Abstract
Air pollution and the emission of toxic gases represent a critical global concern, posing significant threats to human health and environmental stability. Resistive gas sensors are widely employed to detect toxic gases, owing to their cost-effectiveness, high stability, sensitivity, and swift dynamics. Among various sensing materials, comparatively less attention has been paid to CeO2 despite its good catalytic activity and high stability. In this review paper, we are focusing on CeO2 gas sensors in pristine, doped, decorated, and composite forms. Using numerous examples, we have shown the great potential of CeO2 for gas sensing. The main features of CeO2 as a gas sensor include excellent environmental stability, the abundance of oxygen vacancies, high mechanical strength, cost-effectiveness, and good catalytic activity. However, low electrical conductivity is the main shortage of CeO2 as a gas sensor. With a high emphasis on the sensing mechanism, we believe that this review paper is highly useful for researchers working in this field.
1. Introduction
Rare earth (RE) oxides have special properties due to the presence of the 4f shell in RE elements. Cerium has the highest abundance among REs (~0.0046 wt% of the Earth’s crust), and it is the least expensive RE element with a ground state valence configuration of 4f15d16 s2 [1,2]. Two common oxides of Ce are Ce2O3 and CeO2. CeO2 with a pale-yellow color has a fluorite structure where eight O2− anions are coordinated around each Ce4+ cation at the corners of a cube, with each O2− coordinated by a tetrahedron of four Ce4+ ions [3]. More details about the structural properties of CeO2 can be found in [4].
The main point defects in CeO2 are cerium vacancy () and oxygen vacancy () and interstitial Ce () and oxygen defects () [5]. Among them, oxygen vacancies are the most important defects for gas sensing applications, resulting in the formation of non-stoichiometric cerium oxide or ceria (CeO2−x; 0 < x < 0.28), which is an n-type semiconductor with Eg around 2.8–3.1 eV [6]. Oxygen vacancies in CeO2−x can be formed by reduction of Ce4+ to Ce3+, with the formation of oxygen vacancies as follows [7]:
There are many non-stoichiometric CeO2−x phases such as CeO1.65, CeO1.717, CeO1.775, CeO1.812 [8]. The ionic radius of Ce3+ (115 pm) is larger than that of Ce4+ (101 pm), which leads to lattice expansion relative to stoichiometric CeO2 [9]. Oxygen vacancy, derived from the reduction of Ce4+ to Ce3+, has a promising effect on the electrical and gas sensing features of CeO2 [10]. CeO2 has good mechanical properties, high thermal stability, high ionic conductivity, and photoluminescence in the UV-vis range. It is noteworthy that, despite its high ionic conductivity, CeO2−x exhibits low conductivity at low temperatures.
CeO2 is widely used in photocatalysts due to redox characteristics caused by Ce3+/Ce4+ transitions, capacity for oxygen storage, and the presence of oxygen vacancies [11]. In particular, CeO2 is employed in three-way catalysts in car exhaust to decrease the emission of CO, NOx, and hydrocarbons from automobiles, owing to its oxygen vacancies and low redox potential between Ce3+ and Ce4+ associated with oxygen vacancies [12]. Vacancies with high mobility are reactive sites for oxygen activation in CeO2 and are critically important for the oxygen storage [13]. Apart from catalyst applications of CeO2 [14], it is used in the realization of UV blocking and shielding devices, due to its high absorption cross-section on UV light and high stability upon exposure to UV irradiation [15]. Other applications include corrosion protective coating [16], biomedical applications [17], photodetectors [18], solar cells [19], batteries [20], and supercapacitors [21]. In particular, CeO2 has also been used in the realization of various types of gas sensors, including electrochemical [22,23], optical [24], plasmonic [25], surface acoustic wave [26], impedance [27], resistive [28,29], and triboelectric nanogenerator [30] gas sensors. Also, due to lower phonon energy and high luminescence quantum yields, CeO2 is used in cataluminescence gas sensors [31]. Like most of the semiconducting metal oxides [32,33], CeO2 has good potential for the realization of gas sensors. The main features of CeO2 as a material for the realization of gas sensors are cost-effectiveness, excellent environmental stability, the abundance of oxygen vacancies, high mechanical stability, and good catalytic activity. However, low electrical conductivity is the main shortage of CeO2 as a gas sensor.
As indicated in Table S1 [34], resistive gas sensors are among the best types of gas sensors due to their high sensitivity, high stability, fast response time, and low cost. To our knowledge, there is no review paper on the gas sensing properties of CeO2. This review paper explains different aspects of CeO2-based resistive gas sensors for the first time. Also, we have included the results of some theoretical studies. The ongoing advancements in sophisticated supercomputers and the improvement of computational power have led to a better understanding of the properties of materials. Given that gas sensor reactions involve adsorption, reaction, and desorption phenomena, in which the bonds are formed or broken, usually accompanied by charge transfer, quantum methods are excellent in examining gas–surface interactions, as they effectively model adsorption mechanisms, calculate adsorption energy, analyze charge transfer, and assess electronic modifications and structural changes following gas adsorption. In this context, density functional theory (DFT) calculations stand out as a robust technique for simulating the gas-sensing capabilities of various materials without adverse effects. DFT is essential for interpreting experimental results at the molecular level and serves as a predictive tool for designing new sensing materials [35,36,37,38].
2. General Gas Sensing Mechanism of Resistive Gas Sensors
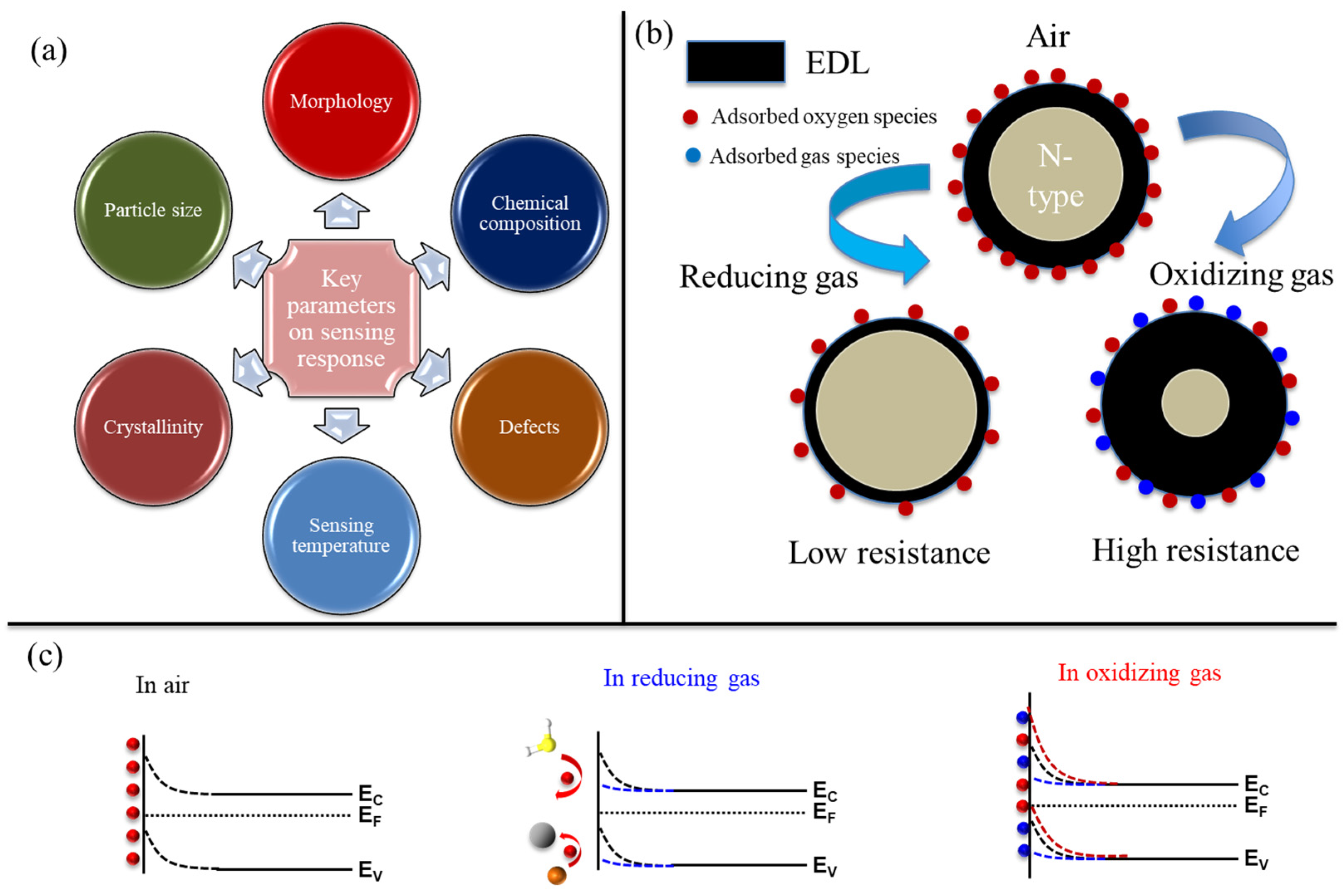
Like most other gas sensors, such as quartz crystal microbalance [39], in resistive gas sensors, the target gas should be adsorbed on the sensor surface to be sensed; hence, morphology is a key parameter in gas sensors. Obviously, the morphologies with higher surface area are more beneficial for gas sensing applications as they provide more adsorption sites for gas molecules. Furthermore, chemical composition is another affecting parameter on the gas response. In particular, in nanocomposites, interfaces between two materials act as powerful sources of resistance modulation. Defects are another parameter in boosting gas response. They act as favorable sites for gas species, and in this regard, oxygen vacancies are highly favorable for the adsorption of oxygen gas at high temperatures. Sensing temperature itself affects the sensing response, as high temperatures generally increase the rates of gas diffusion and sensing reactions, leading to a higher sensing response. However, the rate of desorption is also high at higher temperatures, and this leads to the occurrence of maximum net adsorption at a particular temperature, known as the optimal sensing temperature. Crystallinity is another important factor, as highly crystalline materials can better provide the pathways for the flow of charge carriers. Finally, the particle size of the sensing material should be considered. When the particle size is very fine, the whole particle can be depleted of electrons in the air, and by exposing it to a reducing gas, a significant amount of resistance modulation occurs, resulting in the appearance of a high sensing signal. These factors are summarized in Figure 1a. When an n-type metal oxide such as CeO2 is exposed to air, the oxygen with high electron affinity can be adsorbed on the surface of the sensor, resulting in the creation of an electron depletion layer (EDL) where the concentration of electrons is much lower relative to the core region of the sensor. Upon exposure to a reducing gas, it reacts with adsorbed oxygen species, resulting in the release of electrons. Thus, the width of EDL significantly decreases, and this is reflected in a reduction in resistance. In contrast, when an n-type gas sensing is exposed to an oxidizing gas, further electrons are abstracted from the sensor surface, resulting in an expansion of EDL and an increase in resistance. (Figure 1b). Also, corresponding band diagrams are depicted in Figure 1c, where band bending decreases and increases in the presence of reducing and oxidizing gases, respectively [40,41].
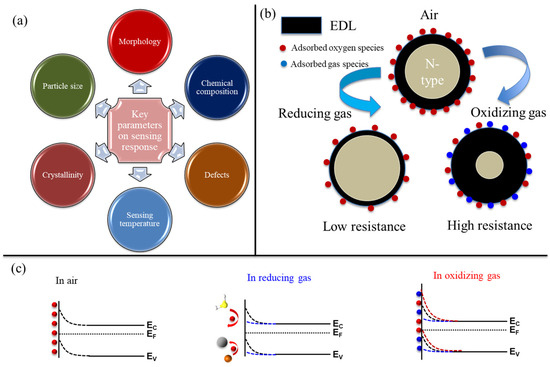
Figure 1.
(a) Main parameters affecting the sensing performance of gas sensors. (b) Changes in the thickness of the EDL of an n-type gas sensor in the presence of reducing and oxidizing gases. (c) Corresponding band diagrams.
3. CeO2-Based Resistive Gas Sensors
3.1. Pristine CeO2 Gas Sensors
Pristine CeO2 gas sensors have been employed for the detection of various gases, including NH3 [42], oxygen [43], H2 [44], and other gases. Notably, operating a gas sensor at RT not only significantly increases its stability but also significantly decreases power consumption, which is crucial from an energy-saving perspective. Therefore, Li et al. [45] synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles (NPs) using a hydrothermal approach at 180 °C for 48 h and subsequently annealed them at 800, 900, and 1000 °C. The NPs annealed at 900 °C had the highest total amount of oxygen vacancies and adsorbed oxygen species. Also, the band gap values of the CeO2 NPs annealed at the above-mentioned temperatures were 3.28, 3.18, and 3.30 eV, respectively. Among all sensors, the sensor annealed at 900 °C displayed the largest response (Ra/Rg) of 23 to 500 ppm NH3 gas at room temperature (RT). This improvement was primarily due to the existence of oxygen vacancies, leading to the adsorption of a significant amount of oxygen, and hence, more sensing reactions occurred. In another research, Li et al. [46] synthesized CeO2 nanorods (NRs) NPs (8–12 nm), and (NSs) (100–140 nm) by the solvothermal method at 100 °C for 24 h and at 160 °C for 8 h, respectively. At 100 °C, the response (Ra/Rg) of CeO2 NRs gas sensor to 1000 ppm H2 gas was ~6, while that of CeO2 NPs gas sensor was only 3. The enhanced performance was attributed to the availability of more adsorption sites on CeO2 NRs. In fact, the specific surface area (SSA) values of NRs and NPs were 21 and 3.5 m2/g, respectively, resulting in providing of more anchoring sites for H2 molecules.
Hussain et al. [47] synthesized CeO2 nanostructures using a hydrothermal route at 160 °C for 12 and 24 h. The SSA of the samples prepared for 12 and 24 h (polyhedron nanostructures) was 65 and 99 m2/g, respectively. The sensor prepared for 24 h indicated a response (Ra/Rg) of 150 to 100 ppm TEA at 100 °C. The sensing mechanism was attributed to high SSA, providing numerous sites for gas adsorption. Furthermore, the exposed facets in the optimal sensor were favorable sites for gas adsorption, and they also accelerated the adsorption of gas molecules. Meanwhile, the dissociation energy of HCHO was less than that of interfering gases, indicating the ease of breaking the C-H-O bond and dissociating into smaller molecules, which then undergo oxidation on the sensor surface.
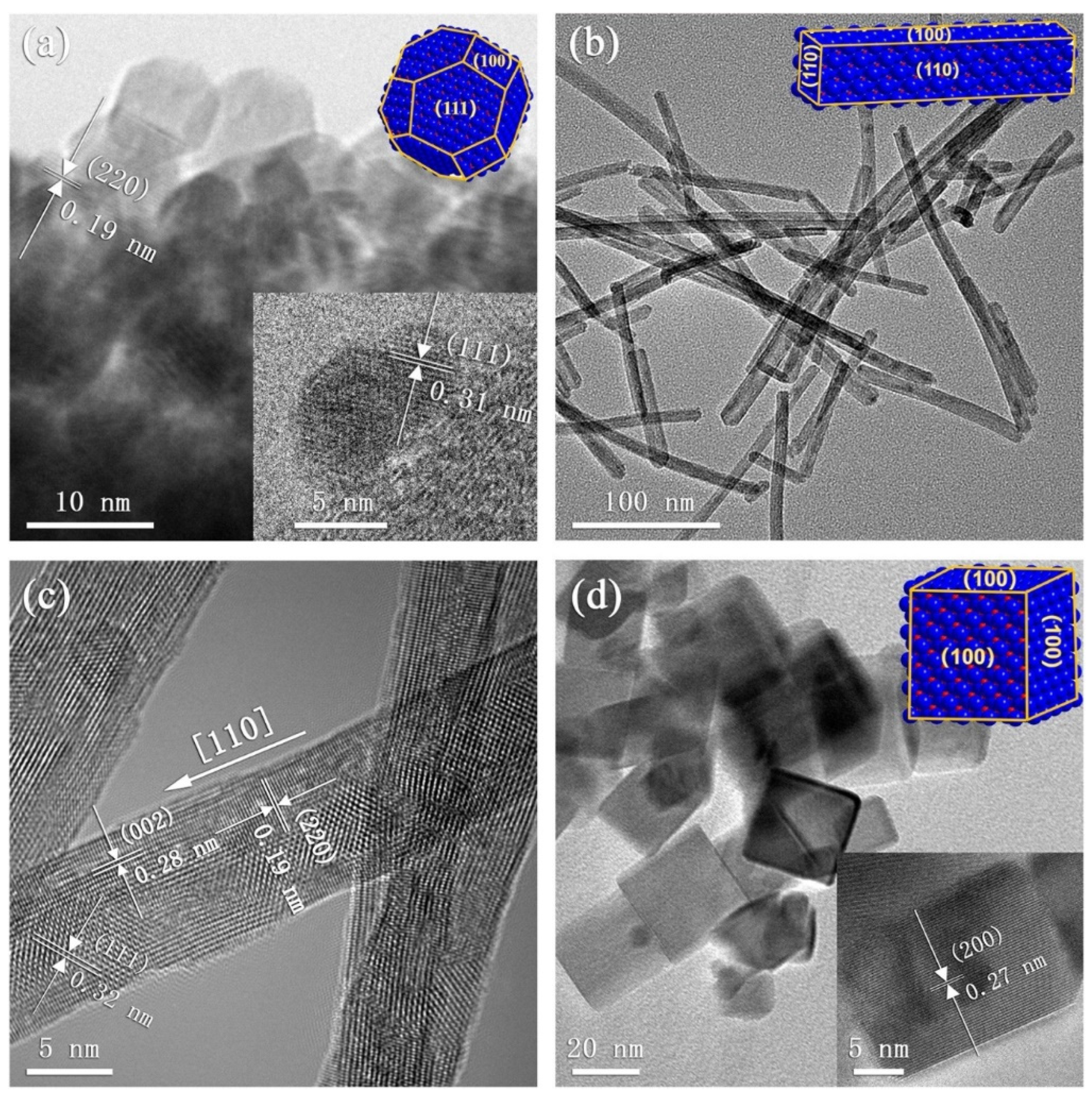
Polar facets of CeO2 are highly effective in accelerating the adsorption of oxygen and enhancing the gas response. Bi et al. [48] synthesized CeO2 nanopolyhedra, NRs, and nanocubes (NCs) by a hydrothermal reaction at 100 °C in the presence of different amounts of NaOH (Figure 2a–d). Amounts of oxygen vacancies in nanopolyhedra, NRs, and NCs were 32.7, 33.8, and 34.7%, respectively. Also, SSA of nanopolyhedra, NRs, and NCs were estimated to be 110.60, 101.70, and 27.25 m2/g, respectively. At 300 °C, the response (Ra/Rg) of gas sensors fabricated from nanopolyhedra, NRs, and NCs was 10, 2, and 150, respectively, to 100 ppm dimethylamine (DMA). In case of {100} and {111} facets, only cerium atoms are terminated in the planes; however, each Ce atom on the {100} facet has two dangling bonds, while in the {111} facet, it has only one dangling bond. This led to a higher adsorption capacity of {100} facets compared to {111} ones. Also, the amount of oxygen vacancies was higher in {100} relative to {110} and {111} nonpolar facets. Furthermore, the stability of {100} was lower than that of {111} and {110} facets, reflecting the higher selectivity of {100} facets towards gas adsorption. Therefore, in the optimal sensor, there were a greater number of exposed {100} facets, along with a higher content of oxygen vacancies, giving rise to a higher response to gas (Table 1).
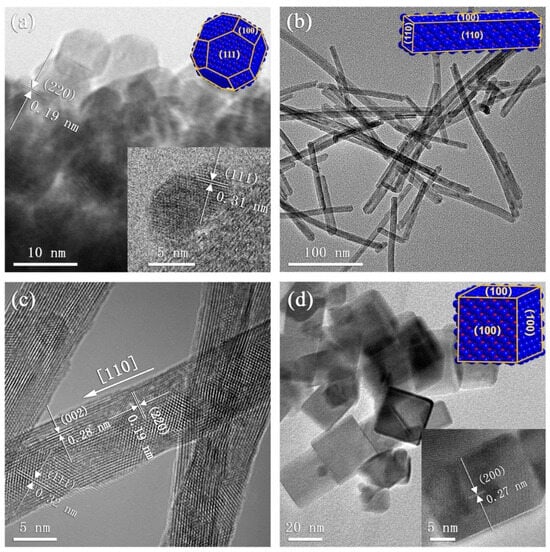
Figure 2.
TEM images of CeO2 (a) nanopolyhedra, (b) NRs, and (d) NCs, (c) HRTEM image of NRs. With permission from Elsevier. Copyright (2021).

Table 1.
Comparison of features of different facets in CeO2.
Hollow nanostructures have the advantage of high SSA, in which both inside and outside of the nanostructure are suitable sites for gas adsorption. Lyu et al. [49] synthesized hollow CeO2 microspheres (300 nm) using a hydrothermal approach at 130 °C for 24 h using a SiO2 template. At 260 °C, the sensor gave a response [(ΔR)/Ra) × 100] of 270% to 100 ppm acetone. The SSA of synthesized powders was 137 m2/g, providing numerous sites for acetone gas adsorption. Based on DFT calculations, the band gap of the sensor was modulated from 2.75 eV to 1.90 eV upon exposure to acetone, due to the transfer of electrons from acetone to the sensor.
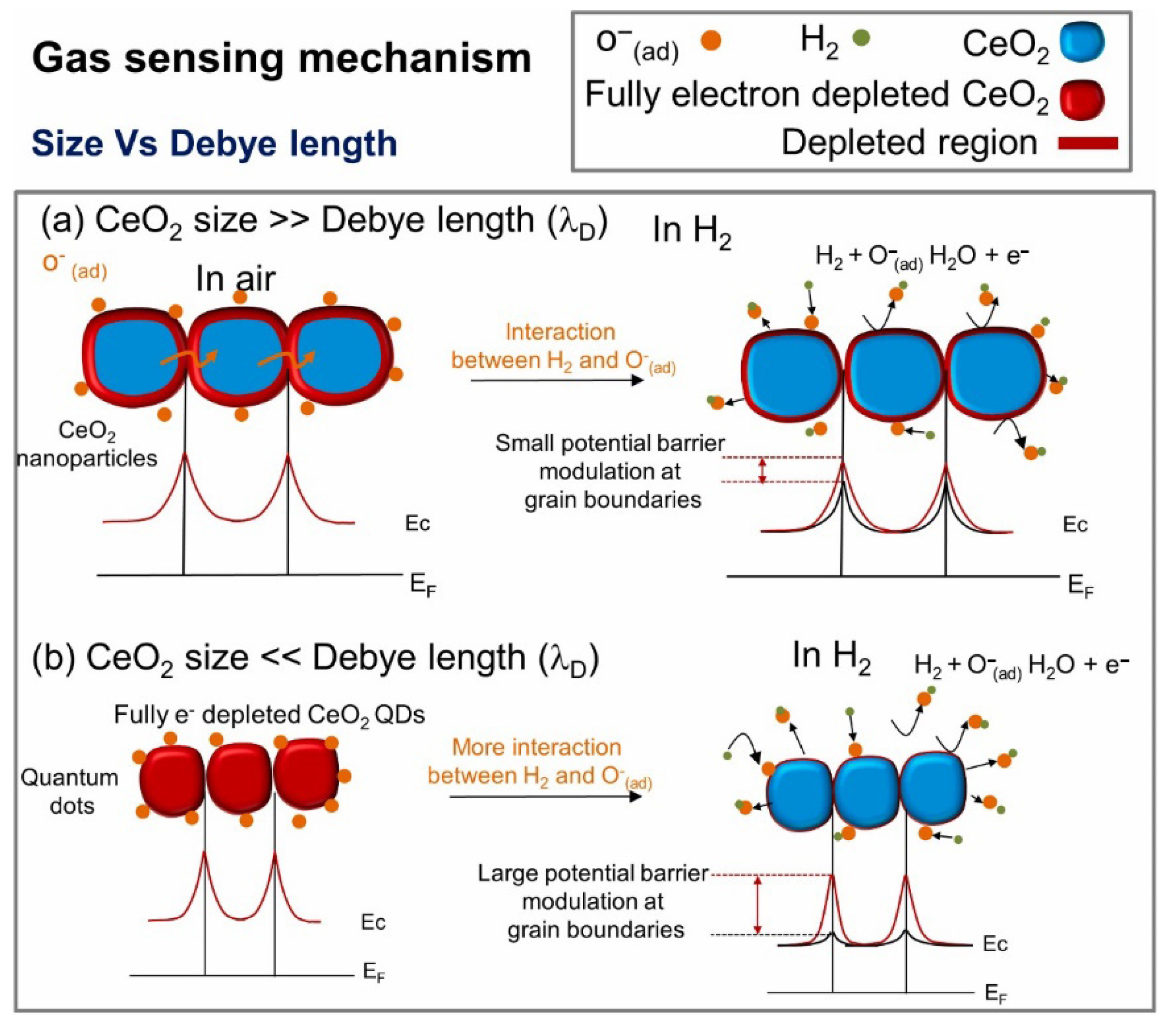
Quantum dots (QDs) with ultrafine size and unique electrical properties are highly promising for sensing applications [50]. Rohit et al. [51] synthesized CeO2 quantum dots (QDs), nanopebbles, with sizes of 3, 15, and 30 nm, respectively, using a hydrothermal approach at 110 °C for 5 h. Among fabricated sensors, the sensor fabricated from CeO2 QDs revealed a response (Ra/Rg) of 4.2 to 10 ppm H2 gas at 220 °C. It was related to the formation of more homojunctions between CeO2 QDs relative to other morphologies. Furthermore, the size of CeO2 QDs was smaller than the Debye length of CeO2, resulting in depletion of the entire QDs in the presence of air, and by exposure to H2 gas, a remarkable modulation of resistance led to large resistance modulation in the presence of gas relative to other gas sensors (Figure 3).
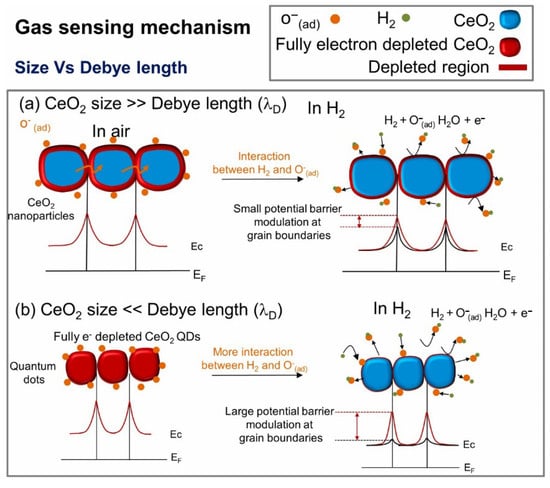
Figure 3.
H2 gas sensing mechanism of CeO2 QDs. (a) Limited changes in the EDL of CeO2 when the size of CeO2 NPs is larger than that of the Debye length. (b) Significant changes in the EDL of CeO2 when the size of CeO2 NPs is smaller than that of the Debye length. With permission from Elsevier. Copyright (2024).
3.2. Doped CeO2 Gas Sensors
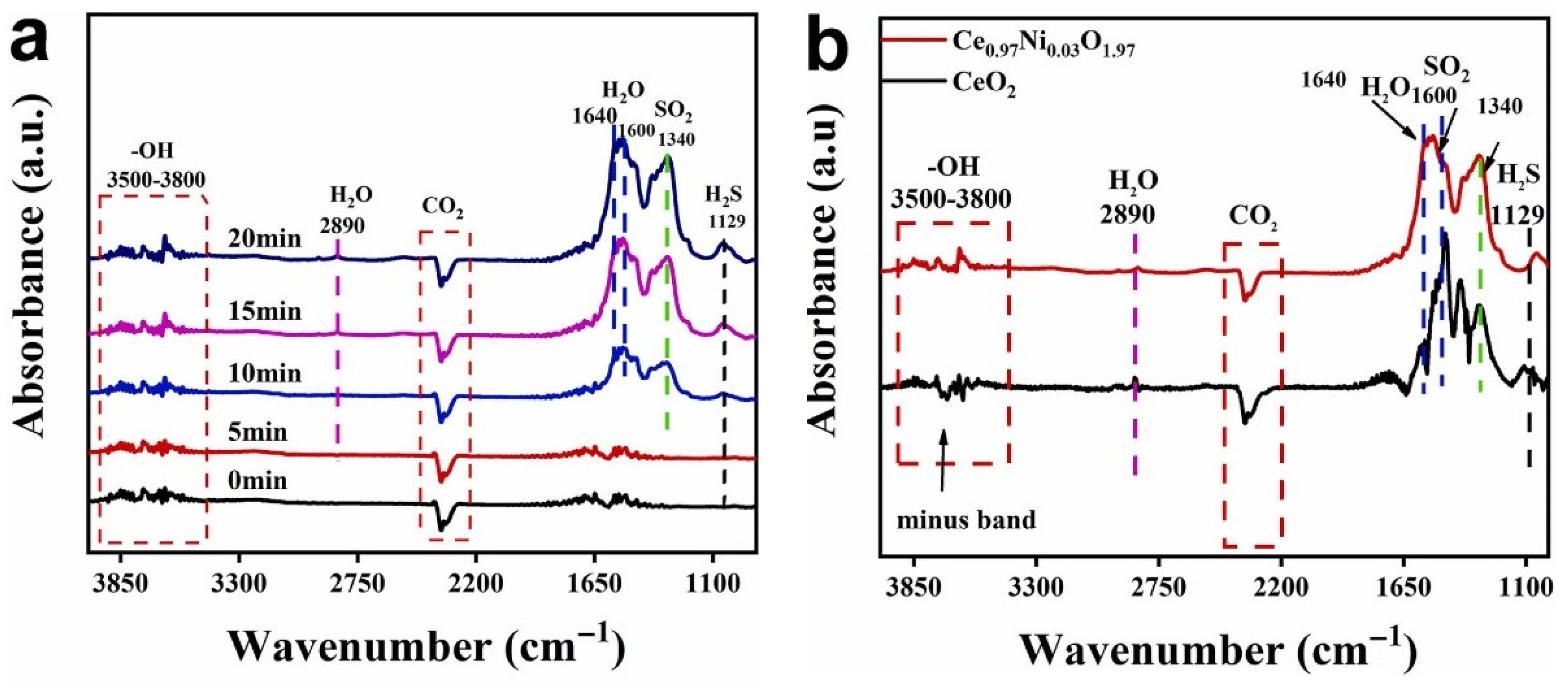
Doping of cations with different valences into the CeO2 lattice causes the formation of structural defects. For instance, when acceptor cations are doped into the CeO2 lattice, oxygen vacancies are formed to maintain charge neutrality [52]. Dong et al. [53] synthesized Ni-doped CeO2 flower-like structures through a precipitation method. The samples were coded as Ce1−xNixO2−x, where x = 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.06. The size of pristine CeO2 flower-like structures was 3 µm, and upon Ni2+ doping, lattice distortion and contraction occurred, which eventually changed the initial morphology of CeO2. At 200 °C, the sensor with a composition of Ce0.97Ni0.03O1.97 revealed an enhanced response (Ra/Rg) of 3.2 to 500 ppb H2S gas. While SSA of pristine CeO2 was 49 m2/g, it increased to 66 m2/g for the optimal gas sensor. With Ni doping, the number of Ce3+ increased while that of Ce4+ decreased, which eventually led to formation of more oxygen vacancies. They acted a favorable site for oxygen gas adsorption at sensing temperature. In situ DRIFTS measurement (Figure 4a,b) confirmed that H2S diffused into the sensing layer and adsorbed onto the basic sites to produce S2− ions. Subsequently, they were oxidized to SO2 by Ni3+ with the formation of Ni2+ and oxygen vacancies. In next step, Ni2+ was oxidized, and oxidation of Ce3+ to Ce4+ occurred by oxygen gas. Based on DFT calculations, H2S had lower energy to be adsorbed on the {110} facet of the gas sensor.
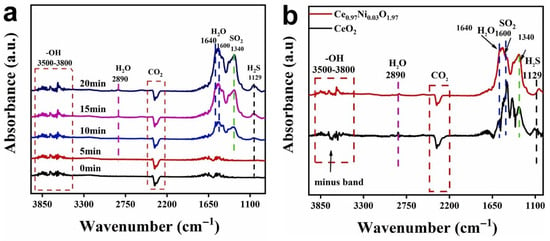
Figure 4.
(a) In situ DRIFTS of H2S absorption at 200 °C on Ce0.97Ni0.03O1.97 during 20 min (b) In situ DRIFTS spectra of H2S absorption on CeO2 and Ce0.97Ni0.03O1.97 at 200 °C [53]. With permission from Elsevier. Copyright (2022).
Tofu with low-fat and high-protein is easily deteriorated during storage, with the release of NH3. Thus, monitoring of NH3 released during storage is a reliable way to evaluate the freshness of Tofu [54]. In-doped CeO2 nanostructures were obtained using a hydrothermal approach at 160 °C for 12 h [55]. As a result of In-doping, oxygen vacancies were generated inside the CeO2 lattice. The sensor gave an ultra-high response (Ra/Rg) of 5412.93 to 1000 ppm NH3 gas at RT. Also, little change was observed in the response in a highly humid environment. Furthermore, the sensor had very fast dynamics, with a response time and recovery time of 1.3 and 1.4 s, respectively. Based on the DFT study, the In-doped CeO2 sensor had the highest adsorption energy for NH3, relative to other gases. Furthermore, NH3 had the highest net charge transfer due to the polarity of the gas. The authors tested the sensor against tofu stored at 4 °C, 27 °C, and 37 °C every 5 h, and it successfully detected increased emission of NH3 from tofu over time.
Wu et al. [56] obtained pristine and Ce-doped (0.17, 0.43, and 0.85 at%) TiO2 nanostructures using a hydrothermal route at 120 °C for 1 h. The SSA of the samples with 0, 0.17, and 0.43 at% Ce-doping were 213.2, 148.7, and 267 m2/g, respectively. The sensor with 0.43 at% Ce-doping yielded a response (Ra/Rg) of 25 to 20 ppm NH3 at RT, surpassing that of the pristine sensor by more than five times. The improved response was not only related to the high SSA of the sensor but also due to the presence of the largest amount of oxygen vacancies in the optimal sensor. During the spoilage process, fish’s fatty acids will be decomposed, and NH3 can be released from the fish. The authors successfully detected the release of NH3 from fish stored at RT. In another study [57] related to Al-doped CeO2, the enhanced response to NO2 gas was due to the generation of oxygen vacancies as a result of Al-doping.
Tungsten, a refractory metal due to its high valence and small ionic radius (rW6+ = 62 pm), can be doped into CeO2 to adjust the Ce3+/Ce4+ ratio, which increases the amount of oxygen vacancies, resulting in enhanced gas sensing output. Duan et al. [58] synthesized W6+-doped (1–12 at%) CeO2 NPs using a hydrothermal route at 160 °C for 24 h. After doping, the morphology remained unchanged, while the porous nature increased. In particular, the SSA (96.32 m2/g) of 7 at% W6+-CeO2 was higher than that of pristine CeO2 (58.63 m2/g), offering more adsorption sites for gas molecules. W-doping regulated the oxygen vacancies by changing the concentration of Ce3+. For the sample with 7 at%, W6+-doping revealed the highest amount of oxygen vacancies. At 225 °C, the sensor with 7 at% W-doping revealed the highest response (Ra/Rg) of 18.6 to 10 ppm H2S in the presence of 80% RH. Based on DFT calculations, the adsorption energy of H2S on 7 at% W-doped CeO2 was almost four times more negative than that of the pristine sensor, demonstrating higher sensitivity of the doped sensor relative to the pristine sensor. A linear discriminant analysis (LDA) algorithm was constructed for classifying various concentrations of H2S and ethanol. An accuracy of 89% was obtained through cross-validation. Also, as proof of application, a total of 15 breath samples were collected from healthy people, and some of the samples were mixed with 100 ppb of H2S in bags to simulate halitosis in exhaled samples. Furthermore, in some simulated halitosis exhaled samples, 200 ppb of ethanol was mixed. The fabricated device was able to identify the samples containing TEA even in the presence of ethanol with 100% accuracy.
Xylene is a toxic and carcinogenic VOC, and thus, the development of xylene gas sensors is important [59]. Qin et al. [60] developed a series of Ru-doped (0.12–1.16 wt%) CeO2 nanosheets synthesized using a solvothermal method. The incorporation of Ru effectively modulated the morphology from NRs to porous NSs. The WO3/Ru-doped CeO2 bilayer sensor was constructed by using WO3 NFs as the lower sensitive layer and Ru-doped CeO2 as the upper catalytic layer. At 160 °C, the response (Ra/Rg) of the sensor with 0.9 wt% Ru dopant to 5 ppm xylene was 37, which was higher than that of the WO3 NF sensor. The combination of online mass spectrometry and DFT calculations was employed to validate the enhanced sensing performance arising from the synergistic mechanism between the catalytic and sensing materials. In another study [61], it was reported that Ru doping in CeO2 resulted in enhanced response to formaldehyde due to the catalytic effect of Ru and the creation of oxygen vacancies.
Jin et al. [62] synthesized Gd-doped CeO2 NPs using a chemical synthesis method. The responses of the pristine CeO2 gas sensor to 20 ppm H2S gas were 1.542, while the response of the Gd-doped gas sensor to the same gas concentration was 3.489. The enhanced response of the GDC gas sensor to H2S gas was mainly related to the formation of oxygen vacancies as a result of Gd-doping in CeO2, and good selectivity to H2S was attributed to the sensing temperature, the higher reactivity of H2S relative to other gases, and the small bond energy of H-SH.
The production of H2 and the utilization of biomass for sustainable energy conversion and storage require the availability of gas sensors with the ability to discriminate between H2 and CO gases. Baier et al. [63] synthesized mesoporous Cu-doped CeO2 NPs with large SSA and uniform porosity by a nanocasting method. Both Cu and Ce elements existed in both Cu+/Cu2+ and Ce3+/Ce4+ oxidation states. While the pristine CeO2 sensor revealed poor performance without selectivity, the Cu-doped sensor revealed a larger response to CO than to H2 and low cross-sensitivity to humidity. Thus, Cu had a promising role for selective sensing behavior of the gas sensor, due to its high catalytic activity towards CO gas oxidation.
Various dopants have been used in CeO2 gas sensors, and the researchers have reported enhanced gas sensing capability after doping. Mainly related to the creation of oxygen vacancies in the CeO2 lattice. However, no specific dopant has been reported for a specific gas.
3.3. Noble Metal Decorated CeO2 Gas Sensors
Noble metals have high catalytic activity towards the oxidation of gases and VOCs [64]. Thus, noble metals generally enhance the gas sensing properties of CeO2, due to their catalytic effect as well as electronic sensitization [65,66,67,68]. Generally, resistive sensors have weak selectivity, and a good approach to increasing their selectivity is to apply a filter on top of the sensing layer. In physical filters, interfering gases cannot pass through the apertures of the filter, and only desired gas molecules pass through the filter barrier. In fact, filters act as molecular sieves [69]. In contrast, chemical filters either convert interfering gases into inert substances or enhance the activity of the desired gas [70]. Li et al. [71] applied a catalytic filter using Pt-loaded CeO2 over a porous SnO2 layer. The special design avoided the problems of element diffusion and low adhesion caused by the poor contact between the sensitive film and the filter film. The filter was able to oxidize CO and ethanol into CO2 and H2O and activate CH4 during the diffusion process. As a result, it promoted the breakage of C-H bonds in CH4 and enhanced the interaction with SnO2 sensing layer. Optimal sensor with 2 wt% Pt loading in filter layer, revealed a high response (Ra/Rg) of 12.4 to 1000 ppm CH4 at 350 °C. Lower amount of Pt loading cause limited catalytic activity, while higher amount of Pt content led to agglomeration of Pt NPs and again decreased effective catalytic activity of Pt.
Pd is a highly active noble metal for the dissociation of hydrogen gas [72,73]. Wang et al. [74] synthesized CeO2-ZnO NRs composite by a hydrothermal approach at 180 °C for 5 h, and then Pd (0.5, 1.5, and 2.5 wt%) was decorated on it using an impregnation method. At RT, the sensor with 1.5 wt% Pd loading revealed the enhanced response (Ra/Rg) of 300 to 1000 ppm H2 gas. A lower amount of Pd did not provide sufficient catalytic activity, whereas a higher amount resulted in the agglomeration of Pd NPs, a decrease in effective SSA of Pd, and a decrease in catalytic activity. Also, Schottky junctions were formed at interfaces between Pd and CeO2, resulting in the generation of potential barriers for the flow of electrons in air at these interfaces. Upon exposing to acetone and release of electrons, the height of Schottky barriers significantly decrease, resulting in generation of a sensing signal. Meanwhile, Pd can adsorb H2 and form PdHx with different electrical characteristics than metallic Pd.
3.4. Composite CeO2 Gas Sensors
Composite sensors based on intimate contact of CeO2 with other materials have been used for the identification of various gases in different composite systems [75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. Since CeO2 has high resistance at RT, it is difficult to realize pristine CeO2 gas sensors that can operate at RT. Therefore, adding graphene with high conductivity to CeO2 can reduce resistance, and the resultant sensor can work at RT. Naganabonia et al. [84] synthesized graphene-CeO2 nanocomposite and fabricated a sensor on a cellulose paper as substrate, having features such as non-toxicity, low cost, light weight, abundance, biocompatibility, and mechanical flexibility. The synthesized nanocomposite had a flower-like morphology comprised of plenty of nanosheets (NSs). At RT, the sensor showed a response (Ra/Rg) of 1.5% to 10 ppm CO gas with a response time of 120 s and a recovery time of 240 s. Also, the performance of the sensor after bending 300 times under a curvature radius of 10 mm remained unchanged, demonstrating the good flexibility of the sensor. The sensing mechanism was related to the formation of p-n heterojunctions between graphene and CeO2, the high surface area of graphene, and the presence of defects on graphene, acting as favorable sites for gas adsorption. Although the sensor was able to work at RT, its performance was not satisfying for practical applications due to low sensitivity and long dynamics.
Oxygen vacancies are highly beneficial for gas sensing applications; however, their amounts must be optimized to acquire the best sensing performance. Zhang et al. [85] synthesized CeO2-graphene nanocomposite through a hydrothermal approach at 200 °C for 24 h. The response to NO2 increased when the concentration of Ce3+ increased from 14.6 wt% to 50.7 wt%, and then the response decreased. At RT, the optimal sensor exhibited a response [(ΔR)/Ra) × 100] of 10.6% to 5 ppm NO2 gas. According to DFT calculations, when the amount of Ce3+ ions was less than 50.7 wt%, the surface of CeO2 became metallic and the Fermi level shifted upward due to the existence of low-electronegativity Ce3+ ions. This led to a decrease in the height of the Schottky barrier between CeO2 and graphene, improving interfacial charge transfer and boosting the sensor response. However, a deep energy level was induced when the amount of Ce3+ was > 50.7 wt%, and the Fermi level pinning occurred at the interface. It resulted in a decrease in the density of free electrons, giving rise to an increase in the height of the Schottky barrier and a decrease in the gas sensing response.
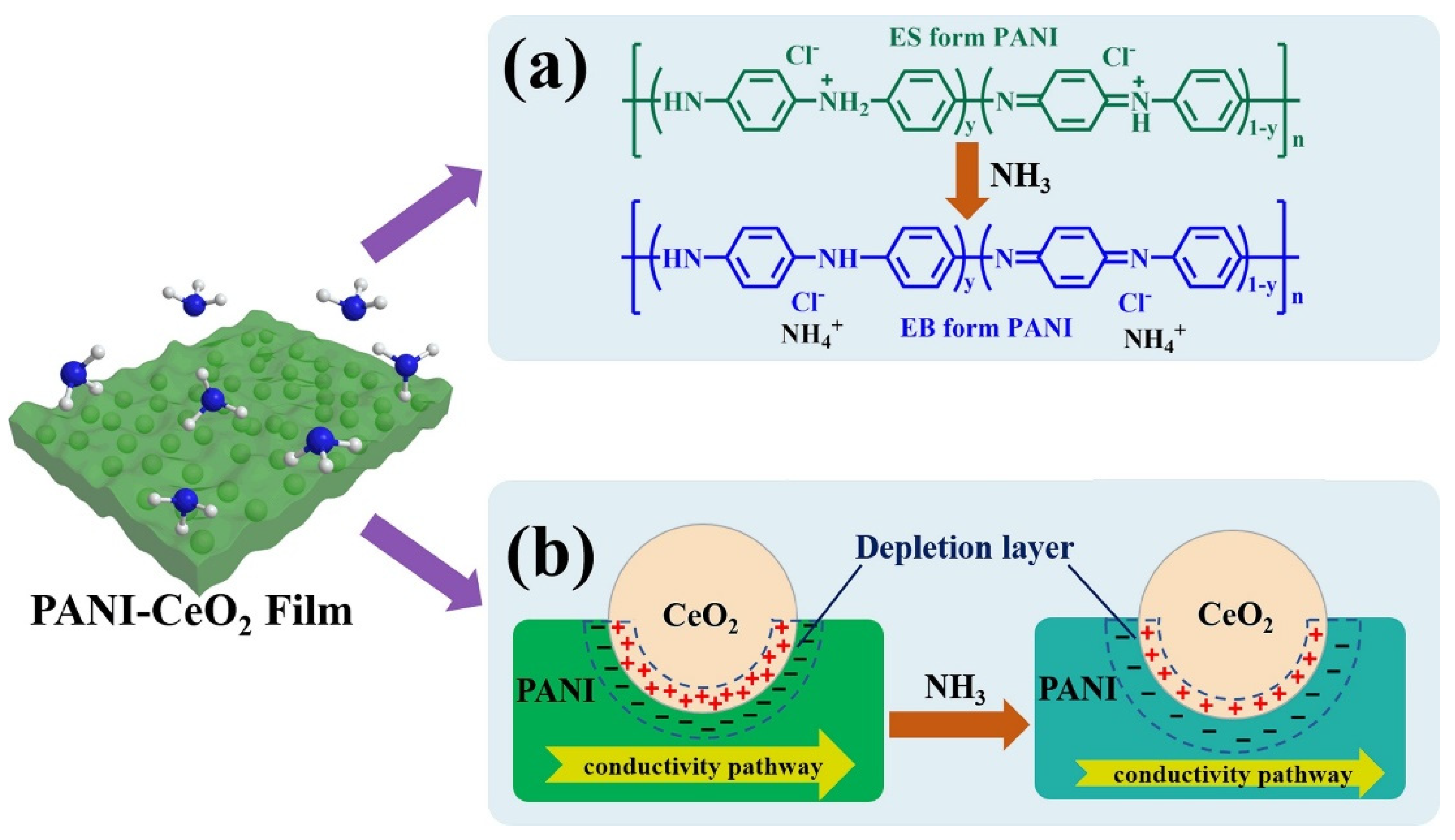
Conducting polymers (CPs) with high electrical conductivity, low density, simple synthesis process, low sensing temperature, and compatibility with flexible substrates are highly popular materials for gas sensing usages [86,87]. Among them, polyaniline (PANI) is highly popular owing to its reversible doping/de-doping, mechanical flexibility, high electrical conductivity, environmental stability, and the ease of synthesis [88]. Accordingly, it has been used in combination with CeO2 for gas sensing purposes [89]. Liu et al. [90] synthesized PANI-CeO2 nanocomposite and prepared a thin film sensor on a flexible polyimide (PI) substrate. CeO2 NPs were wrapped in PANI, resulting in a decrease in agglomeration among them. At RT, the PANI-CeO2 sensor revealed a higher response [(ΔR)/Ra) × 100] of 107% to 10 ppm NH3 than that of the pristine PANI sensor with a response [(ΔR)/Ra) × 100] of 82% to 10 ppm NH3, confirming the promising role of CeO2 NPs for enhanced gas response. Also, after bending for 500 cycles and bending under an angle of 40°, no noticeable changes in the sensing performance was observed, confirming excellent flexibility of the sensor, due to the high mechanical flexibility of PANI and PI substrate as well as good adhesion of sensing layer to substrate through electrostatic interaction which resulted in tightly and uniformly adhesion of film to PI substrate. The NH3 abstracted holes from =NH+—and =NH2+—groups of PANI, resulting in conversion from emeraldine salt (ES) form to emeraldine base (EB) form (Figure 5a), increasing the resistance of the sensor. Furthermore, the modulation of depletion layers in p-n junctions in the presence of NH3 gas remarkably contributed to the improved sensing performance (Figure 5b). The protonation degree of PANI was improved by the addition of CeO2 NPs, which led to an increase in the amount of =NH+ groups, which provided more adsorption sites for NH3 molecules.
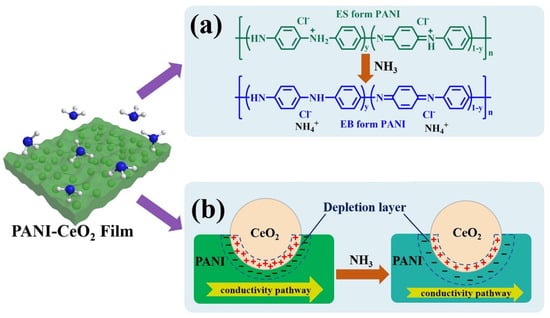
Figure 5.
NH3 gas sensing mechanism. (a) PANI conversion of ES form of PANI to EB form with higher resistance. (b) PANI-CeO2 nanocomposite by modulation of the widths of EDL and HAL on CeO2 and PANI [90]. With permission from Elsevier. Copyright (2018).
As pointed out before, the {100} facet of CeO2 has higher reactivity relative to both {111} and {110} facets, and thus, controlling the growth condition of CeO2 is essential to achieve the highest sensing performance. Ema et al. [91] synthesized {100} CeO2 NCs/SnO2 NSs and {111} CeO2 nanooctahedron/SnO2 NSs composites for gas sensing studies. The {100} facet in CeO2 not only had a higher amount of oxygen vacancies, but also more dangling bonds. Accordingly, it had less stability relative to the {111} facet, facilitating more adsorption of oxygen and gases. At 550 °C, the response (Ra/Rg) of {100} CeO2 NCs/SnO2 NSs gas sensor to 20 ppm acetone was 14.8, while that of {111} CeO2 NCs/SnO2 NSs sensor was only 1.7. The high response was related to the high gas adsorption and enhanced oxidation capacity of the metastable {100} facet of CeO2. Furthermore, heterojunctions between SnO2 and CeO2 were formed, resulting in the generation of potential barriers, acting as robust sources of resistance modulation.
SnO2 is a highly sensitive metal oxide, due to its high mobility of electrons. In this context, Motaung et al. [92] synthesized SnO2-CeO2 nanocomposite via a hydrothermal method at 200 °C for 10 h. The SSA of the synthesized composite was 47 m2/g. The sensor revealed a high response (Ra/Rg) of 1323 to 60 ppm H2 gas at 300 °C. The formation of n-n CeO2-SnO2 heterojunctions and high SSA of the sensor accounted for the enhanced response to H2 gas. Also, plenty of oxygen vacancies resulted in improved adsorption of oxygen and enhanced sensing response. In another study performed by Oosthusian et al. [93], the promising role of oxygen vacancies in the CeO2 gas sensor towards enhancement in response to NO2 and H2S gases was demonstrated.
Generally, the response of a resistive gas sensor decreases in the presence of humidity, and it is a difficult task to obtain a high response in a highly humid environment. In fact, in a highly humid environment, hydroxyl or water molecules can be adsorbed on the surface of the sensor, resulting in a decrease in available sites for incoming gas molecules [94]. Accordingly, the response decreases in the presence of humidity. However, some approaches, such as coating with a hydrophobic layer [95] or defect engineering [96], can decrease the humidity influence on the gas sensing response. Zhu et al. [97] synthesized a hydrophobic CeO2-SnO2 nanocomposite by depositing the CeO2 layers with thicknesses in the nanoscale range onto the SnO2 films through a sputtering method. The sensor manifested high performance in terms of TEA. At 200 °C, it revealed a response (Ra/Rg) of 22.5 to 20 ppm TEA in a highly humid environment. As a proof of study, a portable, wireless sensor was fabricated for the real-time monitoring of TEA released from a spoiled fish.
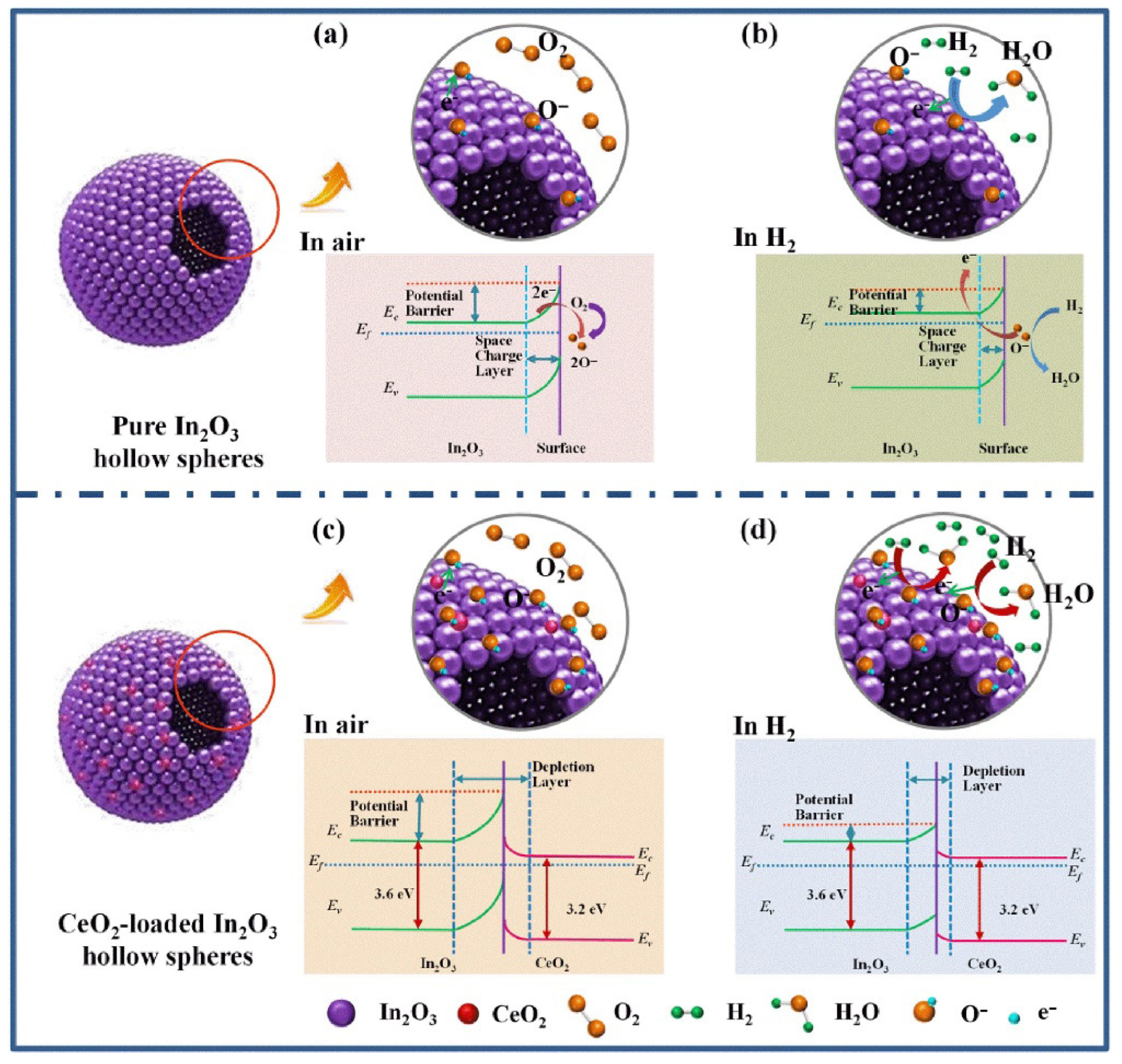
H2 with a flammable and explosive nature is considered a highly efficient and green source of energy, producing only water vapor upon combustion [98]. Nevertheless, it is a colorless, tasteless, and odorless gas that cannot be detected by human senses, highlighting the urgent need for the development of reliable hydrogen gas sensors [99]. Therefore, Hu et al. [100] synthesized CeO2 (0.5–6 at%)-In2O3 hollow composite spheres (diameter 0.5–1.5 μm; wall thickness 20–30 nm) using a hydrothermal route at 160 °C for 12 h. The sensor with 2 at% CeO2 manifested a response (Ra/Rg) of 20.7 to 50 ppm H2 at 160 °C, while that of the pristine sensor was only 6.9. The enhanced response was related to the formation of n-n heterojunctions between CeO2 and In2O3 and the generation of potential barriers at the interface areas. In an H2 atmosphere, the height of potential barriers significantly decreased, contributing to the generation of a sensing signal (Figure 6).
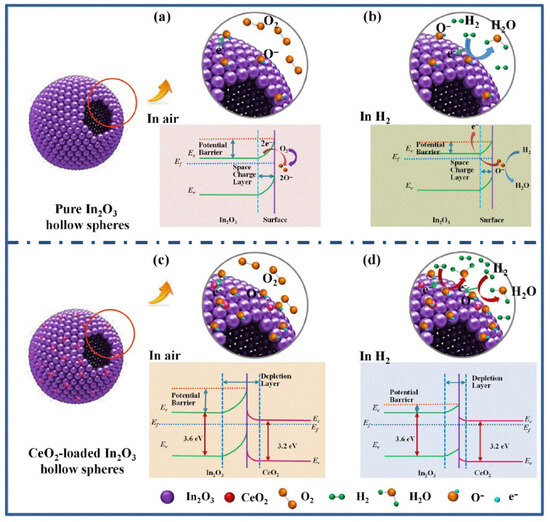
Figure 6.
H2 gas sensing mechanism of pristine hollow In2O3 spheres and CeO2-loaded hollow In2O3 spheres; Schematic presentation of electron transportation and energy band diagrams of pure In2O3 hollow spheres exposed to (a) air, (b) H2 gas ambient, and CeO2-loaded In2O3 hollow spheres to (c) air, (d) H2 gas ambient. With permission from Elsevier. Copyright (2018).
Furthermore, Ce4+ adsorbed the electrons, resulting in the generation of Ce3+ ions and oxygen vacancies as follows:
By subsequent release of electrons via oxygen vacancies, more oxygen species were adsorbed on the sensor surface, and hence, more sensing reactions occurred.
Metal oxides with nanowire (NW) morphology offer a high surface area for gas adsorption and gas sensing reactions. Therefore, Yuan et al. [101] synthesized CeO2 nanodot-decorated WO3 NWs via a hydrothermal route followed by thermolysis. It revealed a response (Ra/Rg) of 1.30 to 500 ppb acetone based on a miniaturized microelectromechanical system device. The improved performance was related to the formation of WO3-CeO2 heterojunctions, the presence of a large amount of oxygen vacancies, large SSA, availability of a large number of adsorption sites, and high conductivity of WO3.
Neri et al. [102] synthesized CeO2-Fe2O3 nanocomposite by a co-precipitation method. Thanks to the lower electronegativity of the Ce4+ ion relative to Fe3+, CeO2 was more basic than Fe2O3. Therefore, the basicity of the nanocomposite increased with the addition of CeO2. At 400 °C, the sensor with 50 mol% CeO2 revealed a response of 4 (Ig/Ia) to 100 ppm methanol. Based on the profile methanol conversion, the Fe2O3 sample completely converted methanol at 230 °C, while the composite sample with 50 mol% CeO2 completely converted methanol at 210 °C. The oxidation of methanol was related to the number of basic sites on the sensor surface. On CeO2-Fe2O3 nanocomposite, methanol molecules at low temperature, adsorbed via oxygen to the coordinatively unsaturated cations (Me = Fe3+, Ce4+) acting as Lewis acids, and the hydrogen of the O–H group adsorbed on lattice oxygen acting as basic sites.
Li et al. [103] synthesized CeO2-(5 and 10 at%) CdS composite NWs with a diameter of 30 nm for gas sensing applications. While CdS showed a response (Ra/Rg) of 20 to 100 ppm acetone gas at 210 °C, 5 at% CeO2 decoration led to a significant enhancement in the response (Ra/Rg) of 52 at 160 °C. The improved performance was related to the formation of CeO2-CdS heterojunctions and high SSA as a result of the decoration of CeO2 on CdS NWs.
Silica (SiO2) can stabilize metal oxide NPs, and due to the presence of numerous hydroxyl groups on the surface of silica, it has a high ability to adsorb water molecules. Wang et al. [104] synthesized SiO2 modified (3, 8, and 14 mol%) CeO2 NPs using a sol–gel method followed by a hydrothermal method at 150 °C for 10 h. Among the fabricated sensors, that with 8 mol% SiO2 revealed a high response [(ΔR)/Ra) × 100] of 3245% to 80 ppm NH3 gas at RT. However, the response time was 750 s and the recovery time was 2750 s, both of which were too long for practical applications. Also, in a humid environment, the response increased with the increase in RH from 30% to 70%. In fact, due to the abundant hydroxyl groups on SiO2, many water vapor molecules were adsorbed on the sensor surface, and subsequently, NH3 gas reacted with water molecules to produce NH4+ and OH− ions, resulting in a decrease in resistance in the presence of humidity.
Resistive gas sensors are even able to detect gases at ppt level [105]. In this regard, Fang et al. [106] synthesized CeO2-decorated CuO NSs with Cu to Ce proportions of 1:0, 100:1, 20:1, 5:1, and 0:1 via a hydrothermal approach at 120 °C for 16 h. The thickness of CuO NSs was approximately 45 nm. The sensor with a Cu to Ce ratio of 20:1 revealed an enhanced response (Ra/Rg) of 6.96 to 20 ppm NO2 gas at 100 °C. It was also able to theoretically detect 600 ppt NO2 gas. This improvement was primarily due to the formation of CeO2-CuO heterojunctions and the presence of the highest amount of oxygen vacancies in the optimal sensor, which acted as highly favorable sites for gas adsorption. In addition, the optimal sensor had a high SSA of 49 m2/g, meaning it was able to provide plenty of adsorption sites for NH3 gas molecules.
Li et al. [107] synthesized hierarchical CeO2-ZnO composites via a solvothermal route at 90 °C for 4 h. The Optimal sensor exhibited a high response (Ra/Rg) of 92 to 100 ppm TEA at 200 °C. Also, upon mixing TEA with other VOCs, the response did not change significantly, implying excellent selectivity of the sensor. The C-N bond in the TEA molecule has low bond energy, making it easily broken, which results in enhanced selectivity to TEA. Furthermore, the response was almost the same upon an increase in humidity to 75%. The creation of CeO2-ZnO heterojunctions and the special morphology of sensing materials, which offered numerous adsorption sites, both affected the sensing performance.
Bi2O3 is a semiconductor with non-toxicity, chemical stability, abundance, and the ease of synthesis [108]. Meng et al. [109] synthesized hierarchical Bi2O3-CeO2 core–shell nanocomposites via hydrothermal reaction at 200 °C for 24 h. Molar ratios of Bi2O3 to CeO2 were 1:1, 1:2, 1:3, and 2:1. A lot of CeO2 NSs were grown on Bi2O3 as a core with a size of 2.5 µm. At RT, the sensor with a Bi2O3 to CeO2 of 1:2 manifested the highest response [(ΔR)/Ra) × 100] of 137% to 100 ppm HCHO, which was 6.6 times that of Bi2O3 (20.7%). The boosted response stemmed from the formation of a sufficient number of heterojunctions at interfaces between Bi2O3 and CeO2. However, an excessive amount of CeO2 resulted in the full encapsulation of Bi2O3. It led to the development of a compact CeO2 overlay on the Bi2O3 surface, which partially limited the interaction between HCHO and Bi2O3, resulting in a reduced response. Also, based on DFT calculations, the adsorption of formaldehyde by the Bi2O3-CeO2 composite was significantly higher relative to that of Bi2O3 sensor due to a larger adsorption energy.
MoSe2 belongs to the TMD group with a high surface area and high mobility of electrons. It has several phases, and the effect of phase changing during gas sensing applications should be investigated. Singh et al. [110] investigated the effect of phase transition on the sensing features of MoSe2-CeO2 nanocomposite to distinguish NH3 and TEA gases at RT. When the 2H phase of MoSe2 was dominant, the sensor revealed more selective behavior to NH3, whereas when the 1T phase was dominant, the sensor showed more selectivity to TEA gas. The sensing performance was related to the high SSA of the sensor, formation of n-n heterojunctions, the presence of oxygen vacancies in CeO2, high conductivity of WS2, and the synergistic effect of CeO2 and WS2 in combined form.
DMA is a breath biomarker for Parkinson’s disease [111], and hence, the detection of this VOC in exhaled breath is important. Wu et al. [112] synthesized CeO2-coated Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanofiber for DMA detection at RT. The high conductivity of MXene, along with C–Ti–O bonds and a sp2 hybridized carbon structure, increased the effective surface active sites for the fabricated gas sensor. Furthermore, Ce3+ ions accelerated the formation of surface-active oxygen species, while the MXene-CeO2 heterojunction expanded the width of EDL inside of CeO2, and upon exposure to DMA gas and release of electrons, significant resistance modulation occurred. Furthermore, the response of the sensor was almost constant even in a highly humid environment with relative humidity of 80%, making it highly useful for DMA analysis in exhaled breath.
Table 2 compares the gas sensing properties of CeO2-based gas sensors. Overall, they have been successfully used for the detection of various gases at various temperatures down to RT. The detection of NH3 and TEA is crucial for specific food industry applications, including tofu and fish spoilage. On the other hand, detecting other toxic gases and VOCs, such as CO, NO2, H2S, acetone, and xylene, is primarily associated with environmental monitoring and industrial applications. They are generally found in our environment and various industries. Hence, the development of gas sensors for the detection of these gases is important.

Table 2.
Gas sensing properties of CeO2-based gas sensors.
4. Conclusions and Outlooks
We reviewed the gas sensing features of CeO2-based gas sensors. Ce is the most abundant rare earth element, and thus, CeO2 is a relatively cheap material for gas sensing fabrication. CeO2-based gas sensors have been successfully used for the realization of high-performance gas sensors to detect various gases at different temperatures down to RT. Although pristine CeO2 gas sensors have demonstrated the capability to detect various gases, their performance can be further increased by various strategies such as doping, noble metal decoration, and nanocomposite formation.
Doping with cations can result in the creation of oxygen vacancies within the lattice of CeO2. They serve as desired sites for adsorption of oxygen and thus can increase the sensing reactions with gases. Noble metals with catalytic activity and electronic sensitization are also highly effective in enhancing the sensing characteristics of CeO2 gas sensors. They not only increase the selectivity but also decrease the sensing temperature. Thanks to the generation of Schottky junctions between noble metal and CeO2, a significant modulation of the resistance occurs, resulting in the generation of a large sensing signal. Nanocomposites are another promising architecture for sensing improvement, due to the generation of numerous heterojunctions between different components of the composite. Thus, the amount of resistance change sources increases significantly. CeO2, in combination with other materials such as CP and MXenes, holds strong potential for the development of flexible gas sensors, which are highly required for new applications such as wearable applications where rigid sensors cannot be used.
Future directions in the field of CeO2 sensors are as follows: (i) decreasing sensing temperature by illumination of sensing material with UV light, (ii) working the gas sensor in self-heating mode to decrease sensing temperature, and (iii) increasing the selectivity by decoration of bimetallic noble metals on the surface of CeO2. Bimetallic NPs have higher catalytic activity as well as more stability relative to single noble metals [113] (iv) functionalization with self-assembled molecules (SAM) to increase selectivity of the gas sensor. By selecting an appropriate SAM with a high tendency towards reaction with specific gases, the selectivity can be tuned towards desired gases [114] (v) synthesis of CeO2 in morphologies with high SSA to offer more adsorption sites for gas molecules. (vi) In general, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS)-based gas sensors have important features like small sizes, extremely low power consumption, long-term reliability, and reduced batch fabrication cost. Since CeO2-based gas sensors work at high temperatures, an elevated temperature is often needed to activate the sensing mechanism. Therefore, the appropriate electrothermal and structural design of a microheater, i.e., having fast response, uniform temperature distribution over sensing area, and minimal residual/thermal-stress-induced membrane deflection, is very important for MEMS-based CeO2 gas sensors [113,114,115,116]. (vii) In addition, AI-assisted sensing, multi-gas arrays, and non-resistive hybrid sensor platforms are promising strategies to significantly improve sensing performance in terms of sensitivity and selectivity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors13080298/s1. Table S1: Comparison of parameters of various types of gas sensors.
Author Contributions
Investigation, writing—original draft preparation, M.T.C.; Conceptualization, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, and writing—review and editing, A.M.; J.-H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the INHA UNIVERSITY Research Grant.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Momeni, M.M.; Mohammadinejad, F.; Ghasemipur, F.; Lee, B.-K. Asymmetric Photo-Assisted Supercapacitor and Symmetric Flexible Supercapacitors Based on CeO2-MnO2 Supported on Carbon Cloth. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1029, 180761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.P.H.; Pham, M.-T.; Bui, X.-T.; Wang, Y.-F.; You, S.-J. CeO2 as a Photocatalytic Material for CO2 Conversion: A Review. Sol. Energy 2022, 240, 443–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montini, T.; Melchionna, M.; Monai, M.; Fornasiero, P. Fundamentals and Catalytic Applications of CeO2-Based Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5987–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gupta, V.K.; Khosya, M.; Singh, S.; Kumar, U. Comparative computational and experimental insights into the structural, electrical, and biological properties of CeO2 fluorite ceramics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Z.; Yang, T.; Tao, L.; Zou, Y.; Wang, S. Defect Engineering on CeO2-Based Catalysts for Heterogeneous Catalytic Applications. Small Struct. 2021, 2, 2100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhang, S.; Wen, T.; Gu, P.; Li, L.; Zhao, G.; Niu, F.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Wang, X. A Critical Review on Visible-Light-Response CeO2-Based Photocatalysts with Enhanced Photooxidation of Organic Pollutants. Catal. Today 2019, 335, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beie, H.-J.; Gnörich, A. Oxygen Gas Sensors Based on CeO2 Thick and Thin Films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 4, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, S.; Frolov, D.D.; Masunov, A.E.; Seal, S. Structure and Properties of Cerium Oxides in Bulk and Nanoparticulate Forms. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 584, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackland, K.; Coey, J.M.D. Room Temperature Magnetism in CeO2—A Review. Phys. Rep. 2018, 746, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, L.; Liang, Z.; Sun, M.; Wu, T.; Huang, B.; Luo, F.; Du, Y.; Yan, C.-H. A Review on CeO2-Based Electrocatalyst and Photocatalyst in Energy Conversion. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2021, 2, 2000063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaev, M.A.; Salaeva, A.A.; Kharlamova, T.S.; Mamontov, G.V. Pt–CeO2-Based Composites in Environmental Catalysis: A Review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 295, 120286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Effect of Pd Chemical States on Three-Way Catalytic Reaction and C3H8 Total Combustion Reaction in Pd/CeO2-ZrO2-Al2O3 Catalysts. Fuel 2024, 372, 132052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Feng, J.; Song, S.; Shi, W.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H. Unraveling the Physical Chemistry and Materials Science of CeO2-Based Nanostructures. Chem 2021, 7, 2022–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Wang, Z.; Kondamareddy, K.K.; Xie, L.; Yang, J.; Ho, W.; Khosla, A.; Lu, D. Assembling Lamellar G-C3N4 on a Hydrophobic PVDF Film Induced Spatial Electric Field to Construct a Piezotronic Effect-Enhanced CeO2/g-C3N4/PVDF Hybrid Flexible Film Photocatalyst. Appl. Mater. Today 2025, 44, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Yu, Y. Tuning the UV Absorbing Ability of CeO2 Nanoparticles with F− Doping. FlatChem 2023, 39, 100494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Muthuraj, A.; Rajagounder, N.E. Review on CeO2-Based Corrosion Coatings. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2022, 81, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, P.; Pan, S.; Qi, Z.; Fu, C.; Yu, Z.; Kong, W.; Chang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; et al. The Advances of Ceria Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications in Orthopaedics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7199–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godavarthi, S.; Kushvaha, S.S.; Saha, D.; Altaf, M.; Nallabala, N.K.R.; Yuvaraj, C.; Reddy, M.R.; Kesarla, M.K.; Bakash, K.R.; Krishna, G.G.; et al. Realization of CO2 Gas Sensors and Broadband Photodetectors Using Metal/High-k CeO2/p-Si Heterojunction. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 31845–31858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.; Valsalakumar, S.; Ali, M.S.; Mallick, T.K.; Hinshelwood, J.; Sundaram, S. Influence of Adjustable CeO2 Morphology on the Performance of Ambient Hole Transport Layer-Free Carbon-Based Perovskite Solar Cells. Energy Fuels 2025, 39, 9566–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.; Li, W.; Ning, F.; Wen, Q.; He, C.; Chai, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhou, X. Rare Earth Doped CeO2 Uniformly Enwraps Graphite Felt as High Current Density Electrode for All Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. J. Power Sources 2025, 628, 235921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobade, R.G.; Pandit, B.; Khedulkar, A.P.; Raykar, V.S.; Sarawade, P.B.; Shaikh, S.F.; Huang, C.; Ambare, R.C. Electrochemical Investigation of Crinum Asiaticum-like BaO-CeO2 Nanostructure for High-Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitor. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 177, 114370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Oide, N.; Kamada, K.; Hyodo, T.; Shimizu, Y. Improved Toluene Response of Mixed-Potential Type YSZ-Based Gas Sensors Using CeO2-Added Au Electrodes. ECS Sens. Plus 2022, 1, 013604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, Y.; Di, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C. High-Sensitivity CO Electrochemical Gas Sensor Based on a Superconductive C-Loaded CuO-CeO2 Nanocomposite Sensing Material. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 271, 115272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, B.; Rao, S.K.; Ganesan, A.R.; Deepak, A. Investigating the Gas Sensing Potential in CeO2 Fiber Optic Sensor via Trivalent Gadolinium Ion Substitution at Room Temperature. Mater. Lett. 2022, 325, 132766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, N.A.; Nandasiri, M.I.; Rogers, P.H.; Jiang, W.; Varga, T.; Kuchibhatla, S.V.N.T.; Thevuthasan, S.; Carpenter, M.A. Selective Plasmonic Gas Sensing: H2, NO2, and CO Spectral Discrimination by a Single Au-CeO2 Nanocomposite Film. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; Cai, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, T. Electrospun CeO2 Nanoparticles/PVP Nanofibers Based High-Frequency Surface Acoustic Wave Humidity Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, Y. Pt-CeO2 Nanofibers Based High-Frequency Impedancemetric Gas Sensor for Selective CO and C3H8 Detection in High-Temperature Harsh Environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jia, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Song, H. Highly Sensitive and Low Detection Limit of Ethanol Gas Sensor Based on CeO2 Nanodot-Decorated ZnSnO3 Hollow Microspheres. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 14865–14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfayaz, F.; Khodadadi, A.; Mortazavi, Y.; Mohajerzadeh, S.S. CeO2 Doped SnO2 Sensor Selective to Ethanol in Presence of CO, LPG and CH4. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, S.; Yadav, B.C. Gigantic Enhancement in Response of Heterostructured CeO2/CdS Nanospheres Based Self-Powered CO2 Gas Sensor: A Comparative Study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 377, 133085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Song, H.; Hu, J.; Lv, Y.; Xu, K. A Cataluminescence Gas Sensor for Triethylamine Based on Nanosized LaF3–CeO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, S. Gas Sensors Based on Copper Oxide Nanomaterials: A Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaev, A.V.; Karipbayev, Z.T.; Kakimov, A.B.; Yakovlev, N.N.; Kukenov, O.I.; Korchemagin, A.O.; Akmetova-Abdik, G.A.; Kumarbekov, K.K.; Zhunusbekov, A.M.; Mochalov, L.A.; et al. High-Temperature Methane Sensors Based on ZnGa2O4:Er Ceramics for Combustion Monitoring. Technologies 2025, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Semiconductor Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Bharath, S.P.; Kim, J.-Y.; Pawar, K.K.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. N-Doped Graphene and Its Derivatives as Resistive Gas Sensors: An Overview. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, W.; Deng, N.; Pan, Y.; Sun, W.; Ni, J.; Kang, X. TiO2 Gas Sensors Combining Experimental and DFT Calculations: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.J.S. Gas Sensing Applications of 1D-Nanostructured Zinc Oxide: Insights from Density Functional Theory Calculations. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 437–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Martínez, H.; Rojas-Chávez, H.; Montejo-Alvaro, F.; Peña-Castañeda, Y.A.; Matadamas-Ortiz, P.T.; Medina, D.I. Recent Developments in Graphene-Based Toxic Gas Sensors: A Theoretical Overview. Sensors 2021, 21, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Ma, Z.; Gao, C.; Ye, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, D.; Cao, Y. A Multi-Functional VOC Sensor Based on Cascaded Quartz Crystal Resonators. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2025, 46, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navale, S.; Shahbaz, M.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Effect of Ag Addition on the Gas-Sensing Properties of Nanostructured Resistive-Based Gas Sensors: An Overview. Sensors 2021, 21, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.R.; Mirzaei, A.; Shokrollahi, H.; Kumar, R.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, H.W.; Kumar, M.; Kim, S.S. Flexible/Wearable Resistive Gas Sensors Based on 2D Materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 6528–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, L.D.; Mandawade, A.S.; Bhoye, L.N.; Ahemad, H.I.; Tayade, S.S.; Aher, Y.B.; Gite, A.B.; Nikam, L.K.; Shinde, S.D.; Jain, G.H.; et al. Sol-Gel and Hydrothermal Synthesis of CeO2 NPs: Their Physiochemical Properties and Applications for Gas Sensor with Photocatalytic Activities. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 164, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izu, N.; Shin, W.; Murayama, N.; Kanzaki, S. Resistive Oxygen Gas Sensors Based on CeO2 Fine Powder Prepared Using Mist Pyrolysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 87, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuscik, P.; Wojcieszak, D.; Domaradzki, J.; Weichbrodt, W.; Mazur, M.; Chodasewicz, P.; Kosto, Y.; Morales, C.; Flege, I. Analysis of Gas Sensing Properties of Thin Film Coating Based on Cerium Oxides. In Proceedings of the 17 th International Conference on Optical and Electronic Sensors COE 2024, Wrocław, Poland, 24–26 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wang, B.; Qin, C.; Han, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y. Band-Gap-Tunable CeO2 Nanoparticles for Room-Temperature NH3 Gas Sensors. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 19232–19240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, X. The Gas Sensor Utilizing CeO2 Nanorods for the Low Temperature Detection of Hydrogen. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Aslam, N.; Yang, X.Y.; Javed, M.S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Qiao, G. Unique Polyhedron CeO2 Nanostructures for Superior Formaldehyde Gas-Sensing Performances. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 19624–19630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Zhang, L.-X.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, J.-J.; Yin, J.; Bie, L.-J. Morphology-Controlled Synthesis of CeO2 Nanocrystals and Their Facet-Dependent Gas Sensing Properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 330, 129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Xie, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Cen, W.; Luo, S.; Yang, W.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zou, P.; et al. A Novel CeO2 Hollow-Shell Sensor Constructed for High Sensitivity of Acetone Gas Detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 571, 151337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kordrostami, Z.; Shahbaz, M.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive-Based Gas Sensors Using Quantum Dots: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit; Kaur, S.; Hussain, S.; Park, J.Y.; Katoch, V.; Parkash, B.; Katoch, A.; Jamwal, D. Size Dependent Dual Functionality of CeO2 Quantum Dots: A Correlation among Parameters for Hydrogen Gas Sensor and Pollutant Remediation. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 142959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matussin, S.N.; Harunsani, M.H.; Khan, M.M. CeO2 and CeO2-Based Nanomaterials for Photocatalytic, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. J. Rare Earths 2023, 41, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Fan, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. 3D Flower-like Ni Doped CeO2 Based Gas Sensor for H2S Detection and Its Sensitive Mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 357, 131227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Tofu products: A review of their raw materials, processing conditions, and packaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3683–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C. Preparation and Freshness Detection of Tofu Based on In-Doped CeO2 Ammonia Gas Sensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 669, 160506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Debliquy, M.; Zhang, C. Room Temperature Gas Sensors Based on Ce Doped TiO2 Nanocrystals for Highly Sensitive NH3 Detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.K.; Bharathi, P.; Govind, A.; Archana, J.; Navaneethan, M.; Harish, S. Detection of NO2 at Ppm-Level Using Al-Doped CeO2 Based Gas Sensor with High Sensitivity and Selectivity at Room Temperature. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Ying, B.; Li, T.; Chen, B.; Li, H.-Y.; Liu, H. W-CeO2 Nanospheres Gas Sensor Array for Accurate and Selective H2S Detection in Exhaled Breath. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive-Based Gas Sensors for Detection of Benzene, Toluene and Xylene (BTX) Gases: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4342–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Yuan, Q.; Yu, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, S.; Li, G.; et al. WO3/Ru@CeO2 Bilayer Gas Sensor for Ppb-Level Xylene Detection Based on a Catalytic-Sensitive Synergistic Mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 16920–16931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, M.; Kadian, A.; Ganesan, A.; Dong, C.-L.; Singh, A.; Dev, K.; Selvaraj, M.; Subramanian, A.; Marappan, S. Ru-Doped CeO2 Nanoparticles as Sensing Materials for the Detection of Formaldehyde. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 4680–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.E.; Mirzaei, A.; Roh, J.W.; Choi, S.-W.; Choi, M.S. Gadolinium-Doped CeO2 Gas Sensor for H2S Sensing. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2023, 61, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, D.; Priamushko, T.; Weinberger, C.; Kleitz, F.; Tiemann, M. Selective Discrimination between CO and H2 with Copper–Ceria-Resistive Gas Sensors. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Xin, Q.; Fu, Y.; Hua, Z.; Dong, Y.; Ran, M.; Song, H.; Liu, S.; Qu, R.; Yang, Y.; et al. Efficient Catalytic Oxidation of Chlorinated Volatile Organic Compounds over RuO2-WOx/Sn0.2Ti0.8O2 Catalysts: Insight into the Cl Poisoning Mechanism of Acid Sites. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; He, B.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S.-H.; Kong, X.-L.; Chen, Z.; Pan, G.-B. Three-Dimensional CeO2@carbon-Quantum-Dots Scaffold Modified with Au Nanoparticles on Flexible Substrates for High Performance Gas Sensing at Room Temperature. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 1946–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashtroudi, H.; Yu, A.; Juodkazis, S.; Shafiei, M. Ultra-Sensitive Photo-Induced Hydrogen Gas Sensor Based on Two-Dimensional CeO2-Pd-PDA/rGO Heterojunction Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, S.A.; Amini, M.H.; Ahmadi, S.H. CeO2/Ni–Al Layered Double Hydroxide Composite Decorated with Ag Nanoparticles as a Gas Sensor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2024, 178, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Mai, H.X.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, H.B.; Li, J.C.; Liu, C.; Yan, C.H.; Shen, Z.X.; Yu, T. Single CeO2 Nanowire Gas Sensor Supported with Pt Nanocrystals: Gas Sensitivity, Surface Bond States, and Chemical Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 9061–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobek, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Bechelany, M.; Vallicari, C.; Julbe, A.; Kim, S.S. MOF-Based Membrane Encapsulated ZnO Nanowires for Enhanced Gas Sensor Selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8323–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Me’nil, F.; Lucat, C.; Debe’da, H. The Thick-Film Route to Selective Gas Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 25, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, R.; Tian, X.; Han, L.; Chen, T.; Yang, B.; Zhi, Z.; Hua, Z.; Fan, S. A Catalytic Filter Based on Pt-CeO2 for Selective Methane Detection with SnO2 Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 389, 133872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Mirzaei, A.; Osada, M.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Hydrogen Sensing Characteristics of Pd-Decorated Ultrathin ZnO Nanosheets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Yousefi, H.R.; Falsafi, F.; Bonyani, M.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. An Overview on How Pd on Resistive-Based Nanomaterial Gas Sensors Can Enhance Response toward Hydrogen Gas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 20552–20571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Fan, Y.; Sun, X.; Lei, R.; Guo, L.; Cao, J.; Qin, C. Visible Light-Assisted Room-Temperature Hydrogen Sensors Using Pd/CeO2/ZnO Nanocomposites. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 149, 150121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, T.; Sun, P.; Liang, X.; Lu, G.; Shimanoe, K.; Yamazoe, N. Enhanced Gas Sensing Properties of SnO2 Hollow Spheres Decorated with CeO2 Nanoparticles Heterostructure Composite Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6669–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.; Zhu, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Pan, G.; Wang, Z. Highly Sensitive Ethanol Gas Sensor Based on CeO2/ZnO Binary Heterojunction Composite. Mater. Lett. 2020, 278, 128453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuhaili, M.F.; Durrani, S.M.A.; Bakhtiari, I.A. Carbon Monoxide Gas-Sensing Properties of CeO2–ZnO Thin Films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 3033–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabure, A.A.; Shirke, B.S.; Mane, S.R.; Garadkar, K.M. Microwave-Assisted Sol-Gel Synthesis of CeO2–NiO Nanocomposite Based NO2 Gas Sensor for Selective Detection at Lower Operating Temperature. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takte, M.A.; Ingle, N.N.; Dole, B.N.; Tsai, M.-L.; Hianik, T.; Shirsat, M.D. A Stable and Highly-Sensitive Flexible Gas Sensor Based on Ceria (CeO2) Nano-Cube Decorated rGO Nanosheets for Selective Detection of NO2 at Room Temperature. Synth. Met. 2023, 297, 117411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Xu, L.; Song, J.; Xing, R.; Song, H. Highly Enhanced Gas Sensing Properties of Porous SnO2–CeO2 Composite Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Liang, X.; Song, H.; Ma, S.; Lu, Y. Synthesis of Porous CeO2-SnO2 Nanosheets Gas Sensors with Enhanced Sensitivity. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoresi, R.A.C.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Cichetto, L.; Desimone, P.M.; Aldao, C.M.; Ponce, M.A.; Gracia, L.; Sambrano, J.R.; Longo, E.; Andres, J.; et al. Pure and Ni2O3-Decorated CeO2 Nanoparticles Applied as CO Gas Sensor: Experimental and Theoretical Insights. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 14014–14025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabure, A.A.; Shirke, B.S.; Mane, S.R.; Garadkar, K.M.; Sargar, B.M.; Pakhare, K.S. LPG Gas Sensor Activities of CeO2-Fe2O3 Nanocomposite Thin Film at Optimum Temperature. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganaboina, V.R.; Singh, S.G. Graphene-CeO2 Based Flexible Gas Sensor: Monitoring of Low Ppm CO Gas with High Selectivity at Room Temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 563, 150272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K.; Chu, P.K.; Ma, F. Oxygen Vacancy Enhanced Gas-Sensing Performance of CeO2/Graphene Heterostructure at Room Temperature. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9821–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farea, M.A.; Mohammed, H.Y.; Shirsat, S.M.; Sayyad, P.W.; Ingle, N.N.; Al-Gahouari, T.; Mahadik, M.M.; Bodkhe, G.A.; Shirsat, M.D. Hazardous Gases Sensors Based on Conducting Polymer Composites: Review. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 776, 138703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, W.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, M.; Zhang, J. Conducting Polymer-Based Nanostructures for Gas Sensors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 462, 214517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, P.; Li, G.; Wu, Z.; Meng, F.; Li, L.; et al. Recent Progress in Polyaniline-Based Chemiresistive Flexible Gas Sensors: Design, Nanostructures, and Composite Materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 6190–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, C.; Ashtiani, S.; Regmi, C.; Laposa, A.; Voves, J.; Kroutil, J.; Friess, K.; Povolny, V.; Lotfian, S. Preparation and Characterisation of NH3 Gas Sensor Based on PANI/Fe-Doped CeO2 Nanocomposite. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tai, H.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, Z.; Du, X.; Xie, G.; Jiang, Y. A High-Performance Flexible Gas Sensor Based on Self-Assembled PANI-CeO2 Nanocomposite Thin Film for Trace-Level NH3 Detection at Room Temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ema, T.; Choi, P.G.; Takami, S.; Masuda, Y. Facet-Controlled Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles for High-Performance CeO2 Nanoparticle/SnO2 Nanosheet Hybrid Gas Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 56998–57007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motaung, D.E.; Mhlongo, G.H.; Makgwane, P.R.; Dhonge, B.P.; Cummings, F.R.; Swart, H.C.; Ray, S.S. Ultra-High Sensitive and Selective H2 Gas Sensor Manifested by Interface of n–n Heterostructure of CeO2-SnO2 Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuizen, D.N.; Motaung, D.E.; Swart, H.C. Gas Sensors Based on CeO2 Nanoparticles Prepared by Chemical Precipitation Method and Their Temperature-Dependent Selectivity towards H2S and NO2 Gases. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Mirzaei, A.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Selective H2S sensing without external heat by a synergy effect in self-heated CuO-functionalized SnO2-ZnO core-shell nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 300, 126981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.Y.; Nguyen, L.H.T.; Nguyen, H.L.; Mirzaei, A.; Tran, V.N.H.; Mai, N.X.D.; Tran, N.Q.; Oum, W.; Kim, E.B.; Kim, H.M.; et al. Titanium-Based Metal-Organic-Framework-Coated SnO2 Nanowires with Enhanced NO2 Gas Sensing Capability in Humid Environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 394, 134425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.H.; Kwon, Y.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Mirzaei, A.; Lee, H.Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, S.S.; Jeong, Y.K.; Kim, H.W. Proton-Beam Engineered Surface-Point Defects for Highly Sensitive and Reliable NO2 Sensing under Humid Environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Chang, X.; Tang, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, W.; Niu, S.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, S. Humidity-Tolerant Chemiresistive Gas Sensors Based on Hydrophobic CeO2/SnO2 Heterostructure Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25680–25692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.C.; Yaw, C.S.; Shaffee, S.N.A.; Samad, N.A.A.; Koi, Z.K.; Chong, M.N. Elevating the Prospects of Green Hydrogen (H2) Production through Solar-Powered Water Splitting Devices: A Systematic Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 40, e00972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, M. A Review of Chemoresistive Hydrogen Gas Sensors Based on Low-Dimensional Materials. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025, 50, 6195–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Lian, K.; Zhuiykov, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y. Highly Sensitive and Ultra-Fast Gas Sensor Based on CeO2-Loaded In2O3 Hollow Spheres for Ppb-Level Hydrogen Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Cao, Q.; Yang, J.-H.; Li, X.-X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lu, H.-L.; Zhang, D.W. Fabrication of a Micro-Electromechanical System-Based Acetone Gas Sensor Using CeO2 Nanodot-Decorated WO3 Nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14095–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, G.; Bonavita, A.; Rizzo, G.; Galvagno, S.; Capone, S.; Siciliano, P. Methanol Gas-Sensing Properties of CeO2–Fe2O3 Thin Films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ren, W.; Wu, R.; Zhang, M. CeO2 Enhanced Ethanol Sensing Performance in a CdS Gas Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yan, S.; Cao, B.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y. Enhanced NH3 Gas-Sensing Performance of Silica Modified CeO2 Nanostructure Based Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjiri, M.; Benmansour, N.; Alonizan, N.H.; Neri, G. Ppt Level Gas Sensing by Resistive Gas Sensors: A Review. Microchem. J. 2025, 213, 113670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Shang, E.; Wang, D.; Ma, X.; Zhao, B.; Han, C.; Zheng, C. A Chemiresistive Ppt Level NO2 Gas Sensor Based on CeO2 Nanoparticles Modified CuO Nanosheets Operated at 100 °C. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Highly Sensitive and Selective Triethylamine Gas Sensor Based on Hierarchical Radial CeO2/ZnO n-n Heterojunction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 367, 132031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Muraikhi, M.D.; Ayesh, A.I.; Mirzaei, A. Review of Nanostructured Bi2O3, Bi2WO6, and BiVO4 as Resistive Gas Sensors. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 60, 106003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Kang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, G.; Shao, Z.; Wu, L. Core-Shell Bi2O3/CeO2 Heterojunction for Enhanced Formaldehyde Gas Sensor. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 6067–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Shin, K.Y.; Moon, S.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Phase-Engineered MoSe2/CeO2 Composites for Room-Temperature Gas Sensing with a Drastic Discrimination of NH3 and TEA Gases. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 3994–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Geng, Z.; Yang, L.; Shen, B.; Kan, Z.; Qi, Y.; Hu, S.; Dong, B.; Bai, X.; Xu, L.; et al. A Wearable Healthcare Platform Integrated with Biomimetical Ions Conducted Metal–Organic Framework Composites for Gas and Strain Sensing in Non-Overlapping Mode. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2207663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Fu, G.; Xu, P.; Fan, C.; Shen, L.; Yang, G.; Wen, C.; Liu, W. Ultrasensitive Detection of Dimethylamine Gas for Early Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease Using CeO2-Coated Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanofibers. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 6400–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.Y.; Kim, Y.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Bimetal-Decorated Resistive Gas Sensors: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2025, 13, 9930–9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Vivod, D.; Kim, S.; Mirzaei, A.; Zahn, D.; Park, C.; Kim, S.S.; Halik, M. Chemical-Recognition-Driven Selectivity of SnO2-Nanowire-Based Gas Sensors. Nano Today 2021, 40, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Wang, F. A Review of MEMS-Based Metal Oxide Semiconductors Gas Sensor in Mainland China. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2022, 32, 054003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P. Technological Journey Towards Reliable Microheater Development for MEMS Gas Sensors: A Review. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2014, 14, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).