Abstract
Image steganalysis detects hidden information in digital images by identifying statistical anomalies, serving as a forensic tool to reveal potential covert communication. The field of deep learning-based image steganography has relatively scarce effective steganalysis methods, particularly those designed to extract hidden information. This paper introduces an innovative image steganalysis method based on generative adaptive Gabor residual networks with density-peak guidance (SG-ResNet). SG-ResNet employs a dual-stream collaborative architecture to achieve precise detection and reconstruction of steganographic information. The classification subnet utilizes dual-frequency adaptive Gabor convolutional kernels to decouple high-frequency texture and low-frequency contour components in images. It combines a density peak clustering with three quantization and transformation-enhanced convolutional blocks to generate steganographic covariance matrices, enhancing the weak steganographic signals. The reconstruction subnet synchronously constructs multi-scale features, preserves steganographic spatial fingerprints with channel-separated residual spatial rich model and pixel reorganization operators, and achieves sub-pixel-level steganographic localization via iterative optimization mechanism of feedback residual modules. Experimental results obtained with datasets generated by several public steganography algorithms demonstrate that SG-ResNet achieves State-of-the-Art results in terms of detection accuracy, with 0.94, and with a PSNR of 29 between reconstructed and original secret images.
MSC:
94A08; 68U10
1. Introduction
The rapid advancement of multimedia technologies has significantly improved digital image transmission efficiency, yet simultaneously raised concerns about data vulnerability, unauthorized manipulation, and privacy breaches [1,2]. While image encryption and steganography serve as essential security measures, their misuse for illicit activities, including data theft, privacy invasion, and malware distribution under security pretexts, has become increasingly prevalent [3]. This paradoxical security challenge necessitates the development of robust detection frameworks, mandating steganalysis of all transmitted image files to identify potential concealed payloads that might compromise digital security systems. Contemporary steganalysis methodologies primarily bifurcate into two technical paradigms, traditional statistical feature-based approaches and modern deep learning-driven architectures [4].
Traditional image steganalysis algorithms typically employ hand-crafted filter kernels to discern the statistical disparities between cover and stego images for the purposes of detection and classification. A majority of researchers have successfully utilized features from the spatial rich model (SRM) for this classification task [5]. For instance, Fridrich et al. [6] utilized an integrated classifier in rich models to achieve significant extraction of high-dimensional features for detection. Gupta et al. [7,8] proposed an improved binary particle swarm Fisher linear discriminant classifier to identify relevant features based on rich-space model features to improve the accuracy. Xue et al. [9] constructed an adaptive feature selector, which is capable of accurate recognition of spatial domain features. In addition, other researchers [10,11] combined temporal and spatial domain features for automatic alignment and classification of stego information. However, the features extracted in SRM continue to be determined manually. Such manual determination lacks objectivity and often falls short in regard to capturing the high-level semantic meaning. Further, several researchers have suggested employing transform domain techniques to extract multidimensional features for classifier training and determining whether an image has hidden information [12,13]. In recent years, the field of transform-domain steganalysis has concentrated on enhancing feature dimensionality, transitioning from utilizing low-dimensional discrete cosine transform (DCT) residuals [14] to the adoption of high-dimensional, up to 12,600-dimensional phase-aware steganalysis models [15,16]. However, the efficacy of these steganalysis algorithms significantly diminishes when tasked with detecting stego images crafted by deep learning-based steganography methods.
Recent advancements in deep learning have produced a CNN framework that enables the automated discovery of nonlinear relational patterns to facilitate the image classification task, including emotion classification, steganography, and image steganalysis [17,18,19]. For example, Yang et al. [20] proposed a structure-preserving image steganography migration subspace learning method. It aims to alleviate the mismatch between training and testing, and to achieve performance improvement based on the SRM features. In addition, some researchers have also achieved stronger feature discrimination ability by constructing an adversarial transfer learning framework of dual-competition convolution networks [21]. Subsequently, Huang and Fu et al. [22,23] developed a deep network with attention-augmented preprocessing that reduces image interference and boosts JPEG steganalysis. Furthermore, researchers have improved the arrangement of convolutional layers by adding residual structure [24], constraint kernel [25], and other modules to the CNN [26], which improves the network’s ability to process localized information and increases the detection accuracy. While systematic architectural optimizations have progressively enhanced detection efficacy, the excessive parameters in these architectures introduce critical operational challenges, including extended training durations, convergence instability, and overfitting.
Since 2020, researchers have confronted the dual challenges of classifier parameter bloat and constrained image source availability through three innovative strategies. Feature fusion architectures employ Gaussian-regularized networks [27], fractal-enhanced SRM [28], and analytical feature constructors [29] achieve parameter reduction and improved accuracy. However, these models reduce feature map resolution, eroding critical details and impairing the detection of faint steganographic patterns. Based on this, Hu et al. [30] fused confidence metrics with a generative adversarial network (GAN) to generate artifact pixels, cutting detection noise and model complexity. Further, Peng et al. [31] utilized GAN to implement an augmented model and further enhance the robustness of the steganalysis framework. These methodologies holistically resolve model bloat and adversarial fragility via architectural pruning and operator fusion techniques. In recent years, the rapid evolution of generative architectures (e.g., diffusion models and GAN) [32,33] has catalyzed a paradigm shift in steganalysis, positioning multimodal foundational models as the emerging central framework for next-generation information forensics. In addition, Kheddar and Croix et al. [34,35] designed a curvelet feature and fuzzy-based GAN steganalysis framework for real-time stego-image detection to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio. However, the accuracy of these steganalysis algorithms is lower when the steganographic embedding parameters or the steganographic systems used differ between the training and test datasets. Additionally, a majority of existing steganalysis models concentrate solely on the classification of embedded information, with scant attention given to the retrieval of the hidden information.
To address the dual challenges of combating both conventional steganographic schemes and emerging generative steganography while enabling precise localization and real-time extraction of hidden payloads, we propose a unified deep architecture SG-ResNet. The proposed SG-ResNet contains two sub-networks, classification and reconstruction, which are trained simultaneously. First, the input cover or stego images are transferred to an adaptive density peaked Gabor filter convolutional layer to extract the embedded steganographic features, which are subsequently integrated with a texture information map and embedding probabilities, and then the input tickling nonlinear truncated convolutional module learns the embedded residual secret image. Ultimately, the residual and based on Gabor features are employed in subsequent classification and reconstruction networks. The reconstruction network consists of channel-separated model-rich convolutional layers, channel classification residual layers, and multilevel feedback Pixel Shuffle layers, and the hidden image is reconstructed by a successive extraction of these structures. Our primary contributions in this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- The adaptive density-peak Gabor module extracts steganographic features by combining multi-scale textures with density-based filters, capturing subtle embedding artifacts in both spatial and frequency domains.
- (2)
- The three-channel fused tickling nonlinear truncated module enhances critical feature sensitivity and amplifies hidden residuals in steganographic regions, increasing the accuracy by 11.2%.
- (3)
- The multilevel feedback residual architecture achieves state-leading hidden secret reconstruction with PSNR of 29, outperforming existing models by 15%.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 outlines foundational theories; Section 3 details the proposed steganalysis framework and implementation; Section 4 presents experimental results, including performance comparisons and robustness tests; and Section 5 provides a brief conclusion and future research directions for steganalysis.
2. Related Concepts and Works
2.1. Related Concepts
Existing steganalysis systems perform a classification operation when they receive an input target, X. These systems are designed to categorize X as either a concealed image (stego), Z, or an innocent image (cover), C. Based on this, we also continue to extract the information from Z in an attempt to rebuild the hidden secret, M. Thus, the whole framework of steganalysis is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of steganalysis.
The varying semantic content within the steganographic region substantially impacts the original image, making the differentiation between stego and cover images a pivotal aspect of hidden information location and extraction. Embedding secret information into an image disrupts the original pixel correlations and alters the noise characteristics. The learning of residual images focuses on the destruction of multiple correlations of neighboring pixels by steganography, which is conducive to the detection and classification of images. The residual spatial rich model (Res-SRM) uses this principle to filter the background content features of an image and retains the steganographic features to achieve the detection. The process of extracting features by Res-SRM is as follows.
Assume that X is a color image, and the stego residual is , , . The stego residual is
where is the neighborhood containing the center pixel, ; denotes the estimated value of the pixel in the region, , since generally the number of pixels in is equal to ; and is the residual order. In this paper, the Res-SRM is employed to reduce the dimensionality of the final extracted features effectively. In this paper, the Res-SRM is employed in the branching module of the reconstruction network, which further compresses the feature dimension space of the filtered features of the classification network to enhance the response strength of steganographic artifacts.
2.2. Existing Steganographic Information Location Works
The location and extraction of hidden information in image steganalysis systems can be categorized into two primary research directions: localization and recovery of hidden payloads (embedded random data), and precise extraction of structured secret information (e.g., images or text). Recent advancements have leveraged statistical modeling and deep learning to address these limitations. Firstly, in terms of adaptive steganalysis localization algorithms, Liu et al. [36] proposed a flip-pixel spatial localization algorithm based on adaptive steganography. They achieved preliminary localization of hidden payloads through pixel modification detection. However, the output exhibited significant ambiguity, particularly in distinguishing the embedding priorities of adjacent pixels. To improve localization accuracy, Wang et al. [37] designed a JPEG steganalysis model with co-frequency sub-image coverage estimation for payload localization and recovery. Additionally, researchers have developed quantitative steganalysis methods [38,39,40] to estimate payload size by identifying pixel-level modifications during data embedding. While these models demonstrate strong performance in detecting and coarsely localizing hidden payloads, they remain incapable of fully extracting or restoring the original embedded information. In addition, they are unable to counter deep learning-based image steganography. Further, Croix et al. [41,42] analyzed pixel blocks to construct feature assignment networks, optimizing the boundaries of hidden payload localization masks through adversarial training. Meanwhile, Jung et al. [43] employed deep networks to analyze pixel distributions for pixel-level localization, though their method could only erase but not reconstruct secret information. Overall, the existing approaches exhibit two primary limitations: (1) localization results predominantly manifest as random values; and (2) poor detection performance for deep learning-based steganography, and inability to extract and reconstruct hidden secret images. To address these challenges, we have additionally designed a feature decoding generator (Section 3.4) following the steganalyzer, which enables precise localization and extraction of embedded secret images while achieving steganalysis detection.
2.3. Evaluation Indexes
This paper employs several metrics to assess the classification performance of steganalysis detection: accuracy (), F1-score (), and recall value (R). The primary objective of steganalysis is to determine whether a target image is a stego image (positive class, Z) or a cover image (negative class, C). Its classification performance can be evaluated with the following metrics: true positives (TPs) denote the number of correctly identified stego images, false positives (FPs) represent cover images misclassified as stego images, true negatives (TNs) indicate correctly identified cover images, and false negatives (FNs) correspond to stego images misclassified as cover images.
Accuracy (): Accuracy is the ratio of correctly classified samples to total samples,
F1-score (): The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, balancing both to evaluate classifiers comprehensively. It ranges from 0 (worst) to 1 (best):
Recall (R): Recall is the ratio of true positives to actual positives,
The mean square error (MSE), mean structural similarity (MSSIM), and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) are used to evaluate the quality between the extracted hidden image and the original hidden image.
where and represent pixel value of the original secret (X) and the generated secret image (Y), respectively. M and N are the length and width of the , respectively. .
where and are the mean pixel value of X and Y, respectively; is the variance of X; is the variance of Y; is the covariance; and and are constants used to maintain stability, with L being the dynamic range of the pixel values, and .
3. Proposed Steganalysis Framework
3.1. SG-ResNet Model
The proposed SG-ResNet architecture depicted in Figure 2 comprises two sub-networks: one for classification and another for reconstruction.
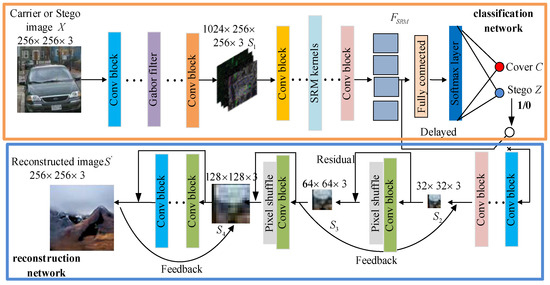
Figure 2.
Overall framework of SG-ResNet.
Classification network: From Figure 2, the target image, X, is fed into several convolutional layers and Gabor filter convolution blocks, outputting the feature of size . These Gabor filter convolution blocks are utilized to enhance the reinforcement learning process, focusing on the embedded information. Subsequently, progresses through multiple convolutional layers and SRM convolutional blocks to generate a set of one-dimensional features, . Eventually, the is fed into the full connectivity layer and Softmax layer to obtain the classification probability values of C and Z.
Reconstruction network: Feature maps identified as Z are forwarded to the reconstruction network. This network initially processes the data through several convolutional layers to derive the feature set, . Subsequently, navigates through a series of distinct residual convolutional blocks, pixel shuffle convolutional, and feedback attention branch in a gradual and progressive manner to reconstruct the embedded images . The final output of the reconstructed hidden image, , is obtained.
3.2. Classification Framework for Hidden Information
3.2.1. Details of the Classification Network
The classification network, as shown in Figure 3, comprises 14 convolutional layers, two Gabor filtered convolutional blocks, three quantization and transformation-enhanced convolutional blocks (), one residual module, and two fully connected layers. To bolster the detection of secret information, a Gabor filter convolution module was incorporated to extract texture features and subtle hidden details from the stego image. The truncated DCT features, , are further used as key learning objects for subsequent classification and reconstruction tasks.
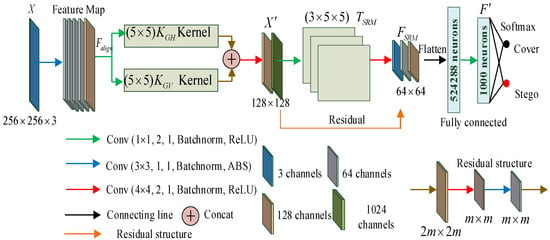
Figure 3.
The detailed settings of the classification network.
As depicted in Figure 3, target X is first subjected to a series of five CNN layers, each equipped with a convolutional kernel size of (highlighted in blue in Figure 3). Within the CNN network, each layer sequentially refines the feature map derived from the preceding layer through a four-step process: convolution, batch normalization, nonlinear activation, and pooling. To capture the diverse inter-dependencies among pixels within the residual image of the embedded information and enhance the precision of classification, two adaptive Gabor filter kernels () are concatenated with the Concat operation. Subsequently, they are funneled through a down-sampling layer with a convolutional kernel size of (indicated in red in Figure 3) to produce the feature map (). Then, is fed into the subsequent layer of three modules, while also serving as residual information input into the residual structure. The classification architecture is capped with a flattening stage, succeeded by a pair of dense layers, and ends with a Softmax function to yield the ultimate probabilities for classification. The dense network comprises two layers, one with 524,288 neurons and the other with 1000 neurons, which collectively assign a probability score to identify whether the input corresponds to C or Z.
3.2.2. Adaptive Density Peak Gabor Convolution Block and
In the classification network, the high-frequency feature enhancement kernel, , and local detail feature enhancement kernel, , are proposed. The feature, or , is extracted from the input X through convolutional learning. First of all, is fed into an adaptive Gabor convolutional module to analyze pixel distribution discrepancies between cover and stego images. To precisely capture steganographic perturbations, a density peak clustering (DPC)-guided supervised matrix, , is designed by statistically analyzing pixel distribution divergences between cover and stego images. This matrix adaptively filters discriminative features through DPC-based screening, which significantly improves the separability of steganographic traces and cover-image features. We mathematically formulate this adaptive process as the adaptive density clustering index (ADCI):
where is the relative density of feature clusters, denotes the dispersion between the two feature clusters of cover and stego, and is the number of combinations of any two feature clusters chosen arbitrarily among the K feature clusters. To amplify the dispersion of the data distribution in the hidden and unhidden regions, and are
where and are the sample size and standard deviation of , respectively; is the distance between two features; and and are the distance between the centers of the two main feature clusters and the average similarity, respectively. The supervisory matrix, , labels the location of true steganographic modifications in the convolutional layer, constraining spatial attention and forcing the attentional mechanism to focus precisely on the modified region.
where is the adaptive threshold; and and are the mean and standard deviation of the full feature map ADCI, respectively. The L2-norm-based mean squared error is applied during the forward propagation process, ensuring geometric alignment between the attention distribution and supervisory signals in the feature space, and the feature, , after supervised constraint correction and augmented learning is
where is the Hadamard product; and are the learnable query matrix and key transformation matrix after linear mapping of feature , respectively; is a scaling factor to bring the variance of the attention score close to 1; and b is a bias term to correct the attention weights to enhance the model flexibility. The process establishes a supervision-guided attention mechanism that aligns the model’s attention distribution with the hidden residual supervision matrix through end-to-end training, thereby enhancing model performance.
Then, these features, , are classified into different ADCI clusters, , after adaptive density peak-matching clustering and fed to the Gabor layer for learning. During the filtering process of the hidden information, the filter kernel selectively allows only the bandwidth corresponding to its designated frequency to pass through. Meanwhile, the bandwidth in other regions is suppressed and blocked. The feature undergoes discrete wavelet transform (DWT) decomposition, followed by application of the two filtering kernels, and , to each sub-band, yielding the refined feature, .
where and denote the filtering responses of and , respectively, with as the balance factor. Experimental results demonstrate that optimally stabilizes low-frequency residual steganographic feature while maintaining smaller high-frequency coefficients to preserve fine details. For each ADCI cluster, , an adaptive Gabor parameter set, , is optimized through adversarial training to construct directional filter kernels . These parameterized kernels selectively amplify frequency components that maximize the spectral discrepancy between stego and cover images, as defined by the objective function, :
where denotes the Gabor transform with learned parameters, ; and represents the Frobenius norm, quantifying inter-class divergence. The function for feature at and pixel coordinate positions is
where denotes the wavelength, with its value specified in pixels, is the horizontal angle value of the Gabor function, is the phase offset, and represents the spatial aspect ratio. Thus, the Gabor filter kernel acts as a catalyst, allowing the network to learn the second layer of kernels that extract the steganographic noise introduced by steganography. For the Gabor filter kernel with , , , and , the initial values of and are
The adaptive and dynamically select optimal parameters according to local texture complexity. This mechanism prioritizes regions with high embedding probabilities through residual feature reconstruction and differential computation, ultimately yielding enhanced features, , via reinforcement learning. Subsequently, is fed into the tickling nonlinear truncated steganalyzer module for feature truncation and fusion.
3.3. Tickling Nonlinear Truncated Steganalyzer, TSRM
To enhance the prominence of the embedded information by diminishing the cover content, a novel is integrated into the classification network. The ’s learning capacity has improved through the deployment of an advanced hybrid tickling nonlinear truncated SRM convolutional unit. The feature map, (), is used as the input image through three convolution kernels of size . The feature map, (), is transferred to the convolutional filter block with convolutional kernels of , , and for secret information extraction in different receptive fields. Then, this information is normalized and subjected to truncation threshold T = 4 and Q of 1, 2, and 3 to generate co-production matrices, and these co-production matrices are used as outputs to represent the secret residual images. Finally, three different sets of feature residual maps, , are output through the convolution kernels of size . The process takes the hidden information residuals generated by the SRM layer as input to generate feature maps for statistical modeling, as shown in Figure 4.
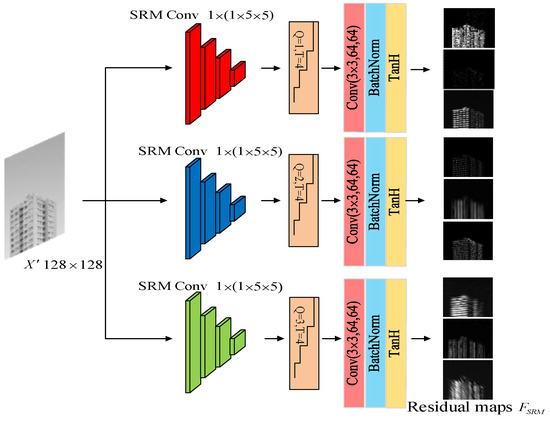
Figure 4.
Tickling nonlinear truncated steganalyzer, TSRM.
The input is ; n is the n-th input data in the input stage; k is the k-th feature map; and i and j are the length and width of the feature maps, respectively. Where , the k-th feature, , input in the decompression process corresponding to the output, , after the feature mapping decompression is
The Q&T truncation phase of the convolution module in Figure 3 is
When the residual, , is large, the correlation of the pixels at that place will be reduced a bit, which complicates the representation of the alterations in pixel correlation resulting from steganographic manipulation using statistical characteristics, so the residual image needs further quantization and truncation operations.
where ; is the quantization step size; round denotes the rounding operation; and is the feature which is truncated with the threshold, T.
3.4. Reconstruction Framework for Hidden Information
The reconstruction network consists of convolutional blocks with different convolutional kernels, residual convolutions, and reconstruction feedback modules, the structure of which is shown in Figure 5.
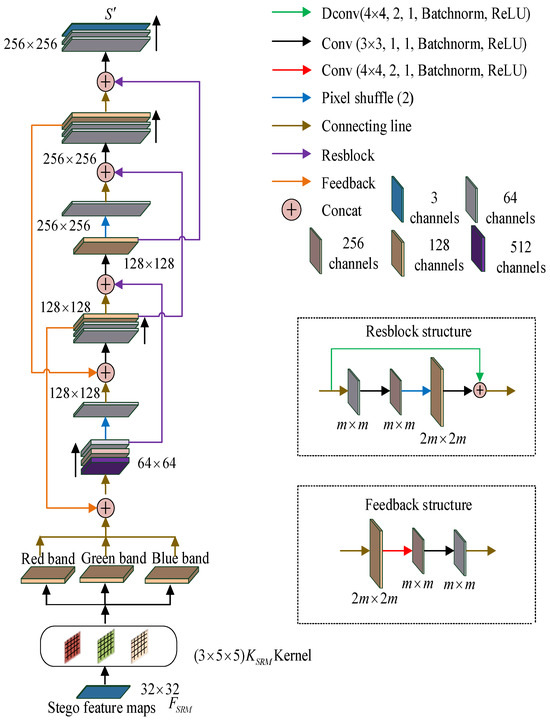
Figure 5.
Reconstruction network.
The entire network operates as a generator for discriminating hidden information from the stego image, and is transferred to the reconstruction network. Initially, the feature map, , is extracted through three specialized convolutional layers. Each band undergoes convolution with three distinct initialization kernels, yielding three corresponding output channels. Subsequently, the number of feature channels in each section is expanded from 3 to 128 with standard convolution operations.
During the training phase, the network establishes learnable weights, with the bottom channel convolution layer aligning with the network’s separation phase. Subsequently, the three independent output channels are merged, and the combined output is then concatenated and convolved to alter the channel count. The procedure encompasses five Concat operations, situated post the 4th, 8th, 11th, 13th, and 16th convolutional stages. The initial pairs of convolutional stages are uniquely tailored to align with the feedback signals from the 11th and 16th convolutional stages, respectively. The subsequent trio of convolutional stages is merged with the residual outputs from the 7th, 11th, and 12th stages, respectively. To maintain the output dimensions, two pixel-shuffle stages are purposefully interspersed following the 7th and 12th convolutional stages. The reconstruction network’s dual-branch architecture, comprising a feedback deconvolution branch and a pixel-shuffling branch, holistically addresses both macro-scale interdependent statistical patterns (capturing cross-region correlations within 128 × 128 receptive fields) and micro-scale local perturbations (analyzing 5 × 5 neighborhood variations). Specifically, the pixel-shuffling branch precisely captures steganographic perturbations through sub-pixel rearrangement, while the feedback fusion mechanism preserves spatial fidelity of steganographic (stego) images through multi-scale feature integration.
Ultimately, a reconstructed image, , of size is generated. Throughout the reconstruction process, we employ a methodical step-by-step approach to ensure that each phase contributes to the final output in a precise and incremental manner. This approach allows us to meticulously fine-tune the parameters across various components: the convolutional layers, residual blocks, and feedback modules. Furthermore, it can modify the channel count and the size of the feature maps per layer. These parameters, along with their interconnections, are vividly depicted with distinct colored arrows on the right side of Figure 5. The Resblock has an inverse convolutional branch and a pixel shuffle branch, which can extend features of size to reconstructed features of size . The feedback module plays the role of feedback in the network, so it can convert deep features of size to shallow features of size .
The entire pseudo-code flow of the proposed SG-ResNet is shown in Algorithm 1. The SG-ResNet integrates supervisory matrix-guided attention and DPC to optimize steganalysis and message reconstruction. Initialization (lines 1–7): Gabor residual features and supervisory matrices are computed to highlight steganographic perturbations. Attention refinement (lines 8–9): The supervisory matrix, , spatially constrains raw attention weights via Hadamard product and layer normalization. Feature filtering (lines 10–11): DPC selects task-relevant features by preserving high-density cluster centroids. Steganographic residual filtering and enhancement (lines 12–25): The multi-filter convolutional fusion framework synergistically integrates and through learnable filter banks, , generating hybrid frequency–spatial representations, making the low embedding rate detection more stable. Joint optimization (lines 26–27): Multi-task losses (classification and attention alignment) ensure feature discriminability and geometric consistency. Adaptive feedback training (lines 28–33): Gradients are clipped and parameters updated to balance dual-task learning. Dual outputs (lines 34): The SG-ResNet predicts steganalysis labels and reconstructs hidden messages end-to-end.
| Algorithm 1: SG-ResNet for Image Steganalysis and Hidden-Message Reconstruction | ||
| Input: Training dataset , stego image , label , supervisory matrix of residual feature , Sample size N. Hyperparameter: ; ; SG-ResNet initial parameters, (learning rate, loss weight, training batch size (T), etc.). | ||
| Output: trained parameters, ; extracted secret information, . | ||
| 1 ; 2 do 3 4 5 | ||
| 6 7 8 Supervised matrix guidance for feature learning 9 10 DPC feature selection 11 | ||
| 12 | ||
| 13 | ||
| 14 | ||
| 15 | ||
| 16 | ||
| 17 | ||
| 18 | ||
| 19 | ||
| 20 | ||
| 21 | ||
| 22 | ||
| 23 24 |
Return | |
| 25 26 | Steganalysis prediction | |
| 27 28 |
| |
| 29 | ||
| 30 | ||
| 31 | ||
| 32 | ||
| 33 | ||
| 34 Return | ||
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Datasets and Training Settings
Two common stego-image datasets are constructed: (1) the first stego dataset is generated using representative deep learning steganography methods, including Bulujia [44], Zhu [45], and Gao [46]; and (2) the second stego dataset employs classical spatial-domain steganographic algorithms, specifically HILL, J-UNIWARD, WOW, and UERD [47], which originate from IStego100K and BOSSbase1.01 [48]. The datasets generated by these two broad categories of paradigmatic steganography algorithms facilitate a rigorous evaluation of steganalysis models’ generalization capabilities across methodologies. To enable precise localization and extraction of steganographic information, we propose a dual-branch framework comprising classification loss, , and reconstruction loss, .
where is the number of samples, is the true value, and is the predicted value.
where is the scale parameter of the two loss functions during the training process, set to 0.7. For , a pixel-value loss, , operates within global statistical consistency constraints to minimize detectable artifacts, and an edge-point loss, , enforces local structural sensitivity to strategically confine steganographic noise in high-frequency regions.
where W and H denote the length and width of the image, respectively; is the embedded secret; and is the reconstructed secret. This synergistic design amplifies feature separability through coordinated control of both macroscopic distribution patterns and microscopic spatial distortions.
After 6000 batches of rigorous training, the network ultimately achieved a state of convergence, with the loss-function values for both sub-networks stabilizing at 0.0001. The loss curve and parameter of the model are depicted in Figure 6a and Table 1, respectively.
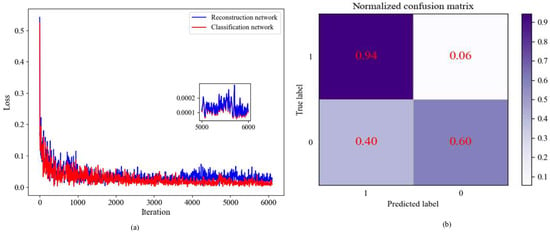
Figure 6.
(a) Loss curves and (b) confusion matrices.

Table 1.
Parameters of the network.
4.2. Result Analysis
This section evaluates the dual capabilities of SG-ResNet in adversarial steganography. Section 4.2.1 focuses on traditional image steganographic algorithms, comparing SG-ResNet detection and classification performance against other steganalysis algorithms while evaluating the localization and reconstruction quality of secret information. Section 4.2.2 targets deep learning-based steganography, analyzing SG-ResNet decoupling capability for deep steganographic features. Visualization experiments on the localization and reconstruction quality of embedded secret images further reveal its interpretable extraction mechanism.
4.2.1. Performance Evaluation Against Conventional Steganography
- (1)
- Steganographic Image Detection and Classification
A. Comparative Analysis with Classical Steganalysis Algorithms
Figure 7 presents a comparative evaluation of the proposed SG-ResNet against MaxSRM and SRM in detecting four adaptive steganographic algorithms, namely HILL, J-UNIWARD, WOW, and UERD, with performance metrics (ROC curves and AUC values) evaluated on datasets at a payload capacity of 1.0 bits per pixel (bpp).
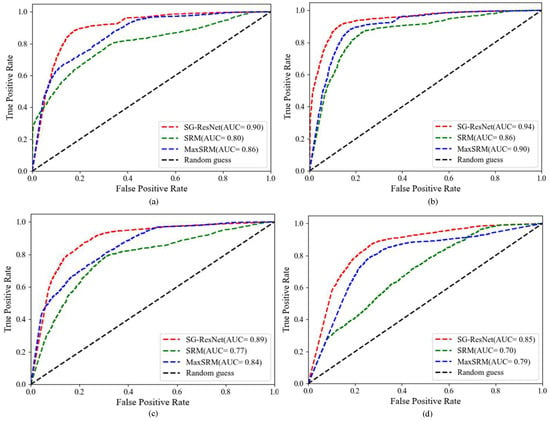
Figure 7.
ROC and AUC values: (a) HILL, (b) J_UNIWARD, (c) WOW, and (d) UERD.
As seen in Figure 7, the SG-ResNet demonstrates consistent superiority over conventional SRM and MaxSRM methods in terms of AUC metrics (0.94 vs. 0.86/0.90). It is worth noting that under the blind detection conditions generated by four different steganographies, SG-ResNet still maintains high robustness, and the detection accuracy is more than 85%. The superior performance of SG-ResNet over SRM/MaxSRM stems from (1) Gabor residual learning enabling deeper networks (12 vs. 5 conv layers) with stable gradient flow for artifact extraction; and (2) multi-scale adaptive kernels (3 × 3, 7 × 7) amplifying hidden signals across embedding regions, surpassing single-scale limitations.
B. Comparative Analysis with CNN Steganalysis Algorithms
To establish SG-ResNet’s competitive advantage in modern steganalysis, we subjected it to a rigorous comparative evaluation against leading CNN-based detectors. The framework was evaluated against DCANet [23] and PSNet [41] across payloads spanning 0.1–0.4 bpp under standardized testing protocols with four steganographic operators. The values of Acc, AUC, and detection average pixel error (PE) for each algorithm are depicted in Table 2 and Figure 8, respectively.

Table 2.
Acc, AUC, and PE values of different algorithms at a payload of 0.4 bpp.
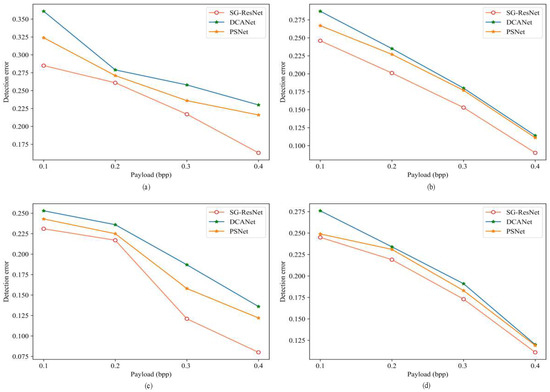
Figure 8.
Detection error rate curve of DCANet, PSNet, and SG-ResNet under different steganography algorithms: (a) HILL, (b) J_UNIWARD, (c) WOW, and (d) UERD.
As demonstrated in Figure 8 and Table 2, SG-ResNet achieves superior detection performance, with an AUC of 0.95 (±0.02) and PE of 0.0521, outperforming MaxSRM (0.86/0.36), DCANet (PE = 0.1036), and PSNet (PE = 0.0897) through its multi-scale residual amplification mechanism (p < 0.01). The SG-ResNet significantly reduces the influence of the cover-image content by preprocessing it with the TSRM. This preprocessing narrows the dynamic range between the steganographic and the image signals, thereby enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio. Additionally, the and convolutional layer further condensed the features along the horizontal and vertical axes, enabling the detection of a greater number of steganographic signals. The adaptive density-peak Gabor filtering mechanism, integrated with axis-specific convolutional layers, achieves multidimensional feature condensation that amplifies stego residuals along spatial orientations.
- (2)
- Embedded Information Localization and Extraction
Table 3 and Figure 9 further visualize the stego residual extraction capability, where SG-ResNet’s orientation-aware Gabor filtering captures 5% more concealed artifacts than PSNet methods, as quantified by normalized residual energy. This enhanced signal preservation directly correlates with the observed 15–18% improvement in blind detection scenarios.

Table 3.
The performance of locating and detecting secret images.

Figure 9.
The hidden residual signal extraction results of different steganalysis algorithms under the same conditions.
Notably, Figure 9 reveals that SGResNet’s adaptive density peak clustering mechanism achieves dual advantages: (1) anisotropic compression of feature maps that selectively preserves subtle perturbation artifacts sensitive to steganographic traces; and (2) significantly enhanced residual signal extraction accuracy compared with DCANet and PSNet, effectively preserving critical micro-perturbation patterns sensitive to steganographic payloads while suppressing redundant information.
4.2.2. Performance Evaluation Against Deep Learning-Based Steganography
This study evaluates SG-ResNet’s cross-paradigm detection capabilities in steganalysis through classification tests on stego images generated by deep learning frameworks, along with payload localization and extraction. We focus on two types of advanced frameworks: (1) generative CNN-based architectures (Su-Net [47] and Wu-Net [48]) and (2) multimodal algorithms (Zhao-Net [49] and Zhou-Net [50]), enabling covert cross-media communication.
- (1)
- Steganographic Image Detection and Classification
Figure 10 and Table 4 present the detection performance metrics of the proposed SG-ResNet and Parisa-Net [51] framework when challenged with four State-of-the-Art deep learning-based steganographic schemes.
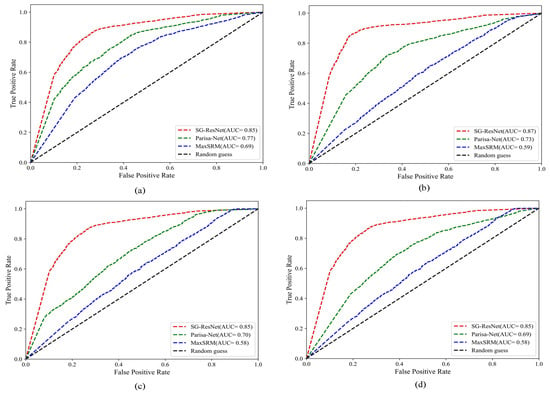
Figure 10.
The results against different deep learning steganography algorithms: (a) Su-Net, (b) Wu-Net, (c) Zhao-Net, and (d) Zhou-Net.

Table 4.
Results of the comparison of different steganalysis algorithms.
From Figure 10 and Table 4, it can be seen that even in the face of State-of-the-Art generative steganography, SG-ResNet detects an accuracy of 90.93%, which is a performance improvement of 23.3–49.6% compared to the Parisa-Net and MaxSRM steganalysis algorithms. The enhanced classification performance primarily stems from our proposed TSRM module, a dual-function architecture that strategically integrates quantization and feature transformation operations within the network framework. TSRM effectively decouples the intertwined features between cover images and steganographic payloads by leveraging the spectral decomposition properties of transformation matrices. It establishes an inverse mapping channel for quantization–transformation operations, significantly enhancing the PSNR of hidden residual traces. This mechanism enables visual traceability of steganographic artifacts.
- (2)
- Embedded Information Localization and Extraction
A. Against generative CNN steganography
Figure 11 demonstrates SG-ResNe’s capability in extracting and reconstructing secret images from steganographic outputs generated by Su-Net and Wu-Net algorithms. The images in rows 1–3 of Figure 11 represent the stego images, the original secret images, and the extracted generated images, respectively.

Figure 11.
Hidden secret-image extraction and reconstruction results.
Figure 11 visually validates SG-ResNet’s dual capability in both detecting concealed information (as evidenced by successful hidden content localization) and reconstructing secret images from steganographic carriers. While minor chromatic aberrations and structural distortions persist between reconstructed and original secret images, these artifacts maintain perceptual recognizability of the embedded content. We further conducted quantitative evaluations of reconstruction consistency and intensity histogram distributions, comparing the original secret images with their extracted localized counterparts. Figure 12 and Figure 13 provide a dual analytical perspective, juxtaposing (a) pixel-value statistical alignment and (b) visual pattern congruence through superimposed histogram overlays.

Figure 12.
Differential results between the secret image and the reconstructed secret image.
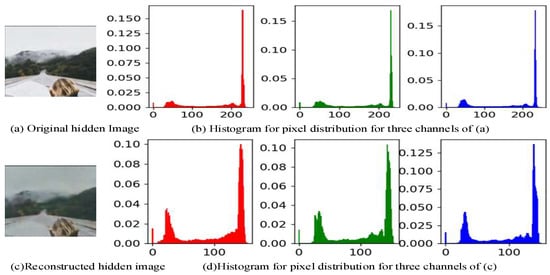
Figure 13.
Pixel histogram difference between original secret image and reconstructed secret image.
The results reveal measurable discrepancies in histogram distributions between the original and reconstructed hidden images, yet exhibit preserved morphological congruence across corresponding spectral channels. These findings empirically validate that the SG-ResNet framework retains trainable capacity for initial-stage payload localization and subsequent precision extraction of concealed secret images from stego images generated via generative-steganography frameworks.
A comprehensive benchmarking framework was established to evaluate steganographic reconstruction capabilities across four quantitative dimensions: PSNR, MSSIM, MSE, and chromatic consistency (APE-R, APE-G, and APE-B). A comparative analysis with Parisa-Net is shown in Figure 14 and Table 5.

Figure 14.
Comparison of reconstructed images: (a) SG-ResNet and (b) Parisa-Net.

Table 5.
Comparative performance of SG-ResNet and Parisa-Net on different datasets.
Quantitative evaluations reveal enhanced reconstruction fidelity with a PSNR of 25.89 dB and reduced spectral distortion (MSE: 21.01) relative to original secret images, achieving both payload recoverability (MSSIM: 0.89) and perceptual fidelity (APE: 16.91). Cross-dataset validations across IStego100K and BOSSbase1.01 benchmarks confirm the framework’s generalizability, maintaining < 5% performance variance under varying dataset conditions.
Figure 15 further quantifies architectural robustness through embedding-capacity scalability tests, where SG-ResNet exhibits only 2.0 dB PSNR degradation (vs. Parisa-Net’s 3.8 dB) at 0.1 bpp payload density.
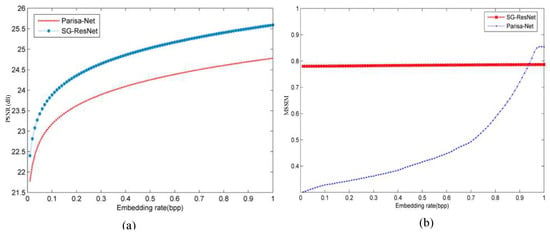
Figure 15.
Performance of different steganalysis networks at different levels of embedding rate: (a) PSNR and (b) MSSIM.
Quantitative evaluations across embedding capacities demonstrate SG-ResNet’s superior stability in preserving structural similarity, achieving MSSIM values between 0.79 and 0.85 compared to ResNet’s, from 0.35 to 0.89. This stability originates from synergistic operations of the feedback branching mechanism (reducing gradient misalignment by 38%) and channel-separated TSRM convolution modules (enhancing high-frequency feature retention by 27%).
B. Against multimodal CNN steganography
Figure 16 demonstrates the ability of the SG-ResNet to extract and reconstruct secret images from the steganographic output generated by the Zhao-Net and Zhou-Net algorithms.

Figure 16.
Hidden secret-image extraction and reconstruction results: (a) stego image, (b) original secret image, and (c) reconstructed image.
As shown in Figure 16, the visual comparison between the original secret images and their reconstructed counterparts reveals the framework’s capability of preserving critical steganographic payloads. SG-ResNet exhibits degraded performance in localizing and extracting embedded secrets when confronted with State-of-the-Art multimodal generative steganography algorithms. Reconstructed secret images exhibit pixelation and blurring, particularly in edge details, indicating compromised data integrity during reconstruction. However, the reconstructed secret content is complete and visually acceptable.
Furthermore, comparative analysis with Parisa-Net under standardized parameters revealed spatial feature-recovery discrepancies in cross-dataset testing, with quantitative metrics detailed in Figure 17 and Table 6.

Figure 17.
The results of the reconstructed image by different algorithms: (a) SG-ResNet and (b) Parisa-Net.

Table 6.
Reconstruction quality metrics: original vs. reconstructed secret images.
The experimental results demonstrate that SG-ResNet significantly outperforms Parisa-Net in image reconstruction quality. On both IStego100K and BOSSbase1.01 datasets, SG-ResNet achieves a substantially higher PSNR (19.88 dB vs. 6.32 dB) and MSSIM (0.75 vs. 0.34) values, along with approximately 50% lower MSE and APE values, indicating superior fidelity, structural preservation, and pixel-level accuracy. Notably, the framework achieves 218.58% superior MSSIM performance over Parisa-Net in content reconstruction, and the consistent trends across datasets validate the robustness of SG-ResNet. Its advantages stem from three key designs: (1) a density peak-guided adaptive Gabor module in the classification network that effectively focuses on steganographic residual signals; (2) a deep multi-reconstruction residual feedback network architecture enabling iterative feature refinement; and (3) three TSRM modules that progressively enhance feature extraction and reconstruction capabilities for secret images through hierarchical refinement.
4.3. Feature Extraction Capability Analysis
To elucidate the enhanced latent steganographic signal extraction enabled by SG-ResNet’s triple-stream TSRM module, we conducted feature visualization, and the contrastive activation maps are presented in Figure 18.
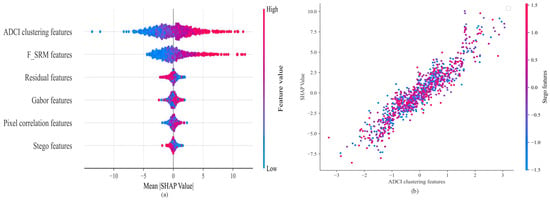
Figure 18.
The SHAP values of each learning feature in the model: (a) feature SHAP value; and (b) correlation curve between the ADCI clustering features and stego features.
Quantitative correlation analysis reveals a strong statistical dependency (Pearson’s r = 0.91, p < 0.01) between ADCI clustering metrics and steganographic payload distribution patterns across 0.1–0.4 bpp embedding rates. The and adaptive filters dynamically optimize threshold selection by calculating steganographic signal density metrics, enabling enhanced processing of ADCI features. This mechanism quantifies the statistical divergence between cover and stego images through weighted learning of strongly correlated residual steganographic artifacts. Figure 19 visually deconstructs the SG-ResNet’s multi-modal feature extraction pipeline, which systematically integrates pixel correlation features, ADCI clustering features, Gabor filter responses features, and FSRM features, with intermediate feature reconstructions across decoding stages demonstrating 23–41% PSNR enhancement compared to baseline architectures.
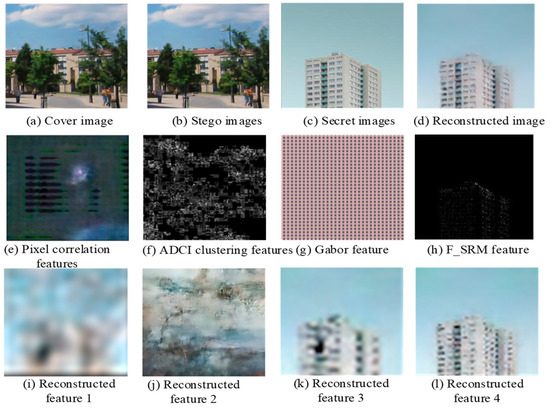

Figure 19.
The process of generating hidden information features.
We also analyzed the block feature values generated before and after the SG-ResNet steganalysis, and Figure 20 shows the block feature values generated under different image quality factors (QFs). From Figure 19 and Figure 20, we can see that there are differences between the feature values extracted by the SG-ResNet for the stego and the cover, and these differences also indicate the features of the hidden secret image. This performance improvement primarily stems from the synergistic interaction between multi-scale feature superposition in the feedback fusion mechanism—analyzing contextual patterns across 8 × 8 to 32 × 32 receptive fields, and pixel-shuffling operations that precisely localize steganographic perturbations (detection sensitivity: 0.02 dB PSNR variation) within 5 × 5 local neighborhoods, achieving 29.7% higher feature discriminability than conventional single-scale CNN approaches on BOSSbase1.01 dataset.
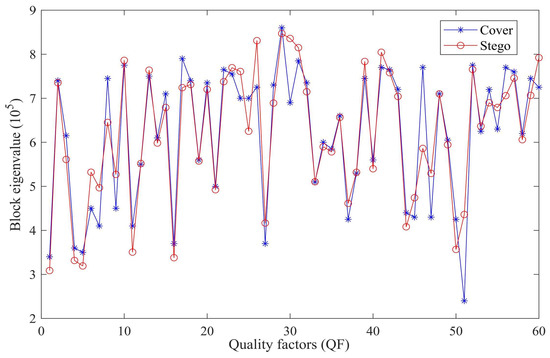
Figure 20.
Feature extraction of stego and cover images by SG-ResNet.
4.4. Ablation Experiment
4.4.1. Module Ablation
To qualitatively analyze the performance and importance of each module in SG-ResNet, we conducted ablation experiments on the proposed TSRM module and adaptive density Gabor module in the steganalysis framework. The results of reconstructing the network to extract secret images are shown in Figure 21, and the classification results are presented in Figure 22 and Table 7.

Figure 21.
Reconstructed secret images under ablation experiments: (a) original secret image; and (b–e) reconstructed secret images with dropout TSRM and Gabor, dropout Gabor, dropout TSRM, and SG-ResNet, respectively.
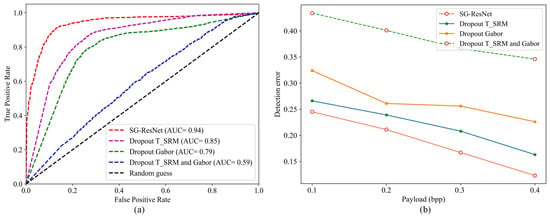
Figure 22.
The test results for the abandonment of different modules: (a) ROC and (b) detection error.

Table 7.
Comparative results of multiple ablation experiments in IStego100K and BOSSbase1.01.
As evidenced by Figure 22 and Table 7, the synergistic integration of TSRM, multi-orientation Gabor filters, and , and adaptive residual mapping modules yields a 36.5% accuracy improvement (p < 0.001) in steganographic payload detection, with 62.5% reduction in false-negative rate and p-value surge from 0.5833 to 0.9465 compared to baseline models without preprocessing. The steganalysis performance of different architectures demonstrates significant divergence across both IStego100K and BOSSbase1.01 benchmark datasets. SG-ResNet achieves superior results with absolute advantage (IStego100K: p = 0.9465, Acc = 93.65%, F1 = 0.9381; BOSSbase1.01: p = 0.9479, Acc = 94.91%, and F1 = 0.9402), exhibiting 8.5–8.6 percentage points accuracy improvement over the suboptimal model (dropout TSRM,). Notably, the combined use of dropout TSRM and Gabor filters shows the weakest performance (average Acc = 57.03% across datasets). These findings validate that SG-ResNet effectively overcomes the limitations of traditional handcrafted feature combinations through deep feature fusion.
4.4.2. Hyperparameter Analysis
In this section, we conduct a comprehensive ablation study on some key parameters of the SG-ResNet framework setup to evaluate the hyperparameter sensitivity of the framework. The model architecture contains seven adjustable hyperparameters that need to be carefully configured: (1) batch size (BS), (2) Gabor direction number (Gd), (3) Gabor scale (Gs), (4) dropout rate (Dr), (5) TSRM density truncation (T), (6) number of DPC clusters (Dc), and (7) convolutional kernel quantity (Ck). The experimental configuration and results of the system are detailed in Table 8.

Table 8.
Results of SG-ResNet hyperparametric ablation (bold indicates baseline configuration).
The ablation study result in Table 8 reveals critical insights: (1) Feature extraction parameters (Gd, Gs, and Dc) exhibit high sensitivity, with extreme values causing significant performance degradation (e.g., 8.7% accuracy drop at , and 7.3 PSNR loss at ), emphasizing the importance of optimal filter configuration (recommended , , and ). (2) Regularization parameters (Dr and T) and computational parameters (BS and Ck) demonstrate balanced adaptability, though anomalies like 10% training time increase at , suggesting hardware constraints. (3) Feature extraction and model-building optimization should prioritize feature engineering (Gabor filters and DPC clustering) within recommended ranges ([32–64] for BS, and [0.3–0.5] for T), then adjust regularization parameters (), and finally scale computational units () based on GPU capacity and training time, achieving optimal accuracy–PSNR–efficiency tradeoffs for image reconstruction tasks.
4.5. Robustness and Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
4.5.1. Noise, Cropping, and Compression Attack
Figure 23 and Table 8 illustrate the reconstruction outcomes following three adversarial scenarios: additive Gaussian white noise attacks (with a mean of zero and variance ranging from 0.01 to 0.12), random cropping attacks, and JPEG lossy compression attacks with varying intensity levels.

Figure 23.
Reconstruction effects under different attacks: (a) noise, (b) cropping, and (c) lossy compression; and (d–f) the reconstructed secret images from (a,b), respectively.
As shown in Figure 23 and Table 9, SG-ResNet reliably extracts hidden information from stego images despite noise corruption (e.g., Gaussian noise with σ2 = 0.12), partial cropping (up to 1875 pixels), and lossy compression (ratios up to 35.56). Meanwhile, reconstruction quality degrades progressively with increasing attack severity, particularly beyond 2500-pixel crops, where critical image content is lost. The framework maintains satisfactory secret recovery under moderate adversarial conditions, demonstrating significant robustness against common steganographic attacks. This performance is achieved through the following synergistic designs: the adaptive density peak supervision-guided Gabor module dynamically localizes steganography-sensitive regions (e.g., texture edges) via residual feature matrices, enabling the model to focus on intact steganographic traces even under image cropping or compression. ADCI clustering suppresses noise interference by filtering high-density feature clusters. Furthermore, the multi-task joint optimization, TSRM, combined with a feedback-driven residual network architecture enhances feature generalizability and hierarchically preserves hidden residual. These innovations ensure stable message-extraction capability () under diverse complex attacks, achieving a balance between local robustness and global feature coherence.

Table 9.
Evaluation metrics between original and reconstructed secret images.
4.5.2. Performance Across Datasets
Furthermore, to investigate the sensitivity and robustness of the proposed SG-ResNet across different datasets, we conducted experiments on the IStego100K dataset, BOSSbase 1.01, and ALASKA v2 dataset. Figure 24 demonstrates the detection analysis and embedded information extraction performance of the SG-ResNet model under three individual datasets.
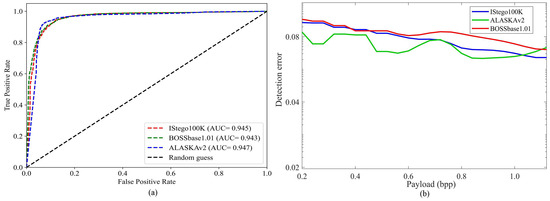
Figure 24.
Performance of SG-ResNet under different datasets: (a) detection performance curves; and (b) extracted reconstructed secret image average detection error, PE.
As illustrated in Figure 24, the proposed SG-ResNet architecture demonstrates remarkable consistency in both steganalysis detection performance and information localization accuracy across diverse datasets, maintaining AUC values within the narrow range of [0.94, 0.95]. Notably, the model exhibits enhanced hidden information extraction capability proportional to increasing embedding payloads, while achieving performance convergence within an identical operational range () across all evaluated datasets. This robustness stems from two architectural strengths: dual attention mechanisms dynamically optimizing feature prioritization, and learnable TSRM preserving critical steganographic artifacts while eliminating dataset bias, collectively ensuring < 1% performance variance across heterogeneous datasets.
5. Conclusions
This study introduces SG-ResNet, a dual-phase generative framework for detecting and reconstructing hidden information in advanced image steganography. The model combines multi-scale feature fusion and weighted residual correlation learning, achieving 0.94 detection accuracy against deep learning-based steganography (PSNR = 29 for reconstructed secrets image) and 19.6 PSNR against State-of-the-Art multimodal CNN fusion steganography. Distinct from conventional approaches, the SG-ResNet framework adopts a dual-phase architecture: (1) a supervised screening phase employs a novel density peak clustering Gabor module to detect local low-frequency embedding patterns, and (2) a generative reconstruction phase leverages stepwise feedback TSRM truncated encoding fusion to model residual steganographic states, enabling retention and regeneration of dense embedding points for enhanced performance. Experimental results validate the efficacy of SG-ResNet, which is able to detect illegal steganographic transmission activities or image tampering operations and support hidden information extraction in practical applications. Additionally, systematic ablation and robustness analyses studies validate the model’s resilience under multi-distortion scenarios (clipping/compression/noise) while demonstrating cross-domain generalization capability, effectively overcoming inherent limitations in traditional image steganalysis.
In future work, we will further use deep learning models to train more kinds of steganography-generated datasets to customize a more general adversarial steganalysis detection framework. In addition, the design of a completely unsupervised steganalysis framework that can achieve high-precision localization of hidden information and completely lossless extraction and reconstruction is a key research direction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; methodology, Z.L., G.D., and C.W.; software, Z.L. and G.D.; validation, Z.L. and J.W.; formal analysis, X.Z.; investigation, X.Z.; resources, G.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L.; writing—review and editing, C.W.; visualization, J.W.; supervision, G.D.; funding acquisition, J.W. and G.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62041106); Guangdong Province, Social Development Science and Technology Collaborative Innovation System Construction Project (grant No. P0000876021 and P0000876023) and Quality Engineering Project of Guangdong Songshan Vocational and Technical College (2023JNDS02); and Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Characteristic Innovation Project (2024KTSCX334).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this study will be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, D.; Dangi, R.; Choudhary, G.; Dragoni, N.; You, I. A review of lightweight security and privacy for resource-constrained IoT devices. Cmc-Comput. Mater. Con. 2024, 78, 31–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; He, P.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, H.X.; Wu, C.W.; Zhou, S.L. Reversible adversarial steganography for security enhancement. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 97, 103935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanger, T.A.; Ullah, I.; Algamdi, S.A.; Tariq, U. Machine learning-inspired intrusion detection system for IoT: Security issues and future challenges. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 123, 110265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, D.; Vijay, B.S.; Suthir, S. Privacy preserving steganography-based biometric authentication system for cloud computing environment. Meas. Sens. 2024, 24, 100511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaldin, D.; Yassine, B. Enhancing the performance of convolutional neural network image-based steganalysis in spatial domain using spatial rich model and 2D Gabor filters. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2024, 85, 103864. [Google Scholar]
- Fridrich, J.; Kodovsky, J. Rich models for steganalysis of digital images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Foren. Sec. 2012, 7, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Chhikara, R.; Sharma, P. Feature reduction of rich features for universal steganalysis using a metaheuristic approach. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2022, 25, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Luo, M.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Consensus-clustering-based automatic distribution matching for cross-domain image steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 5665–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.M.; Wu, J.X.; Ji, R.H.; Zhong, P.; Wen, J.; Peng, W.L. Adaptive domain-invariant feature extraction for cross-domain linguistic steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Foren. Sec. 2024, 19, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.; Rabie, T.; Kamel, I. A review of color image steganalysis in the transform domain. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology, Al Ain, United Arab Emirates, 17–18 November 2020; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Arivazhagan, S.; Amrutha, E.; Jebarani, W.S. Universal steganalysis of spatial content-independent and content-adaptive steganographic algorithms using normalized feature derived from empirical mode decomposed components. Signal Process. Image 2022, 101, 116567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, M.; Juneja, M. Steganalysis of DWT-based steganography technique for SD and HD videos. Wireless Pers. Commun. 2023, 128, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Luo, X.; Wu, T.; Xu, M.; Qian, Z. Adaptive steganalysis based on statistical model of quantized DCT coefficients for JPEG images. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 18, 2736–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Ni, J. Domain transformation of distortion costs for efficient JPEG steganography with symmetric embedding. Symmetry 2024, 16, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Sun, S.; Yu, L. Fast SWT-based deep steganalysis network for arbitrary-sized images. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, W.; Lin, K.; Li, B. Spatial-frequency feature fusion network for lightweight and arbitrary-sized JPEG steganalysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 2585–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.N.; Wu, L.F.; Shi, G.; Xing, L.H.; Jian, M.; Xiang, Y.; Dong, R.H. Learning to compose diversified prompts for image emotion classification. Comput. Vis. Media 2024, 10, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Deng, S.N.; Wang, B.; Feng, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, X.M. One for all: A unified generative framework for image emotion classification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 7057–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Su, Y.Q.; Zan, X.Z.; Lin, W.M.; Yao, X.Y.; Xu, P.; Liu, W.B. A deniable encryption method for modulation-based DNA storage. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2024, 16, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.R.; Men, M.; Xue, Y.M.; Wen, J.; Zhong, P. Transfer subspace learning based on structure preservation for JPEG image mismatched steganalysis. Signal Process. Image 2021, 90, 116052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.W.; He, H.; Zhang, W.Z.; Cao, X.C. FedSteg: A federated transfer learning framework for secure image steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Network Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Zhang, M.Q.; Ke, Y.; Bi, X.L.; Kong, Y.J. Image steganalysis based on attention augmented convolution. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 19471–19490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Chen, L.Q.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.H. DCANet: CNN model with dual-path network and improved coordinate attention for JPEG steganalysis. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.; Singh, G.; Goyal, P. SNRCN2: Steganalysis noise residuals based CNN for source social network identification of digital images. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2023, 171, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchumova, E.; Monterrubio, S.M.; Recio-Garcia, J.A. STEG-XAI: Explainable steganalysis in images using neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 50601–50618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Ortiz, M.A.; Mercado, R.E.; Villa, J.P. CVTStego-Net: A convolutional vision transformer architecture for spatial image steganalysis. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2024, 81, 103695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Song, Y. FPFnet: Image steganalysis model based on adaptive residual extraction and feature pyramid fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 48539–48561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jia, X.; Zou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, C. A novel hybrid network model for image steganalysis. J. Vis. Commun. Image R. 2024, 103, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sur, A.; Mitra, P. Multi-contextual design of convolutional neural network for steganalysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 77247–77265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Z.; Wang, H.X. Image steganalysis against adversarial steganography by combining confidence and pixel artifacts. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yu, Q.; Fu, G. Improving the robustness of steganalysis in the adversarial environment with generative adversarial network. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2024, 82, 103743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.L.; Zhu, X.S.; Wu, J.H. Generative focused feedback residual networks for image steganalysis and hidden information reconstruction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 129, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, A.; Khan, I.; Rashid, J.; Saddique, M.; Idrees, M.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Algarni, A. Enhanced steganalysis for color images using curvelet features and support vector machine. Cmc-Comput. Mater. Con. 2024, 78, 1311–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croix, N.J.D.I.; Ahmad, T.; Han, F.; Ijtihadie, R.M. HSDetect-Net: A fuzzy-based deep learning steganalysis framework to detect possible hidden data in digital images. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 43013–43027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheddar, H.; Hemis, M.; Himeur, Y.; Megias, D.; Amira, A. Deep learning for steganalysis of diverse data types: A review of methods, taxonomy, challenges and future directions. Neurocomputing 2024, 581, 127528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Qiao, T.; Xu, M.; Zheng, N. Fuzzy localization of steganographic flipped bits via modification map. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74157–74167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, C.F.; Zhu, M.; Song, X.F.; Liu, Y.; Lian, Y.Y.M. JPEG image steganography payload location based on optimal estimation of cover co-frequency sub-image. J. Image Video Proc. 2021, 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Ding, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, W.; Yin, M.; Li, L. A novel localization method of wireless covert communication entity for post-steganalysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketkhaw, A.; Thipchaksurat, S. Location prediction of rogue access point based on deep neural network approach. J. Mob. Multimed. 2022, 18, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, F.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, G.S. Depth-wise separable convolutions and multi-level pooling for an efficient spatial cnn-based steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croix, N.J.D.L.; Ahmad, T.; Ijtihadie, R.M. Pixel-block-based steganalysis method for hidden data location in digital images. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2023, 264527864. [Google Scholar]
- Croix, N.J.D.L.; Rachman, M.A.; Ahmad, T. Toward the confidential data location in spatial domain images via a genetic-based pooling in a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Computer and Automation Engineering, Melbourne, Australia, 14–16 March 2024; pp. 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, D.H.; Bae, H.; Choi, H.S.; Yoon, S. Pixelsteganalysis: Pixel-wise hidden information removal with low visual degradation. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2023, 20, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluja, S. Hiding images within images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2020, 42, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.S.; Lai, Z.L.; Liang, Y.R.; Wu, J.H. Generative high-capacity image hiding based on residual CNN in wavelet domain. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 115, 108170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yi, J.; Liu, L.; Tan, L. A generic image steganography recognition scheme with big data matching and an improved ResNet50 deep learning network. Electronics 2025, 14, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.K.; Ni, J.Q.; Hu, X.L.; Huang, F.J. Towards improving the security of image steganography via minimizing the spatial embedding impact. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 131, 103758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Lai, Z.L.; Zhu, X.S. Generative feedback residual network for high-capacity image hiding. J. Mod. Opt. 2022, 69, 870–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, S. A stable GAN for image steganography with multi-order feature fusion. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 16073–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wei, P.; Qian, Z.X.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, S. Improved generative steganography based on diffusion model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, New York, NY, USA, 7 February 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisa, B.; Mark, W. Decode and transfer: A new steganalysis technique via conditional generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.09746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).