Research on Lightweight Citrus Leaf Pest and Disease Detection Based on PEW-YOLO
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose an improved real-time citrus leaf pest and disease detection model, PEW-YOLO, based on YOLOv11. The model is specifically designed to address the challenges of detecting citrus leaf diseases and pests under complex natural environmental conditions.
- (2)
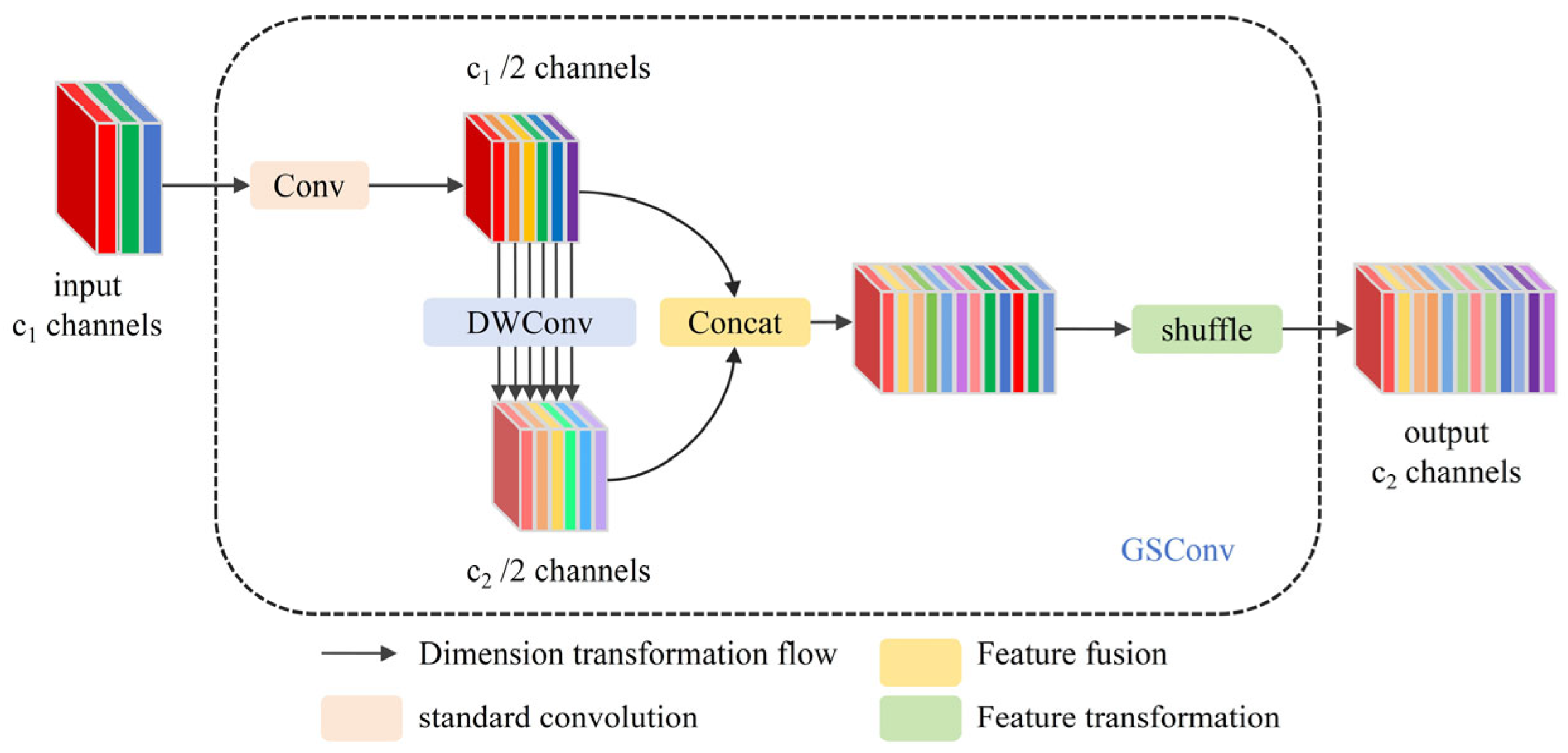
- A lightweight backbone network, PGNet, is designed to enhance the interaction of information between channels. It leverages the novel GSConv convolution to enable efficient citrus leaf feature extraction while significantly reducing computational complexity.
- (3)
- A new neck structure, C3k2_EMA, is introduced to expand the receptive field across pixels and strengthen multi-scale contextual feature fusion. At the same time, it improves the model’s focus on the disease-affected target regions.
- (4)
- The original CIoU loss function is replaced with the Wise-IoU loss function to optimize bounding box regression, thereby improving accuracy and reliability in the detection of small objects associated with citrus leaf diseases and pests.
2. Related Work
2.1. YOLOv11
2.2. Lightweight Object Detection Algorithms
2.3. Attention Mechanisms
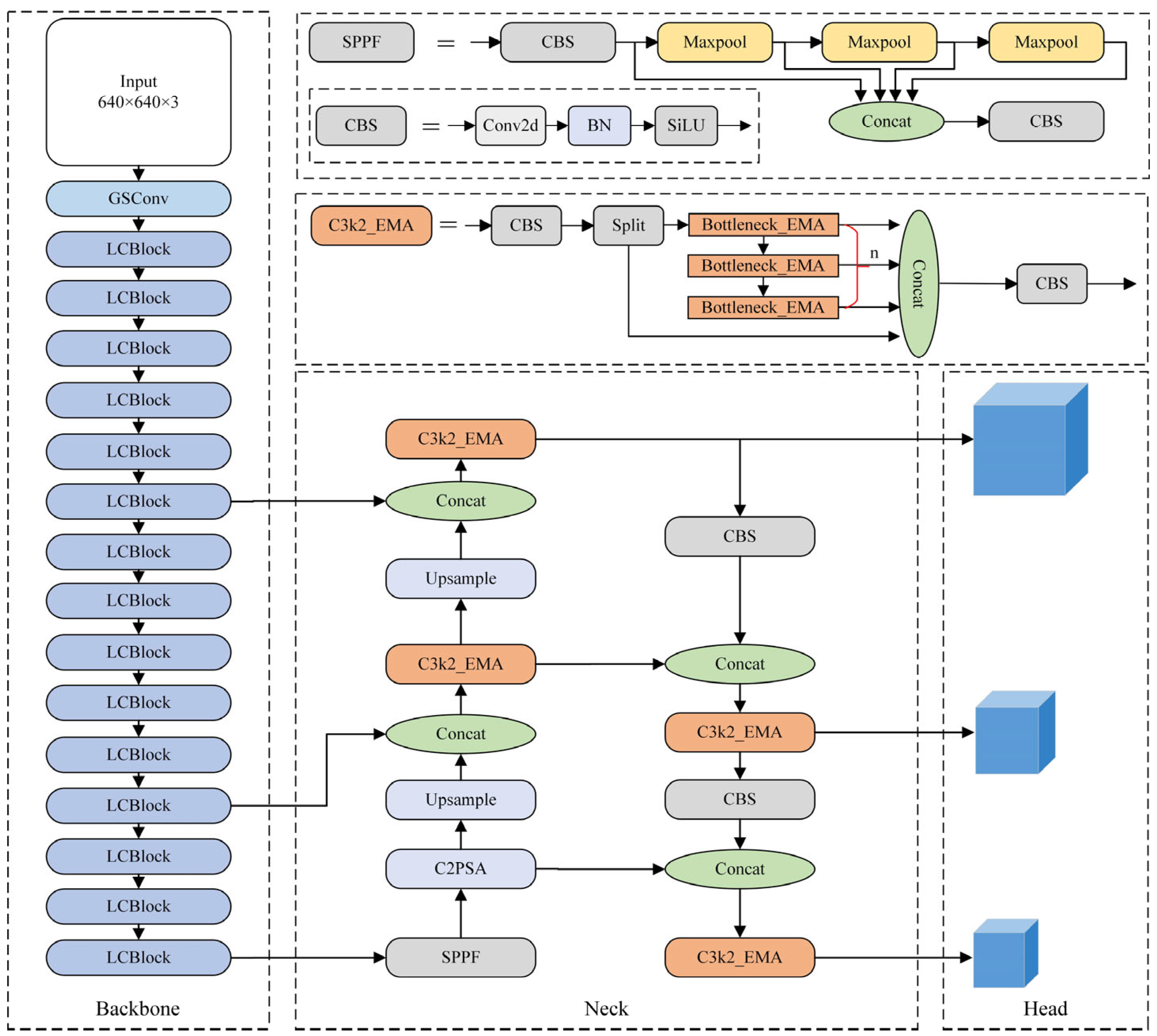
3. Proposed Method
3.1. PGNet Lightweight Backbone Network
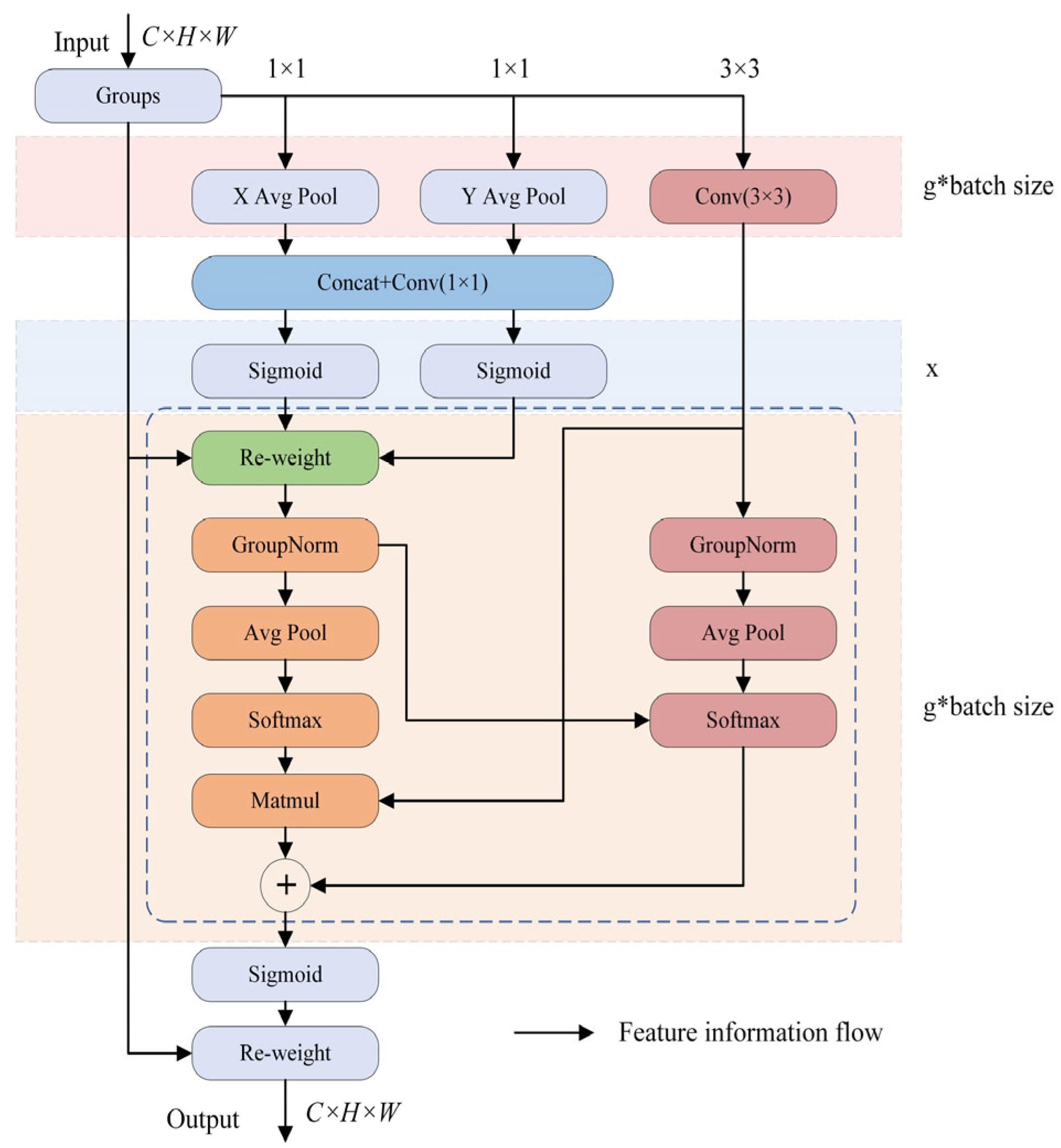
3.2. C3k2_EMA Module
3.3. Design of the Loss Function
3.3.1. Limitations of CIoU
3.3.2. Proposed Wise-IoU Loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experiment Platform
4.3. Model Training
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
4.5. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.5.1. Impact of Different Lightweight Backbone Networks on Model Performance
4.5.2. Impact of GSConv Integration on Network Performance
4.5.3. Effect of Different Attention Mechanisms on Model Performance
4.5.4. Ablation Experiment Results and Analysis of PEW-YOLO
4.5.5. Performance Comparison with Mainstream Models
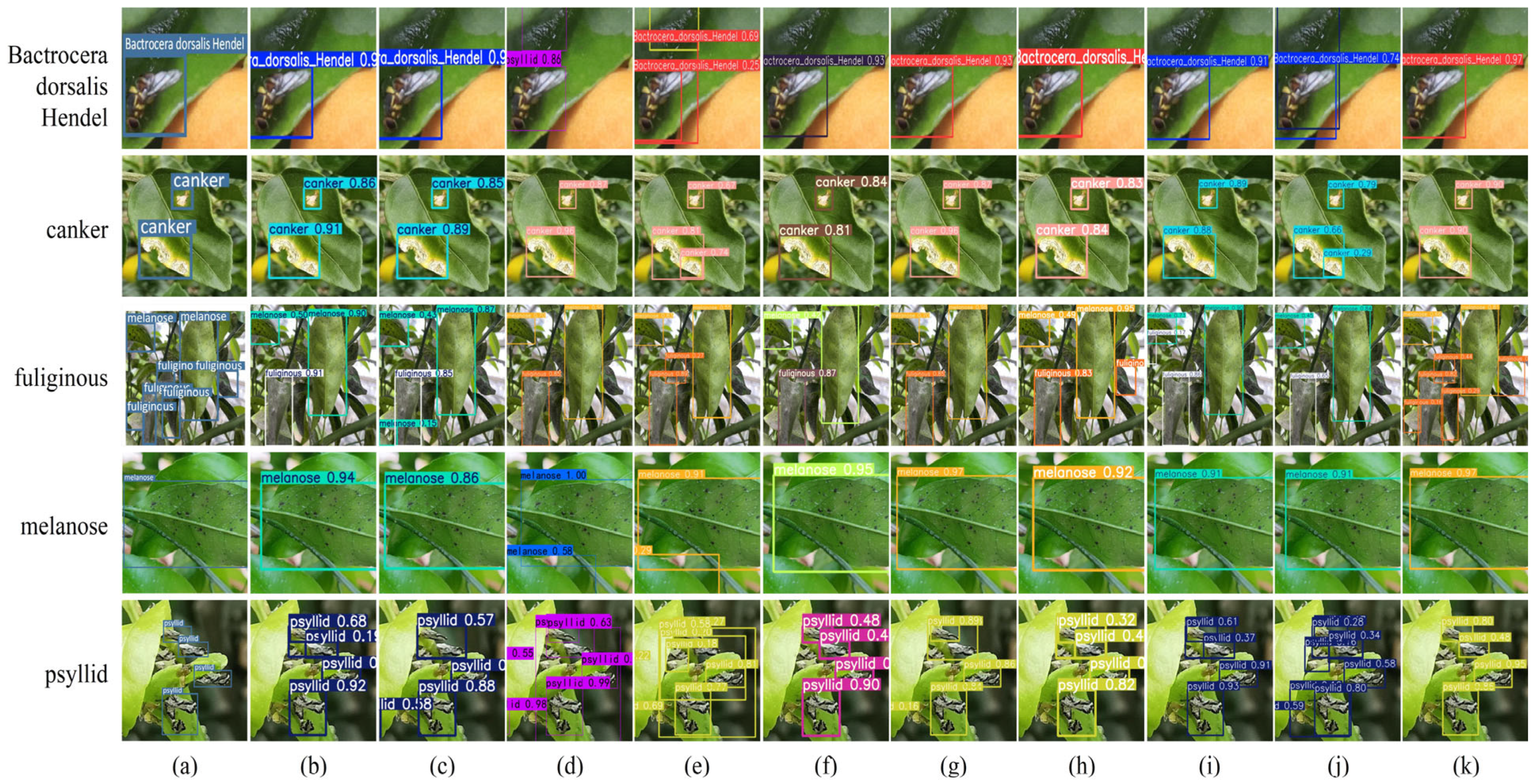
4.5.6. Evaluation on Rice Leaf Disease Dataset
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, K.; Song, X.; Jing, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xu, X.; Guo, J.; Zhu, H.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Citrus Huanglongbing Detection: A Hyperspectral Data-Driven Model Integrating Feature Band Selection with Machine Learning Algorithms. Crop Prot. 2025, 188, 107008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Su, Y.; Li, X. Research on Citrus Fruit Freshness Detection Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Processes 2024, 12, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xun, Y.; Chen, Y. Automated identification of citrus diseases in orchards using deep learning. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 223, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Ding, W.; Wang, J. Research on the Real-Time Detection of Red Fruit Based on the You Only Look Once Algorithm. Processes 2023, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanramaki, M.; Asli-Ardeh, E.A.; Kozegar, E.J.C.; Agriculture, E.i. Citrus pests classification using an ensemble of deep learning models. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 186, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Garg, P.; Chaudhary, N.K.; Joshi, M.V.; Palaparthy, V.S.; Kumar, A. Identifying the source of water on plant using the leaf wetness sensor and via deep learning-based ensemble method. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 7009–7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.K.; Chaudhary, A.; Chouhan, S.S.; Pandey, K.K. Mango leaf disease diagnosis using Total Variation Filter Based Variational Mode Decomposition. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 120, 109795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Musha, Y.; Yang, Y.; Feng, G.J.A.S. CEMLB-YOLO: Efficient detection model of maize leaf blight in complex field environments. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Lee, M.J.S. Classification accuracy improvement for small-size citrus pests and diseases using bridge connections in deep neural networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-L.; Chang, H.-Y.; Chen, K.-H. The pest and disease identification in the growth of sweet peppers using faster R-CNN and mask R-CNN. J. Internet Technol. 2020, 21, 605–614. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Liang, C.; Long, T.; Tang, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, J.; Lan, Y.; Long, Y.J.C.; et al. A detection approach for late-autumn shoots of litchi based on unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) remote sensing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhao, X.; Yue, X.; Yue, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.J.A.S. A Lightweight YOLOv8 Model for Apple Leaf Disease Detection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, A.; Dhaka, V.S.; Rani, G.; Khandelwal, S.; Zumpano, E.; Vocaturo, E. Time and Space Efficient Multi-Model Convolution Vision Transformer for Tomato Disease Detection from Leaf Images with Varied Backgrounds. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 79, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv11: An Overview of the Key Architectural Enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Duan, L.; Zhou, Q. PileNet: A high-and-low pass complementary filter with multi-level feature refinement for salient object detection. J. Visual Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 102, 104186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.G.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Yang, P.; Jung, Y.; Qin, J.; Kim, J.; Sheng, B. Egdnet: An efficient glomerular detection network for multiple anomalous pathological feature in glomerulonephritis. The Visual Computer 2024, 41, 2817–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Volume 11218, pp. 122–138. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Gao, T.; Wei, S.; Du, Y.; Guo, R.; Dong, S.; Lu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, X.; Liu, Q.J.a.p.a. PP-LCNet: A lightweight CPU convolutional neural network. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.15099. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Qin, C.; Hou, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W. LCGSC-YOLO: A lightweight apple leaf diseases detection method based on LCNet and GSConv module under YOLO framework. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1398277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, J. RIC-Net: A plant disease classification model based on the fusion of Inception and residual structure and embedded attention mechanism. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jia, J.; Koltun, V. Exploring self-attention for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10076–10085. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.; Mu, J.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Y. Application of deep learning in image recognition of citrus pests. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Wang, F.; Yang, D.; Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Lan, Y.; Deng, X. Detection method of citrus psyllids with field high-definition camera based on improved cascade region-based convolution neural networks. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 816272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-neck by GSConv: A better design paradigm of detector architectures for autonomous vehicles. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02424. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023–2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Ji, H.; Daković, M.; Cui, X.; Zhu, M.; Stanković, L. Cluster-CAM: Cluster-weighted visual interpretation of CNNs’ decision in image classification. Neural Netw. 2024, 178, 106473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | Params (M) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShuffleNetv2-YOLOv11n | 78.6 | 77.0 | 83.3 | 1.88 | 1.6 |
| GhostNetv2-YOLOv11n | 77.2 | 78.7 | 83.6 | 1.66 | 1.6 |
| MobileNetv3-YOLOv11n | 79.9 | 75.7 | 83.8 | 1.95 | 2.1 |
| PP-LCNet-YOLOv11n | 81.6 | 75.6 | 84.2 | 1.86 | 1.2 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | Params (M) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (YOLOv11n+PP-LCNet) | 81.6 | 75.6 | 84.2 | 1.86 | 1.2 |
| +MBConv | 77.7 | 78.5 | 84.2 | 1.86 | 2.0 |
| +GhostConv | 80.4 | 76.1 | 83.3 | 1.86 | 2.1 |
| +DWConv | 80.3 | 76.6 | 83.3 | 1.86 | 2.0 |
| +GSConv | 82.8 | 80.6 | 85.2 | 1.86 | 1.4 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | Params (M) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 83.8 | 79.1 | 86.8 | 2.58 | 1.3 |
| +LSKAttention | 82.3 | 81.2 | 86.9 | 2.64 | 1.5 |
| +SEAttention | 81.6 | 77.7 | 85.7 | 2.58 | 1.6 |
| +GAMAttention | 80.5 | 82.0 | 86.4 | 3.22 | 1.4 |
| +EMA | 84.0 | 79.9 | 89.2 | 2.47 | 1.4 |
| Model | PP-LCNet | GSConv | C3k2_EMA | Wise-IoU | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | Params (M) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv11n | × | × | × | × | 83.8 | 79.1 | 86.8 | 2.58 | 1.3 |
| YOLO-P | √ | × | × | × | 81.6 | 75.6 | 84.2 | 1.86 | 1.2 |
| YOLO-PG | √ | √ | × | × | 82.8 | 80.6 | 85.2 | 1.86 | 1.4 |
| YOLO-C | × | × | √ | × | 84.0 | 79.9 | 89.2 | 2.47 | 1.4 |
| YOLO-W | × | × | × | √ | 83.9 | 80.7 | 88.6 | 2.58 | 1.7 |
| YOLO-PGC | √ | √ | √ | × | 84.0 | 80.5 | 88.4 | 1.75 | 1.5 |
| PEW-YOLO | √ | √ | √ | √ | 84.3 | 80.9 | 88.6 | 1.75 | 1.6 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | Params (M) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO-World | 79.1 | 81.9 | 86.3 | 4.05 | 2.1 |
| Swin Transformer | 81.5 | 79.6 | 85.4 | 2.51 | 2.5 |
| Faster R-CNN | 77.5 | 72.4 | 79.9 | 28.32 | 23.2 |
| RT-DETR | 78.7 | 76.1 | 81.7 | 8.79 | 2.6 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 83.0 | 79.4 | 85.2 | 6.02 | 2.9 |
| YOLOv8n | 84.0 | 79.2 | 85.9 | 3.01 | 2.2 |
| YOLOv9-t | 82.9 | 80.8 | 87.9 | 2.62 | 8.6 |
| YOLOv10n | 80.7 | 80.5 | 85.7 | 2.70 | 2.0 |
| YOLOv11n | 83.8 | 79.1 | 86.8 | 2.58 | 1.3 |
| PEW-YOLO | 84.3 | 80.9 | 88.6 | 1.75 | 1.6 |
| Model | AP (%) | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria Leaf Blight | Brown Spot | Leaf Smut | ||||
| YOLOv11n | 99.5 | 98.0 | 98.7 | 98.4 | 96.0 | 98.7 |
| PEW-YOLO | 99.5 | 99.3 | 99.4 | 99.4 | 98.2 | 99.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, R.; Wang, L. Research on Lightweight Citrus Leaf Pest and Disease Detection Based on PEW-YOLO. Processes 2025, 13, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051365
Xue R, Wang L. Research on Lightweight Citrus Leaf Pest and Disease Detection Based on PEW-YOLO. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051365
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Renzheng, and Luqi Wang. 2025. "Research on Lightweight Citrus Leaf Pest and Disease Detection Based on PEW-YOLO" Processes 13, no. 5: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051365
APA StyleXue, R., & Wang, L. (2025). Research on Lightweight Citrus Leaf Pest and Disease Detection Based on PEW-YOLO. Processes, 13(5), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051365






