Convective Drying of Pirul (Schinus molle) Leaves: Kinetic Modeling of Water Vapor and Bioactive Compound Retention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Drying Kinetics
2.4. Estimation of Effective Diffusivity Coefficients
2.5. Semi-Empirical Drying Modeling
2.6. Total Flavonoid Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Drying Kinetics of Schinus molle Leaves
3.2. Effective Diffusion and Activation Energy Coefficients
3.3. Semi-Empirical Kinetic Drying Modeling
3.4. Bioactive Compounds During Drying Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramírez-Albores, J.; Richardson, D.; Stefenon, V.; Bizama, G.; Pérez-Suárez, M.; Badano, E. A global assessment of the potential distribution of naturalized and planted populations of the ornamental alien tree Schinus molle. NeoBiota 2021, 68, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, F.L. The Pepper Tree, Schinus molle L. Econ. Bot. 1957, 11, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, D.; Martínez, N.; Arrieta-Garay, Y.; Fariña, L.; Boido, E.; Dellacassa, E. Valorisation of Schinus molle Fruit as a Source of Volatile Compounds in Foods as Flavours and Fragrances. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhoussaine, O.; El Kourchi, C.; Harhar, H.; Bouyahya, A.; El Yadini, A.; Fozia, F.; Alotaibi, A.; Ullah, R.; Tabyaoui, M. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant, Insecticidal Activity, and Comparative Analysis of Essential Oils of Leaves and Fruits of Schinus molle and Schinus terebinthifolius. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 4288890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, M.P.; Fronza, M.; da Silva, A.G.; Vargas, T.S.; de Andrade, T.U.; Scherer, R. Composition and Biological Activity of Brazilian Rose Pepper (Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi) Leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İlgün, S.; Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Polat, Ç.; Şafak, E.; Yücel, Ç.; İnce, U.; Uvat, H.; Akkol, E. Küpeli. Assessment of Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Potential, Antimicrobial Properties, and Antidiabetic Activity in Extracts Obtained from Schinus molle L. Leaves and Fruits. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2023, 28, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezez, D.; Belew, M.; Tekle, H.; Birhanu, H.; Lema, N.K.; Dikamu, M.; Syraji, Y. Phytochemical and Bioactivity Characterization of Schinus molle L. Leaf Extracts. Int. J. Food Prop. 2025, 28, 2553617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Veloz, L.M.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Vázquez González, Y.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Application of Essential Oils and Polyphenols as Natural Antimicrobial Agents in Postharvest Treatments: Advances and Challenges. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Silva, J.C.; Santos, N.M.; Silva, N.S.; Martins, A.C.S.; Dutra, L.M.G.; Dantas, C.E.A.; Lima, M.S.; Tavares, J.F.; da Silva, M.S.; do Nascimento, Y.M.; et al. Characterization of Flours from the Aroeira Leaf (Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi), Obtained by Different Drying Methods. J. Chromatogr. B 2024, 1239, 124126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feriani, A.; Tir, M.; Mufti, A.; Caravaca, A.M.G.; Contreras, M.d.M.; Taamalli, A.; Carretero, A.S.; Aldawood, N.; Nahdi, S.; Alwasel, S.; et al. HPLC–ESI–QTOF–MS/MS Profiling and Therapeutic Effects of Schinus terebinthifolius and Schinus molle Fruits: Investigation of Their Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Properties. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.D.; Raman, V.; Rehman, J.U.; Maia, B.H.L.N.S.; Meneghetti, E.K.; Almeida, V.P.; Silva, R.Z.; Farago, P.V.; Khan, I.A.; Budel, J.M. Schinus molle: Anatomy of Leaves and Stems, Chemical Composition and Insecticidal Activities of Volatile Oil against Bed Bug (Cimex lectularius). Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Yamashita, M.; Mori, K.; Masuoka, C.; Eto, M.; Kinjo, J.; Ikeda, T.; Yoshimitsu, H.; Nohara, T. Sesquiterpenoids, Triterpenoids, and Flavonoids from the Fruits of Schinus molle. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008, 14, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchetti, G.; Garzoli, S.; Masci, L.; Sabia, C.; Iseppi, R.; Giacomello, P.; Tiezzi, A.; Ovidi, E. Antimicrobial Testing of Schinus molle (L.) Leaf Extracts and Fractions Followed by GC-MS Investigation of Biologically Active Fractions. Molecules 2020, 25, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.R.; Arantes, S.; Candeias, F.; Tinoco, M.T.; Cruz-Morais, J. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Toxicological Properties of Schinus molle L. Essential Oils. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopel, R.; Góes Neto, R.; Falcão, M.A.; Cassel, E.; Vargas, R.M.F. Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Schinus molle L. with Co-Solvents: Mathematical Modeling and Antimicrobial Applications. Brazil. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.K.; Kumaresan, G.; Raj, V.A.; Velraj, R. Review of Leaf Drying: Mechanism and Influencing Parameters, Drying Methods, Nutrient Preservation, and Mathematical Models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 536–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Ballesteros, L.C.; González-León, A.; Martínez-Núñez, Y.J.; Robles-Burgueno, M.R.; García-Alvarado, M.A.; Rodríguez-Jimenes, G.C. Impact of Open Sun Drying and Hot Air Drying on Capsaicin, Capsanthin, and Ascorbic Acid Content in Chiltepin (Capsicum annuum L. var. glabriusculum). Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím. 2017, 16, 813–825. [Google Scholar]
- García-Alvarado, M.A.; Pacheco-Aguirre, F.M.; Ruiz-López, I.I. Analytical Solution of Simultaneous Heat and Mass Transfer Equations during Food Drying. J. Food Eng. 2014, 142, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín-Rojas, J.A.; Vázquez-León, L.A.; Salgado-Cervantes, M.A.; Fernández-Barbero, G.; Díaz-Pacheco, A.; García-Alvarado, M.A.; Rodríguez-Jimenes, G.D.C. Water and Phytochemicals Dynamic during Drying of Red Habanero Chili Pepper (Capsicum chinense) Slices. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím. 2019, 18, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.H.; Ferreira, M.C. Drying Schinus terebinthifolius Leaves in a Rotating Drum Dryer—Evaluation of the Product Quality and Energy Consumption by RSM Models. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2024, 38, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goneli, A.L.D.; Vieira, M.C.; Vilhasanti, H.C.B.; Gonçalves, A.A. Modelagem Matemática e Difusividade Efetiva de Folhas de Aroeira Durante a Secagem. Pesqui. Agropecu. Trop. 2014, 44, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbert, P.A.; Oliveira, T.R.; Berbert-Molina, M.A.; Soares, K.J.; Coelho, A.A. Thin-Layer Convective Drying Behaviour of Brazilian Peppertree Leaves. Biosci. J. 2019, 35, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1979; ISBN 0-19-853411-6. [Google Scholar]
- Páramo, D.; García-Alamilla, P.; Salgado-Cervantes, M.A.; Robles-Olvera, V.J.; Rodríguez-Jimenes, G.C.; García-Alvarado, M.A. Mass transfer of water and volatile fatty acids in cocoa beans during drying. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbay, Z.; Icier, F. A Review of Thin Layer Drying of Foods: Theory, Modeling, and Experimental Results. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Parzen, E., Tanabe, K., Kitagawa, G., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 215–222. ISBN 978-1-4612-1694-0. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, J.S.; Sousa, R.P.; Martins, L.H.S.; Costa, C.E.F.; Chisté, R.C.; Lopes, A.S. Thermal Degradation of Carotenoids from Jambu Leaves (Acmella oleracea) during Convective Drying. Foods 2023, 12, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, R.P.F.; Araújo, A.L.; Lopes, A.S.; Pena, R.S. Convective Drying of Purple Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Leaves and Stability of Chlorophyll and Phenolic Compounds during the Process. Plants 2023, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Haj Said, L.; Najjaa, H.; Farhat, A.; Neffati, M.; Bellagha, S. Thin Layer Convective Air Drying of Wild Edible Plant (Allium Roseum) Leaves: Experimental Kinetics, Modeling and Quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfinger, R. Covariance Structure Selection in General Mixed Models. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 1993, 22, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Veloz, L.M.; Olguín-Rojas, J.A.; Gómez-Flores, D.; Vázquez-González, C.; Castro-Díaz, A.S.; González-Pérez, M.; Calderón-Santoyo, M.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A. Development of Polyphenolic Extracts from Mexican Crops as Natural Antimicrobial Agents for Postharvest Treatments. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2023, 26, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Rout, R.K.; Rao, P. Drying Kinetics and Quality Attributes Analysis of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) Leaves under Distinct Drying Methods. J. Food Process Eng. 2024, 47, e14530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidar, N.; Ouhammou, M.; Mghazli, S.; Idlimam, A.; Hajjaj, A.; Bouchdoug, M.; Jaouad, A.; Mahrouz, M. The Impact of Solar Convective Drying on Kinetics, Bioactive Compounds and Microstructure of Stevia Leaves. Renew. Energy 2020, 161, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahbani, A.; Zouari, N.; Elhatmi, H.; Jridi, M.; Fakhfakh, N. Microwave Drying of Garlic (Allium sativum L.) Leaves: Kinetics Modelling and Changes in Phenolic Compounds Profile. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 59, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElGamal, R.; Song, C.; Rayan, A.M.; Liu, C.; Al-Rejaie, S.; ElMasry, G. Thermal Degradation of Bioactive Compounds during Drying Process of Horticultural and Agronomic Products: A Comprehensive Overview. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

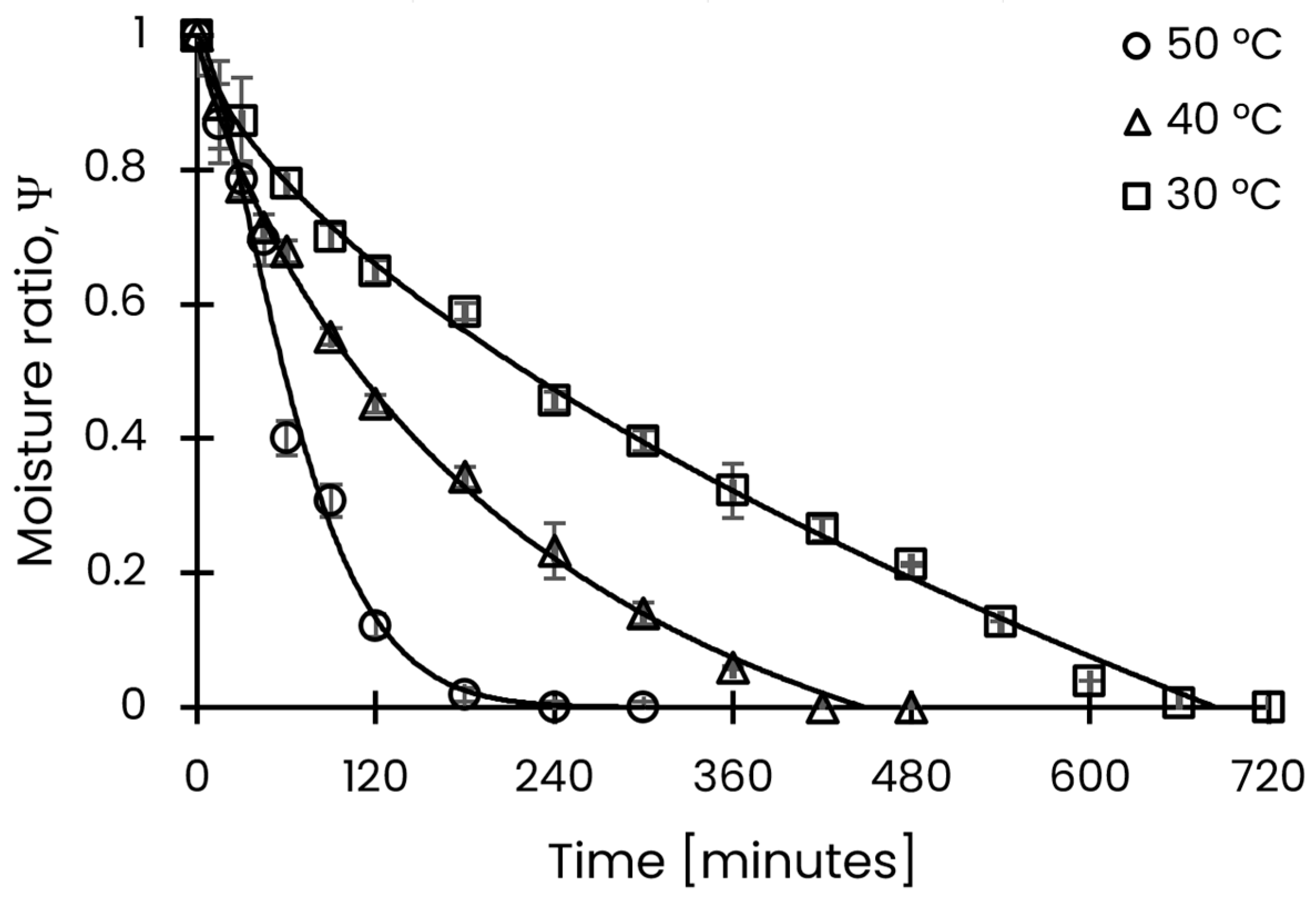
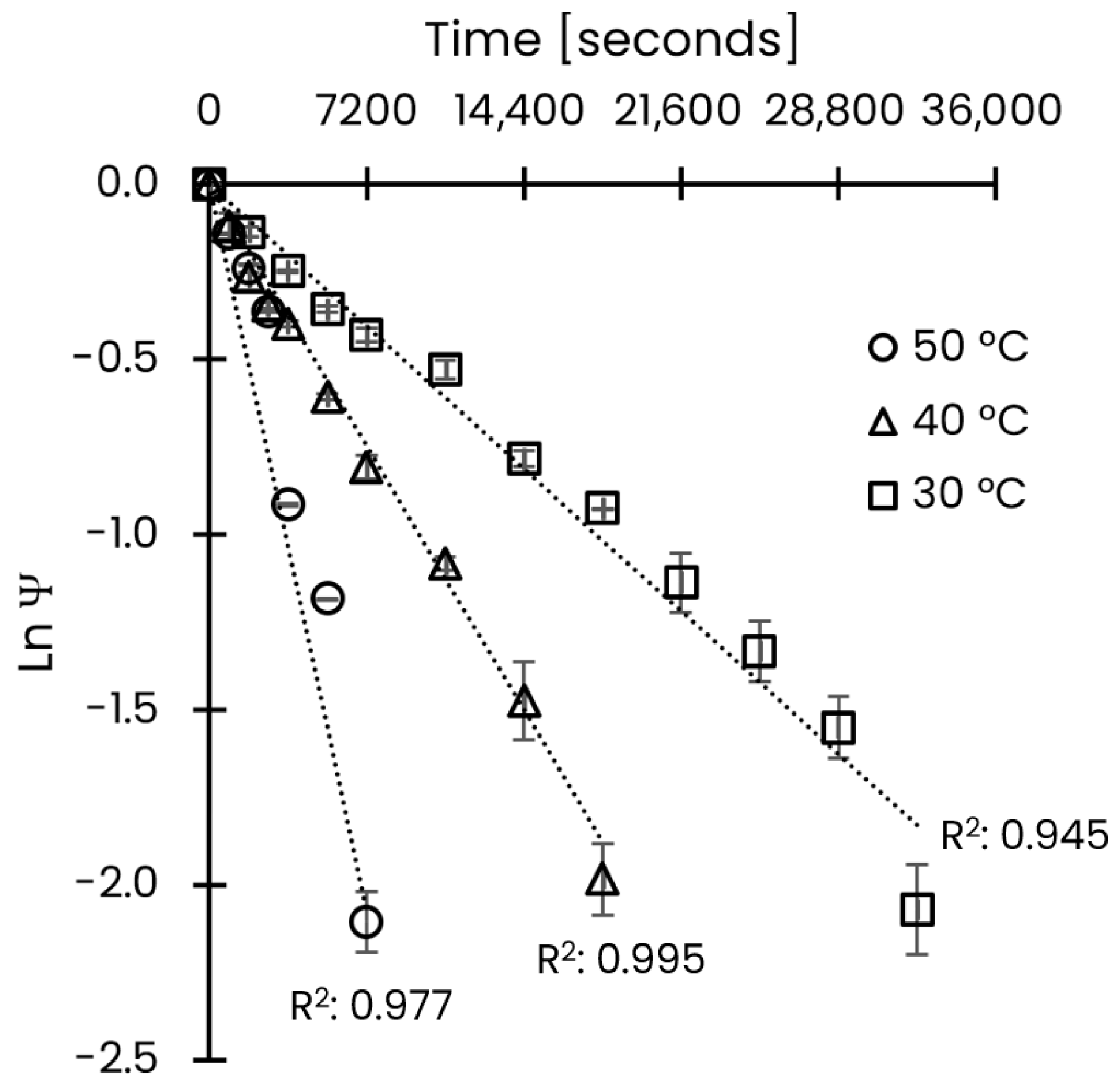
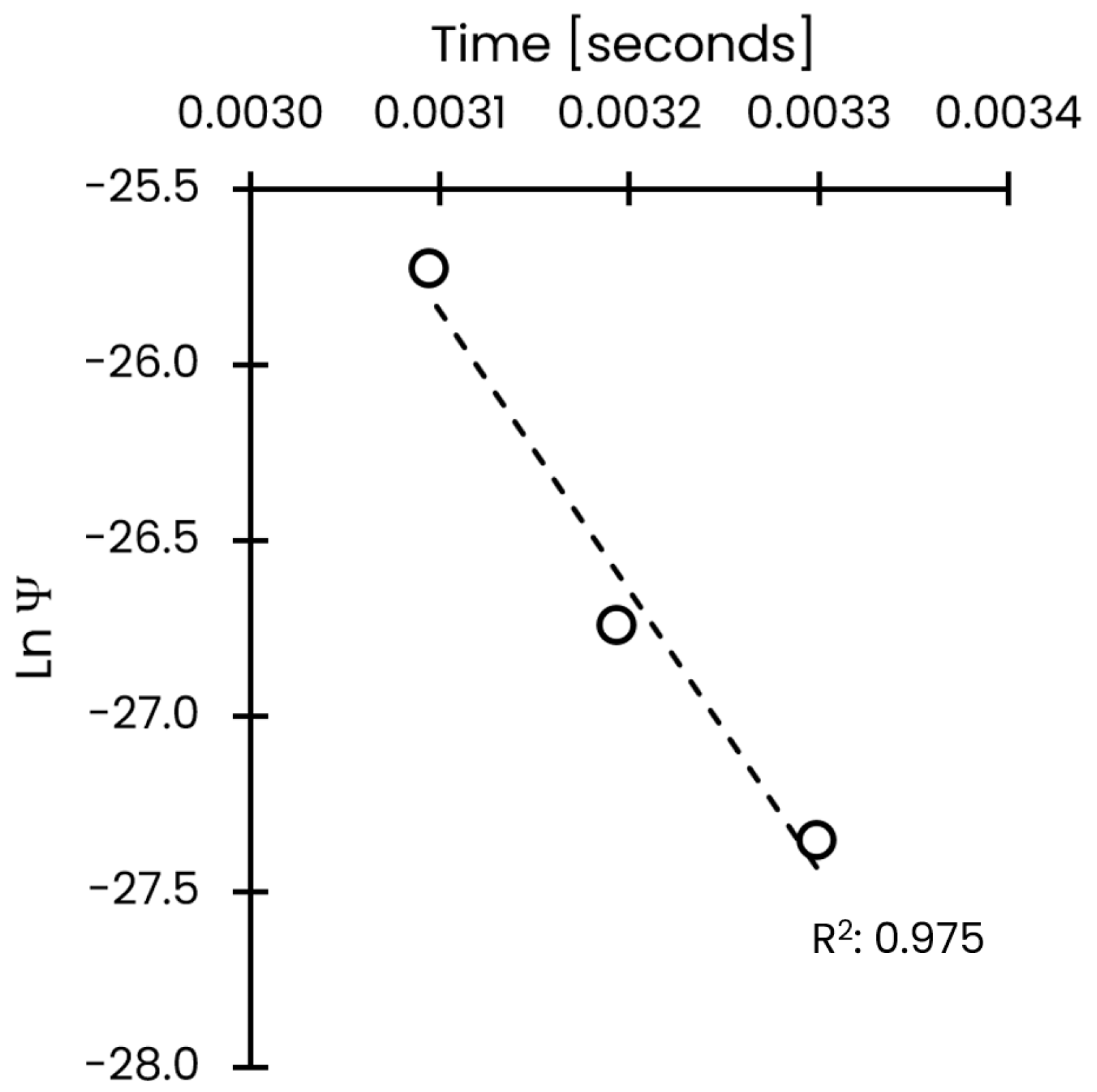

| Temperature [°C] | Effective Diffusivity [m2/s] | 95% CI [m2/s] |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 1.32 × 10−12 | (1.31–1.33) × 10−12 |
| 40 | 2.43 × 10−12 | (2.42–2.44) × 10−12 |
| 50 | 6.71 × 10−12 | (6.58–6.83) × 10−12 |
| Model | Empirical Constants | Statistical Parameters | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 °C | |||||||||||
| RMSE | BIC | ||||||||||
| Lewis | 0.0129 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.961 | 0.073 | 0.005 | −155.367 | −153.966 |
| Page | 0.0017 | 1.4844 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.988 | 0.040 | 0.002 | −188.589 | −185.787 |
| Henderson and Pabis | 0.0014 | 1.5255 | 0.9857 | -- | -- | -- | 0.988 | 0.040 | 0.002 | −187.068 | −182.865 |
| Logarithmic | 0.0014 | 1.5255 | 0.9857 | 8.83 × 10−8 | -- | -- | 0.988 | 0.040 | 0.003 | −185.068 | −179.463 |
| Midilli | 0.0014 | 1.5255 | 0.9857 | 9.0 × 10−8 | -- | -- | 0.988 | 0.040 | 0.002 | −185.068 | −179.463 |
| Two-term | -- | -- | 0.4956 | 0.5768 | 0.0140 | 0.0140 | 0.968 | 0.066 | 0.005 | −155.006 | −149.401 |
| 40 °C | |||||||||||
| Lewis | 0.0067 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.992 | 0.030 | 0.0010 | −263.272 | −261.608 |
| Page | 0.0069 | 0.9940 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.992 | 0.030 | 0.0011 | −261.579 | −258.252 |
| Henderson and Pabis | 0.0054 | 1.0360 | 0.9762 | -- | -- | -- | 0.992 | 0.029 | 0.0011 | −261.897 | −256.906 |
| Logarithmic | 0.0115 | 0.8132 | 1.2394 | −0.2370 | -- | -- | 0.998 | 0.015 | 0.0003 | −298.729 | −292.075 |
| Midilli | 0.0128 | 0.8356 | 1.0012 | −0.0003 | -- | -- | 0.998 | 0.015 | 0.0003 | −297.628 | −290.974 |
| Two-term | -- | -- | 0.5846 | 0.4019 | 0.0066 | 0.0066 | 0.992 | 0.029 | 0.0012 | −259.770 | −253.115 |
| 30 °C | |||||||||||
| Lewis | 0.00351 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.977 | 0.048 | 0.0025 | −268.549 | −266.743 |
| Page | 0.00250 | 1.05921 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 0.978 | 0.047 | 0.0026 | −268.480 | −264.867 |
| Henderson and Pabis | 0.00106 | 1.19406 | 0.9404 | -- | -- | -- | 0.980 | 0.044 | 0.0024 | −272.374 | −266.954 |
| Logarithmic | 0.00249 | 0.64912 | 6.3133 | −5.3115 | -- | -- | 0.997 | 0.018 | 0.0004 | −340.132 | −332.906 |
| Midilli | 0.01415 | 0.65590 | 1.0009 | −0.0005 | -- | -- | 0.997 | 0.018 | 0.0004 | −339.887 | −332.661 |
| Two-term | -- | -- | 0.5959 | 0.3959 | 0.00348 | 0.00348 | 0.977 | 0.048 | 0.0035 | −262.762 | −255.536 |
| Temperature [°C] | Total Flavonoids Content [mg QE/100 g Dry Leaf] (Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|
| Fresh leaves | 57.53 ± 1.54 a |
| 30 | 36.27 ± 1.57 b |
| 40 | 29.31 ± 0.73 c |
| 50 | 21.76 ± 0.7 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olguín-Rojas, J.A.; Martinez-Candelario, A.; Pérez-Landa, I.D.; Aguirre-Lara, P.; González-Urrutia, M.M.; González-Pérez, M. Convective Drying of Pirul (Schinus molle) Leaves: Kinetic Modeling of Water Vapor and Bioactive Compound Retention. Processes 2025, 13, 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103259
Olguín-Rojas JA, Martinez-Candelario A, Pérez-Landa ID, Aguirre-Lara P, González-Urrutia MM, González-Pérez M. Convective Drying of Pirul (Schinus molle) Leaves: Kinetic Modeling of Water Vapor and Bioactive Compound Retention. Processes. 2025; 13(10):3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103259
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlguín-Rojas, José Arturo, Ariana Martinez-Candelario, Irving David Pérez-Landa, Paulina Aguirre-Lara, Maria Mariana González-Urrutia, and Manuel González-Pérez. 2025. "Convective Drying of Pirul (Schinus molle) Leaves: Kinetic Modeling of Water Vapor and Bioactive Compound Retention" Processes 13, no. 10: 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103259
APA StyleOlguín-Rojas, J. A., Martinez-Candelario, A., Pérez-Landa, I. D., Aguirre-Lara, P., González-Urrutia, M. M., & González-Pérez, M. (2025). Convective Drying of Pirul (Schinus molle) Leaves: Kinetic Modeling of Water Vapor and Bioactive Compound Retention. Processes, 13(10), 3259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13103259






