Activities of Daily Living, Playfulness and Sensory Processing in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Spanish Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Type of Study/Design
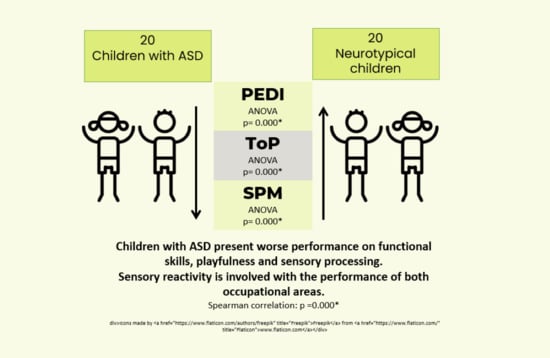
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Assessment Tools
2.4.1. Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI)
2.4.2. Test of Playfulness (ToP)
2.4.3. Sensory Processing Measure (SPM)
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Analyses
3.2. Inferential Analysis
3.3. Correlation between Performance of ADL and Sensory Reactivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiarotti, F.; Venerosi, A. Epidemiology of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review of Worldwide Prevalence Estimates since 2014. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maenner, M.J.; Shaw, K.A.; Baio, J.; Washington, A.; Patrick, M.; DiRienzo, M.; Christensen, D.L.; Wiggins, L.D.; Pettygrove, S.; Andrews, J.G.; et al. Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2016. MMWR. Surveill. Summ. 2020, 69, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, L.; Goddard, L.; Pring, L. Sensory processing in adults with autism spectrum disorders. Autism 2009, 13, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascio, C.J. Somatosensory processing in neurodevelopmental disorders. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2010, 2, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Manual Diagnóstico y Estadístico de Los Trastornos Mentales: DSM-5, 5th ed.; Editorial Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2014; ISBN 9788491103721. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz-Cervera, P.; Pastor-Cerezuela, G.; González-Sala, F.; Tárraga-Mínguez, R.; Fernández-Andrés, M.-I. Sensory Processing in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and/or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in the Home and Classroom Contexts. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, A.J.; Robbins, J. La Integración Sensorial en Niños: Desafíos Sensoriales Ocultos. Edición 25 Aniversario; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2008; ISBN 9788471749277. [Google Scholar]
- Alcantud Marín, F. Trastornos Del Espectro Autista; Ediciones Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ayres, A.J. La Integración Sensorial y el Niño; Trillas: Sevilla, Mexico, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Martín, M.A.; Cuesta Gómez, J.L. Todo Sobre el Autismo: Los Trastornos Del Espectro Del Autismo (TEA): Guía Completa Basada en la Ciencia y en la Experiencia, 2nd ed.; Altaria: Tarragona, Spain, 2013; ISBN 9788494106835. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, B.; May-Benson, T.A.; Bodison, S.C. State of the Science of Sensory Integration Research with Children and Youth. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2017, 72, 7201170010p1–7201170010p4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, S.; Coster, W.; Ludlow, L.; Haltiwanger, J.; Andrellos, P. Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI); New England Center Hospitals/PEDI Research Group: Boston, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- García Bascones, M. Adaptación Transcultural y Versión Española de la Escala de Discapacidad Pediatric Evaluation of Disabiblity Inventory (PEDI). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Severijnen, J. Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI): Calibrating the Dutch Version. Ph.D. Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bundy, A. Test of Playfulness, Version 3; Collins, F., Ed.; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bundy, A.; Nelson, L.; Metzger, M.; Bingaman, K. Validity and Reliability of a Test of Playfulness. Occup. Ther. J. Res. 2001, 21, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muys, V.; Rodger, S.; Bundy, A.C. Assessment of Playfulness in Children with Autistic Disorder: A Comparison of the Children’s Playfulness Scale and the Test of Playfulness. OTJR 2006, 26, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, A.C.; Waugh, K.; Brentnall, J. Developing Assessments That Account for the Role of the Environment: An Example Using the Test of Playfulness and Test of Environmental Supportiveness. OTJR 2009, 29, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, L.; Ecker, C.; Kuhaneck, H.; Henry, D.; Glennon, T. Sensory Processing Measure (SPM): Manual; Western Psychological Services: Los Ángeles, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dugas, C.; Simard, M.-N.; Fombonne, E.; Couture, M. Comparison of Two Tools to Assess Sensory Features in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2017, 72, 7201195010p1–7201195010p9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Andrés, M.I.; Pastor-Cerezuela, G.; Sanz-Cervera, P.; Tárraga-Mínguez, R. A comparative study of sensory processing in children with and without Autism Spectrum Disorder in the home and classroom environments. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 38, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.Y.Y.; Chung, J.C.C.; Chan, C.C.H.; Li-Tsang, C.W.P. Sensory Processing Measure-HK Chinese version: Psychometric properties and pattern of response across environments. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 2636–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanca, M.J.; Alarcón, R.; Arnau, J.; Bono, R.; Bendayan, R. Non-normal data: Is ANOVA still a valid option? Psicothema 2017, 29, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, Y.-C.; Kramer, J.M.; Liljenquist, K.; Tian, F.; Coster, W.J. Comparing the Functional Performance of Children and Youths with Autism, Developmental Disabilities, and no Disability Using the Revised Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory Item Banks. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2012, 66, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pinchover, S.; Shulman, C.; Bundy, A. A comparison of playfulness of young children with and without autism spectrum disorder in interactions with their mothers and teachers. Early Child Dev. Care 2016, 186, 1893–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-L.; Chen, C.-T.; Lin, C.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Prediction of Playfulness by Pretend Play, Severity of Autism Behaviors, and Verbal Comprehension in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaaf, R.C.; Benevides, T.; Blanche, E.I.; Brett-Green, B.A.; Burke, J.P.; Cohn, E.S.; Koomar, J.; Lane, S.J.; Miller, L.J.; May-Benson, T.A.; et al. Parasympathetic functions in children with sensory processing disorder. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case-Smith, J.; Weaver, L.L.; Fristad, M.A. A systematic review of sensory processing interventions for children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism 2015, 19, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A. Making Sense of their World: Sensory Awareness and Sensory Reactivity as Predictors of Social Interaction in Early Childhood. Ph.D. Thesis, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.; Stagnitti, K.; Brown, T.; Bhopti, A. Relationship between Sensory Processing and Pretend Play in Typically Developing Children. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2017, 72, 7201195050p1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C.; Parham, L.D.; Blanche, E.I.; Schell, A.; Chou, C.-P.; Dawson, M.; Clark, F. Autonomic and Behavioral Responses of Children With Autism to Auditory Stimuli. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2012, 66, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, R.C.; Case-Smith, J. Sensory interventions for children with autism. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 2014, 3, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | ASD | Neurotypical | ANOVA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | F | p Values | Ŋ2 Partial | |
| Age of children (months) | 88.15 | 24.384 | 84.65 | 21.695 | 0.230 | 0.634 | 0.006 |
| Age of parents (years) | 42.50 | 5.671 | 41.10 | 3.463 | 0.888 | 0.352 | 0.023 |
| Variables | ASD | Neurotypical | Chi Squared | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | X2 | gl | p Values | ||
| Gender | Male | 16 | 40 | 10 | 25 | 3.956 | 1 | 0.047 * |
| Female | 4 | 10 | 10 | 25 | ||||
| Environment | Urban | 19 | 47.5 | 19 | 47.5 | 0.000 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Rural | 1 | 2.5 | 1 | 2.5 | ||||
| Level of studies of parents | Basic | 2 | 5 | 5 | 12.5 | 7.734 | 4 | 0.102 |
| Baccalaureate | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Further Educ. | 3 | 7.5 | 2 | 5 | ||||
| Higher Educ. | 11 | 27.5 | 6 | 15 | ||||
| Doctoral | 2 | 5 | 7 | 17.5 | ||||
| Variables | ASD | Neurotypical | ANOVA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | F | p Values | Ŋ2 Partial | ||
| PEDI | FS | 121.25 | 28.38 | 185.65 | 8.554 | 94.403 | 0.000 * | 0.713 |
| FS. CP | 42.50 | 14.489 | 68.20 | 3.679 | 59.108 | 0.000 * | 0.609 | |
| FS. Mobility | 50.40 | 5.133 | 57.45 | 1.877 | 33.266 | 0.000 * | 0.467 | |
| FS | 28.35 | 11.249 | 60.00 | 3.741 | 142.538 | 0.000 * | 0.790 | |
| Help from caregiver | 61.35 | 15.363 | 95.25 | 3.537 | 92.476 | 0.000 * | 0.709 | |
| Modifications | 52.75 | 2.971 | 59.25 | 0.85 | 88.457 | 0.000 * | 0.700 | |
| ToP | Extension | 19.90 | 7.475 | 44.15 | 4.145 | 160.956 | 0.000 * | 0.809 |
| Intensity | 5.70 | 2.735 | 10.25 | 1.712 | 39.742 | 0.000 * | 0.511 | |
| Skill | 5.50 | 4.00 | 21.80 | 2.667 | 229.355 | 0.000 * | 0.858 | |
| Variables SPM | ASD | Neurotypical | ANOVA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | F | p Values | Ŋ2 Partial | |
| TOT | 112.70 | 22.98 | 63.15 | 9.80 | 78.661 | 0.000 * | 0.674 |
| Vision | 24.45 | 5.853 | 13.75 | 3.354 | 50.314 | 0.000 * | 0.570 |
| Hearing | 19.35 | 5.214 | 10.70 | 2.079 | 47.487 | 0.000 * | 0.555 |
| Touch | 22.70 | 5.849 | 12.75 | 2.221 | 50.569 | 0.000 * | 0.571 |
| Body awareness | 20.80 | 6.321 | 12.40 | 2.479 | 30.608 | 0.000 * | 0.446 |
| Balance and movement | 20.75 | 6.298 | 11.35 | 2.134 | 31.909 | 0.000 * | 0.456 |
| Social participation | 21.40 | 3.871 | 36.55 | 3.017 | 190.538 | 0.000 * | 0.834 |
| Planning and ideas | 26.85 | 5.363 | 10.40 | 1.465 | 175.073 | 0.000 * | 0.822 |
| Variables | TOT | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman Correlation | p Values | ||
| PEDI | FS | −0.858 | 0.000 * |
| FS. BA. | −0.855 | 0.000 * | |
| FS. Mobility | −0.754 | 0.000 * | |
| FS | −0.850 | 0.000 * | |
| Caregiver help | −0.859 | 0.000 * | |
| Modifications | −0.840 | 0.000 * | |
| ToP | ToP Extension | −0.803 | 0.000 * |
| ToP Intensity | −0.743 | 0.000 * | |
| ToP Skills | −0.797 | 0.000 * | |
| SPM | Social Participation | −0.855 | 0.000 * |
| SPM | Planning and ideas | 0.829 | 0.000 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yela-González, N.; Santamaría-Vázquez, M.; Ortiz-Huerta, J.H. Activities of Daily Living, Playfulness and Sensory Processing in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Spanish Study. Children 2021, 8, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020061
Yela-González N, Santamaría-Vázquez M, Ortiz-Huerta JH. Activities of Daily Living, Playfulness and Sensory Processing in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Spanish Study. Children. 2021; 8(2):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020061
Chicago/Turabian StyleYela-González, Nuria, Montserrat Santamaría-Vázquez, and Juan Hilario Ortiz-Huerta. 2021. "Activities of Daily Living, Playfulness and Sensory Processing in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Spanish Study" Children 8, no. 2: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020061
APA StyleYela-González, N., Santamaría-Vázquez, M., & Ortiz-Huerta, J. H. (2021). Activities of Daily Living, Playfulness and Sensory Processing in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Spanish Study. Children, 8(2), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020061