Abstract
With the rapid development of internet technologies, enhancing security protection for patient information during its transmission has become increasingly important. Compared with traditional image encryption methods, chaotic image encryption schemes leveraging sensitivity to initial conditions and pseudo-randomness demonstrate superior suitability for high-security-demand scenarios like medical image encryption. In this paper, a novel 3D fractional-order memristive Hopfield neural network (FMHNN) chaotic model with a minimum number of neurons is proposed and applied in medical image encryption. The chaotic characteristics of the proposed FMHNN model are systematically verified through various dynamical analysis methods. The parameter-dependent dynamical behaviors of the proposed FMHNN model are further investigated using Lyapunov exponent spectra, bifurcation diagrams, and spectral entropy analysis. Furthermore, the chaotic behaviors of the proposed FMHNN model are successfully implemented on FPGA hardware, with oscilloscope observations showing excellent agreement with numerical simulations. Finally, a medical image encryption scheme based on the proposed FMHNN model is designed, and comprehensive security analyses are conducted to validate its security for medical image encryption. The analytical results demonstrate that the designed encryption scheme based on the FMHNN model achieves high-level security performance, making it particularly suitable for protecting sensitive medical image transmission.
Keywords:
Hopfield neural network (HNN); image encryption; field programmable gate array (FPGA); fractional-order MSC:
65P20; 34C28; 26A33; 92B20
1. Introduction
With the acceleration of medical imaging digitization, ensuring patient privacy protection while maintaining diagnostic accuracy has become a critical challenge in smart healthcare [1]. Traditional block encryption modes expose statistical features of pixel blocks, making them vulnerable to correlation analysis attacks [2]. Consequently, academia has begun exploring chaotic system-based encryption schemes. Compared to conventional methods, chaotic system-based encryption schemes leverage pseudo-randomness, initial value sensitivity, and ergodicity [3] to achieve pixel-level nonlinear confusion and diffusion [4].
Chaotic systems exhibit extreme sensitivity to initial conditions or parameter variations, where minor changes lead to vastly divergent trajectories over time [5], and this property enables their applications in secure communication [6,7], adversarial networks [8], encryption algorithms [9], and signal detection [10]. However, existing studies predominantly focus on low-dimensional integer-order chaotic models [11], which suffer from simple phase-space topologies, low Lyapunov exponents, and limited key spaces, rendering them vulnerable to brute-force attacks [12].
Recent integration of memristors with Hopfield neural networks (HNNs) has opened new avenues for chaotic system innovation. As the fourth fundamental circuit element, memristors emulate biological synaptic plasticity via nonlinear flux–charge relationships [13], and their hysteresis characteristic induces hyperchaos [14], multistability and multi-wing attractors [15], and hidden attractors [16] in HNNs. For instance, Bao et al. proposed the BM-CHNN model, demonstrating chaotic and hyperchaotic behaviors with singular manifold structures and fractal basin boundaries, as well as homogeneous coexisting hyperchaotic attractors [17]. Moreover, their DM-HNN model generates multi-stripe/multi-wave hyperchaotic attractors, where stripe/wave counts increase with memristor state function segments [18]. Deng et al. incorporated a piecewise-linear memristor to couple neurons in a tri-neuron HNN, enabling direct control of butterfly-wing attractor counts via memristor parameters [15].
Nevertheless, integer-order chaotic systems fail to capture biological neurons’ long-term memory effects. Existing high-dimensional models, especially the chaotic models with four or more dimensions (the dimension of independent variables, i.e., the dimension of phase space) [19], increase dynamical complexity but incur exponential hardware resource consumption, conflicting with low-power requirements of medical devices.
Fractional calculus provides a new theoretical breakthrough for the memristors and chaotic systems. Fractional-order memristors enhance chaotic networks’ complexity, controllability, and practicality through memory effects, fractional dynamics, and deep coupling with HNNs [20], manifested as higher Lyapunov exponents and intricate attractor morphologies [21]. It is noteworthy that the existing literature has not explored the application of a 3D fractional-order memristive HNN constructed by integrating two neurons and a fractional-order memristor in image encryption, which provides significant innovation potential for the current study.
Based on the above analysis, this study proposes a 3D fractional-order memristive HNN (FMHNN) and an associated medical image encryption scheme, addressing the high-security requirements of the fast developing smart healthcare. Specifically, the key contributions of this work include the following:
- A simple FMHNN model with only two neurons and a charge-controlled fractional-order memristor is constructed. Numerical simulations confirm that lower fractional orders of the memristor enhance chaotic intensity and phase-space complexity. Moreover, the FPGA-based hardware implementation of the FMHNN validates the consistency between numerical and experimental results.
- Based on the chaotic sequences generated by the proposed FMHNN model, a medical image encryption scheme with superior resistance to statistical attacks, noise interference, and data loss is developed.
- By balancing dimensionality reduction (3D) and fractional-order tuning, the FMHNN model maintains chaotic strength while minimizing hardware resource consumption, supporting embedded security modules for portable medical devices and advancing secure smart healthcare ecosystems.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 outlines theoretical foundations of fractional calculus and numerical methods for fractional differential equations. Section 3 discusses the construction of the memristor and FMHNN model. Section 4 includes an investigation of parameter-dependent dynamical behaviors of the FMHNN model. Section 5 discusses an FPGA implementation of the FMHNN model. Section 6 shares the encryption scheme design and security validation. Section 7 includes conclusions and future directions.
2. Theoretical Foundations of Fractional Calculus
To ensure clarity in the subsequent descriptions of fractional-order equations, this section introduces the definitions related to fractional-order calculus and numerical solution methods for fractional-order differential equations.
Definition 1.
The unified expression of the fractional-order calculus operator is defined [22] as
where is the order of fractional calculus, t is the independent variable, 0 represents the lower bound of the variable, and τ represents the time variable. If , the represents the q-th-order derivative or integral operator of the function with respect to the independent variable t; represents the original signal; and if , then it represents the -th-order integral.
Definition 2.
For a given function , the -order Riemann–Liouville (RL) fractional-order integral [23] is
where is the Gamma function
Definition 3.
The Caputo fractional derivative [23] is
where n is the smallest integer greater than q, and is the n-th-order integer derivative of . The initial condition is the integer-order derivative: .
The solution method of Adomian decomposition method (ADM) [24,25] is as follows:
Suppose the Caputo fractional-order chaotic system is
where is the given function variable, for the autonomous system, is the constant in the system, and f represents the function formula including linear and nonlinear parts.
The system is divided into three parts: linear, nonlinear, and constant.
where is the q-order Caputo fractional derivative operator, L is the linear part of the system equation, N is the nonlinear part of the system equation, and is the initial value of the system. Applying the RL integral operator to both sides of the equation, we get
where is the initial condition of the system.
According to the Adomian decomposition algorithm principle, the solution of the system can be expressed as an infinite series form:
The nonlinear term is decomposed according to the following formula:
If , and , then the nonlinear term can be expressed as
That is, the solution formula of system Equation (5) is
Its derivative relations are
It is worth mentioning that the bigger the derivation terms i in Equation (12), the more accurate the solution of (11), and when i tends towards infinity, the solution of (11) is an exact solution.
However, the derivation terms i are limited in actual calculation, because the calculation volume and calculation time will significantly increase with the increase in i. Moreover, the Adomian decomposition algorithm converges very fast [26,27], and a limited number of derivation terms i can achieve a high-precision solution of Equation (11). Therefore, generally, a finite number of terms are taken to be considered [28,29].
3. Model Construction
In this section, a fractional-order memristor is designed, then a new three-dimensional simple FMHNN model with two neurons and the fractional-order memristor is proposed. Finally, the equilibrium points and system stability analysis of the proposed FMHNN model are conducted.
3.1. Fractional-Order Memristor
The HNN model with memristor has richer dynamic characteristics and behaviors. According to Chua’s detailed definition and explanation of memristors [30] and the detailed definition of the fractional calculus in Section 2, a charge-controlled fractional-order memristor is constructed below:
where , , are, respectively, the input voltage, output current, and memductance function of the memristor. The expression of the input voltage is , and a, b, c, d, p are memristor parameters, while q is the fractional order. The internal state variable is related to the voltage , the self-state, and the fractional order [3,5].
We set the memristor parameters , , , , , the input voltage amplitude , and the fractional order . The pinched hysteresis loop of the memristor at frequencies f of 1.5 Hz, 2.5 Hz, and 5 Hz, respectively, is shown in Figure 1a. It can be seen that with the increase in frequency, the area of the pinched hysteresis loop of the fractional-order memristor gradually decreases.
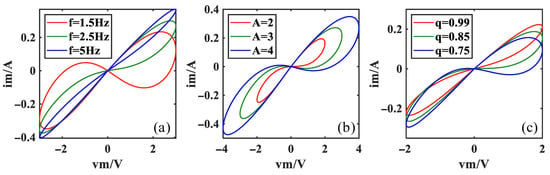
Figure 1.
Pinched hysteresis loops of the fractional-order memristor. (a) Variation with frequency f. (b) Variation with amplitude A. (c) Variation with fractional order q.
Hereby, it is clarified that all parameter values in this paper are determined using a two-step method of “literature-based range delimitation + controlled-variable iterative experimentation”. Specifically, initial parameter ranges are roughly defined through literature research, followed by sequential adjustment of individual parameters while observing output results (such as hysteresis loop characteristics of memristors and phase portrait features of the system model), ultimately screening out parameter combinations capable of stably reproducing target characteristics.
Keeping the other parameters unchanged, when the frequency f = 2 Hz and the fractional order , the pinched hysteresis loop of the memristor with different input voltage amplitudes is shown in Figure 1b. It can be seen that with the increase in amplitude, the area of the pinched hysteresis loop of the fractional-order memristor gradually increases.
With the other conditions remaining unchanged, when the amplitude and the frequency f = 2.2 Hz, the pinched hysteresis loop of the memristor with different fractional orders is presented in Figure 1c. It can be seen that with the decrease in the fractional order, the area of the pinched hysteresis loop of the fractional-order memristor gradually increases.
Based on Figure 1, it is evident that all the pinched hysteresis loops of the fractional-order memristor exhibit distinct nonlinear characteristics, and it indicates that the current–voltage relationship of memristors is nonlinear, which is an important feature that distinguishes the memristor from the traditional linear resistor.
The existence of pinched hysteresis loops shows that memristors have the hysteresis phenomenon, that is, their electrical properties depend on the historical changes in voltage or current, and this property gives memristors potential application value in storage and information processing, etc.
3.2. The Proposed FMHNN Model
The general model of the HNN with n neurons can be represented [31,32] by the following equation;
where , , , and are, respectively, the membrane potential, membrane capacitance, membrane resistance, and external stimulation current of neuron i, and is the synaptic weight coefficient from neuron i to neuron j, that is, the synaptic strength between neurons. The hyperbolic tangent function, , is a classical activation function widely used in Hopfield neural networks.
According to the general expression (14) of the HNN, a new three-dimensional double-neuron fractional-order memristor HNN (FMHNN) model is proposed in Figure 2.
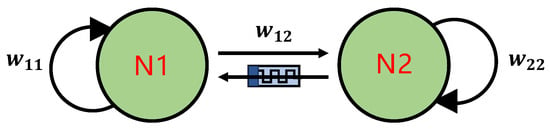
Figure 2.
FMHNN model topological structure.
As can be observed in Figure 2, the proposed FMHNN consists of two neurons ( and ) and one fractional-order memristor (13). Moreover, the parameters are set to , , .
Then, the mathematical expression of the proposed FMHNN model is
where , , , respectively, represent neuron 1, neuron 2, and the state variable of the memristor, a, b, c, d, p are the parameter variables of the memristor, q represents the fractional order, k represents the coupling strength, and , , are the synaptic weight coefficients [13,14].
Because the change in the coupling strength k will affect the dynamic behavior between the two neurons, we will use the coupling strength k as an adjustable parameter to study the dynamic phenomenon of the model. In order to study the influence of the fractional order on the dynamic behavior of the model and the influence of the synaptic weight on the dynamic behavior of the model under other unchanged conditions, we will also set the fractional order q and the synaptic weight as adjustable parameters. Here, the trial-and-error method is used to simulate the numerical value of the system, and finally the representative parameter values of other fixed parameters are set as , , , .
Here, the Adomian decomposition algorithm described in Section 2 is used to solve the above Equation (15). In view of the fact that there are many nonlinear terms in the model (15), to enhance the balance between computational accuracy and efficiency, this paper uses a threshold-based truncation method for determining the number of Adomian decomposition terms. The method involves recursively computing the series terms of the differential equation solution and sequentially checking whether the absolute value of each term is less than a preset threshold of . If the absolute value of the current term is smaller than the threshold, this term and all subsequent terms are truncated; if it exceeds the threshold, the next term is computed until the minimum number of terms is found that satisfies the requirements of high accuracy and efficiency.
Then, the parameter values are , , , , , , , , ; the initial values are ; the fractional order is ; the step size is ; and the number of iterations is . The number of terms is counted starting from zero. When the number of decomposition terms is six, after iterations, the absolute values of the last term are . Among these, the absolute value of is greater than the threshold , so the next term needs to be computed. When the number of decomposition terms is seven, after iterations, the absolute values of the last term are , all of which are less than the threshold .
From this, it can be concluded that when the fractional order , the contributions of the seventh term and subsequent terms to the solution are negligible. Therefore, in the subsequent numerical simulations of this paper, the first six terms (terms 0 to 5) are selected for computation. Due to the complexity of the decomposition process and the excessive length of the resulting final expressions, the detailed decomposition results are provided in Appendix A. Here, the first six terms of the ADM decomposition algorithm of Equation (15) are presented as follows:
where
where represents the j-th term of the i-th state variable.
3.3. Equilibrium Points and Their Stability Analysis
In an HNN, the existence and nature of equilibrium points can reveal the essential characteristics of chaotic systems, that is, the existence of unstable equilibrium points, sensitive dependence on initial conditions, etc. By solving the equilibrium points of the HNN, the stable or critical state of the system can be determined, and it is useful for understanding the internal dynamic behaviors of the system.
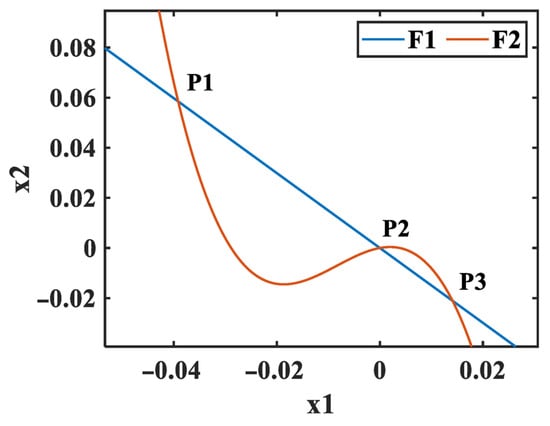
The method of solving the equilibrium points of the FOD equation is the same as that of the IOD equation, that is, by setting the derivative to zero and then solving the ternary linear equations. Under the conditions of , , , , , , , setting the adjustable parameter , , , the adjustable parameters are brought into the fractional-order differential Equation (15), and when we let , we can obtain
When we replace with , we can get two simplified implicit functions as follows:
Then, we can solve Equations (19) and (20), and their curves are plotted in Figure 3. As shown in Figure 3, the three intersection points of curve and curve are . We substitute the three points into Equation (21) to calculate the three equilibrium points as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The equilibrium point and stability of the system (15) under the conditions of , , and .
The difference between the fractional-order HNN system and the IOD equation is that the Jacobian matrix needs to be calculated according to Formula (16). Because its calculation result expression is very long, in Appendix A, we only list the partial derivative of the state variable with respect to itself, that is, the third row and third column expression of the Jacobian matrix.
We substitute the three equilibrium points into the Jacobian matrix, respectively, and solve the corresponding eigenvalue by numerical solution () as shown in Table 1.
In the fractional-order dynamic system with fractional order , the system is asymptotically stable only when all eigenvalues satisfy Formula (22).
By substituting the eigenvalues in Table 1 into Formula (22) for calculation, we can know that the FMHNN model (15) does not satisfy the stability conditions of the fractional-order system at the three equilibrium points, and it is unstable, which means that the proposed FMHNN model cannot stabilize at the equilibrium points. The FMHNN model will not converge to any equilibrium point, and it is likely to be in a chaotic state, manifested as the trajectory diverging and interweaving in the phase space. In this case, the system is highly likely to exhibit chaotic attractors, and small initial condition differences will lead to significant deviations in its system trajectory.
4. Dynamics Analysis of the FMHNN Model
In this section, the chaotic state of the FMHNN model is verified through theoretical analysis and numerical simulations, and its dynamic phenomena with parameter changes is further analyzed in depth. Moreover, the simulation platform is composed of a computer with an i9-13900HX processor and 32-GB dual-channel memory, and the software includes 64-bit Windows 11 and Matlab (version 2021a).
4.1. System Chaotic State Analysis
We set the parameters , , , , , , , and the initial condition is . The total iteration time of the numerical calculation is 2000 unit time, and the iteration step is . When the adjustable parameters , , , the Lyapunov exponent of the FMHNN model (15) changing with time is shown in Figure 4.
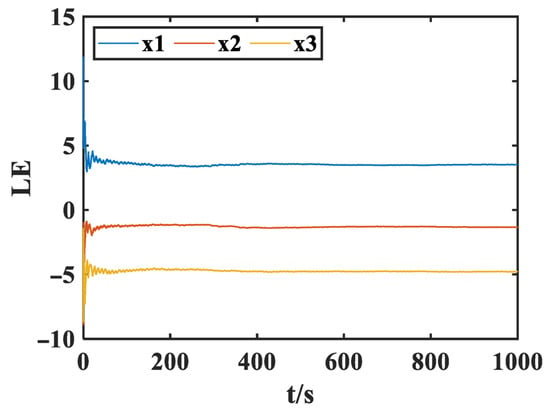
Figure 4.
Lyapunov exponents of model (15) changing with time , , .
Based on Figure 4, we can see that the Lyapunov exponents of the FMHNN model are , , and , and it has a Lyapunov exponent greater than zero (). Therefore, combined with the above stability analysis of its equilibrium points, it can be concluded that the FMHNN model has chaotic characteristics, which means that its phase space is divergent in the direction, and its phase space is convergent in the , directions.
Under these conditions, the phase diagrams of the FMHNN model (15) and its three state variables are shown in Figure 5. Figure 5a–c are the phase diagrams of the FMHNN model in the planes , , , respectively, and Figure 5d is the time-domain waveform of the three state variables of the FMHNN model in the time domain of 450–550 s. Based on Figure 5, we can clearly see that the FMHNN model exhibits a complex and irregular chaotic state, and it generates chaotic attractors.
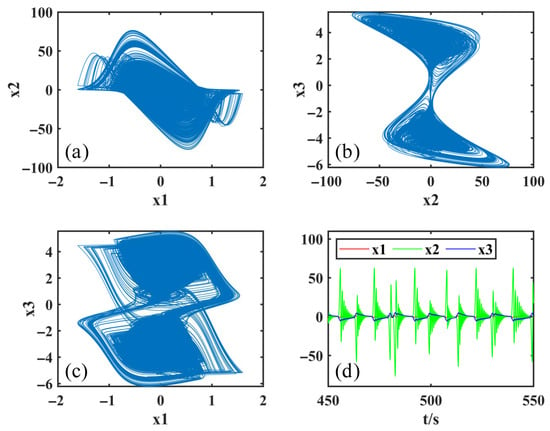
Figure 5.
The phase diagrams (a–c) and time-domain waveform (d) of the FMHNN model (15).
Moreover, the Poincaré map analysis [33] and 0−1 test [34] are used to further validate the chaotic state of the FMHNN model in the plane.
The “0−1” test algorithm is a deterministic analysis method to test whether the system is in a chaotic state. If the system is not chaotic, then the trajectory of the dynamic system in the plane is bounded. If the system is chaotic, then the trajectory of the dynamic system in the plane is similar to Brownian motion. The basic principle is to establish a random dynamic process for the dynamic system and then study the dynamic changes of the stochastic process in the system operation process.
Suppose a certain sequence obtained in the system evolution is . Define any constant c greater than zero, and define two formulas based on .
Through the above formulas, the trajectory of the FMHNN system state variable in the plane is calculated as shown in Figure 6. The trajectory of points in the plane shows a similar Brownian motion, so it can be concluded that the system is in a chaotic state under this condition.
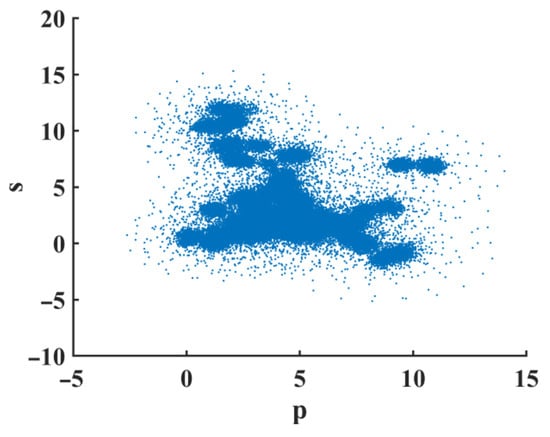
Figure 6.
The plane trajectory of the FMHNN model (15).
The Poincaré map of the FMHNN is shown in Figure 7. The data points in Figure 7 show a relatively obvious scattered state and do not form an obvious aggregation mode, which indicates that the output of the system under this mapping has a certain uncertainty and variability. This kind of dispersion may mean that the system is sensitive to small changes in initial conditions or input parameters. Even if the input has a slight difference, the output may also be quite different. Therefore, it can be inferred that the FMHNN (15) has chaotic characteristics.
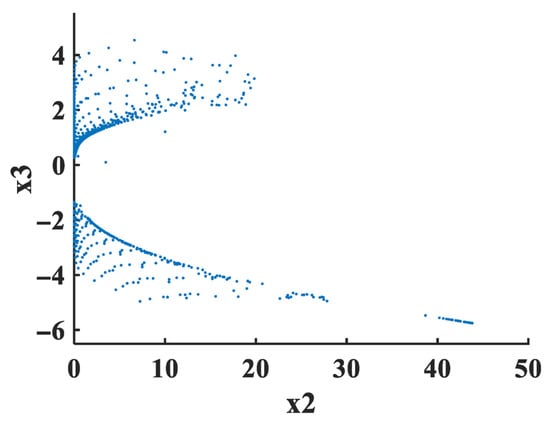
Figure 7.
The Poincaré map of the FMHNN model (15).
4.2. The Dynamic Behaviors of the FMHNN Model Varying with Parameters
In this subsection, we use the Lyapunov exponent, bifurcation diagram, and entropy diagram to analyze the dynamic behaviors of the FMHNN model varying with three parameters: fractional order q, coupling strength k, and synaptic weight .
It should be noted that spectral entropy (SE) [35] is an index that measures the complexity or uncertainty of a signal. In a chaotic system, the change in entropy reflects the complexity of the system state changing with parameters. When the entropy value is higher, the system is more complex and uncertain; when the entropy value is lower, the system is relatively simple and orderly.
We set the synaptic weight and the coupling strength and change the value of fractional order q in the interval with a step size of 0.001; the bifurcation diagram, Lyapunov exponents (LEs), and spectral entropy (SE) of the FMHNN model (15) change with q, and these are presented in Figure 8.
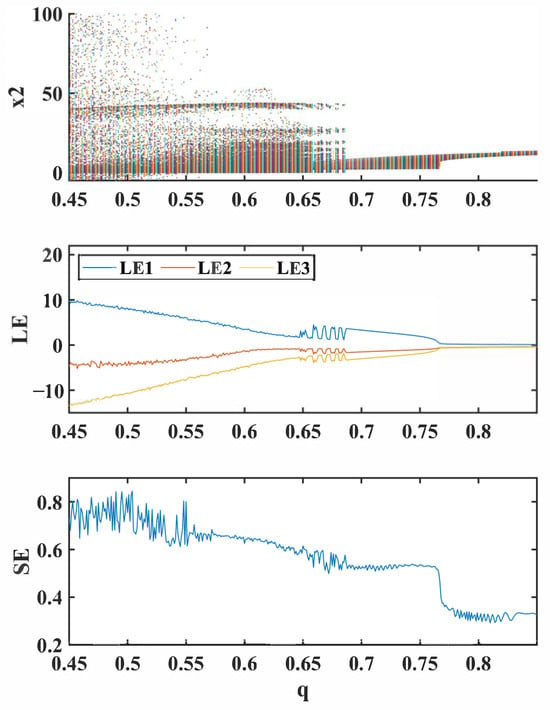
Figure 8.
Bifurcation diagram (top), Lyapunov exponent (LE) (middle), and spectral entropy (SE) (bottom) of the FMHNN model (15) varying with the fractional order q.
From Figure 8, we can see that when the fractional order q is in the interval , the distribution of points in the bifurcation diagram is more complex and divergent, and the Lyapunov exponent , which indicates that the FMHNN model may be in an unstable or irregular state and may exhibit chaotic behavior.
When the fractional order q is in the interval , the points in the bifurcation diagram gradually converge, the Lyapunov exponent , and the entropy curve is relatively stable, which indicates that the degree of chaos in the FMHNN model is relatively high and chaotic attractors may appear.
Then, with the increase in the fractional order q, the bifurcation diagram has several obvious breakpoints, and these breakpoints mean that the FMHNN model may be in a periodic or quasi-periodic state.
When , the system state is relatively densely distributed, the Lyapunov exponent gradually decreases to zero, the entropy value gradually decreases, the degree of chaos of the FMHNN decreases, and it finally may enter a periodic state or a stable state.
Based on the above analysis, it can be known that the smaller the value of the fractional order q, the more chaotic and complex the FMHNN model is.
Keeping the other conditions unchanged, we set the fractional order and synaptic weight , and the bifurcation diagram, Lyapunov exponents (LEs), and spectral entropy (SE) of the FMHNN model (15) varying with the coupling strength k within the interval with a step size of 0.004 are presented in Figure 9.
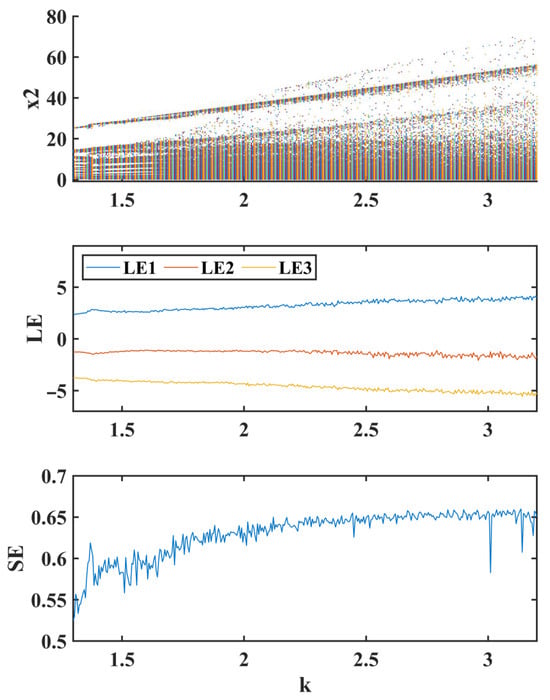
Figure 9.
Bifurcation diagram (top), Lyapunov exponent (LE) (middle), and spectral entropy (SE) (bottom) of the FMHNN model (15) varying with the coupling strength k.
As shown in Figure 9, as the coupling strength k increases, the point cloud in the bifurcation diagram gradually expands outward, indicating increased divergence in the system trajectories. The Lyapunov exponent remains greater than zero throughout the interval, confirming the presence of chaotic behavior. The spectral entropy values exhibit an overall increasing trend, suggesting that the dynamic behavior of the FMHNN model becomes more complex and uncertain as k increases.
These results mean that the dynamic behaviors of the FMHNN model becomes more complex with increasing k, and it has richer dynamic characteristics.
Under the condition that other parameters remain unchanged, by setting the fractional order and coupling strength , and varying the synaptic weight within the interval with a step size of 0.002, the bifurcation diagram, Lyapunov exponents (LEs), and spectral entropy (SE) of the FMHNN model (15) are presented in Figure 10.
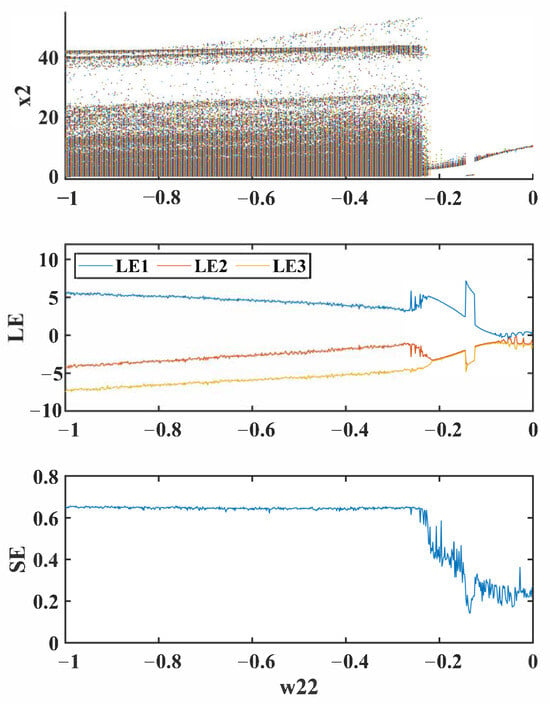
Figure 10.
Bifurcation diagram (top), Lyapunov exponent (LE) (middle), and spectral entropy (SE) (bottom) of the FMHNN model (15) varying with the synaptic weight .
As shown in Figure 10, when is in the range , the points in the bifurcation diagram exhibit scattered distribution, and the Lyapunov exponent remains greater than zero, indicating chaotic behavior of the FMHNN model with sensitive dependence on initial conditions.
When lies within , the point distribution in the bifurcation diagram becomes relatively concentrated, accompanied by a decrease in spectral entropy and value until they approach zero, which indicates that a possible transition of the FMHNN model occurs from chaotic to periodic or quasi-periodic states as increases within this range.
5. FPGA Implementation
With the rapid development of integrated circuits technology, modern FPGAs feature high memory bandwidth, fast multiply–accumulate units, and I/O peripherals, enabling high-speed parallel computing to handle the intensive calculations required for fractional-order systems. Thus, this study implements the proposed FMHNN model using an FPGA.
The FPGA platform employed in this work is the Black Gold ZYNQ7000 (model AX7020, Xinyi Electronic Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), which integrates a dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 and FPGA programmable logic into a single chip using ARM+FPGA SoC technology. The core processor is a Xilinx Zynq7000 series XC7Z020-2CLG400I (Xilinx, San Jose, CA, USA). The board includes a 33.333 MHz active crystal oscillator, providing a stable clock source for the processing system and a 50 MHz active crystal oscillator for the programmable logic.
Additionally, a DA output module utilizing an Analog Devices AD9767 chip (Analog Devices, Norwood, MA, USA) is incorporated. This chip supports dual-channel, 14-bit, 125 MSPS digital-to-analog conversion. The module features a 40-pin female header for FPGA board connectivity and two BNC connectors for analog signal output, allowing direct observation via an oscilloscope using BNC cables. The development tool is Vivado (version 2019.2, Xilinx, San Jose, CA, USA).
In experiments, the Riemann–Liouville (RL) fractional-order integration algorithm is applied for numerical discretization, generating two sets of 16-bit data sequences (size: 200,001; value range: 0–65535). The digital signals are converted to 0–5 V analog voltage signals via the DA module and observed on an oscilloscope (SIGLENT, Shenzhen, China).
The FPGA implementation experiments of the FMHNN model (15) are presented in Figure 11. Figure 11a illustrates the FPGA hardware setup, while Figure 11b–d depict the dynamic trajectories of the FMHNN model on the X–Y, Y–Z, and X–Z orthogonal planes, respectively. Experimental results confirm that the hardware-implemented state evolution aligns closely with numerical simulations. By translating the complex mathematical operations of fractional-order chaotic systems into FPGA-based hardware logic circuits, this work provides a reliable technical pathway for practical applications such as chaotic signal generators and secure communication modules.
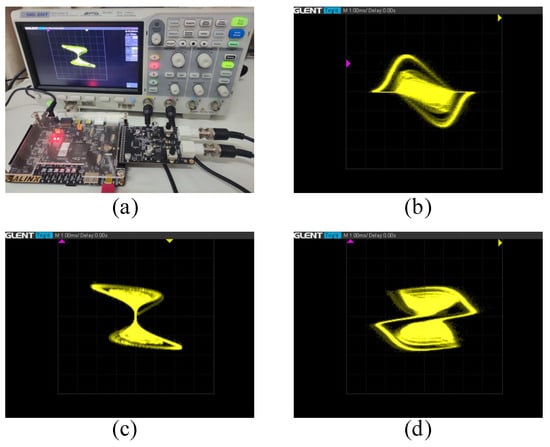
Figure 11.
The FPGA implementation experiments of the FMHNN model (15). (a): the experimental setup of FPGA hardware platform connected to a digital oscilloscope. (b): the experimental result in the - plane. (c): the experimental result in the - plane. (d): the experimental result in the - plane.
6. Medical Image Encryption Application
Compared to traditional encryption methods, chaos encryption algorithms demonstrate significant application value in information security due to their unique dynamic characteristics such as extreme sensitivity to initial conditions, high-dimensional parameter spaces, and non-periodic trajectories [36].
In this study, we propose a medical image encryption algorithm utilizing chaotic sequences generated by the FMHNN model (15). The security of the proposed FMHNN-based encryption scheme is rigorously validated through a multi-dimensional security verification framework, including histogram uniformity analysis, quantitative evaluation of information entropy, and resistance to noise attack testing, which guarantees the effectiveness of the proposed FMHNN-based encryption scheme in securing medical image transmission, offering a novel solution for secure information transfer.
6.1. Encryption and Decryption Algorithms and Results
The images used in this work for the FMHNN-based encryption algorithm are all grayscale images, represented by the matrix . The dimensions of the length and width of the image are represented by H and W, respectively.
The specific encryption steps of the proposed FMHNN-based encryption algorithm are as follows:
- Generate chaotic sequences. According to the above-designed FMHNN model (15), we define the initial parameters as the initial key, and generate three chaotic sequences , , with size .
- Generate pseudo-random sequences. The three generated chaotic sequences , , are used to generate two pseudo-random sequences of length based on the following operations:
- Scramble the original image pixel positions. The original image is changed from an matrix to a column vector . The pseudo-random index sequence is generated by sorting the pseudo-random sequence according to , and then the new column vector is rearranged according to .
- XOR encryption. We use to perform XOR encryption on the image elements according to . Then we rearrange the vector into an H row, W column matrix , and is the final encrypted image.
The corresponding decryption steps of the proposed FMHNN-based encryption algorithm are as follows:
- XOR. Rearrange the encrypted image into a column vector , and decrypt the encrypted image according to .
- Recover the original image pixel positions. Restore the arrangement of image elements through , and then rearrange them to change back to the original image with size .
This study employs two sizes (five images with 512 × 512 resolution and four images with 1024 × 1024 resolution) of medical images as experimental samples for encryption–decryption performance testing. To avoid redundant data presentation, representative images are selected as typical examples as follows: breast abscess image (1024 × 1024), neck lymph node image (1024 × 1024), sesamoid ossicles image (512 × 512), and ovarian dermoid image (512 × 512). In Figure 12, the original plaintext image group (a1–d1), ciphertext image group (a2–d2), and decrypted recovery group (a3–d3) are illustrated. The visual results demonstrate that the encryption process effectively achieves visual information obfuscation, while the decrypted group retains complete lossless visual recovery of image details.
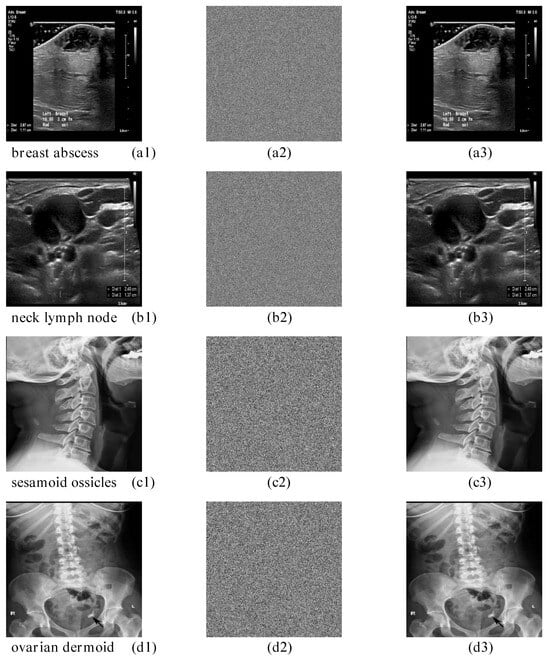
Figure 12.
The encryption and decryption results of the breast abscess image, the neck lymph node image, the sesamoid ossicles image, and the ovarian dermoid image. (a1–d1): the original images of the four pictures. (a2–d2): the encrypted images. (a3–d3): the decrypted images.
6.2. Security Analysis of the FMHNN-Based Encryption Algorithm
To further analyze the security of the FMHNN-based encryption algorithm quantitatively, a key space size validation, key sensitivity testing, pixel distribution histogram analysis, adjacent pixel correlation calculation, information entropy measurement, and robustness against attacks evaluation are used to evaluate its security performance.
6.2.1. Key Space Analysis
Key space dimensionality analysis [37] serves as a critical component in cryptographic strength evaluation. The proposed FMHNN-based encryption algorithm utilizes a 13-dimensional key parameter system , which includes both initial state variables and control parameters of the FMHNN model. Leveraging the effective precision of double-precision floating-point numbers (IEEE 754 standard), each parameter demonstrates independent adjustability within an adjustable range of . Computational results reveal that the total system key entropy reaches bits. This exceeds the NIST-recommended post-quantum resistance standard by three orders of magnitude and surpasses the conventional brute-force defense threshold by nearly six orders of magnitude. These properties mathematically establish an infeasibility barrier against brute-force attacks.
6.2.2. Key Sensitivity Analysis
In cryptographic security evaluation systems, key sensitivity can be quantified using the number of pixel change rate (NPCR) and unified average changing intensity (UACI) metrics [38]. These two parameters are core quantitative standards for assessing the sensitivity of an encryption algorithm to minor key variations.
The NPCR metric represents the ratio of differing pixel values at identical positions between two encrypted images generated before and after a minor key modification. The ideal NPCR value is approximately 99.6094%. When a slight key adjustment triggers nonlinear cascading effects, altering over 99% of pixel positions in the ciphertext image, the encryption is considered to exhibit strong diffusion characteristics. If the measured UACI value stabilizes within 33.45% ± 0.2%, it confirms that key-induced perturbations produce pixel value fluctuations following a uniform distribution, complying with the NIST SP800-22 randomness test criteria. When the NPCR exceeds the 98% threshold and the UACI remains stable within the 30–35% critical range, the encryption system effectively resists differential attacks and statistical analysis attacks.
The formulas for calculating the NPCR and UACI are as follows:
where denotes the encrypted image generated with the original key and the encrypted image generated after a minor key modification. Here, M and N represent the image dimensions (rows and columns), and 255 denotes the maximum pixel value range (8-bit image).
By introducing an incremental adjustment to the control parameter , we generated the original ciphertext and perturbed ciphertext on the medical image sample. The NPCR and UACI values calculated using Equation (25) are presented in Table 2. As shown in Table 2, even a minuscule key perturbation (on the order of ) triggers a nonlinear cascading effect, causing mutations in over 99% of pixel positions, which demonstrates that the proposed FMHNN-based encryption algorithm exhibits strong key sensitivity, where minor key variations lead to significant ciphertext alterations. It can ensure robust resistance to differential and statistical analysis attacks.

Table 2.
The NPCR and UACI values of the images.
6.2.3. Histogram Analysis
Histogram analysis [39] serves as a critical metric for evaluating the encryption effectiveness of image encryption algorithms. It visually reflects the distribution patterns of pixel values. The histogram of an original image (pre-encryption) may exhibit peak-like or concentrated distributions, whereas the histogram of an encrypted image should display uniform distribution across all gray levels. This uniformity effectively disrupts the statistical characteristics of the original image, thereby enhancing the security of information transmission.
As shown in Figure 13, the image histograms before and after the FMHNN-based encryption are illustrated. Figure 13a1–d1 are plaintext images; Figure 13a2–d2 are their plaintext histograms; Figure 13a3–d3 are the encrypted images; and Figure 13a4–d4 are the encrypted image histograms. Clearly, the encrypted histograms exhibit uniform gray-level distributions, indicating enhanced pixel randomness that prevents attackers from deducing image content through statistical features.
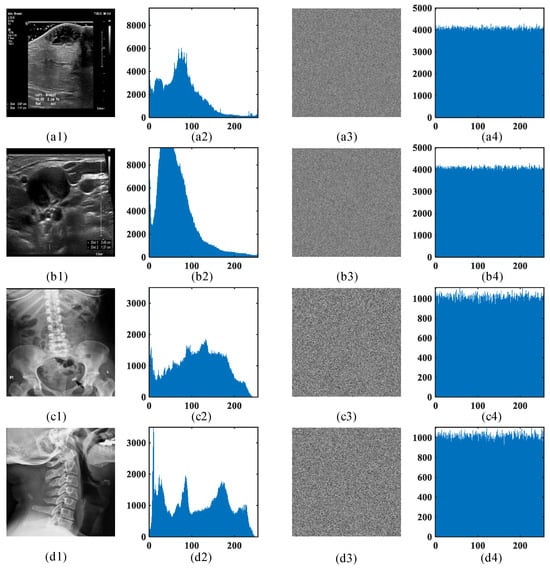
Figure 13.
Histograms of the breast abscess image (a1–a4), the neck lymph node image (b1–b4), the sesamoid ossicles image (c1–c4), and the ovarian dermoid image (d1–d4) before and after the FMHNN-based encryption. (a1–d1): the original images of the four pictures. (a2–d2): the histograms of the original image. (a3–d3): the encrypted images. (a4–d4): the histograms of the encrypted image.
To eliminate subjective visual assessments, a histogram variance quantification model is introduced. Histogram variance reflects the spread and dispersion of data in the histogram. Ideally, the variance of an encrypted image should approximate the theoretical value of a uniform distribution. For example, the theoretical variance for an 8-bit grayscale image under uniform distribution is . If the histogram variance of an encrypted 8-bit grayscale image approaches this theoretical value, it indicates uniform gray-level distribution and stronger resistance to statistical attacks. Conversely, significant deviations from the theoretical value imply weaker statistical attack resistance.
The histogram variance is calculated as follows:
where represents the gray levels of an 8-bit grayscale image, denotes the mean value, and represents the probability of occurrence for each gray level in the image.
The histogram variances of the images before and after the FMHNN-based encryption, calculated using Equation (26), are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Histogram variance before and after the FMHNN-based encryption.
Based on Table 3, it is clear that the histogram variances of the FMHNN-based encrypted images significantly approach the theoretical value for 8-bit grayscale images compared to their pre-encryption state. This demonstrates that the pixel value distribution closely approximates uniformity, confirming the FMHNN-based encryption algorithm’s strong resistance to statistical attacks. Therefore, it can be concluded that the proposed FMHNN-based encryption algorithm satisfies the requirements for resisting statistical analysis-based cryptanalysis.
6.2.4. Correlation Analysis
Correlation analysis [40] serves as a critical metric for evaluating an encryption algorithm’s resistance to statistical attacks. This method quantifies the statistical association between adjacent pixel values in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions of the encrypted and original images, verifying whether the encryption algorithm effectively disrupts the structural features of the original image. In plaintext images, scatter plots of adjacent pixels exhibit an approximately linear distribution, indicating strong correlations. In contrast, encrypted images should display uniformly distributed scatter points, reflecting negligible or weak spatial correlations.
In this experiment, 10,000 pairs of adjacent pixels are randomly selected for correlation analysis. The horizontal, vertical, and diagonal correlation scatter plots for the breast abscess image and the sesamoid ossicles image are illustrated in Figure 14 and Figure 15, respectively. The results clearly show that the scatter plots of the encrypted images exhibit a nearly uniform spatial distribution compared to the original images. This demonstrates that the proposed FMHNN-based encryption algorithm effectively reduces pixel correlations and enhances resistance to attacks.
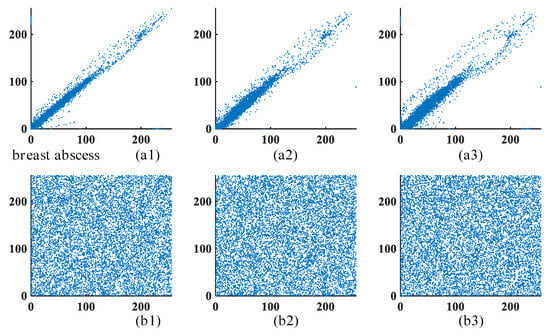
Figure 14.
The breast abscess image correlation scatter plot. (a1–a3) are the scatter plots of the original image in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, respectively. (b1–b3) are the scatter plots of the encrypted image in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, respectively.
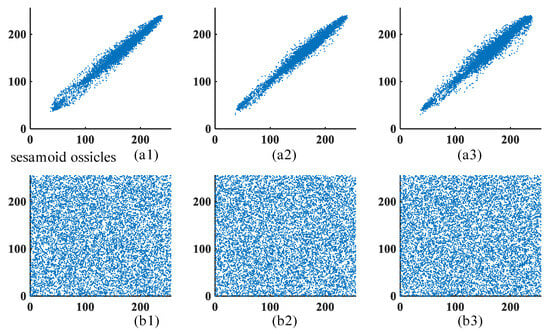
Figure 15.
The sesamoid ossicles image correlation scatter plot. (a1–a3) are the scatter plots of the original image in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, respectively. (b1–b3) are the scatter plots of the encrypted image in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, respectively.
In addition to visual analysis of spatial correlations between adjacent pixels before and after encryption, this study employs Pearson’s correlation coefficient and distance correlation coefficient for quantitative analysis. The correlation coefficients of adjacent pixels in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions of the encrypted image are calculated to assess the linear dependence between pixels. The correlation coefficient of the original image is generally close to 1, while that after encryption should approach 0.
In this paper, Pearson’s correlation coefficient is used to verify the linear correlation between adjacent pixels after image encryption. The formula for calculating the Pearson’s correlation coefficient [41] is as follows:
where denotes the covariance, and represent the variances of datasets x and y, and are the mean values, and N is the number of selected adjacent pixel pairs.
Because the Pearson correlation coefficient cannot capture nonlinear associations, we also introduce the distance correlation coefficient to quantify the nonlinear associations of adjacent pixels in the encrypted image.The distance correlation coefficient is an indicator for measuring the dependence of any form (linear/nonlinear) between two variables and capable of capturing both linear and nonlinear correlations simultaneously. The calculation result of the distance correlation coefficient should fall within the range , where a larger value indicates stronger correlation. The formula for calculating the distance correlation coefficient [42] is as follows:
Among them, is the distance covariance of X and Y (which measures the degree of dependence between variables). and are the distance variances of X and Y, used to measure the degree of dispersion of a single variable. n is the number of samples of variable X or Y. A and B are the distance matrices of variables X and Y, respectively. Performing double centralization on them yields and .
Using Equations (27) and (28), the correlation coefficients in the horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions of the encrypted images are calculated and summarized in Table 4. It can be observed that the post-encryption correlation coefficients of the images are extremely close to zero, confirming that the encrypted images satisfy the requirements for unpredictability and randomness.

Table 4.
Pearson’s correlation coefficient and distance correlation coefficient of the FMHNN-based encrypted images.
6.2.5. Information Entropy Analysis
Information entropy [43] is a critical metric for evaluating the randomness of encrypted images and their resistance to statistical attacks. It quantifies the uniformity of pixel value distributions to reflect the encryption algorithm’s effectiveness. For 256-level (8-bit) grayscale images, the theoretical maximum entropy is 8. The closer the post-encryption entropy value is to this limit, the stronger the algorithm’s ability to balance pixel distributions.
The information entropy is calculated using the following formula:
where represents the probability of the occurrence of pixels with gray value i.
The information entropy values of images before and after the FMHNN-based encryption, calculated using Equation (28), are listed in Table 5. As shown in Table 5, the post-encryption entropy values of the images deviate minimally from the theoretical maximum 8 by only 0.0002–0.0007. Such near-ideal entropy performance confirms that the statistical features of the encrypted images are thoroughly obfuscated, making statistical-based cryptanalysis impractical and highlighting the proposed FMHNN-based algorithm’s robustness against statistical attacks.

Table 5.
Information entropy of the FMHNN-based encrypted images.
To intuitively demonstrate the advantages of the proposed encryption scheme based on the FMHNN, we conducted a quantitative comparison with representative studies in the field of medical image encryption in recent years, and the results are presented in Table 6. The comparison metrics include system dimension, key space, key sensitivity (NPCR/UACI), information entropy, and adjacent pixel correlation, covering the core evaluation dimensions of security, complexity, and attack resistance.
As can be seen from Table 6, the key space of the proposed scheme reaches , which far exceeds that of other schemes (schemes such as [44,45]), theoretically eliminating the possibility of brute-force attacks. The key sensitivity is close to the ideal value (99.6094%, 33.4635%), which is superior to some existing studies (schemes such as [45,46]), verifying the extreme sensitivity to tiny key perturbations. Compared with integer-order systems, minor variations in q within the interval (0,1) (e.g., 0.6 vs. 0.60001) can alter the dynamical characteristics of chaotic sequences. This sensitivity enriches key combinations. Theoretically, this is equivalent to adding a continuously adjustable dimension to the key space without increasing system dimensionality, thereby enhancing resistance to brute-force attacks.
The information entropy is 7.9994, infinitely close to the theoretical maximum of 8 and higher than some reported results (schemes such as [46,47]), indicating better uniformity in the pixel distribution of encrypted images. The horizontal/vertical/diagonal correlation coefficients are all close to 0 and outperform certain studies (schemes such as [9,48]), demonstrating the thoroughness of pixel confusion.
Although the proposed scheme shows comparable performance to certain existing works in some quantitative metrics, it achieves equivalent security with a lower system dimension. Compared with the existing 5-dimensional, 9-dimensional, and even 10-dimensional encryption models in the literature, it can theoretically reduce the number of neurons and synaptic connections, providing a new paradigm that balances “high security” and “low resource consumption” for medical image encryption. Beyond the quantitative metrics presented in the table, the robustness of the proposed scheme will be further verified through data loss attacks and noise attacks in subsequent sections.

Table 6.
Performance comparison of different encryption schemes.
Table 6.
Performance comparison of different encryption schemes.
| References | System Dimension | Key Space | NPCR | UACI | Information Entropy | Horizontal, Vertical, Diagonal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work | 3 | 99.6029% | 33.4897% | 7.9994 | −0.0005, 0.0019, −0.0000 | |
| [9] | 5 | / | 99.6040% | 33.4710% | 7.9993 | −0.0017, −0.0020, 0.0062 |
| [49] | 4 | / | 99.6100% | 33.4700% | 7.9990 | −0.0099, 0.0154, 0.0146 |
| [44] | 4 | 99.5968% | 33.4747% | 7.9993 | −0.0020, 0.0010, 0.0103 | |
| [47] | 5 | / | 99.6078% | 33.4875% | 7.9977 | −0.0024, 0.0005, 0.0047 |
| [45] | 4 | 99.6841% | 33.5539% | 7.9992 | 0.0014, 0.0009, 0.0004 | |
| [48] | 4 | / | 99.6110% | 33.4730% | 7.9992 | 0.0035, −0.0028, −0.0015 |
| [50] | 9 | 99.6104% | 33.4662% | 7.9981 | −0.0017, −0.0008, 0.0133 | |
| [46] | 10 | 99.5953% | 33.5107% | 7.9976 | −0.0005, 0.0089, 0.0039 |
6.2.6. Robust Analysis of the Proposed FMHNN-Based Encryption Algorithm
In image encryption security analysis, robustness evaluation serves as a critical metric to measure an encryption algorithm’s ability to maintain image integrity under attacks. Data loss attacks and noise attacks, as two typical adversarial scenarios, pose significant challenges to the encryption algorithm’s resistance to interference. In data loss attacks, adversaries may compromise encrypted image integrity by intercepting partial regions, leading to information loss, localized errors, or incomplete reconstruction during decryption. For noise attacks, adversaries inject Gaussian or salt-and-pepper noise into encrypted images, disrupting pixel value distributions or frequency-domain coefficient structures, thereby causing blurring or distortion in the inversely transformed images.
Using the breast abscess image and the sesamoid ossicles image as test cases, experimental data demonstrate that the proposed encryption algorithm exhibits remarkable resistance to attacks. As shown in Figure 16, decrypted images retain core diagnostic information even when 1/25, 1/16, and 1/4 of the encrypted data is lost. Similarly, Figure 17 illustrates the decrypted image quality under salt-and-pepper noise attacks with intensities of 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3. The results confirm that key features and detailed information remain discernible despite severe noise interference. These findings validate the algorithm’s superior robustness in resisting data corruption and noise perturbations.
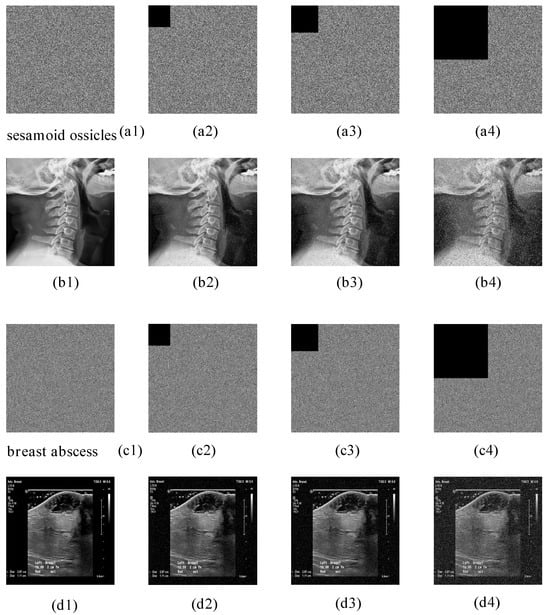
Figure 16.
The decryption effect diagrams of the breast abscess encrypted image and the sesamoid ossicles encrypted image data before and after loss. (a1–d1): without loss. (a2–d2): lost 1/25 of the data. (a3–d3): lost 1/16 of the data. (a4–d4): lost 1/4 of the data.
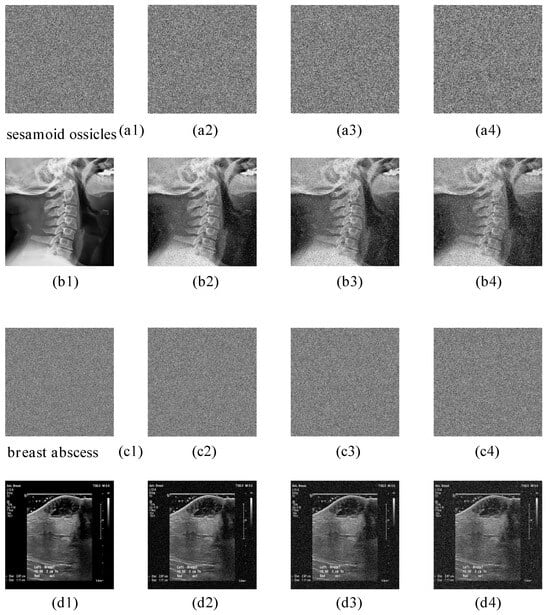
Figure 17.
The decryption effect diagrams of the breast abscess encrypted image and the sesamoid ossicles encrypted image before and after being attacked by noise. (a1–d1): without noise. (a2–d2): contain 10% noise. (a3–d3): contain 20% noise. (a4–d4): contain 30% noise.
7. Conclusions
This paper addresses the high-security requirements in medical image encryption by proposing a three-dimensional chaotic system called the FMHNN model. First, a novel fractional-order memristor is designed and integrated with a two-neuron HNN to construct the FMHNN model. The chaotic characteristics of the FMHNN model are verified through phase diagrams, Lyapunov exponents, Poincaré maps, and 0−1 tests, revealing the complex effects of parameters (e.g., fractional order q, coupling strength k, synaptic weight ) on dynamic behaviors. Second, the chaotic characteristics of the FMHNN model are implemented on an FPGA hardware platform, validating the consistency between numerical simulations and hardware experimental results. Finally, an FMHNN-based medical image encryption scheme is developed using FMHNN-generated chaotic sequences. Superior performance of the FMHNN-based medical image encryption scheme in resisting statistical attacks, noise interference, and data loss is demonstrated through analyses of key space, histogram statistics, correlation, information entropy, NPCR/UACI, and robustness.
Compared with existing high-dimensional memristive chaotic systems, the proposed FMHNN model achieves a balance between complexity and practicality. Its simple structure—only two neurons and one fractional-order memristor—is expected to reduce hardware overhead compared with higher-dimensional memristive models, which benefits resource-constrained medical devices.
The continuous fractional order q introduces a new key dimension that is unavailable in integer-order systems, potentially enlarging the effective key space without additional circuitry and enhancing the security of encryption schemes. These qualitative advantages, however, remain to be quantified through exhaustive resource-power measurements and side-channel evaluations in future work.
However, the current scheme focuses solely on static images. Future work could integrate blockchain technology to achieve traceability and integrity verification of encrypted images, establishing a full-process security framework from acquisition to transmission. Moreover, as quantum computing advances may threaten traditional chaotic encryption, combining more complex algorithms to design hybrid encryption schemes could enhance long-term security. Additionally, exploring dynamic adaptive mechanisms for fractional order q and increasing neuron numbers may improve the complexity and anti-analysis capability of the chaotic system. In summary, the proposed FMHNN model and encryption scheme provide new insights for medical information security, but further exploration is required in model generality and attack resistance to promote practical applications in smart healthcare.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S., L.L., and J.J.; methodology, H.S.; software, H.S. and L.L.; validation, H.S., L.L., and J.J.; formal analysis, H.S.; investigation, J.J.; resources, J.J.; data curation, H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S., L.L., and J.J.; writing—review and editing, H.S., L.L., and J.J.; visualization, H.S. and H.L.; supervision, J.J. and H.L.; project administration, J.J.; funding acquisition, H.S. and J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62273141. This work was also supported by Research on the path of innovation and entrepreneurship education for Information Majors in medical colleges under the background of “government enterprise education innovation competition” xiangjiaotong [202401001536].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ADM | Adomian decomposition method |
| ARM | Advanced RISC machine |
| BM-CHNN | Bimemristor cyclic Hopfield neural network |
| BNC | Bayonet Neill–Concelman |
| DA | Digital-to-analog |
| DM-HNN | Discrete memristive Hopfield neural network |
| IOD | Integral-order differential |
| FMHNN | Fractional-order memristive Hopfield neural network |
| FOD | Fractional-order differential |
| FPGA | Field-programmable gate array |
| HNN | Hopfield neural network |
| HNNs | Hopfield neural networks |
| LE | Lyapunov exponent |
| MSPS | Multiphase serial–parallel–serial storage |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| NPCR | Number of pixels change rate |
| RISC | Reduced instruction-set computer |
| RL | Riemann–Liouville |
| SE | Spectral entropy |
| SoC | System on chip |
| UACI | Unified average changing intensity |
| XOR | Exclusive OR |
Appendix A
References
- Jin, J.; Wu, M.; Ouyang, A.; Li, K.; Chen, C. A novel dynamic hill cipher and its applications on medical IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 14297–14308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jin, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Lu, M.; Ouyang, A. A New-Type Zeroing Neural Network Model and Its Application in Dynamic Cryptography. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2025, 9, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Ma, M. Dynamics in a Memristor-Coupled Heterogeneous Neuron Network under Electromagnetic Radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 16527–16543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sang, H.; Wang, P.; Yu, X.; Yang, Z. A Novel 4D Chaotic System Coupling with Dual-Memristors and Application in Image Encryption. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Q.; Guo, S. Simple Cyclic Memristive Neural Networks with Coexisting Attractors and Large-Scale Amplitude Control. Chaos: Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 33, 07315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Luo, D. Discrete Memristive Delay Feedback Rulkov Neuron Model: Chaotic Dynamics, Hardware Implementation and Application in Secure Communication. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 25559–25567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, G. Discrete Memristive Conservative Chaotic Map: Dynamics, Hardware Implementation, and Application in Secure Communication. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025, 55, 3926–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Bao, H.; Yu, X.; Hua, Z.; Bao, B.; Xu, Q. Hybrid tri-memristor hyperchaotic map and application in Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Nets. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Yang, L.; Hu, G.; Guan, Z.H.; Iu, H.H.C. Constructing Multiscroll Memristive Neural Network with Local Activity Memristor and Application in Image Encryption. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 4039–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Chen, W.; Ouyang, A.; Yu, F.; Liu, H. A time-varying fuzzy parameter zeroing neural network for the synchronization of chaotic systems. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2023, 8, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Min, F.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, H. ReLU-type Hopfield Neural Network with Analog Hardware Implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 167, 113068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Woźniak, M. Exploiting robust quadratic polynomial hyperchaotic map and pixel fusion strategy for efficient image encryption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 246, 123190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Fang, J.; Wei, Z.; Dong, Y.; Du, S.; Wen, S.; Hong, Q. A Riccati Matrix Equation Solver Design Based Neurodynamics Method and Its Application. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 15163–15176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Tang, H.; Su, Y.; Bao, H.; Chen, M.; Xu, Q. Two-Dimensional Discrete Bi-Neuron Hopfield Neural Network with Polyhedral Hyperchaos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 5907–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, G. Memristive Multi-Wing Chaotic Hopfield Neural Network for LiDAR Data Security. Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 113, 17161–17176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. A Complex-Variable Disturbed Laser with Application to Hidden Multi-Scroll Attractor Generation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 113, 10515–10533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Chen, Z.; Ma, J.; Xu, Q.; Bao, B. Planar Homogeneous Coexisting Hyperchaos in Bi-Memristor Cyclic Hopfield Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 16398–16408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Wang, R.; Tang, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Discrete Memristive Hopfield Neural Network with Multi-Stripe/Wave Hyperchaos. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 20902–20912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, W.; Pang, W. Spacecraft Attitude Measurement and Control Using VSMSCSG and Fractional-Order Zeroing Neural Network Adaptive Steering Law. Sensors 2024, 24, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, L.; Amirian, M.M. Stability Analysis of Fractional Order Memristor Synapse-Coupled Hopfield Neural Network with Ring Structure. Cogn. Neurodynamics 2023, 17, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Deng, Q. A Review of Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems of Memristive Neural Networks. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umarov, S. Introduction to Fractional and Pseudo-Differential Equations with Singular Symbols, Developments in Mathematics; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleanu, D.; Diethelm, K.; Scalas, E.; Trujillo, J.J. Fractional Calculus: Models and Numerical Methods, 2nd ed.; Series on Complexity, Nonlinearity and Chaos; World Scientific: Singapore, 2016; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abassy, T.A. Improved Adomian Decomposition Method. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 59, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abassy, T.A.; El-Tawil, M.A.; Saleh, H.K. The Solution of Burgers’ and Good Boussinesq Equations Using ADM–Padé Technique. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2007, 32, 1008–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherruault, Y.; Adomian, G.; Abbaoui, K.; Rach, R. Further Remarks on Convergence of Decomposition Method. Int. J. -Bio-Med. Comput. 1995, 38, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaoui, K.; Cherruault, Y. Convergence of Adomian’s Method Applied to Nonlinear Equations. Math. Comput. Model. 1994, 20, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Nazeer, W.; Tanveer, M.; Mehmood, Q.; Rehman, K. Improvements in Newton-Rapshon Method for Nonlinear Equations Using Modified Adomian Decomposition Method. Int. J. Math. Anal. 2015, 9, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Das, R. Adomian Decomposition Method for a Stepped Fin with All Temperature-Dependent Modes of Heat Transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 82, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Everything You Wish to Know about Memristors but Are Afraid to Ask. Radioengineering 2015, 24, 319–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe. Theories on the Hopfield Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Washington, DC, USA, 18–22 June 1989; Volume 1, pp. 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G. Design and Analysis of Multiscroll Memristive Hopfield Neural Network with Adjustable Memductance and Application to Image Encryption. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 7824–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, C.T.C. Poincare Complexes: I. Ann. Math. 1967, 86, 213–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, G.A.; Melbourne, I. On the implementation of the 0–1 test for chaos. Siam J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 2009, 8, 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, R.R.; de Almeida, M.P.; Sleigh, J.W. Spectral Entropy: A New Method for Anesthetic Adequacy. Rev. Bras. de Anestesiol. 2004, 54, 404–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Iu, H.H.C.; Erkan, U.; Simsek, C.; Toktas, A.; Cao, Y.; Wu, R.; Mou, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, C. A 3D Memristive Cubic Map with Dual Discrete Memristors: Design, Implementation, and Application in Image Encryption. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 7706–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, D.S.; Gopinathan, U.; Naughton, T.J.; Sheridan, J.T. Key-space analysis of double random phase encryption technique. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 6641–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Noonan, J.P.; Agaian, S. NPCR and UACI randomness tests for image encryption. Cyber J. Multidiscip. J. Sci. Technol. J. Sel. Areas Telecommun. 2011, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Carlotto, M.J. Histogram Analysis Using a Scale-Space Approach. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, PAMI-9, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogtay, N.J.; Thatte, U.M. Principles of correlation analysis. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2017, 65, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson Correlation Coefficient. In Noise Reduction in Speech Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, G.J.; Rizzo, M.L. Partial Distance Correlation with Methods for Dissimilarities. Ann. Stat. 2014, 42, 2382–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.Y.; Lee, Y.; Matsuyama, E. Information entropy measure for evaluation of image quality. J. Digit. Imaging 2008, 21, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Jiang, M.; Deng, Y. A Secure Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Hyper-Chaotic and Bit-Level Permutation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Berretti, S.; Wan, S. Medical Image Encryption by Content-Aware DNA Computing for Secure Healthcare. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, D.; Lin, H.; Yu, F.; Sun, Y. High-Dimensional Memristive Neural Network and Its Application in Commercial Data Encryption Communication. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 242, 122513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Shen, H.; Yu, Q.; Kong, X.; Sharma, P.K.; Cai, S. Privacy Protection of Medical Data Based on Multi-Scroll Memristive Hopfield Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Ye, X. A New Fractional-Order Chaos System of Hopfield Neural Network and Its Application in Image Encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 157, 111889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkol, A.S.; Sahin, M.E.; Karakaya, B.; Ulutas, H.; Ascoli, A.; Tetzlaff, R. Real Time Hybrid Medical Image Encryption Algorithm Combining Memristor-Based Chaos with DNA Coding. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 183, 114923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Cui, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, F. Brain-Like Initial-Boosted Hyperchaos and Application in Biomedical Image Encryption. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8839–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).