The Effect of Growth and Body Surface Area on Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: A Cohort Study in Preadolescent Female Swimmers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection Anthropometric and Morphological Characteristics
2.3. Biological Maturation
- Stage 1: No glandular breast tissue palpable;
- Stage 2: Breast bud palpable under the areola;
- Stage 3: Breast tissue palpable outside areola;
- Stage 4: Areola elevated above the contour of the breast and;
- Stage 5: Areolar mound recedes into single breast contour with areolar hyperpigmentation, papillae development, and nipple protrusion.
2.4. Pulmonary Function Test
2.5. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
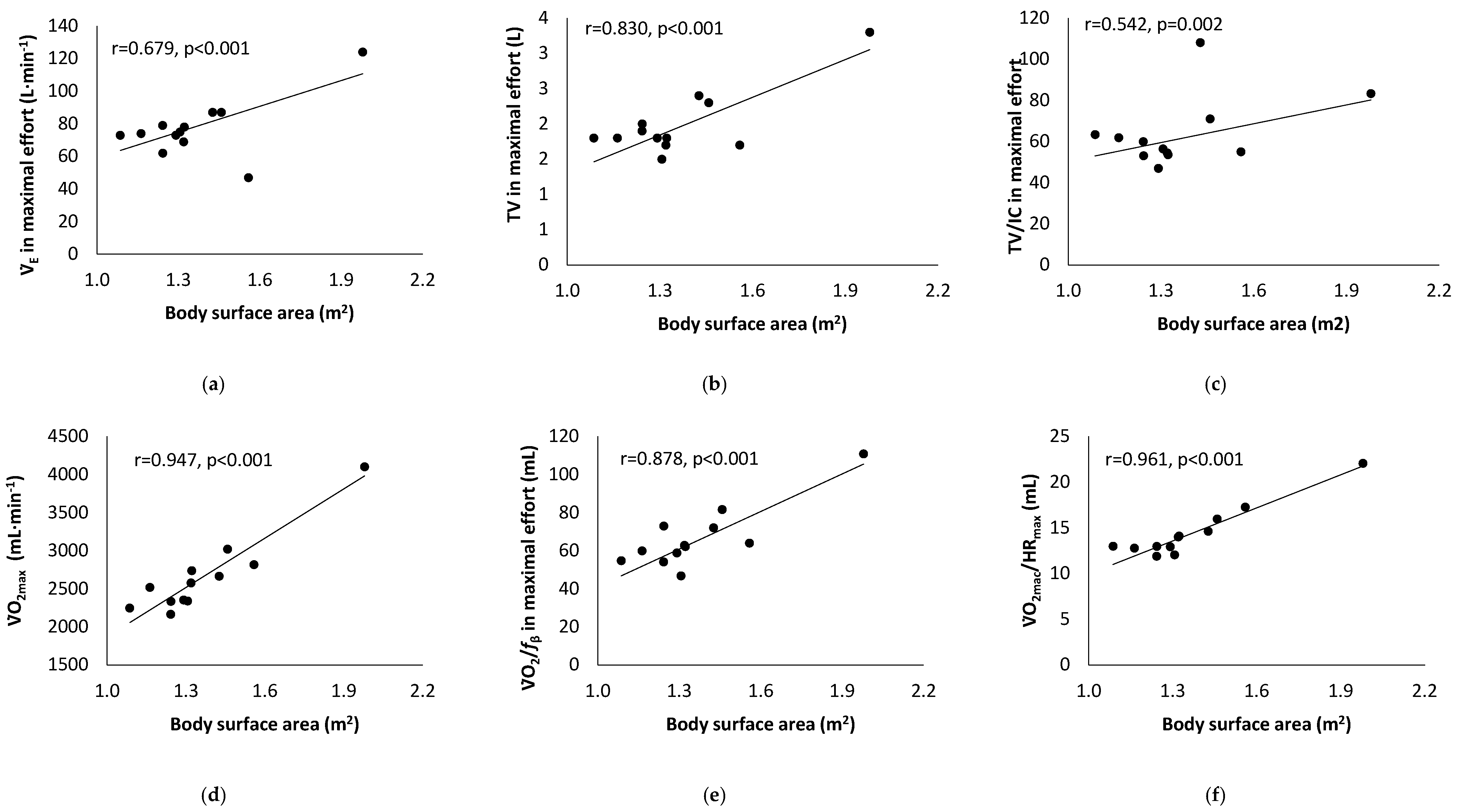
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Strengths
4.2. Recommendations for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Thoracic Society; American College of Chest Physicians. ATS/ACCP statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 211–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleisouras, V. Exercise Physiology, 11th ed.; Broken Hill Publishers LTD: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2011; pp. 225–226. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, J.E.; Barbosa, T.M.; Forte, P.; Silva, A.J.; Marinho, D.A. Young Swimmers’ Anthropometrics, Biomechanics, Energetics, and Efficiency as Underlying Performance Factors: A Systematic Narrative Review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 691919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, R.M.; Bouchard, C.; Bar-Or, O. Growth, Maturation and Physical Activity, 2nd ed.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lobato, C.H.; de Lima Rocha, M.; de Almeida-Neto, P.F.; de Araujo Tinoco Cabral, B.G. Influence of advancing biological maturation in months on muscle power and sport performance in young swimming athletes. Sport Sci. Health 2023, 19, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, J.E.; Silva, A.J.; Marinho, D.A.; Seifert, L.; Barbosa, T.M. Cluster stability as a new method to assess changes in performance and its determinant factors over a season in young swimmers. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, T.M.; Morais, J.E.; Costa, M.J.; Goncalves, J.; Marinho, D.A.; Silva, A.J. Young swimmers’ classification based on kinematics, hydrodynamics, and anthropometrics. J. Appl. Biomech. 2014, 30, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geithner, C.A.; Thomis, M.A.; Eynde, B.V.; Maes, H.H.; Loos, R.J.; Peeters, M.; Claessens, A.L.; Vlietinck, R.; Malina, R.M.; Beunen, G.P. Growth in peak aerobic power during adolescence. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2004, 36, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, V.T.; Astara, K.; Daniil, Z.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Kalabakas, K.; Karagiannis, D.; Basdekis, G. The Reciprocal Association between Fitness Indicators and Sleep Quality in the Context of Recent Sport Injury. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, V.; Tsarouhas, K.; Karetsi, E.; Michos, P.; Daniil, Z.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Adolescent Finswimmers: Early Myocardial Adaptations in Different Swimming Styles. Sports 2018, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiou, O.S.; Peletidou, S.; Vavougios, G.; Karetsi, E.; Stavrou, V.; Zakynthinos, G.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Daniil, Z. Exhaled nitric oxide as a marker of chlorine exposure in young asthmatic swimmers. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 23, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, R.C.R.; Silveira, R.; Kilpatrick, M.W.; Pires, F.O.; Asano, R.Y. The effect of menstrual cycle and exercise intensity on psychological and physiological responses in healthy eumenorrheic women. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 232, 113290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, V.; Vavougios, G.D.; Bardaka, F.; Karetsi, E.; Daniil, Z.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. The effect of exercise training on the quality of sleep in national-level adolescent finswimmers. Sports Med. Open 2019, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, V.T.; Astara, K.; Vavougios, D.G.; Fatouros, G.I.; Metsios, S.G.; Kalabakas, K.; Karagiannis, D.; Daniil, Z.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Βasdekis, G. Athletes with mild post-COVID-19 symptoms experience increased respiratory and metabolic demands: A cross-sectional study. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2023, 5, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Johnson, P.E.; Bolonchuk, W.W.; Lykken, G.I. Assessment of fat-free mass using bioelectrical impedance measurements of the human body. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 41, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosteller, R.D. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 1098. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rauter, S.; Simenko, J. Morphological Asymmetries Profile and the Difference between Low- and High-Performing Road Cyclists Using 3D Scanning. Biology 2021, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanuel, M.; Bokor, B.R. Tanner Stages. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. ATS/ERS Task Force. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, K.; Hansen, J.E.; Sue, D.Y.; Stringer, W.W.; Whipp, B. Principles of Exercise Testing and Interpretation: Including Pathophysiology and Clinical Applications, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004; p. 317. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.E.; Sue, D.Y.; Wasserman, K. Predicted values for clinical exercise testing. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1984, 129, S49–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, G.Z. Body Surface Area Calculator. Available online: https://www.gigacalculator.com/calculators/bsa-calculator.php (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Papadimitriou, A.; Fytanidis, G.; Douros, K.; Bakoula, C.; Nicolaidou, P.; Fretzayas, A. Age at menarche in contemporary Greek girls: Evidence for levelling-off of the secular trend. Acta Paediatr. 2008, 97, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter-Jones, A.D.; Helms, P.; Baines-Preece, J.; Preece, M. Menarche in intensively trained gymnasts, swimmers and tennis players. Ann. Hum. Biol. 1994, 21, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Kujala, U.M.; Tammelin, T.H.; Hirvensalo, M.; Kovanen, V.; Valtonen, M.; Waller, B.; Aukee, P.; Sipilä, S.; Laakkonen, E.K. Adolescent Sport Participation and Age at Menarche in Relation to Midlife Body Composition, Bone Mineral Density, Fitness, and Physical Activity. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, D.P.; Stäcker, I.; Romann, M.; Stöggl, T. Competition age: Does it matter for swimmers? BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Calvo, J.; de la Rubia, A.; Mon-López, D.; Hontoria-Galán, M.; Marquina, M.; Veiga, S. Prevalence and Impact of the Relative Age Effect on Competition Performance in Swimming: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, H.M.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Pfeiffer, K.; Carlson, J.J. Weight status, physical activity, and vascular health in 9- to 12-year-old children. J. Phys. Act. Health 2013, 10, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, H.C.G.; Verschuur, R.; de May, L. Longitudinal changes in aerobic fitness in youth ages 12 to 23. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 1989, 1, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, T.; Miller, K.; Vanderburgh, P.; Goff, D.; Martel, L.; Ferrone, L. Cardiovascular fitness in premenarcheal girls and young women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2000, 21, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bénéfice, E.; Mercier, J.; Guérin, M.J.; Préfaut, C. Differences in aerobic and anthropometric characteristics between peripubertal swimmers and non-swimmers. Int. J. Sports Med. 1990, 11, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodrigues, A.N.; Perez, A.J.; Carletti, L.; Bissoli, N.S.; Abreu, G.R. Maximum oxygen uptake in adolescents as measured by cardiopulmonary exercise testing: A classification proposal. J. Pediatr. 2006, 82, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraff, H.W.; Riiser, A.; Lihagen, M.; Skei, M.; Leirstein, S.; Hallén, J. Longitudinal changes in maximal oxygen uptake in adolescent girls and boys with different training backgrounds. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.E.; Denault, D.; Varacallo, M. Physiology, Oxygen Transport. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Uzunay, H.; Selvi, F.; Bedel, C.; Karakoyun, O.F. Comparison of ETCO2 Value and Blood Gas PCO2 Value of Patients Receiving Non-invasive Mechanical Ventilation Treatment in Emergency Department. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2021, 3, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, V.; Guillaume, M.; Berthelot, G.; Helou, N.E.; Schaal, K.; Quinquis, L.; Nassif, H.; Tafflet, M.; Escolano, S.; Hermine, O.; et al. Women and Men in Sport Performance: The Gender Gap has not Evolved since 1983. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2010, 9, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Goodwin, J. Effect of aging on respiratory system physiology and immunology. Clin. Interv. Aging 2006, 1, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barstow, T.J.; Jones, A.M.; Nguyen, P.H.; Casaburi, R. Influence of muscle fiber type and pedal frequency on oxygen uptake kinetics of heavy exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Harkel, A.D.; Takken, T.; Van Osch-Gevers, M.; Helbing, W.A. Normal values for cardiopulmonary exercise testing in children. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2011, 18, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrou, V.; Voutselas, V.; Karetsi, E.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Acute responses of breathing techniques in maximal inspiratory pressure. Sport Sci. Health 2018, 14, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, V.T.; Vavougios, G.D.; Karetsi, E.; Daniil, Z.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Pulmonary Function Test: Relationship between Adolescent Swimmers and Finswimmers. Cureus 2023, 15, e42711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, O.; Bain, A.R.; Deren, T.M.; Sacheli, M.; Cramer, M.N. Large differences in peak oxygen uptake do not independently alter changes in core temperature and sweating during exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R832–R841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, V.; Toubekis, A.G.; Karetsi, E. Changes in respiratory parameters and fin-swimming performance following a 16-week training period with intermittent breath holding. J. Hum. Kinet. 2015, 49, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, J.L.; Mitchell, G.S.; Nattie, E.E. Breathing: Rhythmicity, Plasticity, Chemosensitivity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 26, 239–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Merghani, A.; Mont, L. Exercise and the heart: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, J.; Agusti, A.G.; Alonso, A.; Poole, D.C.; Viegas, C.; Barbera, J.A.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R.; Ferrer, A.; Wagner, P.D. Effects of training on muscle O2 transport at VO2max. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazaheri, R.; Schmied, C.; Niederseer, D.; Guazzi, M. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test Parameters in Athletic Population: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, P.J.; Alfaro-Magallanes, V.M.; Rael, B.; Castro, E.A.; Romero-Parra, N.; Rojo-Tirado, M.A.; Peinado, A.B.; IronFEMME Study Group. Effect of Menstrual Cycle Phase on the Recovery Process of High-Intensity Interval Exercise-A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaidis, S.P.; Toubekis, A.G.; Mpousmoukilia, S.; Douda, H.T.; Antoniou, P.D.; Tokmakidis, S.P. Alterations in maximal inspiratory mouth pressure during a 400-m maximum effort front-crawl swimming trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2009, 49, 194–200. [Google Scholar]

| Mean ± Sd | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | years | 13.4 ± 1.0 |
| Body mass index | kg/m2 | 21.0 ± 2.5 |
| Body surface area | m2 | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
| Lean body mass | kg | 49.4 ± 4.6 |
| Total body water | % | 51.9 ± 3.0 |
| Swimming style | FR | 100 m (n = 8), 200 m (n = 5) |
| BK | 100 m (n = 6), 200 m (n = 2) | |
| BR | 100 m (n = 4), 200 m (n = 2) | |
| BF | 200 m (n = 1), | |
| IM | 200 m (n = 2) | |
| Tanner scale | score | 2.8 ± 0.7 |
| PSQI | score | 1.3 ± 2.1 |
| FEV1 | L (% of pred) | 3.8 ± 0.8 (125.8 ± 11.9) |
| FVC | L (% of pred) | 4.6 ± 0.7 (122.7 ± 10.6) |
| PEF | L (% of pred) | 6.7 ± 1.2 (108.1 ± 4.1) |
| ERV | L (% of pred) | 1.9 ± 0.8 (148.1 ± 54.0) |
| IC | L (% of pred) | 3.2 ± 0.5 (123.5 ± 17.8) |
| Resting | Maximal Effort | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V̇O2 | mL·min−1 | 244.5 ± 69.9 | 2663.8 ± 542.4 |
| mL·kg−1·min−1 | 4.2 ± 1.3 | 45.1 ± 3.5 | |
| % of pred | 126.2 ± 12.1 | ||
| V̇CO2 | mL·min−1 | 189.7 ± 39.9 | 2834.2 ± 735.0 |
| V̇E/MVV | % | 6.4 ± 1.8 | 59.3 ± 10.0 |
| IC/TV | % | 15.9 ± 5.9 | 61.5 ± 13.2 |
| V̇E/V̇O2 | 29.9 ± 6.5 | 34.7 ± 7.4 | |
| V̇E/V̇CO2 | 23.1 ± 2.3 | 36.5 ± 6.5 | |
| fβ | 1·min−1 | 17.9 ± 3.6 | 41.5 ± 4.3 |
| PETO2 | mmHg | 111.7 ± 7.5 | 111.8 ± 3.3 |
| PETCO2 | mmHg | 30.0 ± 4.0 | 38.3 ± 3.3 |
| Heart rate | bpm (% of pred) | 84.3 ± 7.4 (41.0 ± 3.7) | 185.4 ± 9.1 (90.2 ± 4.4) |
| Load | watts·kg−1 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | |
| CPET duration (3rd stage) | min | 12.4 ± 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stavrou, V.T.; Karetsi, E.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. The Effect of Growth and Body Surface Area on Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: A Cohort Study in Preadolescent Female Swimmers. Children 2023, 10, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101608
Stavrou VT, Karetsi E, Gourgoulianis KI. The Effect of Growth and Body Surface Area on Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: A Cohort Study in Preadolescent Female Swimmers. Children. 2023; 10(10):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101608
Chicago/Turabian StyleStavrou, Vasileios T., Eleni Karetsi, and Konstantinos I. Gourgoulianis. 2023. "The Effect of Growth and Body Surface Area on Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: A Cohort Study in Preadolescent Female Swimmers" Children 10, no. 10: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101608
APA StyleStavrou, V. T., Karetsi, E., & Gourgoulianis, K. I. (2023). The Effect of Growth and Body Surface Area on Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: A Cohort Study in Preadolescent Female Swimmers. Children, 10(10), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10101608









