Identifying Loss of Control Eating within Childhood Obesity: The Importance of Family Environment and Child Psychological Distress
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. LOC Eating Onset and Associated Family Factors
1.2. Identifying LOC Eating in Childhood Obesity
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Instruments of Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Family Environment, Psychological Distress, and Disordered Eating Symptomatology by Weight Status and Their Relationship with Child BMI
3.2. Differences in Family Environment and Psychological Distress by LOC Eating Episodes
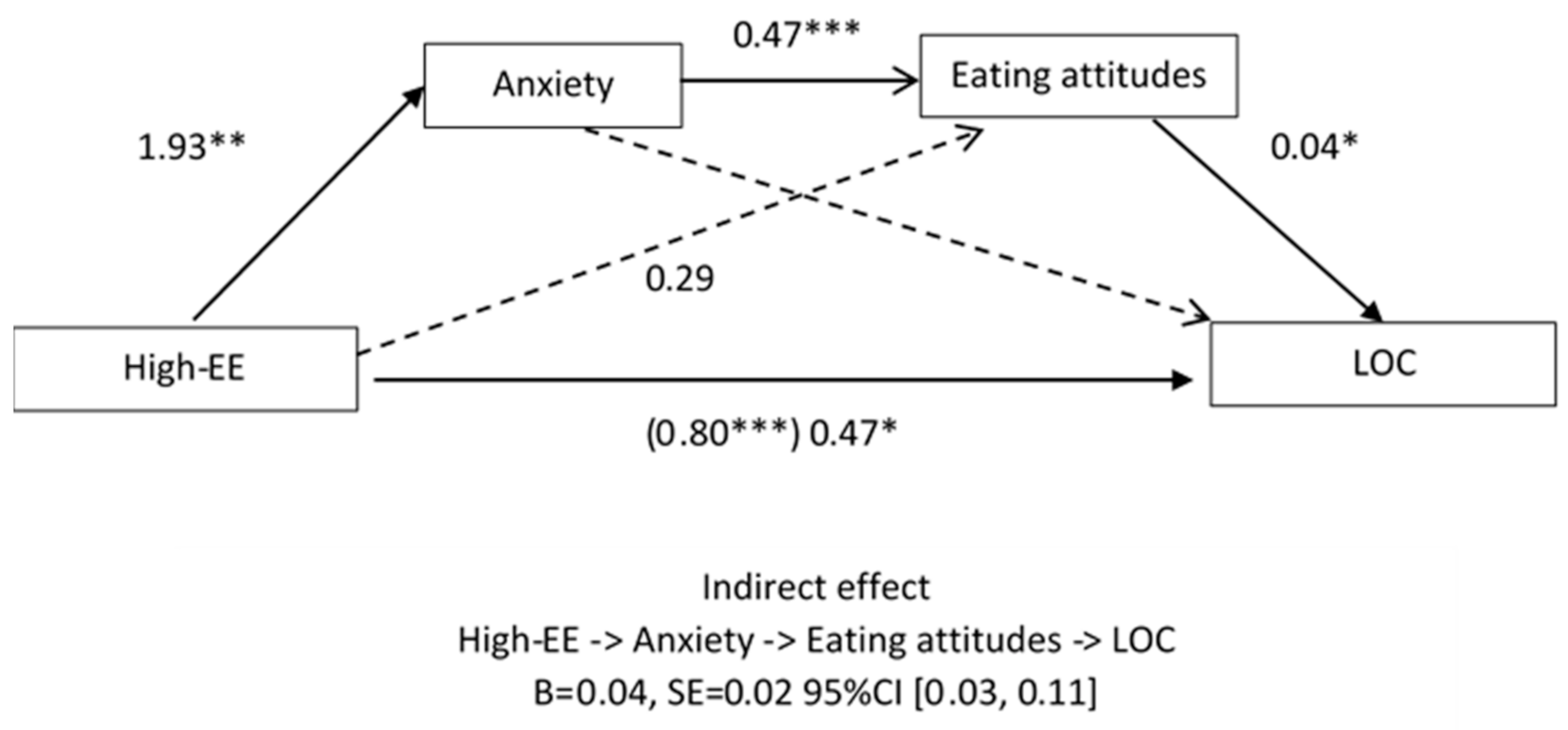
3.3. Effect of EE on LOC Eating Episodes via Psychological Symptomatology (Anxiety and Depression Models)
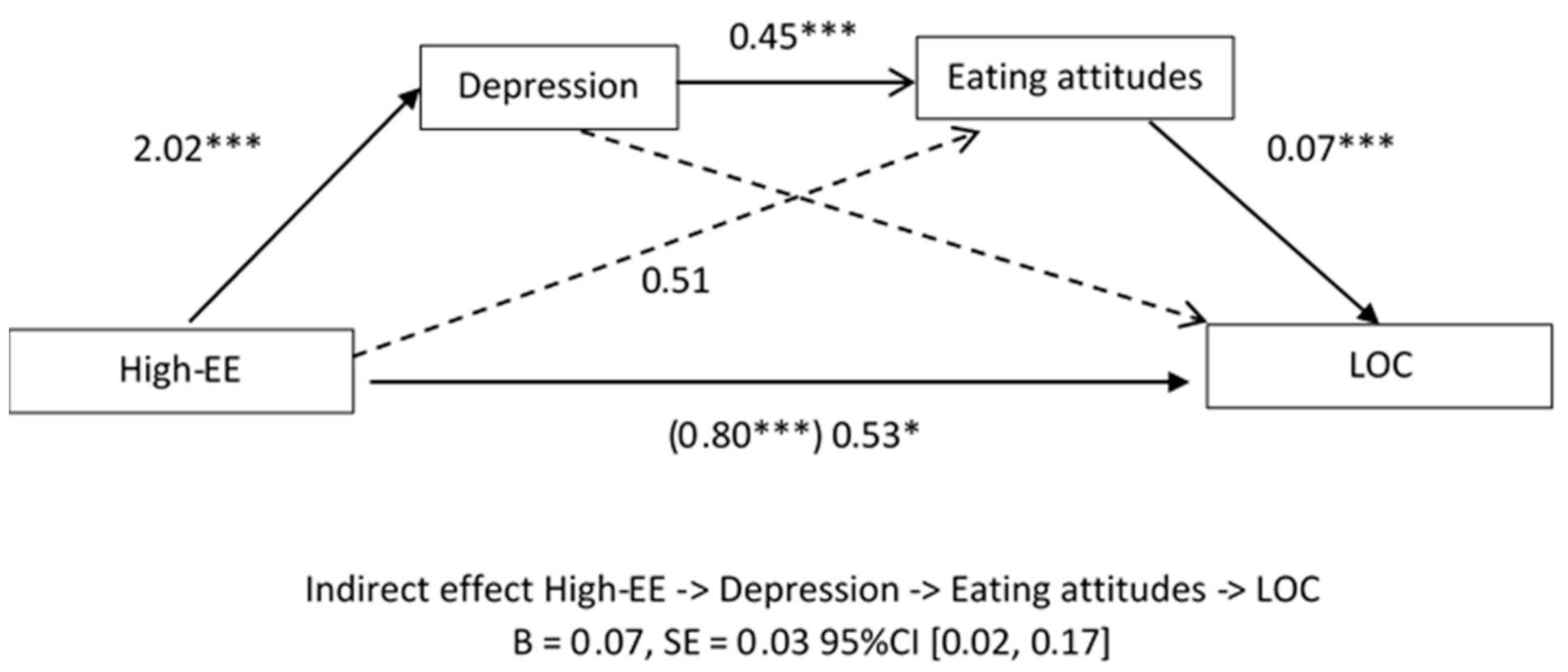
3.3.1. Depression Model for LOC Eating Episodes
3.3.2. Anxiety Model for LOC Eating Episodes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 1. Criticism (FQ) | - | 0.59 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.25 ** | 0.17 * | 0.16 * |
| 2. Emotional Overinvolvement (FQ) | - | 0.36 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.14 * | 0.16 * | |
| 3. Depression (CDI) | - | 0.63 ** | 0.33 ** | 0.14 * | ||
| 4. Trait-Anxiety(STAIC) | - | 0.37 ** | 0.24 ** | |||
| 5. Eating attitudes (ChEAT) | - | 0.29 ** | ||||
| 6. LOC | - |
| Coefficient | SE | 95% CI | ||
| Lower | Upper | |||
| DEPRESSION MODEL | ||||
| Direct effect | 0.53 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 0.97 |
| Indirect effects | ||||
| Total indirect effects | 0.09 | 0.10 | −0.09 | 0.33 |
| High EE->Depression->LOC | −0.02 | 0.08 | −0.20 | 0.16 |
| High EE->Eating Atittudes->LOC | 0.04 | 0.07 | −0.09 | 0.20 |
| High EE->Depression->Eating attitudes->LOC | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.17 |
| ANXIETY MODEL | ||||
| Direct effect | 0.47 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.91 |
| Indirect effects | ||||
| Total indirect effects | 0.12 | 0.08 | −0.08 | 0.32 |
| High EE->Anxiety->LOC | 0.07 | 0.06 | −0.04 | 0.22 |
| High EE->Eating Atittudes->LOC | 0.01 | 0.04 | −0.06 | 0.12 |
| High EE->Anxiety->Eating attitudes->LOC | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.11 |
References
- Bertoli, S.; Leone, A.; Ponissi, V.; Bedogni, G.; Beggio, V.; Strepparava, M.G.; Battezzati, A. Prevalence of and risk factors for binge eating behaviour in 6930 adults starting a weight loss or maintenance programme. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 19, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; (DSM-5); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, M.E.; LeMay-Russell, S.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M. Loss-of-Control Eating and Obesity Among Children and Adolescents. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Marcus, M.D.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A. Loss of control eating disorder in children age 12 years and younger: Proposed research criteria. Eat. Behav. 2008, 9, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Cai, Z.; Fan, X. Prevalence of binge and loss of control eating among children and adolescents with overweight and obesity: An exploratory meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 50, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leehr, E.J.; Krohmer, K.; Schag, K.; Dresler, T.; Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.E. Emotion regulation model in binge eating disorder and obesity—A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.Y.; Allen, K.L.; Davis, E.; Blair, E.; Zubrick, S.R.; Byrne, S.M. The psychosocial burden of childhood overweight and obesity: Evidence for persisting difficulties in boys and girls. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 176, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomaker, L.B.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Ma, C.E.; Wolkoff, L.E.; Columbo, K.M.; Ma, L.M.R.; Roza, C.A.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A.; Ba, L.E.W.; et al. Salience of loss of control for pediatric binge episodes: Does size really matter? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2009, 43, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, A.; Hartmann, A.S.; Czaja, J.; Schoebi, D. Natural course of preadolescent loss of control eating. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2013, 122, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Shomaker, L.B.; Olsen, C.; Roza, C.A.; Wolkoff, L.E.; Columbo, K.M.; Raciti, G.; Zocca, J.M.; Wilfley, D.E.; Yanovski, S.Z.; et al. A prospective study of pediatric loss of control eating and psychological outcomes. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2011, 120, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, A.B. Are loss of control while eating and overeating valid constructs? A critical review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 412–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, T.S.; Miklowitz, D.J. Parental Expressed Emotion and Youth Psychopathology: New Directions for an Old Construct. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2015, 46, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadou, D.; Medina-Pradas, C.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Treasure, J. A systematic review of family caregiving in eating disorders. Eat. Behav. 2014, 15, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, J.M.; Rowley, S.; Trofholz, A.; Hanson, C.; Rueter, M.; MacLehose, R.F.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Childhood Obesity and Interpersonal Dynamics during Family Meals. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, J.A.; Palma, C.L.; Mellor, D.; Green, J.; Renzaho, A.M.N. The relationship between family functioning and child and adolescent overweight and obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 38, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, A.; Tuschen-Caffier, B.; Czaja, J. Eating behavior and familial interactions of children with loss of control eating: A laboratory test meal study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpan, M.; Eray, Ş; Eren, E.; Vural, A.P. Perceived Expressed Emotion, Emotional and Behavioral Problems and Self-Esteem in Obese Adolescents: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2018, 10, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, A.; Schmidt, R.; Brauhardt, A.; Hilbert, A. Family Functioning in Adolescents with Binge-Eating Disorder. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2016, 24, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matherne, C.E.; Munn-Chernoff, M.A.; Thornton, L.M.; Rhee, S.H.; Lin, S.; Corley, R.P.; Stallings, M.C.; Hewitt, J.K. Perceived family functioning among adolescents with and without loss of control eating. Eat. Behav. 2019, 33, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, C.C.; Raimann, T.X.; Gaete, V. Prevención de los trastornos de conducta alimentaria en la era de la obesidad: Rol del clínico. Rev. Med. Clín. Las Condes 2015, 26, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, K.; Rhodes, P.; Hunt, C. The Relationship Between Family Mealtime Interactions and Eating Disorder in Childhood and Adolescence: A Systematic Review. Aust. N. Z. J. Fam. Ther. (Anzjft) 2013, 34, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, B.E.; Camacho, C.; Peterson, C.B.; Rhee, K.E.; Rydell, S.A.; Zucker, N.L.; Boutelle, K.N. The relationship between parent feeding styles and general parenting with loss of control eating in treatment-seeking overweight and obese children. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, J.; Hartmann, A.S.; Rief, W.; Hilbert, A. Mealtime family interactions in home environments of children with loss of control eating. Appetite 2011, 56, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, A.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Ms, L.M.R.; Kelly, N.R.; Ba, L.M.H.; Ba, C.K.P.; Grygorenko, M.V.; Brady, S.M.; Condarco, T.A.; Kozlosky, M.; et al. Puberty and the manifestations of loss of control eating in children and adolescents. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 47, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puder, J.J.; Munsch, S. Psychological correlates of childhood obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, S37–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouteris, H.; McCabe, M.P.; Ricciardelli, L.A.; Milgrom, J.; Baur, L.A.; Aksan, N.; Dell’Aquila, D. Parent–child interactions and obesity prevention: A systematic review of the literature. Early Child Dev. Care 2012, 182, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, A.R.; Solano, S.; Blanco, M.; Lacruz, T.; Graell, M. Prevalence of childhood mental disorders in overweight and obese Spanish children: Identifying loss of control eating. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 267, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Sepúlveda, A.R.; Lacruz, T.; Parks, M.; Real, B.; Román, F.J.; Martin-Peinador, Y. Examining Maternal Psychopathology, Family Functioning and Coping Skills in Childhood Obesity: A Case-Control Study. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2017, 25, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, A.R.; Anastasiadou, D.; Rodríguez, L.; Almendros, C.; Andrés, P.; Vaz, F.; Graell, M. Spanish validation of the Family Questionnaire (FQ) in families of patients with an eating disorder. Psicothema 2014, 26, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Forjaz, M.J.; Cano, P.M.; Cervera-Enguix, S. Confirmatory Factor Analysis, Reliability, and Validity of a Spanish Version of FACES III. Am. J. Fam. Ther. 2002, 30, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seisdedos, N. STAIC, Cuestionario de Autoevaluación; TEA Ediciones SA: Madrid, Spain, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- DaVanzo, P.; Kerwin, L.; Nikore, V.; Esparza, C.; Forness, S.; Murrelle, L. Spanish Translation and Reliability Testing of the Child Depression Inventory. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2004, 35, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gracia, M.; Marcó, M.; Trujano, P. Factores asociados a la conducta alimentaria en preadolescentes. Psicothema 2007, 19, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sobradillo, B.; Aguirre, A.; Aresti, U.; Bilbao, A.; Fernández-Ramos, C.; Lizarraga, A.; Lorenzo, H.; Madariaga, L.; Rica, I.; Ruiz, I.; et al. Curvas y Tablas de Crecimiento. (Estudio Longitudinal y Transversal); Fundación Faustino Orbegozo: Bilbao, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.H.; Portner, J.; Lavee, Y. FACES III (Family Adaptation and Cohesion Scales); St Paul, Minnesota University: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Faden, D.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Wilfley, D.E.; Yanovski, J.A. The perceived onset of dieting and loss of control eating behaviors in overweight children. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2005, 38, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, A.; Rief, W.; Tuschen-Caffier, B.; De Zwaan, M.; Czaja, J. Loss of control eating and psychological maintenance in children: An ecological momentary assessment study. Behav. Res. Ther. 2009, 47, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, A.R.; Solano, S.; Blanco, M.; Lacruz, T.; Veiga, O. Feasibility, acceptability, and effectiveness of a multidisciplinary intervention in childhood obesity from primary care: Nutrition, physical activity, emotional regulation, and family. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2019, 28, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Paya, N.; Ensenyat, A.; Real, J.; Castro-Viñuales, I.; Zapata, A.; Galindo, G.; Solé-Mir, E.; Bosch-Muñoz, J.; Mur, J.M.; Teixido, C. Evaluation of a family intervention programme for the treatment of overweight and obese children (Nereu Programme): A randomized clinical trial study protocol. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NG (N = 76) M (SD) | OWG (N = 81) M (SD) | OG (N = 82) M (SD) | Overall p-Value | NG vs. OWG | NG vs. OG | OWG vs. OG | z-BMI Correlation (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expressed emotion | ||||||||
| Criticism (FQ) | 18.37 (0.78) | 20.92 (0.70) | 20.87 (0.67) | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 0.18 (0.02) |
| Overinvolvement (FQ) | 20.84 (0.67) | 22.99 (0.60) | 24.42 (0.58) | 0.001 | 0.06 | <0.0001 | 0.26 | 0.26 (0.001) |
| Patterns of family functioning | ||||||||
| Adaptability (FACES) | 24.01 (0.79) | 23.61 (0.71) | 23.26 (0.68) | 0.78 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | −0.05 (0.26) |
| Cohesion (FACES) | 39.04 (0.82) | 38.26 (0.73) | 37.44 (0.70) | 0.34 | 1.00 | 0.44 | 1.00 | −0.04 (0.52) |
| Child Psychological distress | ||||||||
| Depression (CDI) | 6.67 (0.80) | 8.41 (0.72) | 9.40 (0.69) | 0.04 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.96 | 0.16 (0.03) |
| Anxiety (STAIC) | 30.02 (1.01) | 32.10 (0.91) | 33.77 (0.87) | 0.02 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 0.20 (0.01) |
| Child disordered eating symptomatology | ||||||||
| Body Esteem (BES) | 19.68 (0.84) | 14.10 (0.75) | 10.94 (0.72) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.009 | −0.50 (<0.0001) |
| Eating attitudes (ChEAT) | 5.27 (1.10) | 8.07 (0.99) | 12.33 (0.95) | <0.0001 | 0.19 | <0.0001 | 0.007 | 0.36 (<0.0001) |
| NG without LOC (N = 72) M (SD) | OWG/OG without LOC (N = 103) M (SD) | OWG/OG with LOC (N = 60) M (SD) | Overall p-Value | NG without LOC vs. OWG/OG without LOC | NG without LOC vs. OWG/OG with LOC | OWG/OG without LOC vs. OWG/OG with LOC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI † | 0.15 (0.10) | 1.96 (0.08) | 2.38 (0.09) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.003 |
| Expressed emotion | |||||||
| Criticism (FQ) | 18.26 (0.83) | 20.43 (0.63) | 21.65 (0.77) | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.66 |
| Cut-off (%) | 16.4 | 27.8 | 40.4 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.003 | 0.11 |
| Overinvolvement (FQ) | 20.72 (0.72) | 23.41 (0.54) | 24.03 (0.67) | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.003 | 1.00 |
| Cut-off (%) | 8.8 | 24.7 | 37.9 | 0.001 | 0.009 | <0.0001 | 0.08 |
| Patterns of family functioning | |||||||
| Adaptability (FACES) | 24.34 (0.83) | 23.39 (0.63) | 23.42 (0.77) | 0.63 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Cohesion (FACES) | 39.06 (0.87) | 38.13 (0.66) | 37.50 (0.80) | 0.43 | 1.00 | 0.59 | 1.00 |
| Child Psychological Distress | |||||||
| Depression (CDI) | 6.50 (0.85) | 8.68 (0.64) | 9.32 (0.79) | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 1.00 |
| Cut-off (%) | 0 | 8 | 7.1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.84 |
| Anxiety (STAIC) | 29.26 (1.06) | 32.51 (0.80) | 34.16 (0.98) | 0.004 | 0.05 | 0.003 | 0.58 |
| Child disordered eating symptomatology | |||||||
| Body Esteem (BES) | 19.88 (0.89) | 13.70 (0.67) | 10.70 (0.82) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.01 |
| Eating attitudes (ChEAT) | 5.05 (1.17) | 8.78 (0.88) | 12.74 (1.08) | <0.0001 | 0.04 | <0.0001 | 0.01 |
| Cut-off (%) | 3.8 | 13.5 | 21.4 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.006 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sepúlveda, A.R.; Lacruz, T.; Solano, S.; Blanco, M.; Moreno, A.; Rojo, M.; Beltrán, L.; Graell, M. Identifying Loss of Control Eating within Childhood Obesity: The Importance of Family Environment and Child Psychological Distress. Children 2020, 7, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110225
Sepúlveda AR, Lacruz T, Solano S, Blanco M, Moreno A, Rojo M, Beltrán L, Graell M. Identifying Loss of Control Eating within Childhood Obesity: The Importance of Family Environment and Child Psychological Distress. Children. 2020; 7(11):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110225
Chicago/Turabian StyleSepúlveda, Ana Rosa, Tatiana Lacruz, Santos Solano, Miriam Blanco, Alba Moreno, Marta Rojo, Lucía Beltrán, and Montserrat Graell. 2020. "Identifying Loss of Control Eating within Childhood Obesity: The Importance of Family Environment and Child Psychological Distress" Children 7, no. 11: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110225
APA StyleSepúlveda, A. R., Lacruz, T., Solano, S., Blanco, M., Moreno, A., Rojo, M., Beltrán, L., & Graell, M. (2020). Identifying Loss of Control Eating within Childhood Obesity: The Importance of Family Environment and Child Psychological Distress. Children, 7(11), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/children7110225





