IGF1 Genetic Polymorphism and the Association between Vitamin D Status and BMI Percentiles in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Vitamin D Status
2.3. Anthropometric Measures
2.4. Genotyping
2.5. Genetic Score
2.6. Statistical Analysis
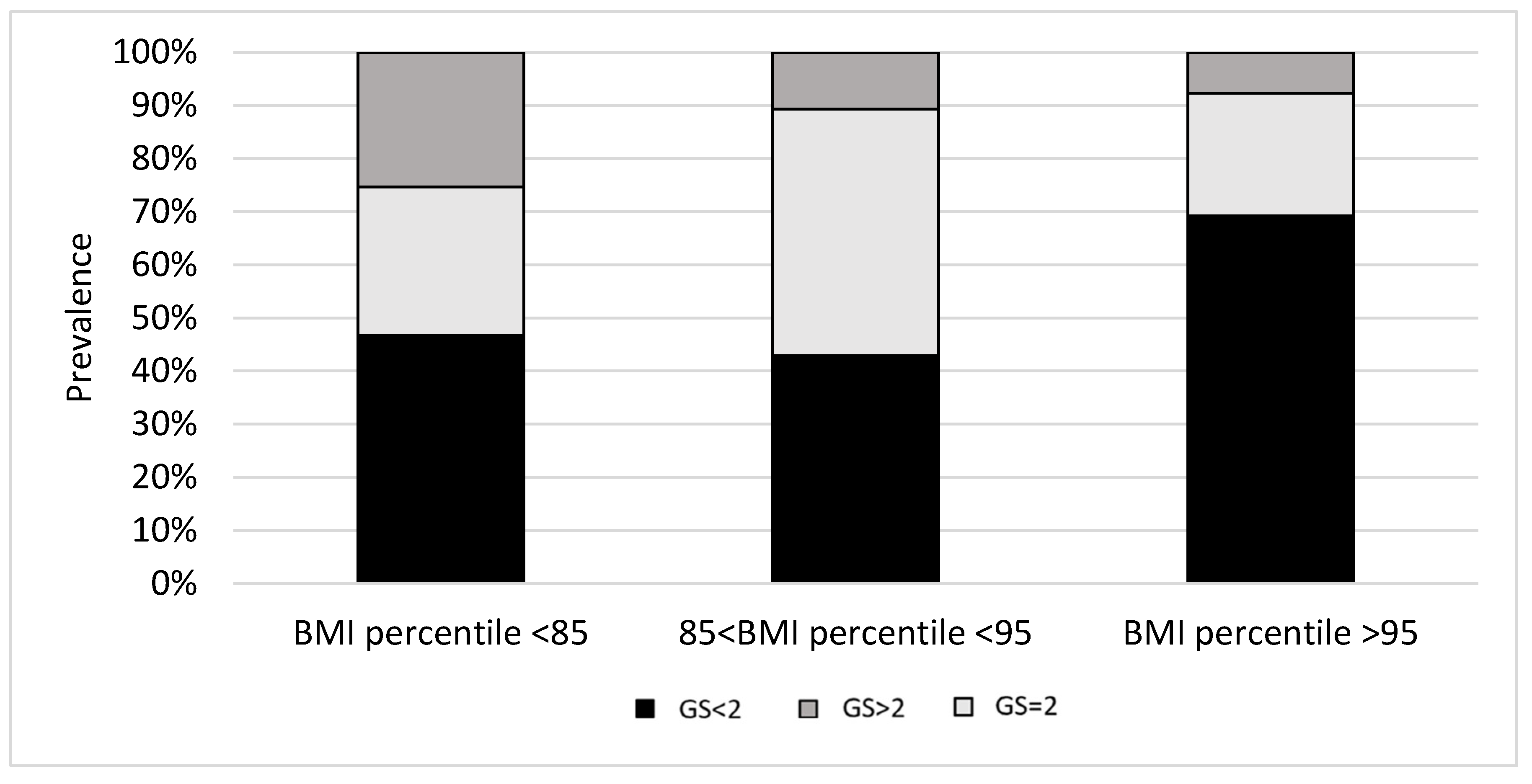
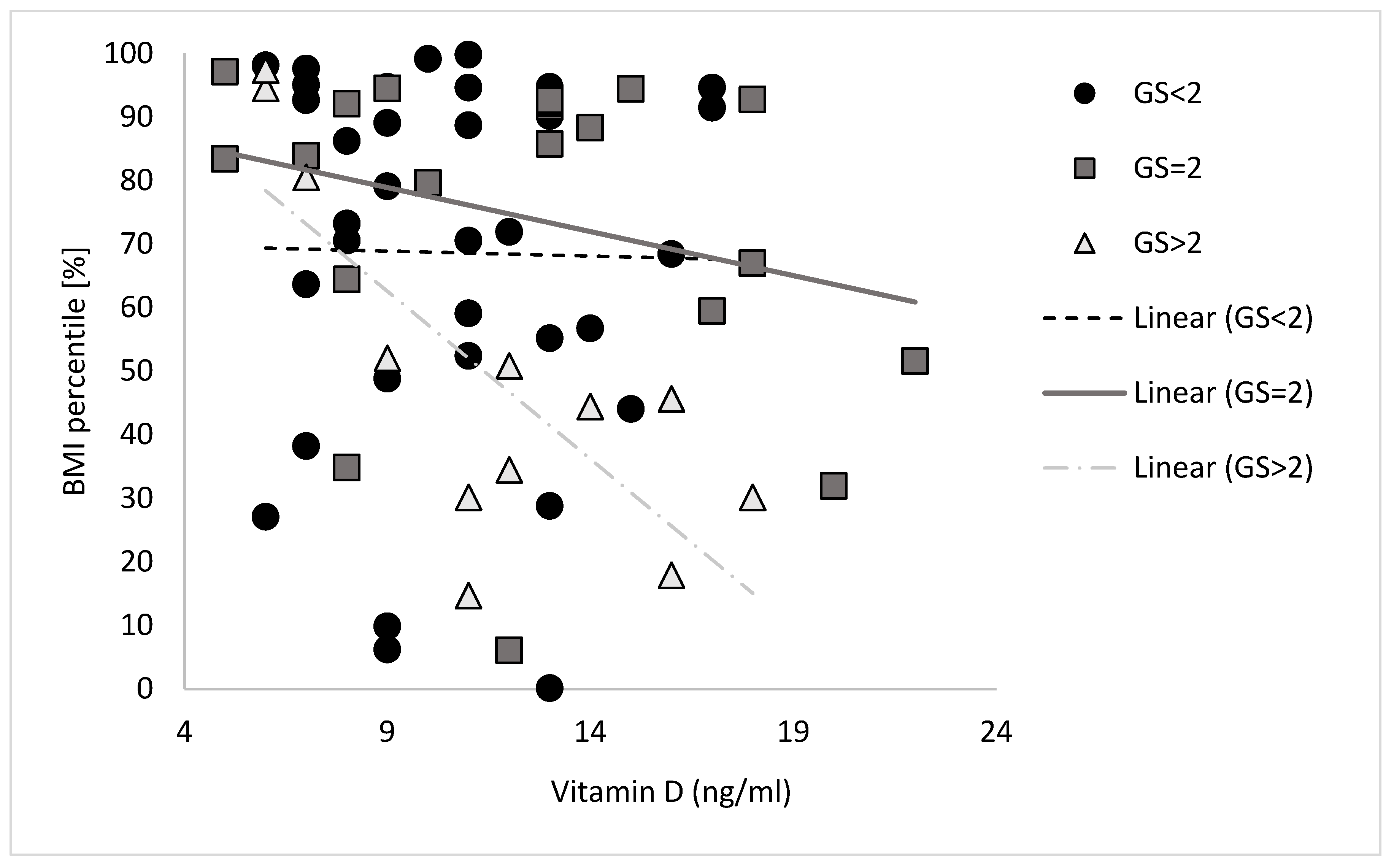
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hebestreit, A.; Börnhorst, C.; Barba, G.; Siani, A.; Huybrechts, I.; Tognon, G.; Eiben, G.; Moreno, L.A.; Fernández Alvira, J.M.; Loit, H.M.; et al. Associations between Energy Intake, Daily Food Intake and Energy Density of Foods and BMI z-Score in 2-9-Year-Old European Children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebestreit, A.; Barba, G.; De Henauw, S.; Eiben, G.; Hadjigeorgiou, C.; Kovács, É.; Krogh, V.; Moreno, L.A.; Pala, V.; Veidebaum, T.; et al. Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations between Energy Intake and BMI z-Score in European Children. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballerini, M.G.; Ropelato, M.G.; Domené, H.M.; Pennisi, P.; Heinrich, J.J.; Jasper, H.G. Differential Impact of Simple Childhood Obesity on the Components of the Growth Hormone-Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-IGF Binding Proteins Axis. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 17, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, H.; Laron, Z. Role of the GH-IGF1 System in Progression of Cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaessen, N.; Janssen, J.A.; Heutink, P.; Hofman, A.; Lamberts, S.W.J.; Oostra, B.A.; Pols, H.A.P.; van Duijn, C.M. Association between Genetic Variation in the Gene for Insulin-like Growth Factor-I and Low Birthweight. Lancet 2002, 359, 1036–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaessen, N.; Heutink, P.; Janssen, J.A.; Witteman, J.C.; Testers, L.; Hofman, A.; Lamberts, S.W.; Oostra, B.A.; Pols, H.A.; van Duijn, C.M. A Polymorphism in the Gene for IGF-I: Functional Properties and Risk for Type 2 Diabetes and Myocardial Infarction. Diabetes 2001, 50, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zou, D.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y.; Guo, R. Association Between Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Rs35767 Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Susceptibility: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 774489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhoeve, P.G.; van Rossum, E.F.C.; Te Velde, S.J.; Koper, J.W.; Kemper, H.C.G.; Lamberts, S.W.J.; de Waal, H.A.D. Association between an IGF-I Gene Polymorphism and Body Fatness: Differences between Generations. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 154, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Chen, T.C. Vitamin D Deficiency: A Worldwide Problem with Health Consequences. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1080S–1086S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Binkley, N.C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Gordon, C.M.; Hanley, D.A.; Heaney, R.P.; Murad, M.H.; Weaver, C.M. Guidelines for Preventing and Treating Vitamin D Deficiency and Insufficiency Revisited. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Jones, G. The Association between Bone Mineral Density, Metacarpal Morphometry, and Upper Limb Fractures in Children: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatahi, S.; Alyahyawi, N.; Albadawi, N.; Mardali, F.; Dara, N.; Sohouli, M.H.; Prabahar, K.; Rohani, P.; Koushki, N.; Sayyari, A.; et al. The Association between Vitamin D Status and Inflammatory Bowel Disease among Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1007725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannell, J.J.; Hollis, B.W. Use of Vitamin D in Clinical Practice. Altern. Med. Rev. J. Clin. Ther. 2008, 13, 6–20. [Google Scholar]
- Holick, M.F. The Vitamin D Deficiency Pandemic and Consequences for Nonskeletal Health: Mechanisms of Action. Mol. Aspects Med. 2008, 29, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugalingam, T.; Bosco, C.; Ridley, A.J.; Van Hemelrijck, M. Is There a Role for IGF-1 in the Development of Second Primary Cancers? Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3353–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, V.; Bianchi, V.E. Effect of GH/IGF-1 on Bone Metabolism and Osteoporsosis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 235060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulei, G.; Orasan, O.H.; Coste, S.C.; Cozma, A.; Negrean, V.; Procopciuc, L.M. Vitamin D and the Insulin-like Growth Factor System: Implications for Colorectal Neoplasia. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 50, e13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, M.S.; Gibson, J.M.; Heald, A.H.; Dunger, D.B.; Wareham, N.J. Association Between Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I: Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-1 Ratio and Metabolic and Anthropometric Factors in Men and Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortsman, J.; Matsuoka, L.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Lu, Z.; Holick, M.F. Decreased Bioavailability of Vitamin D in Obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyppönen, E.; Boucher, B.J.; Berry, D.J.; Power, C. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, IGF-1, and Metabolic Syndrome at 45 Years of Age: A Cross-Sectional Study in the 1958 British Birth Cohort. Diabetes 2008, 57, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diorio, C.; Bérubé, S.; Byrne, C.; Mâsse, B.; Hébert-Croteau, N.; Yaffe, M.; Coté, G.; Pollak, M.; Brisson, J. Influence of Insulin-like Growth Factors on the Strength of the Relation of Vitamin D and Calcium Intakes to Mammographic Breast Density. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, J.M. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor I Components in the Regulation of Vitamin D. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2006, 7, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, J.M.; Maravall, F.J.; Gómez, N.; Navarro, M.A.; Casamitjana, R.; Soler, J. Relationship between 25-(OH) D3, the IGF-I System, Leptin, Anthropometric and Body Composition Variables in a Healthy, Randomly Selected Population. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Stoffwechselforschung Horm. Metab. 2004, 36, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Kumar, M.; Chitkara, A.; Varshney, A.K. Correlation of Vitamin D3, Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 and Insulin Resistance in Pre-Diabetes and Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Diabetol. 2022, 11, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson-Hughes, B.; Heaney, R.P.; Holick, M.F.; Lips, P.; Meunier, P.J.; Vieth, R. Estimates of Optimal Vitamin D Status. Osteoporos. Osteoporos. Int. 2005, 16, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Siris, E.S.; Binkley, N.; Beard, M.K.; Khan, A.; Katzer, J.T.; Petruschke, R.A.; Chen, E.; de Papp, A.E. Prevalence of Vitamin D Inadequacy among Postmenopausal North American Women Receiving Osteoporosis Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 3215–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczmarski, R.J.; Ogden, C.L.; Guo, S.S.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Flegal, K.M.; Mei, Z.; Wei, R.; Curtin, L.R.; Roche, A.F.; Johnson, C.L. 2000 CDC Growth Charts for the United States: Methods and Development; Vital and Health Statistics; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 11, pp. 1–190.
- Petersen, A.C.; Crockett, L.; Richards, M.; Boxer, A. A Self-Report Measure of Pubertal Status: Reliability, Validity, and Initial Norms. J. Youth Adolesc. 1988, 17, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, E.; Skinner, M.; Love, M.; Elder, G.; Conger, R.; Dubas, J.; Petersen, A. The Pubertal Development Scale: A Rural and Suburban Comparison. J. Early Adolesc. 1992, 12, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanock, S.J.; Manolio, T.; Boehnke, M.; Boerwinkle, E.; Hunter, D.J.; Thomas, G.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Abecasis, G.; Altshuler, D.; Bailey-Wilson, J.E.; et al. Replicating Genotype-Phenotype Associations. Nature 2007, 447, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Zaken, S.; Meckel, Y.; Nemet, D.; Eliakim, A. Genetic Score of Power-Speed and Endurance Track and Field Athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheus, M.; McKay, J.D.; Kaaks, R.; Canzian, F.; Biessy, C.; Johansson, M.; Grobbee, D.E.; Peeters, P.H.M.; van Gils, C.H. Common Genetic Variation in the IGF-1 Gene, Serum IGF-I Levels and Breast Density. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 112, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannucci, E.; Pollak, M.N.; Platz, E.A.; Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J.; Majeed, N.; Colditz, G.A.; Speizer, F.E.; Hankinson, S.E. A Prospective Study of Plasma Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Binding Protein-3 and Risk of Colorectal Neoplasia in Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesti, G.; Mannino, G.C.; Andreozzi, F.; Greco, A.; Perticone, M.; Sciacqua, A.; Marini, M.A.; Perticone, F. A Polymorphism at IGF1 Locus Is Associated with Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilatation. Atherosclerosis 2014, 232, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, G.C.; Greco, A.; De Lorenzo, C.; Andreozzi, F.; Marini, M.A.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. A Fasting Insulin–Raising Allele at IGF1 Locus Is Associated with Circulating Levels of IGF-1 and Insulin Sensitivity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palles, C.; Johnson, N.; Coupland, B.; Taylor, C.; Carvajal, J.; Holly, J.; Fentiman, I.S.; dos Santos Silva, I.; Ashworth, A.; Peto, J.; et al. Identification of Genetic Variants That Influence Circulating IGF1 Levels: A Targeted Search Strategy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.V.; Cheng, I.; Canzian, F.; Le Marchand, L.; Thun, M.J.; Berg, C.D.; Buring, J.; Calle, E.E.; Chanock, S.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; et al. IGF-1, IGFBP-1, and IGFBP-3 Polymorphisms Predict Circulating IGF Levels but Not Breast Cancer Risk: Findings from the Breast and Prostate Cancer Cohort Consortium (BPC3). PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzian, F.; McKay, J.D.; Cleveland, R.J.; Dossus, L.; Biessy, C.; Rinaldi, S.; Landi, S.; Boillot, C.; Monnier, S.; Chajès, V.; et al. Polymorphisms of Genes Coding for Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 and Its Major Binding Proteins, Circulating Levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and Breast Cancer Risk: Results from the EPIC Study. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, M.S.; Heald, A.H.; Gibson, J.M.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dunger, D.B.; Wareham, N.J. Circulating Concentrations of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I and Development of Glucose Intolerance: A Prospective Observational Study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, A. Serum Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor I and Its Binding Proteins in Health and Disease; Growth Hormone and IGF Research; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2003; pp. 113–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ybarra, J.; Sánchez-Hernández, J.; Pérez, A. Hypovitaminosis D and Morbid Obesity. Nurs. Clin. North Am. 2007, 42, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Molero, I.; Rojo-Martínez, G.; Morcillo, S.; Gutierrez, C.; Rubio, E.; Pérez-Valero, V.; Esteva, I.; Ruiz De Adana, M.S.; Almaraz, M.C.; Colomo, N.; et al. Hypovitaminosis D and Incidence of Obesity: A Prospective Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameri, P.; Giusti, A.; Boschetti, M.; Bovio, M.; Teti, C.; Leoncini, G.; Ferone, D.; Murialdo, G.; Minuto, F. Vitamin D Increases Circulating IGF1 in Adults: Potential Implication for the Treatment of GH Deficiency. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianda, T.; Hussain, M.A.; Glatz, Y.; Bouillon, R.; Froesch, E.R.; Schmid, C. Effects of Short-term Insulin-like Growth Factor-I or Growth Hormone Treatment on Bone Turnover, Renal Phosphate Reabsorption and 1,25 Dihydroxyvitamin D3. Wiley Online Lirary 1997, 241, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Tanaka, H.; Seino, Y. Local Action of Exogenous Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I on Dihydroxyvitamin D Production in LLC-PK1 Cells. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 139, 454–460. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/ejendo?login=false (accessed on 1 August 2023). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wojcik, M.; Janus, D.; Kalicka-Kasperczyk, A.; Sztefko, K.; Starzyk, J.B. The Potential Impact of the Hypovitaminosis d on Metabolic Complications in Obese Adolescents—Preliminary Results. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overview of the Health Consequences of Obesity in Children and Adolescents—UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-the-health-consequences-of-obesity-in-children-and-adolescents/print (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Franco, C.; Bengtsson, B.-A.; Johannsson, G. The GH/IGF-1 Axis in Obesity: Physiological and Pathological Aspects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2006, 4, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranke, M.B. Short and Long-Term Effects of Growth Hormone in Children and Adolescents With GH Deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.W.; Spencer, S.A.; Cachianes, G.; Hammonds, R.G.; Collins, C.; Henzel, W.J.; Barnard, R.; Waters, M.J.; Wood, W.I. Growth Hormone Receptor and Serum Binding Protein: Purification, Cloning and Expression. Nature 1987, 330, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.I.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-like Growth Factors and Their Binding Proteins: Biological Actions. Endocr. Rev. 1995, 16, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juiz-Valiña, P.; Pena-Bello, L.; Cordido, M.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Pértega, S.; Varela-Rodriguez, B.; Garcia-Brao, M.J.; Mena, E.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Cordido, F. Altered GH-IGF-1 Axis in Severe Obese Subjects Is Reversed after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss and Related with Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggese, G.; Vierucci, F.; Boot, A.M.; Czech-Kowalska, J.; Weber, G.; Camargo, C.A.; Mallet, E.; Fanos, M.; Shaw, N.J.; Holick, M.F. Vitamin D in Childhood and Adolescence: An Expert Position Statement. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, M.; Atapattu, N.; Bhatia, V.; Braegger, C.; Butler, G.; Cassinelli, H.; Dimeglio, L.A.; Frew, E.; Fu, J.; Goldberg, G.; et al. Global Consensus Recommendations on Prevention and Management of Nutritional Rickets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; He, W.; Sun, X. Efficacy of Vitamin D Supplementation on Child and Adolescent Overweight/Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliaccio, S.; Di Nisio, A.; Mele, C.; Scappaticcio, L.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Obesity and Hypovitaminosis D: Causality or Casualty? Int. J. Obes. Suppl. 2019, 9, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranić, L.; Mikolašević, I.; Milić, S. Vitamin D Deficiency: Consequence or Cause of Obesity? Medicina 2019, 55, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Leonardi, A.; Lanciotti, L.; Cofini, M.; Muzi, G.; Penta, L. Vitamin D and Growth Hormone in Children: A Review of the Current Scientific Knowledge. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampela, I.; Sakelliou, A.; Vallianou, N.; Christodoulatos, G.-S.; Magkos, F.; Dalamaga, M. Vitamin D and Obesity: Current Evidence and Controversies. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, M.; Malinen, M.; Saavalainen, K.; Carlberg, C. Regulation of Multiple Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein Genes by 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5521–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Sequences: | Probe Sequences: | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Forward: VIC | Reverse: FAM |
| IGF1 A/G (rs7136446), NC_000012.12 | |||
| AATTGGTTACCTGCTACATTGA | GGAGTTAACGCATCTCCTTACTG | CGCGTAGTCGAGCG | CGCTCGCTGCCCTAAGTGCT |
| IGF1-C1245T (rs35767), NC_000023.11 | |||
| GGATTTCAAGCAGAACTGTGTTTTCA | GGTGGAAATAACCTGGACCTTGAAT | TTTTTCCGCATGACTCT | TTTTTTTTCCACATGCTCT |
| IGF1 T/C (rs6220) | |||
| AACAAAGAGATTTCTACCAGTGAAAGG | GCCTAGAAAAGAAGGAATCATTGT | AGTAAAACCTTGTTT AATAC | AGTAAAACCTCGTTT AATA |
| IGF1R A/G (rs1464430) | |||
| GGATTTCAAGCAGAACTGTGTTTTCA | GGTGGAAATAACCTGGACCTTGAAT | TTTTTTCCGCATGACTCT | TTTTTTTTCCACATGACTCT |
| IGF1_rs3567 | CC | CT + TT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 81 | 33 | ||
| r, p | −0.331, 0.060 | |||
| IGF1_rs7136446 | AA | AG | GG | AG + GG |
| N | 29 | 58 | 27 | 85 |
| r, p | −0.641, 0.014 | |||
| IGF1R_rs1464430 | AA | AC | CC | AC + CC |
| N | 30 | 62 | 22 | 84 |
| r, p | −0.244, 0.081 | |||
| IGF1_rs6220 | TT | TC | CC | TC + CC |
| N | 44 | 51 | 19 | 70 |
| r, p | −0.337, 0.080 |
| Symbol | Polymorphism | MAF | Genetic Score (GS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IGF1 | A/G (rs7136446) | 28% | AA = 2, AG = 0, GG = 0 |
| -C1245T (rs3567) | 30% | CC = 0, CT = 0, TT = 1 | |
| T/C (rs6220) | 36% | TT = 1, TC = 0, CC = 0 | |
| IGF1R | A/G (rs1464430) | 40% | AA = 0, AC = 0, CC = 1 |
| (AVG (SD)) or n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Age | 9.4 (2.6) |
| Mean BMI percentile | 65.0 (29.3) |
| Mean Body Fat | 16.9 (5.7) |
| Overweight prevalence | 38 (33.3) |
| Obesity prevalence | 15 (13.1) |
| Height percentile | 54.2 (35.3) |
| Weight percentile | 63.2 (31.2) |
| Serum vitamin D (mcg/dL) | 11.2 (3.9) |
| Borderline vitamin D (%) | (19.4) |
| Vitamin D deficiency (%) | (80.6) |
| Total | Normal Weight | Overweight/Obese | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF1 rs7136446 A/G | ||||
| AA | 29 (25.4) | 24 (32.4) | 5 (12.5) | 0.052 |
| AG | 58 (50.9) | 34 (45.9) | 24 (60.0) | |
| GG | 27 (23.7) | 16 (21.6) | 11 (27.5) | |
| A—allele | 116 (50.9) | 82 (54.7) | 34 (42.5) | 0.079 |
| G—allele | 112 (49.3) | 68 (45.3) | 46 (57.5) | |
| IGF1 rs1464430 A/C | ||||
| AA | 30 (26.3) | 22 (29.7) | 8 (20.0) | 0.216 |
| AC | 62 (54.4) | 41 (55.4) | 21 (52.5) | |
| CC | 22 (19.3) | 11 (14.9) | 11 (27.5) | |
| A—allele | 122 (53.5) | 85 (57.4) | 37 (46.3) | 0.106 |
| C—allele | 106 (46.5) | 63 (42.6) | 43 (53.7) | |
| IGF1 rs3567 C/T | ||||
| CC | 81 (71.0) | 51 (68.9) | 30 (75.0) | 0.231 |
| CT | 32 (28.1) | 23 (31.1) | 9 (22.5) | |
| TT | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.9) | |
| C—allele | 194 (85.1) | 125 (84.4) | 69 (86.2) | 0.717 |
| T—allele | 34 (14.9) | 23 (15.6) | 11 (13.8) | |
| IGF1 rs6220 T/C | ||||
| TT | 44 (38.6) | 30 (40.5) | 14 (35.0) | 0.708 |
| TC | 51 (44.7) | 31 (41.9) | 20 (50.0) | |
| CC | 19 (16.7) | 13 (17.6) | 6 (15.0) | |
| T—allele | 139 (60.9) | 91 (61.5) | 48 (60.0) | 0.827 |
| C—allele | 89 (39.1) | 57 (38.5) | 32 (40.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eilat-Adar, S.; Kassem, E.; Sindiani, M.; Ben-Zaken, S. IGF1 Genetic Polymorphism and the Association between Vitamin D Status and BMI Percentiles in Children. Children 2023, 10, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101610
Eilat-Adar S, Kassem E, Sindiani M, Ben-Zaken S. IGF1 Genetic Polymorphism and the Association between Vitamin D Status and BMI Percentiles in Children. Children. 2023; 10(10):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101610
Chicago/Turabian StyleEilat-Adar, Sigal, Eias Kassem, Mahmood Sindiani, and Sigal Ben-Zaken. 2023. "IGF1 Genetic Polymorphism and the Association between Vitamin D Status and BMI Percentiles in Children" Children 10, no. 10: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101610
APA StyleEilat-Adar, S., Kassem, E., Sindiani, M., & Ben-Zaken, S. (2023). IGF1 Genetic Polymorphism and the Association between Vitamin D Status and BMI Percentiles in Children. Children, 10(10), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101610





