6-DoF Grasp Detection Method Based on Vision Language Guidance
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel visual language model is introduced, which enhances the multi-head attention mechanism to optimize the training process and improve the model’s recognition and detection capabilities.
- (2)
- A new 6-DoF grasp model is proposed to address the challenges of grasping small and multi-scale targets. This model incorporates a point cloud feature encoder and multiple sampling mechanisms to enhance its ability to grasp small objects.
- (3)
- The end-to-end interactive grasp of small target objects is achieved by integrating the visual language model with the 6-DoF grasp and detection model. A real grasp experiment is conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
2. Related Works
2.1. Visual Language Model
2.2. Grasp Detection Model
3. Method
3.1. Overall Framework
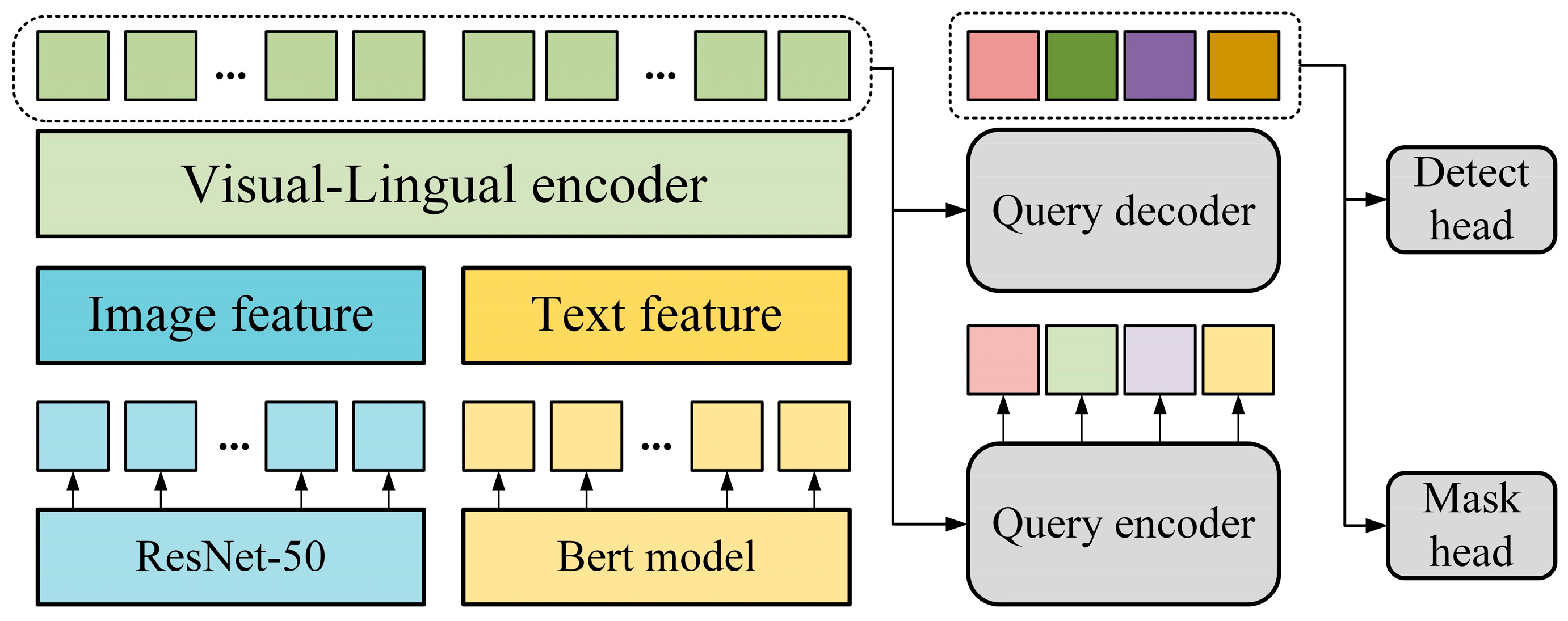
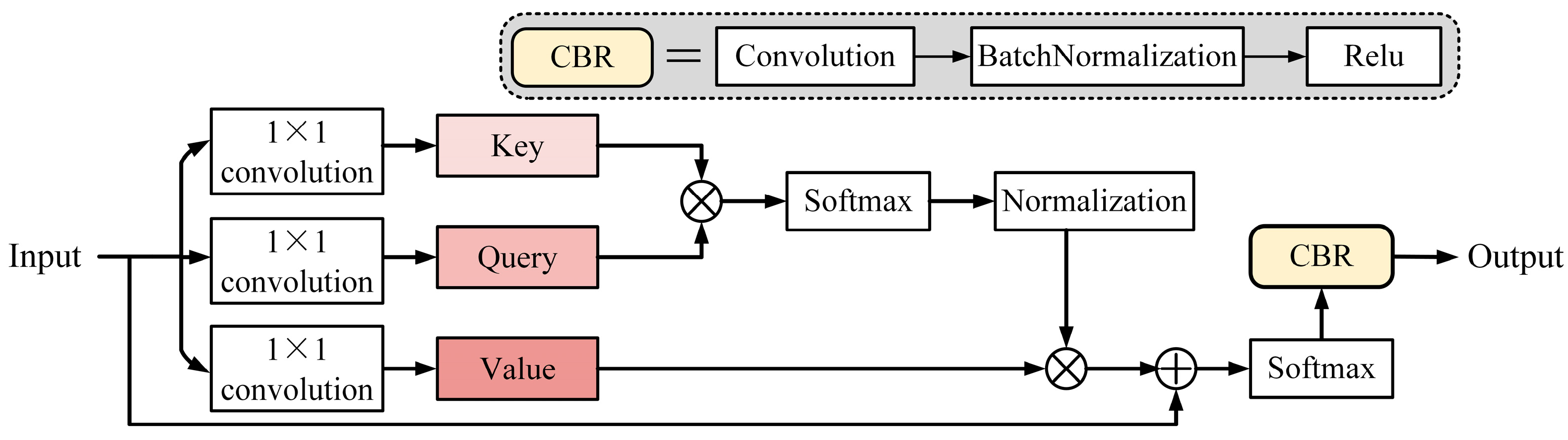
3.2. Improved Visual Language Model
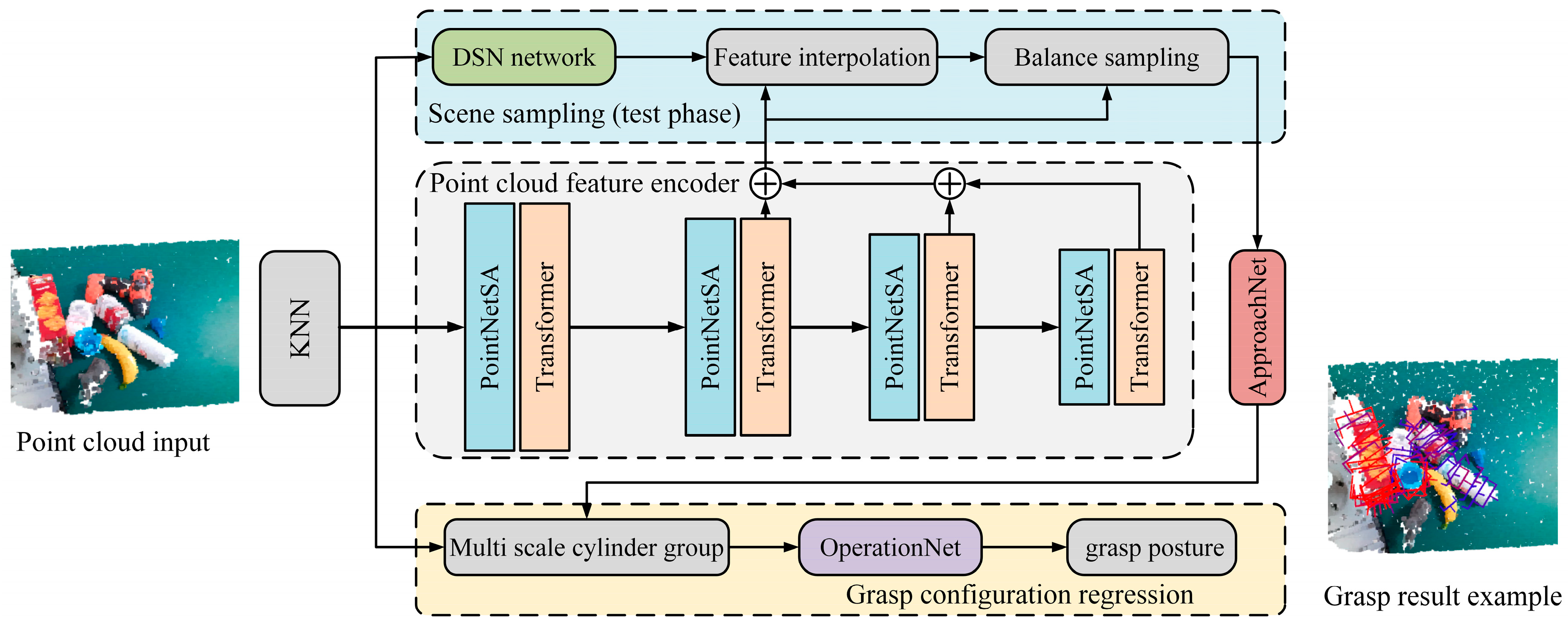
3.3. Improved 6-DoF Grasp Detection Model
3.4. The Proposed Grasp Detection Method
- (1)
- Obtain RGB and depth images to be grasped and describe the objects to be grasped in the scene using English text, including the target object’s type, color, and shape.
- (2)
- The improved visual language model uses RGB images and text as inputs to locate the position of the target object. The multi-head attention mechanism introduced in the model can improve the stability of model training and enhance the model’s feature extraction ability. The improved visual language model can predict segmentation masks and object detection images to guide the subsequent model’s grasp posture selection.
- (3)
- The improved grasp detection model reconstructs the scene point cloud using RGB and depth maps. After scene segmentation, cylindrical feature sampling, and point cloud feature extraction, it predicts all graspable poses in the scene.
- (4)
- We use the detection results of the visual language model to screen all graspable poses in the scene and obtain the optimal gripping pose through nonmaximum suppression and collision detection.
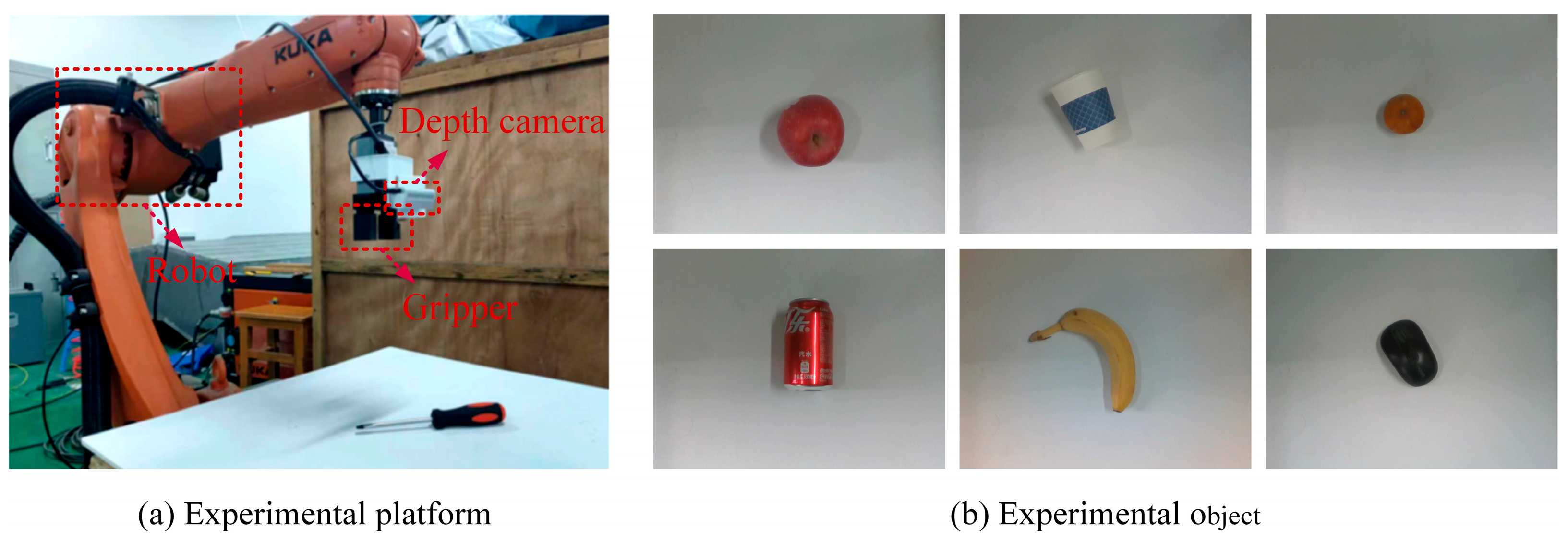
4. Implementation Details
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Loss Calculation and Training Details
5. Results
5.1. Experiments Based on Dataset
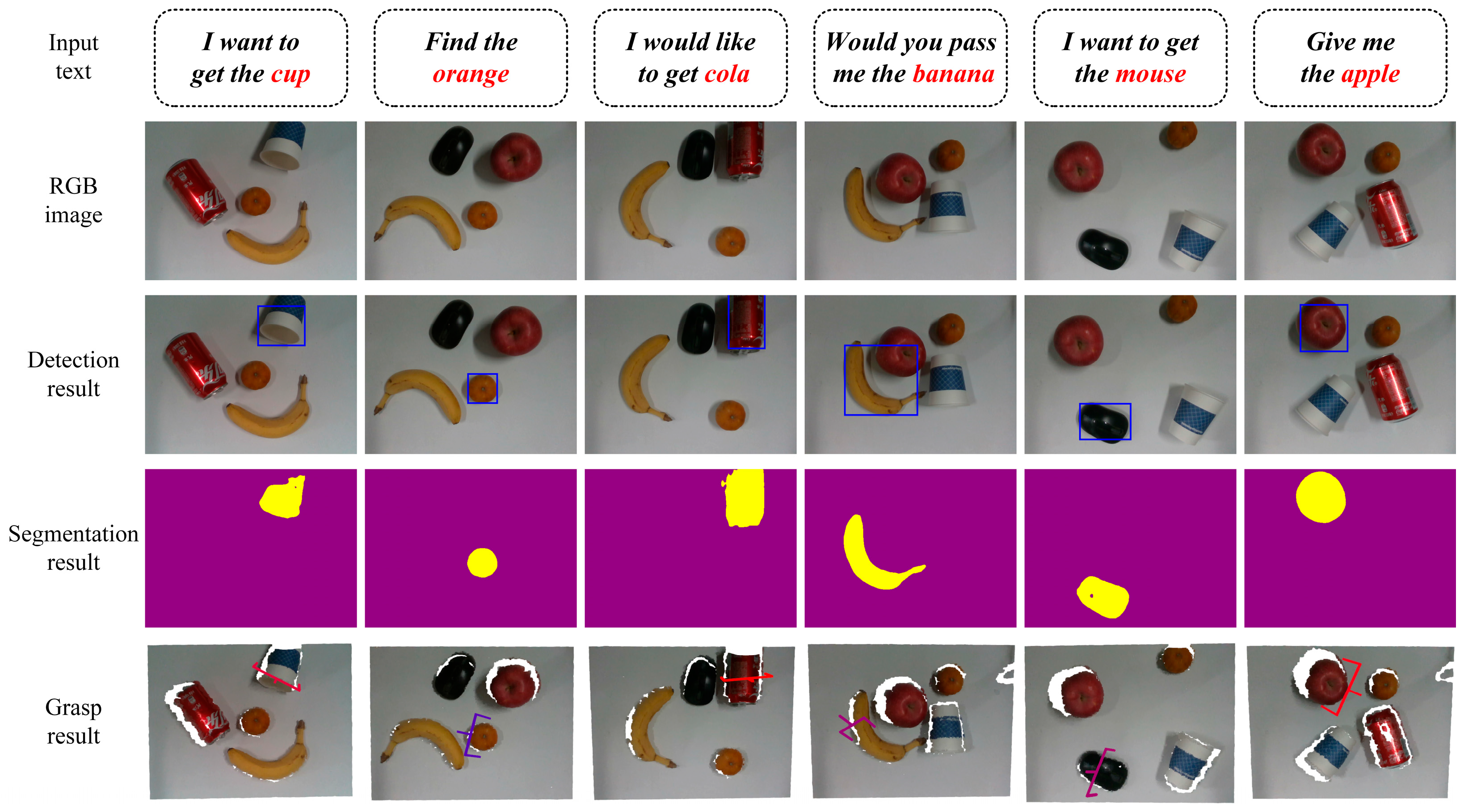
5.2. Real Grasp Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 6-DoF | Six degrees of freedom |
| DyT | Dynamic Tanh |
| IoU | Intersection over union |
| TD | Target detection |
| OS | Object segmentation |
References
- Fu, K.; Dang, X. Light-weight convolutional neural networks for generative robotic grasping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 6696–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Xu, R.; Vela, P. Real-world multiobject, multigrasp detection. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3355–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarz, J.; Tan, J.; Finn, C.; Kalakrishnan, M.; Pastor, P.; Levine, S. How to train your robot with deep reinforcement learning: Lessons we have learned. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2021, 40, 698–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Ma, X.; Li, S.; Michael, G.; Song, T.; Bin, F. Pointnetgpd: Detecting grasp configurations from point sets. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 3629–3635. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrev, Y.; Flores, S.; Vossiek, M. Multi-modal sensor fusion for indoor mobile robot pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Savannah, GA, USA, 11–14 April 2016; pp. 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, D.; Huaping, L.; Fuchun, S.; Min, H. Self-supervised learning for alignment of objects and sound. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 1588–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, K.; Arie, H.; Suga, Y.; Ogata, T. Multimodal integration learning of robot behavior using deep neural networks. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2014, 62, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shridhar, M.; Mittal, D.; Hsu, D. Ingress: Interactive visual grounding of referring expressions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Lin, Y.; Vela, p. A joint network for grasp detection conditioned on natural language commands. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 4576–4582. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Lan, X. Visual manipulation relationship detection based on gated graph neural network for robotic grasping. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 1404–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Deng, B.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Vl-grasp: A 6-dof interactive grasp policy for language-oriented objects in cluttered indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Huebner, K.; Kyrki, V.; Kragic, D. Learning task constraints for robot grasping using graphical models. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 1579–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Murali, A.; Liu, W.; Marino, K.; Chernova, S.; Gupta, A. Same object, different grasps: Data and semantic knowledge for task-oriented grasping. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.06431. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Huang, D.; Ge, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. Graspgpt: Leveraging semantic knowledge from a large language model for task-oriented grasping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 7551–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Bansal, M.; Berg, T. Mattnet: Modular attention network for referring expression comprehension. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1307–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja, V.; Morariu, V.; Davis, L. Modeling context between objects for referring expression understanding. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.00525. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Xu, H.; Rohrbach, M.; Feng, J.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Natural language object retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4555–4564. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Greff, K.; Srivastava, R.; Koutník, J.; Steunebrink, B.; Schmidhuber, J. LSTM: A search space odyssey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 28, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2023, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Liu, W.; Li, B.; Hu, W. Improving visual grounding with visual-linguistic verification and iterative reasoning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 9499–9508. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Encoder fusion network with co-attention embedding for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15506–15515. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Sigal, L. Referring transformer: A one-step approach to multi-task visual grounding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 19652–19664. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Cao, L.; Wu, C.; Deng, C.; Ji, R. Multi-task collaborative network for joint referring expression comprehension and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10034–10043. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, I.; Lee, H.; Saxena, A. Deep learning for detecting robotic grasps. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumra, S.; Joshi, S.; Sahin, F. Antipodal robotic grasping using generative residual convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 9626–9633. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. Learning robust, real-time, reactive robotic grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wang, C.; Gou, M.; Lu, C. Graspnet-1billion: A large-scale benchmark for general object grasping. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11444–11453. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Liang, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J. Improving object grasp performance via transformer-based sparse shape completion. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2022, 104, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Huang, D. Towards scale balanced 6-dof grasp detection in cluttered scenes. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2004–2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq, M.; Gu, Z. Deep residual learning for image recognition: A survey. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Ma, J. HybridNorm: Towards Stable and Efficient Transformer Training via Hybrid Normalization. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.04598. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.02413. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D.; Conceicao, A. A Fast 6DOF Visual Selective Grasping System Using Point Clouds. Machines 2023, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollar, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Fang, H.S.; Gou, M.; Fang, H.; Gao, J.; Lu, C. Graspness discovery in clutters for fast and accurate grasp detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 15964–15973. [Google Scholar]
- Ten, A.; Gualtieri, M.; Saenko, K.; Platt, R. Grasp pose detection in point clouds. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2017, 36, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kong, T.; Chu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, L. Simultaneous semantic and collision learning for 6-dof grasp pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 3571–3578. [Google Scholar]




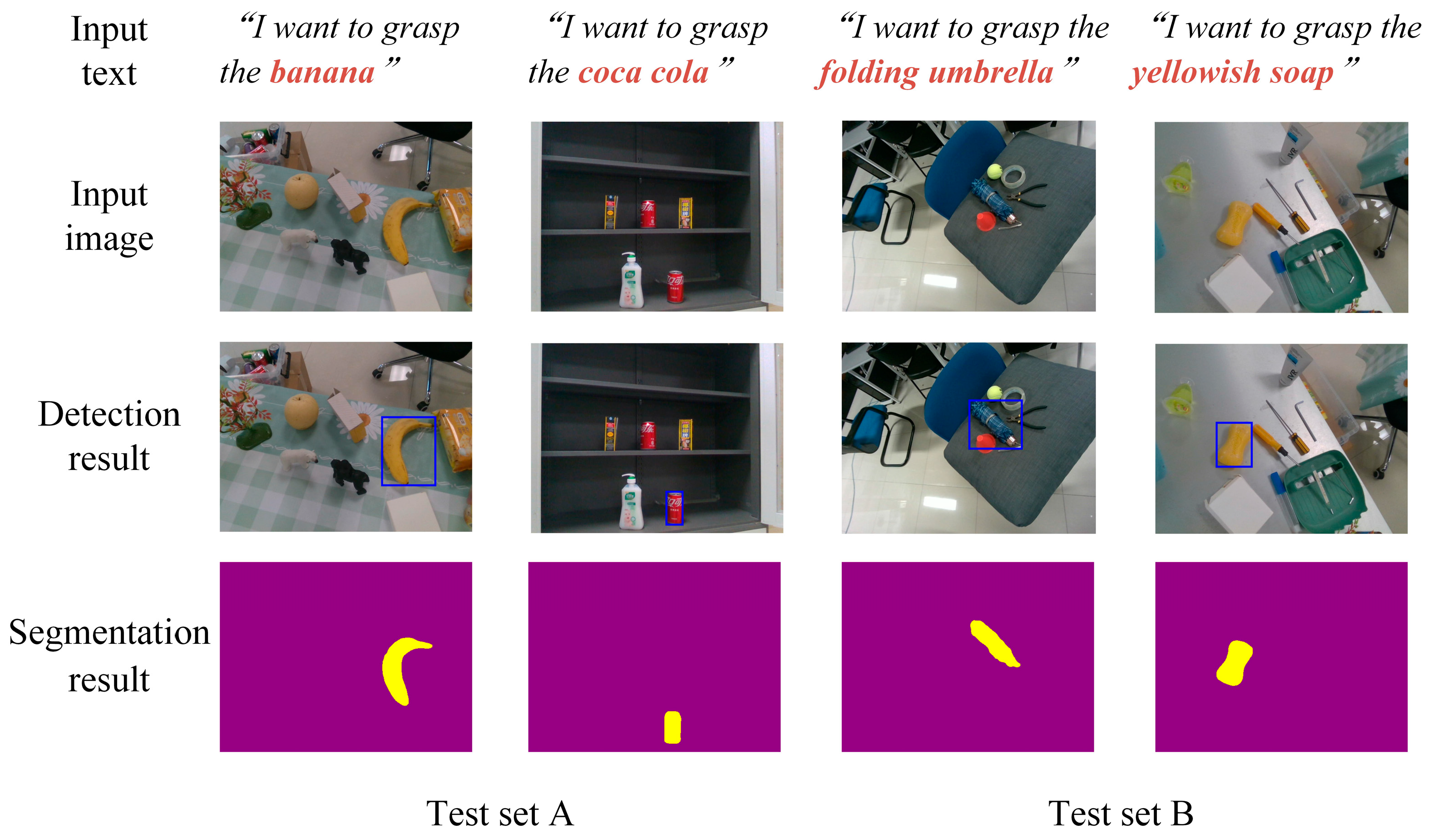

| Method | Backbone Network | Task | Test Set A | Test Set B | Params/MB | Time/ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VL-Grasp [11] | ResNet50 | TD | 86.92 | 54.12 | 127.16 | 44.37 |
| OS | 85.46 | 61.49 | ||||
| ResNet101 | TD | 85.62 | 55.97 | - | - | |
| OS | 83.89 | 60.72 | ||||
| our | ResNet50 | TD | 87.96 | 55.19 | 128.36 | 65.53 |
| OS | 88.23 | 62.44 |
| Method | Seen | Similar | Novel | Params /MB | Time /ms | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP0.8 | AP0.4 | AP | AP0.8 | AP0.4 | AP | AP0.8 | AP0.4 | |||
| GPD [40] | 22.87 | 28.53 | 12.84 | 21.33 | 27.83 | 9.64 | 8.24 | 8.89 | 2.67 | - | - |
| PointnetGPD [4] | 25.96 | 33.01 | 15.37 | 22.68 | 29.15 | 10.76 | 9.23 | 9.89 | 2.74 | - | - |
| GraspNet-1B [28] | 27.56 | 33.43 | 16.95 | 26.11 | 34.18 | 14.23 | 10.55 | 11.25 | 3.98 | 1.03 | 296 |
| Li et al. [41] | 36.55 | 47.22 | 19.24 | 28.36 | 36.11 | 10.85 | 14.01 | 16.56 | 4.82 | - | |
| GSNet [39] | 67.12 | 78.46 | 60.90 | 54.81 | 66.72 | 46.17 | 24.31 | 30.52 | 14.23 | - | - |
| Ma et al. [30] | 63.83 | 74.25 | 58.66 | 58.46 | 70.05 | 51.32 | 24.63 | 31.05 | 12.85 | 1.14 | 43.29 |
| our | 65.13 | 76.15 | 60.24 | 59.87 | 70.90 | 52.29 | 25.10 | 31.67 | 13.17 | 1.58 | 87.83 |
| Method | Seen | Similar | Novel | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APS | APM | APL | APS | APM | APL | APS | APM | APL | |
| Baseline | 9.44 | 45.99 | 54.13 | 5.15 | 35.54 | 47.82 | 4.91 | 15.26 | 19.83 |
| Ma et al. | 18.29 | 52.60 | 64.34 | 10.03 | 42.77 | 57.09 | 9.29 | 18.74 | 24.36 |
| Ours | 19.93 | 55.39 | 70.65 | 10.65 | 45.84 | 64.38 | 10.05 | 20.53 | 27.05 |
| Scene | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grasp times | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Successful grasp | 18 | 19 | 17 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Grasp success rate | 114/120 = 95.00% | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, R.; Liu, T. 6-DoF Grasp Detection Method Based on Vision Language Guidance. Processes 2025, 13, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051598
Li X, Chen J, Wu R, Liu T. 6-DoF Grasp Detection Method Based on Vision Language Guidance. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051598
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xixing, Jiahao Chen, Rui Wu, and Tao Liu. 2025. "6-DoF Grasp Detection Method Based on Vision Language Guidance" Processes 13, no. 5: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051598
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, J., Wu, R., & Liu, T. (2025). 6-DoF Grasp Detection Method Based on Vision Language Guidance. Processes, 13(5), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051598








