Abstract
The objective of this study was to investigate the adsorption of 11 azoles (tebuconazole, ketoconazole, econazole, miconazole, fluconazole, clotrimazole, climbazole, flutriafol, epoxiconazole, tiabendazole, and imazalil) on natural and waste-derived sorbents such as ceramsite, perlite, pumice, sawdust, coconut fibers, heavy oil fly ash (HOFA), activated carbon, and silica gel. The results of adsorption efficiency for most sorbents varied depending on the azole compounds and their concentration. The highest adsorption for all tested compounds was obtained for activated carbon and heavy oil fly ash, reaching about 100% in both tested concentrations (0.2 mg L−1 and 0.02 mg L−1). The HOFA material was characterized in terms of elemental analysis (CHNS), confirming the elemental contents of 52% C, 0.65% H, 0.4% N, and 2.3% S. The specific surface area of HOFA was 11.2 m2 g−1, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) results showed the spherical yet porous nature of the particles. Furthermore, the calculated adsorption isotherms demonstrated that for most tested azoles, the Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R) isotherm best fits the data, with R2 = 0.93 or more, which is characteristic of porous carbon materials. The results highlight the significant potential of the tested HOFA sorbent for effectively removing azoles, as the tests performed showed that it was possible to remove these compounds with a concentration of up to 0.2 mg L−1 within an hour. This is particularly important because HOFA is an easily accessible waste material. Furthermore, the adsorption of azoles will not increase the cost of HOFA disposal when using the standard procedures currently applied to this waste.
1. Introduction
Although fungi play a crucial role in the environment, such as in decomposing organic matter, they are also responsible for numerous infections in humans and animals. As reported by the Global Action for Fungal Infections, more than 300 million people are afflicted by severe fungal infections, whereas approximately 25% of the worldwide population experiences mild fungal infections concerning the skin, hair, and nails [1]. Additionally, fungi cause plant diseases that reduce crop yields; for example, discontinuing azole fungicides in Europe could lead to a 10% drop in wheat production [2]. This drives an increase in sales of antifungal agents such as azole compounds for applications in both medicine and personal care products, as well as agriculture. An analysis of pharmaceutical sales data reveals that global fluconazole consumption increased from 0.14 to 0.23 defined daily doses (DDD) per 1000 inhabitants per day between 2008 and 2018, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 4.77% [3]. Moreover, it is estimated that the combined annual sales of fungicides and bactericides exceed 160,000 tons [4].
Among the most frequently applied antifungal agents are azole compounds. Their mechanism of action involves disrupting ergosterol biosynthesis by inhibiting the cytochrome P450-dependent 14α-demethylase enzyme, resulting in an increase in the permeability of fungal cell membranes, ultimately inhibiting fungal growth or causing cell death [5]. Azoles are categorized into imidazole and triazole derivatives based on their chemical structure. They are characterized by relatively high lipophilicity and persistence in soil and aquatic environments, as well as stability against hydrolytic, photolytic, and biological degradation [6,7]. The removal efficiency of fluconazole during treatment with activated sludge reached a maximum of 16.7% in Swedish wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) [8] and up to 68% in Swiss WWTPs [9]. As a result, the presence of azole compounds has been detected in the environment, such as in surface waters in South Africa [10], Germany [11], China [12,13,14], Poland [15], and Spain [16], as well as in soil samples in China [7,17]. Hence, supportive or alternative methods are required for eliminating azoles.
Indeed, the problem of azoles in the environment has been downplayed for years. Despite existing publications and reports showing incomplete biodegradation of azoles and their presence in the environment, only a few compounds have been banned. The European Commission has decided to discontinue the use of products containing flutriafol and epoxiconazole [18,19]. The problem of azoles in the environment became particularly important when it was noticed that the use of azole fungicides causes the spread of azole-resistant Aspergillus spp. [20]. As a result, some azoles have been selected for the 5th Watch List under the Water Framework Directive. No proposal for the limits has been made; however, the Predicted No-Effect Concentrations have been included in the document, ranging from 0.008 to 1.6 µg L−1 [21]. In this context, the complete removal of azoles in WWTPs is very important, and reports of their incomplete biodegradation are particularly worrying [22,23,24].
One of the methods of removing environmental pollutants is adsorption. It is a process in which a molecule present in the liquid or gas phase is attached to the surface of a solid adsorbent [25]. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon primarily driven by surface forces and the affinity of molecules to the sorbent. Based on the kind of interaction between the adsorbed molecules and the surface of the adsorbent, two types of adsorption are distinguished: physisorption and chemisorption [26]. Physisorption is induced by weak forces like electrostatic attraction and van der Waals forces, which makes it a reversible and relatively low-energy process. It usually results in multilayer formation on the surface of the adsorbent, which is characterized by high surface area and porous structure, such as activated carbon. On the contrary, chemisorption is based on the creation of chemical bonds (covalent or ionic) between the adsorbate and the adsorbent surface, forming a monolayer [27,28]. For this kind of adsorption, metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and zeolites are used as sorbents, providing greater specificity and irreversibility. The effectiveness of adsorption is determined by several factors, including the characteristics of the adsorbate, and the surface area and porosity of the adsorbent, as well as operational parameters such as temperature and pressure [29]. The main advantages of adsorption include its relatively low price, ease of operation, and lack of hazardous reaction products [30].
Adsorbents are generally categorized into three types: natural organic adsorbents, natural inorganic adsorbents, and synthetic adsorbents [31]. The former are characterized by wide availability and low price, and can be divided into agricultural waste materials (rice husk [32] almond shell [33], cotton waste [34], coconut shell [35,36]), fruit waste (citrus peel [37]), and plant waste (sawdust [38], plant leaf powder [39]) as well as bio-adsorbents (eggshell [40]). Natural inorganic sorbents include materials such as clays, ceramsite, pumice, and perlite, because of their porous structure and mineral composition [41]. The most commonly used natural inorganic adsorbent is activated carbon, with its outstanding porosity and large surface area. It can be produced from a wide variety of raw, carbon-rich materials, such as coal or wood, at high temperatures under limited oxygen conditions [25]. Activated carbon is frequently used in water and air purification to remove contaminants such as dyes [42,43], antibiotics [44], endocrine disruptors [45], volatile organic compounds [46], and heavy metals [47,48]. An additional inorganic sorbent of natural origin is silica gel, used in the removal of moisture and drying of gases, as well as adsorption of chlorinated organic compounds [49] and heavy metals [50]. The low-cost adsorbents also include industrial by-products such as heavy oil fly ash (HOFA). This is a waste product of heavy fuel oil combustion at power stations. Due to its high carbon content (40–60 wt.%) and porous structure, it is suitable for adsorption applications [51,52].
The removal of azole compounds by adsorption was studied with the use of various adsorbents. Some of them belonged to the group of carbon materials of natural origin, such as activated carbon [53,54], hydrochar [55], and biochar [56]. Lu et al. investigated the adsorption of azole fungicides on novel composites such as a metal–organic framework functionalized magnetic lignosulfonate [57] as well as a magnetic composite synthesized from magnetic wheat straw biochar and a bimetallic organic framework [58]. However, adsorption of azoles on carbon-based waste materials available in large quantities, such as HOFA, has not been investigated.
The main objective of this study was to investigate the adsorption process on low-cost materials as a method of removing eleven azole antifungals (clotrimazole, climbazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, econazole, tebuconazole, epoxiconazole, flutriafol, tiabendazole, and imazalil) from a water solution. In the presented research, the following sorbents were tested: ceramsite, pumice, perlite, sawdust, coconut shell, activated carbon, silica gel, and heavy oil fly ash. Furthermore, the material with the highest removal efficiencies was characterized in terms of elemental analysis (CHNS), loss on ignition, specific surface area, SEM, and EDX. Then, the adsorption mechanism was examined through adsorption kinetics and isotherm investigation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Equipment
The study used 11 azole standards. Climbazole (CLI), clotrimazole (CLO), econazole (ECO), ketoconazole (KET), and miconazole (MIC) were obtained from Pol-Aura (Poznań, Poland), while epoxiconazole (EPO), fluconazole (FLU), flutriafol (FLUTR), imazalil (IMAZ), and thiabendazole (TIAB) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich/Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Tebuconazole (TEB) was obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). All standards had a purity of ≥98.0%. A list of them, along with chemical formulas and properties, is provided in Table S1. MS-grade acetonitrile and formic acid (≥97.5%), both supplied by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), were used to prepare the mobile phase for chromatography. Ultrapure water was produced via reverse osmosis using a Demiwa system (Watek, Ledec nad Sazavou, Czech Republic), followed by double distillation in a Heraeus Bi 18 E quartz apparatus (Hanau, Germany).
2.2. Adsorbents Tested for Removal of Azoles
For the purpose of the study, several adsorbents were tested. As the aim of the study was to find inexpensive sorbents capable of adsorbing azoles, nature-derived and waste materials were chosen. These include ceramsite fraction 8–16 mm from AGRO CS (Rikov, The Czech Republic), perlite from EKODARPOL (Poznań, Poland), pumice milled type FFF (16 µm granules) from AnVit (Bilczyce, Poland), coconut fibers from AQUEL (Warsaw, Poland), sawdust from Vitakraft (Zooplus, Wrocław, Poland), heavy oil fly ash (HOFA) from Re-Solve (Malbork, Poland), activated carbon from Wessper (Rzezawa, Poland), and silica gel with a size of 3.5 mm, 60 Å mean pore size, and surface area of 500 m2 g−1 from Sigma-Aldrich (Steinheim, Germany). Coarse materials were crushed or shredded to obtain a fraction of 0.01–0.1 mm.
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of HOFA
Surface area was analyzed using the Autosorb iQ analyzer from Quantachrome (USA). Elemental analysis of HOFA for the contents of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur was conducted using the Elementar Analyser Vario EL from Elementar Analysensysteme (Langenselbold, Germany).
A scanning electron microscope (SEM, S-3400N, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) was used to study the surface and morphologies of HOFA. The microscope is equipped with a tungsten wire cathode serving as the primary electron beam source, working at an acceleration voltage from 0.3 to 30 kV. Vacuum in the working chamber is below 0.001 Pa. Resolution is 3.0 nm at 30 kV for the SE detector and 4.0 nm at 30 kV for the BSE detector. The working magnification range is from 5 to 300,000×, while the measurements were performed at magnifications of 50×, 500×, and 5000×. Thermo Scientific NSS spectral imaging software was used for elemental analysis of HOFA using Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS).
2.4. Azole Adsorption
The sorption material was ground using a mortar or laboratory grinder and then sieved to obtain a fraction of 50 to 160 µm. The adsorbent in the amount of 0.5 g was weighed into 40 mL orange glass vials (to prevent photodegradation during tests), and then 20 mL of an aqueous solution of the corresponding azole was introduced at two concentration levels, i.e., 0.2 and 0.02 mg L−1. The samples prepared in this way were inserted into a shaker to better mix the components and ensure constant adsorption conditions. The experiment lasted 24 h, and samples were collected for analysis during the run. The first samples were taken as soon as they were prepared, and subsequent samples were taken after 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 10 h, and 24 h. The sample was diluted 2-fold before LC-MS/MS analysis and filtered through a PTFE syringe filter with a pore size of 0.2 µm. Each experiment was repeated in order to obtain reliable results.
2.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis
Azoles contained in the samples were determined using an LC-MS/MS apparatus comprising an UltiMate 3000 HPLC chromatograph (Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) coupled with a 4000 QTRAP mass spectrometer (ABSciex, Foster City, CA, USA). The system was equipped with a Kinetex Evo C18 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm I.D., 2.6 µm particle size) from Phenomenex (Torrance, CA, USA). A 5 μL sample was injected, and the column was maintained at a constant temperature of 35 °C. The mobile phase consisted of ultrapure water containing 0.1% formic acid (phase A) and acetonitrile (phase B), delivered at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. Chromatographic separation was achieved using a gradient elution program, in which the proportion of the organic solvent was increased according to the following schedule—20% at 0 min, 60% at 4 min, and 100% at 4.5 min—and maintained at 100% until 6.5 min.
The column effluent was introduced into the mass spectrometer via a Turbo Ion Spray electrospray ionization source operating in positive ion mode. The mass spectrometer was configured with the following parameters: ESI temperature of 450 °C, ion spray voltage of 4500 V, curtain gas pressure at 10 psi, nebulizer gas at 40 psi, auxiliary gas at 45 psi, and collision gas set to high. The dwell time for each mass transition was 100 ms. The monitored MRM (multiple reaction monitoring) transitions and specific parameters for each analyte are listed in Table S2.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption of Azoles
Guided by the need to find a low-cost adsorbent, one should consider materials that are available in large quantities, including natural and waste materials. This type of material was used in the present study to remove contaminants from the azole group. For this purpose, eight sorbents were selected, such as minerals (ceramsite (expanded clay aggregate), perlite (amorphous volcanic glass), pumice (vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass)), wastes of plant origin (sawdust and coconut fibers), heavy oil fly ash (HOFA, a waste material containing carbon and silica), activated carbon, and silica gel. Adsorption of 11 azoles on these materials was tested at two concentrations, 0.2 mg L−1 (a relatively high concentration at which all tested azoles were soluble in water) and 0.02 mg L−1. The results are presented in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3.
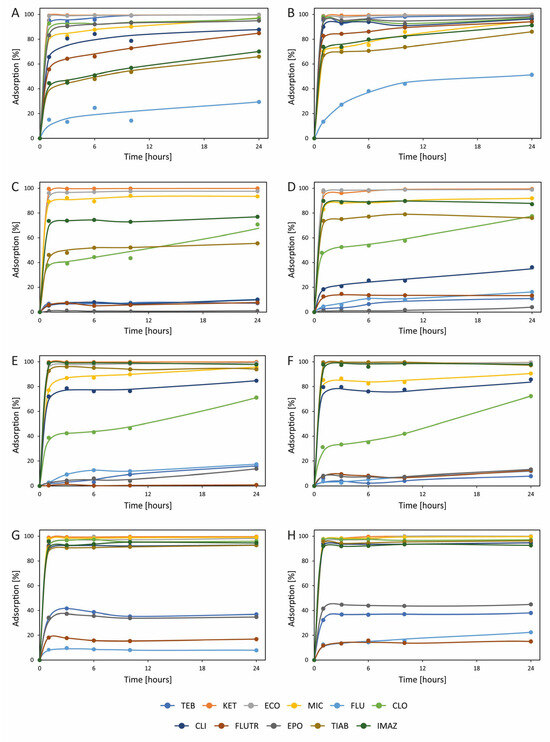
Figure 1.
Adsorption of azoles on (A) ceramsite at 0.2 mg L−1, (B) ceramsite at 0.02 mg L−1, (C) perlite at 0.2 mg L−1, (D) perlite at 0.02 mg L−1, (E) pumice at 0.2 mg L−1, (F) pumice at 0.02 mg L−1, (G) silica gel at 0.2 mg L−1, and (H) silica gel at 0.02 mg L−1. TEB—tebuconazole; KET—ketoconazole; ECO—econazole; MIC—miconazole; FLU—fluconazole; CLO—clotrimazole; CLI—climbazole; FLUTR—flutriafol; EPO—epoxiconazole; TIAB—tiabendazole; and IMAZ—imazalil. Detailed results, together with standard deviations, are presented in Table S3.
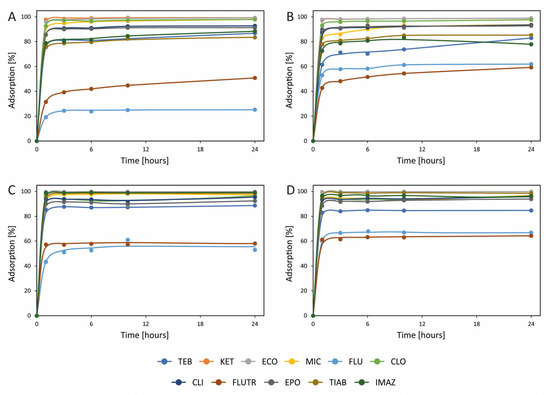
Figure 2.
Adsorption of azoles on (A) sawdust at 0.2 mg L−1, (B) sawdust at 0.02 mg L−1, (C) coconut fibers at 0.2 mg L−1, and (D) coconut fibers at 0.02 mg L−1. TEB—tebuconazole; KET—ketoconazole; ECO—econazole; MIC—miconazole; FLU—fluconazole; CLO—clotrimazole; CLI—climbazole; FLUTR—flutriafol; EPO—epoxiconazole; TIAB—tiabendazole; and IMAZ—imazalil. Detailed results, together with standard deviations, are presented in Table S3.
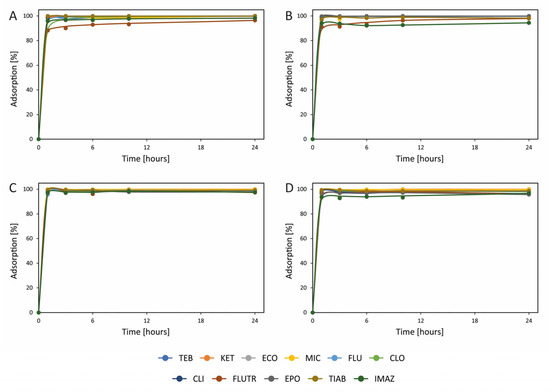
Figure 3.
Adsorption of azoles on (A) heavy oil fly ash (HOFA) at 0.2 mg L−1, (B) HOFA at 0.02 mg L−1, (C) activated carbon at 0.2 mg L−1, and (D) activated carbon at 0.02 mg L−1. TEB—tebuconazole; KET—ketoconazole; ECO—econazole; MIC—miconazole; FLU—fluconazole; CLO—clotrimazole; CLI—climbazole; FLUTR—flutriafol; EPO—epoxiconazole; TIAB—tiabendazole; and IMAZ—imazalil. Detailed results, together with standard deviations, are presented in Table S3.
Among the sorbents studied, perlite and pumice (both of natural origin) contain a high percentage of silicon and silica itself. These materials are often used in the removal of contaminants from wastewater [41,59]. Both perlite and pumice are of volcanic origin and have considerable porosity, although pumice is naturally porous and perlite is expanded at high temperatures. Interestingly, even though a high content of acidic silica should favor the adsorption of basic azoles, this is not observed for most tested compounds. For perlite, adsorption of TEB, FLU, FLUTR, and EPO is below 20% at both studied concentrations (Figure 1). CLI adsorption from a 0.2 mg L−1 solution is below 10%, while from 0.02 mg L−1, it exceeds 30%. For TIAB, adsorption is over 50% at 0.2 mg L−1 and about 80% at 0.02 mg L−1. Due to their low weight, porous structure, and large surface area, perlite and pumice have typical characteristics of adsorbents. However, these materials did not perform well for removing all tested azoles. Also, adsorption on pure silica gel was low for some azoles, including FLU and FLUTR (both below 20%) as well as TEB and EPO (both about 40%). Considerably better adsorption was noted on expanded clay aggregate, which is also produced from silicon-containing minerals present in clay. For this material, relatively low adsorption was noted only for FLU (about 30% at 0.2 mg L−1 solution and about 50% at 0.02 mg L−1), which, compared to other azoles, has the lowest pKa value (2.56) and the lowest octanol–water partition coefficient (0.4). About 60% of TIAB and IMAZ was adsorbed from a 0.2 mg L−1 solution, and about 90% from a 0.02 mg L−1 solution. Better results were obtained for FLUTR (about 80% and 90% from 0.2 mg L−1 and 0.02 mg L−1 solutions, respectively). Adsorption of other azoles was greater—about 100%. Interestingly, the lowest adsorption on silica gel, perlite, and pumice, which also contain silica, was noted for both FLU and FLUTR. Both these compounds are acidic (low pKa) and lowly extractable by octanol (low KOW), hence their low affinity for silica gel and silica-containing materials, which are highly polar and acidic.
Other interesting sorption materials are sawdust, a common by-product of the wood industry, and coconut fibers from coconut husk, which is a type of agricultural by-product. Both of these materials come at a negligible price and are among the most widely used adsorbents, having been used to remove different compounds, e.g., dyes [60,61]. Currently, sawdust and coconut fibers play an important role in the adsorption of wastewater pollutants because they contain numerous functional groups, such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenolic, and amide groups, in their structure, which can be beneficial for adsorbing a wide range of compounds. The major chemical constituents of sawdust are hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. The chemical composition translates into the formation of pores, thus determining their volume and surface area.
Adsorption of azoles was also tested on sawdust and coconut fibers, which are waste materials available in large quantities (Figure 2). The results were considerably better than those obtained for perlite, pumice, and silica gel. However, in comparison with ceramsite, similar results were found; i.e., considerably lower than 100% adsorption was noted for the same azoles, including FLU and FLUTR, for both sorbents, as well as TIAB and IMAZ for sawdust. On the other hand, slightly lower adsorption than for ceramsite was observed on sawdust and coconut fibers for TEB. This similarity of sawdust and coconut fibers with ceramsite shows that the interactions between these sorbents and azoles may be of a similar type, in contrast to adsorption on perlite, pumice, and silica gel.
Sawdust and lignocellulosic materials like coconut fibers are freely accessible and abundant (up to 24.15 million m3 per year worldwide [62]) and can also be used to obtain activated carbon, which is widely applied as an ideal sorbent. However, while the materials used to obtain this sorbent are inexpensive, unfortunately, energy input is required to obtain it [63].
The greatest adsorption of azoles was observed for both activated carbon and HOFA (Figure 3). About 100% adsorption was found for all azoles on both these materials, showing their great similarity in terms of azole removal. Also, no substantial difference was noted between the adsorption of azoles from 0.2 mg L−1 and 0.02 mg L−1 solutions. Importantly, previous studies also showed good adsorption of azoles on activated carbon [54]. The present study has shown that HOFA can successfully replace activated carbon in the removal of azoles, opening a new path for the use of this waste material. Importantly, the similarity of HOFA to activated carbon in terms of the adsorption of azoles is promising for the removal of many other pollutants, since the use of activated carbon for the adsorption of pollutants is quite common [43,45,47,54]. Moreover, HOFA is available in large quantities at a low cost. The material is managed through various methods, including disposal in landfills and utilization in construction materials like asphalt and concrete. Similar means of disposal may be used for HOFA containing azoles. This will enable the simultaneous removal of these two types of contaminants, making the process very economical.
3.2. Characterization of Heavy Oil Fly Ash
Since HOFA showed the best adsorption properties among the tested materials, it was decided to characterize it in more detail. HOFA is fly ash from the combustion of heavy petroleum fractions obtained based on the description given in patent application [64]. The main components of HOFA are unburned carbon—from 30% to more than 90%—and inorganic components such as SiO2, Fe2O3, aluminosilicates, and sulfur, as well as heavy metals, mainly vanadium, nickel, and iron. Most of the metallic components are leached out of it with water under acidic conditions, and the water extract of HOFA (L:S ratio 1:10) has a pH in the range of 1.0–3.5 due to the content of sulfur oxides that form strong acids with water. At the same time, HOFA is used as a raw material for extracting valuable metals, mainly vanadium and nickel, or as an additive in the production of building materials [65,66,67].
The material used in the study is the residue from the aqueous extraction of soluble components from raw HOFA. Its extraction was carried out under acidic conditions, and the extraction residue was rinsed with water until the conductivity of the rinsing water was below 3 mS. The minerals contained in washed HOFA are mainly silica and/or silicates. It contains 52% C, 0.65% H, 0.4% N, and 2.3% S. Other batches of the same material contained 46–68% C, 0.6–0.7% H, 0.4–1.0% N, and 2.3–3.5% S. Loss on ignition at 650 °C was 87% (other batches 80–91%), mineral components represented 13% (other batches 9–20%), the specific surface area was 11.2 m2 g−1 (other batches 8.5–13.5 m2 g−1), and 90% of the grain was between 40 and 80 µm (other batches 20–120). The SEM results show the spherical yet porous nature of the particles (Figure 4), although the pore volume of HOFA materials synthesized in our laboratory is only ~5 × 10−2 cm3 g−1, and the average pore size is ~15 nm. Nevertheless, despite its significantly lower porosity than typical activated carbons, HOFA’s properties still enable satisfactory removal of azoles.
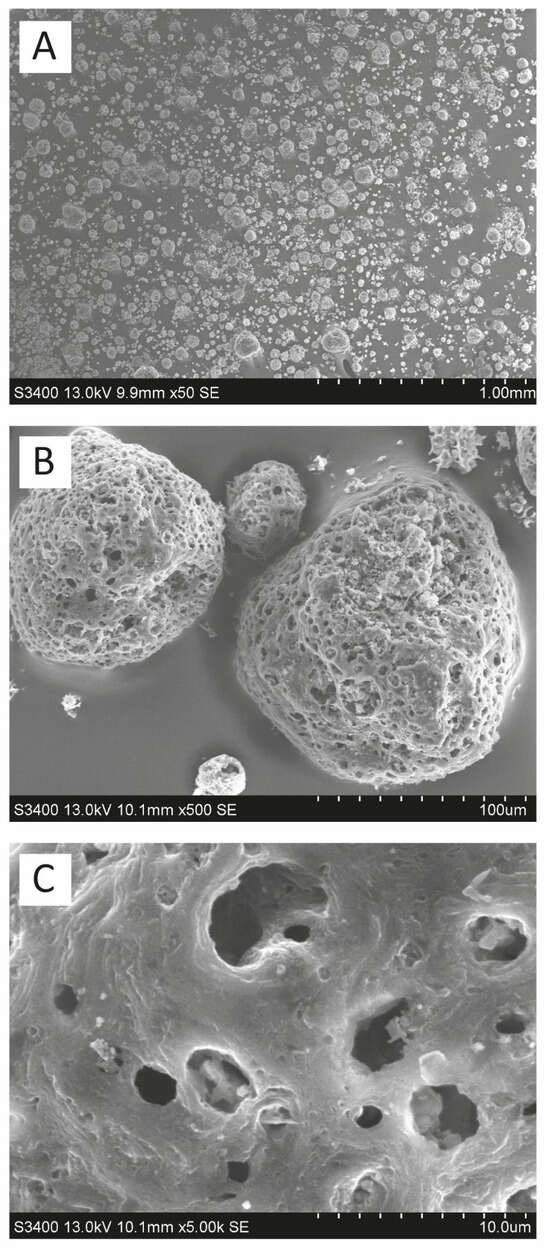
Figure 4.
SEM images of heavy oil fly ash (HOFA) at different magnifications. (A) 50×; (B) 500×; (C) 5000×.
The EDS measurement of the HOFA material shows that its main component is carbon, which accounts for about 68.2% by weight (Figure 5). Oxygen (11.6%), vanadium (7.1%), sulfur (4.4%), iron (4.1%), and nickel (3.4%) are also important components. On the other hand, silicon accounts for only 0.55% by weight. The black spots on the microscopic image originate from the empty spaces (pores), the matrix of the material is gray, and white inclusions are visible. The bright spots are characteristic of materials with a specific gravity higher than that of the gray-colored material. This shows that the material is not fully homogeneous. The EDS measurement focused on the gray area shows that it consists of nearly 80% carbon. Oxygen accounts for 7.5%, while sulfur, vanadium, iron, and nickel account for 4.6%, 3.8%, 2.2% and 2.1%, respectively (Figure S1). On the other hand, the white area contains less than 30% carbon, and much higher amounts of oxygen (18.7%) and heavy metals, i.e., 23.5% V, 8.5% Fe, and 16.8% Ni (Figure S2).
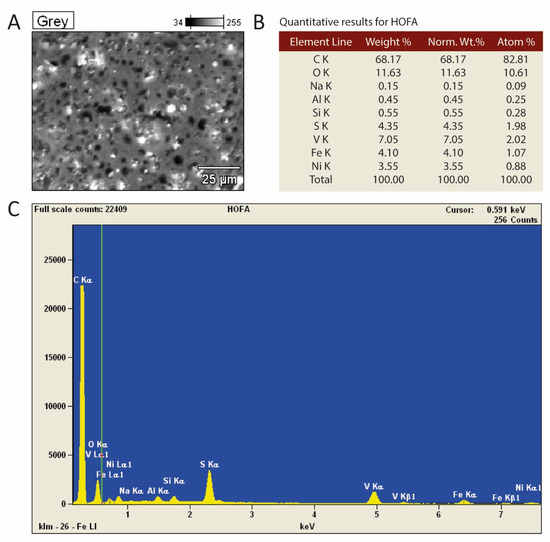
Figure 5.
The EDS measurements with (A) a microscopic photograph of the tested area, (B) the contents of elements in the tested area, and (C) a spectral chart with lines characteristic of detected elements.
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics
HOFA was further characterized to gain more information about its ability to adsorb azoles. Thus, adsorption isotherms were calculated for each azole. The gathered data were matched to four different models. The results presented in Table 1 and Table 2 show that for most tested compounds, the Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R) isotherm best fits the data, with R2 = 0.93 or more. Interestingly, for CLO, the Langmuir isotherm, and for FLUTR, the Freudlich isotherm, correlated better than the D-R isotherm. Nevertheless, the difference was very small, and the adsorption of both these compounds could also be described using the D-R model. Similarly, for ECO, the best fit was obtained for the Temkin model, while the D-R model was the second possible fit. Only for KET was no good fit obtained, as this compound was found to adsorb completely in the tested concentration range.

Table 1.
The R2 values obtained for different adsorption isotherms (Langmuir, Freudlich, Temkin, and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R)). The heat-map shows data fit to different isotherm types—green color shows the best fit, and red the worst.

Table 2.
The Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms obtained for the adsorption of azoles.
The D-R isotherm is widely found appropriate for the description of adsorption on microporous materials, in particular those of carbon origin [68,69,70]. Studies showed many applications of different carbonaceous materials, mainly activated carbon, for the adsorption of organic substances as well as metals [70]. In this context, the tested HOFA material resembles activated carbon as it contains porous carbon structures and adsorbs readily, and the adsorption process can be characterized by the D-R isotherms.
Adsorption of azoles on the tested HOFA material is highly dependent on the compound (Figure 6). Some azoles are easily adsorbed on HOFA in a wide concentration range from 0.02 to 2 mg L−1. These include KET, ECO, MIT, and TIAB, as well as TEB and EPO. For other azoles, adsorption is highly dependent on their concentrations, including CLI, CLO, FLUTR, IMAZ, and, most of all, FLU. Interestingly, the lowest adsorption of FLU can be connected with its low logKow. Thus, it is too polar for easy adsorption on relatively non-polar carbon material like HOFA.
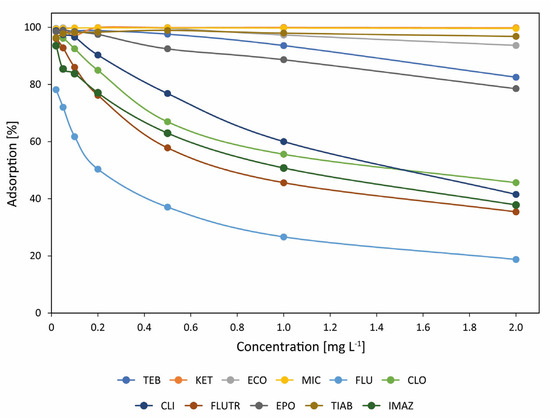
Figure 6.
Adsorption of azoles on heavy oil fly ash (HOFA) depending on their initial concentration in solution.
The adsorption energy calculated for azoles adsorbed on HOFA is between 34.1 and 51.4 kJ mol−1 (Table 2). These values are between the ranges observed for physical (0 to 20 kJ mol−1) and chemical (80 to 400 kJ mol−1) adsorption [71]. Thus, the obtained results show physicochemical adsorption, which may be connected with different mechanisms involved in the process. Not only are different kinds of adsorption sites possible (as a part of carbon forming aromatic rings, HOFA contains oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur atoms), but also tested compounds contain azoles and phenolic aromatic rings as well as hydroxy, ketone, and etheric oxygen atoms (Figure 7).
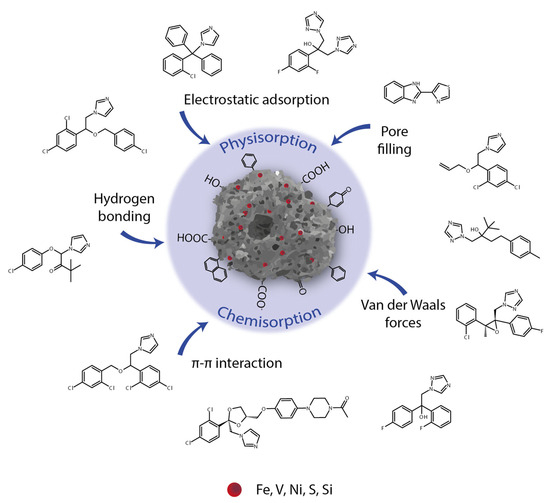
Figure 7.
Possible mechanisms of azole adsorption on HOFA.
Data obtained for the adsorption of azoles on HOFA fit the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, with R2 values ranging from 0.9998 to 1.0000 depending on the azole (Table 3). In this model, the rate-limiting step is chemical adsorption, and it also assumes that abundant active sites exist in the adsorbent [72]. This shows the great applicability of the tested HOFA sorbent for the removal of azoles.

Table 3.
The pseudo-2nd-order kinetics obtained for the adsorption of azoles.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the potential application of low-cost natural and waste materials as sorbents for the removal of azole compounds from water solutions. The results indicate that minerals such as perlite and pumice, which contain a high amount of silica, as well as silica gel itself, are not suitable materials for removing azoles, noting adsorption below 20% for fluconazole and flutriafol on pure silica gel. The reason for this is that both compounds are acidic and have low extractability by octanol, resulting in their limited affinity for silica gel and silica-containing materials, which are highly polar and acidic. Notably better results were obtained for ceramsite, sawdust, and coconut fibers, which may be driven by similar types of interaction as well as their porosity and high surface area. However, the most efficient adsorption results were observed for both activated carbon and HOFA, achieving complete removal of all azole compounds. The analysis of HOFA material showed that it contains a high amount of carbon, as well as the porous nature of the particles. The results of adsorption isotherms and energy calculations indicated that physicochemical adsorption took place due to the various possible kinds of adsorption active sites. This study proves that HOFA, as a waste and low-cost material, can successfully replace activated carbon upon water purification challenges using the adsorption technique. HOFA, as a waste product available in large quantities, is managed through various methods, including disposal in landfills and utilization in construction materials. The same disposal procedures may be used for HOFA containing adsorbed azoles, which will enable the simultaneous removal of two types of contaminants at low cost.
The tests performed showed that it was possible to remove a range of azoles with a concentration of up to 0.2 mg L−1 within an hour. However, although the tests were very extensive, they were limited to laboratory systems. Therefore, the adsorption capacity of HOFA is currently being verified for real surface water and treated wastewater samples.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13103197/s1, Table S1: Structures and properties of azole compounds used in adsorption tests. Table S2: Parameters of mass spectrometric detection for selected multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) transitions (protonated molecule [M+H]+ m/z –> fragment ion m/z). Table S3: Adsorption of azoles on sorbents (SD—standard deviation). Figure S1: The EDS measurements with (A) a microscopic photograph of the tested area—a point on a gray-colored HOFA matrix; (B) the contents of elements in the tested area; and (C) a spectral chart with lines characteristic of detected elements. Figure S2: The EDS measurements with (A) a microscopic photograph of the tested area—a point on a white-colored HOFA inclusion in a gray-colored matrix; (B) the contents of elements in the tested area; and (C) a spectral chart with lines characteristic of detected elements. References [6,10,16,73,74,75] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.P. and A.Z.-G.; methodology, J.P. and A.Z.-G.; formal analysis, J.P., R.F., T.G., W.U., and A.Z.-G.; investigation, J.P. and R.F.; resources, A.Z.-G.; data curation, A.Z.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.P. and A.Z.-G.; writing—review and editing, J.P., T.G., W.U., and A.Z.-G.; visualization, R.F.; supervision, A.Z.-G.; project administration, A.Z.-G.; funding acquisition, A.Z.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (Poland)—grant number 0911/SBAD/2506.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- GAFFI—Global Action Fund for Fungal Infection. Available online: https://gaffi.org/ (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Parker, J.E.; Warrilow, A.G.S.; Price, C.L.; Mullins, J.G.L.; Kelly, D.E.; Kelly, S.L. Resistance to Antifungals That Target CYP51. J. Chem. Biol. 2014, 7, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathadka, S.; Yan, V.K.C.; Neoh, C.F.; Al-Badriyeh, D.; Kong, D.C.M.; Slavin, M.A.; Cowling, B.J.; Hung, I.F.N.; Wong, I.C.K.; Chan, E.W. Global Consumption Trend of Antifungal Agents in Humans From 2008 to 2018: Data From 65 Middle- and High-Income Countries. Drugs 2022, 82, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrino, D.A.M.; Mucha, A.P.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Carvalho, M.F. Microbial Degradation of Two Highly Persistent Fluorinated Fungicides—Epoxiconazole and Fludioxonil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Valcárcel, A.I.; Tadeo, J.L. Influence of Moisture on the Availability and Persistence of Clotrimazole and Fluconazole in Sludge-amended Soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Ying, G.-G. Occurrence, Fate and Ecological Risk of Five Typical Azole Fungicides as Therapeutic and Personal Care Products in the Environment: A Review. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, S.; Peng, X.; Wei, G.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.; Li, L. Development of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Commonly Used Azole Antifungals in Soils. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5265–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, R.H.; Fick, J.; Tysklind, M. Screening of Antimycotics in Swedish Sewage Treatment Plants—Waters and Sludge. Water Res. 2010, 44, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, M.; Buerge, I.J.; Hauser, A.; Müller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Azole Fungicides: Occurrence and Fate in Wastewater and Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assress, H.A.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Azole Antifungal Drugs in Water and Wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, A.; Fink, G.; Ternes, T.A. Comparison of Electrospray Ionization and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization for Multi-Residue Analysis of Biocides, UV-Filters and Benzothiazoles in Aqueous Matrices and Activated Sludge by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2088–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Lai, H.-J.; Chen, F.; Su, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-S.; Peng, F.-Q.; Zhao, J.-L. Determination of Biocides in Different Environmental Matrices by Use of Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 3175–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Peng, X. Chiral Profiling of Azole Antifungals in Municipal Wastewater and Recipient Rivers of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8890–8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, W.; Wan, Y.; Xu, S. Azole and Strobilurin Fungicides in Source, Treated, and Tap Water from Wuhan, Central China: Assessment of Human Exposure Potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płatkiewicz, J.; Frankowski, R.; Cieślak, A.; Grześkowiak, T.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Long-term study of azoles in surface water and treated wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 124820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, J.; Rodríguez, I.; Ramil, M.; Cela, R. Selective Determination of Antimycotic Drugs in Environmental Water Samples by Mixed-Mode Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1339, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Ma, Y.-B.; Lai, H.-J.; Chen, F.; Pan, C.-G. Typical Azole Biocides in Biosolid-Amended Soils and Plants Following Biosolid Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6198–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/726 of 4 May 2021; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2022/643 of 10 February 2022; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; European Chemicals Agency; European Environment Agency; European Medicines Agency; European Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC). Impact of the use of azole fungicides, other than as human medicines, on the development of azole-resistant Aspergillus spp. EFSA J. 2025, 23, e9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission: Joint Research Centre; Gomez Cortes, L.; Porcel Rodriguez, E.; Marinov, D.; Sanseverino, I.; Lettieri, T. Selection of Substances for the 5th Watch List Under the Water Framework Directive; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2025; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/956398 (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Cai, W.; Ye, P.; Yang, B.; Shi, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ying, G. Biodegradation of typical azole fungicides in activated sludge under aerobic conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 103, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Distribution, behavior and fate of azole antifungals during mechanical, biological, and chemical treatments in sewage treatment plants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iancu, V.I.; Chiriac, L.F.; Paun, I.; Pirvu, F.; Dinu, C.; Kim, L.; Pascu, L.F.; Niculescu, M. Occurrence and distribution of azole antifungal agents in eight urban Romanian waste water treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of Adsorption Process for Effective Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water and Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Berwanger, J.; Polesya, S.; Mankovsky, S.; Ebert, H.; Giessibl, F.J. Chemical Bond Formation Showing a Transition from Physisorption to Chemisorption. Science 2019, 366, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kecili, R.; Hussain, C.M. Mechanism of Adsorption on Nanomaterials. In Nanomaterials in Chromatography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Amrane, A.; Rtimi, S. Mechanisms and Adsorption Capacities of Biochar for the Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants from Industrial Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3273–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Ali, S.; Zaman, W. Innovative Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal: Exploring the Latest Research and Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Joshiba, G.J.; Femina, C.C.; Varshini, P.; Priyadharshini, S.; Karthick, M.S.A.; Jothirani, R. A Critical Review on Recent Developments in the Low-Cost Adsorption of Dyes from Wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 172, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Le, V.V.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.M.S.; Nguyen, D.N.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.M.S.; Noor, M.M.; Pham, V.V. An Absorption Capacity Investigation of New Absorbent Based on Polyurethane Foams and Rice Straw for Oil Spill Cleanup. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, V.; Di Natale, F.; Alfe, M. From Agricultural Wastes to Advanced Materials for Environmental Applications: Rice Husk-Derived Adsorbents for Heavy Metals Removal from Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goksu, A.; Tanaydin, M.K. Adsorption of Hazardous Crystal Violet Dye by Almond Shells and Determination of Optimum Process Conditions by Taguchi Method. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 88, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleño Cabarcas, M.T.; Torres Ramos, R.; Valdez Salas, B.; González Mendoza, D.; Mendoza Gómez, A.; Curiel Álvarez, M.A.; Castillo Sáenz, J.R. Application of Cotton Stalk as an Adsorbent for Copper(II) Ions in Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.Y.; Tam, Y.J. Bioremediation of Dyes Using Coconut Parts via Adsorption: A Review. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wu, S.; Cheng, M.; Tao, P.; Shao, M.; Gao, G. Adsorption Studies of Coconut Shell Carbons Prepared by KOH Activation for Removal of Lead(II) From Aqueous Solutions. Sustainability 2013, 6, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Fernando, P.S.A.; Ahmed, R.T.; Srinath, R.; Priyadharshini, M.; Vignesh, A.M.; Thanjiappan, A. Effect of Temperature on the Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye onto Sulfuric Acid-Treated Orange Peel. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2014, 201, 1526–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, R.H.; Oda, A.M.; Omran, A.R.; Mottaleb, A.S.; Mubarakah, T.M. Study of Adsorption Characteristics a Low-Cost Sawdust for the Removal of Direct Blue 85 Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Indones. J. Chem. 2018, 18, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.T.; Rahman, M.A.; Rukanuzzaman, M.; Islam, M.A. A Potential Low Cost Adsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2831–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatan, O.G.; Alaba, P.A.; Oni, B.A.; Akpojevwe, K.; Efeovbokhan, V.; Abnisa, F. Performance of Eggshells Powder as an Adsorbent for Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium and Cadmium from Wastewater. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshraftar, Z.; Masoumi, H.; Ghaemi, A. On the Performance of Perlite as a Mineral Adsorbent for Heavy Metals Ions and Dye Removal from Industrial Wastewater: A Review of the State of the Art. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, N.U.M.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Mahmoudi, E.; Halim, A.A.; Mohammad, A.W. The Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from an Aqueous Solution Using Biomass-Based Activated Carbon. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maguana, Y.; Elhadiri, N.; Benchanaa, M.; Chikri, R. Activated Carbon for Dyes Removal: Modeling and Understanding the Adsorption Process. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 2096834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Z. Carbon-Based Materials as Adsorbent for Antibiotics Removal: Mechanisms and Influencing Factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.; Cassavela, C.; Cansado, I.; Castanheiro, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Pagnanelli, F. Adsorption of Bisphenol A by Granular Activated Carbon Prepared with Different Silicates as Binders. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 3719–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, W.K.; Yusoff, R.; Aroua, M.K. A Review on Activated Carbon Adsorption for Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 649–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dong, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Duan, W.; Park, J.; Gao, L.; Lu, Y. Comparative Study on the Adsorption Characteristics of Heavy Metal Ions by Activated Carbon and Selected Natural Adsorbents. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Suo, C.; Zhang, N.; Yuan, R.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B. Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Activated Carbon: Effect of Natural Organic Matter and Regeneration Methods of the Adsorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 252, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Lo, I.-T. Theoretical and Experimental Adsorption of Silica Gel and Activated Carbon onto Chlorinated Organic Compounds in Water: A Case Study on the Remediation Assessment of a Contaminated Groundwater Site. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnib, M.; Kabbani, A.; Holail, H.; Olama, Z. Heavy Metals Removal Using Activated Carbon, Silica and Silica Activated Carbon Composite. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramuscio, P.; De Stefano, L.; Seggiani, M.; Vitolo, S.; Narducci, P. Preparation of Activated Carbons from Heavy-Oil Fly Ashes. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; El-Sayed Seleman, M.M.; Zaky Ahmed, M.M.; Harb, S.; Goren, S.; Howsawi, E. Recovery of Vanadium and Nickel from Heavy Oil Fly Ash (HOFA): A Critical Review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 6327–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kårelid, V.; Larsson, G.; Björlenius, B. Pilot-Scale Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Municipal Wastewater: Comparison of Granular and Powdered Activated Carbon Treatment at Three Wastewater Treatment Plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Exposito Saintemarie, A.; Rocchi, S.; Fourmentin, M.; Jeanvoine, A.; Millon, L.; Morin-Crini, N. Simultaneous Removal of Five Triazole Fungicides from Synthetic Solutions on Activated Carbons and Cyclodextrin-Based Adsorbents. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinipuu, M.; Bergknut, M.; Boily, J.-F.; Rosenbaum, E.; Jansson, S. Influence of Water Matrix and Hydrochar Properties on Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30333–30341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Valizadeh, K. The Sorption of Tebuconazole and Linuron from an Aqueous Environment with a Modified Sludge-Based Biochar: Effect, Mechanisms, and Its Persistent Free Radicals Study. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 2912054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-H.; Lv, D.-Z.; Zhou, D.-D.; Yang, Z.-H.; Wang, M.-Y.; Abdelhai Senosy, I.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhuang, L.-Y. Enhanced Removal Efficiency towards Azole Fungicides from Environmental Water Using a Metal Organic Framework Functionalized Magnetic Lignosulfonate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-H.; Wang, M.-Y.; Zhou, D.-D.; Senosy, I.A.; Yang, Z.-H.; Lv, D.-Z.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, L.-Y.; Chen, M. Integration of Bimetallic Organic Frameworks and Magnetic Biochar for Azole Fungicides Removal. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gisi, S.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and Adsorption Capacities of Low-Cost Sorbents for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K.; Basu, G.; Mishra, L. Role of Major Constituents of Coconut Fibres on Absorption of Ionic Dyes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 117, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikri, R.; Elhadiri, N.; Benchanaa, M.; El Maguana, Y. Efficiency of Sawdust as Low-Cost Adsorbent for Dyes Removal. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8813420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Fan, M. Preparation of Bio-Composite from Wood Sawdust and Gypsum. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 74, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ahmad, T. A Review on Utilization of Wood Biomass as a Sustainable Precursor for Activated Carbon Production and Application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 87, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cymański, M.; Olejarczyk, M.; Urbaniak, W.; Szymańska, J.; Szostak, M.; Paukszta, D. Composites of Polyolefin Thermoplastic Polymers with Mineral Fillers. Patent Application PL 441763 A1, 18 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Degs, Y.S.; Ghrir, A.; Khoury, H.; Walker, G.M.; Sunjuk, M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Characterization and Utilization of Fly Ash of Heavy Fuel Oil Generated in Power Stations. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 123, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburizaiza, A. Sequential Leaching of Vanadium from Heavy Fuel Oil Fly Ash Generated from Saudi Arabia Thermal Power Plants. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Georgiou, A.; Chousidis, N.; Ioannou, I. Self-Compacting Cementitious Composites with Heavy Fuel Fly Ash Replacement. Constr. Mater. 2022, 2, 276–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-T.; Teng, H. Langmuir and Dubinin-Radushkevich Analyses on Equilibrium Adsorption of Activated Carbon Fabrics in Aqueous Solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Do, D.D. The Dubinin–Radushkevich Equation and the Underlying Microscopic Adsorption Description. Carbon 2001, 39, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, L.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Guo, Y. Application Studies of Activated Carbon Derived from Rice Husks Produced by Chemical-Thermal Process—A Review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 163, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpola, P.D.; Odetti, H.S.; Fertitta, A.E.; Vicente, J.L. Thermodynamic Analysis of Adsorption Models of Phenol in Liquid Phase on Different Activated Carbons. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2013, 58, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Kinetic models and thermodynamics of adsorption processes: Classification. Interface Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Hertfordshire, 2020. PPDB: Pesticide Properties DataBase [WWW Document]. Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/index.htm (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Cui, N.; Wang, P.; Xu, N. Sorption Behaviour of Tebuconazole on Microplastics: Kinetics, Isotherms and Influencing Factors. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 3937–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Tang, C.; Peng, X. Determination of Commonly Used Azole Antifungals in Various Waters and Sewage Sludge Using Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography– Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).