Adsorption of Oil by 3-(Triethoxysilyl) Propyl Isocyanate-Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
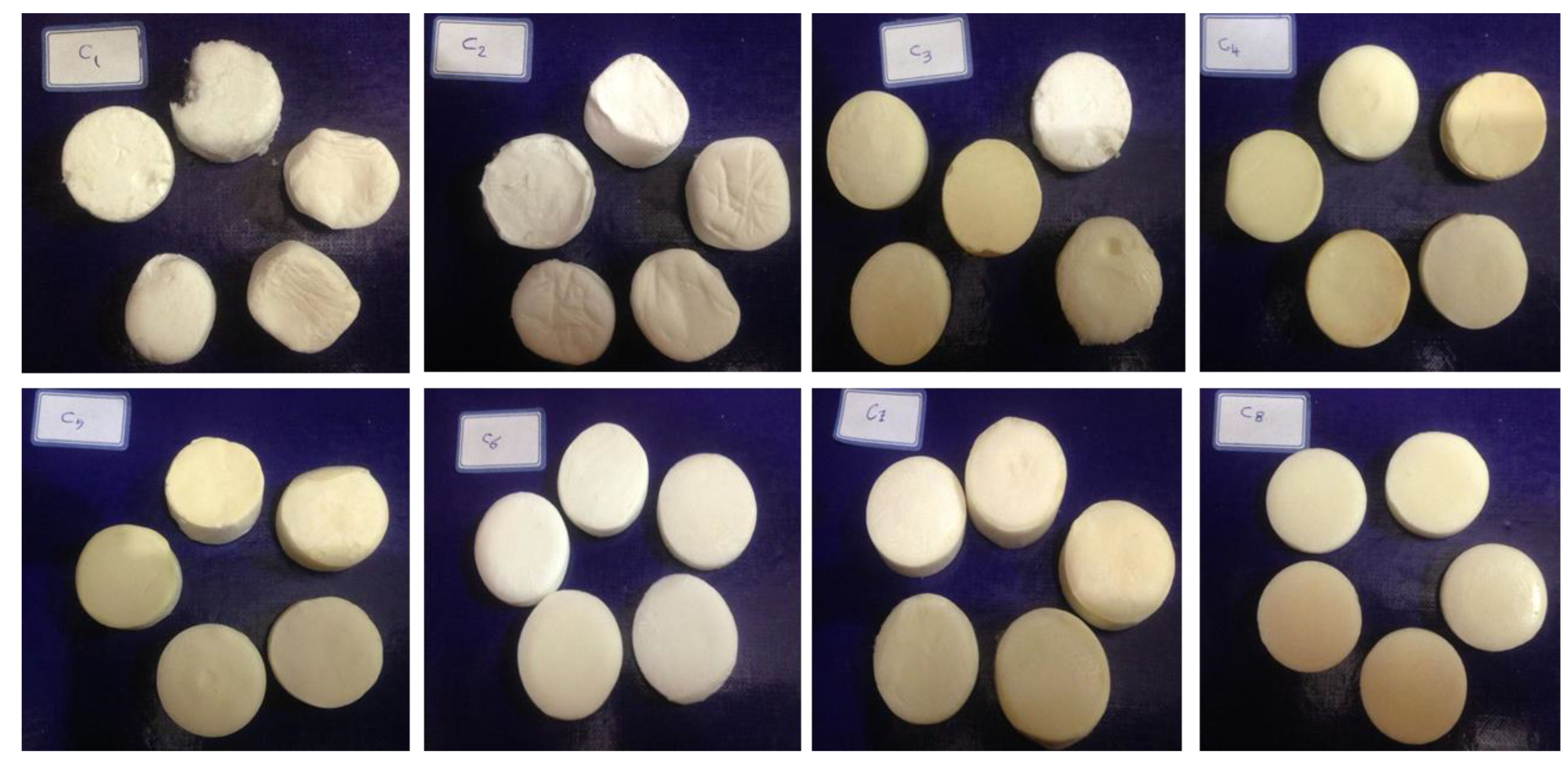
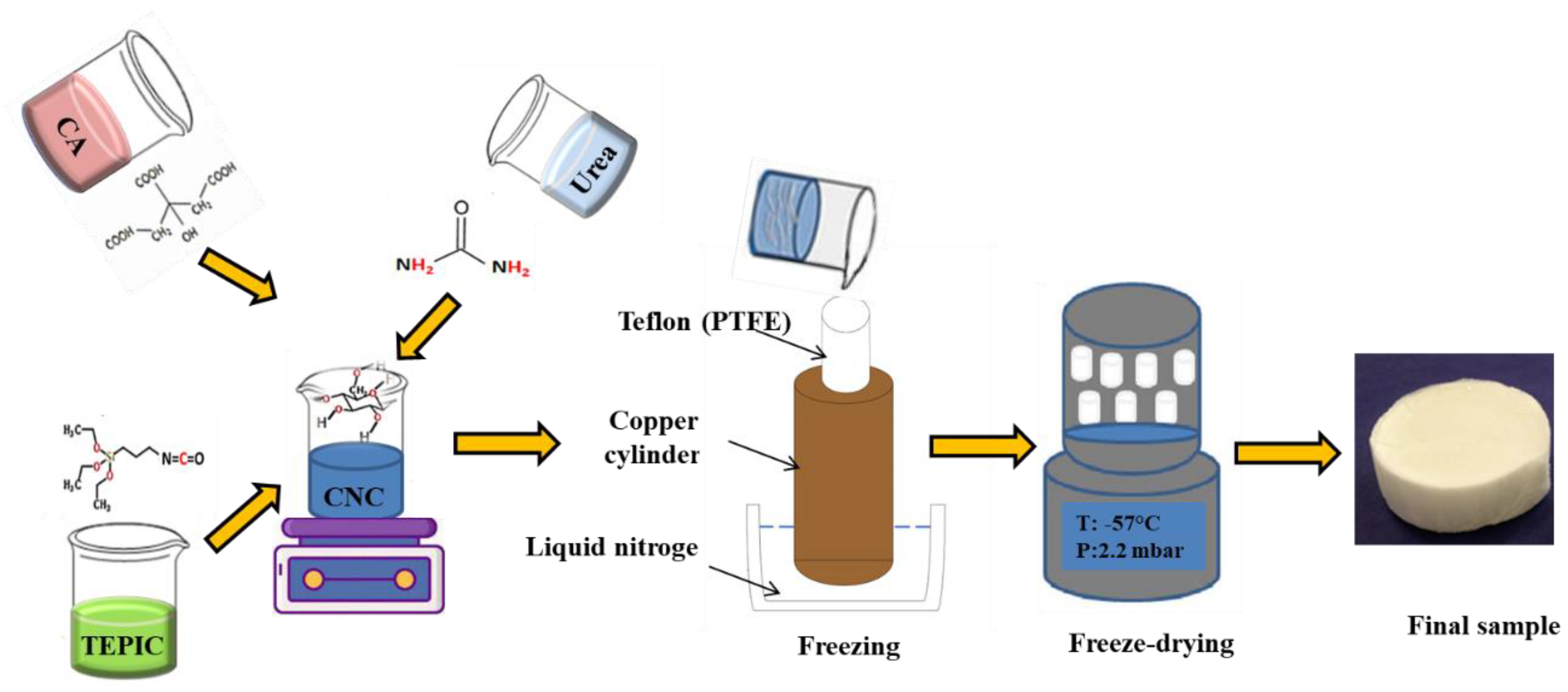
2.2. Aerogel Preparation
2.3. Characterizations
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Density and Porosity
2.3.3. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) Analysis
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.5. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
2.3.6. Compression Testing
2.3.7. Oil Adsorption
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
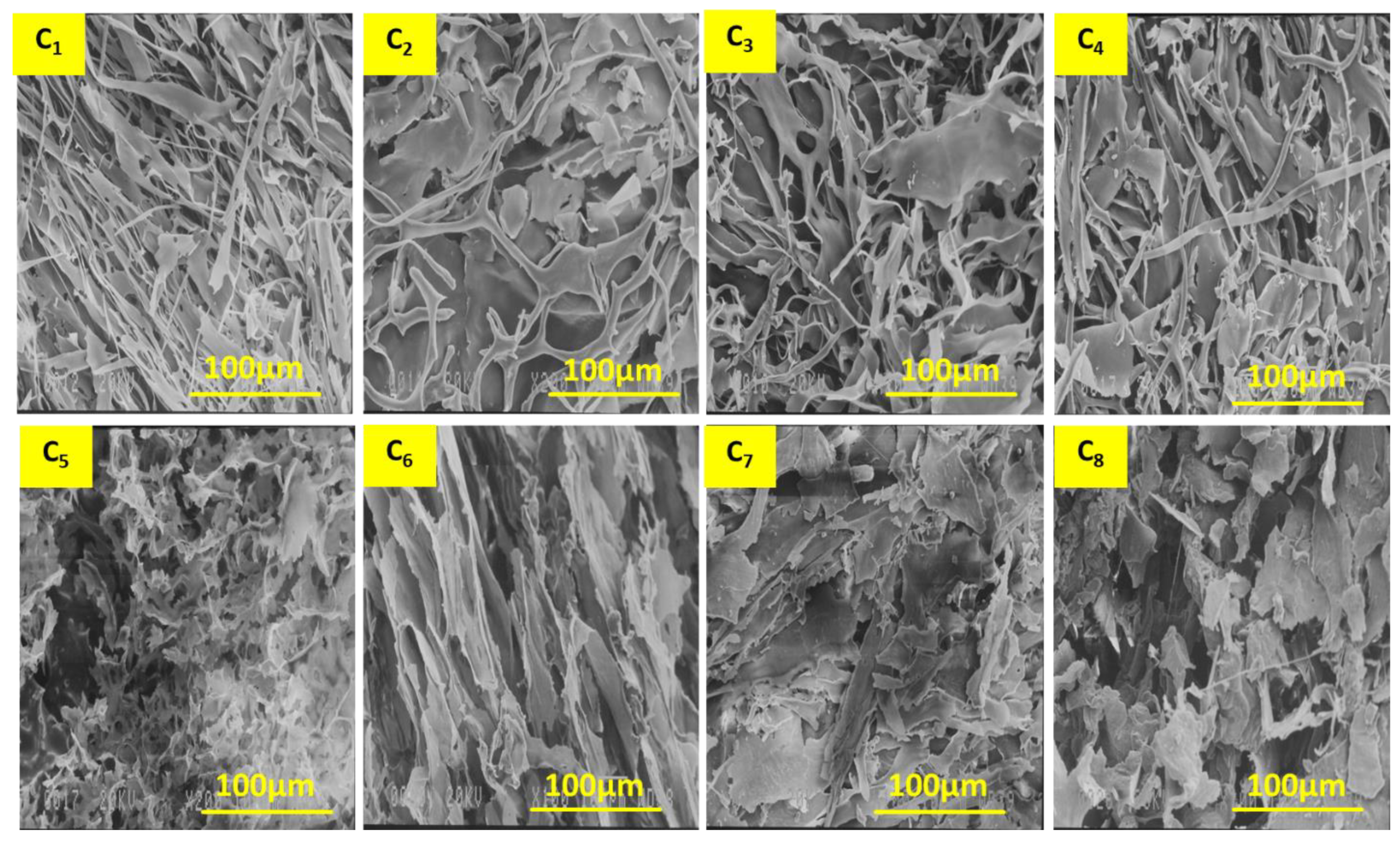
3.1. SEM
3.2. Aerogel Characteristics
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
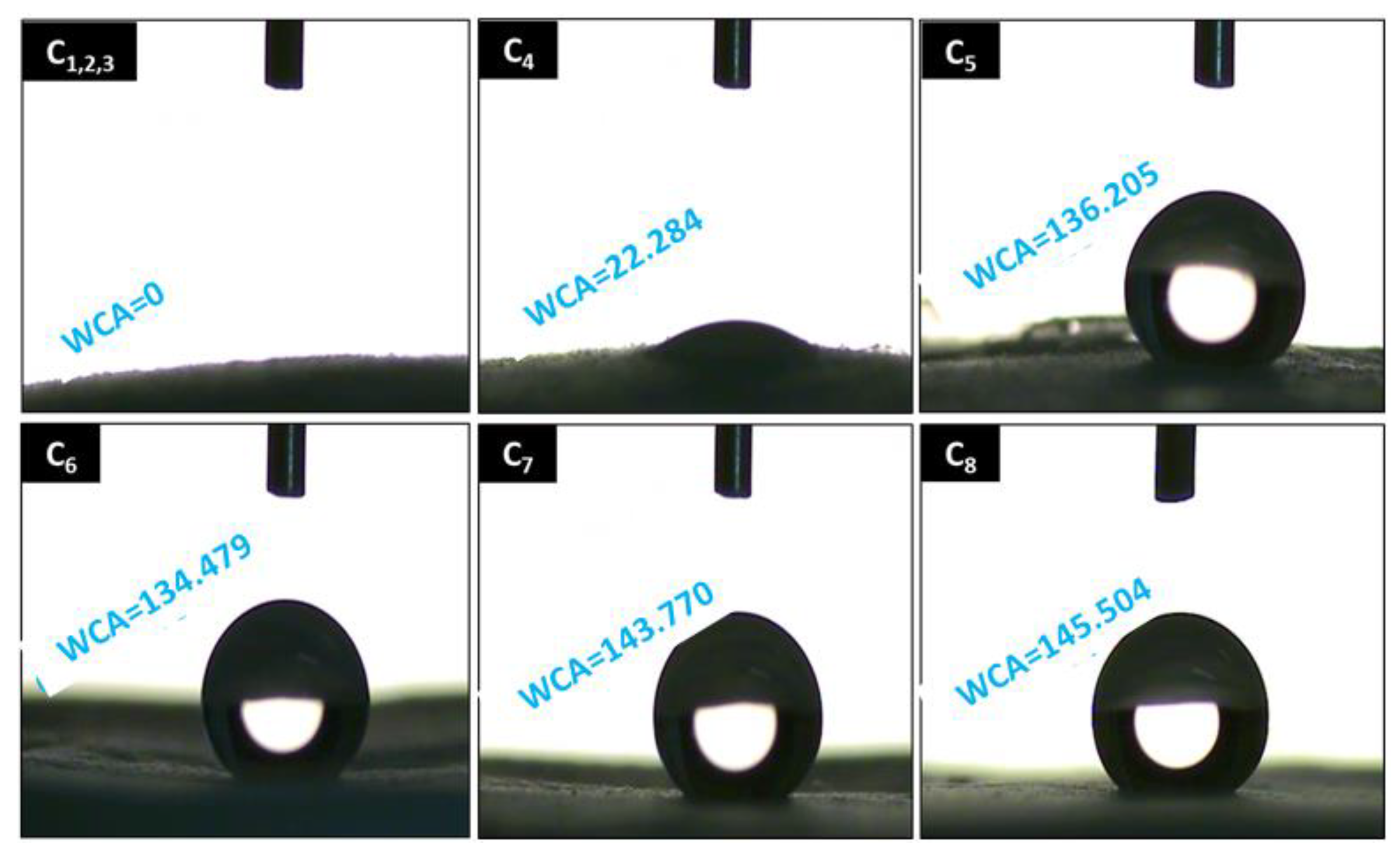
3.4. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
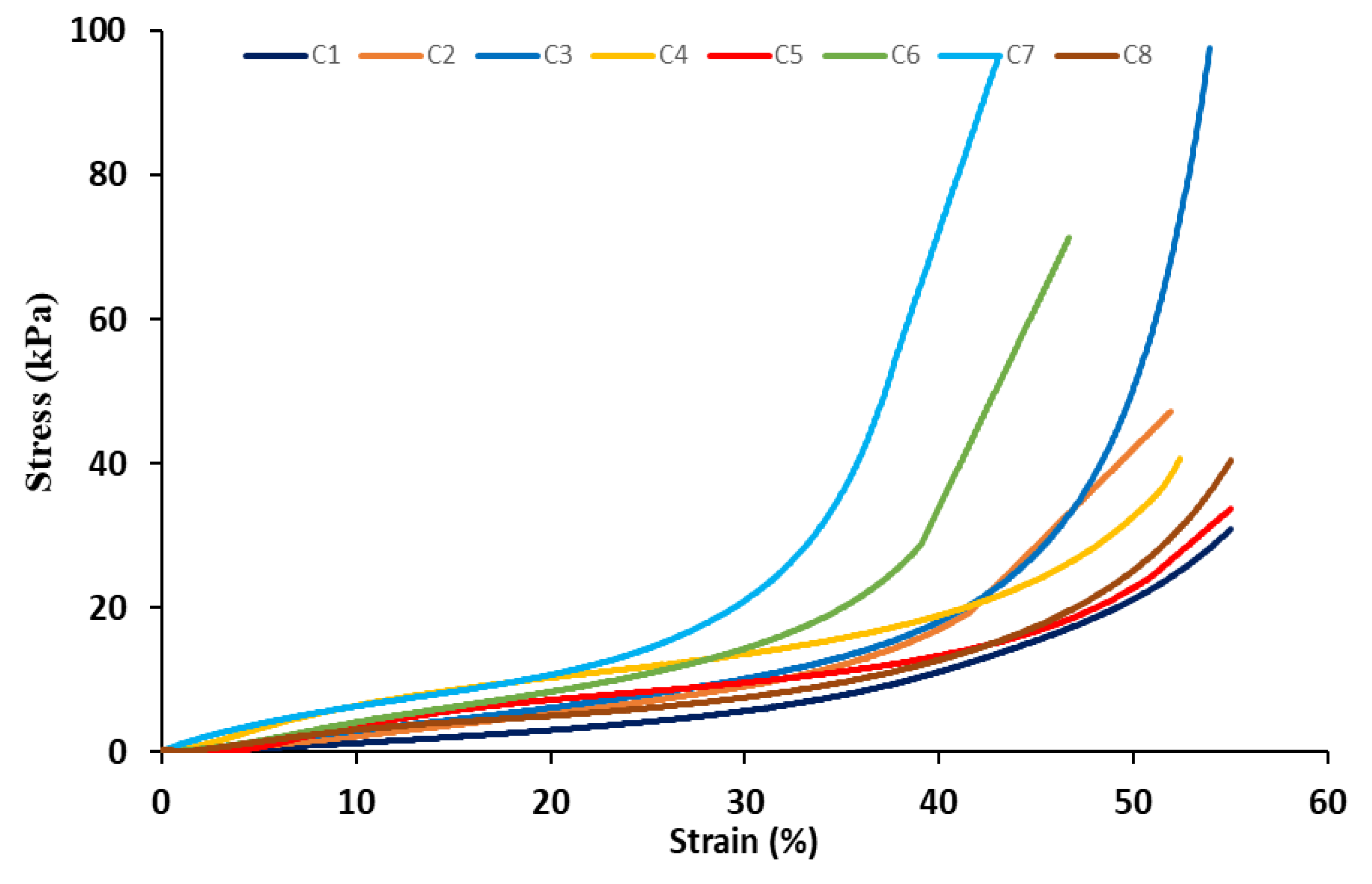
3.5. Compression Testing
3.6. Oil and Glycerol Ladsorption
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oribayo, O.; Feng, X.; Rempel, G.L.; Pan, Q. Synthesis of lignin-based polyurethane/graphene oxide foam and its application as an absorbent for oil spill clean-ups and recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Fan, Z.; Duong, H.M. Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieian, F.; Hosseini, M.; Jonoobi, M.; Yu, Q. Development of hydrophobic nanocellulose-based aerogel via chemical vapor deposition for oil separation for water treatment. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4695–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Shang, Y.Y.; Sun, P.Z.; Li, Z.; Li, X.M.; Wei, J.Q.; Wu, D.H.; Cao, A.Y.; Zhu, H.W. Oil spill cleanup from sea water by carbon nanotube sponges. Front. Mater. Sci. 2013, 7, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoine, N.; Desloges, I.; Dufresne, A.; Bras, J. Microfibrillated cellulose–Its barrier properties and applications in cellulosic materials: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 90, 735–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, R.; Jonoobi, M.; Amirabad, L.M.; Oksman, K.; Taheri, A.R. Fabrication and characterization of novel bilayer scaffold from nanocellulose based aerogel for skin tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Parveen, T.; Umar, K.; Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N. Role of Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Wastewater: A Review. Water 2020, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Coated kapok fiber for removal of spilled oil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 69, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, K.; Yaqoob, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Parveen, T.; Safian, M.T.U. Environmental applications of smart polymer composites. In Smart Polymer Nanocomposite; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; pp. 295–312. ISBN 9780128199619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oribayo, O.; Feng, X.; Rempel, G.L.; Pan, Q. Modification of formaldehyde-melamine-sodium bisulfite copolymer foam and its application as effective sorbents for cleanup of oil spills. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 160, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Feng, J.; Ng, S.K.; Wong, J.P.; Tan, V.B.; Duong, H.M. Advanced thermal insulation and absorption properties of recycled cellulose aerogels. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2014, 445, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, J. Preparation of magnetic hydrophobic polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–cellulose nanofiber (CNF) aerogels as effective oil absorbents. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetens, R.; Jelle, B.P.; Gustavsen, A. Aerogel insulation for building applications: A state-of-the-art review. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepahvand, S.; Jonoobi, M.; Ashori, A.; Gauvin, F.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Oksman, K.; Yu, Q. A promising process to modify cellulose nanofibers for carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorption. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 230, 115571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepahvand, S.; Jonoobi, M.; Ashori, A.; Rabie, D.; Gauvin, F.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Yu, Q.; Mekonnen, T.H. Modified cellulose nanofibers aerogels as a novel air filters; synthesis and performance evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjanzadeh, H.; Behrooz, R.; Bahramifar, N.; Pinkl, S.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Application of surface chemical functionalized cellulose nanocrystals to improve the performance of UF adhesives used in wood based composites-MDF type. Carbohydr. polym. 2019, 206, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De France, K.J.; Hoare, T.; Cranston, E.D. Review of hydrogels and aerogels containing nanocellulose. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4609–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, S.; Goenaga, G.A.; Meng, X.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Ragauskas, A.J. Chemically cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels for effective removal of cation dye. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabouni, O.; Boufi, S. Cellulose nanofibrils/polyvinyl acetate nanocomposite adhesives with improved mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonoobi, M.; Ashori, A.; Siracusa, V. Characterization and properties of polyethersulfone/modified cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposite membranes. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Dahrazma, B.; Adelifard, M. Facile and novel ambient pressure drying approach to synthesis and physical characterization of cellulose-based aerogels. J. Porous Mater. 2020, 27, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fu, Q.; Liu, H.; Gu, H.; Guo, Z. Solvent-free nanoalumina loaded nanocellulose aerogel for efficient oil and organic solvent adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.K.; Lee, K.T.; Mohamed, A.R. Current status and challenges on microalgae-based carbon capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2012, 10, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahi, R.; Chuah, L.A.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Ngaini, Z.; Nourouzi, M.M. Oil removal from aqueous state by natural fibrous sorbent: An overview. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 113, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Li, A.; Lin, B.; Chen, T.B.Y.; Yang, W.; Lu, H.D.; Yeoh, G.H. Recent progress in bio-based aerogel absorbents for oil/water separation. Cellulose 2019, 26, 6449–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepahvand, S.; Jonoobi, M.; Ashori, A.; Gauvin, F.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Yu, Q. Surface modification of cellulose nanofiber aerogels using phthalimide. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepahvand, S.; Bahmani, M.; Ashori, A.; Pirayesh, H.; Yu, Q.; Dafchahi, M.N. Preparation and characterization of air nanofilters based on cellulose nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, A.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Shang, S.; Liu, S.; Song, J. Porous aerogels prepared by crosslinking of cellulose with 1, 4-butanediol diglycidyl ether in NaOH/urea solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42854–42862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.Y.; Weng, Y.X.; Wang, Y.Z. Cellulose Aerogels: Synthesis, Applications, and Prospects. Polymers 2018, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rafieian, F.; Jonoobi, M.; Yu, Q. A novel nanocomposite membrane containing modified cellulose nanocrystals for copper ion removal and dye adsorption from water. Cellulose 2019, 26, 3359–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieian, F.; Mousavi, M.; Yu, Q.; Jonoobi, M. Amine functionalization of microcrystalline cellulose assisted by (3-chloropropyl) triethoxysilane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanjanzadeh, H.; Behrooz, R.; Bahramifar, N.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Bacher, M.; Edler, M.; Griesser, T. Surface chemical functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Sèbe, G.; Rentsch, D.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özmen, N.; Sami Çetin, N.; Tingaut, P.; Sèbe, G. Transesterification reaction between acetylated wood and trialkoxysilane coupling agents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorey, R.; Gupta, A.; Mekonnen, T.H. Hydrophobic modification of lignin for rubber composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 174, 114189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Tang, X.; Ge, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Cranston, E.D. Chemically cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels with shape recovery and superabsorbent properties. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6016–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, N.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 2, 2445–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wu, X.; Fang, J. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic “sponge-like” aerogels for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 5115–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, M.; Lavoratti, A.; Lazzari, L.K.; Galiotto, D.; Pagnocelli, M.; Baldasso, C.; Zattera, A.J. Producing aerogels from silanized cellulose nanofiber suspension. Cellulose 2017, 24, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Li, C.; Liang, H.W.; Chen, J.F.; Yu, S.H. Ultralight, flexible, and fire-resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels from bacterial cellulose. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 2997–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyad Amin, J.; Vared Abkenar, M.; Zendehboudi, S. Natural sorbent for oil spill cleanup from water surface: Environmental implication. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 10615–10621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, D.; Dhiman, S.; Rattan, G.; Monga, S.; Singhal, S.; Kaushik, A. Superhydrophobic modification of cellulose sponge fabricated from discarded jute bags for oil water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CNC Concentration (wt%) | TEPIC Concentration (wt%) | CA Concentration (wt%) | Urea Concentration (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 2 | - | - | - |
| C2 | 2 | - | 3 | - |
| C3 | 2 | - | - | 50 |
| C4 | 2 | - | 3 | 50 |
| C5 | 2 | 3 | - | - |
| C6 | 2 | 6 | - | 50 |
| C7 | 2 | 3 | - | 50 |
| C8 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 50 |
| Sample | Density (mg/cm3) | BET (m2/g) | Aver. Size of Pores (nm) | Porosity (%) | Volume of Pores (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 8.5 ± 0.54 e | 214 ± 16.8 e | 29.2 ± 1.81 a | 99.3 ± 0.82 a | 95.2 ± 3.18 a |
| C2 | 8.9 ± 0.46 de | 227 ± 14.2 e | 28.9 ± 1.21 a | 99.2 ± 1.01 a | 93.6 ± 4.32 a |
| C3 | 9.4 ± 0.36 d | 231 ± 8.2 de | 28.7 ± 1.43 ab | 98.8 ± 0.92 ab | 85.6 ± 3.22 b |
| C4 | 10.1 ± 0.76 cd | 244 ± 18.2 d | 27.4 ± 1.03 b | 98.6 ± 0.32 ab | 72.1 ± 4.32 c |
| C5 | 12.4 ± 0.82 b | 262 ± 11.2 c | 26.1 ± 1.02 b | 98.3 ± 0.32 ab | 69.7 ± 2.42 cd |
| C6 | 13.7 ± 0.56 b | 298 ± 8.8 ab | 23.6 ± 1.08 c | 98.2 ± 0.48 ab | 66.4 ± 3.38 d |
| C7 | 15.6 ± 0.87 a | 311 ± 8.8 a | 21.8 ± 1.16 d | 97.9 ± 0.16 b | 63.5 ± 3.62 de |
| C8 | 16.4 ± 0.71 a | 318 ± 10.7 a | 18.7 ± 1.27 e | 97.5 ± 0.47 b | 58.2 ± 3.77 e |
| Samples | After 300 s | After 1 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetable Oil (g g−1) | Motor Oil (g g−1) | Glycerol (g g−1) | Vegetable Oil (g g−1) | Motor Oil (g g−1) | Glycerol (g g−1) | |
| C1 | 21.36 ± 3.38 d | 25.24 ± 3.32 f | 18.58 ± 1.18 e | 29.37 ± 2.13 f | 31.03 ± 2.18 f | 26.09 ± 1.86 e |
| C2 | 12.23 ± 1.23 e | 9.25 ± 0.42 g | 9.89 ± 0.23 f | 14.43 ± 1.02 g | 12.10 ± 1.01 g | 11.67 ± 0.92 f |
| C3 | 49.82 ± 3.23 c | 48.67 ± 3.23 e | 37.14 ± 2.31 d | 58.43 ± 3.54 e | 54.32 ± 3.57 e | 41.90 ± 2.65 d |
| C4 | 51.80 ± 4.23 c | 68.97 ± 3.43 c | 43.25 ± 2.98 c | 69.88 ± 4.12 d | 83.67 ± 6.43 c | 50.53 ± 3.82 c |
| C5 | 103.89 ± 7.32 a | 109.65 ± 4.43 a | 76.44 ± 4.39 b | 120.51 ± 4.75 a | 130.61 ± 7.22 a | 95.28 ± 4.82 a |
| C6 | 102.53 ± 4.88 a | 99.01 ± 3.43 b | 76.14 ± 3.13 b | 120.35 ± 5.28 a | 122.95 ± 6.18 ab | 87.51 ± 6.08 b |
| C7 | 88.21 ± 6.26 b | 54.58 ± 4.54 d | 38.79 ± 2.43 d | 94.00 ± 3.16 c | 77.03 ± 3.16 d | 47.39 ± 3.26 c |
| C8 | 97.59 ± 5.17 ab | 102.63 ± 2.32 b | 86.21 ± 5.89 a | 108.69 ± 7.03 b | 115.69 ± 5.47 b | 95.16 ± 4.67 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jonoobi, M.; Mekonnen, T.H. Adsorption of Oil by 3-(Triethoxysilyl) Propyl Isocyanate-Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals. Processes 2022, 10, 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102154
Jonoobi M, Mekonnen TH. Adsorption of Oil by 3-(Triethoxysilyl) Propyl Isocyanate-Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals. Processes. 2022; 10(10):2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102154
Chicago/Turabian StyleJonoobi, Mehdi, and Tizazu H. Mekonnen. 2022. "Adsorption of Oil by 3-(Triethoxysilyl) Propyl Isocyanate-Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals" Processes 10, no. 10: 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102154
APA StyleJonoobi, M., & Mekonnen, T. H. (2022). Adsorption of Oil by 3-(Triethoxysilyl) Propyl Isocyanate-Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals. Processes, 10(10), 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102154







