The Feasibility and Validity of Home Spirometry for People with Cystic Fibrosis: Is It Comparable to Spirometry in the Clinic?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Spirometry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
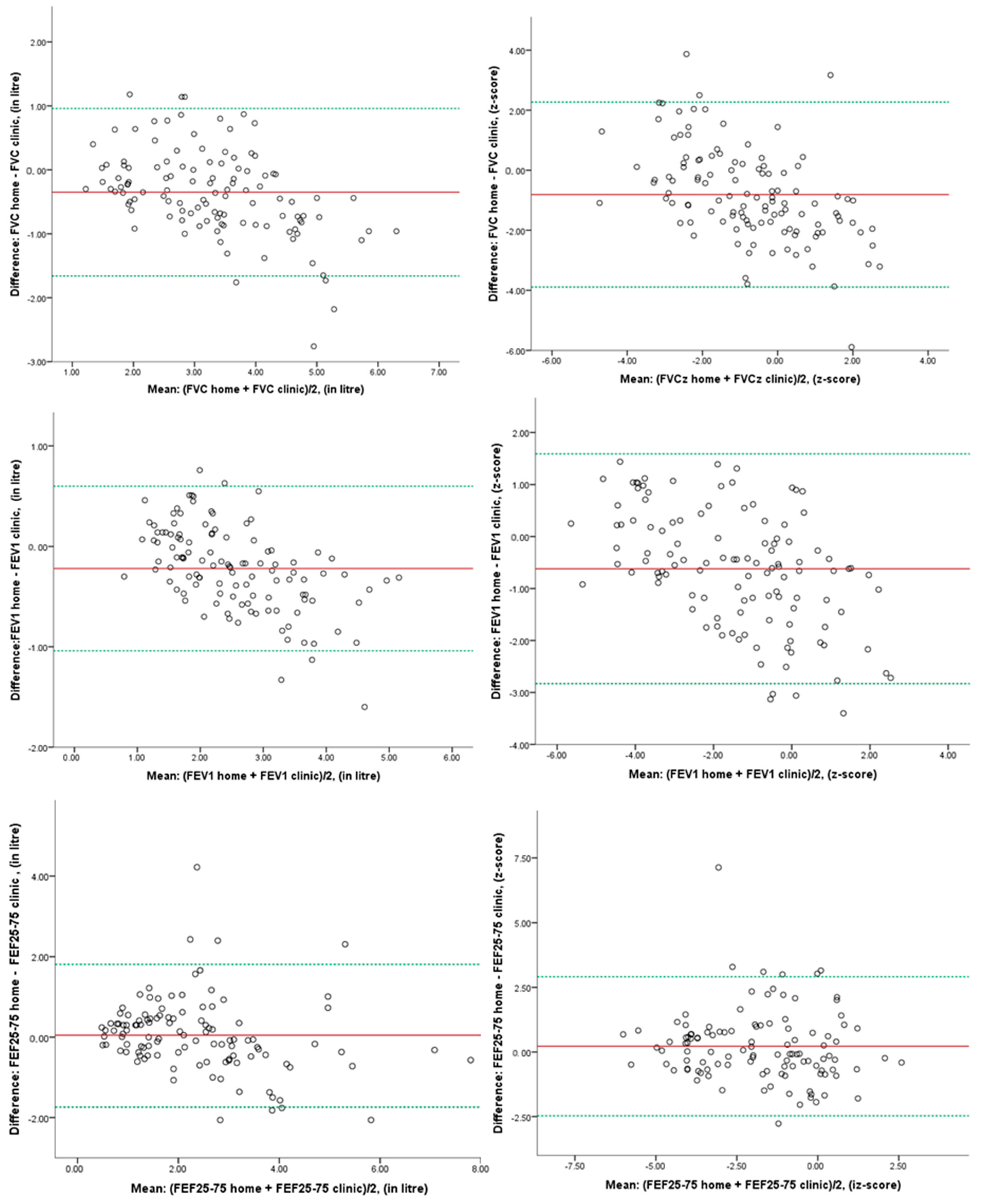
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CF | Cystic fibrosis |
| pwCF | People with cystic fibrosis |
| ATS/ERS | American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society |
| ICC | Intra-correlation coefficient |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in the first sec |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| ppFEV1 | Percent predicted forced expiratory volume in one second |
| FEF25-75 | Forced expiratory flow at 25% and 75% of pulmonary volume |
| BEV | Back extrapolated volume |
| GLI | Global Lung Initiative equations |
| GEE | Generalized estimating equations |
| LoA | Limits of agreement |
References
- Shteinberg, M.; Haq, I.J.; Polineni, D.; Davies, J.C. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2021, 397, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, C.; Duff, A.J.A.; Bell, S.C.; Heijerman, H.G.M.; Munck, A.; Ratjen, F.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Southern, K.W.; Barben, J.; Flume, P.A.; et al. ECFS best practice guidelines: The 2018 revision. J. Cyst. Fibrosis. 2018, 17, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, C.H.; Orr, N.J.; Ollosson, S.L.; Irving, S.J.; Balfour-Lynn, I.M.; Carr, S.B. Initiating home spirometry for children during theCOVID-19 pandemic—A practical guide. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2021, 42, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, S.M.; Budd, J.R.; Warwick, W.J.; Kujawa, S.J.; Wielinski, C.L.; Ewing, L.B. Feasibility and compliance studies of a home measurement monitoring program for cystic fibrosis. J. Chronic Dis. 1986, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, E.; Dick, K.; Ollosson, S.; Jones, D.; Mattock, H.; Bentley, S.; Saunders, C.; Matthews, J.; Dobra, B.; King, J.; et al. Telemedicine and cystic fibrosis: Do we still need face-to face clinics? Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2021, 42, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais-Almeida, M.; Barbosa, M.T.; Sousa, C.S.; Almeida, I.; Pimenta, L.; Aguiar, R. Spirometry Outside the Hospital. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2021, 57, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masa, J.F.; Gonzalez, M.T.; Pereira, R.; Mota, M.; Riesco, J.A.; Corral, J.; Zamorano, J.; Rubio, M.; Teran, J.; Farré, R. Validity of spirometry performed online. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruderman, I.; Abboud, S. Telespirometry: Novel System for Home Monitoring of Asthmatic Patients. Telemed. J. 1997, 3, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanthikumar, S.; Ruseckaite, R.; Corda, J.; Mulrennan, S.; Ranganathan, S.; Douglas, T. Telehealth use in Australian cystic fibrosis centers: Clinician experiences. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 2906–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.; Strang, A.; Shenoy, A.; Selhorst, D.; Chidekel, A. Education and implementation of home spirometry in an adolescent cystic fibrosis population. Respir. Med. Res. 2023, 84, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elm E von Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, B.G.; Stocks, J.; Hall, G.L.; Culver, B.; Steenbruggen, I.; Carter, K.W.; Thompson, B.R.; Graham, B.L.; Miller, M.R.; Ruppel, G.; et al. The Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) Network: Bringing the world’s respiratory reference values together. Breathe 2017, 13, e56–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement Between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, J.S.; Blower, W.C.; Feldstein, J.F.; Koch, B.A.; Munlin, A.L.; Hardie, W.D. Acceptability and repeatability of spirometry in children using updated ATS/ERS criteria. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2008, 43, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruizinga, M.D.; Essers, E.; Stuurman, F.E.; Yavuz, Y.; de Kam, M.L.; Zhuparris, A.; Janssens, H.M.; Groothuis, I.; Sprij, A.J.; Nuijsink, M.; et al. Clinical validation of digital biomarkers for pediatric patients with asthma and cystic fibrosis: Potential for clinical trials and clinical care. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 59, 2100208. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Ryan, M.; Marchetti, P.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Greenberg, J.; Bacon, C.; Kaur, R.; Scalia, S.; Sawicki, G.S. Real-world feasibility of short-term, unsupervised home spirometry in CF. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerzon, F.L.G.R.; Jöbsis, Q.; Bannier, M.A.G.E.; Winkens, B.; Dompeling, E. Discrepancy between Lung Function Measurements at Home and in the Hospital in Children with Asthma and CF. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, J.; Buffels, J.; Van Dijck, Y.; Decramer, M.; Nemery, B. Accuracy of Office Spirometry Performed by Trained Primary-Care Physicians Using the MIR Spirobank Hand-Held Spirometer. Respiration 2012, 83, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukharesh, L.; Ryan, M.; Hayden, L.P.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Gaffin, J.M. Comparison of Pneumotachometer and Portable Digital Turbine Spirometry for Field-Based Assessment: An Air Quality, Environment, and Respiratory Outcomes in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2023, 36, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakkottai, A.; Kaciroti, N.; Kasmikha, L.; Nasr, S.Z. Impact of home spirometry on medication adherence among adolescents with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanconato, S.; Meneghelli, G.; Braga, R.; Zacchello, F.; Baraldi, E. Office Spirometry in Primary Care Pediatrics: A Pilot Study. Pediatrics 2005, 116, e792–e797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exarchos, K.P.; Gogali, A.; Sioutkou, A.; Chronis, C.; Peristeri, S.; Kostikas, K. Validation of the portable Bluetooth® Air Next spirometer in patients with different respiratory diseases. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian-Lee, Y.; Chavasse, R.; Richter, H.; Seddon, P. Assessment of a low-cost home monitoring spirometer for children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2002, 33, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlinski, A.; Leisenring, P.; Willis, L.; King, S. Home Spirometry in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.; Kenia, P.; Nagakumar, P.; Gupta, A. Paediatric and adolescent asthma: A narrative review of telemedicine and emerging technologies for the post-COVID-19 era. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 51, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paynter, A.; Khan, U.; Heltshe, S.L.; Goss, C.H.; Lechtzin, N.; Hamblett, N.M. A comparison of clinic and home spirometry as longitudinal outcomes in cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 21, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, C.; Westrupp, N.; Short, C.; Seddon, P.; Olden, C.; Wallis, C.; Brodlie, M.; Baxter, F.; McCormick, J.; MacFarlane, S. Unsupervised home spirometry is not equivalent to supervised clinic spirometry in children and young people with cystic fibrosis: Results from the CLIMB-CF study. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 2871–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer, J.; Hanania, N.A.; Chaudhuri, R.; Sagara, H.; Bailes, Z.; Fowler, A.; Peachey, G.; Pizzichini, E.; Slade, D. Clinic vs Home Spirometry for Monitoring Lung Function in Patients with Asthma. Chest 2023, 164, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Miller, M.R.; Thompson, B.; Aliverti, A.; Barjaktarevic, I.; Cooper, B.G.; Culver, B.; Derom, E.; Hall, G.L.; et al. ERS/ATS technical standard on interpretive strategies for routine lung function tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, R.; McLeese, R.; Busby, J.; Stewart, J.; Clarke, M.; Man, W.D.C.; Bradley, J. Unsupervised home spirometry versus supervised clinic spirometry for respiratory disease: A systematic methodology review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2023, 32, 220248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaufils, F.; Enaud, R.; Gallode, F.; Boucher, G.; Macey, J.; Berger, P.; Fayon, M.; Bui, S. Adherence, reliability, and variability of home spirometry telemonitoring in cystic fibrosis. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1111088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfaraz, S.; Sund, Z.; Jarad, N. Real-time, once-daily monitoring of symptoms and FEV1 in cystic fibrosis patients—A feasibility study using a novel device. Clin. Respir. J. 2010, 4, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechtzin, N.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; West, N.E.; Allgood, S.; Wilhelm, E.; Khan, U.; Aitken, M.L.; Ramsey, B.W.; Boyle, M.P.; Mogayzel, P.J., Jr.; et al. Home Monitoring of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis to Identify and Treat Acute Pulmonary Exacerbations. eICE Study Results. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanbrook, M.B.; Corey, M.; Tullis, D.E. The repeatability of forced expiratory volume measurements in adults with cystic fibrosis. Chest 2004, 125, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppelaar, M.C.; Emond, Y.; Bannier, M.A.G.E.; Reijers, M.H.E.; van der Vaart, H.; van der Meer, R.; Altenburg, J.; Conemans, L.; Rottier, B.L.; Nuijsink, M. Potential, Pitfalls, and Future Directions for Remote Monitoring of Chronic Respiratory Diseases: Multicenter Mixed Methods Study in Routine Cystic Fibrosis Care. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e54942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N (%), Mean (StDev) | |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| 6–11 y.o | 7 (14.58) |
| 12–17 y.o | 21 (43.75) |
| >18 y.o | 20 (41.67) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 22 (45.83) |
| Female | 26 (54.17) |
| Pseudomonas colonization | |
| None | 35 (72.92) |
| Intermittent | 9 (18.75) |
| Chronic | 4 (8.33) |
| Disease severity | |
| Mild (ppFEV1 > 80%) | 34 (70.83) |
| Moderate (ppFEV1 60–80%) | 8 (16.67) |
| Severe (ppFEV1 < 60%) | 6 (12.50) |
| Mutations | |
| ΔF508/ΔF508 | 20 (41.67) |
| ΔF508/other | 20 (41.67) |
| None | 8 (16.67) |
| Spirometry data | Mean (sd) |
| FVC (lt) | 3.27 (1.03) |
| FVC pp | 94.03 (25.56) |
| FEV1 (lt) | 2.59 (0.86) |
| FEV1 pp | 84.98 (20.94) |
| FEF25-75 (lt/sec) | 2.49 (1.26) |
| FEF25-75 pp | 69.89 (29.57) |
| Home Spirometry Mean (SD) | Clinic Spirometry Mean (SD) | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p-Value | 95% LoA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FVC (lt) | 3.27 (1.05) | 3.63 (1.35) | −0.37 (−0.54, −0.19) | <0.001 * | −1.66, +0.96 |
| FVC z-score | −0.72 (1.38) | 0.03 (1.92) | −0.76 (−1.17, −0.34) | 0.001 * | −3.89, +2.27 |
| FEV1 (lt) | 2.59 (0.91) | 2.81 (1.11) | −0.22 (−0.32, −0.12) | <0.001 * | −1.04, +0.60 |
| FEV1 z-score | −1.34 (1.58) | −0.77 (2.02) | −0.58 (−0.85, −0.30) | <0.001 * | −2.83, +1.59 |
| FEF25-75 (lt/s) | 2.50 (1.34) | 2.44 (1.40) | 0.06 (−0.13, 0.25) | 0.526 | −1.74, +1.81 |
| FEF25-75 z-score | −1.54 (1.67) | −1.72 (1.72) | 0.18 (−0.09, 0.46) | 0.189 | −2.47, +2.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sopiadou, A.; Gioulvanidou, M.; Kogias, C.; Chrysochoou, E.-A.; Kalaitzopoulou, I.; Hatziagorou, E. The Feasibility and Validity of Home Spirometry for People with Cystic Fibrosis: Is It Comparable to Spirometry in the Clinic? Children 2025, 12, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030277
Sopiadou A, Gioulvanidou M, Kogias C, Chrysochoou E-A, Kalaitzopoulou I, Hatziagorou E. The Feasibility and Validity of Home Spirometry for People with Cystic Fibrosis: Is It Comparable to Spirometry in the Clinic? Children. 2025; 12(3):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030277
Chicago/Turabian StyleSopiadou, Athina, Maria Gioulvanidou, Christos Kogias, Elissavet-Anna Chrysochoou, Ioustini Kalaitzopoulou, and Elpis Hatziagorou. 2025. "The Feasibility and Validity of Home Spirometry for People with Cystic Fibrosis: Is It Comparable to Spirometry in the Clinic?" Children 12, no. 3: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030277
APA StyleSopiadou, A., Gioulvanidou, M., Kogias, C., Chrysochoou, E.-A., Kalaitzopoulou, I., & Hatziagorou, E. (2025). The Feasibility and Validity of Home Spirometry for People with Cystic Fibrosis: Is It Comparable to Spirometry in the Clinic? Children, 12(3), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030277







