Abstract
An illustrative sketch style expresses important shapes and regions of objects and scenes with salient lines and dark tones, while abstracting less important shapes and regions as vacant spaces. We present a framework that produces illustrative sketch styles from various photographs. Our framework is designed using a generative adversarial network (GAN), which comprised four modules: a style extraction module, a generator module, a discriminator module and RCCL module. We devise two key ideas to effectively extract illustrative sketch styles from sample artworks and to apply them to input photographs. The first idea is using an attention map that extracts the required style features from important shapes and regions of sample illustrative sketch styles. This attention map is used in the generator module of our framework for the effective production of illustrative sketch styles. The second idea is using a relaxed cycle consistency loss that evaluates the quality of the produced illustrative sketch styles by comparing images that are reconstructed from the produced illustrative sketch styles and the input photographs. This relaxed cycle consistency loss focuses on the comparison of important shapes and regions for an effective evaluation of the quality of the produced illustrative sketch styles. Our GAN-based framework with an attention map and a relaxed cycle consistency loss effectively produces illustrative sketch styles on various target photographs, including portraits, landscapes, and still lifes. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework through a human study, ablation study, and Frechet Inception Distance evaluation.
1. Introduction
The illustrative sketch art style has been expressed by many artists for a long time. Artists express salient objects in a scene through a series of lines and dark tones and omit unimportant details as vacant spaces. Many artists apply this style to draw various artworks, such as portraits, landscapes and still lifes. In computer graphics and computer vision, many researchers have developed computational models of various backgrounds that produce illustrative sketch styles. Early approaches apply explicit computational models that produce lines and tonal expressions from an input photograph [1,2,3,4,5]. Many recent approaches apply rapidly progressing deep learning (DL) techniques [6,7,8,9,10].
Early approaches produce illustrative sketch styles on an input photograph by extracting salient features from the input photograph. They produce thick and solid lines on the features that mimic the strokes of artistic media. Several schemes, including line integral convolution (LIC) [2], bilateral filters [3], the difference of Gaussian (DoG) [4], and spline curves [1] are applied to extract and produce lines. The less important regions are filled with smooth and less salient stroke or texture patterns [5]. Although they produce visually convincing illustrative sketch styles, they have several limitations. These approaches rely on the robust extraction of salient features, which is a challenge in several cases. The produced lines and tones frequently reveal serious artifacts. The produced styles cannot cover diverse artistic illustrative sketch styles.
Recent DL-based approaches have applied feature maps extracted from convolutional neural network (CNN) models. Since feature maps possess many clues to recognizing objects in a scene, they can play a key role in recognizing salient features to produce illustrative sketch styles. Many DL models for style transfer can produce illustrative sketch styles [6,7,8]. These models, however, have limitations in the clear expression of salient edges, smooth tones, and vacant spaces, because they produce styles using texture transfer. Some dedicated models produce illustrative sketch styles from portraits [9,10]. Although they successfully produce visually convincing illustrative sketch images, they have limitations in the production of illustrative styles for photographs, which are not included in their training dataset.
We present a generative adversarial network (GAN)-based framework that produces illustrative sketch styles of various photographs. Our framework comprised four modules: a style extraction module, a generator module, a discriminator module and RCCL module.
Our first idea is to apply an attention map to extract the style features from illustrative sketch samples and to apply them to the input photographs. Since an illustrative sketch style expresses salient features using strokes and dark tones, concentrating on salient features enriches illustrative sketch styles. Therefore, an attention map that effectively extracts salient features is applied in the style extraction module. We apply the attention map approach in our generator to more effectively produce illustrative sketch styles. Since our model employs the style features that were extracted from sample images using an attention map, our approach is very effective for illustrative sketch styles that apply thick stroke patterns and dark tones in important regions.
Our second idea is to apply a relaxed cycle consistency loss (RCCL) [10] to evaluate the quality of the produced illustrative sketch styles. We reconstruct the input photograph from the produced illustrative sketch styles and compare it with the input photograph to evaluate the styles. Several researchers have applied cycle consistency loss [7] for comparison. In our framework, however, we should concentrate more on important features instead of using all features to evaluate illustrative sketch styles. Thus, we applied the RCCL [10], which emphasizes important features more, ignoring less important features.
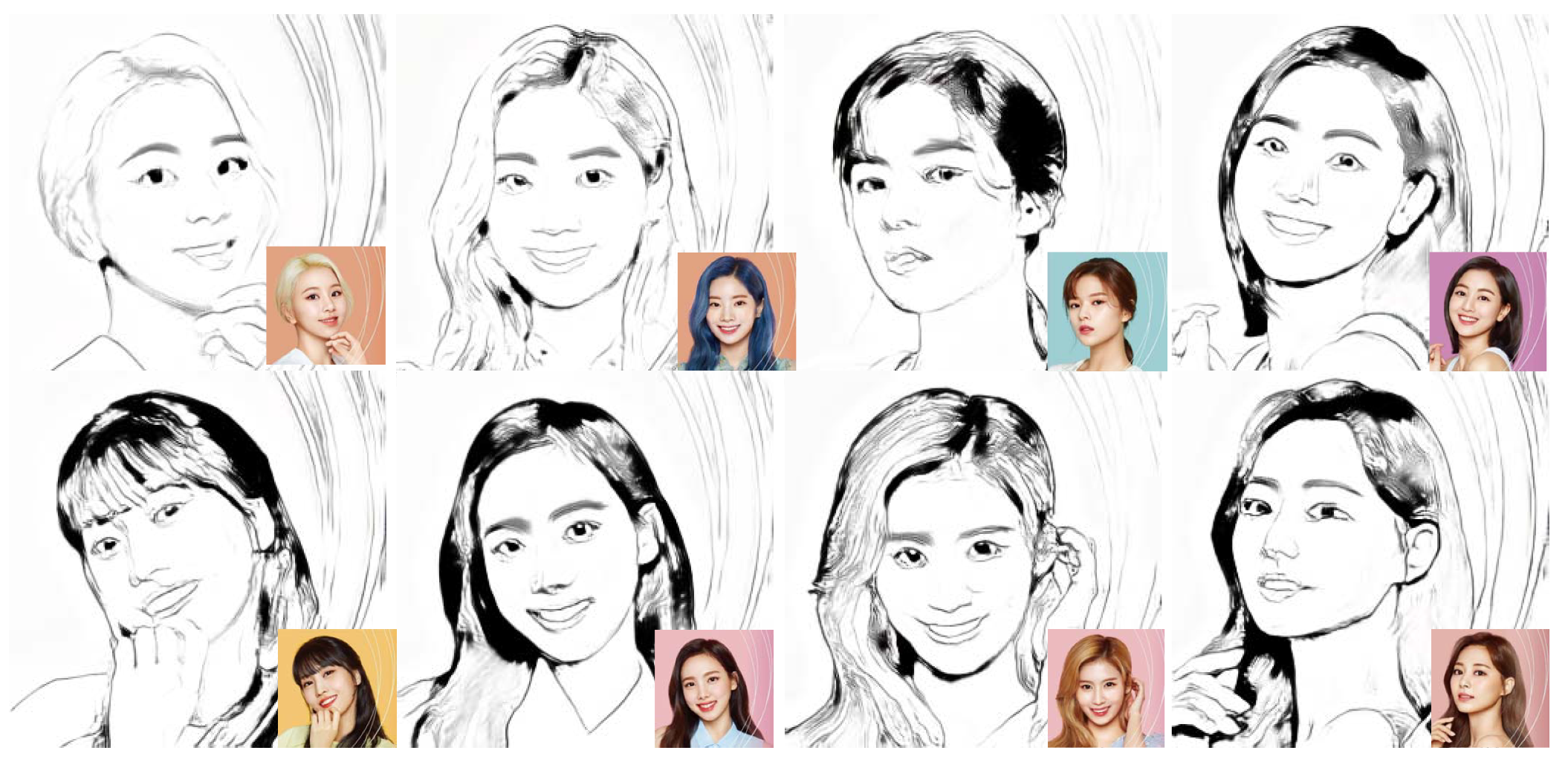
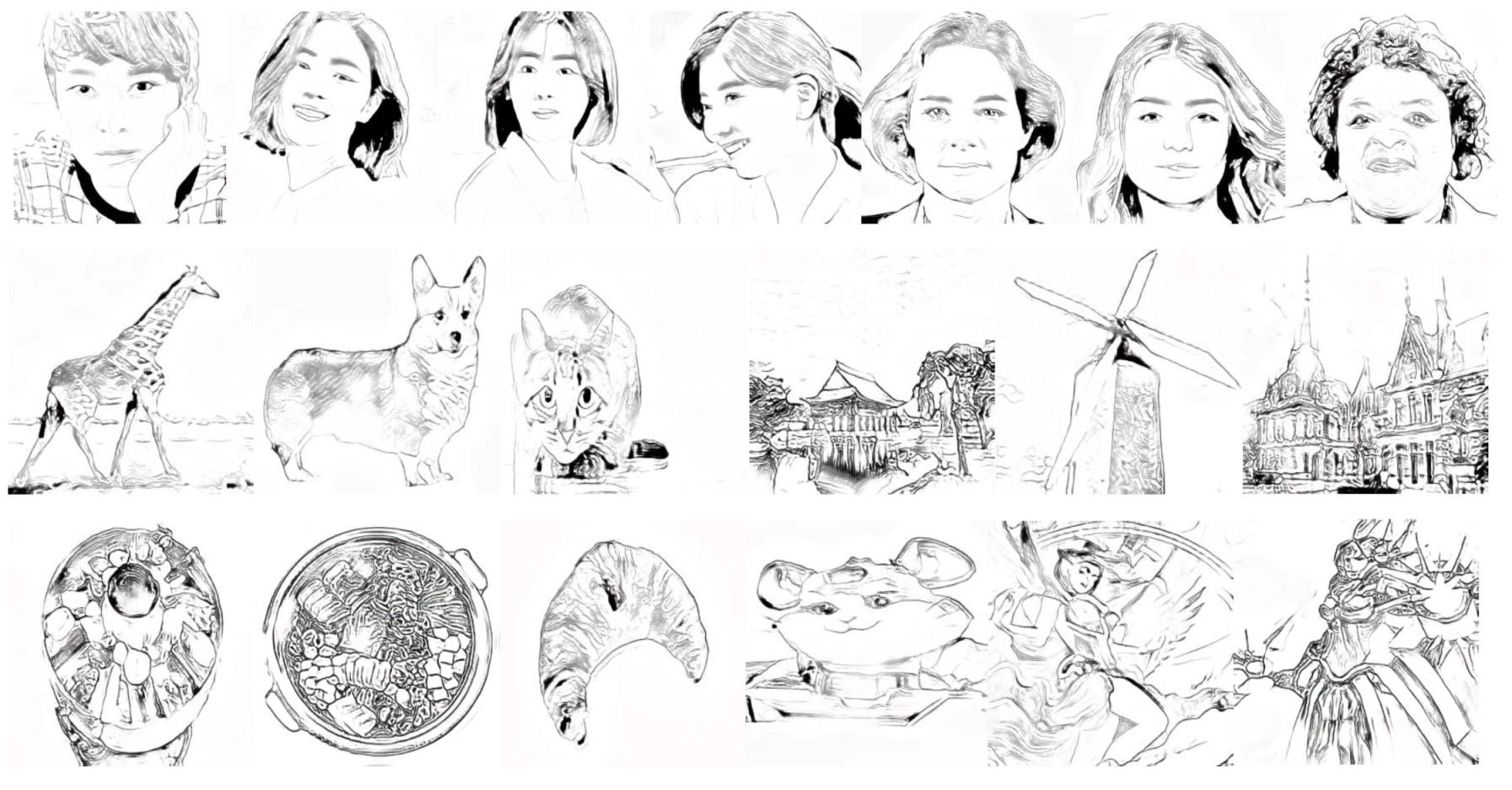
We collect 64 portraits to construct the training dataset in this study. Our challenge is to produce illustrative sketch styles on various photographs including landscapes, animals and still lifes using our model, trained only by portraits. Most portraits include salient features such as eyes, lips, and chin lines, but they lack tiny textures. Figure 1 presents our teaser images that show illustrative sketches for various photographs. Furthermore, we apply our model to various categories of sketches, including landscapes and still lifes.
Figure 1.
The teaser images of our study.
The contributions of this study can be summarized as follows:
- We present a GAN-based framework that produces illustrative sketch styles from various photographs. To facilitate its production, we apply two ideas: an attention map-based approach for style extraction and production and a relaxed cycle consistency to evaluate the produced styles.
- We present an efficient training strategy for illustrative sketch styles. Our framework is trained on a dataset of portraits, and can be applied to produce illustrative sketch styles from landscapes, animals or objects.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the existing works on illustrative sketches and Section 3 presents the outline of our framework. We explain our framework and its components in Section 4 and the loss functions in Section 5. We present the implementation details and results in Section 6 and analyze our results by comparing existing schemes in Section 7. Finally, we conclude this study and present future work in Section 8.
2. Related Work
2.1. Conventional Schemes for Illustrative Sketches
In computer graphics, many techniques that convey the shape of 3D meshes or objects in a photograph have been proposed. DeCarlo et al. [1] presented a suggestive contour that expresses the shape of 3D meshes using contours and some import lines. Kang et al. [2] presented a coherent line, which extracts a salient line from a photograph by performing an LIC through an edge tangent flow. Some researchers have presented hatching-based approaches to express dark tones of 3D meshes.
Kim et al. [11] presented a line art illustration scheme on dynamic objects by drawing hatching lines through principal directions on the surface of objects. Paiva et al. [12] presented a flow-based hatching scheme to produce tonal expression on 3D meshes. They express strokes of line illustration by generating particles on surfaces and integrating them through smooth flow fields on the surface. Coconu et al. [13] presented a pen-and-ink illustration on a photograph by simplifying the scene that is embedded in the photograph. They rendered the scene using stylized silhouette, hatching and abstract shading.
Xu and Kaplan [14] presented an artistic thresholding scheme that produces a black-and-white image from a scene by thresholding the tone of the scene using a proper value. They segment the scene into a planar subdivision graph and apply a combinatorial optimization on the graph to produce the black-and-white image. Mould and Grant [15] presented a similar scheme that produces stylized black-and-white renderings from photographs. They aim to preserve as many details as possible while producing large regions of a solid color. They apply an energy minimization scheme for separate layers of the image. Rosin and Lai [16] proposed an artistic minimal rendering scheme that abstracts an input photograph as a series of dark tones. Inspired by Warhol’s artworks, their scheme re-renders input photographs with a minimal set of tones. They apply a combination of refined lines and blocks to abstract the photographs by considering a tradeoff between the reduction in information and the preservation of shapes.
Benard et al. [17] presented active strokes that produce lines by animating 3D models in a coherent way. Their scheme connects and smooths unorganized line samples to build a coherent parameterization to support the active contours that automatically update the geometry and topology of animating objects. Their scheme can render complex and actively moving objects in a series of thick contour lines. Winnemoller et al. [4] proposed an XDoG algorithm that simplifies the complex shape of input photographs in black-and-white abstracted images. They extend classic DoG edge extraction operator to depict a photograph in various styles.
2.2. General DL Schemes for Illustrative Sketches
The recent DL progress, including CNNs and GANs, has presented an innovative approach to applying various styles to photographs. Among these, pix2pix [6] presents an impressive framework for alternating the styles of paired images. They apply an encoder–decoder structure or U-net structure to their generator. The generation process is performed to input paired images and losses between the generated and original images are computed and minimized to improve the quality of the generated images. Since this generation is performed in both directions, the styles of one domain are transferred to those of the other domain and vice versa. The pix2pix scheme, however, has a limitation: it works only for paired datasets.
Zhu et al. [7] improved the pix2pix framework by releasing requirements for a paired dataset by applying cycle consistency. Their framework, known as CycleGAN, successfully converts styles between two domains instead of two images by minimizing the cycle-consistency loss, which is defined between the original image and the reconstructed image from the original image through cyclic process of style transfer.
Yi et al. [18] presented a DualGAN, which is an improvement of the conditional GAN (CGAN), for cross-domain image-to-image translation. Their scheme does not require human labeled datasets to train their model. The primal GAN of their framework learns to translate from one domain to another, and DualGAN learns to translate in the reverse direction. This closed translation loop learns the translation and reconstruction process of their framework. Huang et al. [8] proposed MUNIT, which presents a multimodal, unsupervised image-to-image translation. They address the problem of producing diverse styles from one source domain image by decomposing an image into a content code and a style code. They apply various styles to the source domain image by combining various style codes to a content code of the image.
These frameworks can translate an input photograph into an illustrative sketch style, which depicts shapes with salient lines and monochrome tones. Nevertheless, these schemes have a limitation: they require heavy training processes and high-quality datasets.
2.3. Dedicated DL Schemes for Illustrative Sketches
Recently, Yi et al. [9] have presented APDrawingGAN that produces an illustrative sketch-styled portrait generation scheme from input photographs. They segment the face into six local regions, including the left eye, right eye, nose, lip, skin and background, and generate each region into an illustrative sketch style using different networks. Finally, they combine the regions into one portrait image. Although they can produce visually pleasing illustrative sketch-styled portraits, their frame is limited to face photographs taken by the front angle. Yi et al. [10] extended their framework in [9] to unpaired portrait drawing by applying asymmetric cycle mapping. For an unpaired portrait transfer without unwanted artifacts, which are frequently observed by cycle consistency-preserving schemes, they propose an asymmetric cycle mapping only embedded in selective regions. They also devise local discriminators for facial regions to preserve important facial features.
An attention map, which is devised for natural language processing, is used in image-to-image translation. Tang et al. [19] and Xie et al. [20] presented an attention-guided GAN for unsupervised image-to-image translation. Kim et al. [21] presented a U-GAT-IT that transforms face photographs into cartoon style portraits. Although they do not produce illustrative sketch-styled portraits, their scheme can be considered an important related work, since they have very successful results in image-to-image translation. They apply an attention map to distinguish important regions in a photograph. Furthermore, they apply a new AdaIN layer to improve shape and texture control on a significant scale. Consequently, they successfully translate face photographs into exaggerated cartoon images.
3. Outline of Our Framework
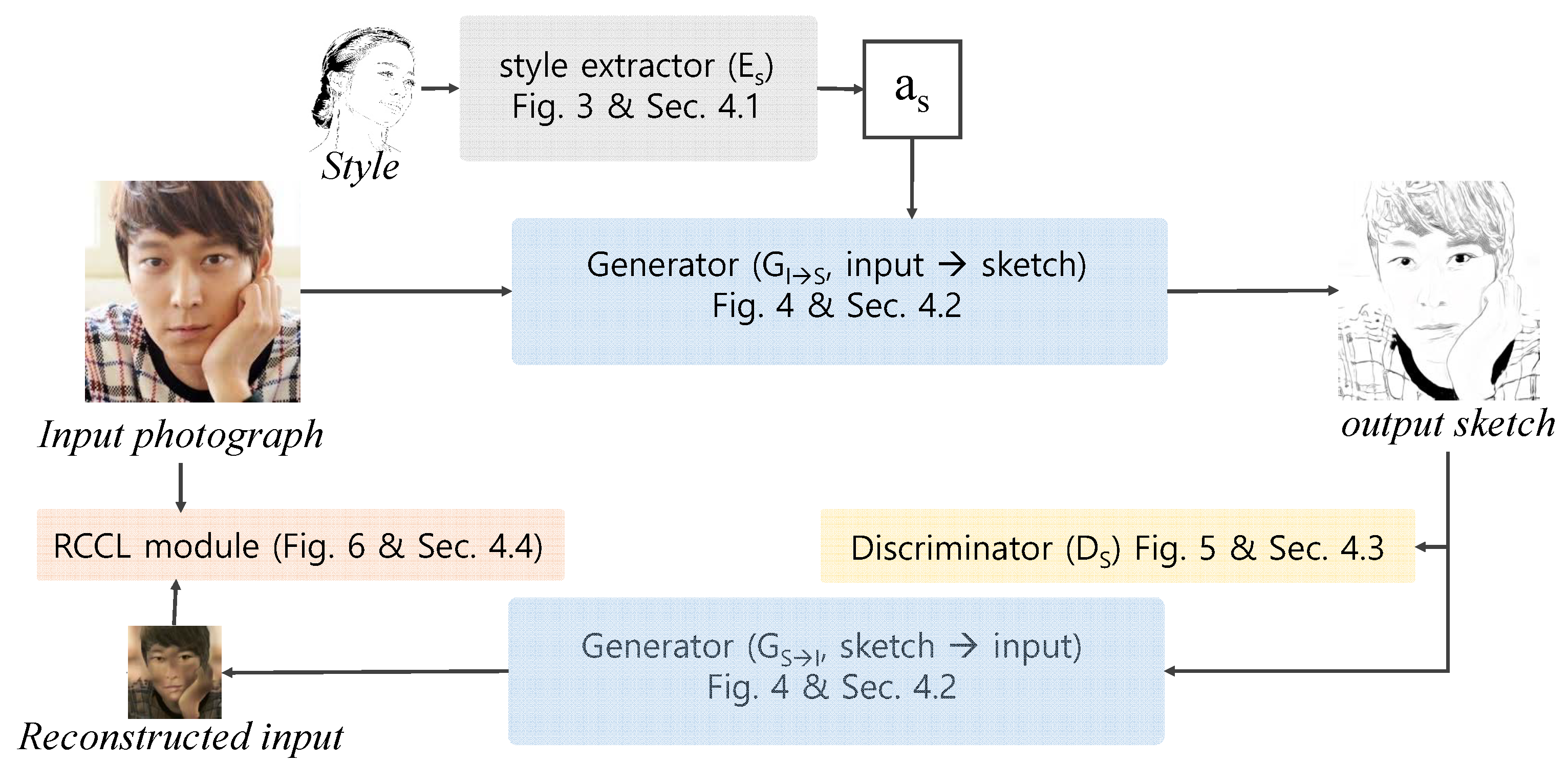
Our framework consists of three main modules: a style extraction module, a generator, a discriminator, and an RCCL module. As illustrated in Figure 2, the style extraction module, denoted as produces a style attention map from the sample style image S. The generator, which is denoted as and , transforms an input image into an illustrative sketch using and converts an illustrative sketch into an input image using . As an input for the transformation, applies I, the input photograph, and , a style attention map extracted by , and produces , an illustrative sketch. The discriminator, denoted as , measures the quality of the illustrative sketch that was transferred to . Additionally, the generator reconstructs the original input image, , from the input image and . The RCCL module extracts and compares the edge of the image and I to measure the RCCL.
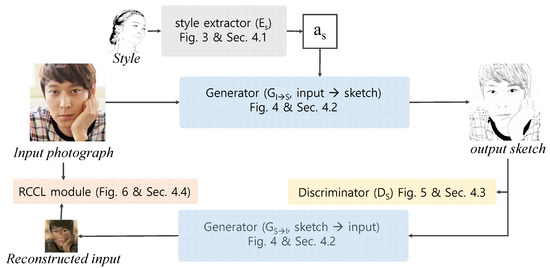
Figure 2.
The process of our framework.
4. Modules of Our Framework
In this section, we explain our framework by describing the modules of our framework.
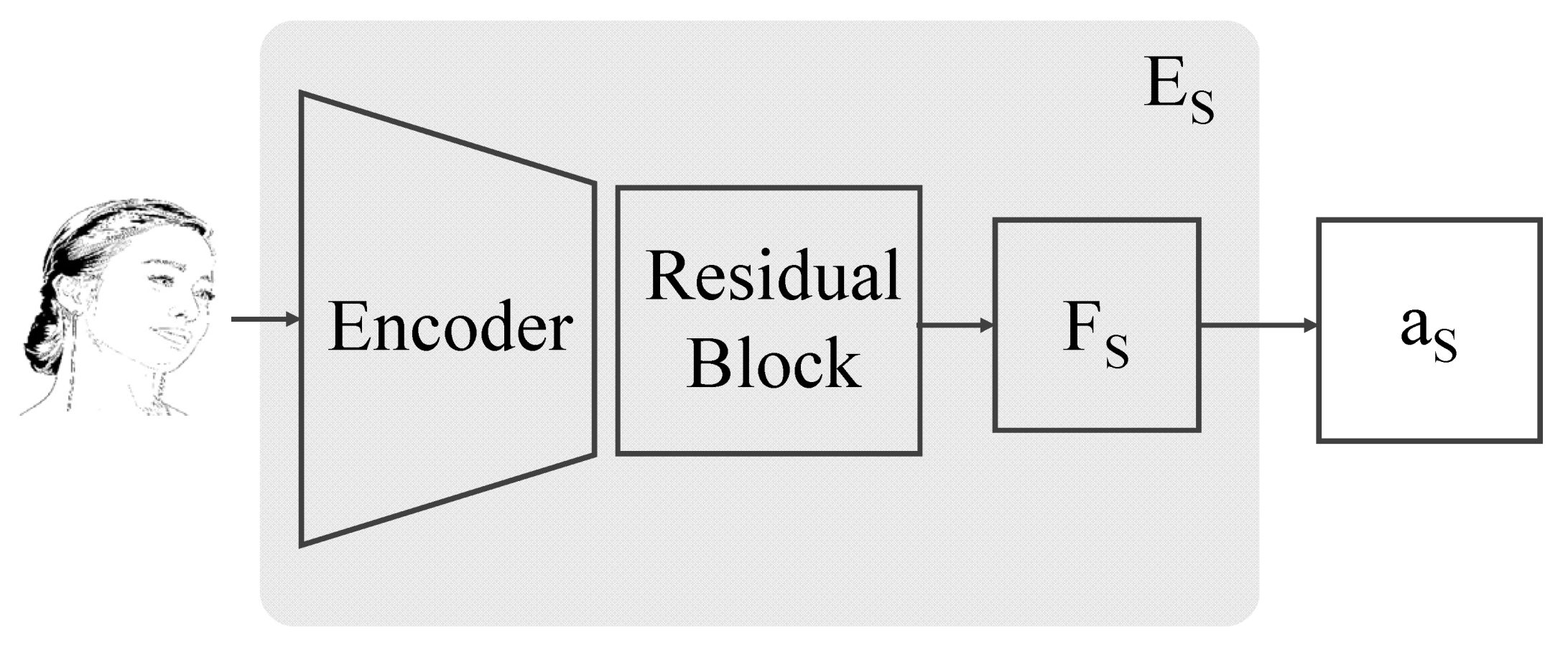
4.1. Style Extraction Module
The style extraction module, , extracts a style attention map of the illustrative sketch sample image S. The style extraction module, which is illustrated in Figure 3, has an encoder-based structure. The output of the encoder is processed through a residual block to produce a feature map , which is further processed to extract through a fully connected layer.
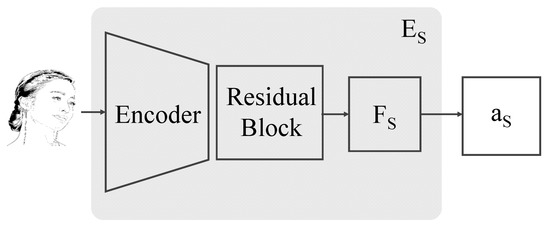
Figure 3.
The structure of our style extractor.
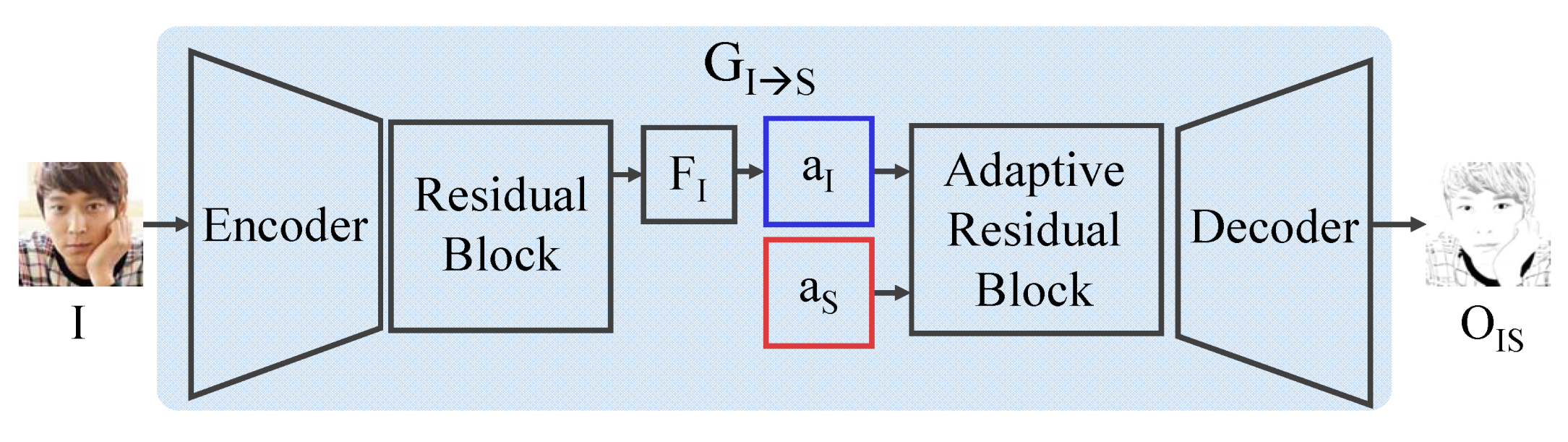
4.2. Generator
We devise two generator modules in our model. One generator, , transforms the input image I into an illustrative sketch and the other generator, , reconstructs from . In the generator, an encoder with residual block extracts a feature map , which is further processed to an attention map . With , , an attention map from the style extraction module, is processed through a decoder with an adaptive residual block to produce , the illustrative sketch result. In , , an attention map from the generated illustrative sketch, and , an attention map from the input image, are employed to reconstruct the input image. The structure of our generator is illustrated in Figure 4.
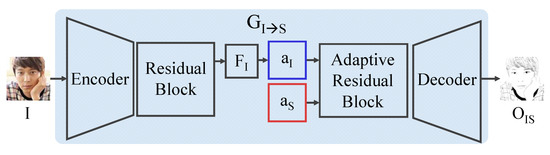
Figure 4.
The structure of our generator.
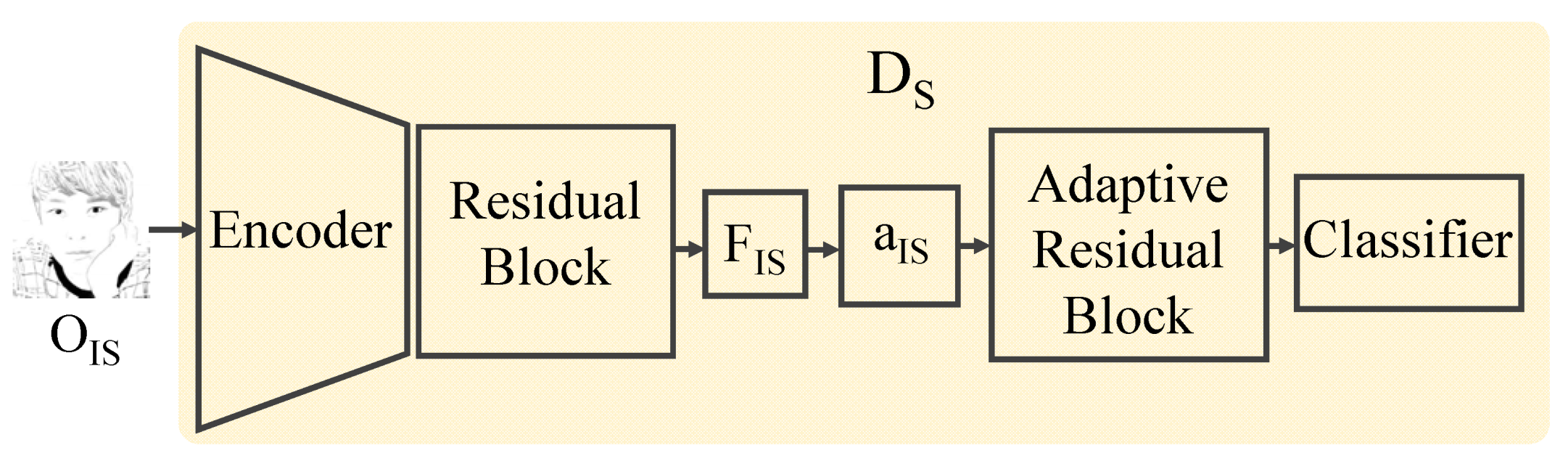
4.3. Discriminator
The discriminator module, , is a module that measures the quality of the generated illustrative sketch . This module is designed on the basis of an encoder and a classifier (See Figure 5). In the first step, an attention map is extracted from the feature map , which is generated through the encoder and its residual block. Next, an adaptive residual block and a classifier estimate the logit for the probability of a successful illustrative sketch using .
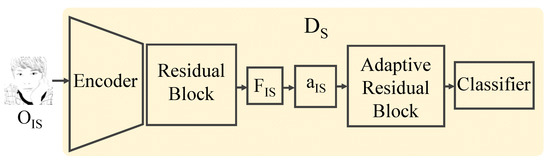
Figure 5.
The structure of our discriminator.
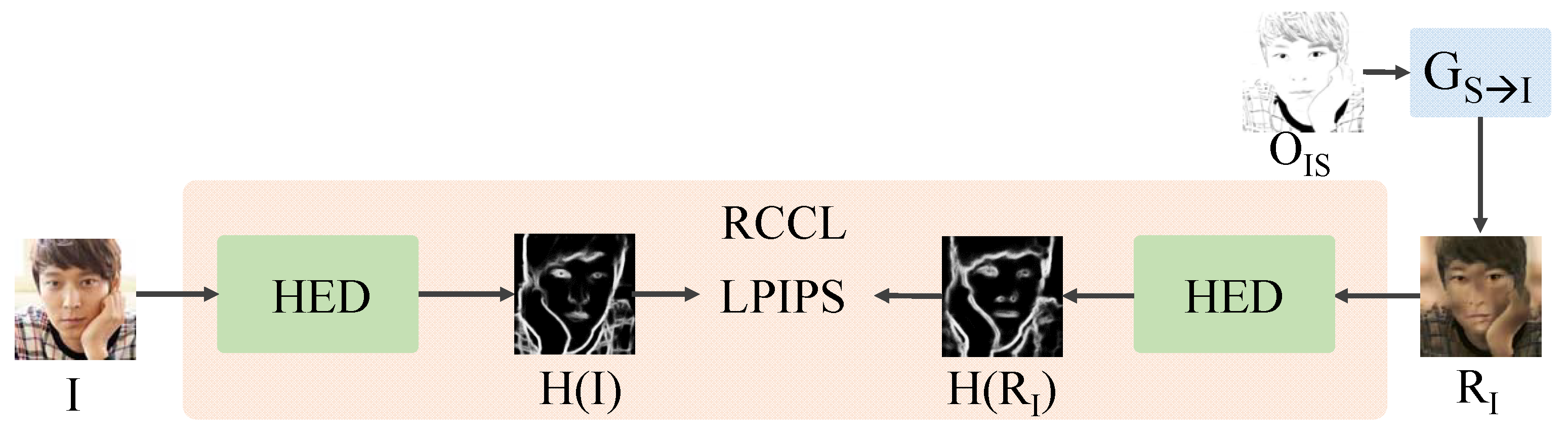
4.4. RCCL Module
The RCCL module compares the edge () of an input image I and the edge () of reconstruction image . RCCL is composed of holistically nested edge detection (HED) [22] extracting edges and learned perceptual image patch similarity (LPIPS) [23] comparing the extracted edges (Figure 6).
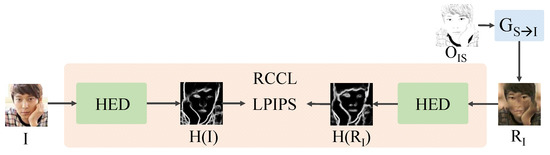
Figure 6.
The structure of our RCCL module.
The structure of our generator and discriminator is explained in Table 1 and the structure of our RCCL module in Table 2.

Table 1.
The layers of generator and discriminator.

Table 2.
The layers of RCCL module.
5. Loss Function
In this section, we explain the terms of our loss function.
5.1. Adversarial Loss
The adversarial loss is used to construct an elaborated generator module by measuring the quality of the image, which is an input to the discriminator :
5.2. Cycle Consistency Loss
In Zhu et al.’s work [7], a cycle consistency loss is devised to measure the loss between the style-transferred image and the reconstructed image from the style-transferred image. This loss term is used to force these two images to remain similar:
In Equation (2), the difference between the style-transferred image x and the reconstructed image is measured and compared. In our model, the most important feature of an illustrative sketch is the line depicting the shape of objects embedded in a scene. Thus, we employ an RCCL to compare the difference between the edges of the input image and the reconstructed image. We concentrate on comparing the lines of the image instead of the entire scene. Therefore, the loss is measured by removing unnecessary information, such as color, from the illustrative sketch as follows:
Equation (3) measures the loss of the edge extracted from the input image I and the edge extracted from the reconstructed image through the LPIPS metric.
5.3. Identity Loss
The identity loss is used to match the color distribution between the input and the generated images:
Equation (4) measures the loss between the input image I and the illustrative sketch generated from the input I. The purpose of this loss term is to create an illustrative sketch image while preserving the input image as much as possible.
5.4. CAM Loss
A class activation map (CAM) loss employs the CAM approach, where areas have a large impact on the classification of objects into a specific class:
In Equation (5), represents the probability of the domain x being the input image. This information allows you to focus on characteristic areas such as the eyes, mouth, and noses.
In Equation (6), discriminates the two domains by determining whether the input x is real or fake using an attention map.
5.5. Total Loss
We devise the effects of the loss terms to be adjusted through the variables , , and , and the experiment was performed by assigning , , , and .
6. Implementation and Results
In this section, we explain how we implemented our model and describe the results.
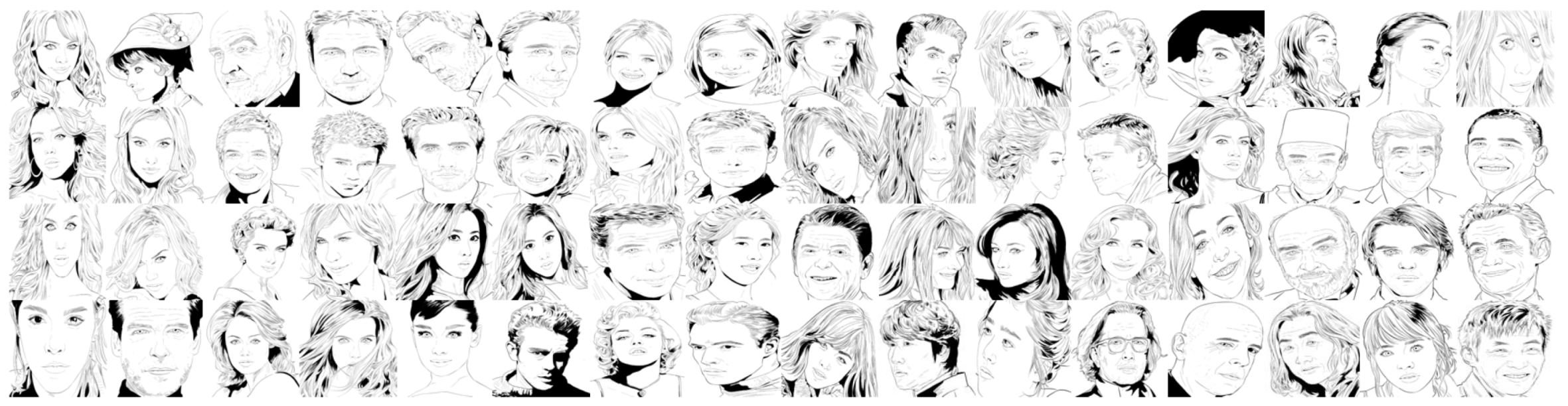
6.1. Training Dataset
To train our framework, we hire a professional artist to draw sample images. She drew 64 illustrative sketch images from various portrait photographs of celebrities. Figure 7 illustrates our training samples.

Figure 7.
The training dataset of our framework.
6.2. Implementation Environments
We implemented our model in a personal computer with an Intel Core i9-9900x CPU, 128 GByte main memory and nVidia Titan RTX GPU. The software environment is the Pytorch library implemented on Linux of Ubuntu version.
6.3. Results
In our implementation, we executed 50 K training epochs. Total time required for the training is 44,545 s. Each training epoch takes 0.8909 s. The number of parameters in our model is approximately 134 M. We present our results in the following order.
6.3.1. Results with Ground Truth
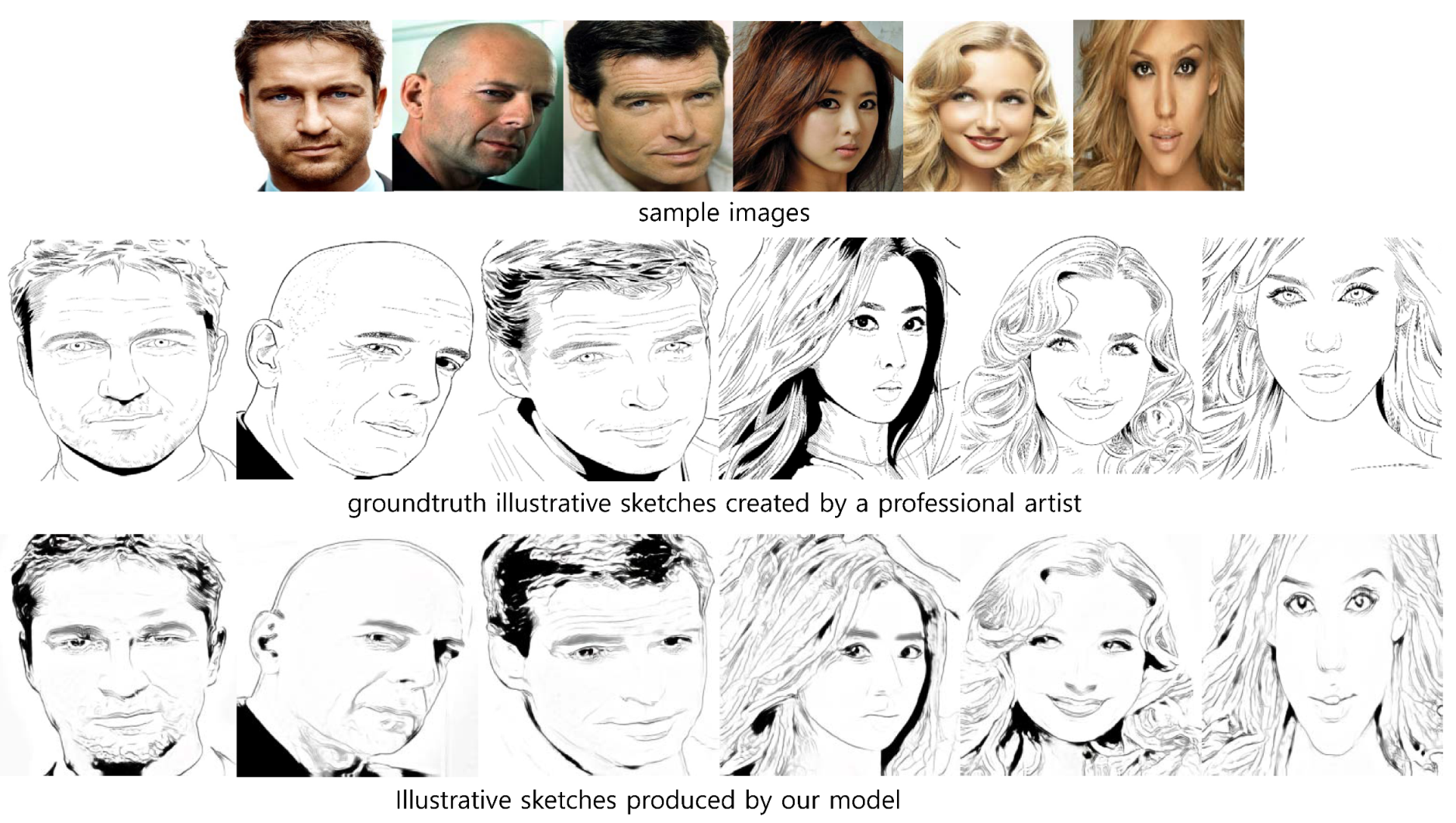
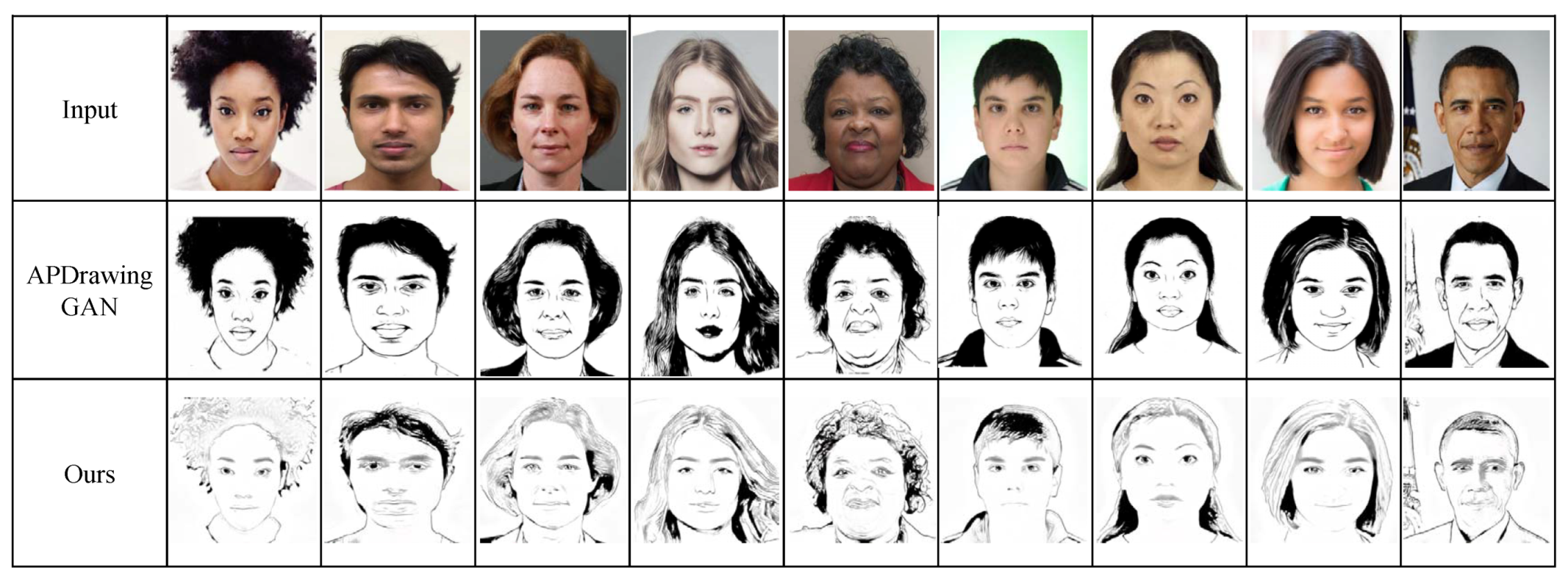
We collect our groundtruth illustrative sketch artwork images from portraits of celebrities. We compare our resulting illustrative sketches with their corresponding groundtruth artwork sketches in Figure 8. Our result can capture the details of portraits, such as the eyebrows, eyes, pupils, and lips, very successfully. Our results in were limited in the depiction of the hair. The smooth flow of hair in the groundtruth artwork sketches is unsuccessfully depicted in our results.

Figure 8.
Our illustrative sketch portraits compared to the groundtruth artwork sketches produced by a professional artist.
6.3.2. Results from Various Images
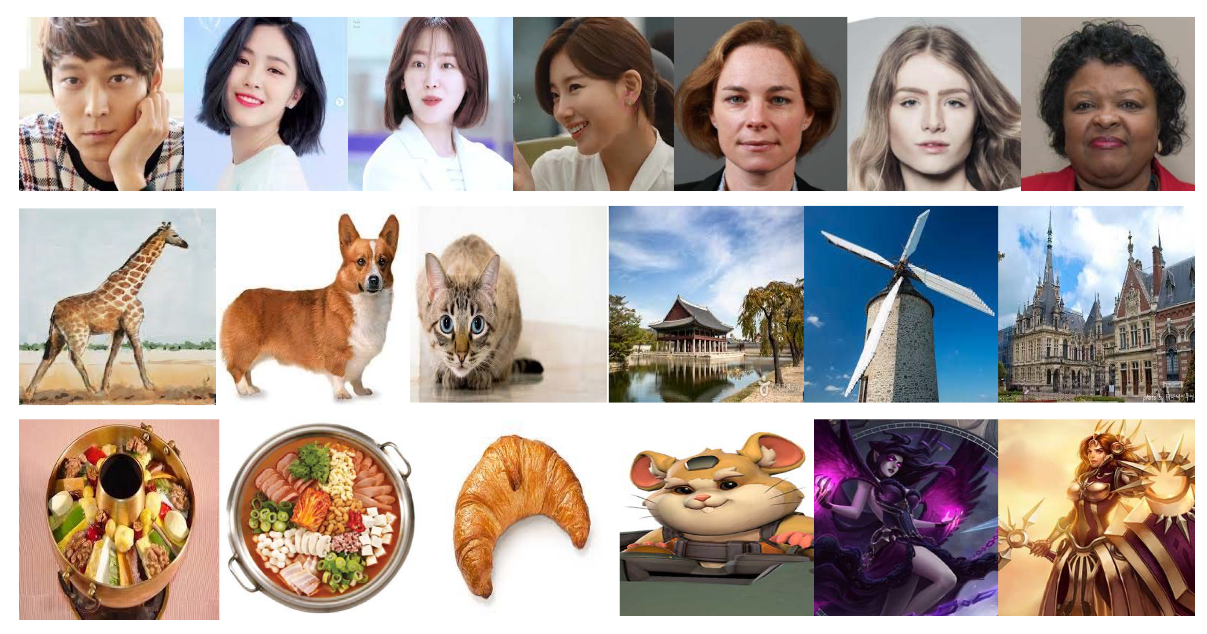
Since our groundtruth images are from portraits, we have several doubts about the production of illustrative sketch images for portraits not included in the groundtruth datasets and for other images including animals, landscapes, still lifes and synthesized scenes. We attempted to transform input images from different domains into illustrative sketch images to prove the superiority of our model. The input images are suggested in Figure 9 and their resulting illustrative sketch images are presented in Figure 10.

Figure 9.
Input images.

Figure 10.
Our illustrative sketch images from various sources including portraits, animals, landscapes, still-lifes and synthesized scenes.
6.3.3. Comparison with Existing Works
In this section, we compare our results with various existing works including pix2pix [6], DualGAN [18], CycleGAN [7], FDoG [2], UGATIT [21], and MUNIT [8]. We compare their results with ours in Figure 11 and Figure 12. We also compare our results with those from state-of-the-art works [9] in Figure 13. We further compare the computation time required for training and testing our model in Table 3.

Figure 11.
Our illustrative sketch images compared with existing works: The portraits are contained in blue cells and animals in orange.

Figure 12.
Our illustrative sketch images compared with existing works: The landscapes are contained in yellow cells and synthesized in green.

Figure 13.
Our illustrative sketch portraits compared with APDrawingGAN [9], one of the state-of-the-art works.

Table 3.
Comparison of computation time for training and test. Train time is recorded as seconds for all training epochs and test time as the seconds taken to process one image. Note that the train time for FDoG is Not Available, since it is not a deep-learning-based method.
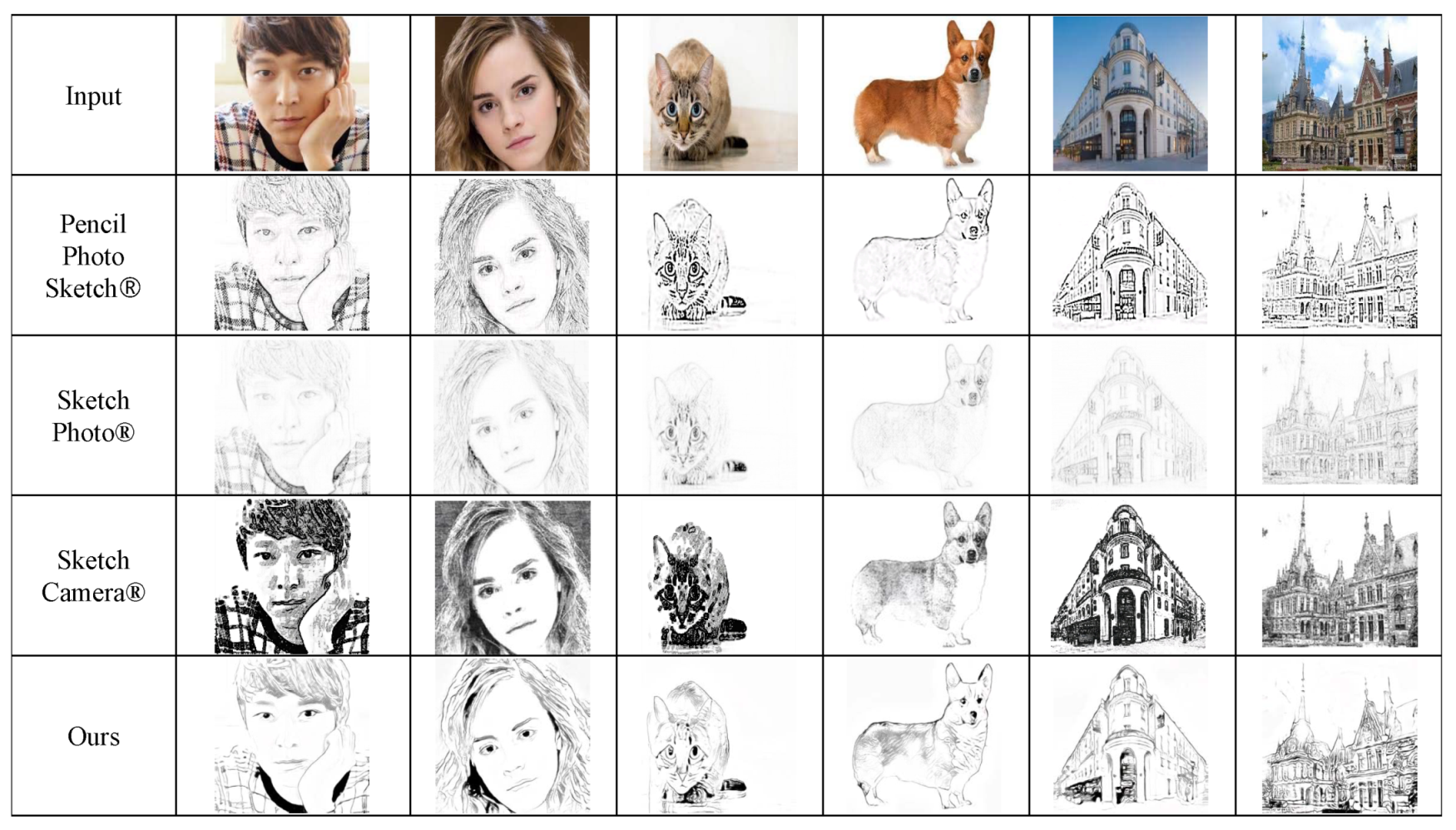
6.3.4. Comparison with Commercial Apps
We select the three most frequently used commercial apps that produce sketch styles from input photographs and compare the results in Figure 14. Even though these commercial apps successfully convert the input images into reasonable sketch styles, their results is somewhat far from the illustrative sketch styles in the processing of salient features. Furthermore, ours successfully reduce artifacts to complete the illustrative sketch styles.

Figure 14.
Comparison with the apps available on mobile phones: Pencil Photo Sketch, Sketch Photo and Sketch Camera.
7. Analysis
In this section, we analyze our results through various evaluation schemes.
7.1. Evaluations
7.1.1. Human Study
To evaluate our results, we conduct a human study with 10 participants. The images used for the human study are illustrated in Figure 11 and Figure 12. We prepare 20 sample images, which are categorized into four groups: human, animal, landscape and synthesized. Each group contains five images, respectively.
We ask the participants to choose one image among seven candidates, including ours, that best fits the following questions.
- (Q1: Quality) Which of the images looks most visually pleasing?
- (Q2: Similarity) Which of the images looks most similar to the input image in the rightmost column?
- (Q3: Artifact) Which of the images show the fewest artifacts?
The results of this human study are given in Table 4, which shows that our result receives the most votes from the participants. For the three questions, ours receive more than half of the first votes.

Table 4.
The results of user study.
The result of our user study shows that most of the votes are concentrated in CycleGAN, MUNIT and ours. The quality of the sketch images comes from the details most similar to the input images and the sketch styles they mimic. The three models they vote on successfully produce sketch styles while preserving details. Other schemes, such as pix2pix and FDoG produce, too many artifacts. DualGAN and UGATIT cannot present the salient features of the input images. Our result shows the fewest artifacts among these models. Furthermore, ours present the edges and dark tone in detail.
7.1.2. Ablation Study
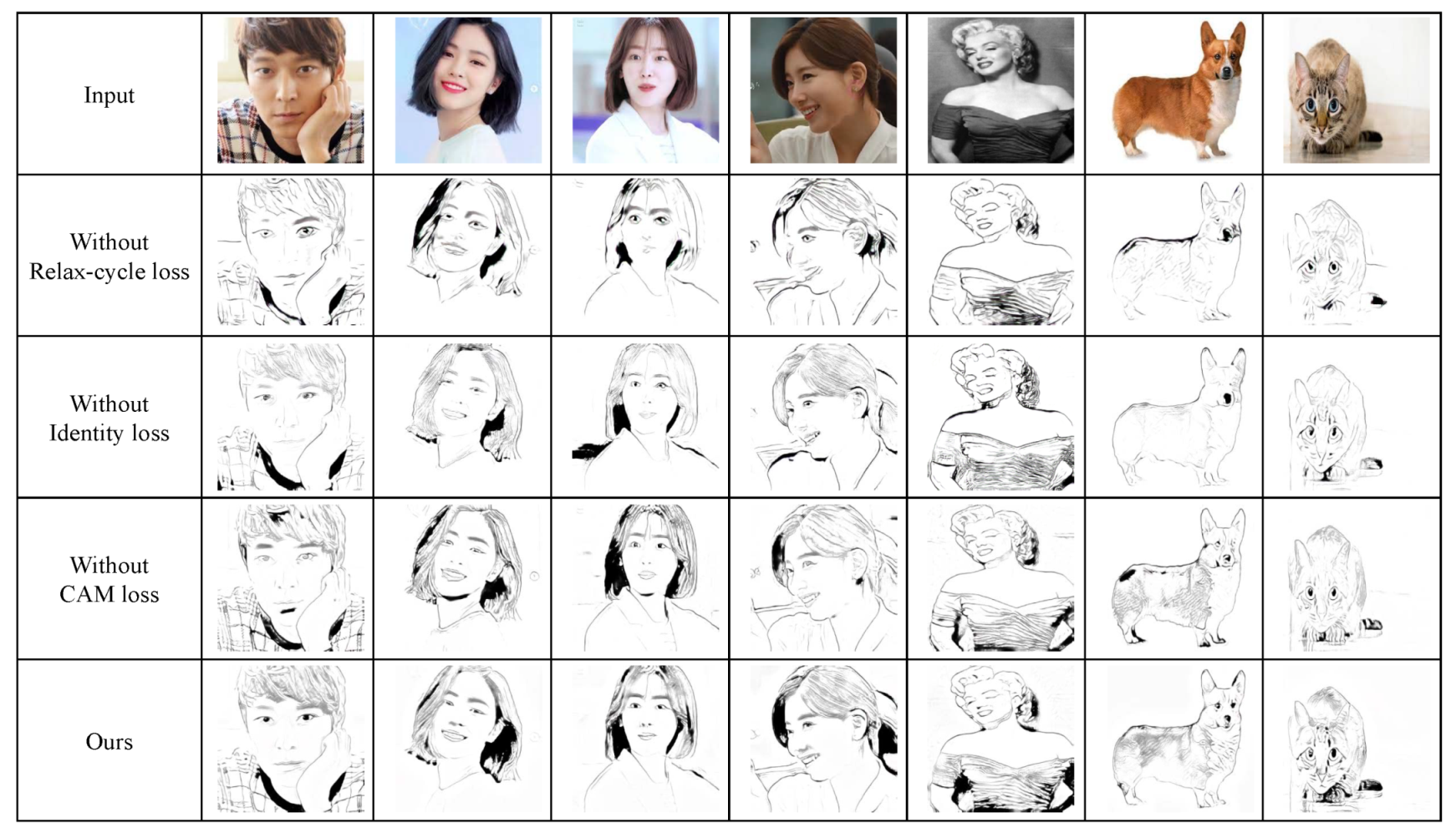
We conducted two ablation studies in this paper and compared their results. The first ablation study we conducted was on loss terms. Our loss function is composed of four terms: , , , and . Among the four terms, we remove three terms: , , and . As illustrated in Figure 15, the result without RCCL () lacks salient lines in the result. The result without an identity loss () has several important but tiny features such as the eyes in the dog. The result without a cam loss () looks most similar to our result. However, it has limitations in conveying regions of dark tones, such as the tone of the hair in the third column.
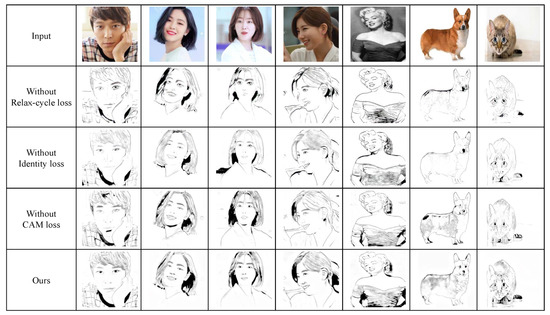
Figure 15.
Ablation study on loss terms.
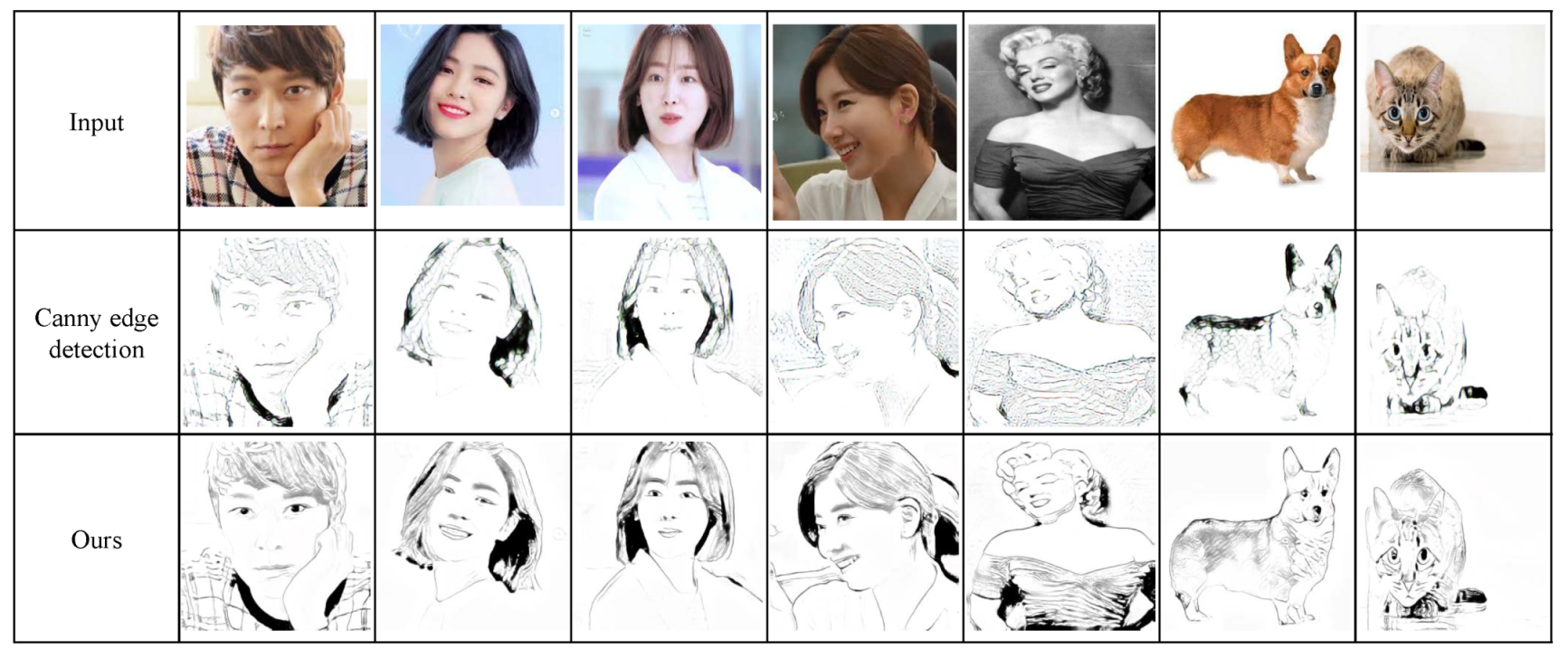
The second study is on the edge detection scheme. We replace our RCCL scheme with the widely used Canny edge detection scheme. As illustrated in Figure 16, the Canny edge scheme performs poorly in depicting the salient features of the results.

Figure 16.
Ablation study on edge extraction schemes.
7.1.3. FID Evaluation
The quality of our result is estimated through Frechet Inception Distance (FID). Lower FID values indicate better results. We evaluate FID values for the 20 images of four categories in Figure 11 and Figure 12. The FID values are presented in Table 5. We draw two conclusions from Table 5. First, our results show the lowest FID values among the six existing schemes, meaning that ours show the best result. Second, the FID values of the portrait show the lowest values, whereas the FID values of the landscape show the highest values.
7.2. Discussion
We evaluated our framework using various metrics including human study, ablation study and FID evaluation. Through the human study, we have proved that the quality, similarity and artifact of our scheme outperforms many existing schemes. As described in Table 4, more than half of the participants recognize that our results are better than those of the existing schemes. We have demonstrated how our results evolve through the loss terms in the ablation study. As illustrated in Figure 15, our framework incorporates loss terms to depict the salient features of the objects and to suppress unwanted artifacts. In Figure 16, we also prove that the RCCL scheme improves the translation results by comparing them with those from Canny edge detection schemes.
Finally, we estimate FID values from the result images to compare our results with the results that were quantitatively obtained by the existing schemes. This analysis also proves that our scheme produces more visually convincing illustrative sketch styles than the existing schemes. We measure the effect size of the FID values by estimating Cohen’s d values. The Cohen’s d values from the schemes compared in Table 5 are presented in Table 6. From this table, we can recognize that the effect sizes between those schemes and our scheme are greater.

Table 6.
Effect size of the FID values estimated by Cohen’s d value. We test twenty samples for the estimation.
7.3. Limitation
First, our framework cannot properly produce illustrative sketch styles on monotonal dark regions, such as dark-colored hair and shadow. As the CNN, which is the base technique of our framework, has a limitation in the extraction of feature maps from monotonal dark regions, our synthesized styles for the regions unsuccessfully mimic the styles that were sampled from the training data.
Second, our framework has a limitation in producing sketch styles for regions filled with tiny textures, such as a tree, animal or building. We found that our framework cannot express tiny texture regions due to our training dataset. Since our framework is trained on portraits, it is not familiar with tiny texture styles. This limitation influences our models to produce a poor illustrative sketch style in expressing tiny texture regions.
8. Conclusions and Future Work
We presented a GAN-based framework that produces illustrative sketch styles from various photographs. To facilitate our framework for the production, we apply an attention map to extract and produce styles and a relaxed cycle consistency to evaluate the produced styles. We train our model on portrait style samples and produced illustrative sketch styles from various photographs, including landscapes, animals and still lifes. We prove the effectiveness of our framework by analyzing its results through human study, ablation study and FID evaluation.
We aim to extend our framework to produce a controllable, illustrative sketch style. For this purpose, we aim to develop a framework that separates the lines and tones of the style. By seperately processing the lines and tones, we can enrich styles at a significant scale. Another goal is to concentrate on illustrative sketch portraits, which present various poses and expressions. To do this, we aim to employ various face rotation and reenactment modules.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Y., K.M.; Software, J.Y.; Supervision, K.M., H.Y.; Writing—original draft, H.Y. Writing—review and editing, K.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- DeCarlo, D.; Finkelstein, A.; Rusinkiewicz, S.; Santella, A. Suggestive Contours for Conveying Shape. ACM Trans. Graph. 2003, 22, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Chui, C. Coherent Line Drawing. In Proceedings of the NPAR 2007, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–5 August 2007; pp. 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Winnemoller, H.; Olsen, S.; Gooch, B. Real-time video abstraction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2006, 25, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnemoller, H.; Kyprianidis, J.E.; Olsen, S.C. XDoG: An EXtended Difference-of-Gaussians Compendium Including Advanced Image Stylization. Comput. Graph. 2012, 36, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Kwon, Y.; Min, K. A Stylized approach for pencil drawing from photographs. Comput. Graph. Forum 2012, 31, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Liu, M.Y.; Belongie, S.; Kautz, J. Multimodal unsupervised image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 172–189. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, R.; Liu, Y.; Lai, Y.; Rosin, P.L. APDrawingGAN: Generating Artistic Portrait Drawings From Face Photos With Hierarchical GANs. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10735–10744. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, R.; Liu, Y.J.; Lai, Y.K.; Rosin, P.L. Unpaired Portrait Drawing Generation via Asymmetric Cycle Mapping. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2020, Online, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8217–8225. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Yu, J.; Yu, X.; Lee, S. Line-Art Illustration of Dynamic and Specular Surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 156:1–156:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Brazil, E.; Petronetto, F.; Sousa, M.C. Fluid-based hatching for tone mapping in line illustrations. Vis. Comput. 2009, 25, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coconu, L.; Deussen, O.; Hege, H.-C. Real-Time Pen-and-Ink Illustration of Landscapes. In Proceedings of the NPAR 2006, Annecy, France, 5–7 June 2006; pp. 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Kaplan, C.S. Artistic thresholding. In Proceedings of the NPAR 2008, Annecy, France, 9–11 June 2008; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Mould, D.; Grant, K. Stylized Black and White Images from Photographs. In Proceedings of the NPAR 2008, Annecy, France, 9–11 June 2008; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rosin, P.L.; Lai, Y.-K. Towards Artistic Minimal Rendering. In Proceedings of the NPAR 2010, Annecy, France, 7–10 June 2010; pp. 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Benard, P.; Lu, J.; Cole, F.; Finkelstein, A.; Thollot, J. Active Strokes: Coherent Line Stylization for Animated 3D Models. In Proceedings of the NPAR 2012, Annecy, France, 4–6 June 2012; pp. 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tan, P.; Gong, M. DualGAN: Unsupervised Dual Learning for Image-to-Image Translation. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2849–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Xu, D.; Seba, N.; Yan, Y. Attention-Guided Generative Adversarial Networks for Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation. In Proceedings of the IJCNN 2019, Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. AT-GAN: Attention Transfer GAN for Image-to-Image Translation. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Online, 19–21 June 2020; pp. 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Kang, H.; Lee, K. U-gat-it: Unsupervised generative attentional networks with adaptive layer-instance normalization for image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2020, Online, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Tu, Z. Holistically-Nested Edge Detection. In Proceedings of the ICCV 2015, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1395–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).