Abstract
Mycotoxins are a group of secondary metabolites produced by different species of filamentous fungi and pose serious threats to food safety due to their serious human and animal health impacts such as carcinogenic, teratogenic and hepatotoxic effects. Conventional methods for the detection of mycotoxins include gas chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry or other detectors (fluorescence or UV detection), thin layer chromatography and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. These techniques are generally straightforward and yield reliable results; however, they are time-consuming, require extensive preparation steps, use large-scale instruments, and consume large amounts of hazardous chemical reagents. Rapid detection of mycotoxins is becoming an increasingly important challenge for the food industry in order to effectively enforce regulations and ensure the safety of food and feed. In this sense, several studies have been done with the aim of developing strategies to detect mycotoxins using sensing devices that have high sensitivity and specificity, fast analysis, low cost and portability. The latter include the use of microarray chips, multiplex lateral flow, Surface Plasmon Resonance, Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering and biosensors using nanoparticles. In this perspective, thin film sensors have recently emerged as a good candidate technique to meet such requirements. This review summarizes the application and challenges of thin film sensor devices for detection of mycotoxins in food matrices.
1. Introduction
Mycotoxins are a group of secondary fungal metabolites produced by different species of filamentous fungi [1], among which the most important belong to the genera Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Penicillium [2].
Considering the agro-economic aspects and the impact on global agriculture, as well as the possible implications on the public health, the most relevant mycotoxins are aflatoxins (AFs), citrinin (CIT), deoxynivalenol (DON), fumonisin B1 (FB1), ochratoxin A (OTA), patulin (PAT), T-2 toxin (T-2), and zearalenone (ZEA) [3,4,5]. These toxins are found worldwide as natural contaminants in many food matrices of plant origin, like aromatic herbs, cereal grains, coffee beans, dried fruits, fruits, oilseeds, spices, and vegetables, as well as in wine, and beer. Mycotoxins can also be found in animal-derived foods due to the intake of contaminated feeds [6,7,8,9,10,11].
The presence of mycotoxins in foods has severe implications on human and animal health even at very low levels, due to their mutagenic, teratogenic, carcinogenic, nephrotoxigenic, and immunosuppression effects [12]. Table 1 summarizes the main mycotoxins and their respective toxic effects, as well as the producing fungal species and the regulatory limit ranges established in the European Union (EU), when applicable [13,14,15,16].

Table 1.
Representative mycotoxins and their respective toxic effect and main producing fungal species.
Consequently, sensitive and accurate methods of analysis are needed to gather adequate information on the levels of exposure to mycotoxins and to assess the relevant toxicological risk for humans and animals. In addition, analytical methods should allow the measurement of such contaminants at levels lower than the legal limits fixed by the EU or other national or international regulations with good accuracy and precision, allowing us to establish monitoring programs and so to ensure international trade safety [17].
2. Conventional Analytical Methods for Mycotoxins Detection
Chromatography is the most commonly used method used for mycotoxin analysis in food and feed [29]. The thin layer chromatography (TLC) was the first chromatographic method to be applied for mycotoxin determination and, nowadays, is still a routine technique used in several laboratories. TLC is presently used as a rapid visual screening method for certain mycotoxins (AFM1, AFG1, AFG2, FB1 and OTA) allowing a qualitative evaluation or, if coupled with instrumental densitometry, enabling a semi-quantitative assessment [30,31,32]. However, current trends in mycotoxin analysis in foods are focused on the application of robust, fast, easy to use, and cheap technologies that are able to detect and quantify simultaneously various mycotoxins with a high sensitivity and selectivity in a single run [33]. To meet those needs, many chromatographic methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with ultraviolet (UV), diode array (DAD), fluorescence (FLD), or mass spectrometry (MS) detectors; and, ultra-HPLC (UHPLC) or UPLC with reduced column packing material (1–2 µm) have been developed [34]. Additionally, gas chromatography (GC) coupled with electron capture (ECD), flame ionization (FID), or MS detectors have been also used to identify and quantify volatile mycotoxins [34]. Due to the high polarity and low volatility of some mycotoxins, GC analysis often requires a derivatization step. Thus, this method is used rarely in mycotoxins analysis [35]. Mycotoxin analysis has been greatly enhanced by coupling liquid chromatography techniques with mass-spectrometry (e.g., LC-MS; LC-MS/MS) [29]. While HPLC-MS coupled with mass spectrometric or fluorescence detectors are usually applied for mycotoxins analysis in foods, other chromatographic techniques (e.g., TLC) are rarely used due to the limited sensitivity and specificity [34,36,37].
Chromatographic methods, namely LC and GC, typically require additional steps prior to detection, including extraction, clean-up and separation that are crucial, though time consuming, for a successful protocol, and directly affect the final choice for the detection procedure [29]. Although these methods have high sensitivity and selectivity, they are not suitable for rapid, on-site testing because they are laboratory-based and require skilled operators and expensive equipment. In addition, they are time-consuming, involve high costs, often require large amounts of hazardous reagents and solvents during the analysis process, and may exhibit a lack of accuracy for low analyte concentrations [38]. A comparison between the conventional analytical methods to detect mycotoxins in food and feed samples is summarized in Table 2. In this table, some examples of mycotoxin detection/quantification limits are given for the conventional analytical techniques commonly used, although it should be remarked that the referred techniques may allow achieving lower detection limits depending on the type of food matrix and/or on the target mycotoxin.

Table 2.
Comparison between the conventional analytical methods for mycotoxins analysis.
Additionally, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) are an important analytical technique that has been widely used in the detection of mycotoxins [39,40]. The technique principles are based on the competitive interactions between mycotoxins (acting as an antigen) and specific antibodies labelled with toxin-enzyme conjugates [41]. ELISA can be performed in several ways such as direct assay, direct competitive assay, and indirect competitive assay, with competitive direct assay being the most commonly used method [42]. This technique provides a fast screening, and commercial kits are available. These have been validated for a wide variety of food matrices and are available for the detection and quantification of mycotoxins including AFs, DON, FB, OTA, T-2 toxin, and ZEA [33,41,43]. The ELISA-based method is user-friendly, less expensive, and less time-consuming than HPLC techniques, which, on the other hand, are much more reliable in terms of analyte quantification [44].
The availability of other fast, sensitive, simple, portable and cost-effective methods for rapid determination of mycotoxins and others contaminants is becoming an increasingly significant challenge for the food industry in order to ensure the safety of foods and feeds. Therefore, the use of analytical procedures based on sensors has recently gained increased interest, mainly due to their capability to overcome a large number of analytical challenges, including difficulties in detecting low-level mycotoxin contamination, and the co-occurrence of mycotoxins [45,46]. In this sense, many researchers applied sensor-based devices like microarray chips [38], electrochemical sensors [47], biosensors [48], multiplex lateral flow [24,49], Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) [50], Total Internal Reflection Ellipsometry (TIRE) [51], and Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) [32]. In this perspective, thin film sensors have recently emerged as good candidate techniques to fulfill such requirements, although not all of the above-mentioned types of sensor-based devices would fall within the thin-films sensors classification.
3. Thin Film Based Sensors
A thin film generally refers to a layer of material that ranges from a few nanometers to several micrometers in thickness. Thin film devices play an important role in many conventional and emerging technologies due to the constant advances in nanotechnology, among which the development of functional materials and the use of properties of thin films can be mentioned, such as high surface area, controlled nanostructure for effective charge transfer, and special physical and chemical properties [62].
Thin layers applied in the thin film devices may comprise organic, inorganic, and composite thin layers, sharing analogous functionalities, properties, and fabrication routes. The combination between different thin films can produce a thin film device, like thin film solar cells, thermoelectric devices, actuators and also transistors, for the development of biosensors or other electrochemical sensors for mycotoxins detection [62]. The film layer(s) may be deposited using vapor, liquid or solid precursors or from a combination of several precursors phases, depending on their nature and on the desired functionality and specification of the thin film [62,63,64]. Conducting polymer thin films may be deposited using several solution-processed casting techniques, such as electrochemical deposition, Langmuir–Blodgett (LB) technique, layer-by-layer self-assembly, dip coating, spin coating, drop-casting, spray coating, inkjet printing, as well as using different thermal evaporation techniques at moderate temperatures [65]. In addition, some physical and chemical-vapor deposition methods (PVD and CVD, respectively), such as sputtering and molecular bean epitaxy modes, can also be applied to improve the quality of the deposition [62].
A biosensor is a bioanalytical device constituted by a biorecognition element (DNA, enzyme, antibody, etc.), which is responsible for recognizing an analyte, i.e., a bioreceptor; an immobilization matrix like conducting polymers [48,66], nanomaterials [67,68], sol–gel films [69], and self-assembled monolayers [70], which have been used for the immobilization of a biomolecule; and a transducer unit for converting the biochemical response into a recognizable electrochemical/electric signal.
Biosensors are commonly classified based on the type of transducer, as optical (colorimetry, fluorescence, luminescence, interferometry, spectroscopy, SPR, and TIRE); electrochemical (amperometry, conductimetry, potentiometry, and voltammetry); and piezoelectric (quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) [48,71].
3.1. Optical Sensors
Optical biosensors provide a powerful alternative to conventional methods such as ELISA and chromatographic techniques because they allow high sensitive, nondestructive, and real-time analysis of food toxins without needing extensive and complex sample preparation steps [72].
This kind of biosensor uses a transducer unit capable of converting the interaction between the biorecognition elements and the target analytes into a measurable optical signal. They are classified according to the optical method applied to detect the analyte of interest, which may be based on fluorescence, colorimetry, electrochemiluminescence, and SPR [73,74,75]. Among optical techniques, SPR and fluorescence are the most frequently used.
3.1.1. Fluorescence Sensors
Among the several optical detection methods, fluorescence sensing techniques attracted huge interest due to their easy operation, short analytical time and convenient signal reading [76]. Nanomaterials have been integrated into fluorescent biosensing devices, taking into account their inherent excellent optical and electronic properties [75]. Gold nanoparticles [77], dendrimers [78], quantum dots [79], and graphene oxide [80] have been employed in the mycotoxin sensing. In combination with nanoparticles, specific aptamers were also used to develop some fluorescence thin film sensors for mycotoxin detection [81,82]. The aptamer consists of a synthetic oligonucleotide ligand (either single stranded DNA (ssDNA) or RNA) that comprises less than 80 nucleotides and with less than 25 kDa and are known to exhibit high specificity and strong binding affinity [83].
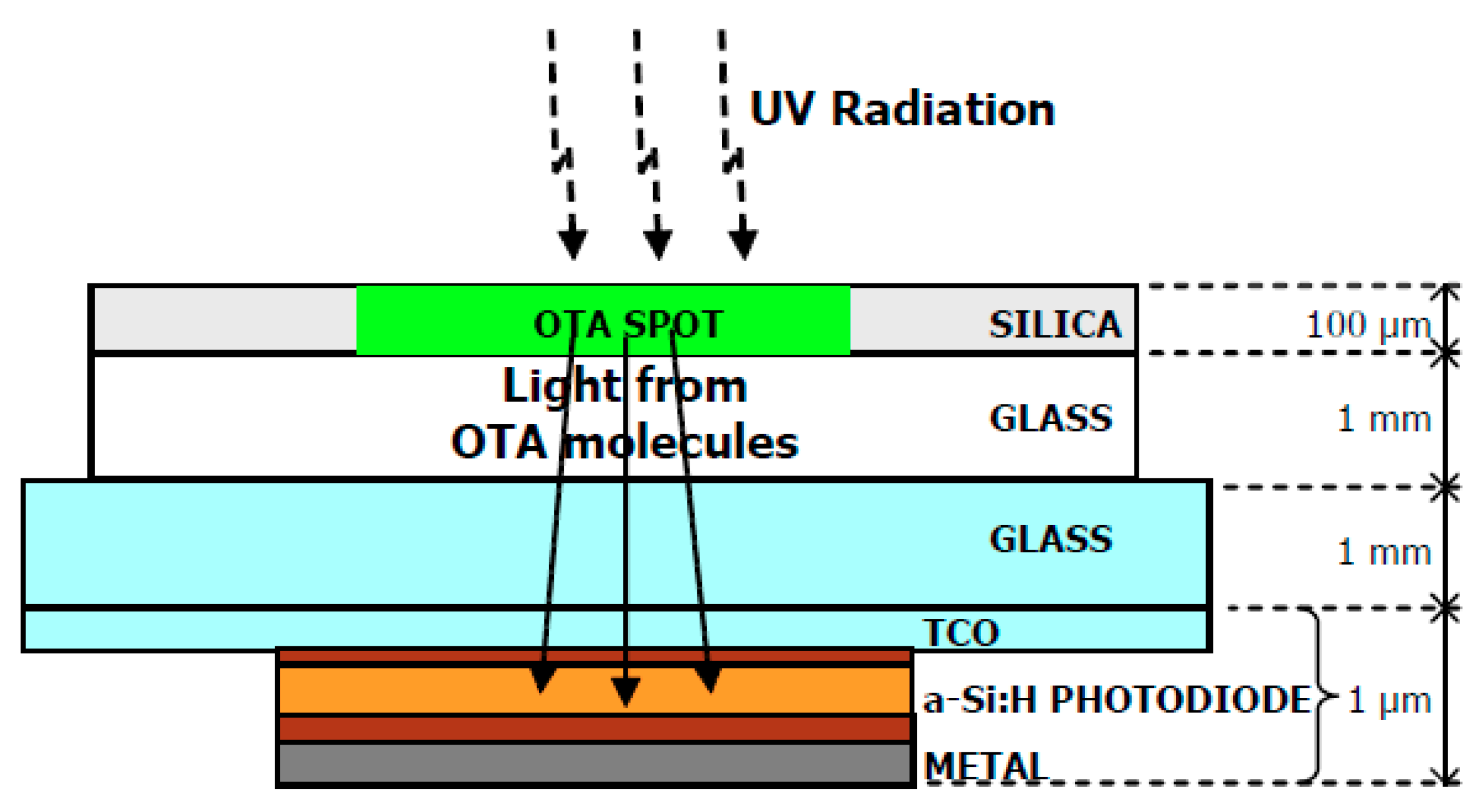
Caputo et al. [84] developed a rapid, compact and innovative method for the detection of OTA based on hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) thin film sensors (Figure 1, reprinted with permission from [84] ©MDPI, 2018). The sensor was constituted by a stacked structure of p-type/intrinsic/n-type a-Si:H layers deposited by plasma enhanced chemical vapor technique (PECVD), which was deposited on a glass substrate allowing improvement of the detection limits. The metal contact surface comprised a three metal layer of chromium/aluminum/chromium, obtained by evaporation under vacuum [84]. As described by the researchers, a high-performance thin layer Chromatography (HPTLC) plate was placed on the silica side, being 2 μL of OTA solutions with different concentrations spotted. The incidence of an UV radiation, at 253.4 nm, allowed exciting the mycotoxin, which re-emitted light (mostly in the green range) passed through the glasses/TCO layers being absorbed by the a-Si:H photosensor, which is aligned with the OTA molecules dropped on the silica. According to Caputo et al. [84], the minimum detected OTA concentration was 0.25 μg·kg−1 (corresponding to 0.1 ng of OTA detected after an extraction process starting from 10 mL of red wine), showing that the presented system has the potential for a low-cost system suitable for the early detection of toxins in foods.
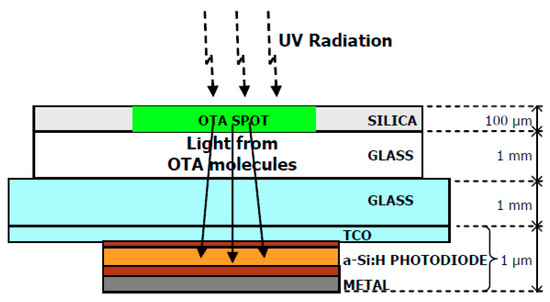
Figure 1.
Qualitative scheme of the fluorescence detection system for OTA molecules. The analyte is confined in an HPTLC plate, optically coupled with a glass substrate, where the a-Si:H photosensor have been deposited. (reproduced with permission from Caputo et al. [84] ©MDPI, 2018).
Using the same system with a-Si:H photosensor, Caputo et al. [85] reported limits of detection of 0.1 ng and 1 ng in standard solutions or in contaminated red wine samples, respectively, allowing to infer if the OTA content in a red wine was above or below the legal limit (2 μg·kg−1) [86].
A portable thin film device for detecting OTA was developed by De Cesare et al. [44]. The device allowed assessing the mycotoxin level of different food commodities, even if it was below the maximum limit imposed by the EU Commission [86] for the specific food evaluated. The prototype device included three main parts: a UV light source that supplied the radiation to induce the OTA fluorescence; a commercial HPTLC plate made of a silica gel-covered glass; an array of amorphous silicon photodetectors (a-Si:H photosensors), positioned behind the back side of the TLC plate. The photosensors were deposited by PECVD on a glass that was optically coupled to the TLC plate. The system performance was evaluated using OTA standard solutions, as well as with OTA extracts from fortified wine or beer samples. The results revealed a quantification limit of 0.2 ng in 2 μL of extracted sample solution (red wine or beer fortified with OTA) which would correspond to 10 ng of OTA in 5 mL of real matrix, being, according to the researchers, a value of 5.5 mL (admitting a 90% extraction efficiency) of sample enough to determine if the OTA concentration was lower than the legal threshold (2 μg·kg−1) [86].
Some fluorescence sensing assays are based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) [80]. In this manner, one chemical group provides energy and the other one accepts the transferred energy. A large overlap between receiver excitation and donor emission must exist in order to achieve FRET. When the distance between donor and acceptor is close enough, the energy will be transferred from the donor to the acceptor. Furthermore, the acceptor and donor in the FRET system can be designed in a biunique or one-to-multiple manners, enabling the simultaneous application of multiple mycotoxin sensing methods [76]. The FRET technique was applied by several researchers, allowing detection of different mycotoxins (e.g., AFM1, AFB1, OTA and FB1) in foods (e.g., milk, peanuts, rice, and/or maize). Antibodies or aptamers were immobilized onto fluorescent nanoparticles-graphene oxide, quantum dots-AuNPs or nanogold-strips, forming thin films and enabling achieving low detection limits (e.g., 0.02 to 0.1 ng·mL−1, depending on the method/mycotoxin) [80,87,88].
3.1.2. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Sensors
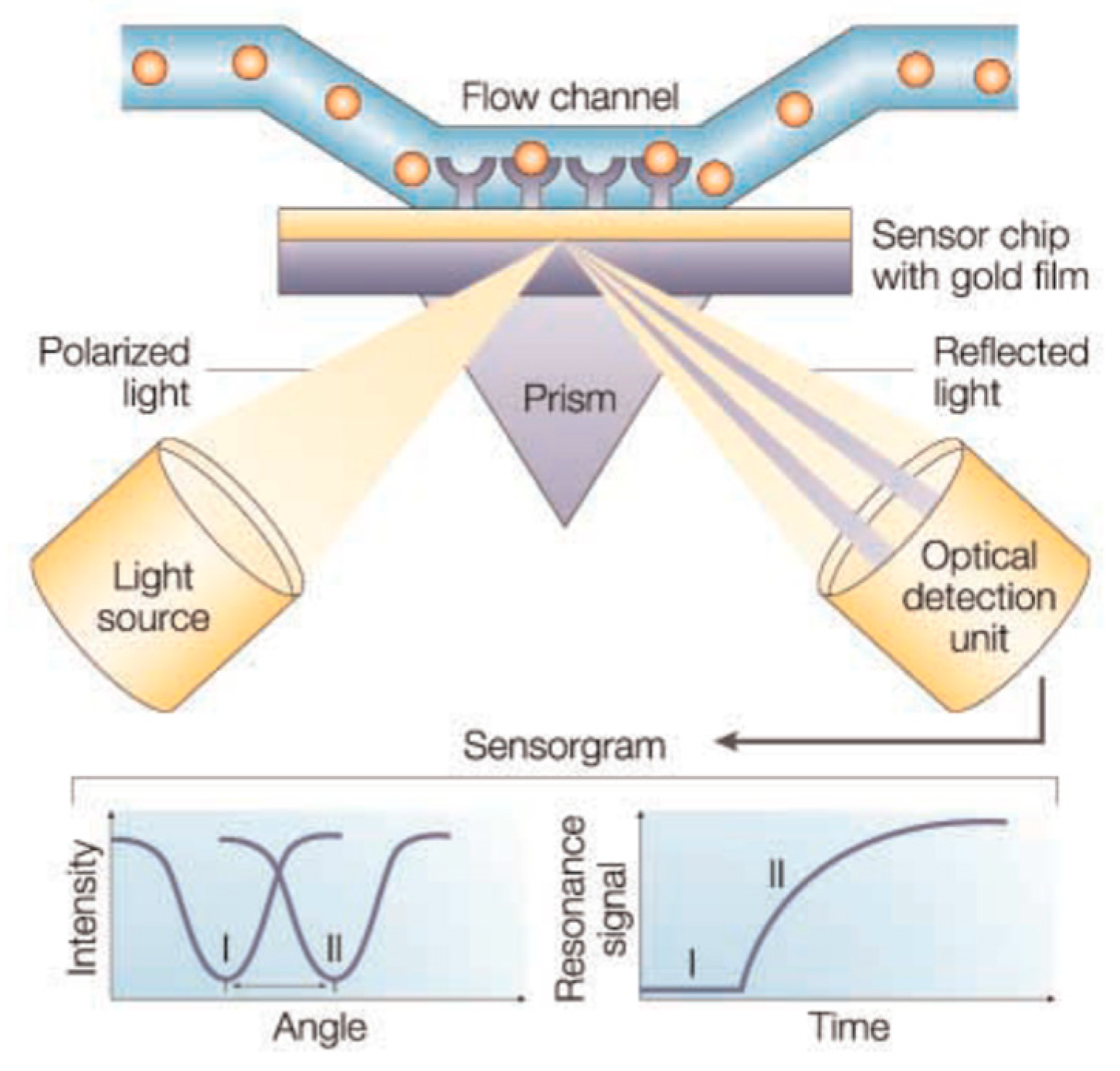
Biosensors based on SPR use a thin metal (usually gold or silver) film between two transparent media with different refractive indices, like, a glass prism and the sample solution. When a polarized light beam passes through the higher refractive index medium (e.g., glass prism) it can undergo a total internal reflection if the incidence angle is above the critical angle, generating an evanescence wave that penetrates the metal layer [89,90]. The interaction of this wave with free oscillating electrons at the metal film surface at a specific angle of incidence will cause the excitation of the plasmon surface, resulting in a decrease in the reflected light intensity. A SPR system thus detects changes in the refractive index of the surface layer of a solution in contact with the sensor chip [81]. Figure 2 (reproduced with permission from reference [91] ©Nature, 2018) shows the SPR biosensor principle, including a typical set-up as well as a common binding cycle.
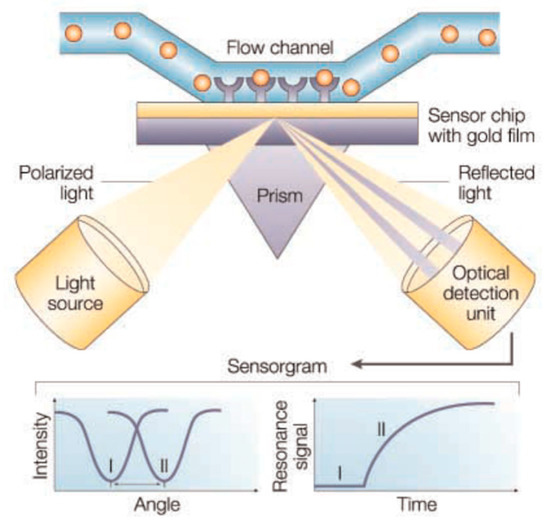
Figure 2.
SPR biosensor principle. Typical set-up for an SPR biosensor. (reproduced with permission from Cooper [91] ©Nature, 2018).
Small compounds, such as mycotoxins, usually do not generate a sufficient change in the refractive index and thus their detection using SPR is more challenging, due to the low signal intensity and poor sensitivity [92]. However, a clear enhancement of the method sensitivity can be achieved by using SPR combined with competitive or inhibitive detection tools together with the use of additional high mass labels.
Indeed, SPR sensing has been used with competitive-inhibition assays and sandwich assays to determine mycotoxins. In competitive methodologies, the sensor surface is coated with an antibody that interacts with the mycotoxin. When a conjugated antigen is added to the sample, it competes with the mycotoxin for the limited number of biding sites on the surface. Therefore, the recorded signal is inversely proportional to the mycotoxin concentration. The inhibition assay relies on mixing a known concentration of antibody with a sample containing an unknown concentration of antigen that is subsequently injected into the flow cell and passed through a sensor surface, to which antigen is immobilized. Then, the amount of bounded antigen to the modified surface antibody is measured and the obtained signal is proportional to the concentration of the mycotoxin [76,93]. In the sandwich format, the antibody is added to the sample to recognize and react with the target, forming a primary complex [50,94,95]. Then, the primary complex is placed in contact with the sensor chip to generate the sandwich complex, which results in a measurable signal [76].
Other approaches to amplify the SPR signal response involve the use of fluorescence or modifications of the sensor chip with metallic nanoparticles. The latter ones are widely used in the construction of biosensors due to their unique physical and chemical properties, good biocompatibility and high catalytic activity for many chemical reactions. Among the large variety of nanomaterials currently available, the implementation of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) has gained huge relevance [75]. The application of silver film over nanospheres has also been a very effective practice due to the high enhancement factor achieved (≥104), the high stability within a wide temperature range and wide analyte concentration ranges, and the good shelf-life (higher than 40 days) [96].
The nanomaterial-based enhanced SPR biosensing systems may be achieved using two common strategies. One promotes the substrate SPR biosensing by applying nanomaterials and, the other uses nanomaterials as amplification labels for SPR biosensing enhancement. As SPR substrate, nanomaterials with large surface area allow the immobilization of several biorecognition elements.
Fu et al. [97] reported a SPR biosensor for OTA detection based on gold hollow balls (AuHBs) with dendritic surface. An electropolymerized thionine (PTh) film was deposited onto a gold electrode, forming a PTh-modified electrode surface with several amino groups. The deposition was achieved using voltammetric cycles between 0 and 1.5 V at a scan rate of 50 mV/s in 0.1 M thionine aqueous solution. The AuHBs were immobilized using a thionine thin film electropolymerized onto the SPR probe surface. Then, anti-OTA monoclonal antibody (anti-OTA, linked to AuHBs, was also immobilized onto the SPR-probe surface. The developed SPR biosensor exhibited a linear detection range from 0.05 to 7.5 ng mL‒1 with a low limit of detection (LOD) (0.01 ng mL‒1), under the optimum operating conditions. Furthermore, this SPR biosensor also enabled a fast detection (<30 min) of OTA in milk samples.
Todescato et al. [98] developed a new sensor prototype capable of detecting OTA, at levels lower than the legal threshold of 0.5 μg/kg, in different food matrices (dried milk, juices, and wheat milk): The sensor device comprised a silver film over nanospheres plasmonic substrates functionalized with a specific anti-OTA antibody (Ag-FON), able to bind with the complex OTA-Alexa Fluor (AF) 647. Briefly, as described by the researchers, polystyrene nanospheres, in an aqueous solution, were spin-coated on top of the clean glass slides to form a self-assembled stack. Silver thin films were then deposited onto the substrates using an Edwards E306A coating system with a bare pressure of 6 × 10−5 mbar. The metal deposition rate was approximately 1 Å/s and the final Ag thicknesses, evaluated by means of a quartz crystal microbalance, were approximately equal to 50, 100 and 150 nm. In the work, OTA concentrations ranging from 0 to 5 µg·kg−1 were incubated on commercial micro arrays or on Ag-FON slides. The Ag-FON array slides allowed detecting OTA concentration as low as 0.05 µg·kg−1, 10 folds lower than the detectable concentrations using commercial microarray slides (0.5 µg·kg−1). Indeed, the limit of quantification (LOQ) of OTA using Ag-FON substrates was of 3.6 ng·kg−1 that is 20 times lower than the LOQ observed for commercial microarray slides (70.7 ng·kg−1). To evaluate the feasibility of the detection strategy for real samples, the authors spiked milk, juices and wheat mix samples with unlabeled OTA and the results showed that the proposed methodology was able to detect OTA concentrations as low as 0.5 µg·kg−1 (E.U. legislation lower tolerable limit) in the spiked samples, whose levels were statistically higher than those observed in the control samples (not spiked with OTA). These findings showed that OTA concentrations higher than 0.5 μg·kg−1 could be detectable in these food matrices when compared to control samples [98].
Karczmarczyk et al. [99] developed an indirect OTA detection method for red wines analysis, based on an AuNPs-enhanced SPR device. The sensor chip comprised a BK7 glass substrate that was coated by applying a sputtering deposition method, with a thick gold film (37 nm). The setup allowed secondary antibodies, conjugated with AuNPs, to interact with antibody–OTA complexes immobilized on a gold sensor chip surface, via self-assembled thiol monolayer (SAM). In order to optimize the enhanced SPR biosensor response for the OTA immunoassay, Ab2-AuNPs conjugates with different diameters (10–40 nm) were used. The LODs were obtained in PBS as well as in red wine samples and were equal to 0.068 and 0.19 ng·mL−1, respectively. The highest signal amplification was obtained for diameters of 40 nm and for distances greater than 50 nm between the nanoparticles and the gold surface leading to enhancement factors greater than 100.
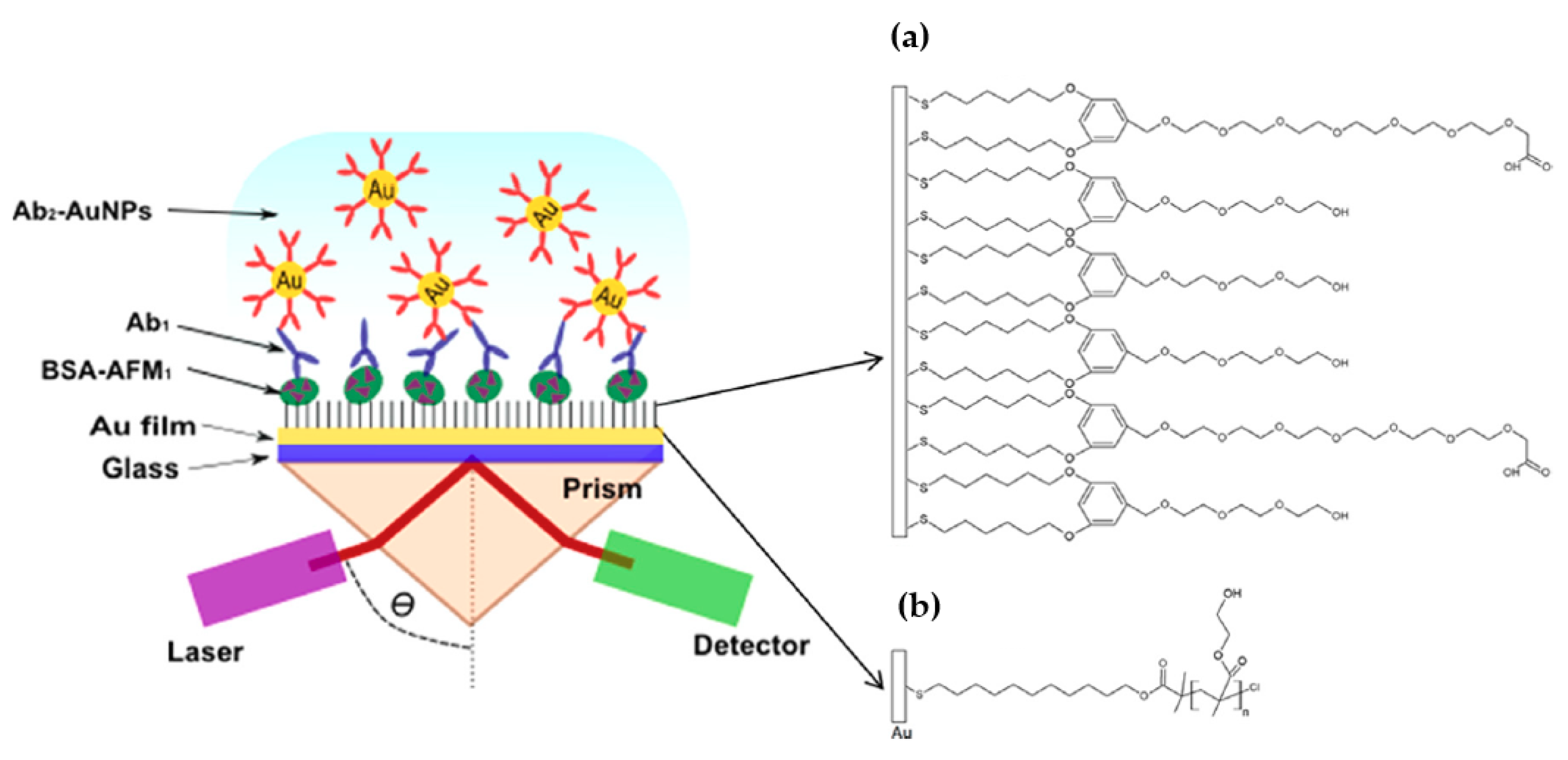
A similar AuNPs enhanced SPR thin film immunosensor was constructed for a fast and sensitive detection of aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) in milk and dairy products by Karczmarczyk et al. [100]. In this work, and similarly to reference [97], the sensor chip was prepared on the top of a BK7 glass substrate that was coated with a 41 nm thick gold layer. Two surface architectures were used for the immobilization of AFM1 and of the primary antibody on the gold surface. The first, (A), was based on a bicomponent SAM with polyethylene glycol (PEG) moieties and, the second, (B), used poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) marked as p(HEMA) brush (Figure 3; reproduced with permission from [100] ©Elsevier, 2018). Both sensors were characterized in terms of surface mass density of the immobilized AFM1 conjugate as well as affinity bound of primary and secondary antibodies. The sensor with thiol mixed SAM with PEG moieties showed a LOD of 26 pg·mL−1 and 38 pg·mL−1 in buffer standard solutions and in milk samples, respectively. On the other hand, the sensor with p(HEMA) exhibited a LOD of 18 pg·mL−1, which is more than two-times lower compared to that on thiol SAM with PEG groups. The biosensor [100] was highly sensitive towards AFM1 in milk, allowing its detection in a low time-period (55 min), showing a sensitivity of at least one order of magnitude higher compared to the those reported by other methods, including electrochemistry [101] or indirect and direct ELISA [102].
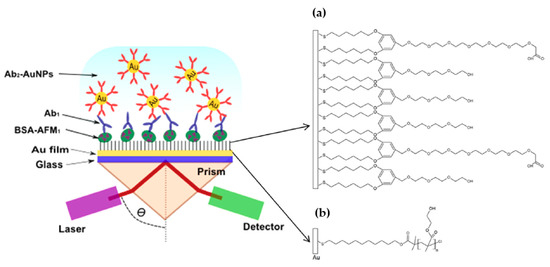
Figure 3.
Scheme of the optical setup and sensor chip with different surface architectures: (a) mixed SAM and (b) p (HEMA) brushes (reproduced with permission from Karczmarczyk et al. [100] ©Elsevier, 2018).
Another interesting optical approach is the use of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR), which has been attracting the attention of researchers because of its potentially high sensitivity [103,104].
3.1.3. Total Internal Reflection Ellipsometry (TIRE)
The method of Total Internal Reflection Ellipsometry (TIRE) combines the advantages of SPR and spectroscopic ellipsometry and allows achieving sensitivities 10 times higher than SPR and, therefore, it became particularly suitable for detection of low molecular weight molecules such as mycotoxins [105].
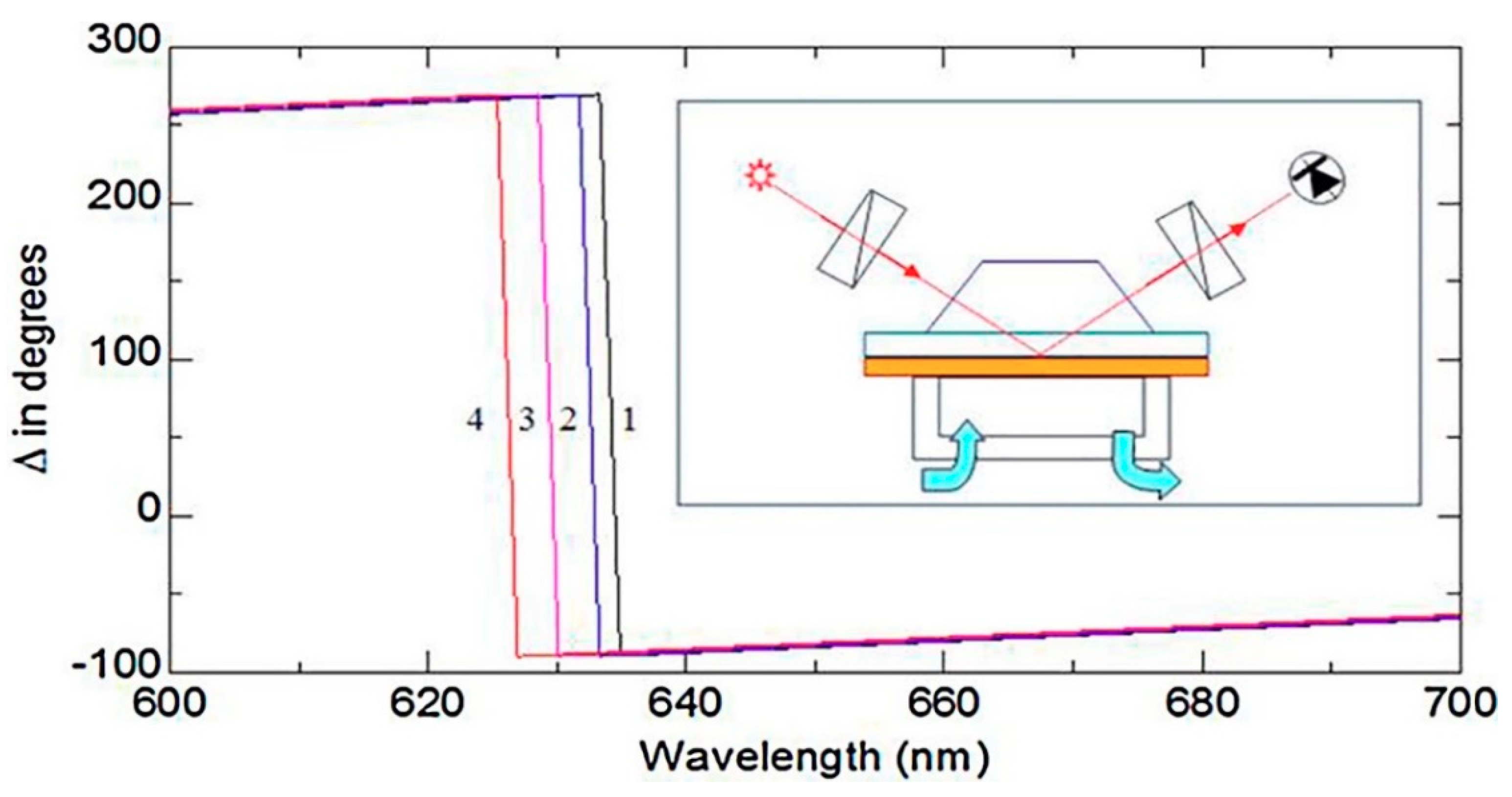
Al Rubaye et al. [82] reported for the first time a label-free optical detection of OTA using a direct assay with highly specific aptamers using the TIRE method (Figure 4; (reproduced with permission from reference [82] ©Elsevier, 2018). Gold layers, of about 25 nm of thickness, were formed by evaporation on glass slides using an Edwards E306A equipment. A thin layer of chromium (2–3 nm) was obtained by evaporation, allowing improvement of the adhesion of the gold layer on the glass surface. Immobilization was carried out by casting the aptamer solution onto the gold coated slides. The reported results showed that the detection of OTA using this aptamer-TIRE method was successful and OTA concentrations as low as 0.01 ng·mL−1 could be detected. This same research group [51] also developed a highly sensitive analytical TIRE method, which combined with LSPR and using nanostructured gold films allowed detecting aflatoxin B1 and M1 in a direct assay based on the use of specific aptamers immobilized on a gold sensor surface. The concentration range for aflatoxin B1 detection ranged from 0.01 ng·mL−1 to 100 ng·mL−1, being obtained LODs of 0.01 ng·mL−1, which is remarkably low for LSPR-based biosensors.
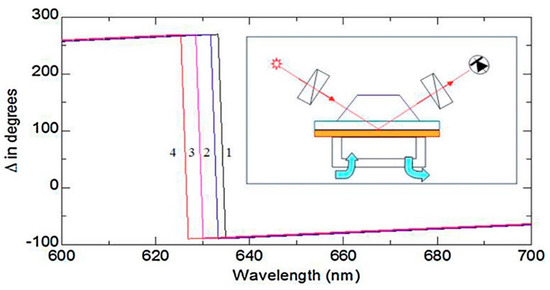
Figure 4.
Total Internal Reflection Ellipsometry (TIRE) spectra recorded on aptamer layer (1) and after binding Ochratoxin A (OTA) of 0.01 ng/mL (2), 1 ng/mL (3) and 10 ng/mL (4). (reproduced with permission from Al Rubaye et al. [82] ©Elsevier, 2018).
3.2. Electrochemical Biosensors
The use of electrochemical biosensors is based on the electroactive characteristics of several analytes, which may be oxidized or reduced on a working electrode surface, generating a measurable electrochemical signal [106]. Most of electrochemical biosensors developed for mycotoxins detection are based on the use of specific antibodies, aptamers or artificial receptors like molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) as affinity ligands that allow binding the analyte to the sensor, with negligible interference from other components that may be present in the sample [107,108].
To transform the mycotoxin interaction into a measurable analytical signal, different electrochemical techniques have been used like (1) amperometric, which measures the changes in the current at a given applied voltage resulting from the oxidation or reduction of an electroactive biological element providing specific quantitative analytical information; (2) potentiometric, which measures the changes in the voltage between the working and the reference electrodes due to the establishment of an electrostatic interaction; (3) conductometric, which measures the changes in the capability of the sensing material to transport charge (electron); and (4) impedimetric, which measures the resistance of the generated electric current at certain applied voltage and combines the analysis of both the resistive and capacitive properties of the materials [109,110,111,112,113]. Many review articles have focused on mycotoxin detection using different electrochemical biosensors [47,107,114,115] and on the application of nanomaterial-mediated bio and immunosensors [21,75,76].
Table 3 summarizes research regarding electrochemical sensors devices recently used for mycotoxin analysis in food samples. It should be remarked that, concerning the electrochemical devices, the majority of the works do not give information regarding the thickness of the detection thin-films formed, usually only reporting the thickness sensor surface where the film layers are formed. Nevertheless, from the overall information gathered for most devices, it could be assumed that the thickness of the film layers (nanocomposites are usually reported) is at nanometer-micrometer level, although for few devices it could be at a millimeter level.

Table 3.
Electrochemical thin film sensors devices recently used in the mycotoxins analysis in food samples.
3.3. Mass-Based Piezoelectric Biosensors (Quartz Crystal Microbalance)
A Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) consists of a thin quartz disk where electrodes are placed. The application of an external electrical potential to a piezoelectric material produces an internal mechanical stress. As the QCM is piezoelectric, an oscillating electric field applied across the device induces an acoustic wave that propagates through the crystal and reaches a minimum impedance when the thickness of the device is a multiple of a half wavelength of the acoustic wave. Another advantage of QCM is its ability to carry out real-time measurements [142].
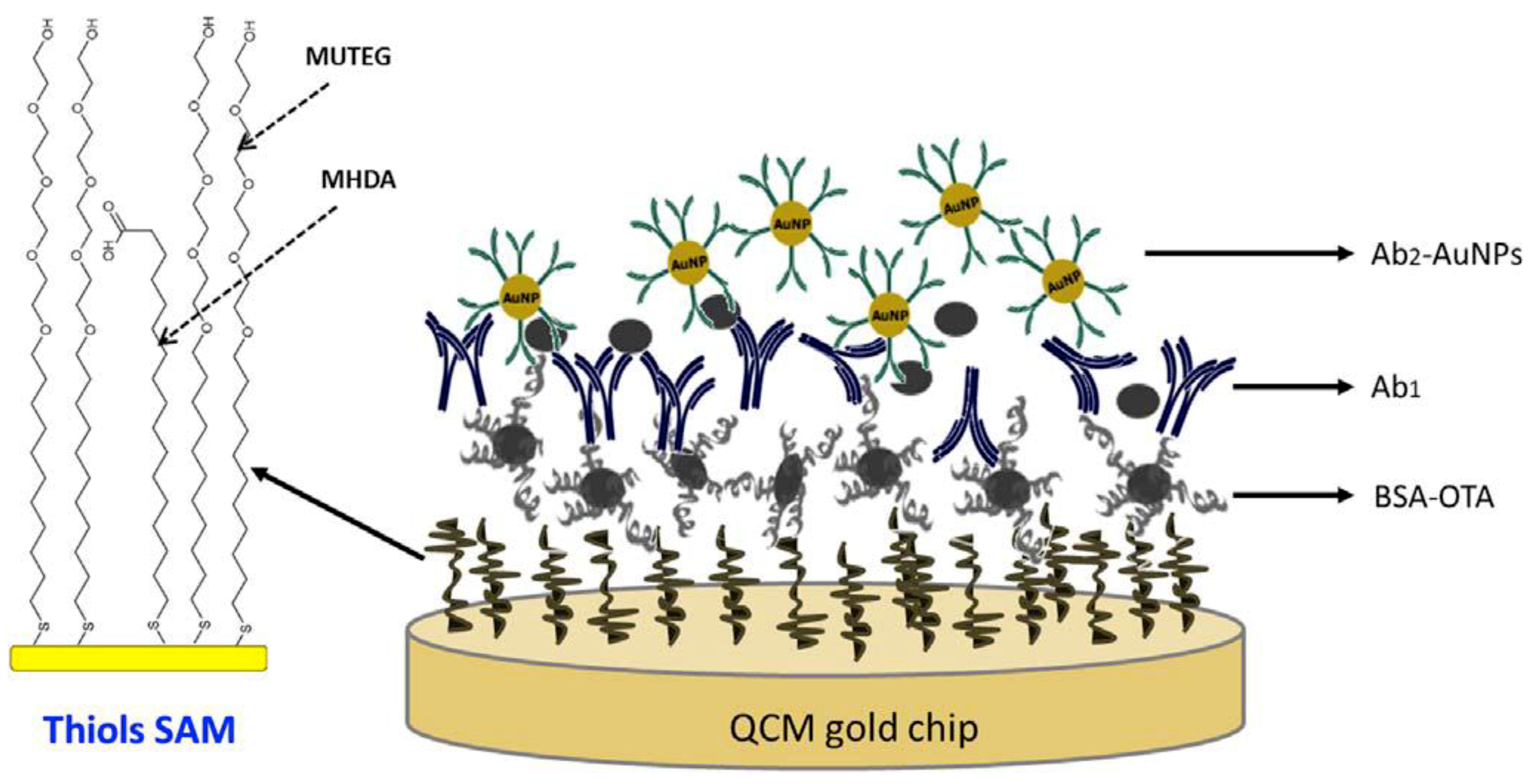
Karczmarczyk et al. [143] developed a novel sensor device based on a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). The sensor consisted of a gold surface modified with a mixed thiol self-assembled monolayer (SAM) to which the BSA-OTA conjugate was attached as shown in Figure 5 (reproduced with permission from Karczmarczyk et al. [143] ©Elsevier, 2018). Antibodies for specific analyte recognition were used, allowing fast and sensitive detection of OTA in red wine. The amplification of the QCM-D signal was achieved by applying secondary antibodies conjugated with AuNPs. The developed QCM-D biosensor exhibited a linear detection range of 0.2–40 ng·mL−1 and a LOD of 0.16 ng·mL−1.
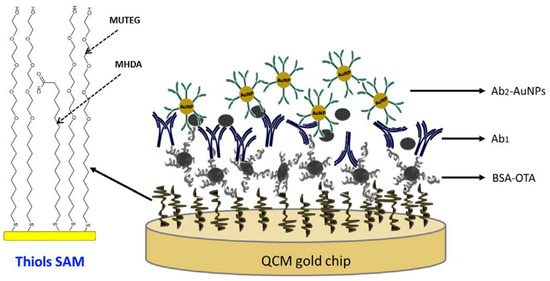
Figure 5.
Scheme of the interfacial molecular architecture for the detection of OTA using a competitive immunoassay-QCM approach (reproduced with permission from Karczmarczyk et al. [143] ©Elsevier, 2018).
A simple and sensitive QCM immunosensing platform was designed by Tang et al. [144] for detecting AFB1 in foodstuffs. Initially, the phenoxy-derived dextran molecule was immobilized on the surface of QCM gold substrate. Then, AFB1-bovine serum albumin (AFB1-BSA) conjugated concanavalin A (Con A) was assembled onto the QCM probe through the dextran-Con A interaction. Glucose-loaded nanoliposome, labeled with monoclonal anti-AFB1 antibody, was used for the amplification of QCM signal. The observed dynamic ranged from 1.0 ng·kg−1 to 10 μg·kg−1 and the LOD was 0.83 ng·kg−1. The accuracy of the immunoassay was evaluated with peanut samples, including naturally contaminated peanut samples and spiked peanut samples. The immunosensing platform showed similar results compared to commercial AFB1 ELISA kits.
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
The need of controlling food contamination is a current and growing worldwide challenge. Therefore, the availability of fast and accurate analytical devices that could be used as a warning preliminary screening tool, allowing the detection of food contamination is of utmost relevance. Thin film biosensor devices are currently one of the most active research areas within the mycotoxins analysis. Comparing with the traditional analytical methods used for mycotoxins analysis, the main advantages of biosensors include the fast analysis time and rapid detection, high sensitivity, easy sample preparation, reusability and low cost. Nanomaterials such as gold, silver, metal oxides and quantum dots have been extensively employed for enhancing the detection capability of biosensors due to their remarkable optical, electronic, thermal, and mechanical properties, allowing the increase of their sensitivity, stability, and selectivity towards mycotoxins. In addition, several studies have been carried out focusing in the use of aptamers, antibodies, and MIPs together with nanoparticles in order to amplify the signal responses and thus guaranteeing a greater selectivity of thin film biosensors. Finally, it should also be mentioned that sensors merging electrochemical and optic detection systems (e.g., electrochemiluminescence and SPR assays) seem to be very promising approaches, demonstrating reliable and sensitive mycotoxins detection, possessing self-checking and self-calibration capabilities. These devices can also be designed for single or multi-analyte testing, single-use or reusable procedures, even allowing continuous monitoring assays. However, some drawbacks must be overcome before these devices may be used as routine techniques for mycotoxins detection. An effort must be made by researchers to convince the industrial partners of the advantages of thin film sensor devices, allowing their commercial exploitation. The use of several non-standard deposition techniques for obtaining the thin layers, the need of incorporating antibodies or aptamers as recognition elements coupled with the nano/microscale of the films poses some practical limitations. Moreover, the availability of user-friendly commercial devices, which are currently not a reality, requires merging several fields of knowledge (e.g., artificial intelligence, digital electronic sensors design, material sciences, microcircuit design, software innovations, and electronic systems integration) that at the actual research and development level is not a straightforward task. Furthermore, although the thin film sensor devices may enhance the mycotoxins detection performance, it should be remarked that the conventional analytical techniques (e.g., ELISA, HPLC, GC, etc.) allow for achieving detection limits of the same order of magnitude (ng·mL−1 or µg·kg−1), fulfilling the legal detection thresholds and so, limiting the need of establishing novel detection strategies. Similarly to other emerging techniques, the key challenge in the near future would be reaching the market, which would require unequivocally demonstrating the practical detection feasibility of such devices as well as the possibility of producing them at an industrial level, or the huge advantages of delivering personalized solutions upon a specific request from a client. Nevertheless, the reported overall satisfactory performances achieved with thin-film sensor based devices for mycotoxins detection in food matrices, even at levels lower than the legally regulated thresholds, allow foreseeing their future practical application, as a routine analytical procedure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.P. and A.O.S.; writing-original draft preparation, A.O.S; Visualization and writing—review and editing, A.V. (Andreia Vaz), P.R., A.C.A.V., A.V. (Armando Venâncio) and A.M.P.; Supervision, A.M.P. and A.V. (Armando Venâncio); Funding Acquisition, A.C.A.V., P.R., A.V. (Armando Venâncio) and A.M.P.
Funding
This work was funded by Project POCI-01–0145-FEDER-006984—Associate Laboratory LSRE-LCM, Project UID/BIO/04469/2013—CEB and strategic project PEst-OE/AGR/UI0690/2014—CIMO all funded by European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through COMPETE2020—Programa Operacional Competitividade e Internacionalização (POCI)—and by national funds through FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia I.P. Andréia O. Santos also acknowledges the research grant provided by the Associate Laboratory LSRE-LCM under the Projects UID/EQU/50020/2013 and POCI-01-0145-FEDER-006984. Andreia Vaz acknowledges the research grant provided by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT), reference number SFRH/BD/129775/2017. The APC was kindly waived by MDPI.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creppy, E.E. Update of survey, regulation and toxic effects of mycotoxins in Europe. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 127, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H. Toxicity, metabolism, and impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Toxicology 2001, 167, 101–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.W.; Subrahmanyam, S.; Piletsky, S.A. Analytical methods for determination of mycotoxins: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirahmadi, M.; Shoeibi, S.; Rastegar, H.; Elmi, M.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. Simultaneous analysis of mycotoxins in corn flour using LC/MS-MS combined with a modified QuEChERS procedure. Toxin Rev. 2017, 37, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.; Venâncio, A.; Lima, N. Mycobiota and mycotoxins of almonds and chestnuts with special reference to aflatoxins. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, W.L. Mycotoxin contamination of the feed supply chain: Implications for animal productivity and feed security. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 173, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrunhosa, L.; Morales, H.; Soares, C.; Calado, T.; Vila-Chã, A.S.; Pereira, M.; Venâncio, A. A Review of Mycotoxins in Food and Feed Products in Portugal and Estimation of Probable Daily Intakes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 56, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Madec, S.; Coton, E.; Hymery, N. Natural Co-Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds and Their in vitro Combined Toxicological Effects. Toxins 2016, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipotnik, Z.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodrigues, P. Aspergillus westerdijkiae as a major ochratoxin A risk in dry-cured ham based-media. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 241, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, H.; Arévalo, F.J.; Granero, A.M.; Robledo, S.N.; Nieto, C.H.D.; Riberi, W.I.; Zon, M.A. Electrochemical Biosensors for the Determination of Toxic Substances Related to Food Safety Developed in South America: Mycotoxins and Herbicides. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EU) No 1881/2006, Setting Maximum Levels for certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, L364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1126/2007 of 28 September 2007 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards Fusarium toxins in maize and maize products (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2007, L255, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EU) No 165/2010 of 26 February 2010 amending Regulation (EC) No1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards aflatoxins (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L50, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EU) No 212/2014 of 6 March 2014 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels of the contaminant citrinin in food supplements based on rice fermented with red yeast Monascus purpureus. Off. J. Eur. Union 2014, L67, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pascale, M.; Visconti, A. Overview of Detection Methods for Mycotoxins. In Mycotoxins: Detection Methods, Management; Leslie, J.F., Bandyopadhyay, R., Visconti, A., Eds.; Public Health and Agricultural Trade, CAB International: Oxfordshire, UK, 2008; pp. 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.H.; Phillips, T.D.; Jolly, P.E.; Stiles, J.K.; Jolly, C.M.; Aggarwal, D. Human aflatoxicosis in developing countries: A review of toxicology, exposure, potential health consequences, and interventions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EU) No 2015/1005 of 25 June 2015 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels of lead in certain foodstuffs (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2015, L161, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.Y.; Watson, S.; Routledge, M.N. Aflatoxin Exposure and Associated Human Health Effects, a Review of Epidemiological Studies. Food Saf. 2016, 4, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Pashazadeh, P.; Hejazi, M.; de la Guardia, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Recent advances in Nanomaterial-mediated Bio and immune sensors for detection of aflatoxin in food products. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 87, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.C.; Lino, C.M.; Pena, A. Mycotoxin food and feed regulation and the specific case of ochratoxin A: A review of the worldwide status. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2010, 27, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulenberg, E.P. Immunochemical Methods for Ochratoxin A Detection: A Review. Toxins 2012, 4, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfossi, L.; Calderara, M.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Arletti, E.; Giraudi, G. Development and application of a quantitative lateral flow immunoassay for fumonisins in maize. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 682, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, A.; Lattanzio, V.M.T.; Pascale, M.; Haidukowski, M. Analysis of T-2 and HT-2 toxins in cereal grains by immunoaffinity clean-up and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1075, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, F.T.; de Oliveira, I.M.; Greggio, S.; Dacosta, J.C.; Guecheva, T.N.; Saffi, J.; Rosa, R.M. DNA damage in organs of mice treated acutely with patulin, a known mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012 50, 3548–3555. [CrossRef]
- Hueza, I.; Raspantini, P.; Raspantini, L.; Latorre, A.; Górniak, S. Zearalenone, an Estrogenic Mycotoxin, Is an Immunotoxic Compound. Toxins 2014, 6, 1080–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovdisova, I.; Zbynovska, K.; Kalafova, A.; Capcarova, M. Toxicological properties of mycotoxin Citrinin. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2016, 5, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, G.S. Current Status of Mycotoxin Analysis: A Critical Review. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, G.S. Chromatographic separation techniques for determination of mycotoxins in food and feed. In Determining Mycotoxins and Mycotoxigenic Fungi in Food and Feed; Saeger, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 71–89. ISBN 978-0-85709-097-3. [Google Scholar]
- Filazi, A.; İnce, S.; Temamoğulları, F. Survey of the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in cheeses produced by dairy ewe’s milk in Urfa city, Turkey. Ankara Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2010, 57, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Tan, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, L.; Shao, K.; Yin, W.; Han, H. Ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 by SERS aptasensor based on exonuclease-assisted recycling amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Jinap, S.; Soleimany, F. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Mycotoxins. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009, 8, 202–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.L.; Fernandes, J.O.; Cunha, S.C. Mycotoxins in cereals and related foodstuffs: A review on occurrence and recent methods of analysis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 96–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orata, F. Derivatization reactions and reagents for gas chromatography analysis. In Advanced Gas Chromatography—Progress in Agricultural, Biomedical and Industrial Applications, 1st ed.; Mohd, M.A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 83–108. ISBN 978-953-51-0298-4. [Google Scholar]
- Anfossi, L.; Giovannoli, C.; Baggiani, C. Mycotoxin detection. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 37, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Liang, G.; Li, A.; Pan, L. Recent Advances in Mycotoxin Determination for Food Monitoring via Microchip. Toxins 2017, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzuman, Z.; Vaclavikova, M.; Polisenska, I.; Veprikova, Z.; Fenclova, M.; Zachariasova, M.; Hajslova, J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in analysis of deoxynivalenol: Investigation of the impact of sample matrix on results accuracy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 406, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.R.G.; Novo, P.; Azevedo, A.M.; Fernandes, P.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Aqueous two-phase systems for enhancing immunoassay sensitivity: Simultaneous concentration of mycotoxins and neutralization of matrix interference. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1361, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.W.; Bramhmbhatt, H.; Szabo-Vezse, M.; Poma, A.; Coker, R.; Piletsky, S.A. Analytical methods for determination of mycotoxins: An update (2009–2014). Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 901, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goryacheva, I.Y.; Saeger, S.D.; Eremin, S.A.; Peteghem, C.V. Immunochemical methods for rapid mycotoxin detection: Evolution from single to multiple analyte screening: A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 24, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogen Veratox®. Available online: http://foodsafety.neogen.com/en/veratox#mycotoxins (accessed on 27 September 2018).
- De Cesare, G.; Nascetti, A.; Scipinotti, R.; Fanelli, C.; Ricelli, A.; Caputo, D. Optoelectronic System for Mycotoxin Detection in Food Quality Control. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 8, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, J.; Siltanen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Revzin, A.; Simonian, A. Biosensor technology: Recent advances in threat agent detection and medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroka, J.; Maragos, C.M. Challenges in the analysis of multiple mycotoxins. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Barfidokht, A.; Tehrani, F.; Mishra, R. Food Safety Analysis Using Electrochemical Biosensors. Foods 2018, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tothill, I.E.; Turner, A.P.F. Biosensors. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Caballero, B., Trugo, L., Finglas, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003; pp. 489–499. ISBN 978-0-12-227055-0. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Njumbe Ediage, E.; Wu, S.; Sun, C.; Saeger, S.; Wu, A. Multiplex Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Mycotoxin Determination. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4995–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, Z. Recent developments and applications of surface plasmon resonance biosensors for the detection of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rubaye, A.; Nabok, A.; Catanante, G.; Marty, J.L.; Takács, E.; Székács, A. Label-Free Optical Detection of Mycotoxins Using Specific Aptamers Immobilized on Gold Nanostructures. Toxins 2018, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dou, X.W.; Zhang, C.; Logrieco, A.; Yang, M.H. A Review of Current Methods for Analysis of Mycotoxins in Herbal Medicines. Toxins 2018, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, D.F.D.L.; Oliveira, M.D.S.; Furlong, E.B.; Junges, A.; Paroul, N.; Valduga, E.; Cansian, R.L. Evaluation of the TLC quantification method and occurrence of deoxynivalenol in wheat flour of southern Brazil. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wei, R.; Logrieco, A.F.; Wei, J.; Wen, J.; Xiao, X.; Yang, M. Occurrence of toxigenic fungi and determination of mycotoxins by HPLC-FLD in functional foods and spices in China markets. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Covarelli, L.; Beccari, G.; Colasante, V.; Mañes, J. Simultaneous analysis of twenty-six mycotoxins in durum wheat grain from Italy. Food Control 2016, 62, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanjer, M.C.; Rensen, P.M.; Scholten, J.M. LC–MS/MS multi-method for mycotoxins after single extraction, with validation data for peanut, pistachio, wheat, maize, cornflakes, raisins and figs. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2008, 25, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosa, J.; Graziani, G.; Gaspari, A.; Chianese, D.; Ferrer, E.; Mañes, J.; Ritieni, A. Multi-Mycotoxin Analysis in Durum Wheat Pasta by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2017, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouafifssa, Y.; Manyes, L.; Rahouti, M.; Mañes, J.; Berrada, H.; Zinedine, A.; Fernández-Franzón, M. Multi-Occurrence of Twenty Mycotoxinsin Pasta and a Risk Assessment in the Moroccan Population. Toxins 2018, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urusov, A.; Zherdev, A.; Petrakova, A.; Sadykhov, E.; Koroleva, O.; Dzantiev, B. Rapid Multiple Immunoenzyme Assay of Mycotoxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levasseur-Garcia, C. Updated Overview of Infrared Spectroscopy Methods for Detecting Mycotoxins on Cereals (Corn, Wheat, and Barley). Toxins 2018, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasiewicz, M.J.; Falade, T.D.O.; Mutuma, M.; Mutiga, S.K.; Harvey, J.J.W.; Fox, G.; Pearson, T.C.; Muthomi, J.W.; Nelson, R.J. Multi-spectral kernel sorting to reduce aflatoxins and fumonisins in Kenyan maize. Food Control 2017, 78, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, M. Inorganic and Organic Solution-Processed Thin Film Devices. Nano-Micro Lett. 2017, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitzi, D.B. Thin-Film Deposition of Organic−Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3283–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.A.; Bergren, A.J.; Porter, M.D. Chemically Modified Electrodes. In Handbook of Electrochemistry, 1st ed.; Zoski, C., Ed.; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 295–327. ISBN 9780080469300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, M.; Chaubey, A.; Malhotra, B. Application of conducting polymers to biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Datta, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Prospects of Nanomaterials in Biosensors. Anal. Lett. 2008, 41, 159–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.R.; Kaushik, A.; Agrawal, V.V.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanostructured metal oxide-based biosensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2011, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Kaushik, A.; Solanki, P.; Malhotra, B. Sol–gel derived nanoporous cerium oxide film for application to cholesterol biosensor. Electrochem Commun. 2008, 10, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Solanki, P.R.; Datta, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Recent advances in self-assembled monolayers based biomolecular electronic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2810–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohanka, M.; Jun, D.; Kuca, K. Mycotoxin Assays Using Biosensor Technology: A Review. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 30, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhand, S.; Kanungo, L.; Pal, S. Chemiluminescence and fluorescence optical biosensor for the detection of aflatoxin in food. In Food Biosensors; Ahmed, M.U., Zourob, M., Tamiya, E., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 161–181. ISBN 978-1-78262-390-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Guo, X. Advances in Biosensors, Chemosensors and Assays for the Determination of Fusarium Mycotoxins. Toxins 2016, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtugyn, G.; Subjakova, V.; Melikishvili, S.; Hianik, T. Affinity Biosensors for Detection of Mycotoxins in Food. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 263–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Ping, J. Recent progress in application of nanomaterial-enabled biosensors for ochratoxin A detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P. Mycotoxin Determination in Foods Using Advanced Sensors Based on Antibodies or Aptamers. Toxins 2016, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Weng, B.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.M.; Yu, C. Aptamer induced assembly of fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots on gold nanoparticles for sensitive detection of AFB 1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tothill, I. Biosensors and nanomaterials and their application for mycotoxin determination. World Mycotoxin J. 2011, 4, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloglazova, N.V.; Speranskaya, E.S.; Wu, A.; Wang, Z.; Sanders, M.; Goftman, V.V.; De Saeger, S. Novel multiplex fluorescent immunoassays based on quantum dot nanolabels for mycotoxins determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Ma, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Multiplexed Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Aptasensor between Upconversion Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide for the Simultaneous Determination of Mycotoxins. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6263–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, F.; Sberna, C.; Petrucci, G.; Reverberi, M.; Domenici, F.; Fanelli, C.; Caputo, D. Aptamer-based sandwich assay for on chip detection of Ochratoxin A by an array of amorphous silicon photosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rubaye, A.; Nabok, A.; Catanante, G.; Marty, J.L.; Takacs, E.; Szekacs, A. Detection of ochratoxin A in aptamer assay using total internal reflection ellipsometry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, N.M.; Bostan, H.B.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Youssefi, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Karimi, G. Ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 and its major metabolite aflatoxin M1 using aptasensors: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 99, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, D.; de Cesare, G.; Fanelli, C.; Nascetti, A.; Ricelli, A.; Scipinotti, R. Innovative Detection System of Ochratoxin A by Thin Film Photodiodes. Sensors 2007, 7, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, D.; de Cesare, G.; Fanelli, C.; Nascetti, A.; Ricelli, A.; Scipinotti, R. Amorphous Silicon Photosensors for Detection of Ochratoxin a in Wine. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 2674–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No 123/2005 of 26 January 2005 amending Regulation (EC) No 466/2001 as regards ochratoxin A (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, L25, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sabet, F.S.; Hosseini, M.; Khabbaz, H.; Dadmehr, M.; Ganjali, M.R. FRET-based aptamer biosensor for selective and sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 in peanut and rice. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, D.; Lei, J. Sample-pretreatment-free based high sensitive determination of aflatoxin M1 in raw milk using a time-resolved fluorescent competitive immunochromatographic assay. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodnik, V.; Anderluh, G. Toxin Detection by Surface Plasmon Resonance. Sensors 2009, 9, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, M.A. Optical biosensors in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J. Small Molecule Immunosensing Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. Sensors 2010, 10, 7323–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J. Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors for Detection of Chemical and Biological Species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, D.; Muriana, P.M. Immunomagnetic bead-based recovery and real time quantitative PCR (RT iq-PCR) for sensitive quantification of aflatoxin B1. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 86, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnedenko, O.V.; Mezentsev, Y.V.; Molnar, A.A.; Lisitsa, A.V.; Ivanov, A.S.; Archakov, A.I. Highly sensitive detection of human cardiac myoglobin using a reverse sandwich immunoassay with a gold nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 759, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieringer, J.A.; McFarland, A.D.; Shah, N.C.; Stuart, D.A.; Whitney, A.V.; Yonzon, C.R.; Young, M.A.; Zhang, X.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: New materials, concepts, characterization tools, and applications. Faraday Discuss. 2006, 132, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X. Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunoassay for Ochratoxin A Based on Nanogold Hollow Balls with Dendritic Surface. Anal. Lett. 2007, 40, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todescato, F.; Antognoli, A.; Meneghello, A.; Cretaio, E.; Signorini, R.; Bozio, R. Sensitive detection of Ochratoxin A in food and drinks using metal-enhanced fluorescence. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Reiner-Rozman, C.; Hageneder, S.; Dubiak-Szepietowska, M.; Dostálek, J.; Feller, K.H. Fast and sensitive detection of ochratoxin A in red wine by nanoparticle-enhanced SPR. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 937, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Dubiak-Szepietowska, M.; Vorobii, M.; Rodriguez-Emmenegger, C.; Dostálek, J.; Feller, K.H. Sensitive and rapid detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk utilizing enhanced SPR and p(HEMA) brushes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinçkaya, E.; Kınık, Ö.; Sezgintürk, M.K.; Altuğ, Ç.; Akkoca, A. Development of an impedimetric aflatoxin M1 biosensor based on a DNA probe and gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3806–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radoi, A.; Targa, M.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Marty, J.L. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) based on superparamagnetic nanoparticles for aflatoxin M1 detection. Talanta 2008, 77, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakouz, T.; Tesler, A.B.; Bendikov, T.A.; Vaskevich, A.; Rubinstein, I. Highly Stable Localized Plasmon Transducers Obtained by Thermal Embedding of Gold Island Films on Glass. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3893–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatynskyi, A.M.; Lopatynska, O.G.; Guo, L.J.; Chegel, V.I. Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor—Part I: Theoretical study of sensitivity—Extended Mie approach. IEEE Sens. 2011, 11, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabok, A.V.; Tsargorodskaya, A.; Hassan, A.K.; Starodub, N.F. Total internal reflection ellipsometry and SPR detection of low molecular weight environmental toxins. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 246, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Radecka, H.; Radecki, J. Electrochemical biosensors for food analysis. Monatshefte fur Chemie 2009, 140, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.C.; Bonel, L.; Ezquerra, A.; Hernández, S.; Bertolín, J.R.; Cubel, C.; Castillo, J.R. Electrochemical affinity biosensors for detection of mycotoxins: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campàs, M.; Garibo, D.; Prieto-Simón, B. Novel nanobiotechnological concepts in electrochemical biosensors for the analysis of toxins. Analyst 2012, 137, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Electroanalytical biosensors and their potential for food pathogen and toxin detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors—Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohanka, M.; Skladal, P. Electrochemical biosensors-principles and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2008, 6, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Laschi, S.; Centi, S.; Mascini, M. Electrochemical arrays coupled with magnetic separators for immunochemistry. Bioanal. Rev. 2010, 3, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhouati, A.; Bulbul, G.; Latif, U.; Hayat, A.; Li, Z.H.; Marty, J. Nano-Aptasensing in Mycotoxin Analysis: Recent Updates and Progress. Toxins 2017, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Goud, K.; Hayat, A.; Bhand, S.; Marty, J. Recent Advances in Electrochemical-Based Sensing Platforms for Aflatoxins Detection. Chemosensors 2016, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, K.Y.; Kalisa, S.K.; Kumar, V.; Tsang, Y.F.; Lee, S.; Gobi, K.V.; Kim, K.H. Progress on nanostructured electrochemical sensors and their recognition elements for detection of mycotoxins: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, F.J.; Granero, A.M.; Fernández, H.; Raba, J.; Zón, M. ACitrinin (CIT) determination in rice samples using a micro fluidic electrochemical immunosensor. Talanta 2011, 83, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.O.; Tothill, I.E. Development of an electrochemical immunosensor for aflatoxin M1 in milk with focus on matrix interference. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2452–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chao, Y.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Pang, X.; Fan, D.; Wei, Q. A label-free amperometric immunosensor for detection of zearalenone based on trimetallic Au-core/AgPt-shell nanorattles and mesoporous carbon. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 847, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for simple and sensitive determination of aflatoxin B1 in wheat. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 115, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dridi, F.; Marrakchi, M.; Gargouri, M.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Dzyadevych, S.; Vocanson, F.; Saulnierb, J.; Renault, N.J.; Lagarde, F. Thermolysin entrapped in a gold nanoparticles/polymer composite for direct and sensitive conductometric biosensing of ochratoxin A in olive oil. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatkin, O.O.; Burdak, O.S.; Sergeyeva, T.A.; Arkhypova, V.M.; Dzyadevych, S.V.; Soldatkin, A.P. Acetylcholinesterase-based conductometric biosensor for determination of aflatoxin B1. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.R.; Kaushik, A.; Manaka, T.; Pandey, M.K.; Iwamoto, M.; Agrawal, V.V.; Malhotra, B.D. Self-assembled monolayer based impedimetric platform for food borne mycotoxin detection. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.K.; Hayat, A.; Catanante, G.; Ocaña, C.; Marty, J.L. A label free aptasensor for Ochratoxin A detection in cocoa beans: An application to chocolate industries. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 889, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istamboulié, G.; Paniel, N.; Zara, L.; Granados, L.R.; Barthelmebs, L.; Noguer, T. Development of an impedimetric aptasensor for the determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Talanta 2016, 146, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, G.; Pal, S.; Kanungo, L.; Bhand, S. A label-free silver wire based impedimetric immunosensor for detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhang, W. A novel impedimetric aptasensor based on AuNPs–carboxylic porous carbon for the ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28655–28660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evtugyn, G.; Porfireva, A.; Stepanova, V.; Kutyreva, M.; Gataulina, A.; Ulakhovich, N.; Evtugyn, V.; Hianik, T. Impedimetric Aptasensor for Ochratoxin A Determination Based on Au Nanoparticles Stabilized with Hyper-Branched Polymer. Sensors 2013, 13, 16129–16145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Quesada-González, D.; Zamora-Gálvez, A.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Merkoçi, A. Label-Free Impedimetric Aptasensor for Ochratoxin-A Detection Using Iridium Oxide Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5167–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunday, C.; Masikini, M.; Wilson, L.; Rassie, C.; Waryo, T.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E. Application on Gold Nanoparticles-Dotted 4-Nitrophenylazo Graphene in a Label-Free Impedimetric Deoxynivalenol Immunosensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 3854–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foguel, M.; Furlan Giordano, G.; de Sylos, C.; Carlos, I.; Pupim Ferreira, A.; Benedetti, A.; Yamanaka, H. A Low-Cost Label-Free AFB1 Impedimetric Immunosensor Based on Functionalized CD-Trodes. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, M.; Floroian, L.; Restani, P.; Cobzac, S.C.A.; Moga, M. Ochratoxin A Detection on Antibody- Immobilized on BSA-Functionalized Gold Electrodes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameil, S.; Schubert, P.; Grundmann, P.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E. Use of 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid as electron donating compound in a potentiometric aflatoxin M1-immunosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 661, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadjou, R.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Heidar-poor, M.; Shadjou, N. Electrochemical monitoring of aflatoxin M1 in milk samples using silver nanoparticles dispersed on α-cyclodextrin-GQDs nanocomposite. J. Mol. Recognit. 2018, 31, e2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.J.; Shuai, H.L.; Chen, Y.X. Layered molybdenum selenide stacking flower-like nanostructure coupled with guanine-rich DNA sequence for ultrasensitive ochratoxin A aptasensor application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X.; Xue, J.; Luo, M.; Xu, X.; Chen, S.; Qiu, J.F. Electrochemical immunosensor using single-walled carbon nanotubes/chitosan for ultrasensitive detection of deoxynivalenol in food samples. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2016, 46, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Seenivasan, R.; Wang, Y.C.; Yu, J.H.; Gunasekaran, S. An Electrochemical Immunosensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Mycotoxins Fumonisin B1 and Deoxynivalenol. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, R. A novel electrochemical immunosensor for ochratoxin A with hapten immobilization on thionine/gold nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.G.; Castro, M.; Machado, S.; Barroso, M.F.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for ochratoxin A detection in food samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Shen, G.; Wang, S.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Electrochemical immunosensor based on Pd–Au nanoparticles supported on functionalized PDDA-MWCNT nanocomposites for aflatoxin B1 detection. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 494, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Baeumner, A.J.; Feller, K.H. Rapid and sensitive inhibition-based assay for the electrochemical detection of Ochratoxin A and Aflatoxin M1 in red wine and milk. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 243, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, G.; Spinella, K.; Poturnayová, A.; Šnejdárková, M.; Mosiello, L.; Hianik, T. Detection of aflatoxin B 1 by aptamer-based biosensor using PAMAM dendrimers as immobilization platform. Food Control 2015, 52, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirinçci, Ş.; Ertekin, Ö.; Laguna, D.; Özen, F.; Öztürk, Z.; Öztürk, S. Label-Free QCM Immunosensor for the Detection of Ochratoxin A. Sensors 2018, 18, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Haupt, K.; Feller, K.H. Development of a QCM-D biosensor for Ochratoxin A detection in red wine. Talanta 2017, 166, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Tang, D.; Zhang, J.; Tang, D. Novel quartz crystal microbalance immunodetection of aflatoxin B1 coupling cargo-encapsulated liposome with indicator-triggered displacement assay. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1031, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).