Simulation and Parametric Evaluation of Pb (II) Adsorption in a Biomass-Packed Bed Using Isothermal Freundlich–LDF and Langmuir II–LDF Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biomaterial Preparation and Experimental Adsorption Tests
2.2. Simulation and Adsorption Column Configuration
- General: This section requires selecting the discretisation method to run the adsorption process simulation. This study employed the Upwind Differencing Scheme 1 (UDS1) method, which utilised 10 nodes.
- Mass/Momentum Balance: Here, the basic assumptions regarding axial dispersion in the liquid phase are defined, as well as how pressure drop is handled in the adsorption column model and whether velocity remains constant or varies along the column. For this study, it was assumed that there is no pressure drop, convection occurs solely in the liquid phase, and velocity remains constant.
- Kinetic Model: This section determines the kinetic model used to describe the rate of the adsorption process. In this case, the linear driving force (LDF) model was selected. This model assumes that mass transfer is driven by a function of concentration and describes the rate at which the contaminant is adsorbed [20].
- Energy Balance: This section defines how the energy balance is performed. For this case, an isothermal energy balance was applied.
2.3. Parametric Evaluation in the Adsorption Column
2.4. Mathematical Fundamentals
3. Results and Discussion
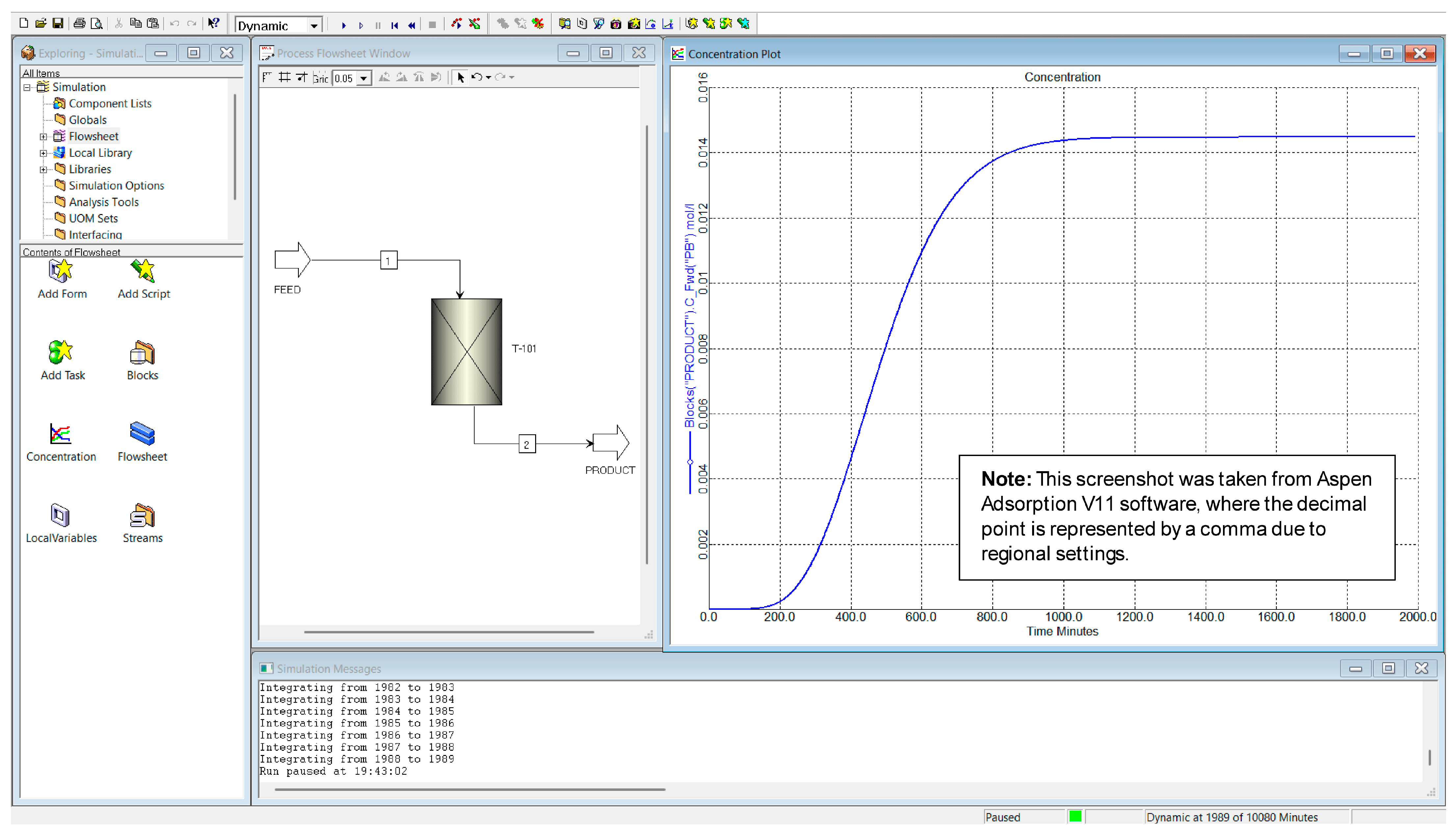
3.1. Establishment of Baseline Conditions for Column Simulation
3.2. Data Obtained from the Adsorption Process Simulation
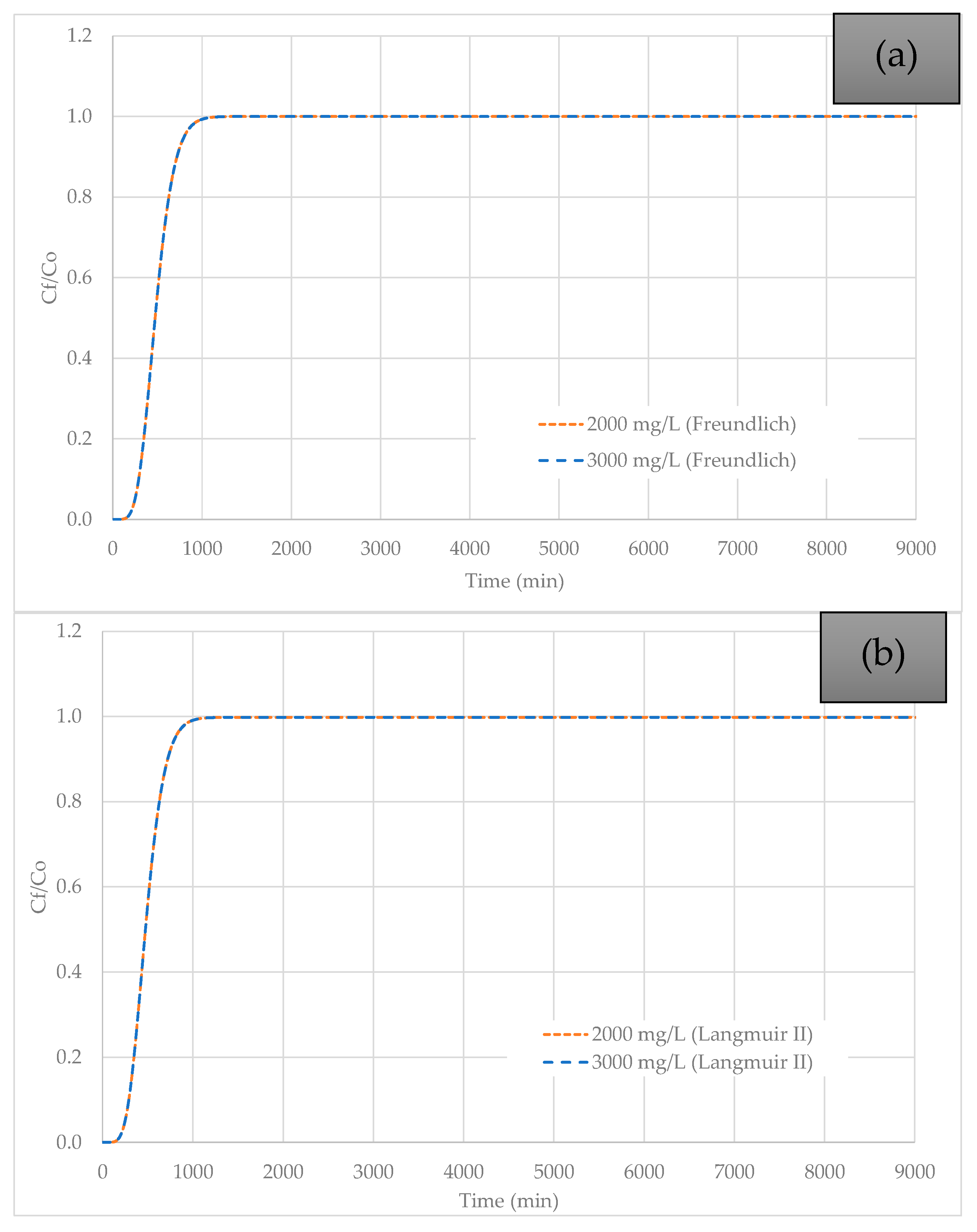
3.3. Effect of Initial Pb (II) Concentration Variation
3.4. Effect of Inlet Flow Rate Variation
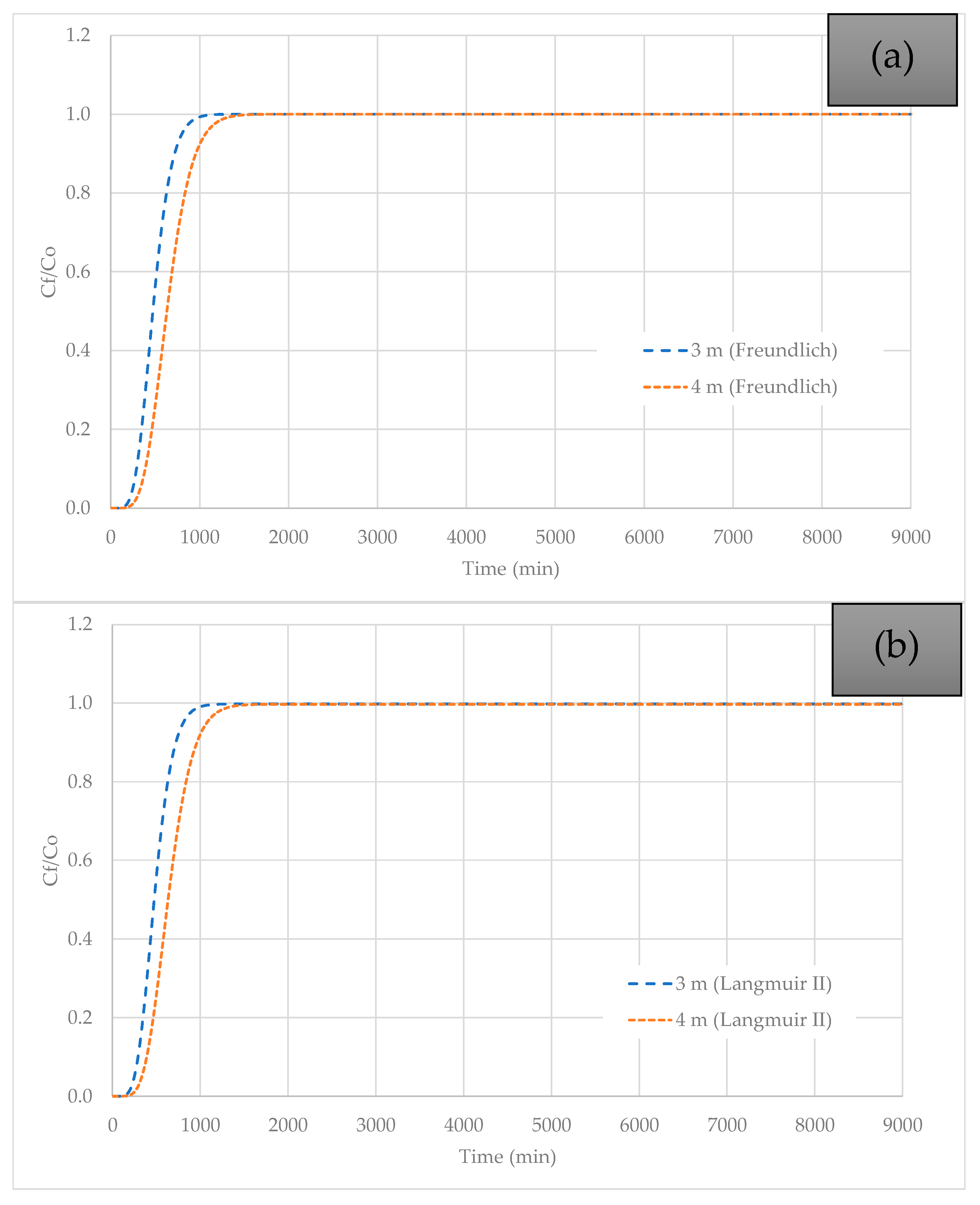
3.5. Effect of Column Height Variation
3.6. Comparison with Other Results Found in the Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Adsorption capacity of contaminant (mg/g) | |
| Freundlich constant indicating adsorption capacity ((mg/g) (mL/g)n) | |
| Concentration of contaminant in solution at equilibrium (mg/L) | |
| Effect of initial concentration on adsorption capacity. | |
| Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | |
| Maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g) | |
| and | Langmuir II affinity constants (bar−1) |
| ∆H | Isosteric heat of adsorption of the solution (J/mol) |
| Gas constant (J/mol*K) | |
| system pressure (bar) | |
| Solution temperature (K) | |
| Porosity of the column | |
| Longitudinal dispersion coefficient (m2/s) | |
| Bed length (m) | |
| Amount of metal ions adsorbed by the adsorbent (mg/g) | |
| Contaminant concentration in the liquid phase (mg/L) | |
| Apparent density of the adsorbent (g/cm3) | |
| Speed at which the fluid passes through the bed (m/s). | |
| Concentration adsorbed on the solid for component k (mg/g). | |
| Amount that should be adsorbed if the system were in instantaneous equilibrium with the fluid phase (mg/g). | |
| Mass transfer coefficient (1/s). |
References
- Ismail, W.N.W.; Syah, M.I.A.I.; Muhet, N.H.A.; Bakar, N.H.A.; Yusop, H.M.; Samah, N.A. Adsorption Behavior of Heavy Metal Ions by Hybrid Inulin-TEOS for Water Treatment. Civ. Eng. J. 2022, 8, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, N.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, T. Pollution, Cumulative Ecological Risk and Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Water Bodies and River Sediments near the Luanchuan Molybdenum Mining Area in the Xiaoqinling Mountains, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhobi, S.H.; Neupane, D.; Koirala, S.; Das Mulmi, D. Waste Tea as Absorbent for Removal of Heavy Metal Present in Contaminated Water. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ouyang, X.K.; Yang, L.Y. Adsorption of Lead Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Porous Cellulose Nanofiber–Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Beads. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 324, 115122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Dwivedi, S.K.; Oh, S. A Critical Review on Lead Removal from Industrial Wastewater: Recent Advances and Future Outlook. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.; Das, A.P. Lead Pollution: Impact on Environment and Human Health and Approach for a Sustainable Solution. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Afyuni, M.; Khademi, H.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Schulin, R. Mapping Risk of Cadmium and Lead Contamination to Human Health in Soils of Central Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 347, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.K.; Salama, R.S.; Mostafa, M.M.M. Natural-based coagulants/flocculants as sustainable market-valued products for industrial wastewater treatment: A review of recent developments. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 19335–19355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinpally, S.; Kolla, A.; Kainthola, J.; Kodali, R.; Vemuri, J. A state-of-the-art review of the electrocoagulation technology for wastewater treatment. Water Cycle 2023, 4, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Iqbal, M.J.; Hussain, M. A State-of-the-Art Review on Wastewater Treatment Techniques: The Effectiveness of Adsorption Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9050–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, M.; Azeh, Y.; Mathew, J.; Umar, M.; Abdulhamid, Z.; Muhammad, A. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm Models: A Review. Caliphate J. Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukmana, H.; Bellahsen, N.; Pantoja, F.; Hodur, C. Adsorption and Coagulation in Wastewater Treatment—Review. Progress. Agric. Eng. Sci. 2021, 17, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwo, A.; Chinyere, N. Sorption Characteristics for Multiple Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions Using Activated Carbon from Nigerian Bamboo. J. Mater. Sci. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Balasubramanian, R. Use of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for removal of heavy metals from water and wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Khairulet, I.; Hasan, M.A.; Khan, H.M.J.; Khan, M.A.R.; Deb, A.; Al Raihan, M.; Rahman, M.W. Adsorption of crystal violet dye by coconut husk powder: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics perspectives. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, M.R. Physical characteristics and the Freundlich model of adsorption and desorption isotherm for fipronil in six types of Egyptian soil. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2023, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Tovar, C.; Villabona-Ortíz, A.; González-Delgado, Á. Adsorption Study of Continuous Heavy Metal Ions (Pb2+, Cd2+, Ni2+) Removal Using Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) Pod Husks. Materials 2022, 15, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.M.; Farghali, A.A.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Selim, A.Q.; Seliem, M.K. Effective removal of Cr(VI) and methyl orange by nano magnetite loaded starch/muscovite biocomposite: Characterization, experiments, advanced modeling, and physicochemical parameters interpretation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Upadhyay, U.; Sreedhar, I.; Anitha, K.L. Simulation Studies of Cu(II) Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Olive Stone. Clean. Mater. 2022, 5, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, S.; Mandal, D.; Dabhade, P. LDF Based Parametric Optimization to Model Fluidized Bed Adsorption of Trichloroethylene on Activated Carbon Particles. Particuology 2022, 65, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhang, D.; Na, P.; Fu, B. The Removal and Capture of CO2 from Biogas by Vacuum Pressure Swing Process Using Silica Gel. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 27, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, R. Derivation of Pseudo-First-Order, Pseudo-Second-Order and Modified Pseudo-First-Order Rate Equations from Langmuir and Freundlich Isotherms for Adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavado-Meza, C.; De la Cruz-Cerrón, L.; Lavado-Puente, C.; Gamarra-Gómez, F.; Sacari-Sacari, E.; Dávalos-Prado, J.Z. Effective Removal of Cd(II) from Aqueous Solutions Using Theobroma cacao Agro-Industrial Waste. Molecules 2023, 28, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.; Bali, G.; Sarangi, S.K. Effect of Lead on Metallothionein Concentration in Lead-Resistant Bacteria Bacillus Cereus Isolated from Industrial Effluent. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 15966–15972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.; Bali, G. Lead biosorption by a bacterium isolated from industrial effluents. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 4, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, U.; Gupta, S.; Agarwal, A.; Sreedhar, I.; Anitha, K.L. Adsorptive removal of Cd2+ ions using dolochar at an industrial-scale process optimization by response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 8403–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Delgado, Á.D.; Tejada-Tovar, C.; Villabona-Ortíz, A. Computer-aided Modeling and Evaluation of a Packed Bed for Chromium (vi) Removal using Residual Biomass of Theobroma cacao L. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 92, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Manzar, M.S.; Khan, S.; Al-Sharafi, M.A.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.S.P.; Ullah, N. Enhanced adsorption of bisphenol-A from water through the application of isocyanurate based hyper crosslinked resin. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 395, 123861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahia, F.; O’Neill, K.E. Enhanced voidage correlations for packed beds of various particle shapes and sizes. Part. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, J.; Tejada, C.; Villabona, A.; Arrieta, A. Adsorción de Plomo y Cadmio En Sistema Continuo de Lecho Fijo Sobre Residuos de Cacao. Rev. ION 2017, 29, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koua, B.K.; Koffi, P.M.E.; Gbaha, P. Evolution of Shrinkage, Real Density, Porosity, Heat and Mass Transfer Coefficients during Indirect Solar Drying of Cocoa Beans. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2019, 18, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Tovar, C.; Lopez-Cantillo, K.; Vidales-Hernandez, K.; Villabona-Ortiz, A.; Acevedo-Correa, D. Kinetics and Bioadsortion Equilibrium of Lead and Cadmium in Batch Systems with Cocoa Shell (Theobroma cacao L.). Contemp. Eng. Sci. 2018, 11, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- González-Delgado, Á.D.; Tejada-Tovar, C.; Villabona-Ortíz, A. Parametric Sensitivity Analysis of Chromium (Vi) Adsorption Using Theobroma cacao L Biomass via Process Simulation. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 92, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liao, X.; Chen, S.; Ou, X.; Sun, S.; Liang, J.; Cai, Y.; Xie, W.; et al. Simultaneous and Efficient Removal of Organic Ni and Cu Complexes from Electroless Plating Effluent Using Integrated Catalytic Ozonation and Chelating Precipitation Process in a Continuous Pilot-Scale System. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xiao, J.; Bénard, P.; Chahine, R. Single- and Double-Bed Pressure Swing Adsorption Processes for H2/CO Syngas Separation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 26405–26418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Abd, A.; Roslee Othman, M. Biogas Upgrading to Fuel Grade Methane Using Pressure Swing Adsorption: Parametric Sensitivity Analysis on an Industrial Scale. Fuel 2022, 308, 121986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Hameed, B.H.; Almomani, F.A.; Usman, M.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Khraisheh, M. Dynamic Simulation of Lead(II) Metal Adsorption from Water on Activated Carbons in a Packed-Bed Column. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 8283–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, A.; Martín-Lara, M.A.; Osegueda, O.; Castillo, V.; Blázquez, G. Scale-up of a packed bed column for wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, H.A.; Zein, S.H.; Holliday, M.C.; Jabbar, K.J.; Ahmed, U.; Jalil, A.A. Comparison of activated carbon and low-cost adsorbents for removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol from wastewater using Aspen Adsorption and response surface methodology. Environ. Technol. 2024, 45, 3029–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption column diameter (m) | 1 | [19] |
| Adsorption column porosity (m3 of void/m3 of column) | 0.67 | [29] |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 0.0365 | [30] |
| Mass transfer coefficient (1/s) | 1.88 × 10−7 | [31] |
| Total void porosity | 0.4 | [29] |
| Freundlich Isotherm Model Parameters | ||
| (mg g−1 (mg L−1)1/n) | 0.453 | [32] |
| 1.476 | [32] | |
| Langmuir II Isotherm Model Parameters | ||
| (mg/g) | 46930.9 | [21,23] |
| (bar−1) | 8.18 × 10−7 | [21,23] |
| (J/mol) (J/mol*K)−1 | 1072.83 | [21,23] |
| (bar−1) | 0.0000318 | [21,23] |
| (K) | 303.15 | [21,23] |
| (bar) | 1 | [21,23] |
| Flow Rate (m3/d) | Column Height (m) | Concentration (mg/L) | Breakthrough Time (min) | Saturation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 3 | 2000 | 492 | 2253 |
| 4 | 2000 | 658 | 2936 | |
| 3 | 3000 | 935 | 1971 | |
| 4 | 3000 | 1244 | 2560 | |
| 250 | 3 | 2000 | 294 | 1371 |
| 4 | 2000 | 393 | 1823 | |
| 3 | 3000 | 563 | 1223 | |
| 4 | 3000 | 749 | 1609 |
| Flow Rate (m3/d) | Column Height (m) | Concentration (mg/L) | Breakthrough Time (min) | Saturation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 3 | 2000 | 492 | 2256 |
| 4 | 2000 | 659 | 2938 | |
| 3 | 3000 | 449 | 1962 | |
| 4 | 3000 | 601 | 2548 | |
| 250 | 3 | 2000 | 294 | 1370 |
| 4 | 2000 | 393 | 1825 | |
| 3 | 3000 | 267 | 1216 | |
| 4 | 3000 | 358 | 1596 |
| Parameter | Pb (II) | Pb (II) | Pb (II) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Olive tree pruning | Activated carbons | Theobroma cacao L. |
| Initial concentration (mg/L) | 100 | 500 | 3000 |
| Inlet flow rate (m3/day) | 128.04 | 42.68 | 250 |
| Bed height (m) | 2.26 | 0.4 | 3 |
| Rupture time (min) | 201.6 | 18 | 563 |
| Saturation time (min) | 503 | - | 1223 |
| Source | [38] | [37] | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villabona-Ortíz, A.; Coronado-Hernández, O.E.; Tejada-Tovar, C. Simulation and Parametric Evaluation of Pb (II) Adsorption in a Biomass-Packed Bed Using Isothermal Freundlich–LDF and Langmuir II–LDF Models. Processes 2025, 13, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061655
Villabona-Ortíz A, Coronado-Hernández OE, Tejada-Tovar C. Simulation and Parametric Evaluation of Pb (II) Adsorption in a Biomass-Packed Bed Using Isothermal Freundlich–LDF and Langmuir II–LDF Models. Processes. 2025; 13(6):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061655
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillabona-Ortíz, Angel, Oscar E. Coronado-Hernández, and Candelaria Tejada-Tovar. 2025. "Simulation and Parametric Evaluation of Pb (II) Adsorption in a Biomass-Packed Bed Using Isothermal Freundlich–LDF and Langmuir II–LDF Models" Processes 13, no. 6: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061655
APA StyleVillabona-Ortíz, A., Coronado-Hernández, O. E., & Tejada-Tovar, C. (2025). Simulation and Parametric Evaluation of Pb (II) Adsorption in a Biomass-Packed Bed Using Isothermal Freundlich–LDF and Langmuir II–LDF Models. Processes, 13(6), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13061655








