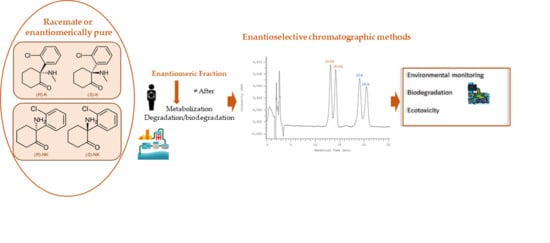
Enantioselective Monitoring of Biodegradation of Ketamine and Its Metabolite Norketamine by Liquid Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Standards
2.2. Enantioseparation
2.3. Enantioseparation Optimization and Method Validation for Quantification of Ketamine and Its Metabolite Norketamine
2.4. Biodegradation Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Enantioseparation Optimization for Ketamine and Its Metabolite Norketamine
3.2. Validation of the Method for Quantification of Ketamine and Norketamine
3.3. Enantioselective Biodegradation Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD. Pharmaceutical Residues in Freshwater: Hazards and Policy Responses; OECD Studies on Water; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, H.; Poiger, T.; Müller, M. Occurrence and environmental behavior of the chiral pharmaceutical drug ibuprofen in surface waters and in wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhnerfuss, H.; Shah, M.R. Enantioselective chromatography-a powerful tool for the discrimination of biotic and abiotic transformation processes of chiral environmental pollutants. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLeod, S.L.; Wong, C.S. Loadings, trends, comparisons, and fate of achiral and chiral pharmaceuticals in wastewaters from urban tertiary and rural aerated lagoon treatments. Water Res. 2010, 44, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, A.S.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Castro, P.M.L.; Tiritan, M.E. Chiral analysis of pesticides and drugs of environmental concern: Biodegradation and enantiomeric fraction. Symmetry 2017, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Baker, D.R. Enantiomeric profiling of chiral drugs in wastewater and receiving waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. Illicit drugs and pharmaceuticals in the environment-forensic applications of environmental data, Part 2: Pharmaceuticals as chemical markers of faecal water contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, I.S.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Afonso, C.M.; Tiritan, M.E.; Castro, P.M. Enantioselective biodegradation of fluoxetine by the bacterial strain Labrys portucalensis F11. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Afonso, C.M.; Castro, P.M.L.; Tiritan, M.E. Enantioselective HPLC analysis and biodegradation of atenolol, metoprolol and fluoxetine. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Afonso, C.M.; Castro, P.M.; Tiritan, M.E. Enantioselective biodegradation of pharmaceuticals, alprenolol and propranolol, by an activated sludge inoculum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 87, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.S.; Castro, P.M.L.; Tiritan, M.E. Integrated liquid chromatography method in enantioselective studies: Biodegradation of ofloxacin by an activated sludge consortium. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1029–1030, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annetta, M.; Iemma, D.; Garisto, C.; Tafani, C.; Proietti, R. Ketamine: New indications for an old drug. Curr. Drug Targets 2005, 6, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.; Simmonds, M. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 84, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, K.; Lambert, D. Ketamine: Its mechanism(s) of action and unusual clinical uses. Br. J. Anaesth. 1996, 77, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clements, J.; Nimmo, W.; Grant, I. Bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and analgesic activity of ketamine in humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Wu, B.; Zhou, W. Ketamine abuse potential and use disorder. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 126 Pt 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Chang, L.; Hashimoto, K. A historical review of antidepressant effects of ketamine and its enantiomers. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 190, 172870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Davisson, J. Stereochemical studies of demethylated ketamine enantiomers. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.B.; Fedgchin, M.; Daly, E.; Xi, L.; Melman, C.; De Bruecker, G.; Tadic, A.; Sienaert, P.; Wiegand, F.; Manji, H.; et al. Intravenous esketamine in adult treatment-resistant depression: A double-blind, double-randomization, placebo-controlled study. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; Dong, C.; Fujita, A.; Fujita, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Expression of heat shock protein HSP-70 in the retrosplenial cortex of rat brain after administration of (R,S)-ketamine and (S)-ketamine, but not (R)-ketamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 172, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hashimoto, K. An update on ketamine and its two enantiomers as rapid-acting antidepressants. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, C.; Chang, L.; Sakamoto, A.; Suzuki, T.; Fujita, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, S.; Pu, Y.; Tan, Y.; et al. Essential role of microglial transforming growth factor-β1 in antidepressant actions of (R)-ketamine and the novel antidepressant TGF-β1. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaddel, R.; Venkata, S.L.; Tanga, M.J.; Bupp, J.E.; Green, C.E.; Iyer, L.; Furimsky, A.; Goldberg, M.E.; Torjman, M.C.; Wainer, I.W. A parallel chiral-achiral liquid chromatographic method for the determination of the stereoisomers of ketamine and ketamine metabolites in the plasma and urine of patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Talanta 2010, 82, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Styszko, K.; Proctor, K.; Castrignano, E.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Occurrence of pharmaceutical residues, personal care products, lifestyle chemicals, illicit drugs and metabolites in wastewater and receiving surface waters of Krakow agglomeration in South Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankes, R.F.; Silver, C.D. Quantitative study of controlled substance bedside wasting, disposal and evaluation of potential ecologic effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Lin, A.Y. Ecotoxicological effect of ketamine: Evidence of acute, chronic and photolysis toxicity to Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Du, P.; Xu, Z.; Gao, T.; Li, X. Occurrence of illicit drugs in surface waters in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.C.; Hsiao, T.C.; Lin, A.Y. Urban wastewater treatment plants as a potential source of ketamine and methamphetamine emissions to air. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Guo, C.; Teng, Y.; Xu, J. Development and application of the analytical method for illicit drugs and metabolites in fish tissues. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, X. Biodegradation of methamphetamine and ketamine in aquatic ecosystem and associated shift in bacterial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, X. Impacts of methamphetamine and ketamine on C.elegans’s physiological functions at environmentally relevant concentrations and eco-risk assessment in surface waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 363, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Dsikowitzky, L.; Yang, F.; Schwarzbauer, J. Emerging contaminants in municipal wastewaters and their relevance for the surface water contamination in the tropical coastal city Haikou, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 235, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Lee, C.L.; Fang, M.D.; Tu, B.W.; Liang, Y.J. Impacts of emerging contaminants on surrounding aquatic environment from a youth festival. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Santos, C.; Goncalves, V.; Ramos, A.; Afonso, C.; Tiritan, M.E. Chiral Drug Analysis in Forensic Chemistry: An Overview. Molecules 2018, 23, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Maia, A.S.; Ribeiro, C.; Tiritan, M.E. Analysis of chiral drugs in environmental matrices: Current knowledge and trends in environmental, biodegradation and forensic fields. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langa, I.; Goncalves, R.; Tiritan, M.E.; Ribeiro, C. Wastewater analysis of psychoactive drugs: Non-enantioselective vs enantioselective methods for estimation of consumption. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 325, 110873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, J.C.; Tiritan, M.E.; Cass, Q.B. Challenges and innovations in chiral drugs in an environmental and bioanalysis perspective. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICH. ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline-Text on Validation of Analytical Procedures Methodology, Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization Committee; ICH Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Maia, A.S.; Moreira, I.S.; Afonso, C.M.; Castro, P.M.; Tiritan, M.E. Enantioselective quantification of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine by HPLC in wastewater effluents. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pereira, A.; Ribeiro, C.; Teles, F.; Gonçalves, R.; Goncalves, V.M.F.; Pereira, J.A.; Carrola, J.S.; Pires, C.; Tiritan, M.E. Ketamine and norketamine: Enantioresolution and enantioselective aquatic ecotoxicity studies. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Gautam, L.; Hall, S.W. The detection of drugs of abuse and pharmaceuticals in drinking water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Lin, C.F. Impact of wastewaters and hospital effluents on the occurrence of controlled substances in surface waters. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Spatial and temporal occurrence of pharmaceuticals and illicit drugs in the aqueous environment and during wastewater treatment: New developments. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454–455, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nuijs, A.L.; Gheorghe, A.; Jorens, P.G.; Maudens, K.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Optimization, validation, and the application of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of new drugs of abuse in wastewater. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.Y.; Bruno, R.; Leung, H.W.; Thai, P.K.; Ort, C.; Carter, S.; Thompson, K.; Lam, P.K.; Mueller, J.F. Estimating daily and diurnal variations of illicit drug use in Hong Kong: A pilot study of using wastewater analysis in an Asian metropolitan city. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 233, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.Y.; Lee, W.N.; Wang, X.H. Ketamine and the metabolite norketamine: Persistence and phototransformation toxicity in hospital wastewater and surface water. Water Res. 2014, 53, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodayan, A.; Afana, S.; Segura, P.A.; Sultana, T.; Metcalfe, C.D.; Yargeau, V. Linking drugs of abuse in wastewater to contamination of surface and drinking water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Equipment | Mobile Phase | Composition (v/v) | Flow Rate (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC-DAD | 20 mM Ammonium Acetate with 0.1% DEA: ACN | 73/27 | 1.1 |
| 65/35 | 1.0 | ||
| 67/33 | |||
| 70/30 | |||
| 73/27 | |||
| 74/26 | |||
| 75/25 | |||
| 70/30 | 0.5 | ||
| 67/33 | |||
| 65/35 | |||
| 20 mM Ammonium Acetate with 0.1% DEA: EtOH | 50/50 | ||
| 60/40 | |||
| 70/30 | |||
| 20 mM Ammonium Acetate: ACN | 70/30 |
| Enantiomer | Linearity | Limits | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (µg/mL) | Linear Regression | Correlation Coefficient (r2) | LOD (µg/mL) | LOQ (µg/mL) | |
| (R)-NK | 1.25–12.5 | y = 5384.7x − 1847 | 0.9908 | 0.5 | 1.25 |
| (S)-NK | 1.25–12.5 | y = 6038.7x − 1608.4 | 0.9918 | 0.5 | 1.25 |
| (R)-K | 2.5–25 | y = 5127.9x + 493.42 | 0.9998 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| (S)-K | 2.5–25 | y = 5896.1x − 843.12 | 0.9994 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| Enantiomer | Concentration (µg/mL) | Validation Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | Recovery (%) | Intra-Day Precision (%RSD) | Inter-Day Precision (%RSD) | ||
| (R)-NK | 2 | 113.6 | 75.4 | 6.1 | 6.7 |
| 6 | 94.8 | 81.9 | 8.1 | 8.4 | |
| 8.5 | 106.9 | 67.9 | 4.5 | 4.8 | |
| (S)-NK | 2 | 105.4 | 69.5 | 6.3 | 8.8 |
| 6 | 101.2 | 76.2 | 8.7 | 8.8 | |
| 8.5 | 105.9 | 64.0 | 5.9 | 6.1 | |
| (R)-K | 4 | 86.6 | 61.0 | 9.4 | 10.5 |
| 12.5 | 104.1 | 86.9 | 2.3 | 3.4 | |
| 17.5 | 102.3 | 71.1 | 1.8 | 2.7 | |
| (S)-K | 4 | 85.9 | 50.1 | 10.4 | 11.3 |
| 12.5 | 104.1 | 79.3 | 2.8 | 2.9 | |
| 17.5 | 103.6 | 69.4 | 3.6 | 3.8 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Pereira, A.; Maia, A.; Gonçalves, V.; Ribeiro, C.; Tiritan, M.E. Enantioselective Monitoring of Biodegradation of Ketamine and Its Metabolite Norketamine by Liquid Chromatography. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9090242
Pérez-Pereira A, Maia A, Gonçalves V, Ribeiro C, Tiritan ME. Enantioselective Monitoring of Biodegradation of Ketamine and Its Metabolite Norketamine by Liquid Chromatography. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(9):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9090242
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Pereira, Ariana, Alexandra Maia, Virgínia Gonçalves, Cláudia Ribeiro, and Maria Elizabeth Tiritan. 2021. "Enantioselective Monitoring of Biodegradation of Ketamine and Its Metabolite Norketamine by Liquid Chromatography" Chemosensors 9, no. 9: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9090242