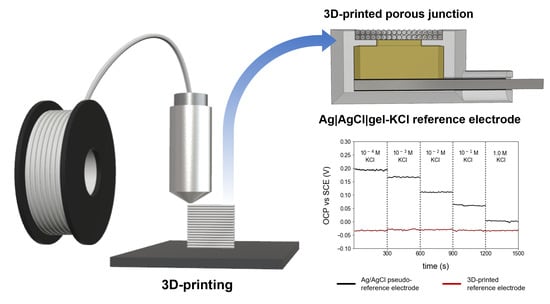
Fabrication of a 3D-Printed Porous Junction for Ag|AgCl|gel-KCl Reference Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instrumentation
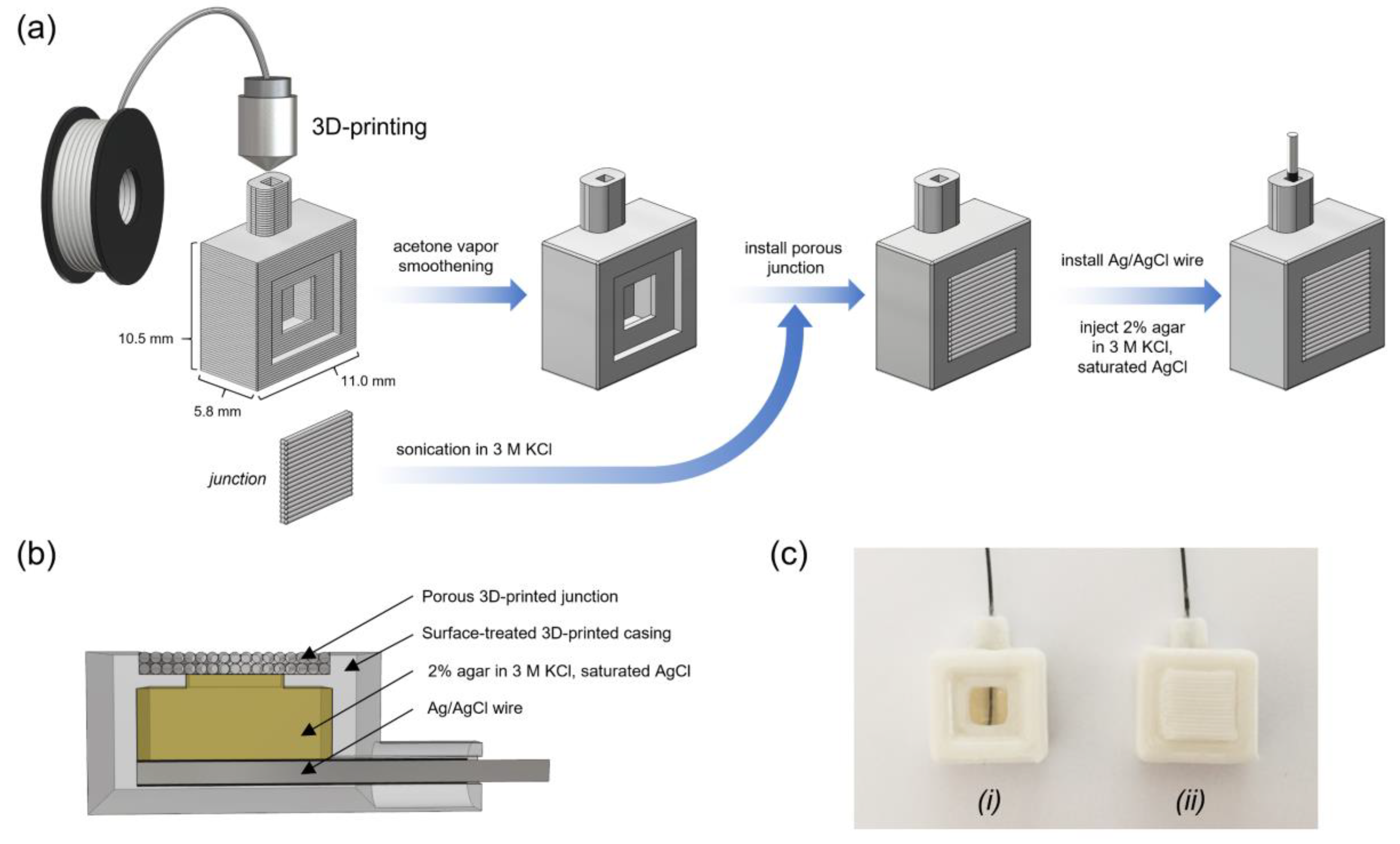
2.2. Fabrication of 3D-RE Components
2.3. Water Absorption Study
2.4. 3D-RE Assembly
2.5. Characterization of 3D-RE
2.6. Application of 3D-RE
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of 3D-RE
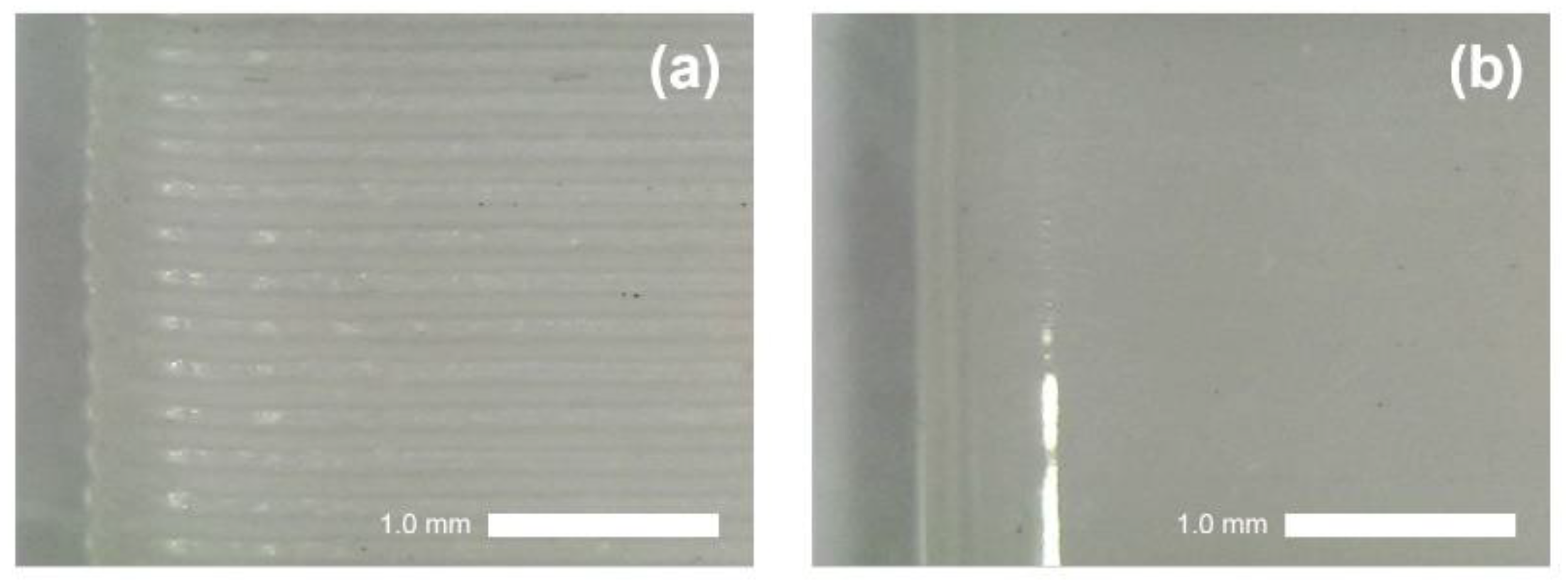
3.1.1. Fabrication of 3D-RE Casing
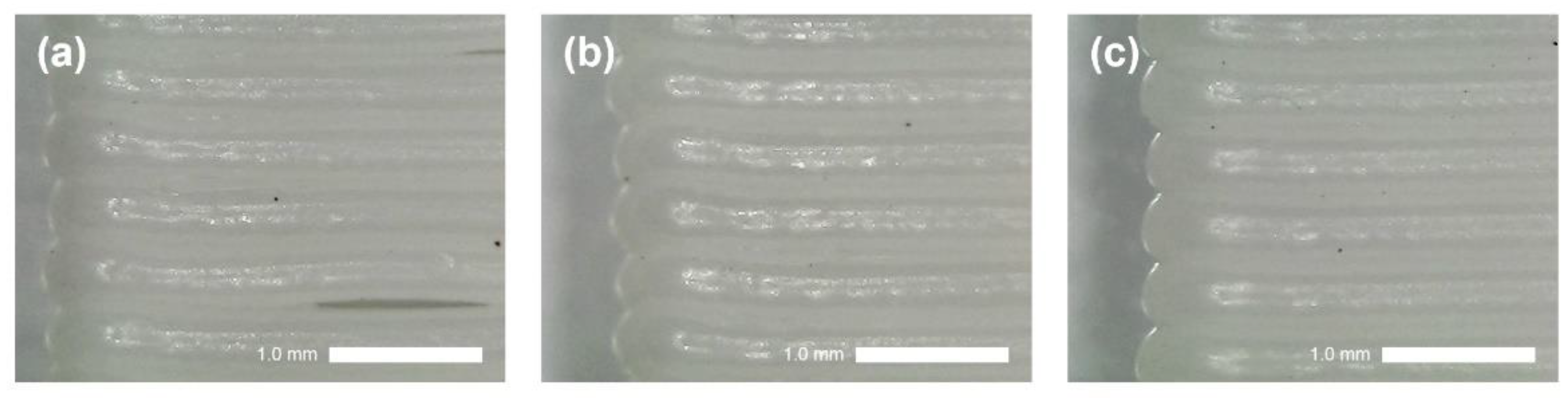
3.1.2. Fabrication of 3D-Printed Junction
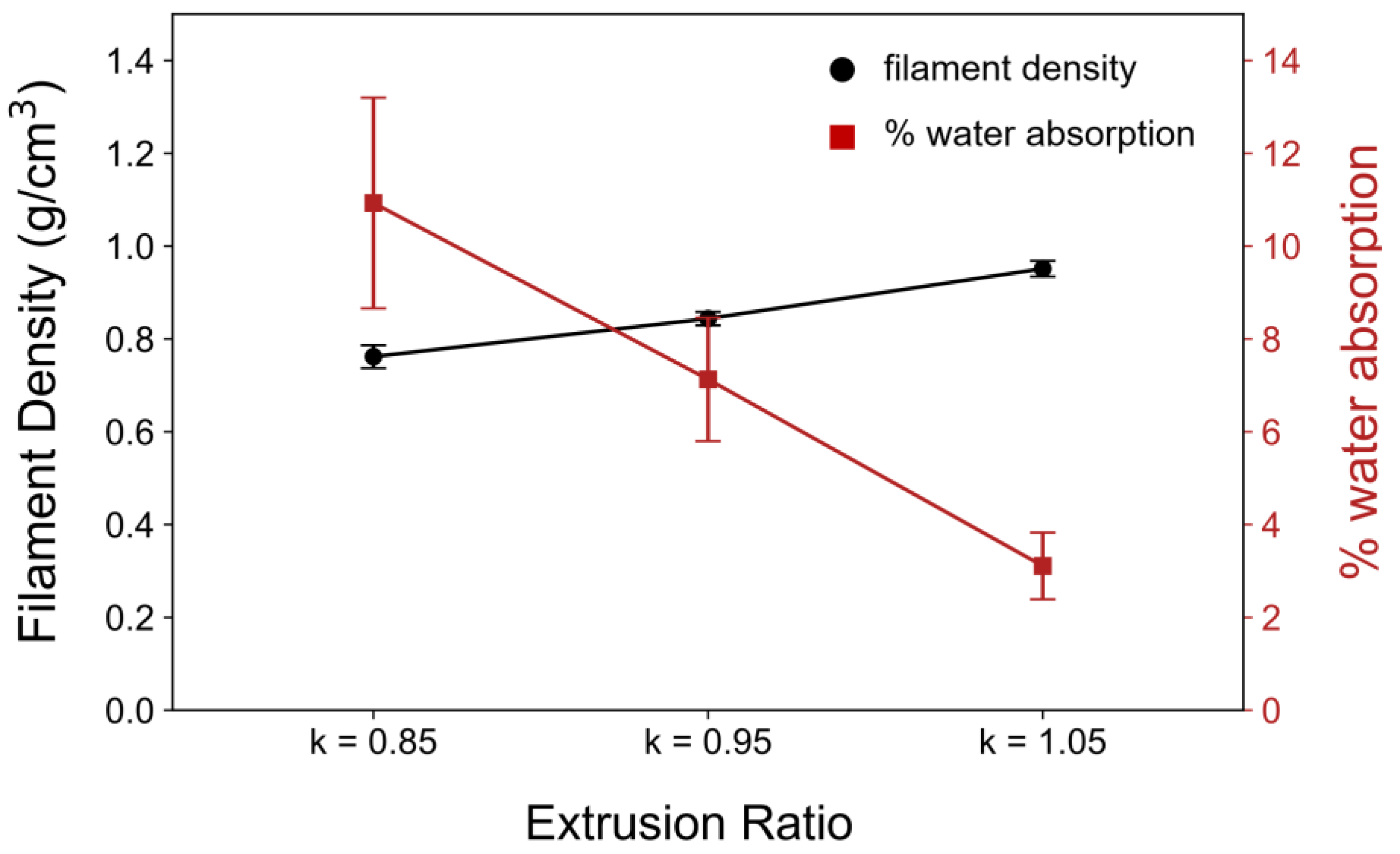
3.2. Optimization of 3D-RE Junction Porosity
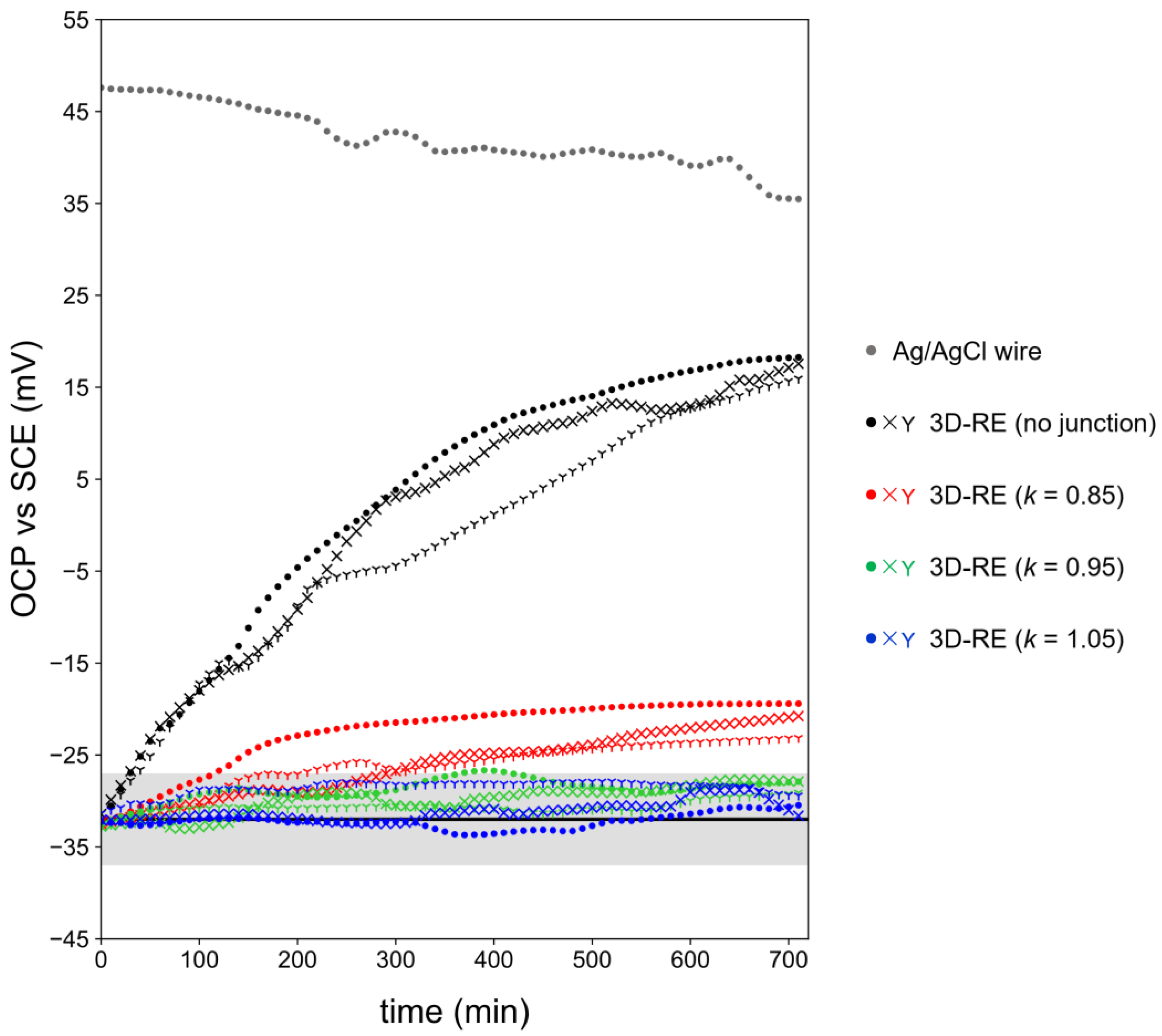
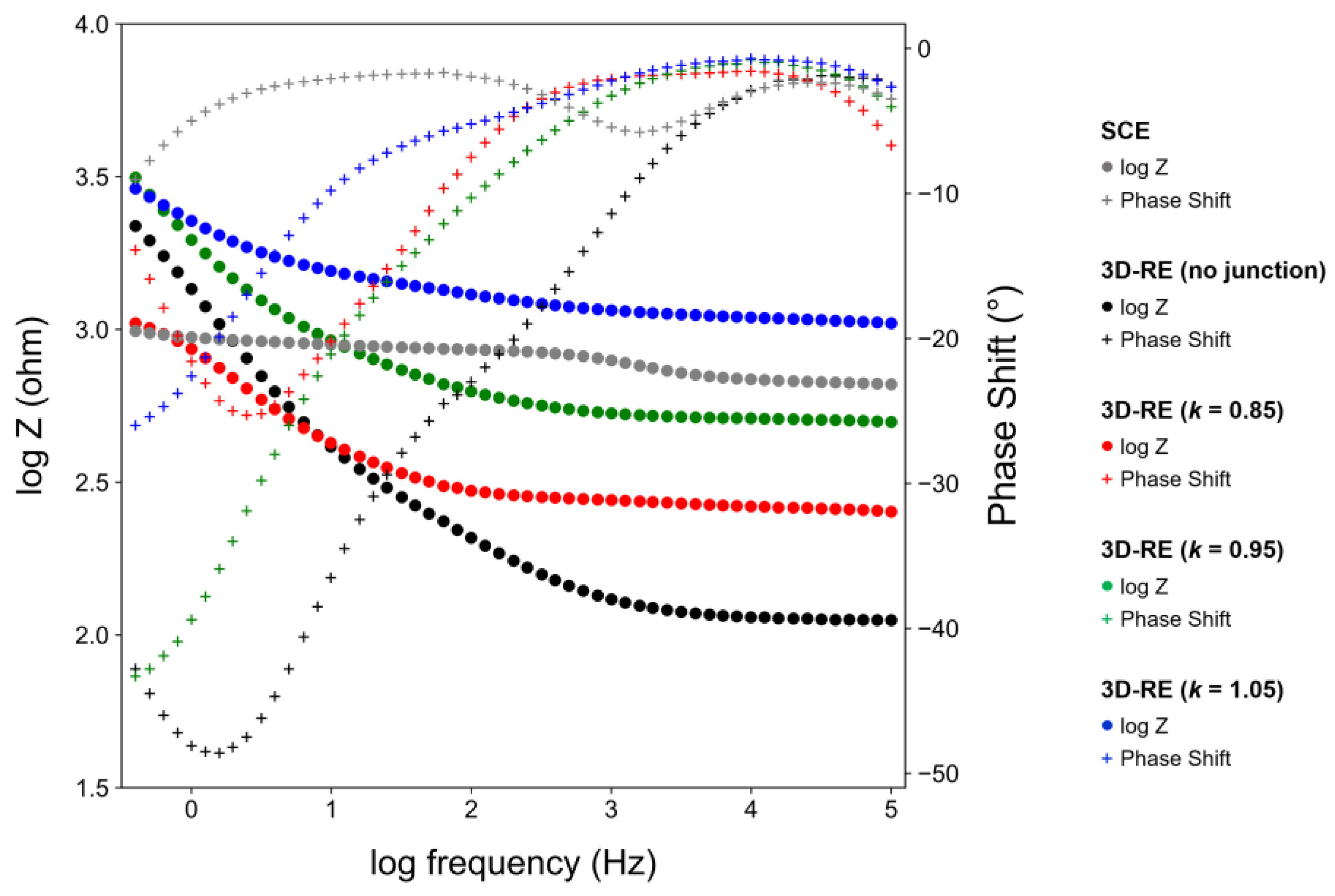
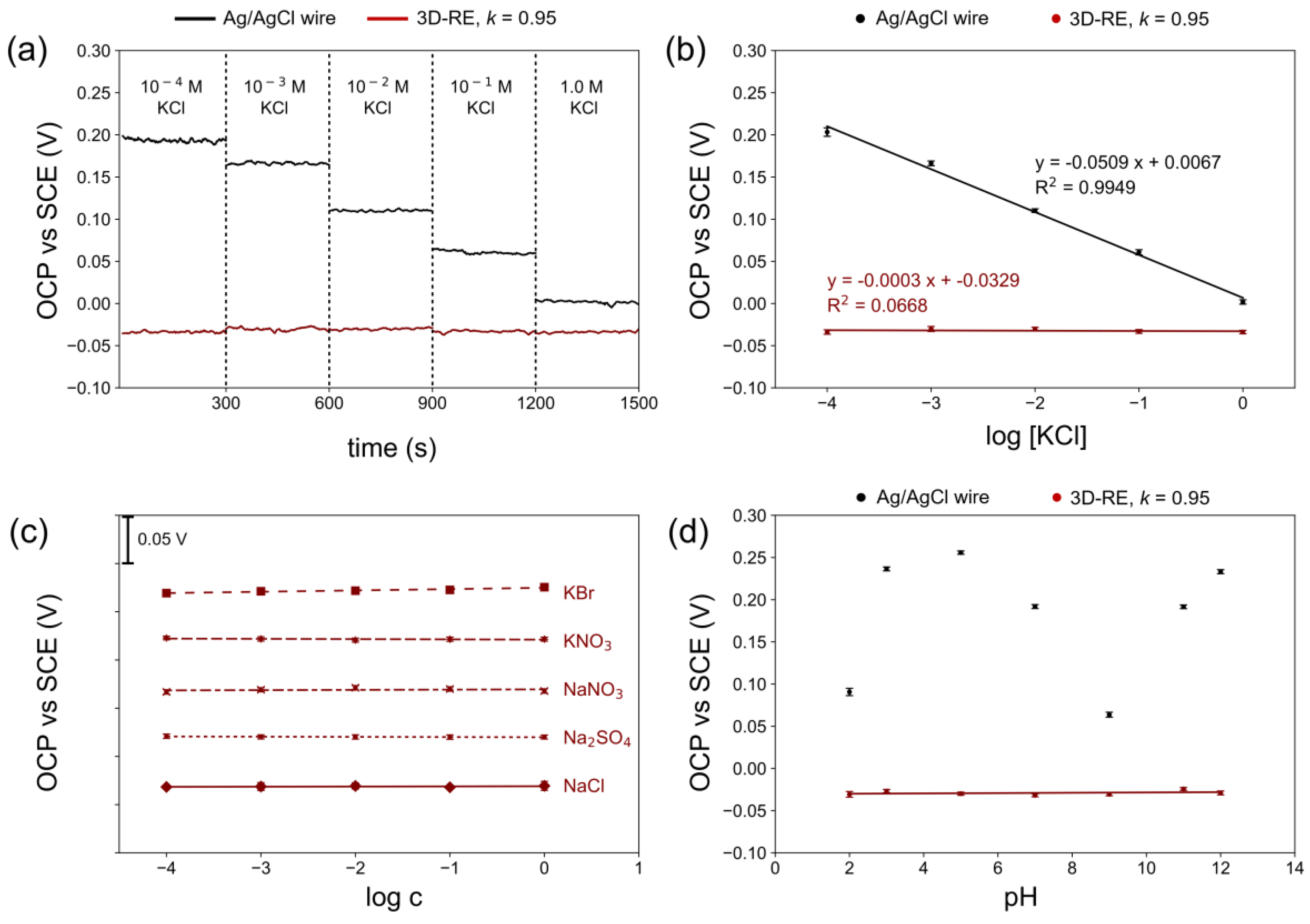
3.3. Characterization of Optimized 3D-RE
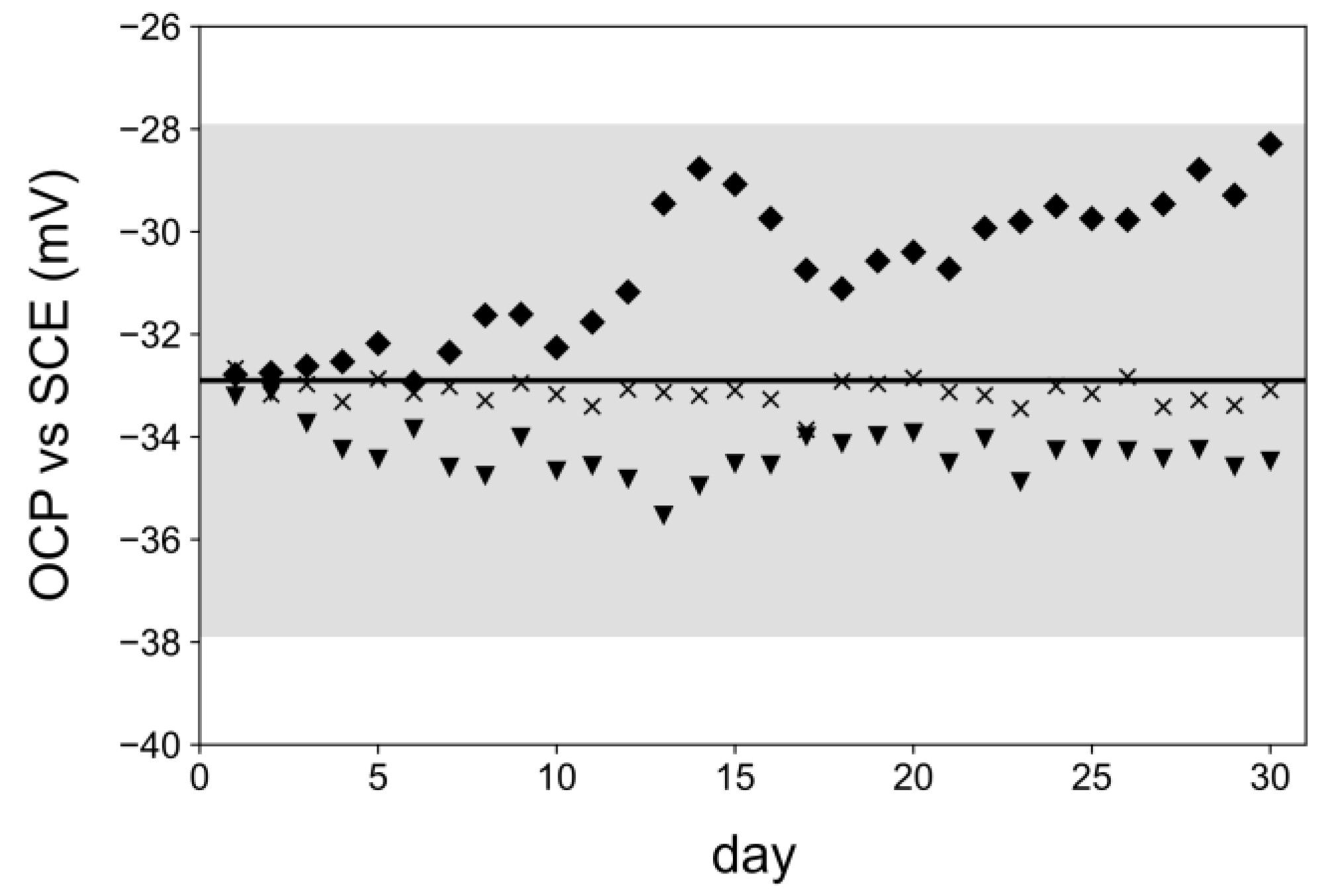
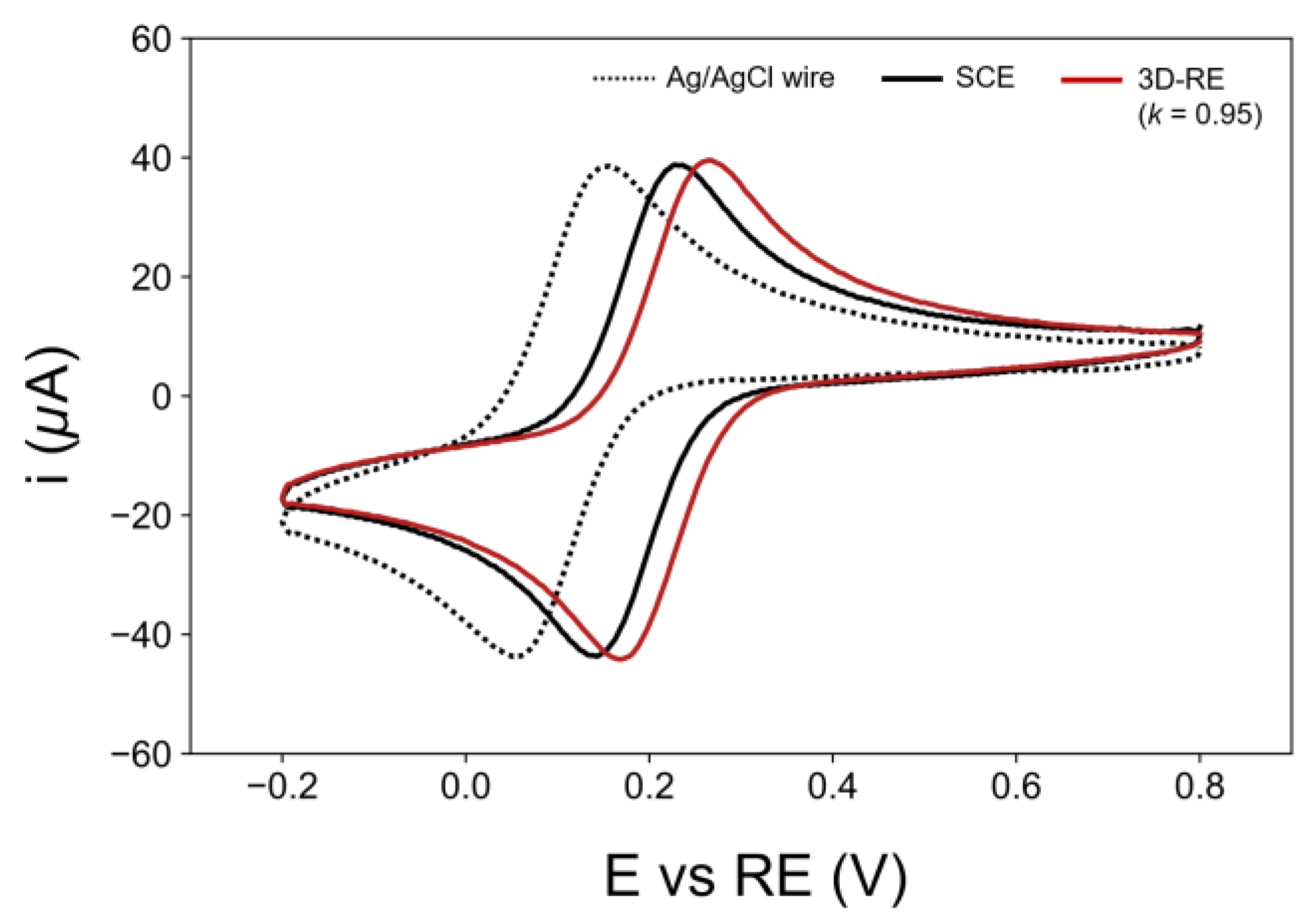
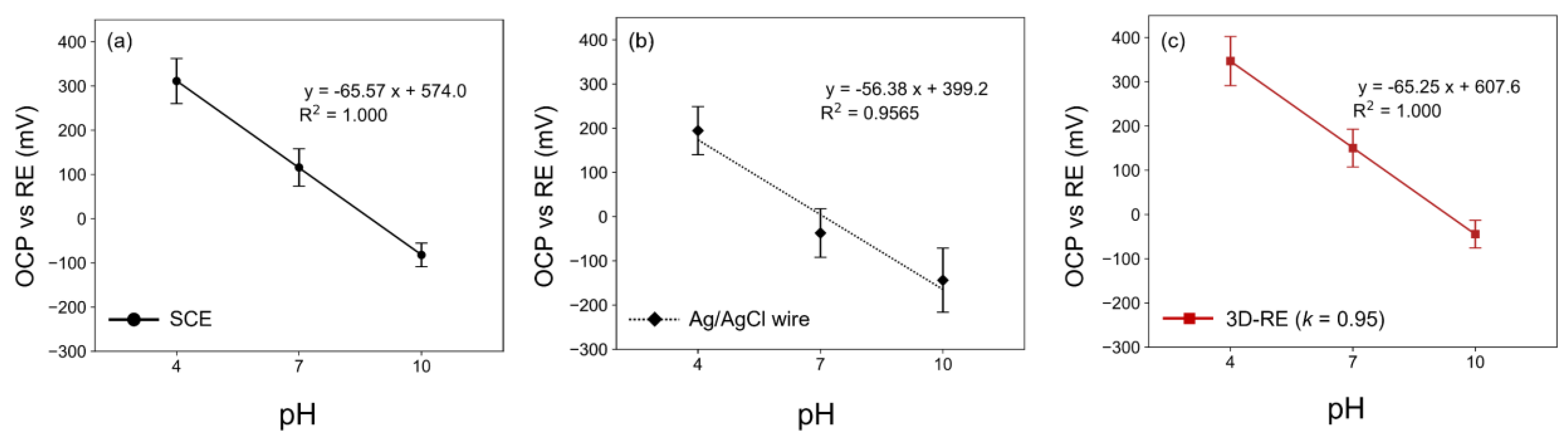
3.4. Application of Optimized 3D-RE
3.5. Outlook
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T.; Merkoçi, A.; Manz, A.; Urban, G.A.; Güder, F. Disposable Sensors in Diagnostics, Food, and Environmental Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Luo, F.; Wang, P.; Lin, Z. Miniaturized electrochemical sensors and their point-of-care applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, A.; Pumera, M. 3D-printing technologies for electrochemical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2740–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, R.M.; Mendonça, D.M.H.; Silva, W.P.; Silva, M.N.T.; Nossol, E.; da Silva, R.A.B.; Richter, E.M.; Muñoz, R.A.A. 3D printing for electroanalysis: From multiuse electrochemical cells to sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1033, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, G.D. Toward single-step production of functional electrochemical devices using 3D printing: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 20, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 2, ISBN 9780123813749. [Google Scholar]
- Waleed Shinwari, M.; Zhitomirsky, D.; Deen, I.A.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Jamal Deen, M.; Landheer, D. Microfabricated reference electrodes and their biosensing applications. Sensors 2010, 10, 1679–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.J.; Stevenson, K.J. Reference electrodes. In Handbook of Electrochemistry; Zoski, C.G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 9780444519580. [Google Scholar]
- Sophocleous, M.; Atkinson, J.K. A review of screen-printed silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) reference electrodes potentially suitable for environmental potentiometric sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 267, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.T.S.G.; Miserere, S.; Kubota, L.T.; Merkoçi, A. Simple on-plastic/paper inkjet-printed solid-state Ag/AgCl pseudoreference electrode. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10531–10534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohaizad, N.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Novotný, F.; Webster, R.D.; Pumera, M. 3D-printed Ag/AgCl pseudo-reference electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 103, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzelt, G.; Lewenstam, A.; Scholz, F. Pseudo-reference Electrodes. In Handbook of Reference Electrodes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.-Y.; Huang, R.S. Fabrication and characterization of a new planar solid-state reference electrode for ISFET sensors. Thin Solid Films 2002, 406, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; Scott, D.C. An Integrated Sensor for Electrochemical Measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1986, BME-33, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Hirakawa, T.; Sasaki, S.; Karube, I. Micromachined liquid-junction Ag/AgCl reference electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1998, 46, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, F.; Galfione, M.; Carrara, S.; De Micheli, G. All-solid-state Reference Electrodes for analytical applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Workshop Advances Sensors Interfaces, IWASI, Otranto, Italy, 13–14 June 2019; pp. 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, U.; Gerlach, F.; Decker, M.; Oelßner, W.; Vonau, W. Solid-state reference electrodes for potentiometric sensors. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingenfelter, P.; Bartoszewicz, B.; Migdalski, J.; Sokalski, T.; Bućko, M.M.; Filipek, R.; Lewenstam, A. Reference electrodes with polymer-based membranes—Comprehensive performance characteristics. Membranes 2019, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinovart, T.; Crespo, G.A.; Rius, F.X.; Andrade, F.J. A reference electrode based on polyvinyl butyral (PVB) polymer for decentralized chemical measurements. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 821, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bananezhad, A.; Jović, M.; Villalobos, L.F.; Agrawal, K.V.; Ganjali, M.R.; Girault, H.H. Large-scale fabrication of flexible solid-state reference electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 847, 113241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.Y.; Chou, T.C. Fabrication of a planar-form screen-printed solid electrolyte modified Ag/AgCl reference electrode for application in a potentiometric biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4219–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Bian, C.; Tong, J.; Xia, S. Fabrication of a miniature multi-parameter sensor chip for water quality assessment. Sensors 2017, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Chu, C.-C.; Chiu, C.-T. Improved solid-state planar Ti/Pd/Ag/AgCl/KCl-gel microreference electrode by silicon cap sealing package. J. Micro/Nanolithography MEMS MOEMS 2009, 8, 033050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.M.; Kalinke, C.; Rocha, R.G.; dos Santos, P.L.; Rocha, D.P.; Oliveira, P.R.; Janegitz, B.C.; Bonacin, J.A.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A. Additive-manufactured (3D-printed) electrochemical sensors: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, G.D.; Ahmed, S.; Halloran, K.; Janusz, J.N.; Rodríguez, A.; Terrero Rodríguez, I.M. Single-step fabrication of electrochemical flow cells utilizing multi-material 3D printing. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 99, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katseli, V.; Economou, A.; Kokkinos, C. Single-step fabrication of an integrated 3D-printed device for electrochemical sensing applications. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 103, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katseli, V.; Thomaidis, N.; Economou, A.; Kokkinos, C. Miniature 3D-printed integrated electrochemical cell for trace voltammetric Hg(II) determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 308, 127715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katseli, V.; Economou, A.; Kokkinos, C. A novel all-3D-printed cell-on-a-chip device as a useful electroanalytical tool: Application to the simultaneous voltammetric determination of caffeine and paracetamol. Talanta 2020, 208, 120388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walgama, C.; Nguyen, M.P.; Boatner, L.M.; Richards, I.; Crooks, R.M. Hybrid paper and 3D-printed microfluidic device for electrochemical detection of Ag nanoparticle labels. Lab Chip 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- João, A.F.; Squissato, A.L.; Richter, E.M.; Muñoz, R.A.A. Additive-manufactured sensors for biofuel analysis: Copper determination in bioethanol using a 3D-printed carbon black/polylactic electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, D.P.; Squissato, A.L.; da Silva, S.M.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A. Improved electrochemical detection of metals in biological samples using 3D-printed electrode: Chemical/electrochemical treatment exposes carbon-black conductive sites. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 335, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, E.M.; Rocha, D.P.; Cardoso, R.M.; Keefe, E.M.; Foster, C.W.; Munoz, R.A.A.; Banks, C.E. Complete Additively Manufactured (3D-Printed) Electrochemical Sensing Platform. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12844–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewenstam, A.; Bartoszewicz, B.; Migdalski, J.; Kochan, A. Solid contact reference electrode with a PVC-based composite electroactive element fabricated by 3D printing. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 109, 106613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeev, E.G.; Galushko, A.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Improvement of quality of 3D printed objects by elimination of microscopic structural defects in fused deposition modeling. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, H.A.; Alkahari, M.R.; Ramli, F.R.; Hasan, R.; Maidin, S. Strength and porosity of additively manufactured PLA using a low cost 3D printing. In Proceedings of the Mechanical Engineering Research Day, Melaka, Malaysia, 31 March 2016; Volume 1, pp. 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- McCullough, E.J.; Yadavalli, V.K. Surface modification of fused deposition modeling ABS to enable rapid prototyping of biomedical microdevices. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Batish, A. On Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy of FDM Parts after Cold Vapor Treatment. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Batish, A. Chemical vapor treatment of ABS parts built by FDM: Analysis of surface finish and mechanical strength. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 2175–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.; Varanda, A.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Silva, A.; Vaz, M.F. Mechanical properties and water absorption of surface modified ABS 3D printed by fused deposition modelling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner Instruments: Chloriding Ag/AgCl Electrodes. Available online: https://www.warneronline.com/sites/default/files/2018-09/Chloriding%20Ag-AgCl%20electrodes%20%28090728%29.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2020).
- Bacalzo, N.P.; Go, L.P.; Querebillo, C.J.; Hildebrandt, P.; Limpoco, F.T.; Enriquez, E.P. Controlled Microwave-Hydrolyzed Starch as a Stabilizer for Green Formulation of Aqueous Gold Nanoparticle Ink for Flexible Printed Electronics. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zea, M.; Moya, A.; Fritsch, M.; Ramon, E.; Villa, R.; Gabriel, G. Enhanced Performance Stability of Iridium Oxide-Based pH Sensors Fabricated on Rough Inkjet-Printed Platinum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, S.A.M.; Ufer, S.; Buck, R.P.; Johnson, T.A.; Dunlap, L.A.; Cascio, W.E. Electrodeposited iridium oxide pH electrode for measurement of extracellular myocardial acidosis during acute ischemia. Anal. Chem. 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.M.; Tenje, M.; Heiskanen, A.R.; Masuda, N.; Castillo, J.; Bentien, A.; Émneus, J.; Jakobsen, M.H.; Boisen, A. Gold cleaning methods for electrochemical detection applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2009, 86, 1282–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhin, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Revealing interactions of layered polymeric materials at solid-liquid interface for building solvent compatibility charts for 3D printing applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.O.; Simon, G.P. Biodegradation of 3D-printed polylactic acid milliprojections under physiological conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassel, A.W.; Fushimi, K.; Seo, M. An agar-based silversilver chloride reference electrode for use in micro-electrochemistry. Electrochem. Commun. 1999, 1, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Fu, F.; You, F.; Dong, X.; Dai, M. Resistivity and its anisotropy characterization of 3D-printed acrylonitrile butadiene styrene copolymer (ABS)/carbon black (CB) composites. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamry Instruments Measuring the Impedance of Your Reference Electrode. Available online: https://www.gamry.com/application-notes/instrumentation/measuring-the-impedance-of-your-reference-electrode/ (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Metrohm Autolab B.V. Autolab Application Note EC02: Reference Electrodes and Their Usage. Available online: https://www.metrohm-autolab.com/download/Applicationnotes/Autolab_Application_Note_EC02.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Menzel, J.; Frąckowiak, E.; Fic, K. Agar-based aqueous electrolytes for electrochemical capacitors with reduced self-discharge. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Use of a charcoal salt bridge to a reference electrode in an alkaline solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 859, 113872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, S.A.M. Improved electrodeposited iridium oxide pH sensor fabricated on etched titanium substrates. Anal. Chem. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrestani, S.; Ismail, M.C.; Kakooei, S.; Beheshti, M.; Zabihiazadboni, M.; Zavareh, M.A. Iridium Oxide pH Sensor Based on Stainless Steel Wire for pH Mapping on Metal Surface. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, J.; Kakooei, S.; Ismail, M.C.; Karimzadeh, R.; Mahmood, M.R. Development of iridium oxide sensor for surface pH measurement of a corroding metal under deposit. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.D.; Cao, H.; Deb, S.; Chiao, M.; Chiao, J.C. A flexible pH sensor based on the iridium oxide sensing film. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 169, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelco Chemical Compatibility Chart: ABS. Available online: http://www.kelco.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2009/02/abs-chemical-compatibility-guide.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Pine Research Overview of Reference Electrodes and Alternative Reference Electrodes Brief Discussion about Standard and Pseudo Reference Electrodes. Available online: https://pineresearch.com/shop/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/10/DRK10053-Overview-of-Reference-Electrode-Operation-and-Alternative-Reference-Electrodes-REV001.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- CP Lab Safety Nylon Chemical Compatibility. Available online: https://www.calpaclab.com/nylon-chemical-compatibility-chart/ (accessed on 7 November 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sibug-Torres, S.M.; Go, L.P.; Enriquez, E.P. Fabrication of a 3D-Printed Porous Junction for Ag|AgCl|gel-KCl Reference Electrode. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040130
Sibug-Torres SM, Go LP, Enriquez EP. Fabrication of a 3D-Printed Porous Junction for Ag|AgCl|gel-KCl Reference Electrode. Chemosensors. 2020; 8(4):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040130
Chicago/Turabian StyleSibug-Torres, Sarah May, Lance P. Go, and Erwin P. Enriquez. 2020. "Fabrication of a 3D-Printed Porous Junction for Ag|AgCl|gel-KCl Reference Electrode" Chemosensors 8, no. 4: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040130
APA StyleSibug-Torres, S. M., Go, L. P., & Enriquez, E. P. (2020). Fabrication of a 3D-Printed Porous Junction for Ag|AgCl|gel-KCl Reference Electrode. Chemosensors, 8(4), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040130