Sensitivity Analysis of MTPA Control to Angle Errors for Synchronous Reluctance Machines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Electromechanical Conversion in Synchronous Machines
- The vector amplitude corresponds directly to the amplitude of the phase currents in the stator windings due to the application of amplitude invariant transformation;
- The conduction power loss is proportional to ;
- The speed controller typically provides the amplitude of the stator current as the basis for determining reference values for the current controllers.
2.2. Conduction Power Loss Optimization Control Strategy
2.2.1. Minimum Current for a Reference Torque
2.2.2. Maximum Torque for a Reference Current
2.3. Estimation and Implementation of the MTPA Strategy in Control Schemes
3. Analysis of Suboptimal Operation
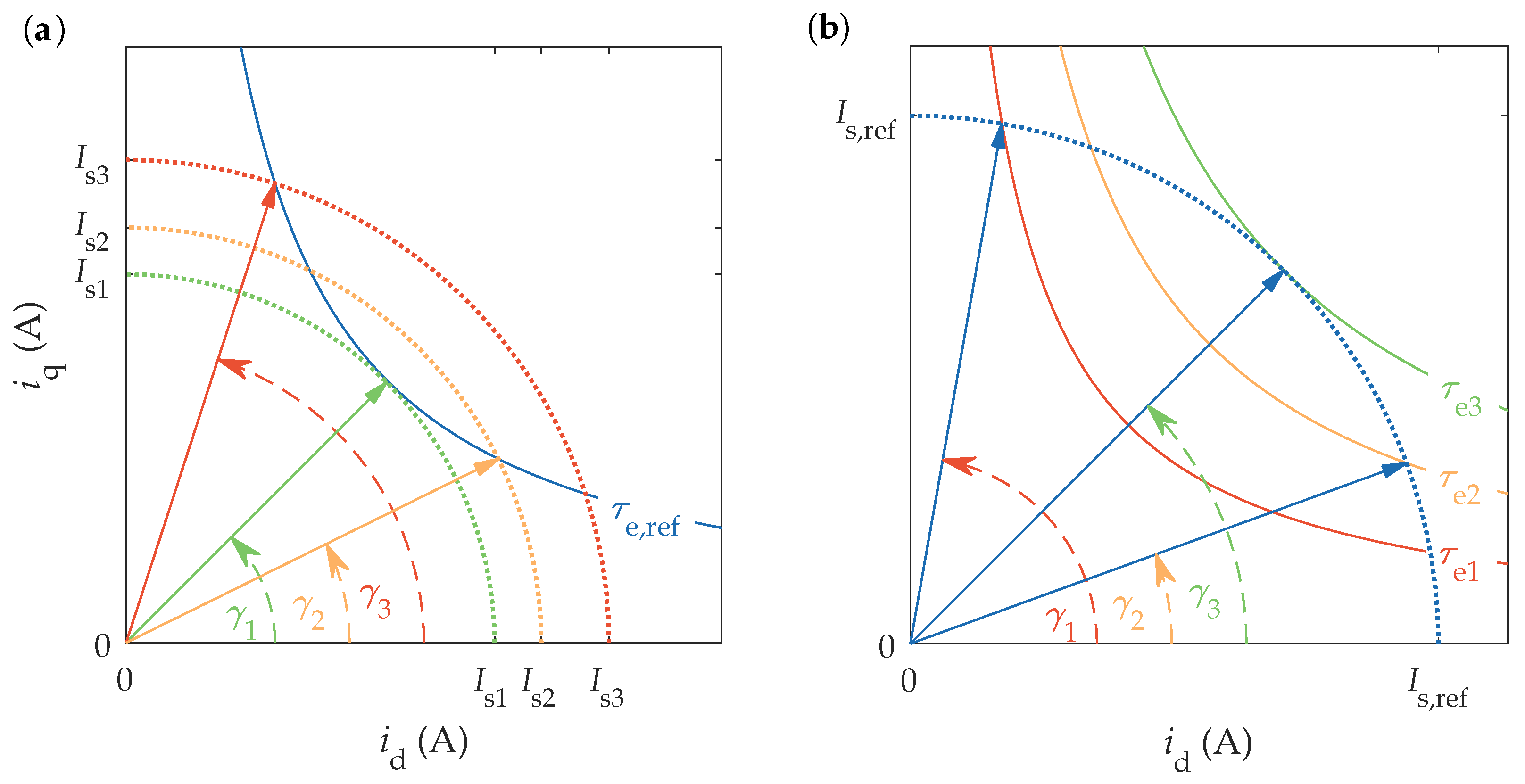
3.1. Methodology
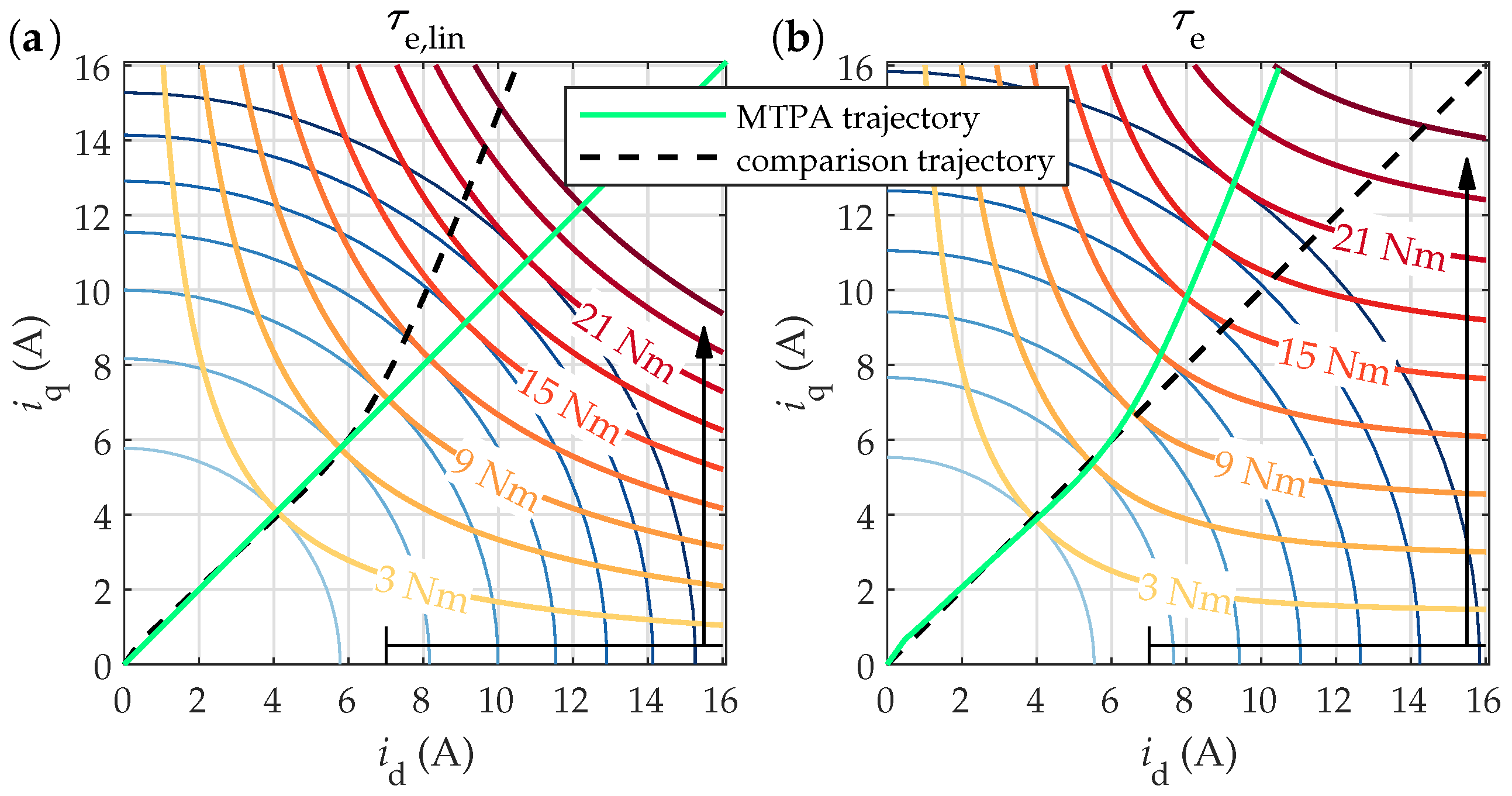
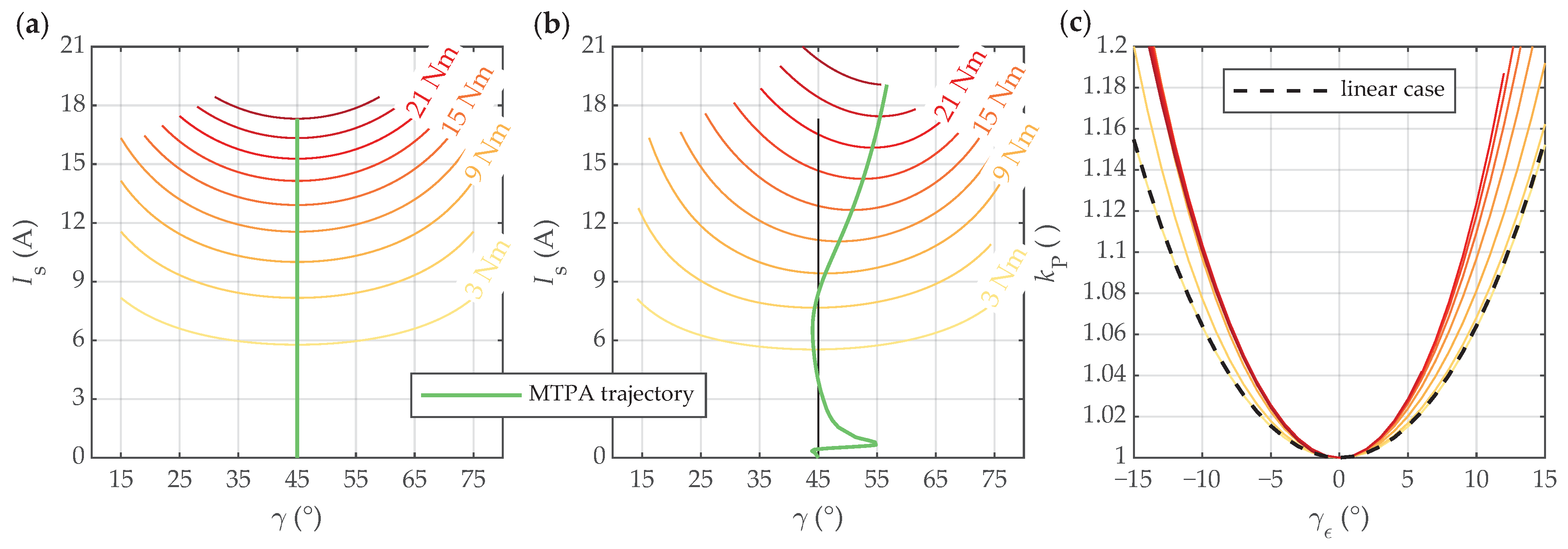
3.2. Analytical Evaluation Assuming a Linear Flux–Current Relationship
3.3. Numerical Evaluation Assuming a Nonlinear Flux–Current Relationship
4. Results
- The presented numerical analysis can be performed with free open-source software (Matlab can be substituted with GNU Octave);
- SyR-e provides template designs for several machine types;
- In this research, SyR-e was used to generate numerical data (i.e., torque and flux linkage maps , , and ) for a selected template SynRM. The gathered data were saved and analyzed further in Matlab 2023b according to the presented methodology. The numerical analysis was performed on a standard desktop computer. This approach allows all interested researchers to replicate and expand upon the presented research.
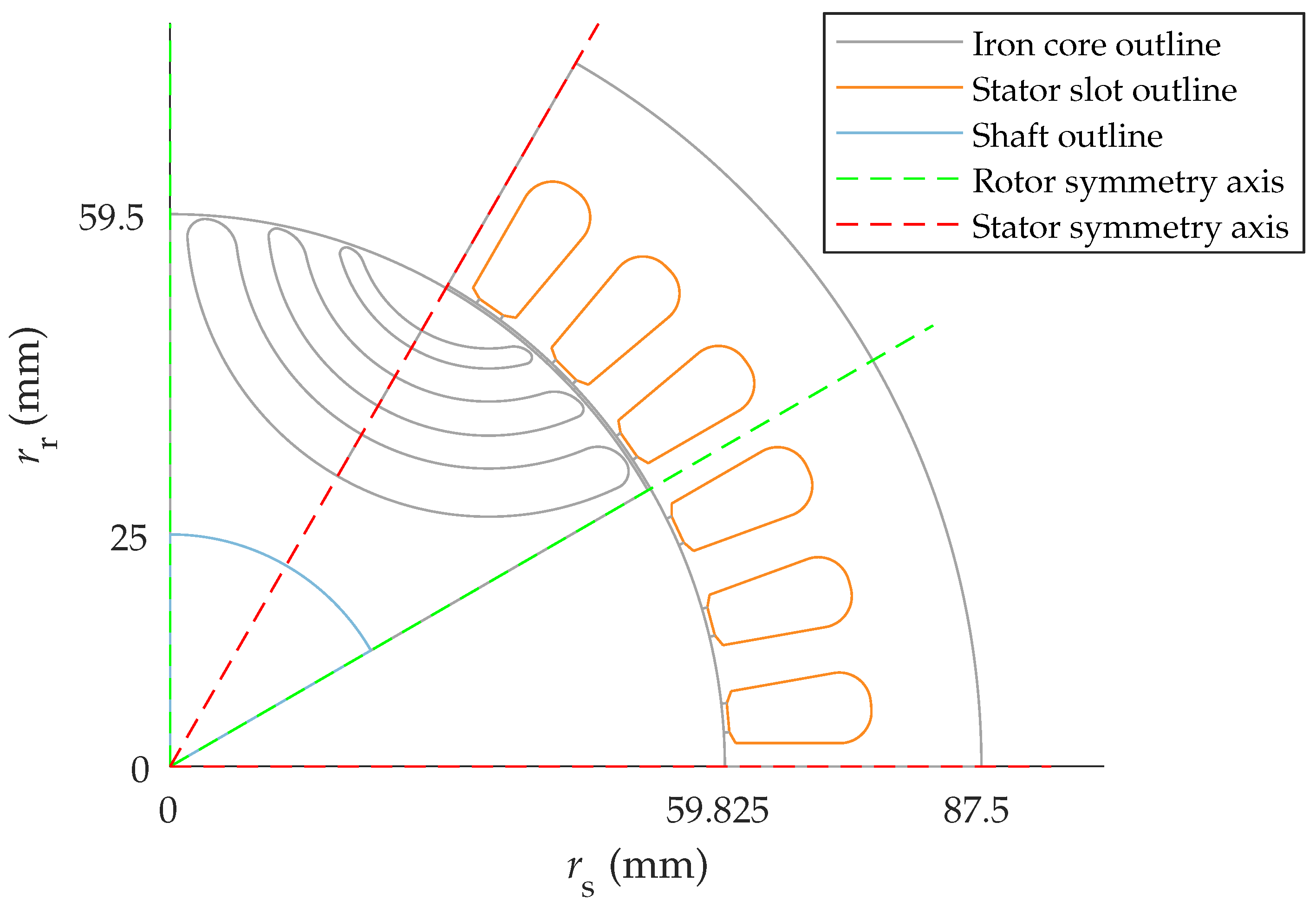
4.1. Design of the Analyzed Synchronous Reluctance Machine
4.2. Numerical Evaluation of the Nonlinear Properties
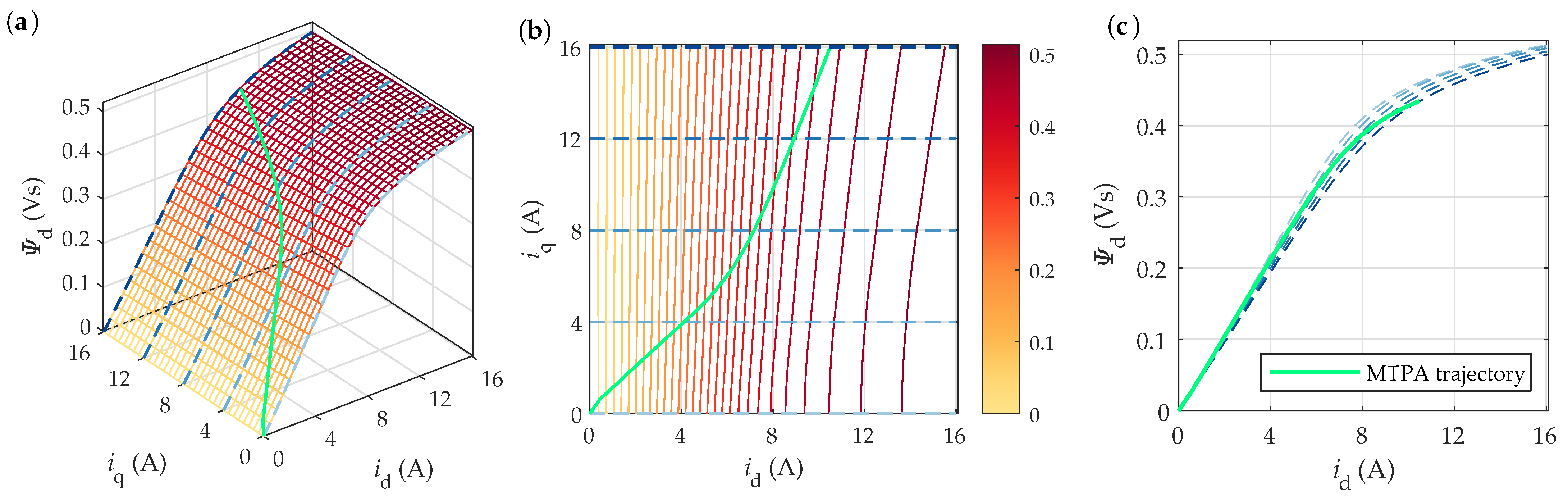
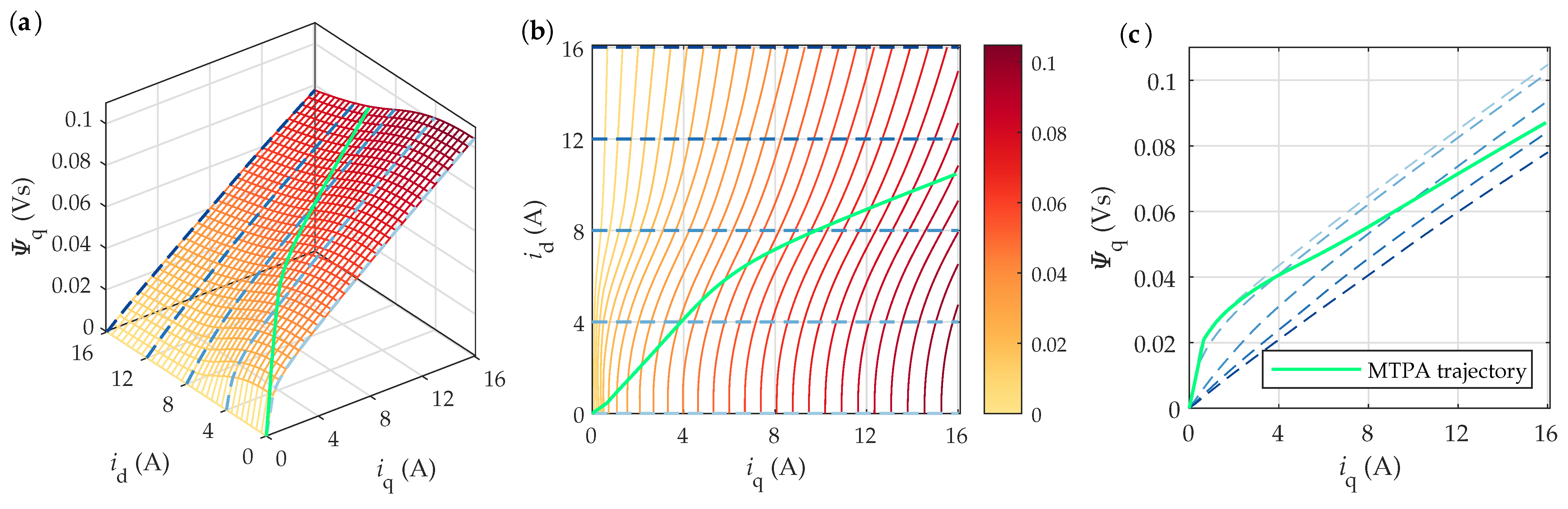
4.2.1. Flux Linkage Maps
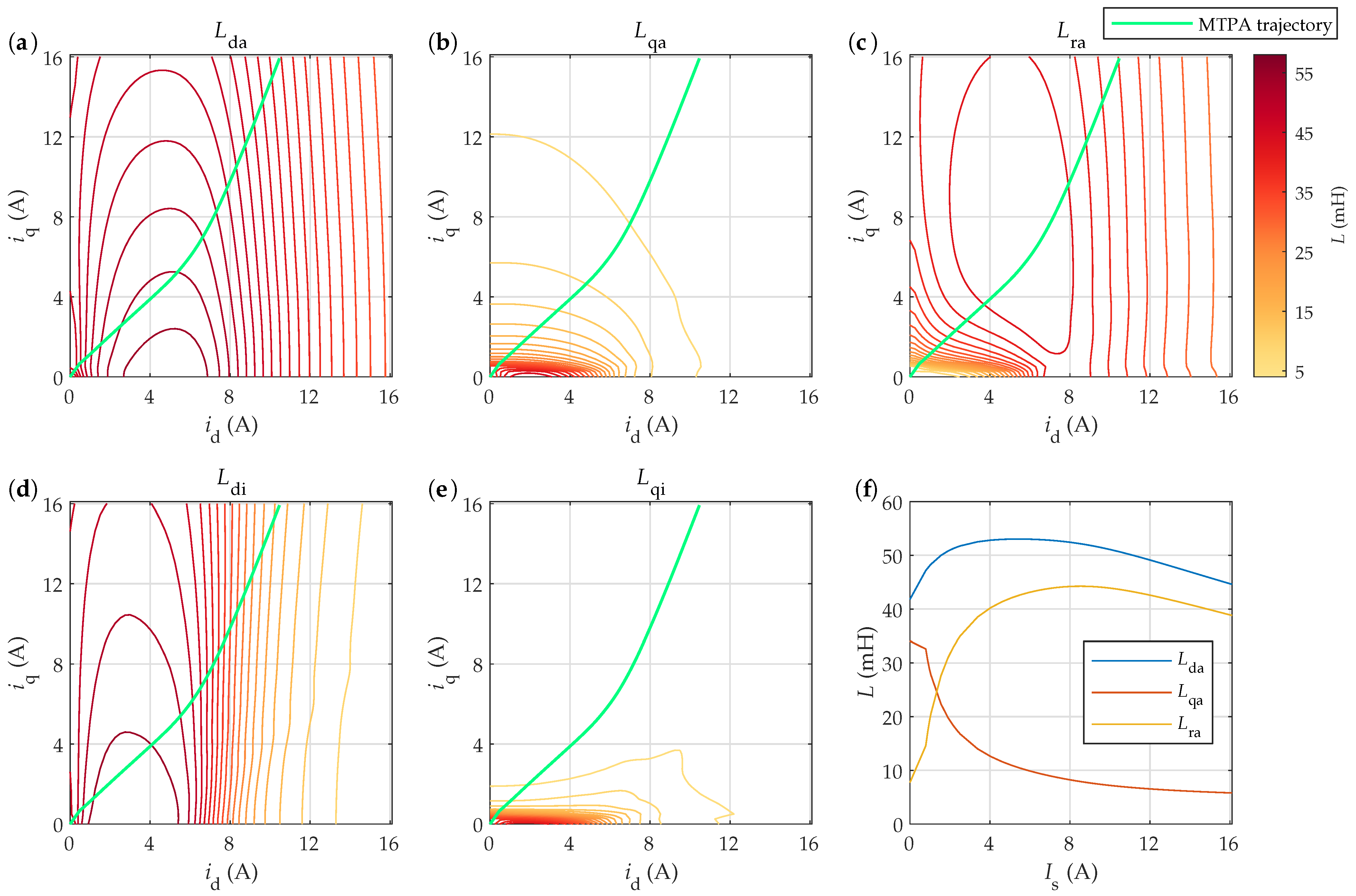
4.2.2. Inductance Maps
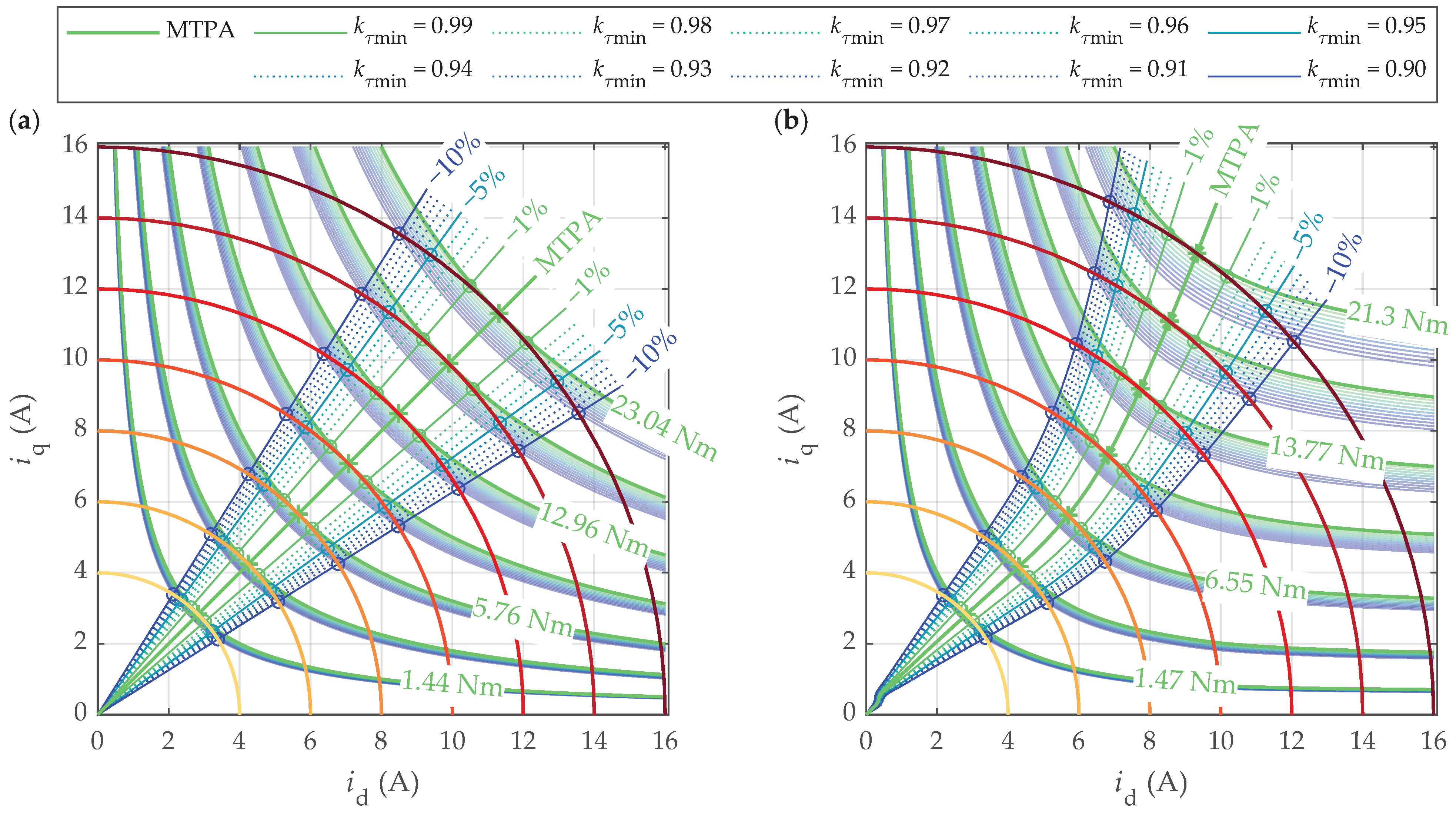
4.2.3. Torque Maps and MTPA Trajectories
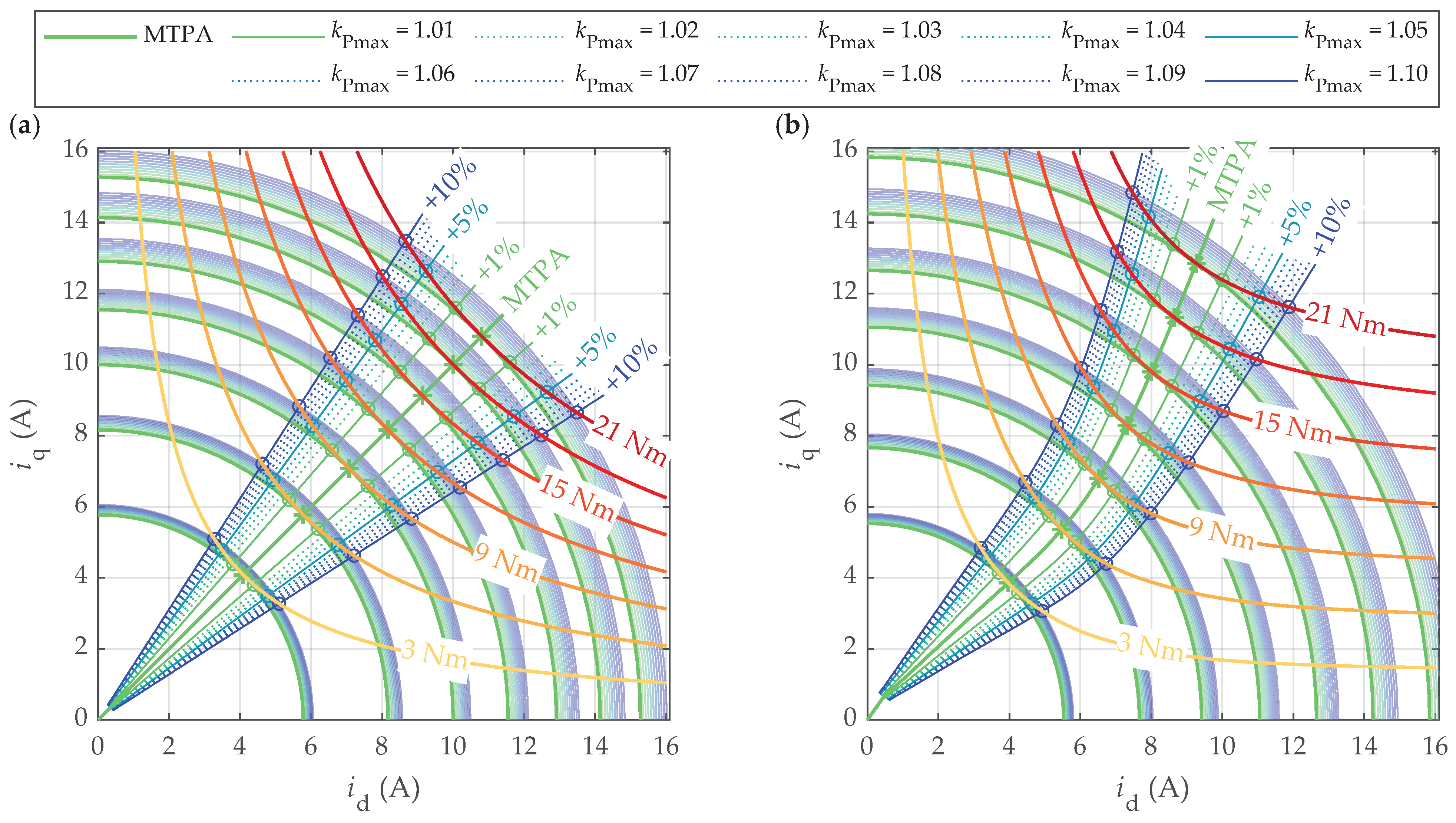
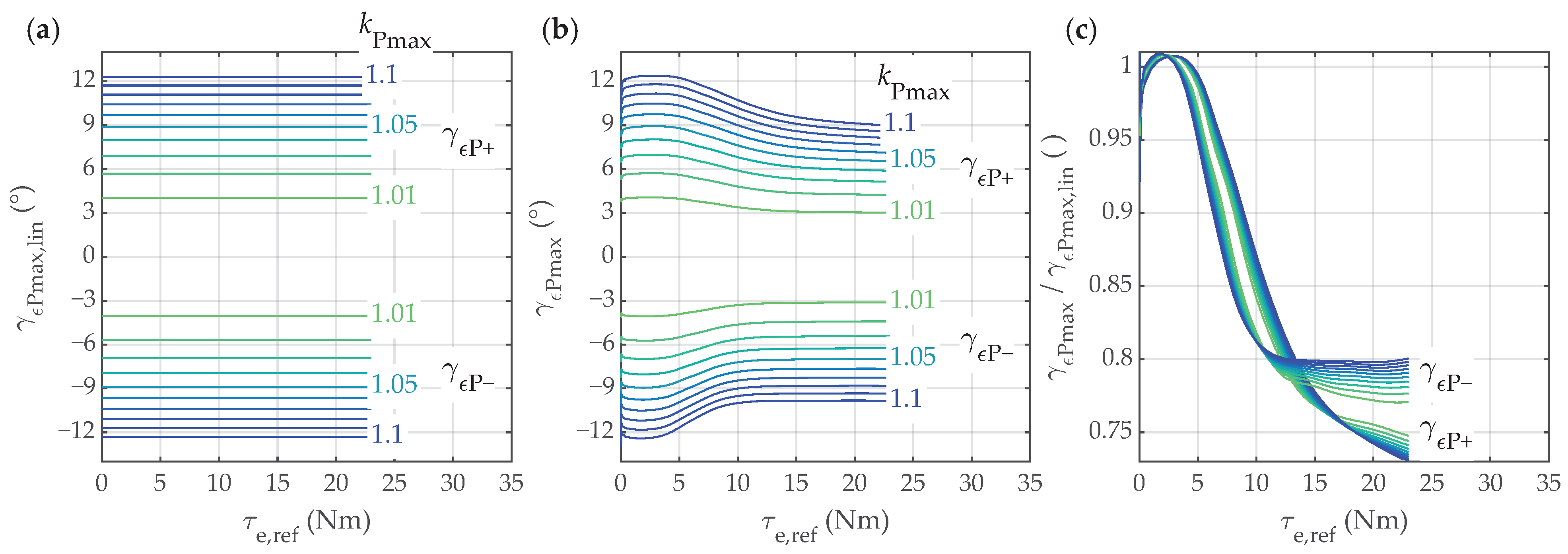
4.3. Power Loss Increase Due to Angle Errors in Suboptimal Operation
4.4. Torque Decrease Due to Angle Errors in Suboptimal Operation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Alternating Current |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| FEMM | Finite Element Method Magnetics (open-source software) |
| FOC | Field-Oriented Control |
| KPI | Key Performance Indicator |
| MTPA | Maximum Torque Per Ampere |
| PI | Proportional–Integral |
| PM | Permanent Magnet |
| RAWP | RAW Power |
| SynRM | Synchronous Reluctance Machine |
| SyR-e | Synchronous Reluctance-evolution (open-source software) |
References
- Murataliyev, M.; Degano, M.; Di Nardo, M.; Bianchi, N.; Gerada, C. Synchronous Reluctance Machines: A Comprehensive Review and Technology Comparison. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 382–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Rassõlkin, A.; Kallaste, A.; Vaimann, T.; Andriushchenko, E.; Belahcen, A.; Lukichev, D.V. A Review of Synchronous Reluctance Motor-Drive Advancements. Sustainability 2021, 13, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degano, M.; Murataliyev, M.; Di Nardo, M. Reluctance motors (including switched reluctance motors). Encycl. Electr. Electron. Power Eng. 2023, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S. Design, Analysis and Testing Procedures for Synchronous Reluctance and Permanent Magnet Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino, G.; Jahns, T.M.; Bianchi, N.; Soong, W.; Cupertino, F. The Rediscovery of Synchronous Reluctance and Ferrite Permanent Magnet Motors, Tutorial Course Notes, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Hu, C. Comprehensive Comparative Study on Permanent-Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motors and Other Types of Motor. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Babetto, C.; Bacco, G. Synchronous Reluctance Machines: Analysis, Optimization and Applications, 1st ed.; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AngayarKanni, S.; Ramash Kumar, K.; Senthilnathan, A. Comprehensive Overview of Modern Controllers for Synchronous Reluctance Motor. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2023, 14, 1345792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvolik, V.; Buticchi, G.; Prystupa, D.; Wang, S.; Aboelhassan, A.; Peresada, .S.; Galea, M. Comparative Study on Torque Ripple Reduction Considering Minimum Losses for Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 6527–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, G.; Cupertino, F.; Gerada, C. Automatic Design of Synchronous Reluctance Motors Focusing on Barrier Shape Optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credo, A.; Petrov, I.; Pyrhönen, J.; Villani, M. Impact of Manufacturing Stresses On Multiple-Rib Synchronous Reluctance Motor Performance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, H.; Liu, W. Torque Ripple Suppression of Synchronous Reluctance Motors for Electric Vehicles Based on Rotor Improvement Design. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 4328–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Pellegrino, G. FEAfix: FEA Refinement of Design Equations for Synchronous Reluctance Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, M.R.; Abbaszadeh, K.; Nasiri-Zarandi, R. Torque ripples reduction in a synchronous reluctance motor by rotor parameters optimization. COMPEL—Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 40, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Jang, I.G. Topology Optimization of Synchronous Reluctance Motors Considering the Optimal Current Reference in the Field-Weakening and Maximum-Torque-Per-Voltage Regions. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 1950–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladetola, O.D.; Ouari, M.; Saadi, Y.; Mesbahi, T.; Boukhnifer, M.; Adjallah, K.H. Advanced Torque Ripple Minimization of Synchronous Reluctance Machine for Electric Vehicle Application. Energies 2023, 16, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmaram, B.; Mousavi, M.S.; Davari, S.A.; Flores-Bahamonde, F.; Wheeler, P.; Rodriguez, J.; Fazeli, M. Full-Cycle Iterative Observer: A Comprehensive Approach for Position Estimation in Sensorless Predictive Control of SynRM. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 5246–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Sensorless Back EMF Based Control of Synchronous PM and Reluctance Motor Drives—A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 10290–10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianov, A.; Tinazzi, F.; Calligaro, S.; Bolognani, S. Review and Classification of MTPA Control Algorithms for Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 3990–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinazzi, F.; Bolognani, S.; Calligaro, S.; Kumar, P.; Petrella, R.; Zigliotto, M. Classification and review of MTPA algorithms for synchronous reluctance and interior permanent magnet motor drives. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE ’19 ECCE Europe), Genova, Italy, 3–5 September 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Raja, R.; Sebastian, T.; Rajashekara, K. Torque Ripple Minimization Control Strategy in Synchronous Reluctance Machines. IEEE Open J. Ind. Appl. 2022, 3, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boztas, G.; Aydogmus, O. Implementation of sensorless speed control of synchronous reluctance motor using extended Kalman filter. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Depernet, D.; Lanfranchi, V. Analysis of torque ripple reduction in a segmented-rotor synchronous reluctance machine by optimal currents. Math. Comput. Simul. 2019, 158, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, J.; Jang, P.; Nam, K. On-Line MTPA Control Method for Synchronous Reluctance Motor. Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, S.; Gu, C.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gerada, C. High Precision Online MTPA Algorithm Considering Magnet Flux Parameter Mismatch for a PMa-SynRM. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.-H.; Wan, W.-J.; Wang, J. Analysis of Parameter Matching on the Steady-State Characteristics of Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motors under Vector Control. Actuators 2024, 13, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credo, A.; Collazzo, F.P.; Tursini, M.; Villani, M. A Unified Approach for the Commissioning of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Jiang, D.; Qu, R. A MTPA and Flux-Weakening Curve Identification Method Based on Physics-Informed Network Without Calibration. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 12370–12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-G.; Lin, F.-J.; Huang, M.-S.; Yeh, S.-P.; Sun, T.-S. Proximate Maximum Efficiency Control for Synchronous Reluctance Motor via AMRCT and MTPA Control. IEEE/Asme Trans. Mechatronics 2023, 28, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Yu, B.; Luo, P.; Luo, X.; Shen, A.; Xia, Y.; Xu, J. Second Harmonic Seamless Splicing Technique Based on Maximum Active-Voltage Vector for Online MTPA Tracking Control of SynRM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 10958–10968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-J.; Tsai, M.-C. Robust Scalar Control of Synchronous Reluctance Motor With Optimal Efficiency by MTPA Control. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32599–32612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accetta, A.; Cirrincione, M.; Piazza, M.C.D.; Tona, G.L.; Luna, M.; Pucci, M. Analytical Formulation of a Maximum Torque per Ampere (MTPA) Technique for SynRMs Considering the Magnetic Saturation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 3846–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi Kamarposhti, M.; Shokouhandeh, H.; Colak, I.; Eguchi, K. Performance Improvement of Reluctance Synchronous Motor Using Brain Emotional Learning Based Intelligent Controller. Electronics 2021, 10, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, D.; Qu, R. Saturated dq-Axis Inductance Offline Identification Method for SynRM Based on a Novel Active Flux Observer Orientation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 10670–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaq, M.S.; Jung, J.-W. A Comprehensive Review of State-of-the-Art Parameter Estimation Techniques for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors in Wide Speed Range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 4747–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhano, S.A.; Pescetto, P.; Awan, H.A.A.; Hinkkanen, M.; Pellegrino, G.; Bojoi, R. Parameter Identification and Self-Commissioning in AC Motor Drives: A Technology Status Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 3603–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S. SyR-e Synchornous Reluctance—Evolution Design. Available online: https://github.com/SyR-e/syre_public/releases/tag/v3.8.2 (accessed on 20 November 2024).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrun, M.; Černelič, J. Sensitivity Analysis of MTPA Control to Angle Errors for Synchronous Reluctance Machines. Mathematics 2025, 13, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13010038
Petrun M, Černelič J. Sensitivity Analysis of MTPA Control to Angle Errors for Synchronous Reluctance Machines. Mathematics. 2025; 13(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13010038
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrun, Martin, and Jernej Černelič. 2025. "Sensitivity Analysis of MTPA Control to Angle Errors for Synchronous Reluctance Machines" Mathematics 13, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13010038
APA StylePetrun, M., & Černelič, J. (2025). Sensitivity Analysis of MTPA Control to Angle Errors for Synchronous Reluctance Machines. Mathematics, 13(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13010038





