Fluorescence and Naked-Eye Detection of Pb2+ in Drinking Water Using a Low-Cost Ionophore Based Sensing Scheme
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Experimental
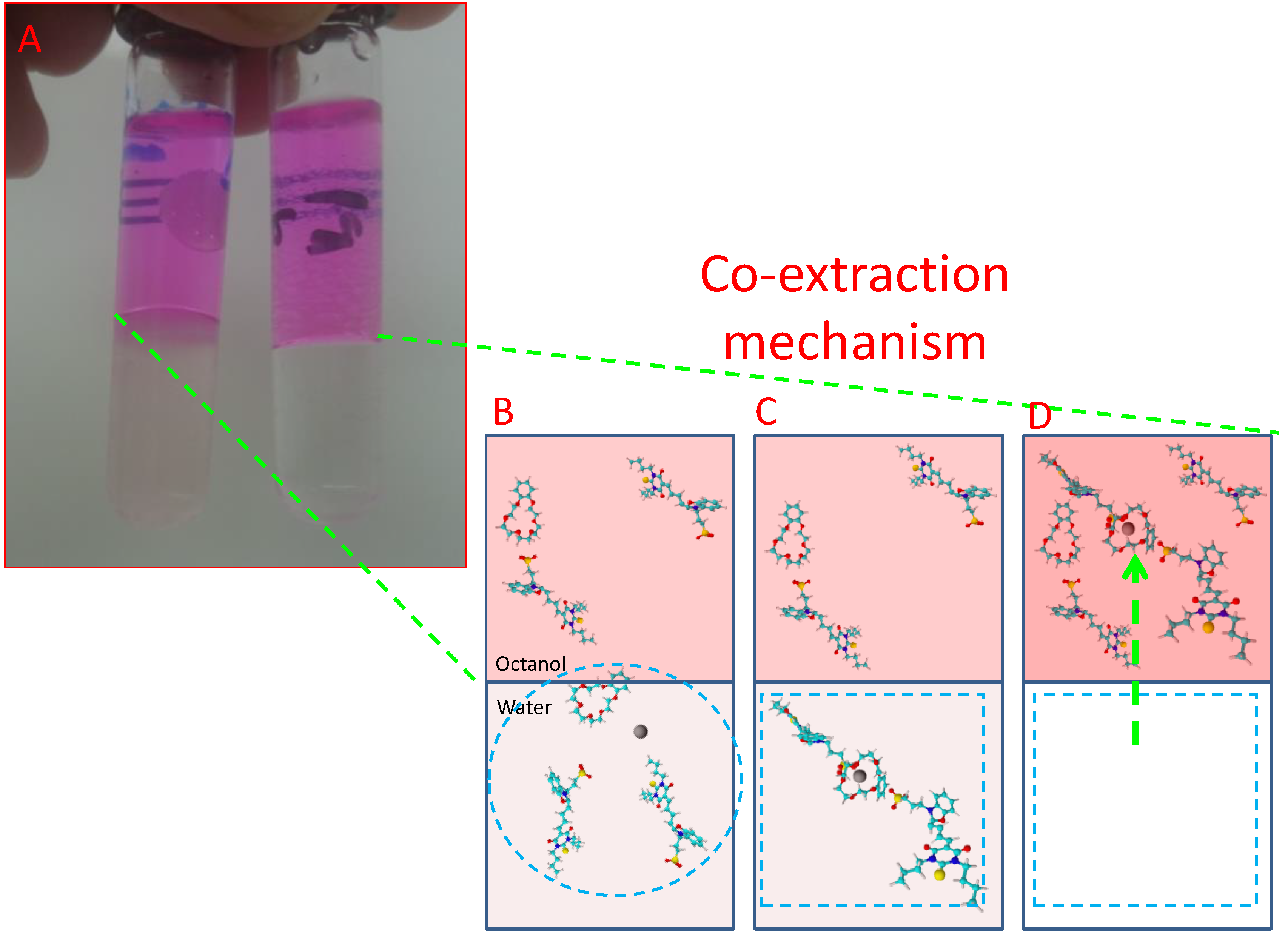
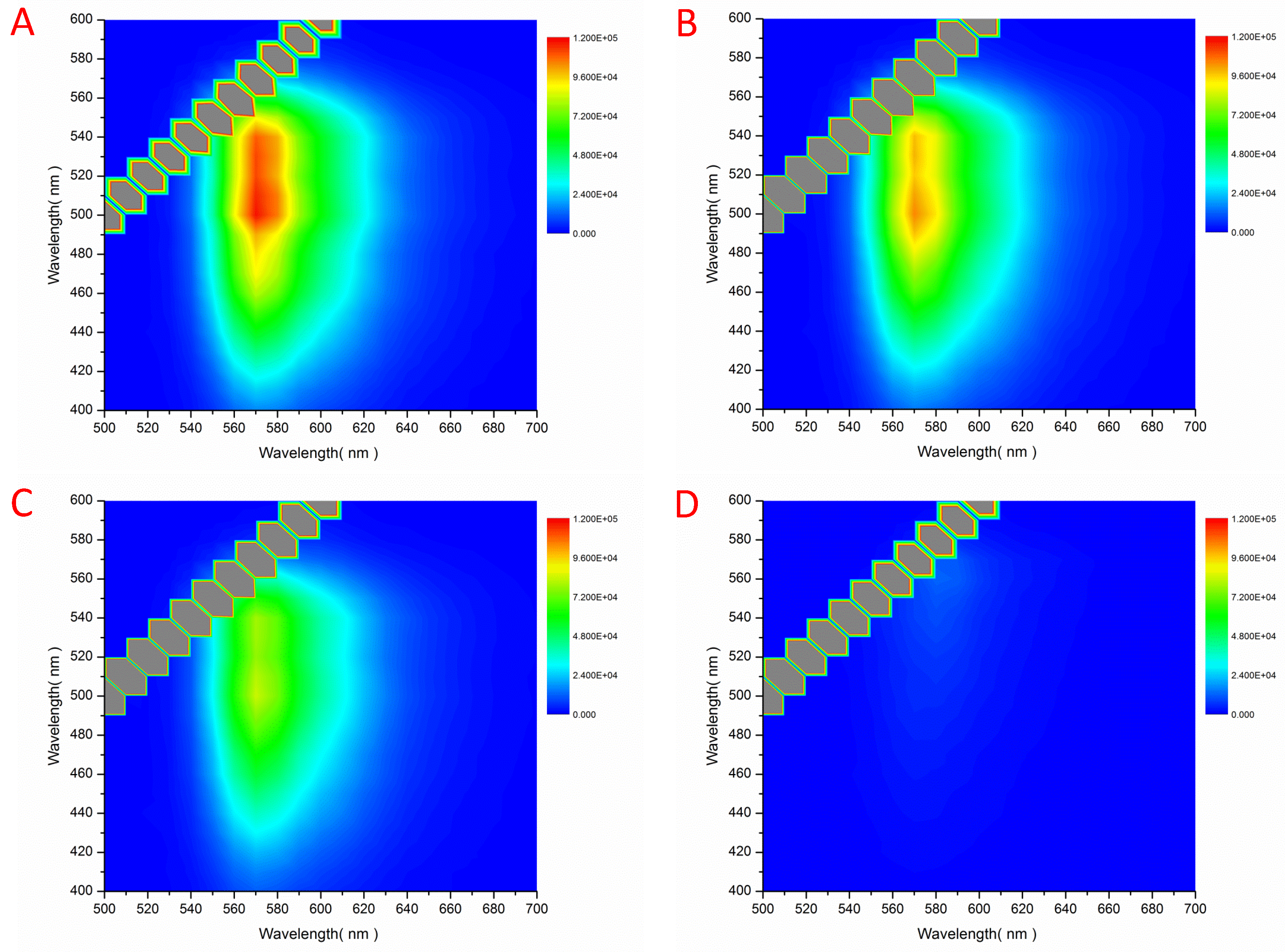
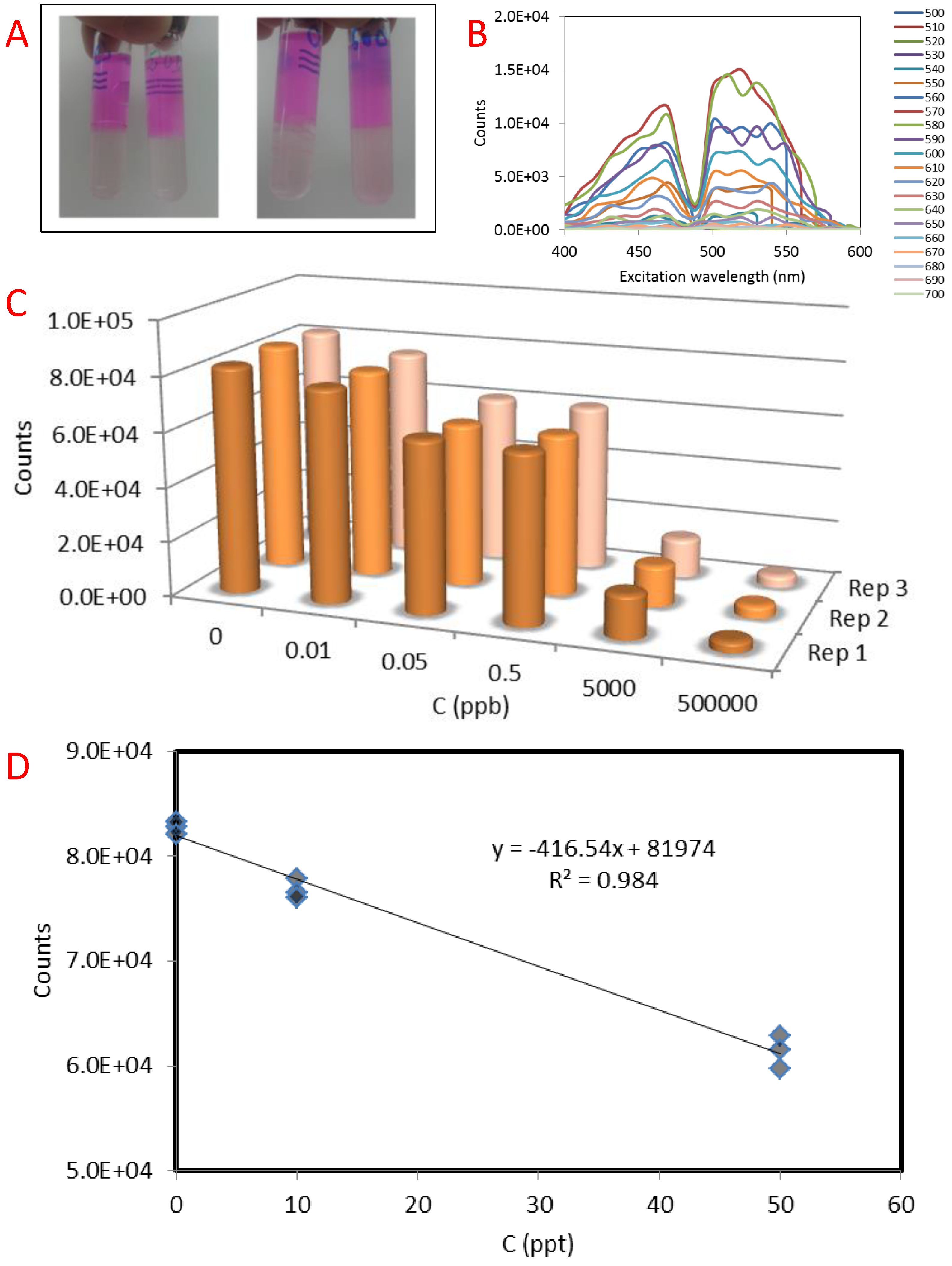
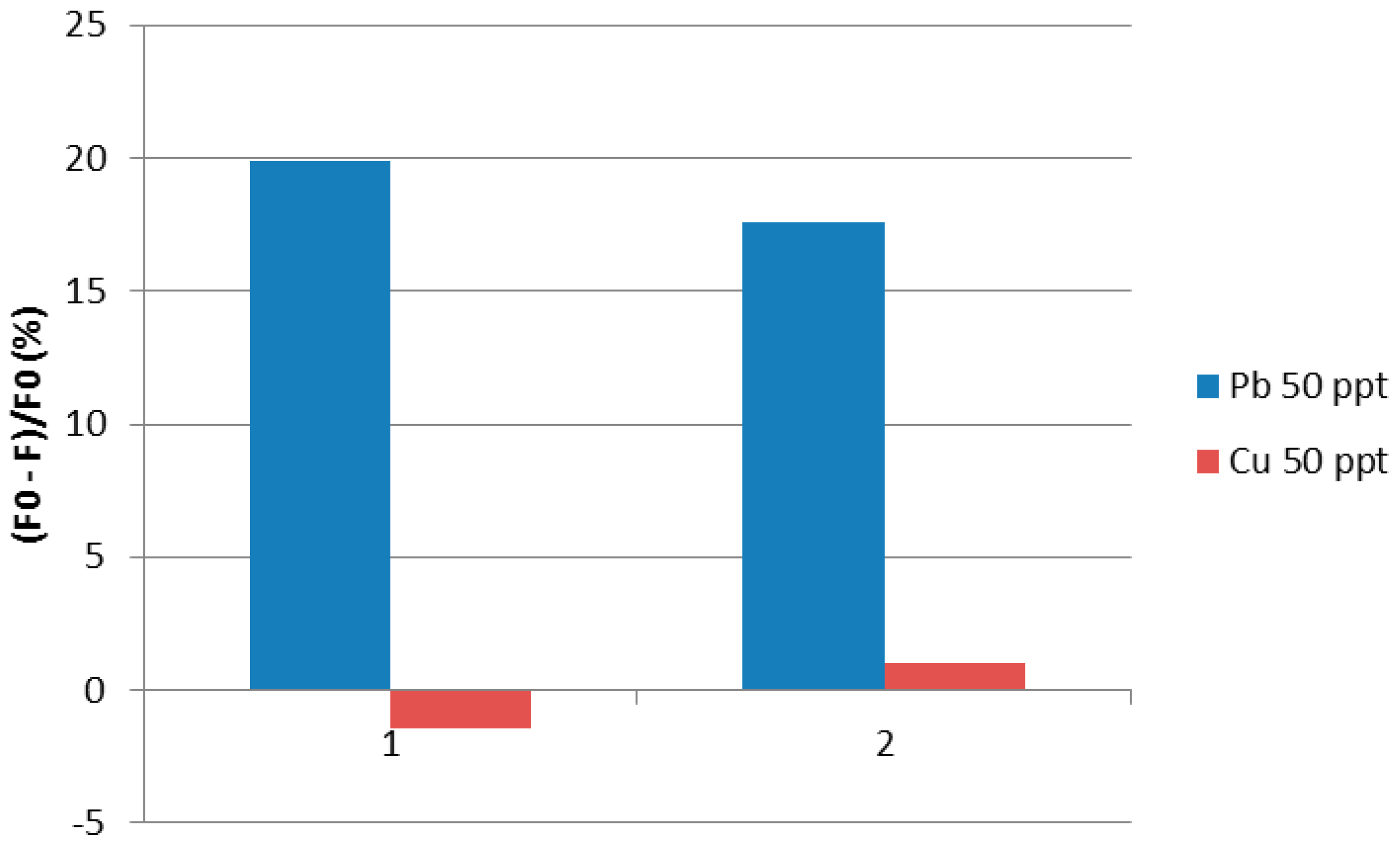
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maity, A.; Sui, X.; Tarman, C.R.; Pu, H.; Chang, J.; Zhou, G.; Ren, R.; Mao, S.; Chen, J. Pulse-Driven Capacitive Lead Ion Detection with Reduced Graphene Oxide Field-Effect Transistor Integrated with an Analyzing Device for Rapid Water Quality Monitoring. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, É.F.; Augusto, A.D.S.; Pereira-Filho, E.R. Chemometric evaluation of Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni (inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry) and Pb (graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry) concentrations in lipstick samples intended to be used by adults and children. Talanta 2016, 150, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnarathorn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Dungchai, W. Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of lead using maleic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 2015, 132, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Yerga, D.; Álvarez-Martos, I.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Henry, C.S.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Point-of-need simultaneous electrochemical detection of lead and cadmium using low-cost stencil-printed transparency electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 981, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šrámková, I.H.; Horstkotte, B.; Fikarová, K.; Sklenářová, H.; Solich, P. Direct-immersion single-drop microextraction and in-drop stirring microextraction for the determination of nanomolar concentrations of lead using automated Lab-In-Syringe technique. Talanta 2018, 184, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Ali, A.; Jamal, R.; Xiang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Abdiryim, T.; Ding, S.; Ali, A.; Jamal, R.; Xiang, L.; et al. An Electrochemical Sensor of Poly(EDOT-pyridine-EDOT)/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Composite for Simultaneous Detection of Cd2+ and Pb2+. Materials 2018, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, C.; Dai, Y.; Liu, C.C. A Simple, Cost-Effective Sensor for Detecting Lead Ions in Water Using Under-Potential Deposited Bismuth Sub-Layer with Differential Pulse Voltammetry (DPV). Sensors 2017, 17, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finšgar, M.; Majer, D.; Maver, U.; Maver, T. Reusability of SPE and Sb-Mmodified SPE Sensors for Trace Pb(II) Determination. Preprints 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.; Xing, C.; Hao, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. Rapid and highly sensitive detection of lead ions in drinking water based on a strip immunosensor. Sensors 2013, 13, 4214–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna-Attisha, M.; LaChance, J.; Sadler, R.C.; Schnepp, A.C. Elevated Blood Lead Levels in Children Associated With the Flint Drinking Water Crisis: A Spatial Analysis of Risk and Public Health Response. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Lead and Copper Rule. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/dwreginfo/lead-and-copper-rule (accessed on 26 May 2018).
- Lead in Drinking-Water Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/lead.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2018).
- Hakonen, A.; Strömberg, N. Diffusion consistent calibrations for improved chemical imaging using nanoparticle enhanced optical sensors. Analyst 2012, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strömberg, N.; Hakonen, A. Plasmophore sensitized imaging of ammonia release from biological tissues using optodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakonen, A.; Strömberg, N. Plasmonic nanoparticle interactions for high-performance imaging fluorosensors. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakonen, A. Plasmon enhancement and surface wave quenching for phase ratiometry in coextraction-based fluorosensors. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakonen, A. Fluorescence ratiometric properties induced by nanoparticle plasmonics and nanoscale dye dynamics. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, E.J.; Blondeau, P.; Crespo, G.A.; Rius, F.X. An effective nanostructured assembly for ion-selective electrodes. An ionophore covalently linked to carbon nanotubes for Pb2+ determination. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2438–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Sun, C.; Sun, X. Screening highly selective ionophores for heavy metal ion-selective electrodes and potentiometric sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 220, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, D.A.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Principles of Instrumental Analysis; Cengage Learning, Inc.: Mason, OH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, C.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. Label free detection of lead using impedimetric sensor based on ordered mesoporous carbon–gold nanoparticles and DNAzyme catalytic beacons. Talanta 2016, 146, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Deng, D.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, B.; Xu, C. Ultrasensitive detection of lead ions based on a DNA-labelled DNAzyme sensor. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-W.; Liu, C.-W.; Chang, H.-T. Fluorescence detection of mercury(II) and lead(II) ions using aptamer/reporter conjugates. Talanta 2011, 84, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, G. A Sensitive and Label-Free Pb(II) Fluorescence Sensor Based on a DNAzyme Controlled G-Quadruplex/Thioflavin T Conformation. Sensors 2016, 16, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakonen, A.; Strömberg, N. Fluorescence and Naked-Eye Detection of Pb2+ in Drinking Water Using a Low-Cost Ionophore Based Sensing Scheme. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040051
Hakonen A, Strömberg N. Fluorescence and Naked-Eye Detection of Pb2+ in Drinking Water Using a Low-Cost Ionophore Based Sensing Scheme. Chemosensors. 2018; 6(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakonen, Aron, and Niklas Strömberg. 2018. "Fluorescence and Naked-Eye Detection of Pb2+ in Drinking Water Using a Low-Cost Ionophore Based Sensing Scheme" Chemosensors 6, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040051
APA StyleHakonen, A., & Strömberg, N. (2018). Fluorescence and Naked-Eye Detection of Pb2+ in Drinking Water Using a Low-Cost Ionophore Based Sensing Scheme. Chemosensors, 6(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6040051




