Simulating Horizontal CO2 Plume Migration in a Saline Aquifer: The Effect of Injection Depth
Abstract
1. Background
2. Literature Review
2.1. CO₂ Sequestration in Saline Aquifers
2.2. CO₂ Storage Mechanisms in Saline Aquifers
- Structural and Stratigraphic Trapping
- Residual Trapping
- Solubility Trapping
- Mineral Trapping
2.3. Aquifer Salinity in Louisiana
2.4. Impact of Injection Depth on CO₂ Migration
2.5. Horizontal vs. Vertical Migration of CO₂ Plumes
3. Methodology
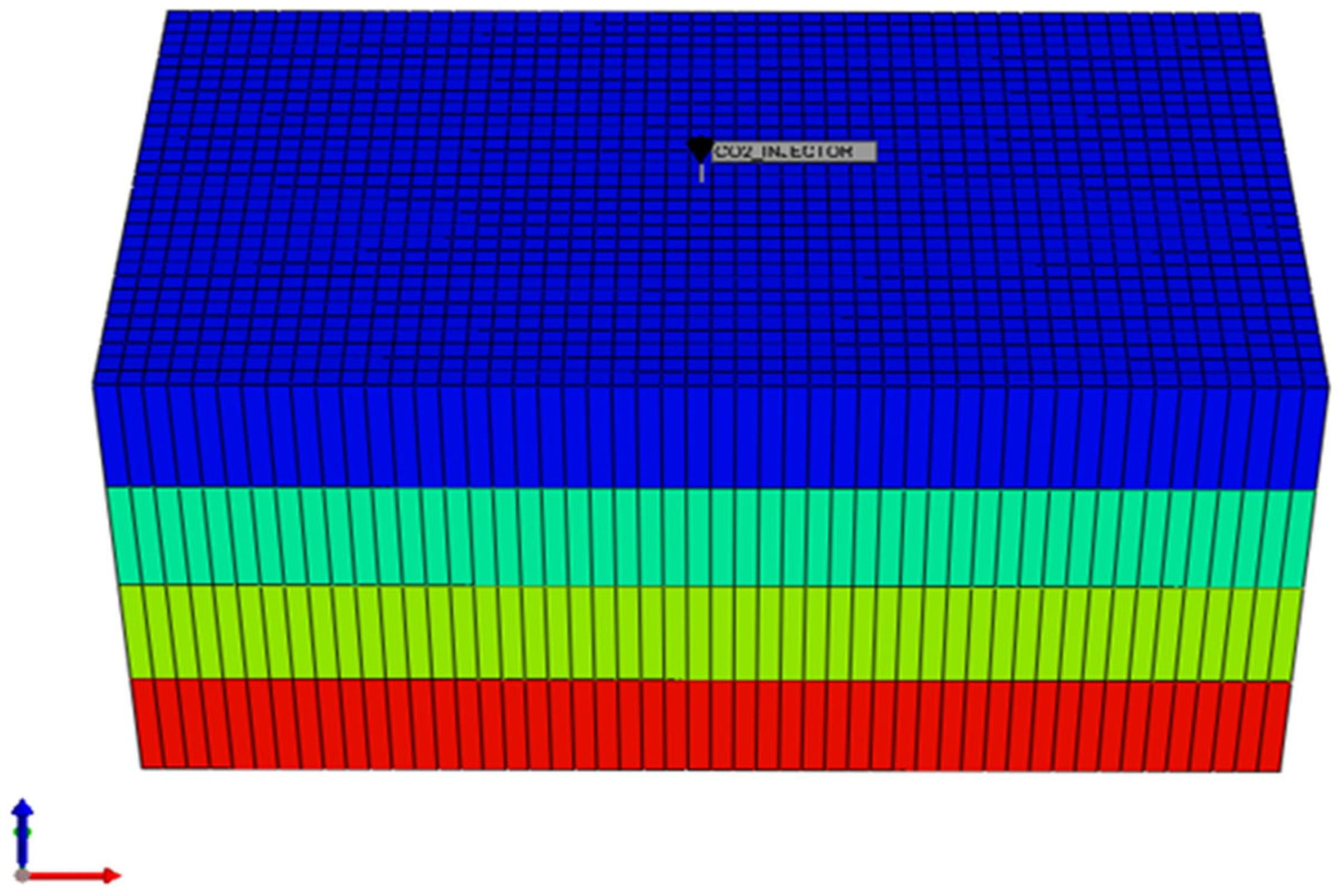
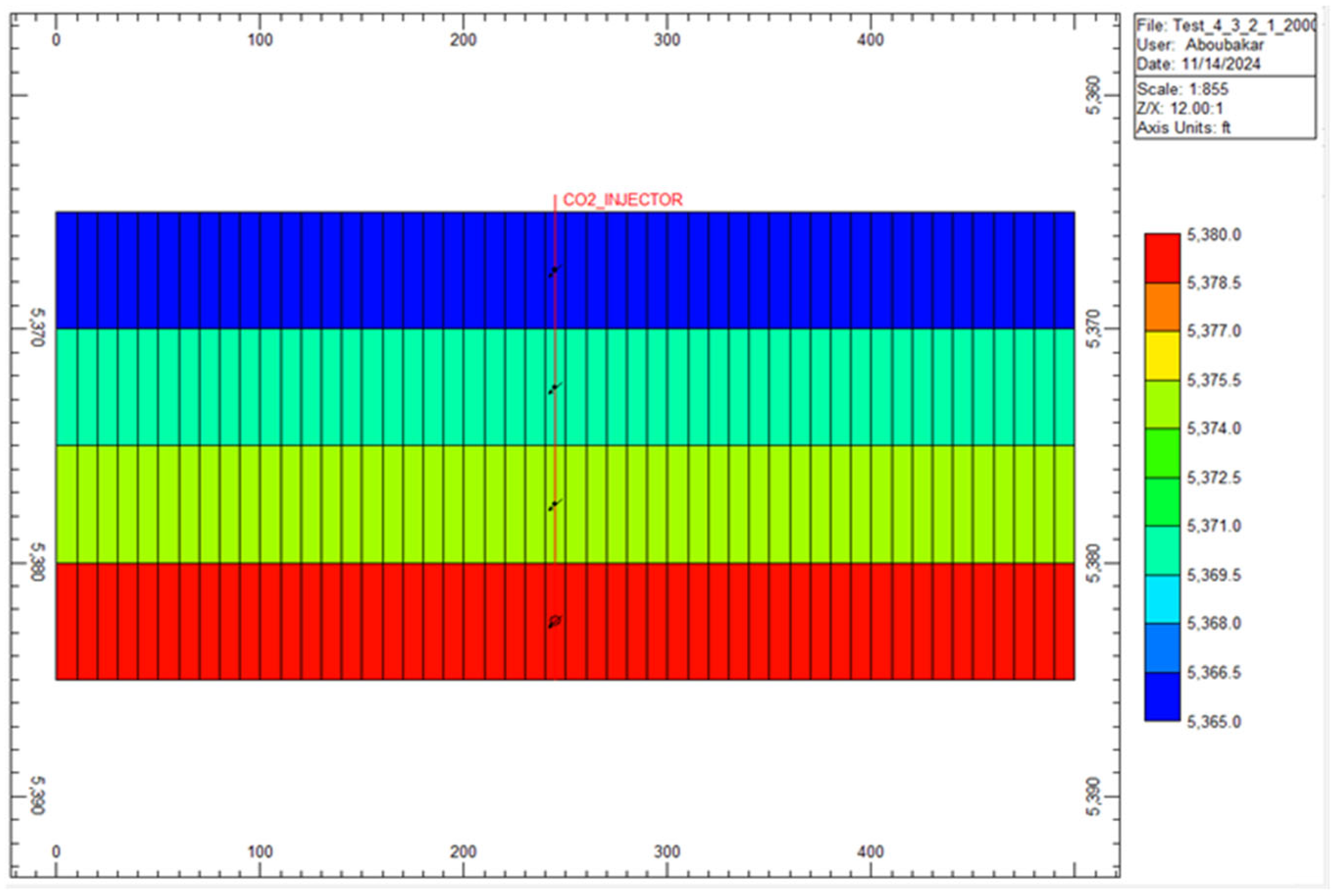
3.1. Model Setup and Grid Configuration
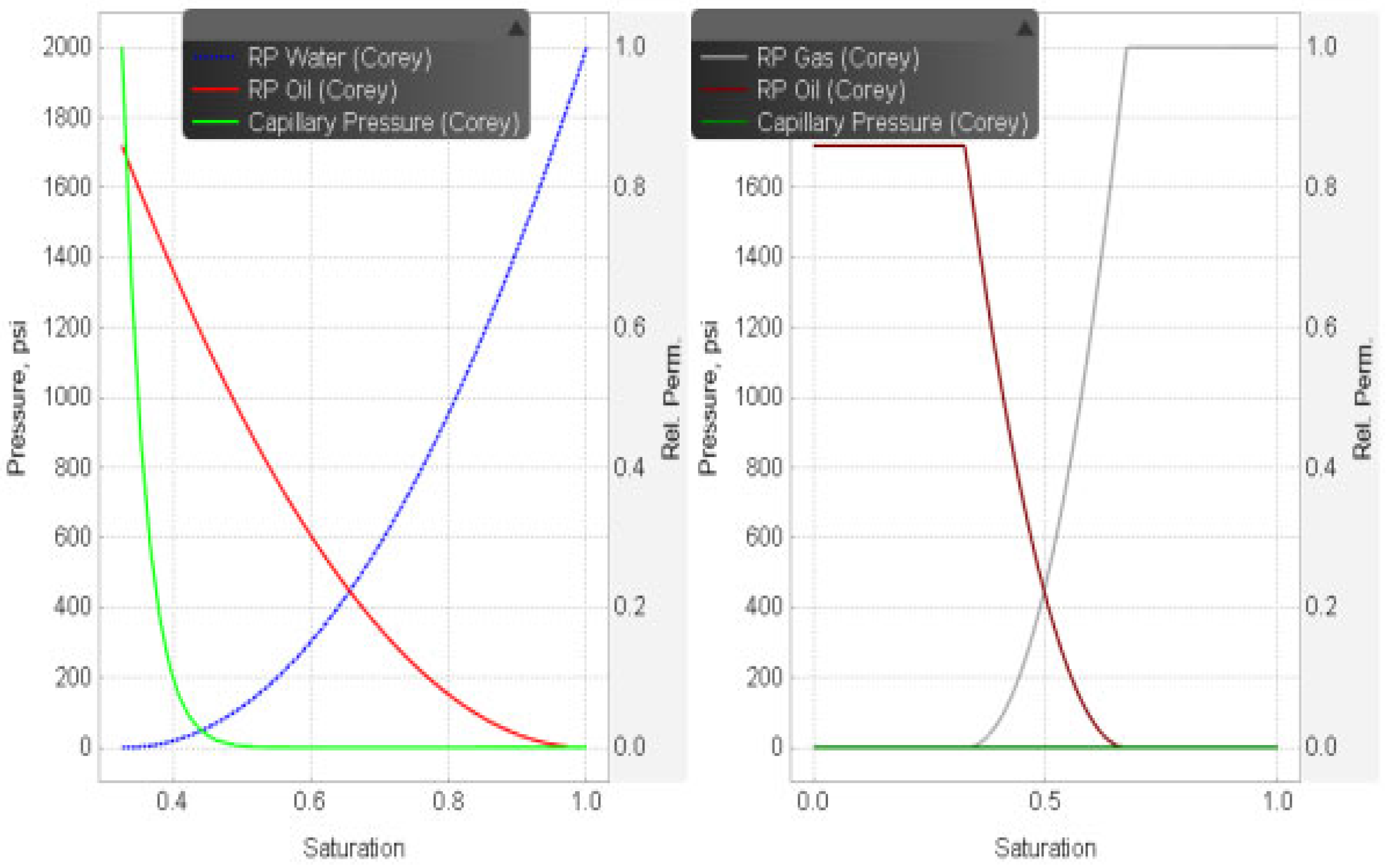
3.2. Reservoir Properties
3.3. Aquifer Salinity Level and Aqueous Phase Components
3.4. CO₂ Injection Parameters
3.5. Simulation Process and Data Collection
- Steady-state Aquifer:
- Well Model:
- Pressure Loss Equation:
- Partial Molar Volume Equation:
- Effect of Salinity:
- Darcy’s Law for Multiphase Flow:
- Peng–Robinson Equation of State (EOS) for Phase Behavior:
4. Results and Discussion
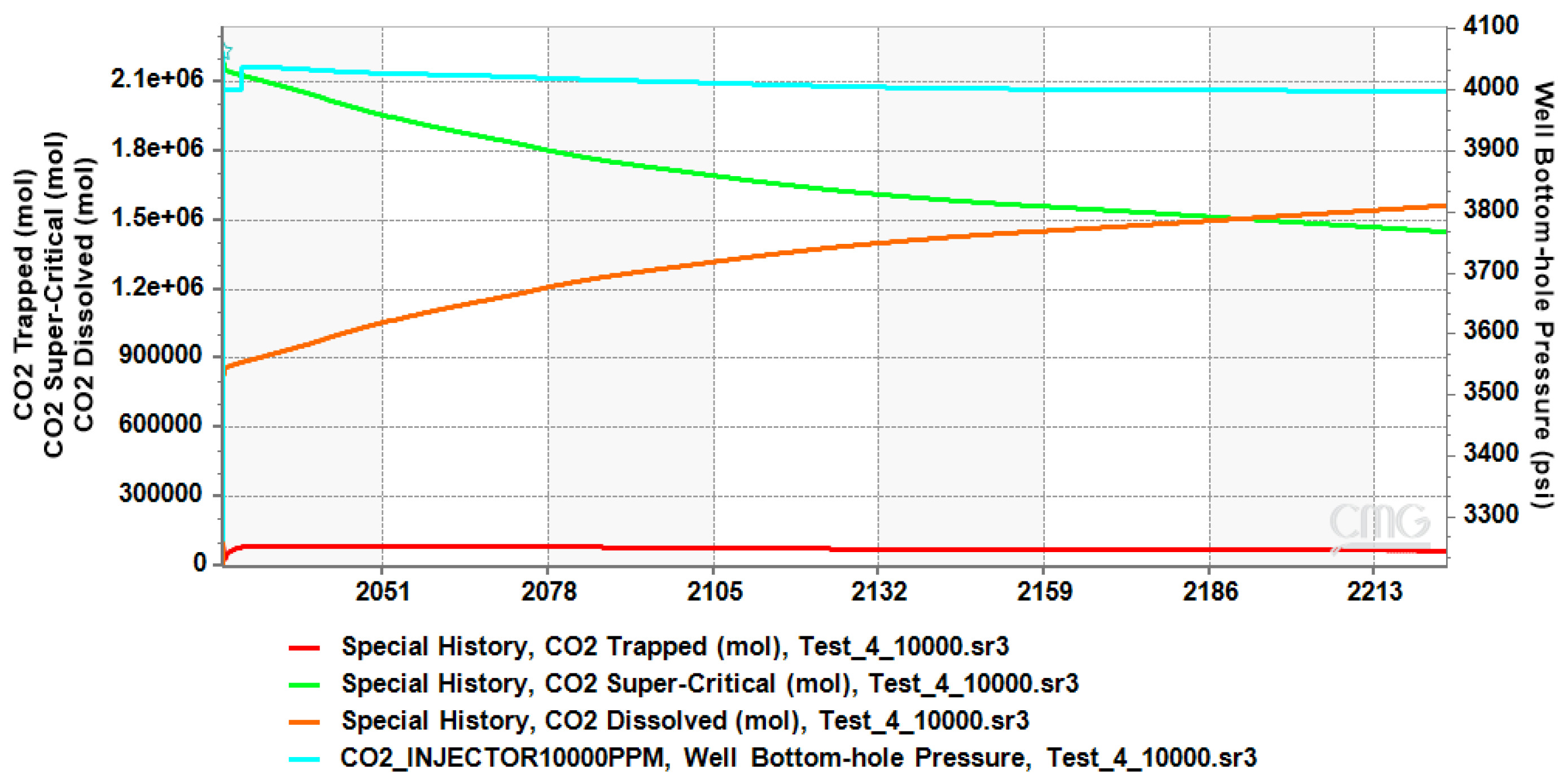
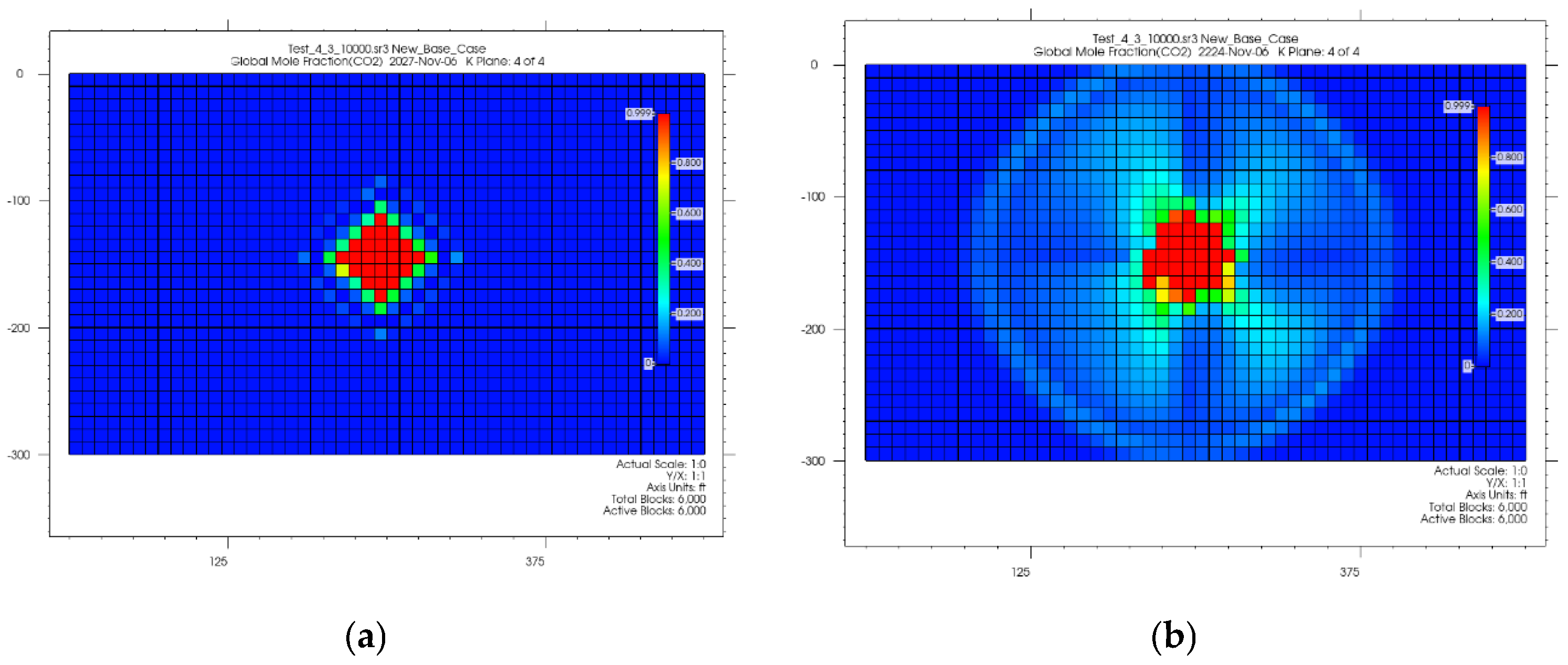
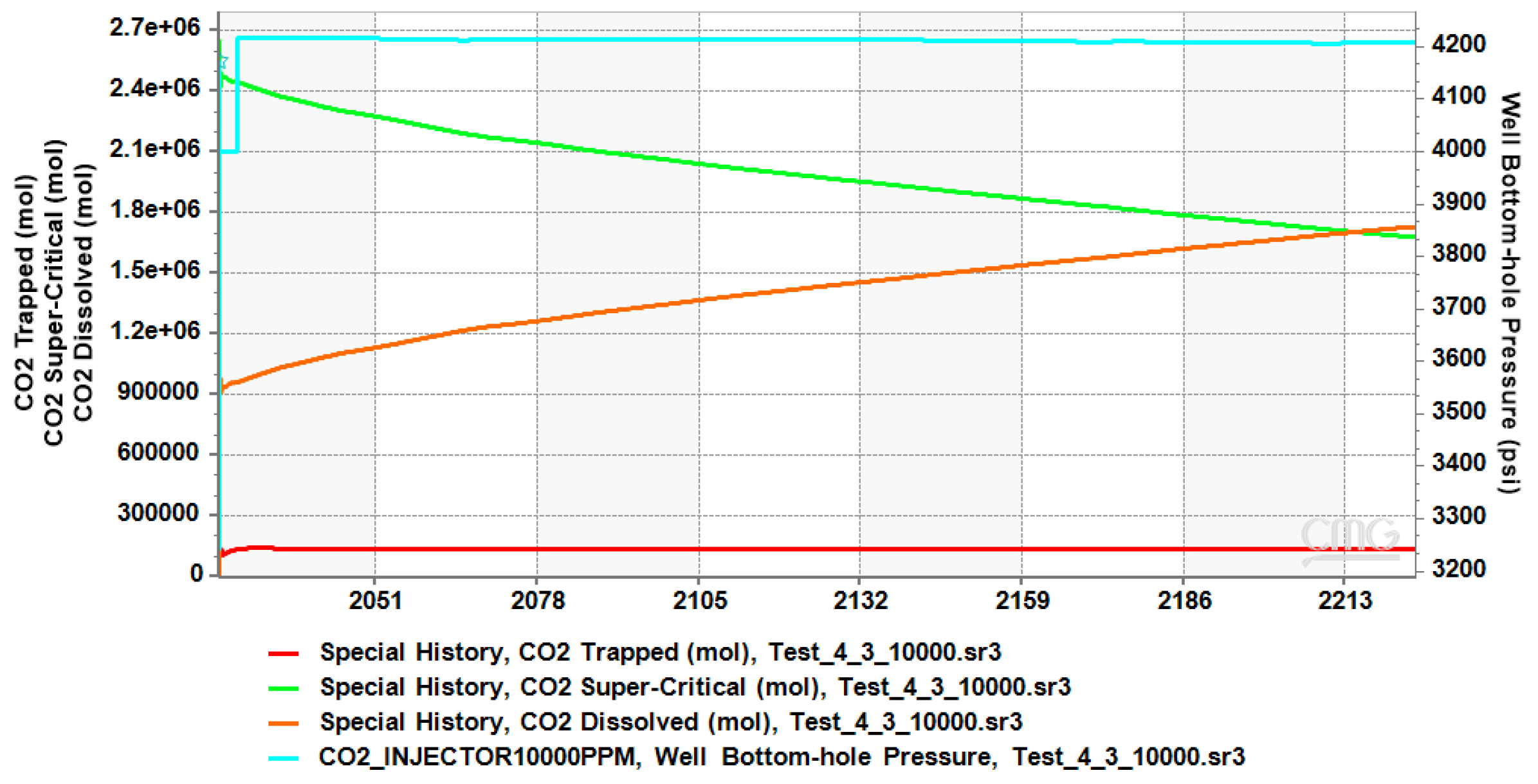
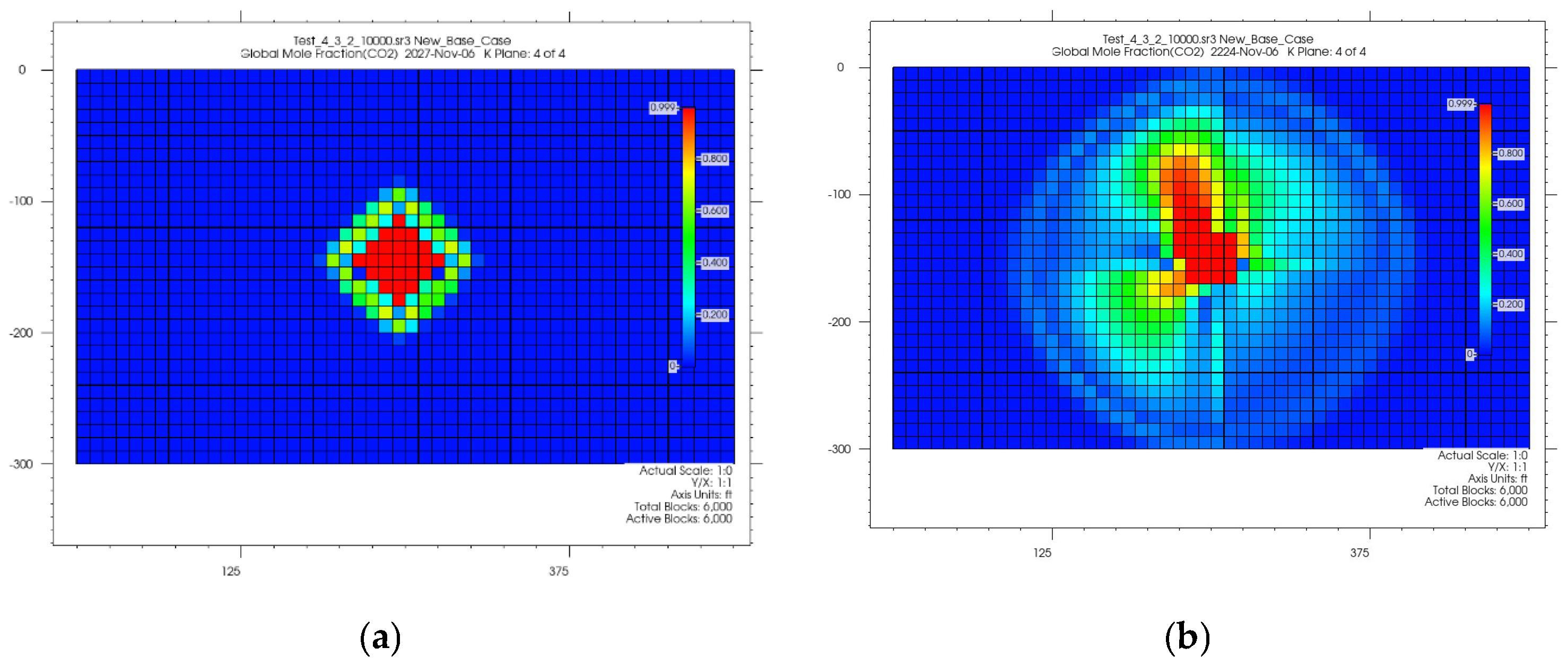
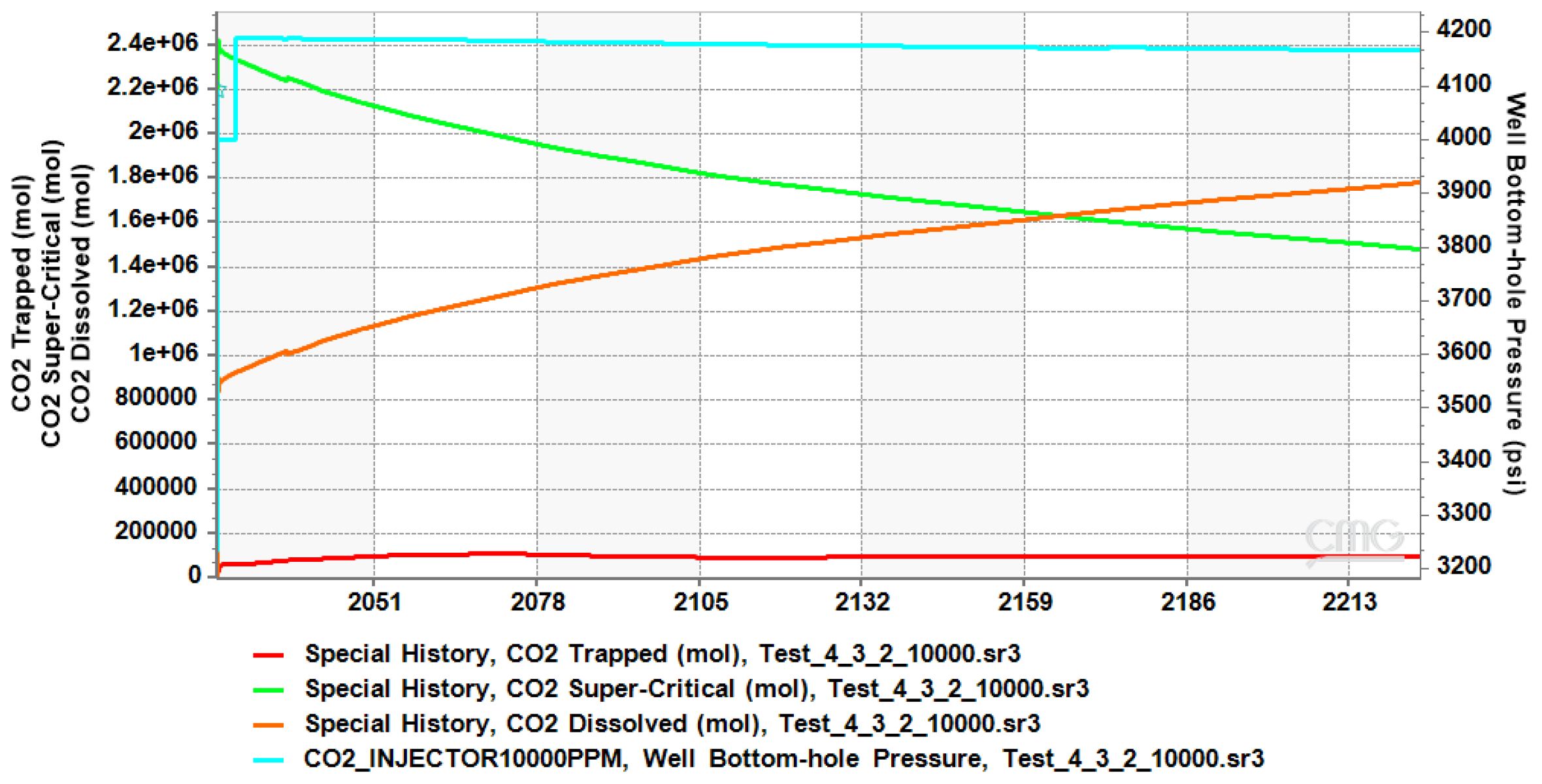
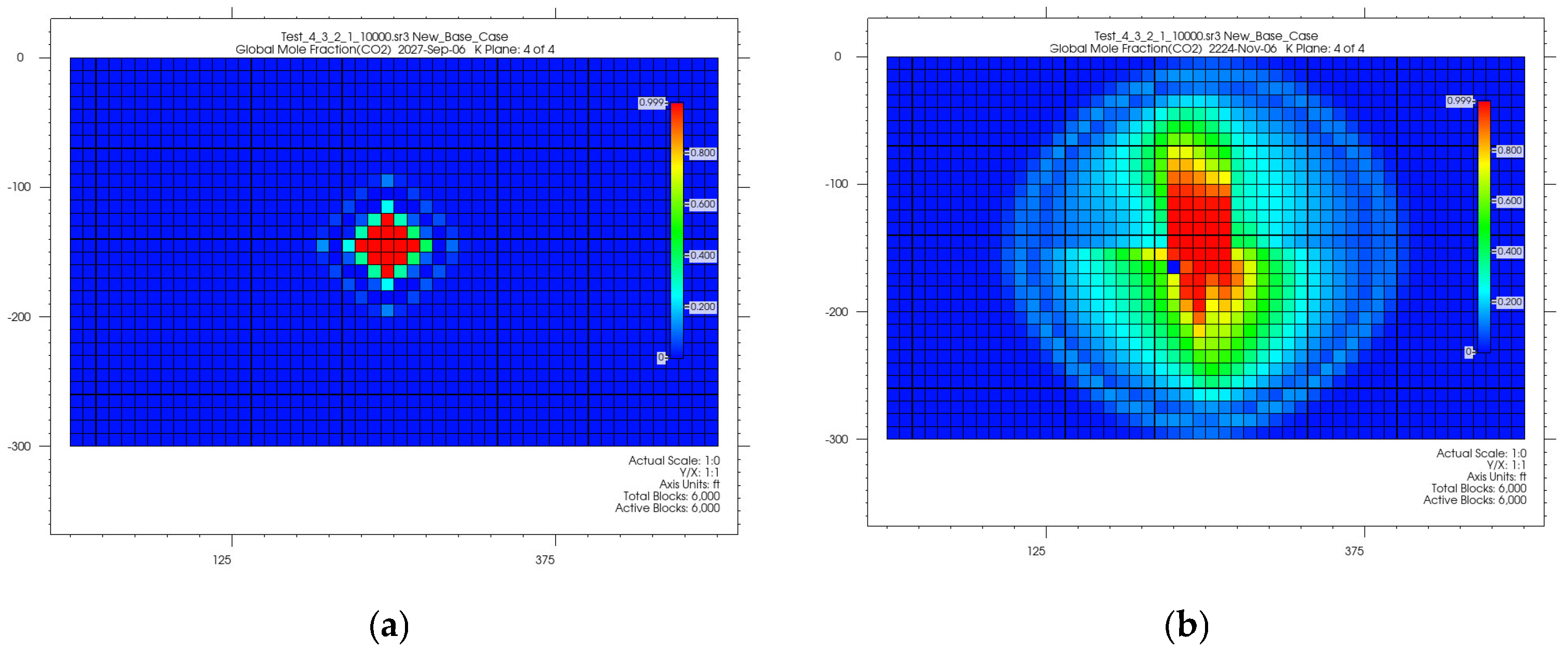
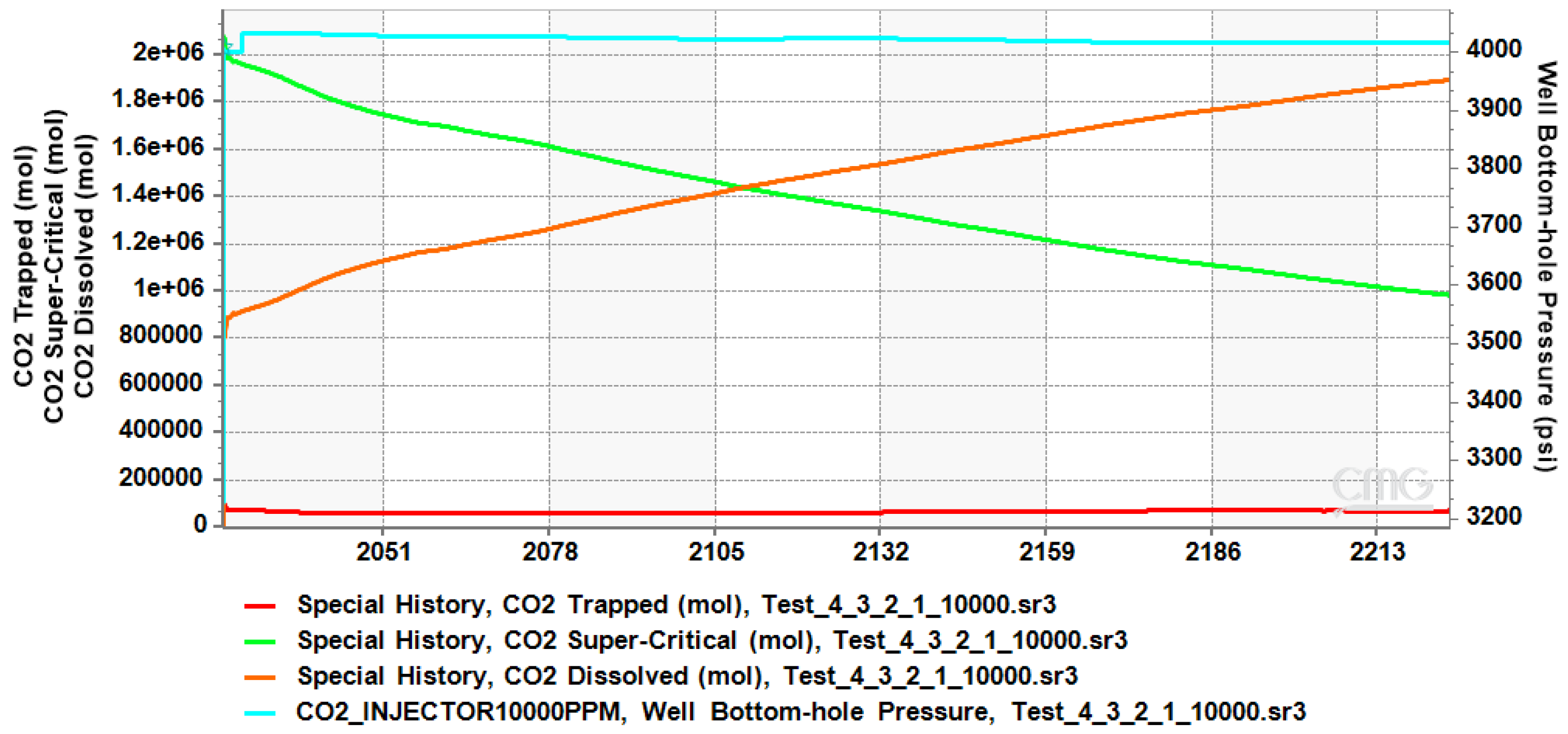
4.1. CO2 Plume Migration in Layer 4 (Bottom Layer)
4.2. CO2 Plume Migration in Layers 3 and 4
4.3. CO2 Plume Migration in Layers 2, 3, and 4
4.4. CO2 Plume Migration in Layers 1 Through 4
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Jackson, C.; Krevor, S. The feasibility of reaching gigatonne scale CO2 storage by mid-century. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Birkholzer, J.T.; Tsang, C.F.; Rutqvist, J. A method for quick assessment of CO2 storage capacity in closed and semi-closed saline formations. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2008, 2, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fominykh, S.; Stankovski, S.; Markovic, V. Analysis of CO2 migration in horizontal saline aquifers during carbon capture and storage process. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Ansari, U.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, C. Hydrate as a by-product in CO2 leakage during the long-term sub-seabed sequestration and its role in preventing further leakage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 77737–77754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Ding, Z. Exploring the influences of salinity on CO2 plume migration and storage capacity in sloping formations: A numerical investigation. Energy 2024, 309, 133160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, K. Effects of fluvial sedimentary heterogeneity on CO2 geological storage: Integrating storage capacity, injectivity, distribution, and CO2 phases. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khdheeawi, E.; Vialle, S.; Barifcani, A.; Sarmadivaleh, M.; Zhang, Y.; Iglauer, S. Impact of salinity on CO2 containment security in highly heterogeneous reservoirs. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 1723. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khdheeawi, E.; Vialle, S.; Barifcani, A.; Sarmadivaleh, M.; Zhang, Y.; Iglauer, S. Influence of injection well configuration and rock wettability on CO2 plume behaviour and CO2 trapping capacity in heterogeneous reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Foroozesh, J.; Edlmann, K.; Rezk, M.; Lim, C. A Comprehensive Review of Value-Added CO2 Sequestration in Subsurface Saline Aquifers. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 81, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwen, R.T.; Stewart, M.T.; Cunningham, J.A. Analytical solution for estimating storage efficiency of dissolved and residual CO2 in saline aquifers. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2010, 4, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Lu, X.; Wang, D.A. Systematic Review of Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage: Status, Progress and Challenges. Energies 2023, 16, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Apps, J.A.; Pruess, K.; Yamamoto, H. Numerical modeling of injection and mineral trapping of CO2 with H2S and SO2 in a sandstone formation. Chem. Geol. 2007, 242, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, N.I.; Smith, S.J.; Seger, C.H. Hydrogeology, Distribution, and Volume of Saline Groundwater in the Southern Midcontinent and Adjacent Areas of the United States. US Geol. Surv. 2013, 15, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, N.; Gu, Y. Enhanced mass transfer for CO2 sequestration in saline aquifers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, F.; Zhao, N. Impact of inner reservoir faults on migration and storage of injected CO2. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2021, 72, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovorka, S.D.; Meckel, T.A.; Treviño, R.H. Monitoring a large-volume injection at Cranfield, Mississippi Project design and recommendations. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 18, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnaweera, T.D.; Ranjith, P.G. Effect of salinity on effective CO2 permeability in reservoir rock determined by pressure transient methods. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 48, 2093–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peaceman, D. Interpretation of well-block pressures in numerical reservoir simulation. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Fall Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, CO, USA, 9–12 October 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Peaceman, D. Interpretation of well-block pressures in numerical reservoir simulation with non-square grid blocks and anisotropic permeability. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1983, 23, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappelear, J.; Williamson, A.E. Representing Wells in Numerical Reservoir Simulation: Part I—Theory Part II—Implementation. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1981, 21, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.; Govier, G.W.; Schowalter, W.R. The Flow of Complex Mixtures in Pipes. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 1973, 2, 404. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhu, C.; Chou, I.M. An improved model for the calculation of CO2 solubility in aqueous solutions containing Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, and SO₄²−. Mar. Chem. 2006, 98, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Sun, R. An improved model calculating CO2 solubility in pure water and aqueous NaCl solutions from 273 to 533 K and from 0 to 2000 bar. Chem. Geol. 2003, 193, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S. The Solubility of Methane, Carbon Dioxide, and Oxygen in Brines from 0 to 300 C; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, R. Computer programs for analysis of fluid inclusion data and for modelling bulk fluid properties. Chem. Geol. Chem. Geol. 2003, 194, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Jiang, X. Numerical Investigation of Multi-layer CO2 Injection in Deep Saline Aquifers with Improperly Abandoned Wells. Energy Procedia 2014, 61, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Values | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Size | 50 × 30 × 4 | block |
| Block Size | 10 | ft |
| Total Blocks | 6000 | |
| Total Volume | 6 × 106 | ft3 |
| Porosity | 30 | % |
| Pore Volume | 9 × 105 | ft3 |
| Permeability X/Y/Z | 200/200/20 | mD |
| Rock Compressibility | 3.2 × 10−6 | psi−1 |
| Initial Temperature | 112 | °F |
| Initial Pressure | 3205 | psi |
| Grid Top Depth | 5365 | ft |
| Brine Salinity | 10 k/20 k | ppm |
| Injection Rate | 350,000 | scf |
| Injector Well Diameter | 0.625 | ft |
| Top Perforation | 5370 | ft |
| Injector Address | 25 15 4/3/2/1 | block |
| Maximum Injection Pressure | 4000 | psi |
| Max STG | 350,000 | ft3/day |
| Injection Period | 3 | years |
| Shut-in Period | 197 | years |
| Simulation Period | 200 | years |
| Reservoir Fluid | Brine | |
| Injected Fluid | CO2 | 100% |
| Max Change Pressure | 30,000 | psi |
| Max Change Saturation | 0.999 | |
| Max Change Global Composition | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kone, A.; Boukadi, F.; Trabelsi, R.; Trabelsi, H. Simulating Horizontal CO2 Plume Migration in a Saline Aquifer: The Effect of Injection Depth. Processes 2025, 13, 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030734
Kone A, Boukadi F, Trabelsi R, Trabelsi H. Simulating Horizontal CO2 Plume Migration in a Saline Aquifer: The Effect of Injection Depth. Processes. 2025; 13(3):734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030734
Chicago/Turabian StyleKone, Aboubakar, Fathi Boukadi, Racha Trabelsi, and Haithem Trabelsi. 2025. "Simulating Horizontal CO2 Plume Migration in a Saline Aquifer: The Effect of Injection Depth" Processes 13, no. 3: 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030734
APA StyleKone, A., Boukadi, F., Trabelsi, R., & Trabelsi, H. (2025). Simulating Horizontal CO2 Plume Migration in a Saline Aquifer: The Effect of Injection Depth. Processes, 13(3), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030734






