Evaluation of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration for Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborn Infants with Hemolytic Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
“In isoimmune hemolytic disease, administration of intravenous γ-globulin (0.5–1 g/kg over 2 h) is recommended if the total serum bilirubin (TSB) is rising despite intensive phototherapy, or the TSB level is within 2 to 3 mg/dL (34–51 mol/L) of the exchange level. If necessary, this dose can be repeated in 12 h.”
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Adverse Events
2.4. Statistical Analysis
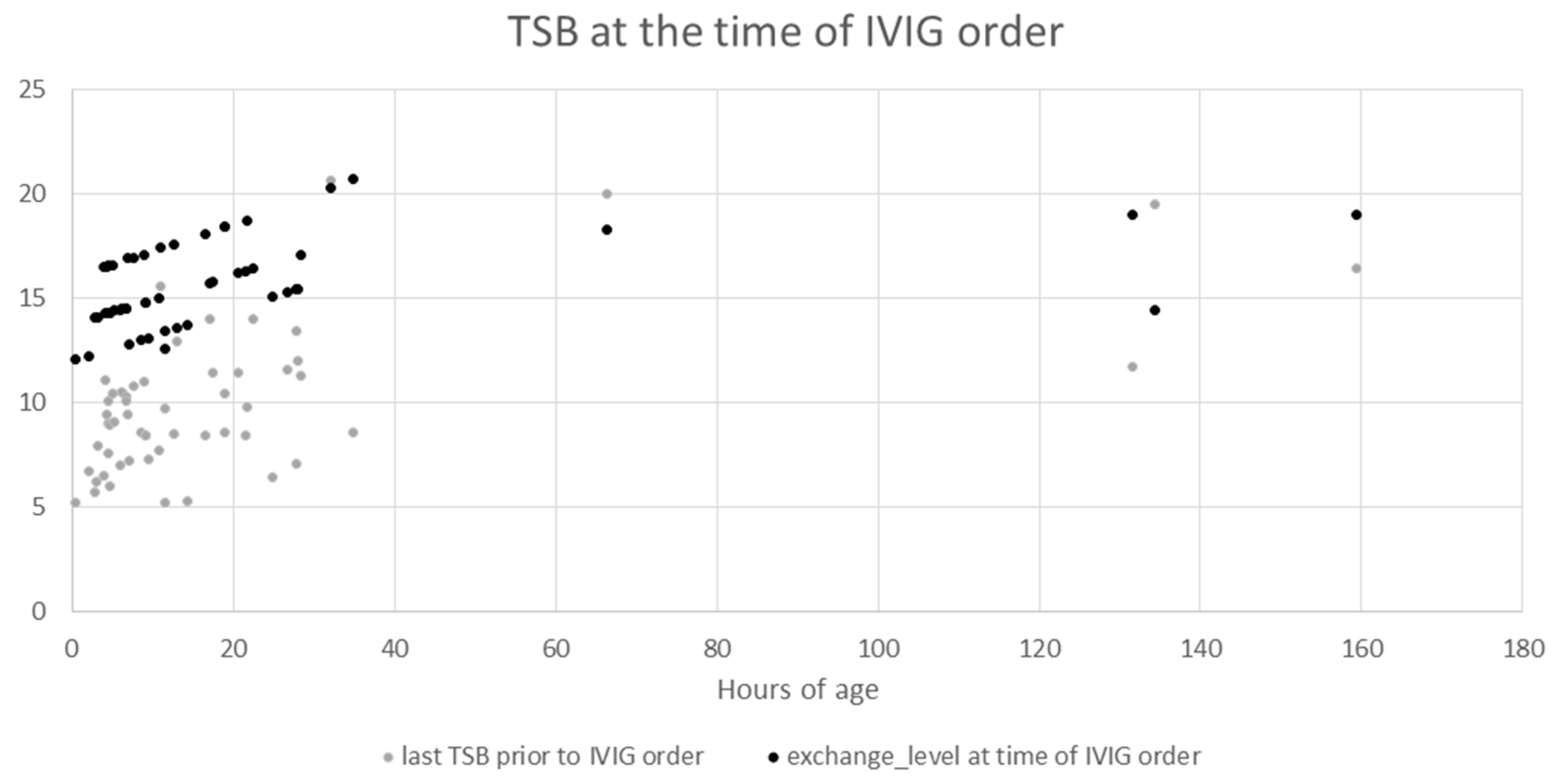
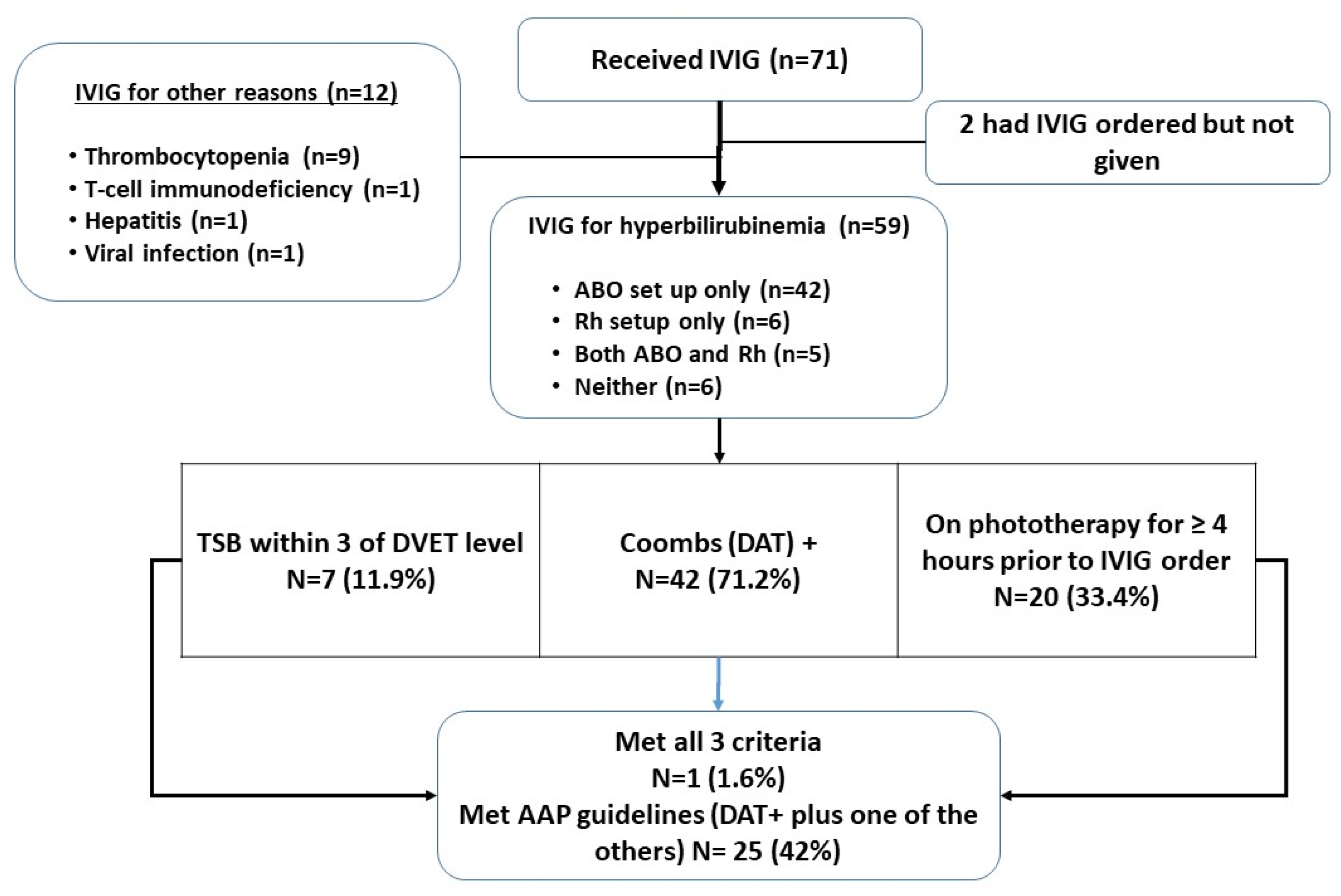
3. Results
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Gestational age ≥ 35 weeks
- (2)
- DAT positive
- (3)
- Either
- TSB level is at or above the escalation of care (EOC) threshold (2 mg/dL below exchange transfusion level) OR
- TSB is rising despite intensive phototherapy of 4 h, within 3 mg/dL of the exchange level and/or there is concern that a timely exchange transfusion will be difficult*.
*This exception is primarily intended for DAT+ infants with an unusual antibody for whom DVET blood procurement may be difficult, or for an infant far from a center that performs DVET commonly
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zwiers, C.; Scheffer-Rath, M.E.; Lopriore, E.; de Haas, M.; Liley, H.G. Immunoglobulin for alloimmune hemolytic disease in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, R.; Diwan, P. Immune hemolytic disease of the newborn. World J. Anemia 2018, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Figueras-Aloy, J.; Rodríguez-Miguélez, J.M.; Iriondo-Sanz, M.; Salvia-Roiges, M.D.; Botet-Mussons, F.; Carbonell-Estrany, X. Intravenous immunoglobulin and necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns with hemolytic disease. Pediatrics 2010, 125, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palabrica, F.R.; Kwong, S.L.; Padua, F.R. Adverse events of intravenous immunoglobulin infusions: A ten-year retrospective study. Asia Pac. Allergy 2013, 3, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Negre, S.; Matoses, M.L.; Golombek, S.G.; Vento, M. Necrotizing enterocolitis following the use of intravenous immunoglobulin for haemolytic disease of the newborn. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, J.J.; Zhou, X.G.; Zhou, X.Y.; Cheng, R.; Hu, Y.H. The effect of immunoglobulin treatment for hemolysis on the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis—A meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. 2016, 20, 3902–3910. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaleem, M. Intravenous immune globulin uses in the fetus and neonate: A review. Antibodies 2020, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolles, S.; Sewell, W.A.; Misbah, S.A. Clinical uses of intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 142, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, B.; Robbins, J.; Hobbs, C. American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 297–316. [Google Scholar]
- Calculator and Clinical Decision Support for the Management of Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborns 35 or More Weeks of Gestation. Available online: https://peditools.org/bili/ (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Watchko, J.F. ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn: A need for clarity and consistency in diagnosis. J. Perinatol. 2023, 43, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, A.R.; Newman, T.B.; Slaughter, J.L.; Maisels, M.J.; Watchko, J.F.; Downs, S.M.; Grout, R.W.; Bundy, D.G.; Stark, A.R.; Bogen, D.L.; et al. Clinical practice guideline revision: Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn Infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022058859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaughter, J.L.; Kemper, A.R.; Newman, T.B. Technical Report: Diagnosis and management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022058865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study (Author Year) | Antibody Status of Subjects | IVIG Dose | IVIG Frequency | Conditions for IVIG Administration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubo (1992) ^ | Rh disease DAT positive | 0.5 g/kg | ×1 | Initiated as soon as Rh disease established |
| Dagoglu (1995) ^ | Rh disease DAT positive | 0.5 g/kg | ×1 | Initiated immediately after birth (typically within 2 h) |
| Alpay (1999) ^ | Rh and/or ABO disease DAT positive | 1 g/kg | ×1 | Bili > 12 mg/dL + retic > 10% (mean time of initiation was HOL 51.5) |
| Miqdad (2004) | ABO disease DAT positive | 0.5 g/kg | ×1 | Bili rising ≥0.5 mg/dL per h |
| Nasseri (2006) | Rh or ABO disease DAT positive | 0.5 g/kg | Q12 h × 3 doses | Bili rising ≥ 0.5 mg/dL per h (mean time of initiation was HOL 22.8) |
| Elafly (2011) | Rh disease DAT positive | 0.5 g/kg and 1 g/kg in separate cohorts | ×1 | Administered at HOL 12 if phototherapy required and/or bili rising ≥ 0.5 mg/dL per h |
| Smits-Wintjents (2011) * | Rh disease DAT positive | 0.75 g/kg | ×1 | Initiated immediately after birth (within 4 h) |
| Santos (2013) * | Rh disease DAT positive | 0.5 g/kg | ×1 | Initiated immediately after birth (within 6 h) |
| Gestational age, weeks (median, IQR) | 39 (37.4, 39.5) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Male | 31 (52.5%) |
| Female | 28 (47.5%) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |
| Black/African-American | 46 (77.9%) |
| Multi-racial | 2 (3.4%) |
| White | 9 (15.3%) |
| Unknown | 2 (3.4%) |
| Rh D mismatch, n (%) | 11 (18.6%) |
| ABO mismatch, n (%) | 47 (79.7%) |
| Positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT), n (%) | 42 (71.2%) |
| Hour of life that phototherapy started (median, IQR) | 7.35 (5.55, 13.05) |
| Total duration of phototherapy, hours (median, IQR) | 85.9 (65.8, 115) |
| Dose # | Doses of IVIG Ordered, n (%) | Dose (g/kg) of IVIG Given (Median, IQR) | Hour of Life IVIG Received (Median, IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 59 (100%) | 1 (0.99, 1.01), n = 59 | 12.62 (10.08, 24.37), n = 59 |
| 2 | 14 (23.7%) | 1 (0.99, 1.01), n = 14 | 40.38 (27.77, 63.37), n = 14 |
| 3 | 2 (2.3%) | 1, n = 1 | 79.5 h, n = 1 |
| Number of Bilirubin Levels Available (In Our Hospital System Data Base) | Number of Patients (n = 59) | Mean (SD) Median (IQR) Of Last TSB (mg/dL) Prior to IVIG | Minimum, Maximum TSB (mg/dL) | Rate of Rise (mg/dL per h) between Two TSB Levels Immediately Prior to IVIG (Mean (SD), Median (IQR)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 (7%) | NA | NA | NA |
| 1 | 24 (41%) | 9.0 (0.43) | 5.2, 15.6 | - |
| ≥2 | 31 (52%) | 10.7 (3.9) | 5.2, 20.6 | 0.43 (0.83) 0.21 (0, 0.44) |
| Last TSB prior to IVIG | 55 | 10.0 (3.5) 9.4 (7.6, 11.4) | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohan, D.R.; Lu, H.; McClary, J.; Marasch, J.; Nock, M.L.; Ryan, R.M. Evaluation of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration for Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborn Infants with Hemolytic Disease. Children 2023, 10, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030496
Mohan DR, Lu H, McClary J, Marasch J, Nock ML, Ryan RM. Evaluation of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration for Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborn Infants with Hemolytic Disease. Children. 2023; 10(3):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030496
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohan, Daniel R., Hannah Lu, Jacquelyn McClary, Jaime Marasch, Mary L. Nock, and Rita M. Ryan. 2023. "Evaluation of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration for Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborn Infants with Hemolytic Disease" Children 10, no. 3: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030496
APA StyleMohan, D. R., Lu, H., McClary, J., Marasch, J., Nock, M. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2023). Evaluation of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration for Hyperbilirubinemia in Newborn Infants with Hemolytic Disease. Children, 10(3), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030496






