A Review on Potential Electrochemical Point-of-Care Tests Targeting Pandemic Infectious Disease Detection: COVID-19 as a Reference
Abstract
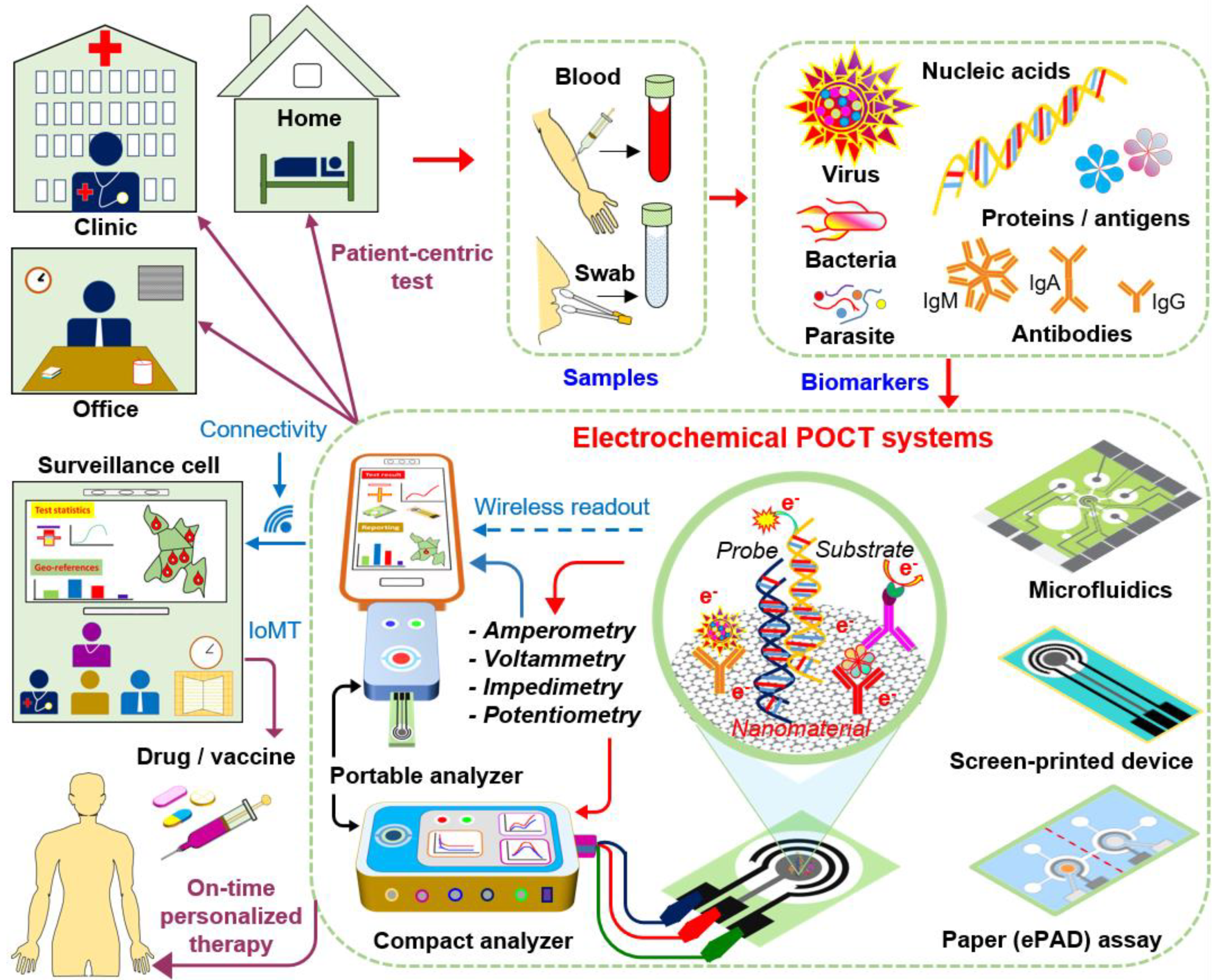
1. Introduction
2. Basics of Electrochemical Biosensors
3. Attributes of POC Electrochemical Biosensors for Pandemic Situations
4. Potential Electrochemical POC Tests
4.1. Chip-Based POC Electrochemical Tests
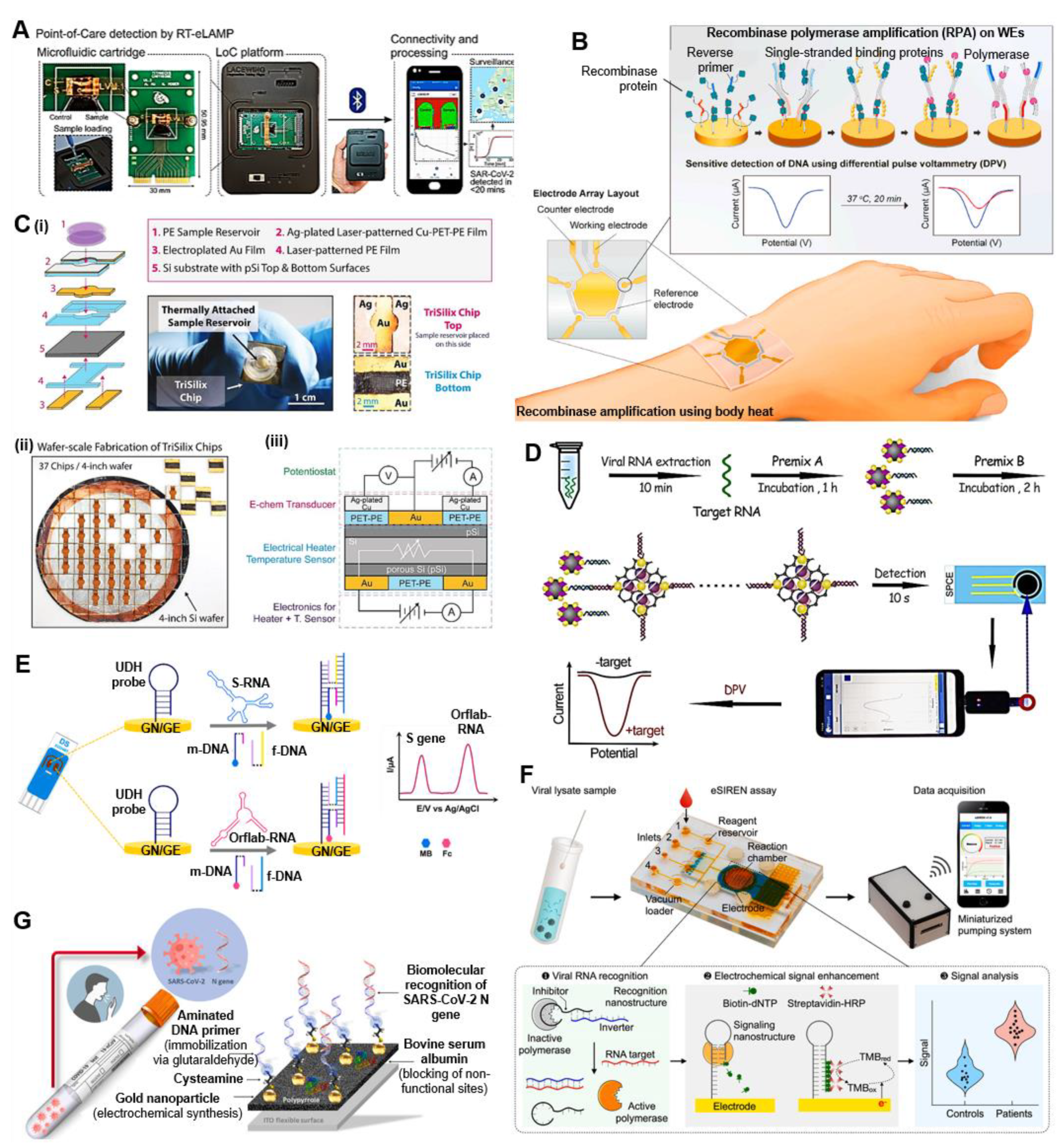
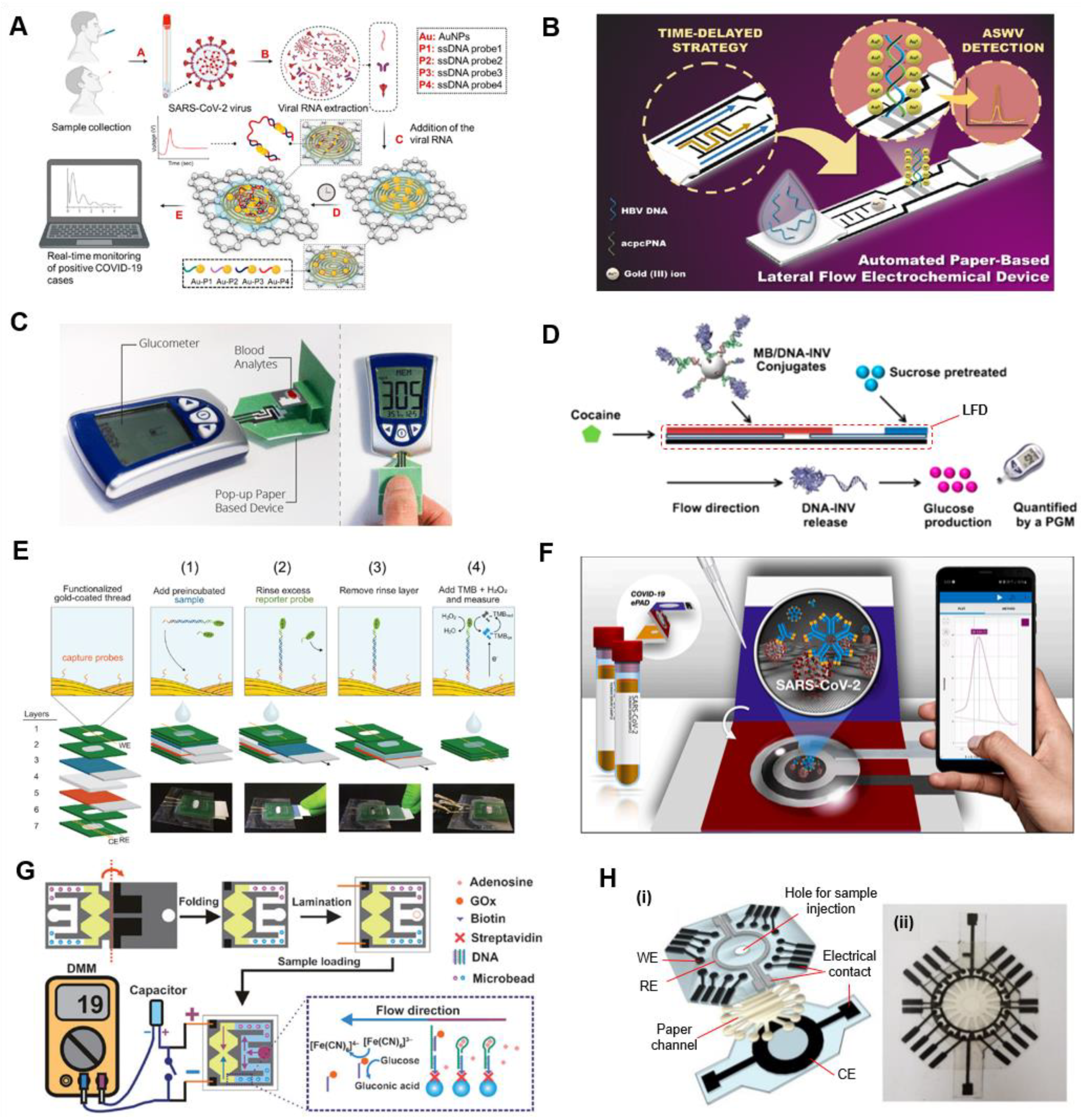
4.1.1. Chip-Based Electrochemical Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT)
Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (iNAATs)
Amplification-Free POC NAT
Label-Free Electrochemical NAT
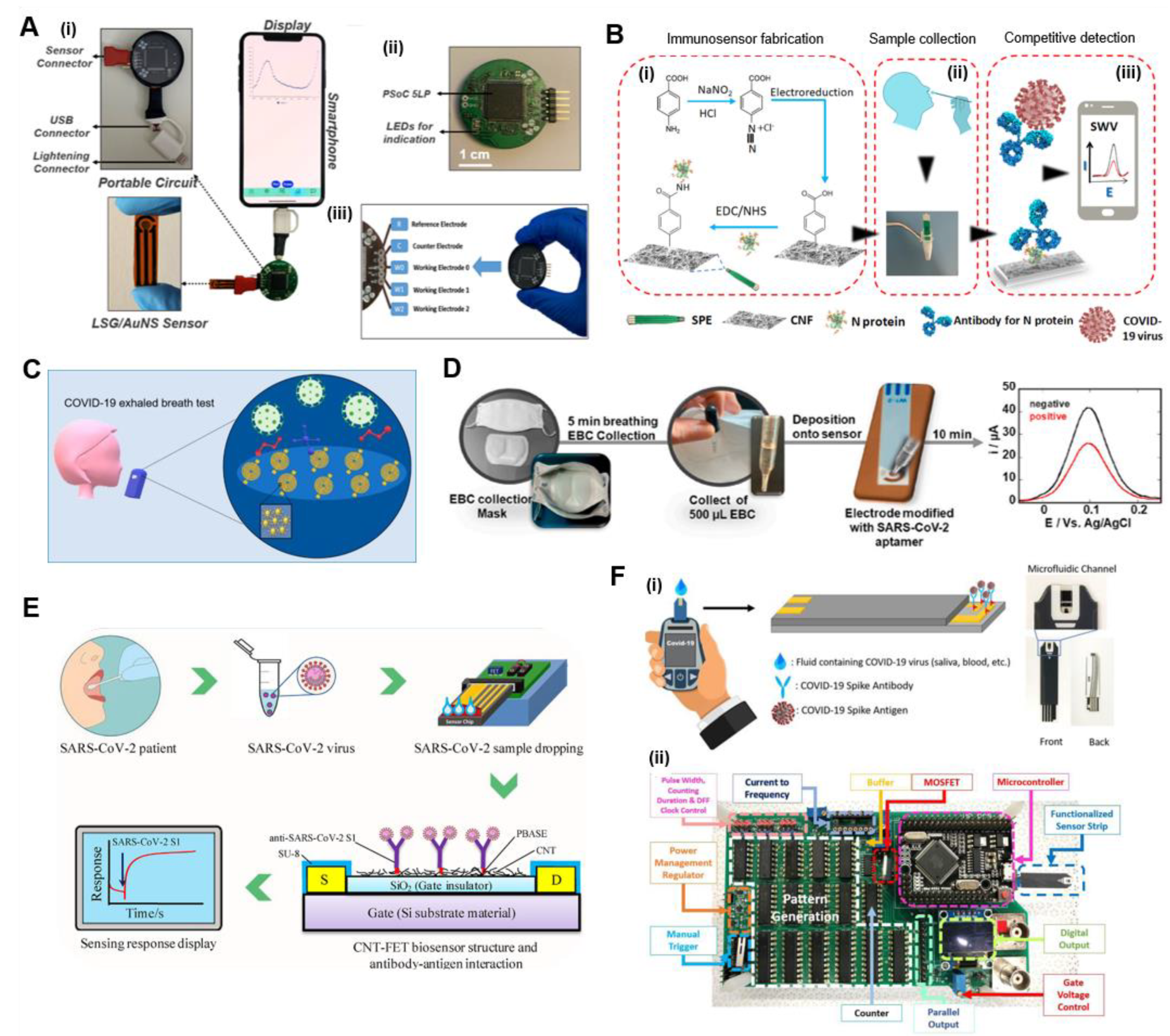
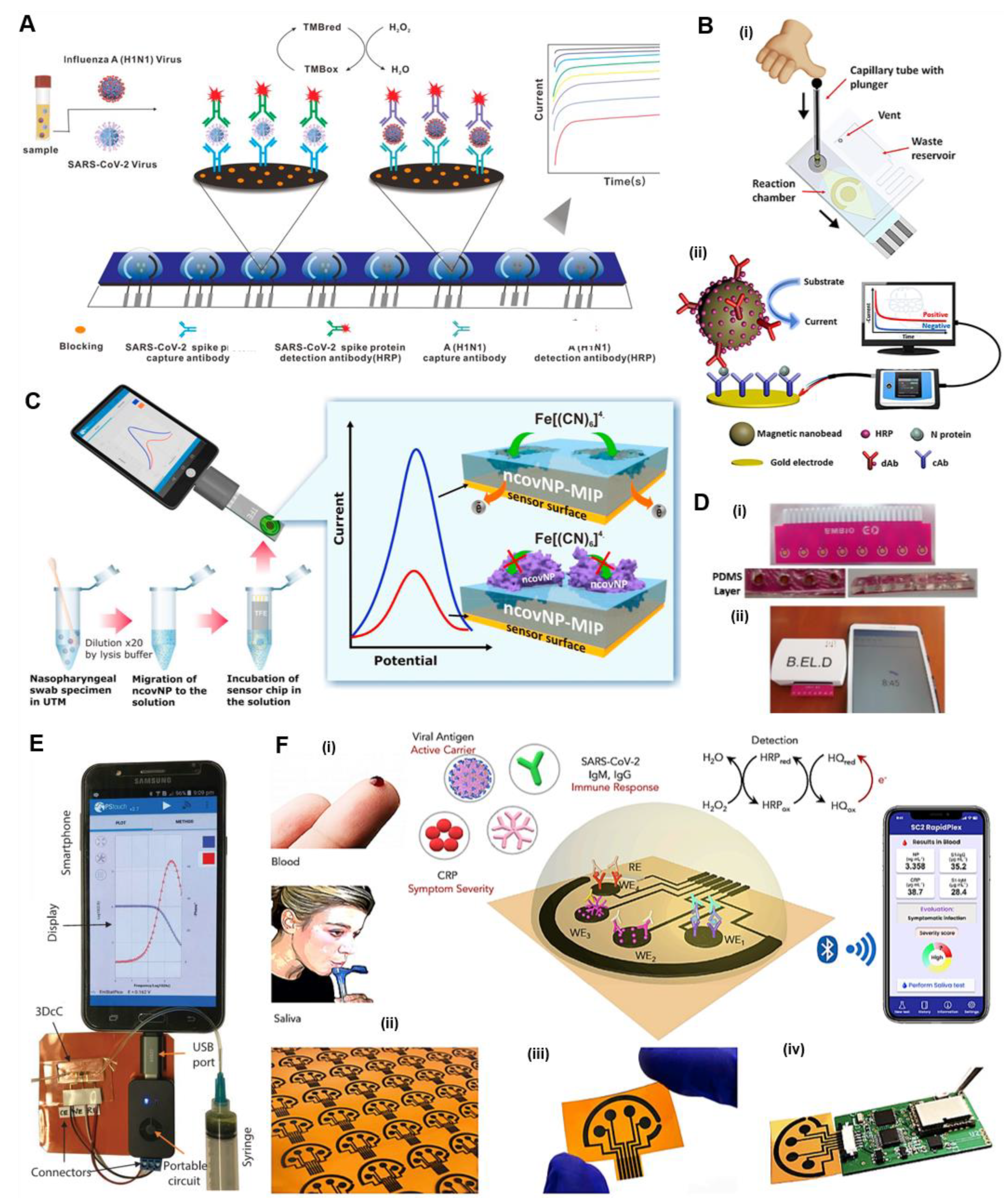
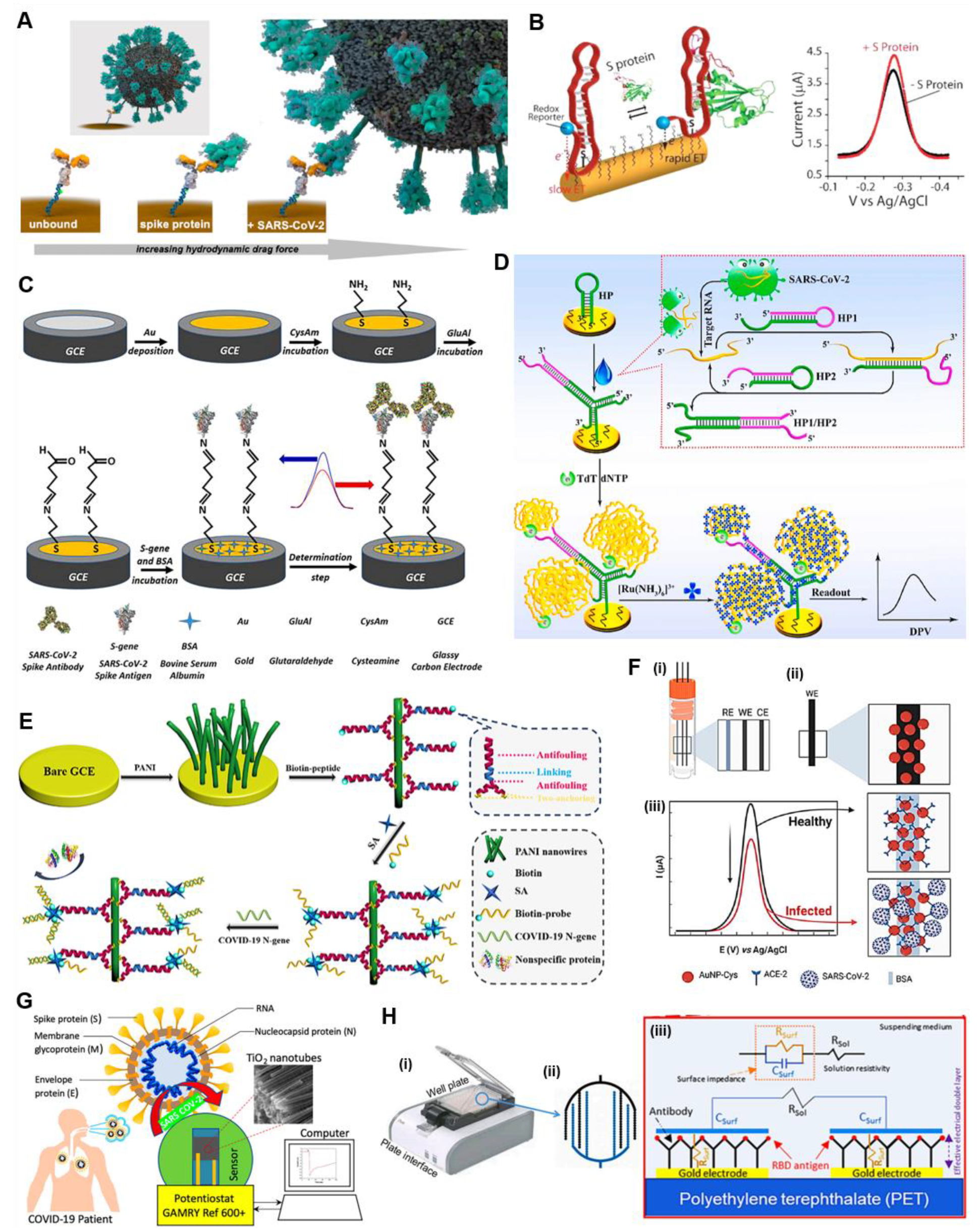
4.1.2. Chip-Based POC Electrochemical Immunoassays
Chip-Based Electrochemical Antigen Detection
Chip-Based Electrochemical Antibody Detection
4.2. Paper-Based POC Electrochemical Tests
4.2.1. Paper-Based Electrochemical Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT)
4.2.2. Paper-Based POC Electrochemical Immunoassays
4.2.3. Complementary POC ePAD Approaches
4.3. Nanomaterials/Nanochemistry-Assisted Electrochemical Tests
5. Smartphone-Assisted Evidence-Based Epidemiological Reporting (or Surveillance)
6. Summary and Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Point-of-care diagnostics for infectious diseases: From methods to devices. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosack, C.S.; Page, A.; Klatser, P.R. A guide to aid the selection of diagnostic tests. Bull. World. Heal. Organ. 2017, 95, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiochia, R. Nanobiosensors as new diagnostic tools for SARS, MERS and COVID-19: From past to perspectives. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, N.P.; Vadnais, C.; Denkinger, C.; Engel, N.; Pai, M. Point-of-Care Testing for Infectious Diseases: Diversity, Complexity, and Barriers in Low- And Middle-Income Countries. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization COVID-19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) Global Research and Innovation forum | 12 February 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-public-health-emergency-of-international-concern-global-research-and-innovation-forum (accessed on 26 December 2020).
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acter, T.; Uddin, N.; Das, J.; Akhter, A.; Choudhury, T.R.; Kim, S. Evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A global health emergency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data | as of 7:21pm CET, 11 February 2022. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Pang, J.; Wang, M.X.; Ang, I.Y.H.; Tan, S.H.X.; Lewis, R.F.; Chen, J.I.-P.; Gutierrez, R.A.; Gwee, S.X.W.; Chua, P.E.Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. Potential Rapid Diagnostics, Vaccine and Therapeutics for 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV): A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Yang, L.; Chu, H.; Fan, M. Effect of delay in diagnosis on transmission of COVID-19. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2020, 17, 2725–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, A.J.; Russell, T.W.; Diamond, C.; Liu, Y.; Edmunds, J.; Funk, S.; Eggo, R.M.; Sun, F.; Jit, M.; Munday, J.D.; et al. Early dynamics of transmission and control of COVID-19: A mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19-16 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---16-march-2020 (accessed on 4 April 2020).
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Protocol: Real-Time RT-PCR Assays for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 | January 2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, C. Coronavirus and the Race to Distribute Reliable Diagnostics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A New Coronavirus Associated with Human Respiratory Disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; AL-Jighefee, H.; Younes, S.; Al-Jamal, O.; Daas, H.I.; Yassine, H.M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Challenges in Laboratory Diagnosis of the Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2020, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellewell, J.; Abbott, S.; Gimma, A.; Bosse, N.I.; Jarvis, C.I.; Russell, T.W.; Munday, J.D.; Kucharski, A.J.; Edmunds, W.J.; Sun, F.; et al. Feasibility of controlling COVID-19 outbreaks by isolation of cases and contacts. Lancet Glob. Heal. 2020, 8, e488–e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, F.; Biswas, G.C.; Suzuki, H. Microfabricated electrochemical sensing devices. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1358–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. New challenges in point of care electrochemical detection of clinical biomarkers. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S. Electrochemical biosensors: Perspective on functional nanomaterials for on-site analysis. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical biosensors: Towards point-of-care cancer diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Kerman, K. Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Viruses. Micromachines 2021, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Shetti, N.P.; Jagannath, S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Electrochemical sensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudr, J.; Michalek, P.; Ilieva, L.; Adam, V.; Zitka, O. COVID-19: A challenge for electrochemical biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteil, S.; Casson, A.J.; Jones, S.T. Electronic and electrochemical viral detection for point-of-care use: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkourani, G.; Brouzgou, A.; Archonti, M.; Papandrianos, N.; Song, S.; Tsiakaras, P. Emerging materials for the electrochemical detection of COVID-19. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 893, 115289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemčeková, K.; Labuda, J. Advanced materials-integrated electrochemical sensors as promising medical diagnostics tools: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, P.; Singhal, A.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, N.; Murali, S.; Sanghi, S.K.; Khan, R. Rapid diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 using potential point-of-care electrochemical immunosensor: Toward the future prospects. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 40, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, G.; Aziz, A.; Qaisrani, R.N.; Chen, W.; Asif, M. Detecting and inactivating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 under the auspices of electrochemistry. Curr. Res. Chem. Biol. 2021, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.K.; Dhau, J.S.; Gohel, H.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kateb, B.; Kim, N.Y.; Goswami, D.Y. Electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 Sensing at Point-of-Care and Artificial Intelligence for Intelligent COVID-19 Management. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7306–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Verma, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Solanki, P.R. The perspectives of biomarker-based electrochemical immunosensors, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Medical Things toward COVID-19 diagnosis and management. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 20, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.T.S.G.; Souto, D.E.P.; Barragan, J.T.C.; Giarola, d.F.J.; Giarola, d.F.J.; de Moraes, A.C.M.; Kubota, L.T. Electrochemical Biosensors in Point-of-Care Devices: Recent Advances and Future Trends. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhera, T.; Kakkar, D.; Wadhwa, G.; Raj, B. Recent Advances and Progress in Development of the Field Effect Transistor Biosensor: A Review. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 7635–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors - Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, J.L.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P.; Carrara, S.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical biosensors and nanobiosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertok, T.; Lorencova, L.; Chocholova, E.; Jane, E.; Vikartovska, A.; Kasak, P.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Biosensors: Mechanistic Principles, Analytical Examples and Challenges towards Commercialization for Assays of Protein Cancer Biomarkers. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 989–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, K.J.; Boeras, D.I.; Chen, X.-S.; Ramsay, A.R.; Peeling, R.W. REASSURED diagnostics to inform disease control strategies, strengthen health systems and improve patient outcomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 4, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culbertson, C.T.; Mickleburgh, T.G.; Stewart-James, S.A.; Sellens, K.A.; Pressnall, M. Micro Total Analysis Systems: Fundamental Advances and Biological Applications. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-León, J.; Svendsen, W.E. Lab-on-a-Chip Devices and Micro-Total Analysis Systems, 1st ed.; Castillo-León, J., Svendsen, W.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Davis, R.W.; Saha, A.K. Microfluidic Point-of-Care Testing: Commercial Landscape and Future Directions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, B.; Soleimani, N.; Rabiee, N.; Kalbasi, A.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Point-of-care microfluidic devices for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qian, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, Z.; Ping, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, H. Nucleic acid amplification free biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 153, 112049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Geng, M.; Peng, Y.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: Serological Tests|FDA Statement, 7 April 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-serological-tests (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Zou, X.; Wu, J.; Gu, J.; Shen, L.; Mao, L. Application of aptamers in virus detection and antiviral therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Nilsen-Hamilton, M. Aptamers for Infectious Disease Diagnosis. In E. Coli Infections-Importance of Early Diagnosis and Efficient Treatment; Rodrigo, L., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, M.; Dutta, N.; Dutta, G. Aptamer-based biosensors and their implications in COVID-19 diagnosis. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 5400–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, G.; Hein, R.; Liu, N.; Luo, X.; Davis, J.J. Antifouling Strategies for Selective In Vitro and In Vivo Sensing. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3852–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Huh, H.J.; Park, E.; Chung, D.R.; Kang, M. Multiplex Molecular Point-of-Care Test for Syndromic Infectious Diseases. Biochip J. 2021, 15, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.C.; Hall, D.A. Point-of-Care Smartphone-based Electrochemical Biosensing. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.E.; Tabei, F.; Park, S.J.; Askarian, B.; Kim, K.H.; Moallem, G.; Chong, J.W.; Kwon, O.S. Smartphone with optical, physical, and electrochemical nanobiosensors. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.; Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.-E. Recent progress, challenges, and prospects of fully integrated mobile and wearable point-of-care testing systems for self-testing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1812–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodouleas, D.C.; Kaur, B.; Chorti, P. From Point-of-Care Testing to eHealth Diagnostic Devices (eDiagnostics). ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 1600–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.S.; Thomas, M.R.; Budd, J.; Mashamba-Thompson, T.P.; Herbst, K.; Pillay, D.; Peeling, R.W.; Johnson, A.M.; McKendry, R.A.; Stevens, M.M. Taking connected mobile-health diagnostics of infectious diseases to the field. Nature 2019, 566, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswajit, P.; Gokul, C.B.; Habib, F. Rashvand IoE: Towards application-specific technology selection. ITU J. Futur. Evol. Technol. 2021, 2, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, N.; Adv, S.; Oliver, N.; Lepri, B.; Sterly, H.; Lambiotte, R.; Delataille, S.; De Nadai, M.; Letouzé, E.; Salah, A.A.; et al. Mobile phone data for informing public health actions across the COVID-19 pandemic lifecycle. Sci. Adv. 2020, 0764, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.; Chughtai, A.; Rabhi, F. Use of Mobile Apps for epidemic surveillance and response–availability and gaps. Glob. Biosecurity 2019, 1, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration PI1109-A ePlex ® SARS-CoV-2 Test Assay Manual. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136282/download (accessed on 15 April 2020).
- LaBarre, P.; Gerlach, J.; Wilmoth, J.; Beddoe, A.; Singleton, J.; Weigl, B. Non-instrumented nucleic acid amplification (NINA): Instrument-free molecular malaria diagnostics for low-resource settings. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC’10, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 1097–1099. [Google Scholar]
- James, A.S.; Alwneh, J.I. COVID-19 infection diagnosis: Potential impact of isothermal amplification technology to reduce community transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Manzano, J.; Malpartida-Cardenas, K.; Moser, N.; Pennisi, I.; Cavuto, M.; Miglietta, L.; Moniri, A.; Penn, R.; Satta, G.; Randell, P.; et al. Handheld point-of-care system for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 extracted RNA in under 20 min. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.E.; Schuck, A.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Kang, M.; Kim, Y.S. Sensitive electrochemical biosensor combined with isothermal amplification for point-of-care COVID-19 tests. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Bajo, E.; Silva Pinto Collins, A.; Kasimatis, M.; Cotur, Y.; Asfour, T.; Tanriverdi, U.; Grell, M.; Kaisti, M.; Senesi, G.; Stevenson, K.; et al. Disposable silicon-based all-in-one micro-qPCR for rapid on-site detection of pathogens. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, F.; Xie, W.; Zhou, T.C.; OuYang, J.; Jin, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; et al. Ultrasensitive supersandwich-type electrochemical sensor for SARS-CoV-2 from the infected COVID-19 patients using a smartphone. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashefi-Kheyrabadi, L.; Nguyen, H.V.; Go, A.; Baek, C.; Jang, N.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, N.H.; Min, J.; Lee, M.H. Rapid, multiplexed, and nucleic acid amplification-free detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using an electrochemical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ho, N.R.Y.; Sundah, N.R.; Natalia, A.; Liu, Y.; Miow, Q.H.; Wang, Y.; Tambyah, P.A.; et al. Accessible detection of SARS-CoV-2 through molecular nanostructures and automated microfluidics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avelino, K.Y.P.S.; dos Santos, G.S.; Frías, I.A.M.; Silva-Junior, A.G.; Pereira, M.C.; Pitta, M.G.R.; de Araújo, B.C.; Errachid, A.; Oliveira, M.D.L.; Andrade, C.A.S. Nanostructured sensor platform based on organic polymer conjugated to metallic nanoparticle for the impedimetric detection of SARS-CoV-2 at various stages of viral infection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 206, 114392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaibun, T.; Puenpa, J.; Ngamdee, T.; Boonapatcharoen, N.; Athamanolap, P.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lertanantawong, B. Rapid electrochemical detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C. Cutting-Edge Infectious Disease Diagnostics with CRISPR. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, M.J.; Koob, J.G.; Gootenberg, J.S. SHERLOCK: Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2986–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, R.; Tang, Z.; Dong, M.; Liu, T.; Kshirsagar, A.; Guan, W. CRISPR-based detection of SARS-CoV-2: A review from sample to result. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Puig, H.; Timilsina, S.; Rainbow, J.; Jolly, P.; Najjar, D.; Durr, N.; Alter, G.; Li, J.Z.; Yu, X.G.; Walt, D.R.; et al. Simultaneous detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA and host antibodies enabled by a multiplexed electrochemical sensor platform. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, R.; Balderston, S.; Tran, T.; DeBoer, T.; Etienne, J.; Sandhu, M.; Wauford, N.A.; Chung, J.Y.; Nokes, J.; Athaiya, M.; et al. Detection of unamplified target genes via CRISPR–Cas9 immobilized on a graphene field-effect transistor. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.N.; Lin, Y.L.; Yu, K.J.; Chiou, Y.E.; Leung, W.H.; Weng, W.H. An Effective SARS-CoV-2 Electrochemical Biosensor with Modifiable Dual Probes Using a Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.C.; Watanabe, T.; Carlen, E.T.; Yokokawa, M.; Suzuki, H. Autonomous microfluidics realized with active hydrophobic valves. In Proceedings of the 2015 Transducers-2015 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, TRANSDUCERS 2015, Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1806–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, G.C.; Watanabe, T.; Carlen, E.T.; Yokokawa, M.; Suzuki, H. Switchable Hydrophobic Valve for Controlled Microfluidic Processing. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Biswas, G.C.; Carlen, E.T.; Suzuki, H. An autonomous electrochemically-actuated microvalve for controlled transport in stand-alone microfluidic systems. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39018–39023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Biswas, G.C.; Rana, M.M.; Kazuhiro, T.; Suzuki, H. A simple micropump based on a freeze-dried superabsorbent polymer for multiplex solution processing in disposable devices. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 182213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, G.C.; Suzuki, H. Simple manual roller pump-driven valve-free microfluidic solution exchange system for urgent bioassay. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 2938–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.; Shi, J.; Fan, Y.; Yang, M. A microfluidic flow-through chip integrated with reduced graphene oxide transistor for influenza virus gene detection. Sensors Actuators B. Chem. 2017, 251, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Su, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, F.; Yuan, Y.; et al. An accurate, high-speed, portable bifunctional electrical detector for COVID-19. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 64, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Singh, S.G. Label-Free Electrochemical Detection of DNA Hybridization: A Method for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiati, S.; Sopstad, S.; Peacock, M.; Akhtar, A.S.; Pinto, I.; Soares, R.R.G.; Russom, A. Flex Printed Circuit Board Implemented Graphene-Based DNA Sensor for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13060–13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Jaiswal, A. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-based Lateral Flow Immunoassay as a Point of Care Diagnostic Tool for Infectious Agents and Diseases. Analyst 2018, 143, 1970–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bange, A.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Microfluidic immunosensor systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2488–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, L.; Jiang, X. Materials for Microfluidic Immunoassays: A Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzadeh Tabrizi, M.; Fernández-Blázquez, J.P.; Medina, D.M.; Acedo, P. An ultrasensitive molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor for the determination of SARS-CoV-2-RBD by using macroporous gold screen-printed electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 196, 113729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raziq, A.; Kidakova, A.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Development of a portable MIP-based electrochemical sensor for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrikou, S.; Moschopoulou, G.; Tsekouras, V.; Kintzios, S. Development of a Portable, Ultra-Rapid and Ultra-Sensitive Cell-Based Biosensor for the Direct Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, J.; Wadekar, S.; DeCubellis, K.; Jackson, G.W.; Chiu, A.S.; Pagneux, Q.; Saada, H.; Engelmann, I.; Ogiez, J.; Loze-Warot, D.; et al. A mask-based diagnostic platform for point-of-care screening of Covid-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazizadeh, E.; Neshastehriz, A.; Firoozabadi, A.D.; Yazdi, M.K.; Saievar-Iranizad, E.; Einali, S. Dual electrochemical sensing of spiked virus and SARS-CoV-2 using natural bed-receptor (MV-gal1). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beduk, T.; Beduk, D.; de Oliveira Filho, J.I.; Zihnioglu, F.; Cicek, C.; Sertoz, R.; Arda, B.; Goksel, T.; Turhan, K.; Salama, K.N.; et al. Rapid Point-of-Care COVID-19 Diagnosis with a Gold-Nanoarchitecture-Assisted Laser-Scribed Graphene Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8585–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Zourob, M. Development of a Low-Cost Cotton-Tipped Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Chem. 2020, 93, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Broza, Y.Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gui, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Multiplexed Nanomaterial-Based Sensor Array for Detection of COVID-19 in Exhaled Breath. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12125–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzami, M.A.; Rabbani, G.; Ahmad, A.; Basalah, A.A.; Al-Sabban, W.H.; Nate Ahn, S.; Choudhry, H. Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNT-FET)-based biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) surface spike protein S1. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 143, 107982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, M.; Luo, H.; Xia, X.; Fares, C.; Carey, P.H.; Chiu, C.-W.; Ren, F.; Shan, S.-S.; Liao, Y.-T.; Hsu, S.-M.; et al. Fast SARS-CoV-2 virus detection using disposable cartridge strips and a semiconductor-based biosensor platform. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2021, 39, 033202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, A.; Mishra, A.; Bisht, H.; Tripathi, R.M. Nanomaterial Based Biosensors for Detection of Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2: A Review. J. Anal. Test. 2021, 5, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasserre, P.; Balansethupathy, B.; Vezza, V.J.; Butterworth, A.; MacDonald, A.; Blair, E.O.; McAteer, L.; Hannah, S.; Ward, A.C.; Hoskisson, P.A.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 aptasensor based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and low-cost gold electrode substrates. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezza, V.J.; Butterworth, A.; Lasserre, P.; Blair, E.O.; MacDonald, A.; Hannah, S.; Rinaldi, C.; Hoskisson, P.A.; Ward, A.C.; Longmuir, A.; et al. An electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 biosensor inspired by glucose test strip manufacturing processes. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 3704–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, R.; Pu, H.; Guo, X.; Chang, J.; Zhou, G.; Kron, M.; Chen, J. Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Ebola Antigen. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.; Choi, M.; Ku, B.; Lee, C.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G.; et al. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens Using Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahari, S.; Roberts, A.; Shahdeo, D.; Gandhi, S. eCovSens-Ultrasensitive Novel In-House Built Printed Circuit Board Based Electrochemical Device for Rapid Detection of nCovid-19 antigen, a spike protein domain 1 of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojsoska, B.; Larsen, S.; Olsen, D.A.; Madsen, J.S.; Brandslund, I.; Alatraktchi, F.A. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using Electrochemical Immunosensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, Z.; Roushani, M.; Hosseini, H.; Choobin, H. Electrochemical immunosensor with Cu2O nanocube coating for detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layqah, L.A.; Eissa, S. An electrochemical immunosensor for the corona virus associated with the Middle East respiratory syndrome using an array of gold nanoparticle-modified carbon electrodes. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Song, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Hao, R. Multichannel Immunosensor Platform for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A(H1N1) Virus. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22262–22270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lillehoj, P.B. Microfluidic Magneto Immunosensor for Rapid, High Sensitivity Measurements of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein in Serum. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azahar Ali, M.; Hu, C.; Jahan, S.; Yuan, B.; Sadeq Saleh, M.; Ju, E.; Gao, S.-J.; Panat, R.; Ali, M.A.; Hu, C.; et al. Sensing of COVID-19 Antibodies in Seconds via Aerosol Jet Nanoprinted Reduced-Graphene-Oxide-Coated 3D Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Lukas, H.; Tu, J.; Min, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Rossiter, H.B.; Gao, W. SARS-CoV-2 RapidPlex: A Graphene-Based Multiplexed Telemedicine Platform for Rapid and Low-Cost COVID-19 Diagnosis and Monitoring. Matter 2020, 3, 1981–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiani, L.; Saroglia, M.; Galatà, G.; De Santis, R.; Fillo, S.; Luca, V.; Faggioni, G.; D’Amore, N.; Regalbuto, E.; Salvatori, P.; et al. Magnetic beads combined with carbon black-based screen-printed electrodes for COVID-19: A reliable and miniaturized electrochemical immunosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuş, E.; Erdemir, E.; Demirbilek, N.; Liv, L. Colorimetric and electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen with a gold nanoparticle-based biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1182, 338939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Pan, Y.; Li, Z.; Qin, Z.; Rini, J.M.; Liu, X. SPEEDS: A portable serological testing platform for rapid electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2-cobas |cobas |FDA-EUA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137605/download (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- Hou, Y.; Lv, C.-C.; Guo, Y.-L.; Ma, X.-H.; Liu, W.; Jin, Y.; Li, B.-X.; Yang, M.; Yao, S.-Y. Recent Advances and Applications in Paper-Based Devices for Point-of-Care Testing. J. Anal. Test. 2022, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochia, R. Paper-based biosensors: Frontiers in point-of-care detection of covid-19 disease. Biosensors 2021, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Akram, M.S.; Lowe, C.R. Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2210–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafeef, M.; Dighe, K.; Moitra, P.; Pan, D. Rapid, Ultrasensitive, and Quantitative Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Antisense Oligonucleotides Directed Electrochemical Biosensor Chip. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17028–17045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisomwat, C.; Yakoh, A.; Chuaypen, N.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O. Amplification-free DNA Sensor for the One-Step Detection of the Hepatitis B Virus Using an Automated Paper-Based Lateral Flow Electrochemical Device. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Hennek, J.W.; Ainla, A.; Kumar, A.A.; Lan, W.J.; Im, J.; Smith, B.S.; Zhao, M.; Whitesides, G.M. A Paper-Based Pop-up Electrochemical Device for Analysis of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6326–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Integration of Solution-Based Assays onto Lateral Flow Device for One-Step Quantitative Point-of-Care Diagnostics Using Personal Glucose Meter. ACS Sensors 2016, 1, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliliazar, S.; Toldrà, A.; Chondrogiannis, G.; Hamedi, M.M. Electroanalytical Paper-Based Nucleic Acid Amplification Biosensors with Integrated Thread Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14187–14195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoh, A.; Pimpitak, U.; Rengpipat, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Chaiyo, S. Paper-based electrochemical biosensor for diagnosing COVID-19: Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Crooks, R.M. Aptamer-Based Origami Paper Analytical Device for Electrochemical Detection of Adenosine. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6925–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, E.L.; Silva, T.A.; do Prado, T.M.; de Moraes, F.C.; Faria, R.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Electrochemical paper-based microfluidic device for high throughput multiplexed analysis. Talanta 2019, 203, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisomwat, C.; Teengam, P.; Chuaypen, N.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Vilaivan, T.; Chailapakul, O. Pop-up paper electrochemical device for label-free hepatitis B virus DNA detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2020, 316, 128077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, F.; Peterson, J.R.; Gooding, J.J. The application of personal glucose meters as universal point-of-care diagnostic tools. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.T.; de Araujo, W.R.; de Lima, L.F.; Ferreira, A.L.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Low-cost biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 at the point of care. Matter 2021, 4, 2403–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.A.; Khan, S.A.; Rehman, A. Screen-Printed Graphene/Carbon Electrodes on Paper Substrates as Impedance Sensors for Detection of Coronavirus in Nasopharyngeal Fluid Samples. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qin, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, T.; Peng, R.; Li, Z.; Rini, J.M.; Liu, X. Enhancing the performance of paper-based electrochemical impedance spectroscopy nanobiosensors: An experimental approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolai, S.; Tabib-Azar, M. Whole virus detection using aptamers and paper-based sensor potentiometry. Med. DEVICES SENSORS 2020, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, A.; Das, J.; Yousefi, H.; Mahmud, A.; Chen, J.B.; Kelley, S.O. Strategies for Biomolecular Analysis and Continuous Physiological Monitoring. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5281–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Cederquist, K.B.; Zaragoza, A.A.; Lee, P.E.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. An ultrasensitive universal detector based on neutralizer displacement. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besant, J.D.; Das, J.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Proximal bacterial lysis and detection in nanoliter wells using electrochemistry. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8183–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Kelley, S.O. Tuning the bacterial detection sensitivity of nanostructured microelectrodes. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7333–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.; Das, J.; Holmes, R.D.; Live, L.; Sage, A.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Solution-based circuits enable rapid and multiplexed pathogen detection. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Das, J.; Mepham, A.H.; Nemr, C.R.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. A fully-integrated and automated testing device for PCR-free viral nucleic acid detection in whole blood. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Mahmud, A.; Chang, D.; Das, J.; Gomis, S.; Chen, J.B.; Wang, H.; Been, T.; Yip, L.; Coomes, E.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Particles Using Direct, Reagent-Free Electrochemical Sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Gomis, S.; Chen, J.B.; Yousefi, H.; Ahmed, S.; Mahmud, A.; Zhou, W.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Reagentless biomolecular analysis using a molecular pendulum. Nat. Chem. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idili, A.; Parolo, C.; Alvarez-Diduk, R.; Merkoçi, A. Rapid and Efficient Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Using an Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensor. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liv, L.; Yener, M.; Çoban, G.; Can, Ş.A. Electrochemical biosensing platform based on hydrogen bonding for detection of the SARS-CoV-2 spike antibody. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 414, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Yi, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, G. An electrochemical biosensor for sensitive analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M.; Ambrosi, A.; Ding, C.; Luo, X. Electrochemical Biosensor with Enhanced Antifouling Capability for COVID-19 Nucleic Acid Detection in Complex Biological Media. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 5963–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, L.F.; Ferreira, A.L.; Torres, M.D.T.; de Araujo, W.R.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Minute-scale detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a low-cost biosensor composed of pencil graphite electrodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlamani, B.S.; Uppal, T.; Verma, S.C.; Misra, M. Functionalized TiO2 Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sensors 2020, 20, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.Z.; Kopechek, J.A.; Priddy, M.C.; Hamorsky, K.T.; Palmer, K.E.; Mittal, N.; Valdez, J.; Flynn, J.; Williams, S.J. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies using electrochemical impedance-based detector. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Wustoni, S.; Koklu, A.; Díaz-Galicia, E.; Moser, M.; Hama, A.; Alqahtani, A.A.; Ahmad, A.N.; Alhamlan, F.S.; Shuaib, M.; et al. Rapid single-molecule detection of COVID-19 and MERS antigens via nanobody-functionalized organic electrochemical transistors. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, A.; Song, J.; Wang, N.; Lam, P.; Li, Y.; Law, H.K.W.; Yan, F. Ultrafast, sensitive, and portable detection of COVID-19 IgG using flexible organic electrochemical transistors. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 8387–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alireza Hashemi, S.; Bahrani, S.; Mojtaba Mousavi, S.; Omidifar, N.; Ghaleh Golab Behbahan, N.; Arjmand, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Bagheri Lankarani, K.; Moghadami, M.; Shokripour, M.; et al. Ultra-precise label-free nanosensor based on integrated graphene with Au nanostars toward direct detection of IgG antibodies of SARS-CoV-2 in blood. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 894, 115341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Yao, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xie, M.; Zhang, K. Entropy-driven amplified electrochemiluminescence biosensor for RdRp gene of SARS-CoV-2 detection with self-assembled DNA tetrahedron scaffolds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, L.; Sadjadi, S.; Sheini, A.; Mohagheghpour, E. A nanoscale genosensor for early detection of COVID-19 by voltammetric determination of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) sequence of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.; Park, N.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.D.; Park, S.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, J.H. Ultra-fast and recyclable DNA biosensor for point-of-care detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 185, 113177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanujam, A.; Almodovar, S.; Botte, G.G. Ultra-Fast Electrochemical Sensor for Point-of-Care COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Non-Invasive Saliva Sampling. Processes 2021, 9, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miripour, Z.S.; Sarrami-Forooshani, R.; Sanati, H.; Makarem, J.; Taheri, M.S.; Shojaeian, F.; Eskafi, A.H.; Abbasvandi, F.; Namdar, N.; Ghafari, H.; et al. Real-time diagnosis of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in fresh sputum by electrochemical tracing; correlation between COVID-19 and viral-induced ROS in lung/respiratory epithelium during this pandemic. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fan, T.; Xiong, R.; Shen, X.; Feng, H.; Meng, H.; Lin, W.; Jiang, W.; et al. The clinical course and its correlated immune status in COVID-19 pneumonia. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 127, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, N.N.; Hassan, U.; Damhorst, G.; Ni, H.K.; Vaid, A.; Rodriguez, W.; Bashir, R. Microfluidic CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocyte counters for point-of-care HIV diagnostics using whole blood. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 214ra170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiew, L.V.; Chang, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Wang, P.W.; Heh, C.H.; Te Liu, C.; Cheng, C.H.; Lu, Y.X.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, Y.X.; et al. Development of flexible electrochemical impedance spectroscopy-based biosensing platform for rapid screening of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 183, 113213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yu, H.; Sun, F.; Ornob, A.; Brisbin, R.; Ganguli, A.; Vemuri, V.; Strzebonski, P.; Cui, G.; Allen, K.J.; et al. Mobile Platform for Multiplexed Detection and Differentiation of Disease-Specific Nucleic Acid Sequences, Using Microfluidic Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification and Smartphone Detection. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11219–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brangel, P.; Sobarzo, A.; Parolo, C.; Miller, B.S.; Howes, P.D.; Gelkop, S.; Lutwama, J.J.; Dye, J.M.; McKendry, R.A.; Lobel, L.; et al. A Serological Point-of-Care Test for the Detection of IgG Antibodies against Ebola Virus in Human Survivors. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DetectaChem MobileDetect Bio BCC19 Test Kit. Available online: https://www.detectachem.com/index.php?p=COVID19 (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- ArcDia Ltd Press release: ArcDia Ltd’s Automated Coronavirus Point-of-Care Test CE Marked and Available-MariPOC. Available online: https://www.arcdia.com/uutiset/mediatiedote-suomalaisen-arcdia-oyn-koronavirustesti-on-ce-merkitty-ja-saatavilla-heti/ (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Spencer Chin Portable Lab Uses Smartphone to Detect Viruses|FierceElectronics, 7 Feb 2020. Available online: https://www.fierceelectronics.com/sensors/use-a-smartphone-to-help-detect-viruses?fbclid=IwAR2SSyP4Vl7NAxVYEB1UjwAOhqw-kbm19hKfBdMovqgZurTvtM1cY8vF8V4 (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Soenksen, L.R.; Donghia, N.M.; Angenent-Mari, N.M.; de Puig, H.; Huang, A.; Lee, R.; Slomovic, S.; Galbersanini, T.; Lansberry, G.; et al. Wearable materials with embedded synthetic biology sensors for biomolecule detection. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Geryak, R.; Geldmeier, J.; Kim, S.; Tsukruk, V.V. Synthesis, Assembly, and Applications of Hybrid Nanostructures for Biosensing. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12942–13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée-Bélisle, A.; Ricci, F.; Plaxco, K.W. Engineering biosensors with extended, narrowed, or arbitrarily edited dynamic range. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2876–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England COVID-19: Rapid Tests for Use in Community Pharmacies or at Home. 15 Mar 2020. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-rapid-tests-for-use-in-community-pharmacies-or-at-home/covid-19-rapid-tests-for-use-in-community-pharmacies-or-at-home (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- He, Q.; Du, Q.; Lau, S.; Manopo, I.; Lu, L.; Chan, S.W.; Fenner, B.J.; Kwang, J. Characterization of monoclonal antibody against SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid antigen and development of an antigen capture ELISA. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 127, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, P.K.H.; Ooi, E.E.; Tan, H.K.; Ong, K.W.; Sil, B.K.; Teo, M.; Ng, T.; Soo, K.C. Healthcare Worker Seroconversion in SARS Outbreak. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jin, R.; Peng, Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, W.; Lv, F.; Gong, S.; Fang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Generation of Antibodies against COVID-19 Virus for Development of Diagnostic Tools. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Academia Sinica Catching Virus Fast! Academia Sinica Discovered Useful Antibodies for Developing Rapid Immune based Test Kit of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.sinica.edu.tw/en/news/6505 (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M.; Henry, B.M. Thrombocytopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 506, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulhaq, Z.S.; Soraya, G.V. Interleukin-6 as a potential biomarker of COVID-19 progression. Med. Mal. Infect. 2020, 50, 382–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiang, X.; Ren, H.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, X.; Long, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q. Serum Amyloid A is a biomarker of severe Coronavirus Disease and poor prognosis. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.C.; Rana, M.M.; Kazuhiro, T.; Suzuki, H. Data from: A simple micropump based on a freeze-dried superabsorbent polymer for multiplex solution processing in disposable devices. Dryad Dataset 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, K.; Zeng, J. Design Automation Methods and Tools for Microfluidics-Based Biochips; Chakrabarty, K., Zeng, J., Eds.; Springer: The Netherlands, 2006; ISBN 9781402051227. [Google Scholar]
- Bezuidenhout, P.; Smith, S.; Joubert, T.H. A Low-Cost Inkjet-Printed Paper-Based Potentiostat. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bioprocessing Approaches | Analytes | Samples | Transducers | Analyzers | LOD | Assay Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) | |||||||
| ePlex SARS-CoV-2 test; Electrowetting-based digital microfluidic chip—automated, sample-to-answer platform—RT-PCR—competitive DNA hybridization | RNA | Nasopharyngeal | Electrochemical | GenMark’s ePlex instrument | 1 × 105 copies/mL | <2h | [62] |
| (i) Isothermal nucleic acid amplification (iNAA)-based electrochemical NAT | |||||||
| RT-eLAMP assay; CMOS-ISFET-based portable microfluidic LOC; epidemiological reporting | RNA (N gene) | Clinical swab samples | Potentiometric | Battery-powered handheld analyzer; Smartphone | 10 RNA copies/reaction | <20 min | [65] |
| Body heat-based on-chip RPA; microchip—Au thin film WE—thiol-modified primers—RPA amplicons— hybridization; K3[Fe(CN)6] | RdRP and N gene | Extracted sample | DPV | CHI 830B instrument (CH Instruments, USA) | 0.972 fg/μL (RdRP gene) and 3.925 fg/μL (N gene) | <20 min | [66] |
| RCA-based single-step sandwich hybridization assay; SPCE—CP-MNB + RCA amplicons + Si-RP (SiMB and SiAO) | N and S genes | Nasopharyngeal and throat swab samples | DPV | Palmsens4 potentiostat with a laptop | 1 copy/mL | <2 h | [72] |
| TriSilix chip; Si–Au, Ag-plated Cu-PET-PE; RCA/PCR; methylene blue redox reporter | cDNA | Synthetic sample | SWV | Handheld potentiostat (PalmSens3) | 20 fg of genomic DNA | Real-time | [67] |
| CRISPR assay; Au Chip/GO-PNA-ssDNA-amplicon; EDC/NHS-antigen | RNA and IgG/IgM | Saliva | CV | Autolab | Attomolar | 1 h | [76] |
| (ii) Amplification-free POC electrochemical NAT | |||||||
| Supersandwich electrochemical assay; SPCE chip—Au@SCX8-RGO-TB nanocomposite—MB—capture DNA probe | RNA | Clinical samples | DPV | Sensit Smart workstation (PalmSens), Smartphone | 200 RNA copies/mL | Few seconds | [68] |
| SPGE-Au nanoneedle-MCH-UDH probe; 4-WJ) hybridization; K3[Fe (CN)6]/K4[Fe(CN)6] redox probe | S and Orf1ab genes | Clinical samples | EIS, SWV | CH instruments | 2 or 3 copies/µL | 1 h | [69] |
| SPCE-streptavidin/biotin-EDC/NHS-ssDNA-FITC probe-HRP-TMB/H2O2 | Mimicked sample sequence | Mimicked sample sequence | Chronoamperometry | Autolab | 1 pM | 1 h | [78] |
| Automated microfluidics; amplification-free; eSIREN; inhibition interaction; SPE chip—inverter DNA sequences—RNA hybridization—biotin/dNTPs—streptavidin/HRP—TMB | RNA | Extracted RNA, Swab sample | Amperometry | Miniaturized potentiostat (PalmSens, EmStat3) | 7 RNA copies/µL | <20 min | [70]. |
| Bifunctional G-FET Chip—PBASE linker—ssDNA probe or antigen; hybridization technique | RNA and IgG/IgM | Oropharyngeal swabs and serums | Electrical (FET) | Home-built detector | ~0.1 and ~1 fg/mL for RNA and antibodies | 10 and 5 min respectively | [85] |
| (iii) Label-free electrochemical NAT | |||||||
| AuNP-electrodeposited titanium substrate—RNA/DNA hybridization; label-free | RNA/c-DNA | - | DPV/EIS | Smartphone analyzer | - | - | [86]. |
| ITO–PPy–AuNP–Cys–primer–BSA; 4[Fe(CN)6]/K3[Fe(CN)6] redox probe | N gene | Synthetic sample | EIS | Autolab (Metrohm) | 258.01 copies/µL | 15 min | [71] |
| Flex PCB—graphene WE- streptavidin/biotin-ssDNA-gene—ferro/ferricyanide redox couple | ORF1ab gene | Synthetic DNA | DPV | - | 5 × 105 copies/µL | 30 min | [87] |
| B. Immunoassays (antigen/antibody testing) | |||||||
| (i) Electrochemical antigen testing | |||||||
| LSG/AuNS Immunosensor; (LSG/AuNS/Cys/EDC:NHS/anti-SARS-CoV-2/BSA) | Spike (S) protein | Blood | DPV, CV | Handmade potentiosta with smartphone | 2.9 ng/mL | 1 h | [96] |
| Cotton-tipped sensor; carbon nanofiber (CNF)-SPE—EDC/NHS—N protein; competitive assay | N protein | Spiked nasal sample | SWV | - | 0.8 pg/mL | 20 min | [97] |
| Pt interdigitated electrode AuNP—organic ligand—VOCs | - | Exhaled breath | Conductivity | Handheld custom-made analyzer | 90% accuracy, 95% specificity | - | [98] |
| Face mask-based EBC collection; aptamer-SPE-Au electrode—thiol/EDC:NHS; ferrocenemethanol redox mediator | S protein | Exhaled breath condensate | DPV | Sensit-Smart smartphone potentiostat (PalmSens) | 10 pfu/mL | 10 min | [94] |
| Thin-film Au WE-optimer/aptamer-TCEP-BSA | S1 protein | Commercialized sample | EIS | - | 80 ng/mL (tested conc.) | 15 min | [102] |
| PCB/thin-film Au E-PFDT-ACE2–spike protein | S Protein | Recombinant protein | EIS | - | 1.68 ng/mL | 30 min | [103] |
| Si/SiO2-CNT-FET-PBASE linker—anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 | S1 protein | Fortified saliva | FET | Keithley 3 probe station | 4.12 fg/mL | 2–3 min | [99] |
| Microfabricated graphene FET chip—PBASE linker—anti-S protein | Spike (S) protein | Nasopharyngeal swab and cultured particle | FET | Semiconductor analyzer and probe station | 242 virus copies/mL; 16 pfu/mL of cultured particles | Real-time to 10 min | [105] |
| Si MOSFET with glucose strip—Au clusters—antibodies; dual detection | S protein and cTnI | Saliva and spiked sample | Pulse method | Custom-made analyzer | 100 fg/mL | - | [100] |
| SPCE-mAb or AuNP- FTO—antibody; K3[Fe(CN)6]/K4[Fe(CN)6] | S protein | Spiked saliva | DPV | Home-built eCovSens | 90 fM | 30 s | [106] |
| Graphene SPE—PBASE - monoclonal anti-spike antibody | S protein | Saliva | EIS/CV | PalmSens 4 | 20 µg/mL | 45 min | [107] |
| SPCE-Cu2ONCs-ProtA—BSA—IgG | S protein | Saliva, artificial nasal swab | EIS | μ-Autolab type III | 0.04/fg mL | 20 min | [108] |
| Multichannel immunoassay (MEIA); SPCE—mAb—HRP—TMB | Spike protein | Clinical samples | Amperometry | Emstat Potentiostat (Palmsens) | 0.15 ng/ mL for SARS-CoV-2 1.12 unit/mL for A(H1N1) | 1 min | [110] |
| Carbon black—SPE—MBs—ALP—pAb | S and N protein | Saliva | DPV | Portable PalmSens3, computer | 19 ng/mL (S), 8 ng/mL (N) | 30 min | [114] |
| Microfluidic chip—SPGE—cAb—dually labeled MB—dAb-HRP—TMB | N protein | Whole serum | Chronoamperometry | PalmSens4, Sensit Smart potentiostat, Smartphone | 50 pg/mL and 10 pg/mL in whole serum and 5-fold diluted serum | <1 h | [111] |
| AU-TFE—MIP(PmPD)—ncovNP; ferri/ferrocyanide redox pair | N protein | Nasopharyngeal swab | DPV | EmStat3 Blue and Sensit Smart (PalmSens), Smartphone | 15 fM | 45 min | [92] |
| MP Au-SPE—MIP (oPD)—SARS-CoV-2-RBD; Fe(CN)6 3-/4-redox probe | RBD protein | Saliva solution | EIS | - | 0.7 pg/mL | 20 min | [91] |
| Bioelectric recognition assay (BERA); eight Au SPE—mammalian cells -electroinserted or membrane-bound antibodies—antigen | S1 protein | Synthesized samples | Potentiometry | Multichannel potentiometer (Embio Diagnostics Ltd., Cyprus), smartphone reader | 1 fg/mL | 3 min | [93] |
| SCPE/GNP-MV-gal1—spiked virus or protein; [Fe(CN)6]−3/−4 redox probe | Virus/antigen | Nasopharyngeal swab | EIS | SP-300 Instruments (SP-300) Texas, USA | 4.57 × 102 copies/mL | ~5 min | [95] |
| AuNP and/or SPE—thiol-EDC/NHS –BSA—mAb | S protein | Recombinant protein | Colorimetric and SWV | Metrohm Dropsens potentiostat | 48 ng/mL (colorimetric), 1 pg/mL (electrochemical) | 10 min | [115] |
| (ii) Electrochemical antibody testing | |||||||
| 3DcC chip—rGO nanoflakes—AuNPs micropillar—EDC:NHS—S1 and RBD | Spike S1 and RBD antibodies | Readymade antibodies | EIS | Sensit Smart workstation (PalmSens), Smartphone | 1.0 pM for spike S1 and 1.0 fM for RBD Ab | 11.5 s | [112] |
| Laser-engraved graphene (LEG) electrodes on polyimide—PBA—DMF—EDC:NHS—MES—capture protein—HRP–TMB; multiplex detection; telemedicine | N protein, S1-IgG, S1-IgM, and C-reactive protein | Saliva and blood | RapidPlex Amperometric | CHI820 electrochemical station, smartphone | - | 1 min | [113] |
| SPCE-streptavidin/biotin- anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD protein-ALP/pAPP | IgG and IgM | Serum | Chronoamperometry | PalmSens EmStat3 Blue, smartphone | 10.1 ng/mL (IgG), 1.64 ng/mL (IgM) | 13 min | [116] |
| Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 assay; microparticles—streptavidin/biotin—magnetic capture—electrode—recombinant antigen labeled with a ruthenium complex | N protein-specific antibodies | Serum and plasma | Electro-chemiluminescence | Cobas e analyzer | Specificity: 99.80%; Sensitivity: 85.3% | 18 min | [117] |
| Bioprocessing Approaches | Analytes | Samples | Transducers | Analyzers | LOD | Assay Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ePAD with graphene—AuNPs—ssDNA—two genes; Hybridization technique | N gene | Nasopharyngeal, nasal Swab and saliva | Electrochemical | Home-built circuit | 6.9 copies/µL | <5 min | [121] |
| ePAD-SPE; GO—EDC/NHS-SP RBD; label-free | IgG and IgM | Clinical sera | SPV, EIS | Wireless PalmSens potentiostat, Smartphone | 1 ng/mL | 30 min | [126] |
| ePAD—carbon and Ag/AgCl inks—gluteraldehyde—ACE 2 receptor | S protein | Nasopharyngeal/oropharyngeal swab | EIS | Sensit Smart (PalmSens) potentiostats, smartphone | 2.8 fg/mL | 4 min | [131] |
| µPAD-SPE—graphene/carbon WE—PBASE or ProtA—IgG antibody; label-free | S, RBD protein | Nasopharyngeal Swab | EIS, CV | PalmSens4 or SensIT BT, smartphone | 0.25 fg/mL (limit of quantification) | 5 min | [132] |
| μPAD—ZnO NWs WE—capture probe—blocking agent; label-free detection | P24 antigen for HIV, IgG for SARS-CoV-2 | Spiked serum | EIS | Autolab | 0.4 pg/mL (HIV) | ~20 min | [133] |
| Bioprocessing Approaches | Analytes | Samples | Transducers | Analyzers | LOD | Assay Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reagent-free sensing with a molecular pendulum; electrode-tethered sensors; Au thin-film WE—thiolated probe/PBS/TCEP—antibody-conjugated complementary probe/MCH—analyte | Spike protein, viral particles | Saliva sample | Chronoamperometry | Epsilon BASi potentiostat | 1 pg of spike protein, 4 × 103 particles per mL | 5 min | [141] |
| reagentless, single-step sensing; Au WE-MCH-Aptamer-Atto MB2 | S protein | Serum and artificial saliva | SWV | - | Clinical range | 5 min | [143] |
| OECTs (PEDOT:PSS Channel)-AuE- SpyTag/SpyCatcher linker- spike protein-specific nanobody; [Fe(CN)6]3−/4 redox probe | Spike proteins | Untreated saliva and nasopharyngeal swab | EIS/CV | Autolab | 23 fM | ~10 min | [150] |
| Flexible OECTs (PEDOT:PSS Channel)-AuE- MAA-GOPS [(3-glycidyloxypropyl)trimethoxysilane]–spike protein–BSA | IgG | Serum and saliva | EIS | Portable meter (PolyU), BlueTooth, Smartphone | 10 fM | 5 min | [151] |
| GCE or SPCE-GO/gold nanostars (Au NS)—antigen; label-free | monoclonal IgG antibodies | Blood plasma | CV, EIS | - | 0.18 × 10−19% V/V | 1 min | [152] |
| GCE/Au/CysOH/S-gene/BSA or GCE/Au/CysAm/GluAl/S gene/BSA | Spike antibody | Synthetic and spiked real sample | SWV, CV | Autolab | 0.03 fg and 0.01 ag/mL respectively | 35 min | [144] |
| HP/MCH/AuE-RNA—dNTP-Ru(NH3)63+ | RNA (26 nt long ORF1ab fragment) | Serum and saliva | EIS | CHI660D Potentiostat | 26 fM | 2 h | [145] |
| Au WE—EDC/NHS—S3 DNA-Ru(bpy)32+ | RdRp gene | Serum | ECL | CHI 660 E | <2.67 fM | 45 min | [153] |
| Carbon paste electrode (CPE)/(HT18C6(Ag))//chitosan/SiQDs@PAMAM—ssDNA | RdRP gene | Sputum | DPV | PGSTAT 302N workstation (Autolab) | 0.3 pM | 25 min | [154] |
| GCE-PANI nanowires—inverted Y-peptides-streptavidin/biotin—capture probe | N-gene | Serum | DPV, CV | CHI 660 E | 3.5 fM | 1 h | [146] |
| Platinum/titanium interdigitated electrodes on glass; APTES-ssDNA probe; label-free | RdRp gene | Synthetic sample | Capacitance–frequency | - | 0.843 nF/nM | Few seconds | [155] |
| Graphite pencil electrode (GPE)–gluteraldehyde– AuNP Cys–EDC/NHS chemistry ACE2 | S protein | Saliva, nasopharyngeal/oropharyngeal swab | SWP | Multi Autolab | 229 fg/mL | 6.5 min | [147] |
| Rotating disc electrode (RDE); Ni disc WE/Pt ring CE/Pt foil RE-NiOOH-protein | S1 protein | Saliva | Chronoamperometry | Gamry Reference 600+ Potentiostat | - | 100 milliseconds | [156] |
| Ti foil WE/Pt CE with Cu wiring—Co-functionalized TiO2 nanotubes (Co-TNTs)—capture protein | S-RBD protein | Nasal swab and saliva | Amperometric | Co-TNT packed PCB with a Gamry reference 600+ potentiostat | 0.7 nM | 30 s | [148] |
| Needle-tip electrode—MWCNTs—ROS/H2O2 | ROS | Sputum | CV | Custom-built device | 94% accuracy and 92% sensitivity | 30 s | [157] |
| 16-well plate with interdigitated electrode beneath the wells—coated with RBD protein | Monoclonal antibody | - | Impedance | Impedance analyzer (Agilent 4294A) | - | 5 min | [149] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswas, G.C.; Choudhury, S.; Rabbani, M.M.; Das, J. A Review on Potential Electrochemical Point-of-Care Tests Targeting Pandemic Infectious Disease Detection: COVID-19 as a Reference. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070269
Biswas GC, Choudhury S, Rabbani MM, Das J. A Review on Potential Electrochemical Point-of-Care Tests Targeting Pandemic Infectious Disease Detection: COVID-19 as a Reference. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(7):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070269
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswas, Gokul Chandra, Swapnila Choudhury, Mohammad Mahbub Rabbani, and Jagotamoy Das. 2022. "A Review on Potential Electrochemical Point-of-Care Tests Targeting Pandemic Infectious Disease Detection: COVID-19 as a Reference" Chemosensors 10, no. 7: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070269
APA StyleBiswas, G. C., Choudhury, S., Rabbani, M. M., & Das, J. (2022). A Review on Potential Electrochemical Point-of-Care Tests Targeting Pandemic Infectious Disease Detection: COVID-19 as a Reference. Chemosensors, 10(7), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070269








