Green Starches: Phytochemical Modification and Its Industrial Applications—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Starch Modification Processes, Benefits, and Uncertainties
3. Circular Economy and Green Chemistry
4. Phytochemical Enrichment of Starch
5. Bioaccessibility of Phytochemicals
6. Digestibility and Controlled Release Using Phytochemically Modified Starches
7. Biofilms and Bioactive Packaging
8. Herbal Excipients for Pharmaceutical and Cosmeceutical Applications
9. Slow and Controlled Release Fertilizers
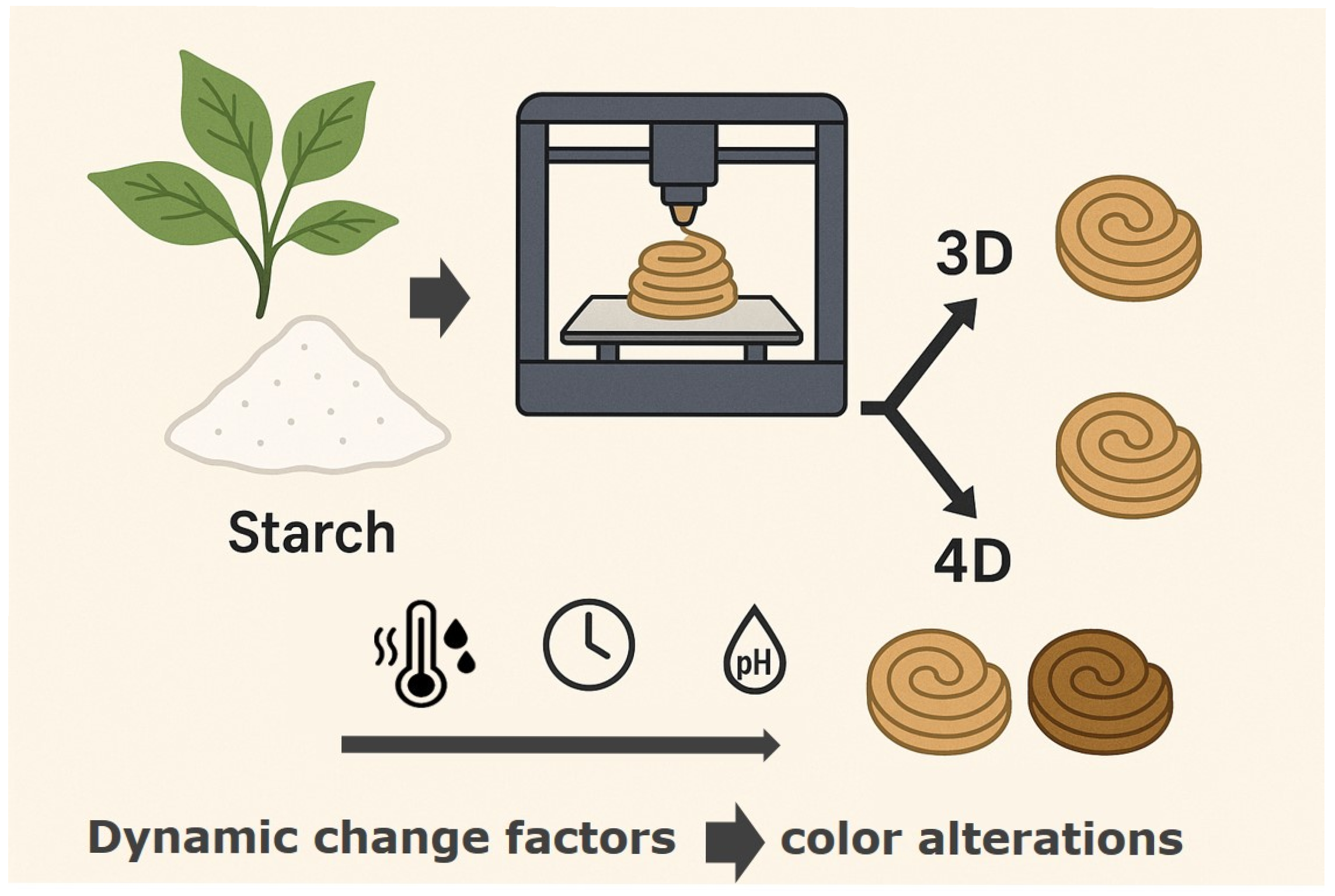
10. Starch-Based 3D and 4D Printed Foods
11. Self-Regulating Starch-Based Wound Dressings
12. Textile Industry and Fabrics Incorporating Bioactive Agents
13. Starch-Based Green Electronics
14. Recent Advances and Future Perspectives
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahsan, H. Dietary carbohydrates-requirement and recommendation in the human diet. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 17, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The burden of carbohydrates in health and disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, B.; Sit, N. Comprehensive review on single and dual modification of starch: Methods, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekanmi, K.O.; Kwaku, G.D.; Naushad, M.E. Hydrolysis and antioxidant activity of starch modified with phenolic extracts from grape pomace and sorghum bran under alkaline conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compart, J.; Singh, A.; Fettke, J.; Apriyanto, A. Customizing starch properties: A review of starch modifications and their applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.L.J.; Santos, N.C.; de Brito, A.C.O.; Leite, A.C.N.; Morais, J.R.F.; de Oliveira, B.F.; Silva, P.B.; Silva, Y.T.F.; Freitas, R.V.S.; Bonfim, K.S.; et al. Dual modification of starch: Synergistic effects of ozonation and pulsed electric fields on structural, rheological, and functional atributes. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, M.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Sun, L.; Dang, W.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Liu, C. Research progress on properties of pre-gelatinized starch and its application in wheat flour products. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S.P.; Sunooj, K.V.; Navaf, M.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Whiteside, W.S. Recent advancements in cross-linked starches for food applications—A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2024, 27, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Kaur, R.; Singh, J. Chemical modification of starch. In Starch in Food; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2024; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, T.; Ma, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Ren, F.; Tian, Y.; Jin, Z. A review of structural transformations and properties changes in starch during thermal processing of foods. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H. A comprehensive review of the factors influencing the formation of retrograded starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Gou, Q.; Yang, L.; Yu, Q.L.; Han, L. Dielectric barrier discharge plasma: A green method to change structure of potato starch and improve physicochemical properties of potato starch films. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 130992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Mhaske, P.; Farahnaky, A.; Kasapis, S.; Majzoobi, M. Cassava starch: Chemical modification and its impact on functional properties and digestibility, a review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qin, L.; Chen, T.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Xie, J. Modification of starch by polysaccharides in pasting, rheology, texture and in vitro digestion: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, F.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Teng, L.; Haroon, M.; Khan, R.; Mehmood, S.; Amin, B.; Ullah, R.; Khan, A.; et al. Advances in chemical modifications of starches and their applications. Carbohydrate. Res. 2019, 476, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaraweera, S.M.; Gunathilake, C.; Gunawardene, O.H.; Fernando, N.M.; Wanninayaka, D.B.; Dassanayake, R.S.; Rajapaksha, S.M.; Manamperi, A.; Fernando, C.A.N.; Kulatunga, A.K. Development of starch-based materials using current modification techniques and their applications: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroha, A.K.; Punia, S. Starch: Structure, Properties and Applications. In Pearl Millet; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałkowska, D.; Kapuśniak, K.; Juszczak, L. Chemically modified starches as food additives. Molecules 2023, 28, 7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hawkins, E.; Seung, D. Towards targeted starch modification in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 60, 102013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Li, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhai, L.; Qin, P.; Yang, L. Starch modification with molecular transformation, physicochemical characteristics, and industrial usability: A state-of-the-art review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.; Huo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Cai, T.; Liu, D. Advancements in nanoscale delivery systems: Optimizing intermolecular interactions for superior drug encapsulation and precision release. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateu-Sanz, M.; Fuenteslópez, C.V.; Uribe-Gomez, J.; Haugen, H.J.; Pandit, A.; Ginebra, M.P.; Hakimi, O.; Krallinger, M.; Samara, A. Redefining biomaterial biocompatibility: Challenges for artificial intelligence and text mining. Trends Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Ye, Q.; Lu, W.; Chen, D.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, L.; Meng, X.; Lee, Y.-C.; Wang, H.-M.D.; Xiao, C. The properties and preparation of functional starch: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 3984–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.E.; Bruce, J.H.; Steenson, S.; Stanner, S.; Buttriss, J.L.; Spiro, A.; Hall, W.L. Interesterified fats: What are they and why are they used? A briefing report from the Roundtable on Interesterified Fats in Foods. Nutr. Bull. 2019, 44, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniglia, B.C.; Castanha, N.; Le-Bail, P.; Le-Bail, A.; Augusto, P.E. Starch modification through environmentally friendly alternatives: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S.P.; Ashogbon, A.O.; Singh, A.; Chaudhary, V.; Whiteside, W.S. Enzymatic modification of starch: A green approach for starch applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 287, 119265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choton, S.; Bandral, J.D.; Singh, J.; Bhat, A.; Sood, M.; Gupta, N.; Kaur, D. Enzymatic modification of starch: A review. Saudi J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Jeong, H.M.; Shin, Y.J.; Hong, J.S.; Choi, H.D.; Shim, J.H. Development of freeze-thaw stable starch through enzymatic modification. Foods 2021, 10, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bao, J. Recent advances in modification approaches, health benefits, and food applications of resistant starch. Starch-Stärke 2023, 75, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, S. Barley starch modifications: Physical, chemical and enzymatic—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, Z.; Seidi, F.; Saeb, M.R.; Jin, Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, H. Elucidating the impact of enzymatic modifications on the structure, properties, and applications of cellulose, chitosan, starch and their derivatives: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 24, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashogbon, A.O. Dual modification of various starches: Synthesis, properties and applications. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; El Halal, S.L.M.; Dias, A.R.G.; da Rosa Zavareze, E. Physical modification of starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing and their applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Qiao, D.; Zhao, S.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xie, F. Nonthermal physical modification of starch: An overview of recent research into structure and property alterations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, C.; Miao, D.; Hou, H.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. The effect of non-thermal physical modification on the structure, properties and chemical activity of starch: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, S.; Singh, A. Modification of starch by novel and traditional ways: Influence on the structure and functional properties. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023, 1, 348–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.T.; Shahid, M.A.; Akter, S.; Ferdous, J.; Afroz, K.; Refat, K.R.I.; Faruk, O.; Jamal, M.S.I.; Uddin, M.N.; Samad, M.A.B. Cellulose and starch-based bioplastics: A review of advances and challenges for sustainability. Polym-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2024, 63, 1329–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makroo, H.A.; Naqash, S.; Saxena, J.; Sharma, S.; Majid, D.; Dar, B.N. Recovery and characteristics of starches from unconventional sources and their potential applications: A review. Appl. Food Res. 2021, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ncube, A.; Mtetwa, S.; Bukhari, M.; Fiorentino, G.; Passaro, R. Circular economy and green chemistry: The need for radical innovative approaches in the design for new products. Energies 2023, 16, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.L.; Rodrigues, L.M.; da Veiga, M.A.M.S.; Souza, L.R.R. Advancing nanomaterial synthesis: Harnessing green chemistry for sustainable innovation. Green Anal. Chem. 2024, 11, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Chauhan, D.S.; Aslam, R.; Banerjee, P.; Aslam, J.; Quadri, T.W.; Zehra, S.; Verma, D.K.; Quraihsi, M.A.; Dubey, S. Principles and theories of green chemistry for corrosion science and engineering: Design and application. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 4270–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombino, S.; Sole, R.; Di Gioia, M.L.; Procopio, D.; Curcio, F.; Cassano, R. Green chemistry principles for nano-and micro-sized hydrogel synthesis. Molecules 2023, 28, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashi, A.; Delavar, A.F.; Zamani, A.; Noshiranzadeh, N.; Ebadipur, H.; Ebadipur, H.; Khanban, F. Green modification of corn starch through repeated freeze-thaw cycles (RFTC), microwave assisted solid state acetic acid esterification (MSAE), and by dual RFTC/MSAE treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, T.; Zhao, L.; Fan, X.; Gu, H. Rapid self-healing, self-adhesive, anti-freezing, moisturizing, antibacterial and multi-stimuli-responsive PVA/starch/tea polyphenol-based composite conductive organohydrogel as flexible strain sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mageed, HM Fronteiras em nanopartículas redefinindo a imobilização enzimática: Uma revisão abordando desafios, inovações e desbloqueando potenciais futuros sustentáveis. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2025, 13, 7. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mageed, H.M.; Nada, D.; Radwan, R.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Gohary, N.A.E.L. Optimization of catalytic properties of Mucor racemosus lipase through immobilization in a biocompatible alginate gelatin hydrogel matrix for free fatty acid production: A sustainable robust biocatalyst for ultrasound-assisted olive oil hydrolysis. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behshad, Y.; Pazhang, M.; Najavand, S.; Sabzi, M. Enhancing Enzyme Stability and Functionality: Covalent Immobilization of Trypsin on Magnetic Gum Arabic Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 5283–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Deng, Z.; Tang, C.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, T.; Hu, X. Formation, structure and properties of the starch-polyphenol inclusion complex: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C.; Yang, L. Development, application and future trends of starch-based delivery systems for nutraceuticals: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 308, 120675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Ji, N.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Bioactive and intelligent starch-based films: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 854–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, M.; Channab, B.E.; El Idrissi, A.; Zahouily, M.; Motamedi, E. A comprehensive review on starch: Structure, modification, and applications in slow/controlled-release fertilizers in agriculture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 322, 121326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.V.; Kusumawardani, S.; Kunyanee, K.; Luangsakul, N. Polyphenol-modified starches and their applications in the food industry: Recent updates and future directions. Foods 2022, 11, 3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayua, E.O.; Nkhata, S.G.; Namaumbo, S.J.; Kamau, E.H.; Ngoma, T.N.; Aduol, K.O. Polyphenolic inhibition of enterocytic starch digestion enzymes and glucose transporters for managing type 2 diabetes may be reduced in food systems. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Li, X.; Ji, S.; Zhong, Y.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Capanoglu, E.; Xiao, J.; Lu, B. Starch modification with phenolics: Methods, physicochemical property alteration, and mechanisms of glycaemic control. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, J.; Kong, X.; Yang, W.; Yin, X.; Xu, E.; Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Ye, X. Physicochemical and digestibility characterisation of maize starch–caffeic acid complexes. LWT 2020, 121, 108857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on the formation and in vitro digestion of Tartary buckwheat starch/flavonoid complexes. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhalaria, R.; Verma, R.; Kumar, D.; Puri, S.; Tapwal, A.; Kumar, V.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K. Bioactive compounds of edible fruits with their anti-aging properties: A comprehensive review to prolong human life. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreiro, S.; Figueirinha, A.; Silva, A.S.; Ramos, F. Bioactive edible films and coatings based in gums and starch: Phenolic enrichment and foods application. Coatings 2021, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makran, M.; Cilla, A.; Haros, C.M.; Garcia-Llatas, G. Enrichment of wholemeal rye bread with plant sterols: Rheological analysis, optimization of the production, nutritional profile and starch digestibility. Foods 2022, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, K.; Brar, J.K.; Singh, A.; Gupta, A.; Kaur, H.; Bains, K. Wheatgrass powder-enriched functional pasta: Techno-functional, phytochemical, textural, sensory, and structural characterization. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 53, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzuwaid, N.T.; Laddomada, B.; Fellows, C.M.; Egan, N.; Sissons, M. Supplementation of durum wheat spaghetti with wheat bran protein concentrate: Impacts on phytochemical profile and starch digestion. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, M.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, S. Macromolecular–structural interactions and phytochemical constituents of therapeutic herbs in pasta altered the functional properties, cooking profile and in vitro starch and protein digestibility. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Wang, L.; Lv, J.; Chen, Z.; Brennan, M.; Ma, Q.; Wang, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Brennan, C. Phenolics from sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) modulate starch digestibility through physicochemical modifications brought about by starch–Phenolic molecular interactions. LWT 2022, 165, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Pan, Y. Influence of food matrix and food processing on the chemical interaction and bioaccessibility of dietary phytochemicals: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6421–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, R.; Rawat, H.; Kumar, V.; Jagtap, C.; Jain, A. The influence of food matrix on the stability and bioavailability of phytochemicals: A comprehensive review. Food Humanit. 2024, 2, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Bian, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, Z.; Song, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, T.; Li, S. Antioxidant potential and in vitro inhibition of starch digestion of flavonoids from Crataegus pinnatifida. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, G.; Rizzi, C.; Pasini, G.; Lucini, L.; Giuberti, G.; Simonato, B. Effect of Moringa oleifera L. leaf powder addition on the phenolic bioaccessibility and on in vitro starch digestibility of durum wheat fresh pasta. Foods 2020, 9, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeike, D.; Vaitkeviciene, R.; Marksa, M.; Juodeikiene, G.; Bendoraitiene, J.; Bartkiene, E.; Lele, V.; Viskelis, P.; Bernatoniene, J.; Jakstas, V. Structural and functional characterisation of compositionally optimised rice bran and lingonberry dietary fibre-based gel-type product enriched with phytochemicals. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3372–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, M.; Aleixandre, A.; Sineiro, J.; Rosell, C.M.; Moreira, R. Interactions between Ascophyllum nodosum seaweeds polyphenols and native and gelled corn starches. Foods 2022, 11, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumroenvidhayakul, S.; Thilavech, T.; Abeywardena, M.; Adisakwattana, S. Investigating the impact of dragon fruit peel waste on starch digestibility, pasting, and thermal properties of flours used in Asia. Foods 2022, 11, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumroenvidhayakul, S.; Thilavech, T.; Abeywardena, M.; Adisakwattana, S. Dragon fruit peel waste (Hylocereus undatus) as a potential ingredient for reducing lipid peroxidation, dietary advanced glycation end products, and starch digestibility in cookies. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camelo-Méndez, G.A.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; Bello-Pérez, L.A. Digestibility of carbohydrates and phytochemicals in pasta. Food Eng. Rev. 2016, 8, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Palanisamy, C.P.; Srinivasan, G.P.; Panagal, M.; Kumar, S.S.D.; Mironescu, M. A comprehensive review on starch-based sustainable edible films loaded with bioactive components for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbar, M.; Shahid, H.; Hira, H.; Kanwal, H. A Comprehensive Review on Antimicrobial Activity of Edible Biofilms. PSM Biol. Res. 2023, 8, 36–55. Available online: https://psmjournals.org/index.php/biolres/article/view/718 (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Chan, S.Y.; Goh, C.F.; Lau, J.Y.; Tiew, Y.C.; Balakrishnan, T. Rice starch thin films as a potential buccal delivery system: Effect of plasticiser and drug loading on drug release profile. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gök, M.K.; Demir, K.; Cevher, E.; Özsoy, Y.; Cirit, Ü.; Bacınoğlu, S.; Özgümüş, S.; Pabuccuoğlu, S. The effects of the thiolation with thioglycolic acid and l-cysteine on the mucoadhesion properties of the starch-graft-poly(acrylic acid). Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, D.N.A.; Siddique, M.B.M.; Chew, J.J.; Su, H.T.; Khairuddin, N.; Khaerudini, D.S.; Hossain, M.S.; Sunarso, J. Characterization of starch biofilm reinforced with cellulose microfibers isolated from Musa Saba’midrib residue and its application as an active packaging film. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, B.; Sarkar, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Saha, S.P.; Thirugnanam, A.; Roy, P.K.; Roy, S. Starch-based biodegradable films amended with nano-starch and tannic acid-coated nano-starch exhibit enhanced mechanical and functional attributes with antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 341, 122321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falah, F.; Zulfiana, D.; Septiano, M.; Nawawi, D.S.; Sari, F.P.; Fatriasari, W.; Solihat, N.N. Antimicrobial activity of food packaging biofilms derived from lignin-starch-poly (lactic acid). AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 2973, 040013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimnuan, P.; Yakaew, S.; Yosboonruang, A.; Luangbudnak, W.; Grandmottet, F.; Viyoch, J. Development of anti-acne film from bio-cellulose incorporating Punica granatum peel extract. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironescu, M.; Lazea-Stoyanova, A.; Barbinta-Patrascu, M.E.; Virchea, L.I.; Rexhepi, D.; Mathe, E.; Georgescu, C. Green design of novel starch-based packaging materials sustaining human and environmental health. Polymers 2021, 13, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, A.; Kuvar, V.; Bharadwaj, S. Bridging the Gap: A Comparative Investigation of Pharmaceutical Excipient Regulations. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2024, 58, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Bhardwaj, S.; Bana, S. Pharmaceutical excipients. In Dosage Forms, Formulation Developments and Regulations; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 311–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, K.R.; Jonans, T. Comparison of Starch from Locally Grown Food Crops as a Pharmaceutical Excipient: A Systematic Review. Afr. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 4, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandar, C.C.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Natural polymers as useful pharmaceutical excipients. In Advances and Challenges in Pharmaceutical Technology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kate, P.; Sawale, V.; Kakade, R.; Karale, R.; Dubey, T. Novel Herbal Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Pharm. Sci 2024, 2, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mam, N.M.; Bias, S.; Manasi, M. Review on herbal excipients. Res. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2023, 15, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ahmad, R.; Jangir, S.; Sharma, D. Current Development and Application on Inclusion of Herbal Phytochemicals in Novel Herbal Drug Delivery System. Nat. Prod. J. 2025, 15, E250324228308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Arpita, S.; Gupta, A.A. A review on herbal excipients. Int. J. Indig. Herbs Drugs 2021, 6, 05–08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, H.S.; Babar, V.B.; Jagtap, P.S.; Doshi, R.V.; Deokate, S.V.; Todkari, A.V.; Mantri, A.S.; Parekar, P.B.; Shivpuje, S. A Comprehensive Review Article on Herbal Cosmetics. South Asian Res. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 6, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mishra, G.; Dinda, S.C. Natural excipients in pharmaceutical formulations. In Evidence Based Validation of Traditional Medicines: A Comprehensive Approach; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 829–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladosu, Y.; Rafii, M.Y.; Arolu, F.; Chukwu, S.C.; Salisu, M.A.; Fagbohun, I.K.; Muftaudeen, T.K.; Swaray, S.; Haliru, B.S. Superabsorbent polymer hydrogels for sustainable agriculture: A review. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, A.; Sharma, S.P.; Kaur, H.; Kaur, H. Novel nanocomposite-based controlled-release fertilizer and pesticide formulations: Prospects and challenges. In Multifunctional Hybrid Nanomaterials for Sustainable Agri-Food and Ecosystems; Elsevier: London, UK, 2020; pp. 99–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrencia, D.; Wong, S.K.; Low, D.Y.S.; Goh, B.H.; Goh, J.K.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Soottitantawat, A.; Lee, L.H.; Tang, S.Y. Controlled release fertilizers: A review on coating materials and mechanism of release. Plants 2021, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Xiong, Q.; Xie, Z.; Cheng, J.; Yu, B.; Zhang, H.; Su, Y.; Zhao, J. Functional, eco-friendly, and starch-based nanocarriers with sustained release of carvacrol for persistent control of tomato gray mold. Crop Health 2023, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, A.F.; Palencia, M.; Arrieta, Á.A. Development of High-Efficiency Fertilizer by Hydrogels Obtained from Cassava Starch and Citric Acid for Slow Release of Ammonium and Potassium. Gels 2024, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, G.; Tang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yan, G.; Xiao, J.; Yan, W.; Cao, Y. Fabrication of dual responsive microcapsules based on starch with enhanced foliar adhesion and photostability for improving control efficacy and reducing environmental risks. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 153290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleckienė, R. Production and properties of native potato Starch-Coated urea. Mater. Sci. 2022, 28, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, R.; Latifah, O.; Ahmed, O.H.; Charles, P.W.; Paiva, Y.F.; Susilawati, K. Potential of rejected sago starch as a coating material for urea encapsulation. Polymers 2023, 15, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Zhang, A.; Ding, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tang, W.; Lyu, F. Hot extrusion 3D printing technologies based on starchy food: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Liu, Y. Investigation on lemon juice gel as food material for 3D printing and optimization of printing parameters. LWT 2018, 87, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.; Medina, J.; Molina, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Rodríguez, B.; Marín, R. Impact of viscoelastic and structural properties from starch-mango and starch-arabinoxylans hydrocolloids in 3D food printing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 39, 101891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Sun, F.; Kong, B. Rheological properties and 3D printability of tomato-starch paste with different types of starch. LWT 2024, 212, 116988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthamma, S.; Preethi, R.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. 4D printing of sago starch with turmeric blends: A study on pH-triggered spontaneous color transformation. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Jin, W.; Xiao, G. Improving color and digestion resistibility of 3D-printed ready-to-eat starch gels using anthocyanins. LWT 2024, 213, 116990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Holmes, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhai, X.; Huang, X.; Zou, X. Color 3D printing of pulped yam utilizing a natural pH sensitive pigment. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 46, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, A.F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Z. Microwave-induced rapid 4D change in color of 3D printed apple/potato starch gel with red cabbage juice-loaded WPI/GA mixture. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hao, F.; Tian, S.; Dong, H.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Targeting polysaccharides such as chitosan, cellulose, alginate and starch for designing hemostatic dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Niu, Q.; Wang, N.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Alginate derived Co/N doped hierarchical porous carbon microspheres for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 485, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punyanitya, S.; Thiansem, S.; Koonawoot, R.; Sontichai, W.; Suchaitanawanit, S. Preparation and Characterization of a New Absorbent Pad from Rice Starch. Mater. Sci. Forum Trans Tech Publ. 2020, 990, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.N.; de Faria, L.L.; Ferreira, D.F.; de Prado, E.M.L.; Severi, J.A.; Resende, J.A.; Villanova, J.C.O. Polymeric films containing pomegranate peel extract based on PVA/starch/PAA blends for use as wound dressing: In vitro analysis and physicochemical evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Sun, X.; Chong, C.; Ren, L.; Tan, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Xia, J.; Zhang, R. Green Starch-Based Hydrogels with Excellent Injectability, Self-Healing, Adhesion, Photothermal Effect, and Antibacterial Activity for Promoting Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 2027–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, C.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Faieta, M.; di Michele, A.; Blasi, F.; Cossignani, L.; Beccari, T.; Oliva, E.; Pittia, P.; Sergi, M. Starch-based sustainable hydrogel loaded with Crocus sativus petals extract: A new product for wound care. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 625, 122067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Bejarano, M.; Santos-Sauceda, I.; Dórame-Miranda, R.F.; Medina-Juárez, L.Á.; Gámez-Meza, N.; García-Galaz, A.; Simsek, S.; Ovando-Martínez, M. Characterization of OSA starch-based films with nut-byproducts extracts for potential application as natural wound dressing. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 13199–13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, C.; Padmaja, V.; Reddy, K.R. Extraction, phytochemical screening and comparison of the disintegrating properties of extracts obtained from natural sources among themselves and with marketed starch. Neuroquantology 2021, 19, 759. [Google Scholar]
- Alemu, R.B.; Babu, K.M.; Tesfaye, T. Studies on healthcare and hygiene textile materials treated with natural antimicrobial bioactive agents derived from plant extracts. AATCC J. Res. 2024, 11, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Versino, F.; López, O.V.; García, M.A. Biobased composites from agro-industrial wastes and by-products. Emerg. Mater. 2022, 5, 873–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zawahry, M.M.; Kamel, M.M.; Hassabo, A.G. Development of bio-active cotton fabric coated with betalain extract as encapsulating agent for active packaging textiles. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Ahmed-Farid, O.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.; Hassan, A.A.; Abdelrazek, A.M.; Khafaga, N.I.; Khattab, T.A. Green and sustainable encapsulation of Guava leaf extracts (Psidium guajava L.) into alginate/starch microcapsules for multifunctional finish over cotton gauze. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18612–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danila, A. Biopolymers in Aromatherapeutic Textiles. In Biopolymers in the Textile Industry: Opportunities and Limitations; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 147–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinropo, O.J.; Oluwafemi, A.; Olumide, A. Tensile Properties and Dye Uptake Assessment of Cotton Fabrics Sized with Corn (Zea mays) Starch and Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) Starch. Earthline J. Chem. Sci. 2021, 5, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, S.; Schwarz, I.; Đorđević, S.; Đorđević, D. Synthesis of corn starch derivatives and their application in yarn sizing. Polymers 2020, 12, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admase, A.T.; Mersha, D.A.; Kebede, A.Y. Cassava starch-based hot melt adhesive for textile industries. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Zhou, H.; Huang, W. Green flexible electronics based on starch. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, H.K.; Marinov, Y.G.; Scaramuzza, N. Review on Microstructural and Ion-conductivity Properties of Biodegradable Starch-Based Solid Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Starch-Stärke 2022, 74, 2100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizundia, E.; Kundu, D. Advances in natural biopolymer-based electrolytes and separators for battery applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2005646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Unique starch polymer electrolyte for high capacity all-solid-state lithium sulfur battery. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3796–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Mai, Z.; Ji, Z.; Du, B.; Huang, S.Y. Self-compounded, tough biohydrogels for robust self-adhesive biointerfaces. Mater. Today Phys. 2022, 29, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Baek, S.; Han, S.; Jang, H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.S. Novel eco-friendly starch paper for use in flexible, transparent, and disposable organic electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peregrino, P.P.; Cavallari, M.R.; Fonseca, F.J.; Moreira, S.G.; Sales, M.J.A.; Paterno, L.G. Starch-mediated immobilization, photochemical reduction, and gas sensitivity of graphene oxide films. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5001–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiang, H.; Li, Z.; Meng, Q.; Li, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, H.; Huang, W. Flexible and degradable multimodal sensor fabricated by transferring laser-induced porous carbon on starch film. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 8, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Lee, J.S. Controlling the resistive switching behavior in starch-based flexible biomemristors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7326–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.K.; Kamilya, T.; Acharya, S. Introduction of triboelectric positive bioplastic for powering portable electronics and self-powered gait sensor. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 5507–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, D.; Akter, F.; Akhter, S.; Siddique, A.; Lipy, E.P.; Hakim, M.; Paul, T.; Chowdhury, F.; Hossain, H.; Hossain, S. Characterization of sweet potato flakes enriched with chia seeds: Nutritional profile, bioactive compounds, sensory attributes, and cardioprotective potential. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 20, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.N.; Borges, K.C.; Matsui, K.N.; Hoskin, R.T. Spray dried acerola (Malpighia emarginata DC) juice particles to produce phytochemical-rich starch-based edible films. J. Microencapsul. 2024, 41, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumasa, T.; Apinanthanuwong, G.; Singh, J.; Kaur, L.; Tian, J.; Phongthai, S.; Tanongkankit, Y.; Issara, U.; Ogawa, Y.; Donlao, N. White mulberry leaf (Morus alba L.) infusion as a strategy to reduce starch digestibility: The influence of particle size of leaf powder. NFS J. 2024, 37, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ma, R.; Zhu, J.; Zhan, J.; Li, J.; Tian, Y. Physicochemical properties, in vitro digestibility, and pH-dependent release behavior of starch–steviol glycoside composite hydrogels. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, C.V.N.; Prabsangob, N. Black Gram (Vigna mungo L.) Husk as a Source of Bioactive Compounds: An Evaluation of Starch Digestive Enzyme Inhibition Effects. Foods 2025, 14, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, N.C.; Almeida, R.L.J.; Albuquerque, J.C.; de Lima, T.L.B.; de Sousa, F.M.; de Alcântara Silva, V.M.; Melo, M.O.P.; Filho, M.T.L.; dos Santos Silva, R.; da Silva Santos Pinheiro, L.; et al. Effect of Ultrasound and Freeze-Drying to Enhance the Extraction of Phenolic Compounds in Dragon Fruit Peels and Apply Them in Edible Starch-Based Films. Package Technol. Sci. 2024, 37, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.K.; Abou-Arab, E.A.; Mohammad, A.A. The Impact of Eggplant Peel Fortification as a Potential Source of Dietary Fibers and Phytochemicals on the Rheological Properties and Quality of Pan Bread. Egypt. J. Chem. 2025, 68, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfenstein, A.A.; Dias, Ê.R.; Reis, I.M.A.; Freitas, E.E.S.; Biondi, I.B.; Branco, C.R.C.; Almeida, J.R.G.d.S.; Cruz, R.S.; Branco, A.; Camilloto, G.P. Mucoadhesive oral film based on high methoxyl pectin and phosphated cassava starch incorporated with Calendula officinalis extract. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 102, 106428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Singh, B.; Srivastava, Y.; Chahal, T.S. Grapefruit albedo-incorporated pasta: Effect on the phytochemical, functional, textural, cooking and sensorial properties of semolina pasta. Food Meas. 2024, 18, 8530–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin-Babaoglu, H.; Aydın, H.; Kumas, R.; Arslan-Tontul, S. Enhancing nutritional and functional properties of rice starch by modification with Matcha extract. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethadevi, R.; Arivuchudar, R. Exploring the Nutritional and Pharmaceutical Potentiality of Edible Wrappers Formulated using Natural Colorants. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2024, 17, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafeuillee, C.; Maharaj, R. A preliminary investigation of the properties of plantain starch-chitosan composite films containing Panadol leaf extracts. Discov. Food 2025, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.F.; Silva, C.W.C.; Silva, B.P.; Britto-Costa, P.H.; Costa, C.S.; Otubo, L.; Carbonari, A.W.; Cabrera-Pasca, G.A. Enhancing Cassava Starch Bioplastics with Vismia guianensis Alcoholic Extract: Characterization with Potential Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Q.; Xie, F.; Zhang, D.; He, Z.; Cheng, S.; Paiva, Y.F.; Cai, J. Self-reinforced multifunctional starch nanocomposite film for litchi fruit postharvest preservation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


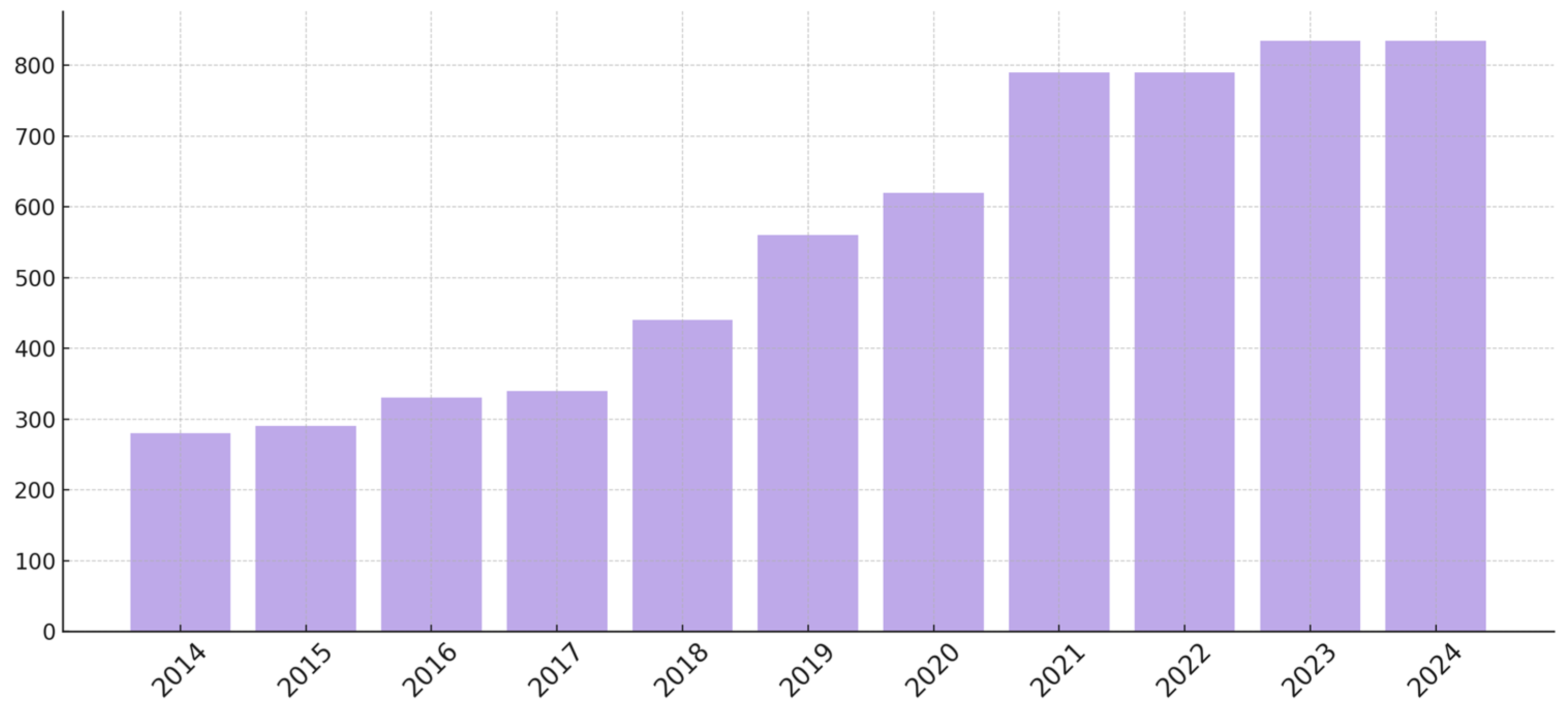


| Starch/Polyphenol Source | Observed Results | Potential Applications | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sweet potato flakes enriched with chia seeds. | Reduced harmful lipids and liver enzyme levels. Preserved heart tissue and reduced inflammatory markers. Showed significant nutritional and cardioprotective benefits. | Therapeutic foods. | [134] |
| Acerola (Malpighia emarginata DC) cassava starch. | Incorporation of polyphenols and increased radical scavenging activity. | Biodegradable edible films. | [135] |
| Japonica rice (cv. Koshihikari) with Morus alba L. leaf powder. | Reduction of glycemic index; decrease in starch particle size. | Functional beverage for reducing postprandial hyperglycemia. | [136] |
| Maize starch–steviol glycoside. | Improved the sensory quality, enhanced the release efficiency of starch hydrogel, and promoted the gelatinization and gelation of starch. | Development of sugar-free starchy foods. | [137] |
| Black gram husk and starch-soluble. | Increased the resistant starch content; reduction of estimated glucose index. | Functional ingredient with antioxidant activity. | [138] |
| Rice starch and Dragon Fruit Peels. | Low solubility, low water vapor permeability, and higher levels of total phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity. | Edible Starch-Based Films. | [139] |
| Eggplant peels, wheat flour. | Increased water absorption, reduced bread volume, and delayed the staling of baked pan bread. | Functional or enriched fiber foods. | [140] |
| High methoxyl pectin (HMP) and phosphated cassava starch (PCS), combined with Calendula officinalis extract (CoE). | Strong interfacial adhesion between HMP and PCS, prolonged disintegration time, higher percentage of elongation, and mucoadhesiveness. | Mucoadhesive oral applications. | [141] |
| Semolina pasta and grapefruit albedo. | Reduced cooking time; weaker matrix due to fiber increment. | Functional foods. | [142] |
| Rice starch by Matcha extract (powder of the leaf of Camellia sinensis). | Solubility and swelling power of starch were increased; reduced the Glycemic Index and resistant starch was increased. | Functional foods. | [143] |
| Wheat flour, potato starch, and rice flour, purple cabbage, black grapes, holy basil, pumpkin, carrot, and beetroot. | Best regarding appearance, color, texture, taste, flavor, and overall acceptability. | Eco-friendly edible wrappers. | [144] |
| Plantain pulp starch and chitosan, Plectranthus barbatus and Plectranthus caninus extracts. | Increased opacity, density, and moisture content alongside decreased swelling indices, and gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria inhibition. | Sustainable food packaging. | [145] |
| Cassava starch and Vismia guianensis. | Improved flexibility and stability of the bioplastic, with significant improvements in mechanical and thermal properties. | Potential use in biomedical applications. | [146] |
| Corn starch, Selenium nanoparticles, litchi fruit. | Reduced dehydration, inhibited microbe growth, and biodegradability. | Multipurpose active food packaging. | [147] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lara, E.Z.; Gomes, J.P.; Figueirêdo, R.M.F.d.; Paiva, Y.F.; Silva, W.P.d.; Queiroz, A.J.d.M.; Hamawand, I. Green Starches: Phytochemical Modification and Its Industrial Applications—A Review. Processes 2025, 13, 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072120
Lara EZ, Gomes JP, Figueirêdo RMFd, Paiva YF, Silva WPd, Queiroz AJdM, Hamawand I. Green Starches: Phytochemical Modification and Its Industrial Applications—A Review. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLara, Emerson Zambrano, Josivanda Palmeira Gomes, Rossana Maria Feitosa de Figueirêdo, Yaroslávia Ferreira Paiva, Wilton Pereira da Silva, Alexandre José de Melo Queiroz, and Ihsan Hamawand. 2025. "Green Starches: Phytochemical Modification and Its Industrial Applications—A Review" Processes 13, no. 7: 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072120
APA StyleLara, E. Z., Gomes, J. P., Figueirêdo, R. M. F. d., Paiva, Y. F., Silva, W. P. d., Queiroz, A. J. d. M., & Hamawand, I. (2025). Green Starches: Phytochemical Modification and Its Industrial Applications—A Review. Processes, 13(7), 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072120








