Comparative Study of Binder Stability for Aqueous Lithium-Ion and Solid-Boosted Flow Batteries
Abstract
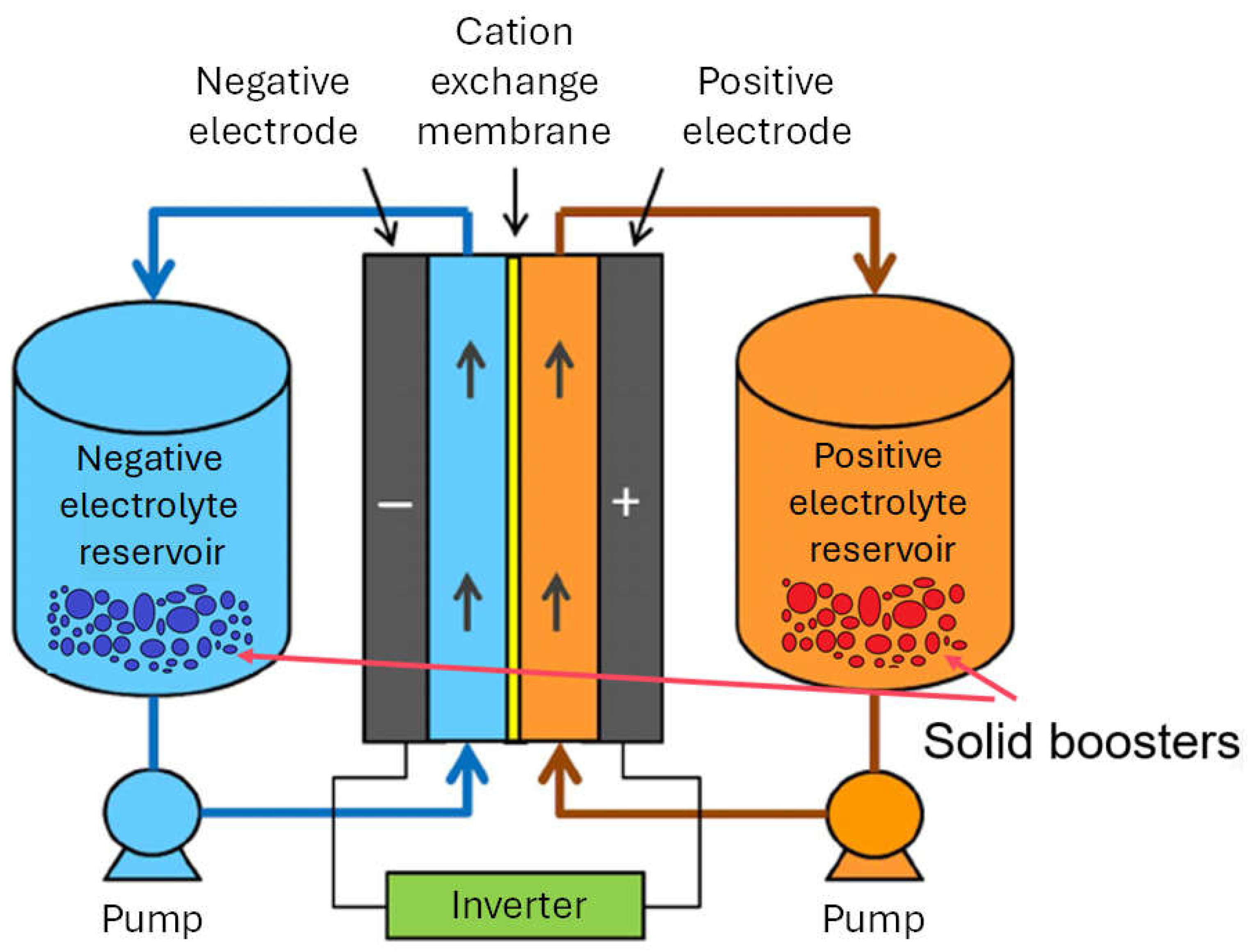
1. Introduction
| Property | PVDF (Baseline) | Ethyl Cellulose (EC) | Cross-Linked Gluten |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binder Type | Synthetic fluoropolymer (non-renewable) | Modified natural polymer (cellulose ether derivative) | Natural protein polymer (wheat gluten), thermally cross-linked |
| Solvent Requirement | NMP (toxic, high boiling point) [11] | Ethanol or isopropanol (benign, low toxicity) [9,10] | Water-based slurry (green process); heat curing required [17,18] |
| Mechanical Properties | Highly flexible and tough; excellent adhesion to particles [6,21] | Good adhesion; moderate flexibility (sufficient for cohesion) [4] | Flexible, rubbery network after crosslinking; strong cohesion [17,18] |
| Water Stability | Hydrophobic and chemically inert in water (no swelling or dissolution) [11] | Water-insoluble; minimal swelling (maintainsstructure) [16] | Water-insoluble after crosslink; slight swelling possible but no dissolution [17] |
| Environmental Impact | Requires toxic solvent; not biodegradable; fluorinated (hazardous disposal) [4,7] | Renewable source; solvent is low-toxic and recyclable; biodegradable over time; no fluorine [9,10] | Renewable and biodegradable; no organic solvent needed; no fluorine—safe disposal [17] |
| Processing Complexity | Established slurry casting with NMP, but needs strict safety controls and drying infrastructure [11] | Simple slurry mixing in alcohol; fast drying; flammable solvent handling needed (standard lab safety) [15] | Easiest: aqueous slurry in ambient conditions; requires thermal cross-link step [17] |
| Electrochemical Stability | Electrochemically inert; stable in wide potential window (up to ~4.2 V vs. Li+ in organics) [19] | Inert within aqueous voltage window; no redox-active groups; stable in neutral pH [8,16] | Largely inert after curing; no significant degradation observed within water stability window (mild conditions) [28] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrode Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
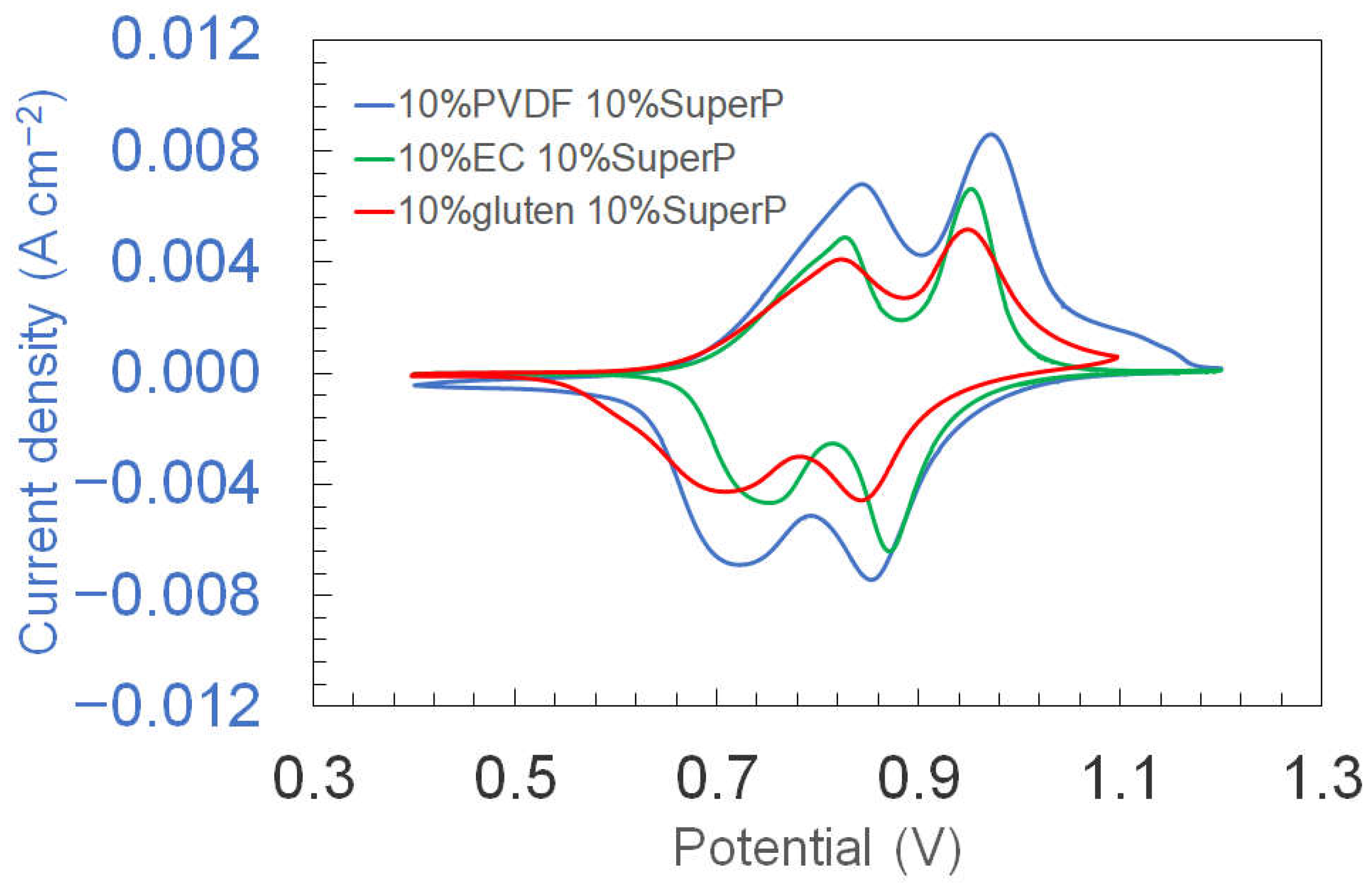
3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry of Electrodes
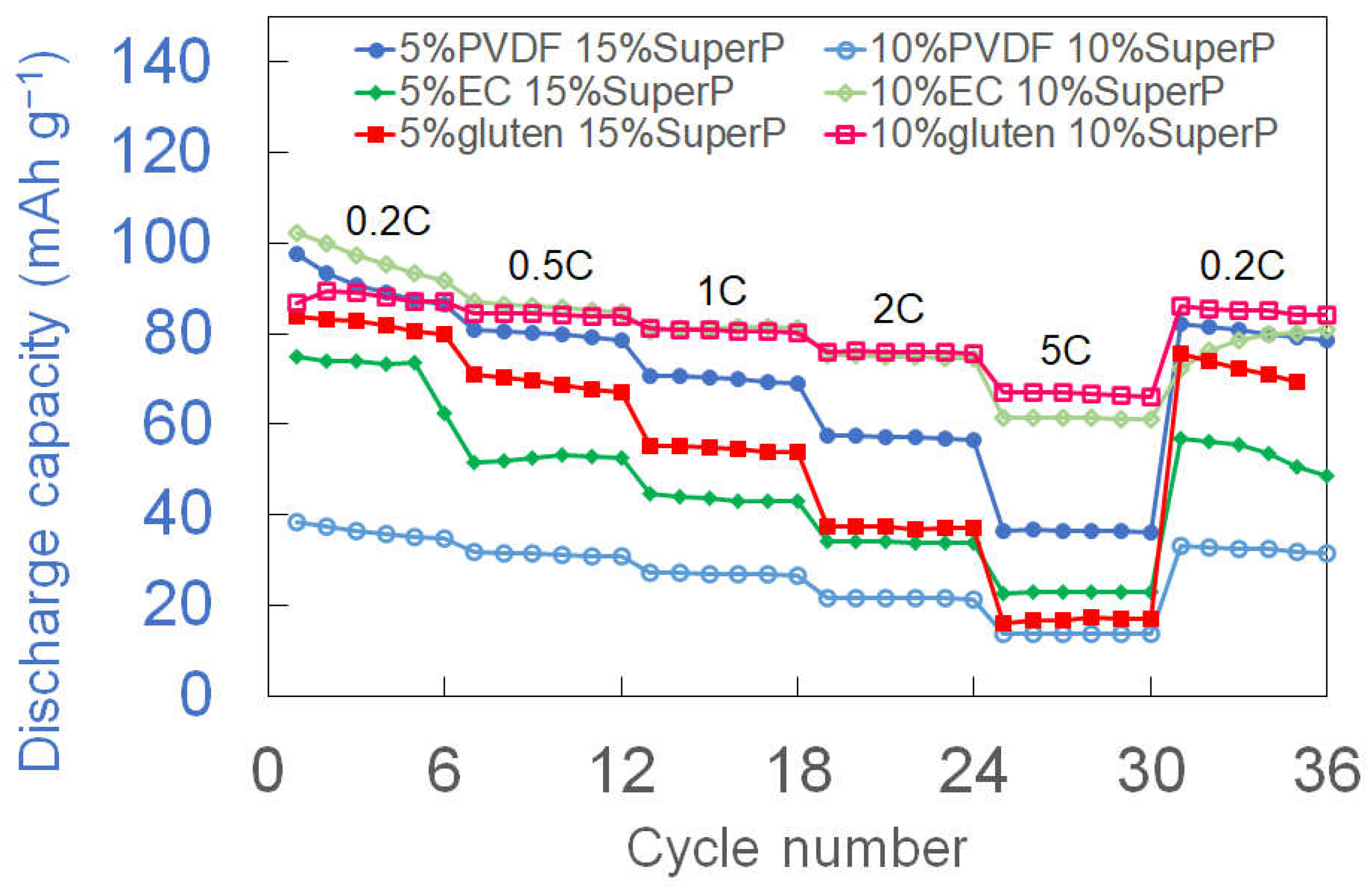
3.2. Rate Performance and Initial Capacity Comparison
3.3. Long-Term Cycling Stability
3.4. Electrode Morphology Studies
4. Discussion
Mechanical and Interfacial Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
| ALIBs | Aqueous Lithium-Ion Batteries |
| FBs | Flow Batteries |
| LMO | Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) |
| NMP | N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone |
| PFAS | Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances |
| EC | Ethyl Cellulose |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| EDS | Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
References
- Moghaddam, M.; Sepp, S.; Wiberg, C.; Bertei, A.; Rucci, A.; Peljo, P. Thermodynamics, Charge Transfer and Practical Considerations of Solid Boosters in Redox Flow Batteries. Molecules 2021, 26, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; He, Y.; Li, Z.-J.; Gao, L.-Z.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, Z.-L. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Spinel LiMn2O4-x(SO4)x Cathode Materials. Chin. J. Chem. 2002, 20, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Gao, L.-Z.; Liu, X.-Q.; Yu, Z.-L. Properties and Structure of Spinel Li-Mn-O-F Compounds for Cathode Materials of Secondary Lithium-Ion Battery. Chin. J. Chem. 2001, 19, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Wang, S.; Huang, S.; Han, D.; Meng, Y. Polymeric Binders Used in Lithium Ion Batteries: Actualities, Strategies and Trends. ChemElectroChem 2024, 11, e202300651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Jin, H.-J. Polymeric Binder Design for Sustainable Lithium-Ion Battery Chemistry. Polymers 2024, 16, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Koo, H.; Kang, H.S.; Oh, K.-H.; Nam, K.W. Advances in Polymer Binder Materials for Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes and Separators. Polymers 2023, 15, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasi, L.; Fiore, S. Environmental Assessment of Lithium-Ion Battery Lifecycle and of Their Use in Commercial Vehicles. Batteries 2024, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kim, G.-T.; Chao, D.; Loeffler, N.; Copley, M.; Lin, J.; Shen, Z.; Passerini, S. Toward Greener Lithium-Ion Batteries: Aqueous Binder-Based LiNi0.4Co0.2Mn0.4O2 Cathode Material with Superior Electrochemical Performance. J. Power Sources 2017, 372, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Cai, S.; Gao, H.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y. Cellulose-Based Separators for Lithium Batteries: Source, Preparation and Performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobryden, I.; Montanari, C.; Bhattacharjya, D.; Aydin, J.; Ahniyaz, A. Bio-Based Binder Development for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials 2023, 16, 5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Lee, C.H.; Jo, M.H.; Jeong, S.K. Electrochemical Decomposition of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Binder for a Graphite Negative Electrode in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 893, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandi, A.C.; de Meatza, I.; Casado, N.; Forsyth, M.; Mecerreyes, D.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C. Unlocking Sustainable Power: Advances in Aqueous Processing and Water-Soluble Binders for NMC Cathodes in High-Voltage Li-Ion Batteries. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 2125–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; You, H.; Yan, X.; Borkiewicz, O.J.; Wiaderek, K.M.; Hui, J.; Hersam, M.C.; Chaudhuri, S.; Rowan, S.J.; Chen, J. Environmentally Sustainable Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Binders Based on Cellulose Nanocrystals. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 33015–33022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Song, T.; Paik, U. Sustainable and Cost-Effective Electrode Manufacturing for Advanced Lithium Batteries: The Roll-to-Roll Dry Coating Process. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 6598–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Yang, T.; Ge, D.; Wood, D.L.; Li, Z. Water-Based Electrode Manufacturing and Direct Recycling of Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes—A Green and Sustainable Manufacturing System. iScience 2020, 23, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholewinski, A.; Si, P.; Uceda, M.; Pope, M.; Zhao, B. Polymer Binders: Characterization and Development toward Aqueous Electrode Fabrication for Sustainability. Polymers 2021, 13, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordqvist, P.; Lawther, M.; Malmström, E.; Khabbaz, F. Adhesive Properties of Wheat Gluten after Enzymatic Hydrolysis or Heat Treatment—A Comparative Study. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 38, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrain, B.; Thewissen, B.G.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Mechanism of Gliadin–Glutenin Cross-Linking during Hydrothermal Treatment. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Mu, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Cui, G. How Do Polymer Binders Assist Transition Metal Oxide Cathodes to Address the Challenge of High-Voltage Lithium Battery Applications? Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2021, 4, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, H.; Song, X.; Battaglia, V.S. Particles and Polymer Binder Interaction: A Controlling Factor in Lithium-Ion Electrode Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 159, A214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Behera, P.; Lim, S.; Yun, T.G.; Hwang, B.; Cheong, J.Y. Review of the Mechanistic and Structural Assessment of Binders in Electrodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Int. J. Energy Res. 2024, 2024, 8893580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado Pico, P.P.; Colonna, S.; Ronci, F. Low-Cost, Sustainable Hybrid Aqueous Zinc Metal Batteries Using Ethyl Cellulose as a Binder. Batteries 2025, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; Wu, F. Biologically Insoluble Binder for High-Performance Cathodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2406032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Feng, L.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Chuan, Y.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Effect of Different Binders on the Electrochemical Performance of Metal Oxide Anode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Li, H. Design of Functional Binders for High-Specific-Energy Lithium-Ion Batteries: From Molecular Structure to Electrode Properties. Ind. Chem. Mater. 2024, 2, 191–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xie, J.; Tian, M.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Feng, Y.; Hu, L. Advanced Cathode Binders for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Molecular Design and Performance Enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2025, 24, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; M. R., A.K.; Zaghib, K. Binders for Li-Ion Battery Technologies and Beyond: A Comprehensive Review. Batteries 2024, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzel, M.; Choi, H.; Wu, F.; Kazzazi, A.; Axmann, P.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Bresser, D.; Passerini, S. Co-Crosslinked Water-Soluble Biopolymers as a Binder for High-Voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4|Graphite Lithium-Ion Full Cells. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvidou, E.K.; Rensmo, A.; Benskin, J.P.; Schellenberger, S.; Hu, X.; Weil, M.; Cousins, I.T. PFAS-Free Energy Storage: Investigating Alternatives for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 21908–21917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigoni, F.; Giorgio, F.D.; Soavi, F.; Arbizzani, C. Sodium Alginate: A Water-Processable Binder in High-Voltage Cathode Formulations. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 164, A6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versaci, D.; Nasi, R.; Zubair, U.; Amici, J.; Sgroi, M.; Dumitrescu, M.A.; Francia, C.; Bodoardo, S.; Penazzi, N. New Eco-Friendly Low-Cost Binders for Li-Ion Anodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 3429–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H. The Effects of Cross-Linking Cations on the Electrochemical Behavior of Silicon Anodes with Alginate Binder. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Park, H.; Goliaszewski, A.; Byeun, Y.; Song, T.; Paik, U. In Situ Cross-Linked Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Polyethylene Glycol Binder for Improving the Long-Term Cycle Life of Silicon Anodes in Li Ion Batteries. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 8123–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

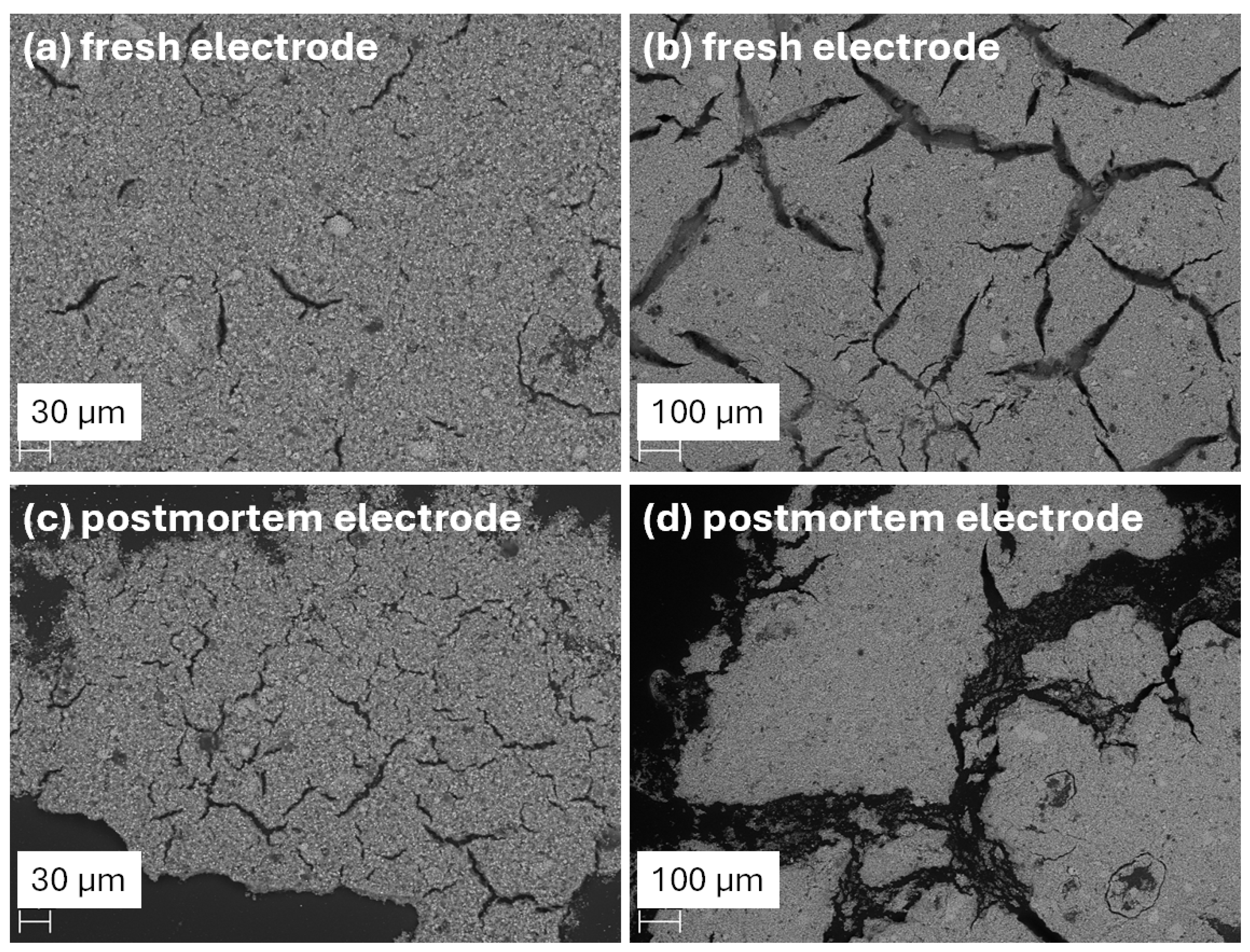

| Element | Fresh Electrode | Post-Mortem Electrode |
|---|---|---|
| Manganese (Mn) | 42 | 34 |
| Carbon (C) | 24 | 33 |
| Sulphur (S) | 0.09 | 0.01 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 3.1 | 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sepp, S.; Paalo, M.; Peljo, P. Comparative Study of Binder Stability for Aqueous Lithium-Ion and Solid-Boosted Flow Batteries. Processes 2025, 13, 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103338
Sepp S, Paalo M, Peljo P. Comparative Study of Binder Stability for Aqueous Lithium-Ion and Solid-Boosted Flow Batteries. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103338
Chicago/Turabian StyleSepp, Silver, Maarja Paalo, and Pekka Peljo. 2025. "Comparative Study of Binder Stability for Aqueous Lithium-Ion and Solid-Boosted Flow Batteries" Processes 13, no. 10: 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103338
APA StyleSepp, S., Paalo, M., & Peljo, P. (2025). Comparative Study of Binder Stability for Aqueous Lithium-Ion and Solid-Boosted Flow Batteries. Processes, 13(10), 3338. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103338








