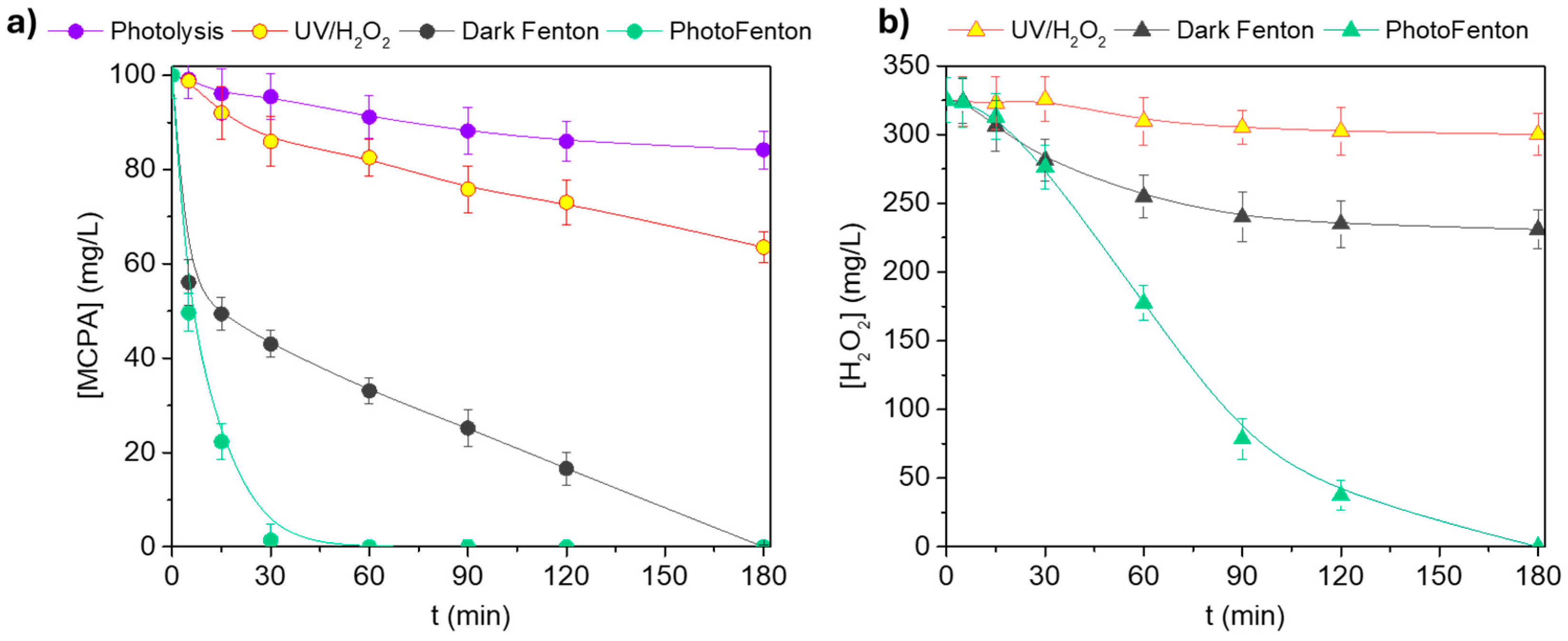


| Process | kapp,MCPA (min−1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|
| Photolysis | 9.90 × 10−4 | 0.967 |
| UV/H2O2 | 2.42 × 10−3 | 0.983 |
| Dark Fenton | 1.20 × 10−2 | 0.949 |
| Photo-Fenton | 1.39 × 10−1 | 0.986 |
| [Fe2+] (mg/L) | kapp,MCPA (min−1) | kspc,MCPA (L/min·gcat) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 2.50 × 10−2 | 16.40 | 0.987 |
| 3.5 | 6.90 × 10−2 | 18.30 | 0.984 |
| 5 | 9.20 × 10−2 | 18.40 | 0.985 |
| 7.5 | 13.97 × 10−2 | 18.60 | 0.986 |
| H2O2 Dose | kapp,MCPA (min−1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|
| 25% | 7.74 × 10−2 | 0.987 |
| 50% | 9.77 × 10−2 | 0.982 |
| 75% | 11.45 × 10−2 | 0.992 |
| 100% | 13.97 × 10−2 | 0.972 |
| pH0 | kapp,MCPA (min−1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|
| 3.5 | 13.97 × 10−2 | 0.972 |
| 4 | 5.17 × 10−2 | 0.950 |
| 5 | 3.78 × 10−2 | 0.985 |
| 6 | 3.35 × 10−2 | 0.953 |
| Matrix | kapp,MCPA (min−1) × 102 | r2 |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrapure water | 3.34 | 0.96 |
| River water | 2.48 | 0.95 |
| WWTP effluent | 2.23 | 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin-Montero, A.; Zapanti, A.M.; Pliego, G.; Casas, J.A.; Garcia-Costa, A.L. Solar Photo-Fenton: An Effective Method for MCPA Degradation. Processes 2025, 13, 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072257
Martin-Montero A, Zapanti AM, Pliego G, Casas JA, Garcia-Costa AL. Solar Photo-Fenton: An Effective Method for MCPA Degradation. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072257
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin-Montero, Alicia, Argyro Maria Zapanti, Gema Pliego, Jose A. Casas, and Alicia L. Garcia-Costa. 2025. "Solar Photo-Fenton: An Effective Method for MCPA Degradation" Processes 13, no. 7: 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072257
APA StyleMartin-Montero, A., Zapanti, A. M., Pliego, G., Casas, J. A., & Garcia-Costa, A. L. (2025). Solar Photo-Fenton: An Effective Method for MCPA Degradation. Processes, 13(7), 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072257











