Abstract
In research of a better description for information uncertainty, Z-numbers, which are related to both the objective information and the subjective criticism, were first conceptualized by Zadeh. Because of its neologism, there have been multitudinous attempts toward continuation and expansion of the prototype. In this paper, we mainly study varieties of theoretical preparations for classical Z-numbers and derive the maximum expected linear programming model of Z-numbers, which are constructed on the basis of reliability conversion factors and proliferation on applications due to their simplicity. Firstly, by means of transforming Z-numbers into LR fuzzy intervals through their reliability variable, the credibility distribution and inverse distribution of converted Z-numbers are stated precisely. Then, the operational law of independent variables and its expected value can be derived via credibility distribution. The maximum expected Z-number linear programming model is determined on the basis of previous theoretical preparations, and it transforms from a classical Z-number chance-constrained model into a crisp one. Finally, with the aim of improving the programming method, its application in pragmatic practice with the realistic examples of a supplier section and optimal portfolio problems are enumerated to interpret the effectiveness of our model.
MSC:
90-05; 90C70; 53B12
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
Linear programming, as the basis of operational decision-making problems, is extensively included in production, supplier selection, portfolio selection and logistics. Though it is a major branch of operational research, there are miscellaneous uncertainties that exist in the practical world that are hard to express using exact real numbers, leading to information errors in programming applications. In this respect, Zadeh proposed Z-number theory [1], which contributed to the calculation of numbers. This style of fuzzy number is an official resume of the dependability or faith in the message communicated by simple natural language statements. Compared with explicit real numbers, Z-numbers, which are defined by constraint and reliability, are more qualified to depict reality. Although the fuzzy number indicates the overall affiliation of its support points, given a natural language statement, the Z-number uses two membership values to quantify the language variable. This gives us ideas about the establishment of linear programming models through Z fuzzy numbers, which utilize the ability to describe uncertain phenomena from fuzzy numbers to ameliorate the shortage of basic linear programming models.
1.2. Literature Review
Z-numbers, proposed by Zadeh [1] in 2011, were created to summarize the reliability and confidence of information from natural language that occurred in certain situations and to maximize their use in daily decision-making modeling, e.g., in economics, risk assessment, prediction and even bio-medicine. Kang et al. [2] introduced the element for processing Z-numbers as operands first, and they suggest converting the Z-numbers of sentences which occur in the fields of modeling, management and decision-making into their fuzzy number equivalents to be the first step for operations based on Z-numbers.
In the first decade, the basic achievement of the development of Z-numbers was concluded by Banerjee et al. [3] in 2022, which included mathematics, natural language processing (NLP) and computing with words (CWW), decision-making and trust models. In their seminal paper, the authors not only proposed the definition and arithmetic rules of Z-numbers, but also outlined the applications of Z-numbers in decision analysis, data mining and control theory, among other fields, and illustrated the existing problems associated with the practical application with Z-numbers.
In order to confirm the statement that humans use a discrete set of linguistic terms to describe real-world phenomena, Aliev et al. [4] studied the arithmetic of discrete Z-numbers first, and then extended it to the computation of continuous Z-numbers, which are expected to solve the practical problems when faced with the imprecise or partially reliable information [5]. Moreover, Aliev et al. [6] defined the operational procedure on addition, multiplication, division, sorting, square and function limits of Z-numbers which came from a method of formalizing Z-number arithmetic operators in terms of horizontal membership function. Jiang et al. [7] proposed an approach to evaluate generalized fuzzy numbers using the notions of centroid, ambiguity and their extensions, which have been widely used in the ranking of Z-numbers. Kang et al. [8] stated the total utility measure of a Z-number as a function of its constraints and reliability parameters, which is common in all styles of membership functions and probability distributions; these are considered to be better facilities for defuzzification and Z-number ordering in multi-criteria circumstances.
To deal with the linear programming problems on Z-numbers, Aliev et al. [9] suggested an innovated differential evolution method, in which both the variables and parameters are expressed by Z-numbers that exempt uncertain factors from reality. By using the discrete Z-number arithmetic operations in [4], the linear programming model was solved. Although fuzzy-LP and Z-LP are similar in their theoretical solutions, Z-LP techniques are synchronized with the real world. Hasankhani et al. [10] proposed a ranking method for Z-numbers for certain linear programming problems that are filled with Z-numbers. This model could be easily applied for all types of constraints, regardless of magnitude. Rao et al. [11] recommended the green supplier selection using the ranking method based on the possibility degree of Z-numbers. Using the example of green supplier selection decision, compared with the existing methods, the implementation, applicability and feasibility of programming models were analyzed.
When it comes to the application of decision-making problems, Z-numbers, which provide a better description of natural language and realistic situations, play the role of parameters in each practical problem. For instance, Kang et al. [12] extended their algorithm as it was depicted in [2] to derive an estimated solution for multiple-criteria decision making on Z-numbers. Within the framework of proposals, the form of Z-number is taken by the values of the condition weights and selective conditions. Bakar and Gegov [13] proposed an innovated multi-level method for the ranking of Z-numbers established by two steps, which extends the classical converted method of Z-numbers to the standardized generalized fuzzy numbers. Then, prolonging their ranking method, Khalif and Gegov [14] theorized a hybrid fuzzy multi-criteria decision model based on the intuitionistic vector centroid, which promoted the development of its defuzzization. Aliev et al. [15] proposed a method of information decision making based on numerical direct computation. The expected utility paradigm it used has the potential to be used in the benchmark decision problems. Liu et al. [16] used former data and expert opinions to construct the Z-numbers after statistics, which solves the disadvantages of traditional fuzzy numbers when dealing with uncertain activity information.
Despite its widespread applications, there are still several challenges that remain in Z-number theory. Zadeh [1] has said that “Problems involving computation with Z-numbers is easy to state but far from easy to solve”. One of the main challenges is the lack of a robust aggregation operator for Z-numbers. More importantly, the complexity of computation based on Z-number theory remains a demanding prompted problem. Although numerous studies on linear programming exist, Z-number based linear programming lacks deep exploration involving complex calculations or niche applications, and thus it has a long way to go.
1.3. Contribution
We make great contributions to derive the credibility measure, operational law, expected value of Z-number and prolong Z-number linear programming problems by establishing classical operational research models, all of which are based on the approach of transforming Z-numbers into LR fuzzy intervals in this paper.
In order to further study the application of linear programming development, we conducted extensive research on the Z-number application. We found that although previous studies had focused on the best decision-making projects and had even been put into use on the portfolio selection, their methods of using the utility functions were too complex and unintelligible to settle the classical linear programming problems. Meanwhile, the great attention paid to the field of investment and supply restricts the application and development of classical Z-number linear programming models. Few linear programming models were developed after the proposal of Z-numbers. Of those that were created, most of them combined intelligent algorithms, e.g., the genetic algorithm, which increase the difficulty of calculation substantially.
In contrast with previous studies, this paper is an extension and development of the maximum expected Z-number linear programming models and innovates a simpler and more accessible method for realistic programming research problems in the real world. Firstly, the credibility distribution of a classical Z fuzzy number is deduced, which correlates the classical Z-number into a calculable status. Secondly, according to operational law and the expected value of regular LR fuzzy intervals, the identity of classical Z-numbers is defined creatively based on their credibility distributions and inverse functions. Finally, in order to extend the realistic application, we establish the classical maximum expected Z-number linear programming model as a paradigm, and list two familiar applications, including supplier selection and investment portfolio, to express the widespread use of this model.
1.4. Structure
The rest of this article is organized as follows. The Z-number theoretical preparation is explained in Section 2 where the converting methods are retrospected first, then the definitions of credibility distribution, operational law and the expected value of Z-numbers are concluded on the basis of some definitions and concepts of LR fuzzy intervals. In Section 3, the maximum expected Z-number programming model is derived. After calculating the expected value and credibility distribution of Z-numbers, their chance-constrained model and crisp equivalent model are constructed as described below. Additionally, for a better explanation of the model’s establishment, two conventional examples are described in Section 4. An optimal decision is made in the supplier selection problem with the constraint of credibility distribution, while the optimal portfolio problem provides the best investment program. Finally, the conclusion is presented in Section 5.
2. Z-Number Theoretical Preparation
Although the algorithm of Z-numbers has developed to a great extent, the expected value and credibility of Z-numbers are hard to figure out, due to the fuzzification. According to the identity of Z-numbers, inspired by the expected value and credibility measure of classical LR fuzzy numbers, there are new definitions of independence based on them.
As for the following establishment linear programming model, the theoretical preparation of Z-numbers is necessary. In this section, it provides the derivation of credibility distribution, operational law and the expected value of Z-numbers through weighted methodology, all of which construct the basis for the maximum expected Z-number programming model. We choose the trapezoidal shaped membership of the constrain A of Z-numbers as a paradigm, owing to its most typical wide spread and easy derivation.
2.1. Methodology
Since Zadeh [1] proposed Z-numbers as an ordered pair of fuzzy numbers , where A manifests a restriction limit for the variable and B stands for the reliability, which has the ability to indicate both subjective and objective values. In this case, the general concept is given as follows.
Definition 1
(Zadeh [1]). Z-number is represented by a couple of ordered arrays. Let them be A and B, written as , where A and B can be either numbers or natural languages. Starting with the uncertain variable Ψ, X stands for the fuzzy restriction of the real-valued function, and stands for the possible value of Ψ, which is depicted as
Zadeh [17] proposed a fuzzy number in 1965 which is defined in Definition A1 of Appendix A, setting a precedent for the study of the fuzzy field and creating more possibilities for operational research. In order to describe this kind of LR fuzzy interval, the definition of regular LR fuzzy interval was first introduced by Liu et al. [18] in Definition A2 of Appendix A. Compared with complicated Z-numbers, LR fuzzy intervals are qualified with many computational properties that have already been put into wider practice, whose definition is indicated in Definition A3 of Appendix A.
Z-number is a fuzzy number of intricate type, which does not offer simplicity during calculation. In the previous study, most of the achievements were based on the complex integral operations or ranking. Therefore, in order to simplify this, we use the converting methodology from Kang et al. [2], who proposed a converting method in 2012 that transforms a Z-number into a classical fuzzy number.
The basic idea of a converting method is simply illustrated in the following three steps: first, the reliability B of a Z-number is used to calculate an exact value as the converting factor contributing to the defuzzification of this Z-number; next, we multiply this exact converting factor to the constraint limit A by weight. In the end, the final result comes from the converted LR fuzzy interval by the rule of approximate invariant of fuzzy expectation.
Step 1: According to Definition 1, we define a Z-number expressed as , from which A and B are classical fuzzy numbers or intervals. We transform the reliability part B into an exact converting factor using the gravity method with following formula:
Step 2: Afterwards, the value of gravitational center of reliability B is used as the weight of constraint limit A. Thus, the weighted value of the Z-number is conveyed by
Step 3: Convert the Z-number with the weighted qualification to a classical fuzzy interval which can be shown through the equation
2.2. Credibility Distribution of Z-Number
As the effective identity of self-duality for credibility, it carries incomplete information for variables. It is worthwhile to study the credibility distribution of fuzzy numbers.
If is regulated to be a fuzzy variable with membership function and r in the real number field, the possibility [19] and necessity [20] of the fuzzy variable are described as follows:
Whereas, due to the limitation of self-duality of ambiguous events in decision-making systems, it is not appropriate to describe the fuzzy variable only through the measurement of possibility or necessity. Faced with this difficulty, the credibility measure of such fuzzy event has been defined by Liu and Liu [21] as
Liu and Liu also proved the identity of increase and self-duality with regard to the credibility measure in [21] which is
Aiming at the description of a fuzzy variable, as the vector of synsemantic information, the credibility distribution of a certain variable is defined.
Definition 2
(Liu [22]). As for the fuzzy variable ξ, its credibility distribution is stated by
where is the credibility distribution, when the solution reference of the fuzzy variable ξ is less than or equal to x.
Liu [22] had already revealed the non-decrease identity of the credibility distribution on the field of that and .
And for the LR fuzzy interval with the membership function in Definition A3, according to Definition 2, through concise calculation, its credibility distribution can be derived as
The inverse credibility distribution is easy to derive from the function 4 shown above, which is expressed as follows.
Definition 3
(Zhao et al. [23]). Let ξ be an LR fuzzy interval whose multi-valued function is named to be the inverse credibility distribution of ξ on the condition of
from which and .
For the sake of simplicity, is indicated by , which is different from the inverse function of .
Moreover, as for the LR fuzzy interval, Zhao et al. [23] had already derived the inverse credibility distribution described as follows.
Theorem 1
(Zhao et al. [23]). Let be a regular LR fuzzy interval whose inverse credibility distribution can be written by
According to the former information on the credibility distribution of the LR fuzzy interval, based on the converting method in Section 2.1, it is valuable to define the credibility distribution and its inverse function, which is as follows.
Definition 4.
Let be a Z-number with the converted factor β from reliability B. Thus, the converted Z-number, named , satisfies the property of the LR fuzzy interval. Since then, the possibility, necessity and credibility measure of fuzzy event A for ζ can be expressed as
Definition 4 is easily derived from the self-duality and monotonousness of converted Z fuzzy interval.
As the inverse credibility measure is the key to the calculation of expected values on Z-numbers, we learned from Definition 1 that the inverse credibility distribution of a converted Z-number is deduced as follows.
Definition 5.
Let be the credibility distribution of the converted Z fuzzy interval whose domain is regulated to be . Then, the inverse credibility distribution of is deduced as
Example 1.
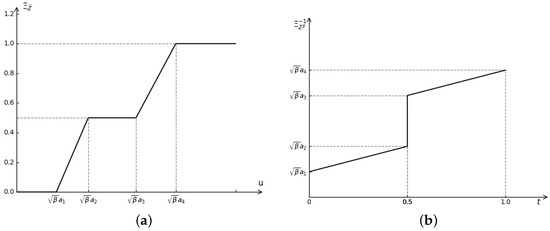
For a Z-number , let A be and B be , the credibility distribution and inverse distribution of (see Figure 1) can be described as:

Figure 1.
Credibility distribution function and its inverse function. (a) Credibility distribution. (b) Inverse credibility distribution.
Remark 1.
From the derivation of the inverse credibility distribution on Z-numbers, differences between the converted inverse functions and regular LR fuzzy interval inverse functions can be observed simply. There are coefficients of parameters added after conversion, which can be expressed as
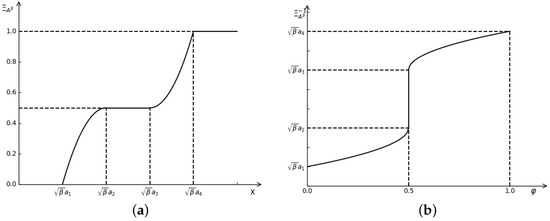
Example 2.
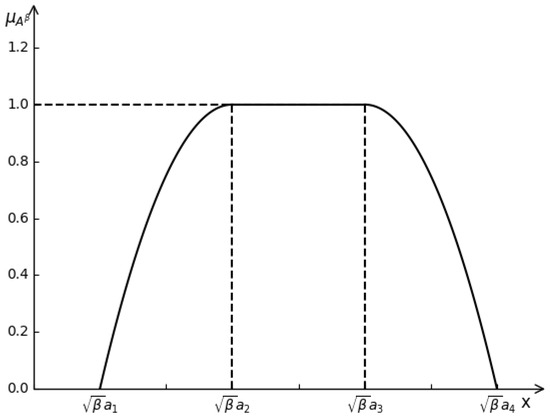
Let be a potential Z fuzzy interval, and after calculating the converting factor β which was calculated by the membership of reliability from Equation (1), it is easy for us to transform the Z-number given into the converted one written as which satisfies the shaping functions that . Therefore, it can be transformed into the form of a regular LR fuzzy interval, expressed as . Then, it has the membership function (see Figure 2) that

Figure 2.
Membership function in Example 2.
Depending on Definition 4, the credibility distribution (see Figure 3a) and its corresponding inverse function (see Figure 3b) could be described as

Figure 3.
Credibility distribution function and its inverse function in Example 2. (a) Credibility distribution in Example 2. (b) Inverse credibility distribution in Example 2.
2.3. Operational Law of Z-Number
The operational law is one of the most fundamental properties as well as Z-numbers, and it can not only help with the calculation of credibility in Definition 4, but also directly influences the establishment of following models. Because of the premise of its application, the definition of independence is introduced first.
The definition of monotone functions is given first, which is introduced explicitly by Liu et al. [24].
Definition 6
(Liu et al. [24]). The function is referred to as monotone in the field of real numbers, on the condition that it increases in terms of and decreases in terms of , that
holds for any with and with . Moreover, while the function meets the circumstance
with any for and for . As a result, it is strictly monotonic.
First, the definition of operational law for LR fuzzy interval is given by Zhao et al. [23], which has established the theoretical basis for the derivation of the Z-number operational law.
Theorem 2
(Zhao et al. [23]). The variables are set to be a series of independent regular LR fuzzy intervals whose credibility distributions are , separately. The function is said to be strictly increasing in , and strictly decreasing in . In this case,
is an LR fuzzy interval whose inverse credibility distribution is
Definition 7.
The Z-number variables are independent if and only if the converted Z-numbers satisfy
for any real sets .
Example 3.
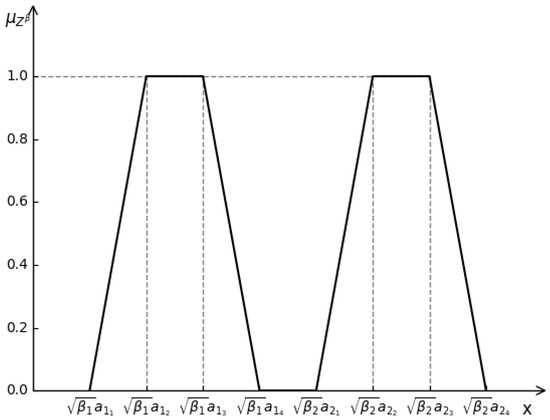
In front of the two converted Z-numbers,
we define these regular LR fuzzy interval to be mutually independent if and only if they satisfy the condition that
The figure of two independent converted Z-numbers set above is shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Two independent converted Z-numbers.
Theorem 3.
According to the former LR fuzzy number operation law, as in the conversion method described above, we define the Z-number operational law as follows.
Set to be a series of independent Z-numbers with credibility distributions separately. Using the converting method from B.Kang [2], we convert each Z-number into a battery of independent normal LR fuzzy numbers which are defined by , where the objective function increases when it comes to and decreases when it comes to . Moreover,
is also a Z fuzzy number whose inverse credibility distribution φ is
where is the credibility distribution of Z-number .
Proof.
According to Kang et al. [2], we set the Z-number converting factor as ; thus, the transforming process can be written as
Thus, if increases with respect to and decreases with respect to , shows the same trend that rises in and drops in . As is a regular LR fuzzy number, with respect to the sustainability about function, remains to be a Z-number.
In addition, on the basis of former LR fuzzy interval operation law in Theorem 2, we know that for LR fuzzy number , which is calculated from the function based on several LR fuzzy numbers , its inverse credibility distribution is stipulated to be
where holds the similar inverse credibility distribution that is described in such a formula.
According to Kang et al. [2], the conversion of membership between Z-numbers and LR fuzzy intervals can be written as
With the credibility distribution correlated to the membership, it is easy to find the multiplying power between them, which is
with the inverse credibility distribution
Thus, in line with the character of functions, the Z-number Z, whose credibility distribution is stated as , satisfies the equation that
□
Example 4.
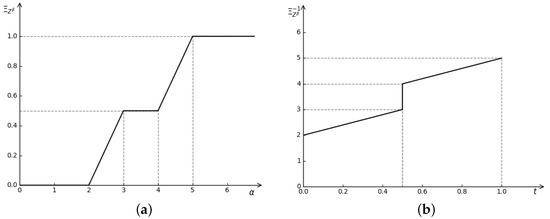
Set to be a converted Z-number that satisfies the property of the regular LR fuzzy interval, which is expressed as . The function f is defined as
which increases, but not strictly. Through the operational law of converted Z-numbers defined above in Theorem 3, the result of can be expressed by , whose credibility distribution is
At the same time, its inverse credibility distribution makes it easy to determine that
Both of these functions are described in Figure 5, where the credibility distributions of converted Z-numbers and their inverse functions are depicted in Figure 5a,b.

Figure 5.
Credibility distribution function and its inverse function in Example 4. (a) Credibility distribution in Example 4. (b) Inverse credibility distribution in Example 4.
2.4. Expected Value of Z-Number
As a significant numerical feature of fuzzy variables, the expected value operator of Z-numbers is significant. However, as far as we know, the former expected value of Z-numbers derived directly via arithmetic of Z-numbers is rarely put into use due to its complexity and inconvenience of calculation. Additionally, there is widespread use of the expected value of the deformed Z-number instead of the classical Z-number. In this case, we define the expected value of Z-numbers based on the former definitions of its credibility.
As the basic definition of modeling, the expected values of a normal fuzzy number and the LR fuzzy interval are given here.
Definition 8
(Liu and Liu [21]). Assuming δ to be a fuzzy variable whose expected value is stated by
where the precondition is that both integrals should be finite at the same time.
Considering the classical fuzzy numbers, in front of the LR fuzzy intervals, the expected value can be easily derived, and this has already been calculated by Zhao [23].
Theorem 4
(Zhao et al. [23]). If the expected value of an LR fuzzy interval exists, then it can be presented as follows
where Ξ is the credibility distribution of .
Based on the former given definition of the expected value of LR fuzzy intervals, combined with the converting method given in Section 2.1, the expected value of classical Z-numbers is derived as follows.
Theorem 5.
Let ζ be a Z-number. While its expected value exists, it can be indicated as
where is the inverse credibility distribution of ζ.
Proof.
The theorem is followed by the definition of expected value operator and credibility measurement in Definition 8 that
As for the converted Z-number, the is also an LR fuzzy interval whose inverse credibility shows the continuity. Therefore, according to Definition 4, in which the function of inverse credibility distribution of converted Z-numbers is provided, we know that the expected value of can be expressed in the same form with a regular LR fuzzy interval, which is
□
On the basis of the Z-number converting method given by Kang et al. [2], we know that the relationship of the expected value between the Z-number and regular LR-fuzzy-number is represented as
Theorem 6.
Let be a converted Z-number, which also fits for the LR fuzzy interval identity and a be a real constant. Thus, the relation can be described as
Proof.
When , learning from Definition 4, we know that the inverse credibility distribution of is . Then, through Theorem 5, it can be deduced that
when , using the same basis, the inverse credibility distribution of is ; then, we have
□
Theorem 7.
The expected value of the Z-number is linear when the series of Z-numbers are independent with a finite expected value. While and are two converted independent Z-numbers with the identity of LR fuzzy interval, we have
Proof.
When and , is strictly increasing monotone in terms of and ; thus, the inverse credibility distribution of is easy to obtain as on the basis of Definition 4. Then, ground on the definition of the expected value in Theorem 5, we have
When and , is strictly increasing monotone in terms of but strictly decreasing in terms of , it follows directly that
As for the other two cases (i.e. and , and ), it is easy to verify that the above proof still holds. □
Example 5.
Let ζ be a Z-number that . Based on the converting step proposed from Kang et al [2], the converted factor is received; thus, ζ is easily transformed into an LR fuzzy interval that is expressed as . As we know from Theorem 4, the expected value of the fuzzy interval can be calculated as follows.
Therefore, by means of the relationship between the classical Z-numbers and the converted Z-numbers in Equation (11), the expected value of ζ is easy to calculate as
Example 6.
According to Theorem 5, the expected value of Z-number in Example 2 is
3. Maximum Expected Z-Number Programming Model
This section introduces one of the most classical linear programming models, the maximum expected programming model. Using the converting factor and expected value we derived before through the inverse credibility distribution and operational law of Z-numbers, we set Z-numbers as a type of parameter, and establish the following models.
3.1. Chance-Constrained Z-Number Programming
As for dealing with the unsure programming, the chance-constrained programming has been created using a stochastic decision model that has managed an effective achievement. Leading with the thought of random chance-constrained programming, a framework is referred by Liu and Iwamura [25]. Then, Zhou et al. [26], regarding the classical chance-constrained fuzzy programming, combined the chance constraints with expected objectives to establish fuzzy chance-constrained programming and proved its validity in artificial translation.
First, we assume is an n-dimensional Z fuzzy number vector, which can be written as . Therefore, with the decision vector x, we define as the objective function and as the constraint functions, where . Learning from the basic property of fuzzy functions, it is not difficult to determine that is also a Z-number variable. However, this means that it is hard to minimize directly. As a result, we attempt to replace it by proposing the minimization of its expected value .
Moreover, it is notable that , as the Z fuzzy number constraint functions, are less than or equal to zero, where , and cannot define the crisp feasible sets. Therefore, we need the confidence levels which are defined as for the Z-number fuzzy constraints. Thus, the credibility of certain is regulated as follows
Thus, to develop a decision system with Z-parameters, a chance-constrained Z-number programming model is proposed as followed.
According to the Z-number fuzzy constraints, the fuzzy programming Model (12), which is subjected to a battery of chance constraints, aims to achieve the minimization decision with its expected objective .
Faced with the complex decision-making environment, the simple constraints from credibility distributions can sometimes make it difficult to satisfy the objective functions and express the special conditions. It is worth noting that, when faced with mutually independent Z-numbers, there are several constraints needed for extra restrictions, which can be represented as
where . Therefore, under certain circumstances, when the maximal risk level is given, the extra price function of Z-numbers can play a role in restriction, which is expressed as
where is the total price amount.
Definition 9.
As long as the vector x is satisfied with the following credibility equation
with , it is defined as a feasible solution for the target function model.
Definition 10.
If the feasible solution is satisfied with the following expected value in equation,
then, is named as an optimal solution among every feasible solutions x in the target function model.
3.2. Z-Number Crisp Equivalent Model
In the Section 3.1, has already been defined as , , where . As a Z-number, is going to represent the decision vector in the following model. Because the classical fuzzy vector is substituted by the Z-number , we obtain a crisp equivalent configuration by using the aforementioned fuzzy chance-constrained programming model with the following theorem.
On the grounds of theorems from Kang et al. [2], it is possible for a Z-number to be transformed into an LR fuzzy interval using the conversion of reliability. Combined with this information, it assumes that
where represents both the restriction and reliability separately, and is the trapezoid-shaped grade of membership function, while is the triangular-shaped grade of membership function.
The crisp equivalent model is built on a basis of the transformation from Z-numbers to normal LR-fuzzy-numbers. Therefore, the first step is to make use of the documentary-given transportation methods and to convert the reliability of Z-numbers using its converting weight, which is defined as
According to the converting method from Kang et al. [2], next, unite the reliability weights of Z-numbers to the restrictions which have been mentioned as , resulting in the expression of . This is the basic weighted Z-numbers, although it is difficult to calculate. In this way, it is worthwhile to derive a fuzzy interval, modifying it as Thus, is successful in transforming into from a Z-number into an LR fuzzy interval.
According to Kang et al. [2], after being weighted by the credibility, the membership function of such a Z-number is also altered by the real constant , such that it is represented as
Meanwhile, the shape grade of an LR fuzzy interval membership function will not be changed under the transition, considering that the membership of is trapezoidal; obviously, remains.
According to the Theorem 5, the equivalent mode of the expected value of an LR fuzzy interval is given using its inverse credibility distribution.
As the equivalent form on LR fuzzy intervals and expected value of Z-numbers are provided, we establish the Z-number expected value, which is stated by its opposite credibility distribution as well.
Theorem 8.
Let the objective function strictly increase when it comes to , but strictly decrease when . If are a battery of independent Z-numbers, then the expected objective function is satisfied by the following equation
where is the inverse credibility distribution of with , and β is the converting factor.
Proof.
In line with Theorem 3, the inverse credibility distribution of can be written as
Furthermore, on the basis of Equation (11), it is simple to determine that
□
Theorem 9.
Assume the constraint function increases strictly when it comes to and decreases strictly when it comes to . While are a series of independent Z-numbers, its chance constraint inequality
founds if and only if
where is a battery of the credibility distributions of with .
Proof.
This theorem is the expansion of Theorem 3, from which the opposite credibility distribution of can be described as
Moreover, it is obvious that Equation (14) is presented if and only if . □
Theorem 10.
Let increases strictly when it comes to and decreases strictly when it comes to . Additionally, increases strictly when related to and decreases strictly when related to with . While are a series of independent Z-numbers, the Z fuzzy number programming Model (12) can be solved using the same method of crisp linear programming,
where are a battery of credibility distributions of with .
Proof.
This theorem can be deduced using Theorems 8 and 9 directly. □
In this issue, through Theorem 10, while the constraint functions with and the objective function are increasing or decreasing strictly in certain domains and Z resists to be a series of independent Z-numbers, it is possible to translate the fuzzy programming model depicted in Section 3.1 to such crisp Model (15). As the compact relation between these models, there are no differences witnessed under the view of mathematics apart from integrals. In this case, certain Z-number optimization problems can be solved under the classical deterministic optimization configuration without the need for special techniques or methods.
4. Example of Maximum Expected Z-Number Programming Model
4.1. Supplier Selection Problem
Additionally, we put the configuration of the Z-number programming model mentioned previously into application and give an example of the installing production line in certain household appliances manufacturers. In order to gain a better understanding of the following examples, the relevant notations are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Notations.
We assume that the household appliance industry plans to invest in a new factory in order to satisfy the requirement in a certain area. It is already known that this company mainly produces three kinds of household appliances, including refrigerators, washing machines and air conditioners. Thus, in this example, . Since each kind of household appliance corresponds to different production lines, the company considers installing several lines for the basic productions, where is the number of installing production lines for refrigerators, washing machines and air conditioners, , separately.
We set the expense of machine of the i-th category as , and the total amount of funds for production planning is a. Thus, the first constraint about capital budget is
The second constraint for the factory relates to the maximum space. As the total coverage area is limited to the establishment of industry, we set S to represent the largest available installing space, where is expressed as the covering area of the i-th type production lines. Thus, the space constraint is as follows
Owing to the malfunctions that may happen on production lines, there are uncertainties about the production efficiency, and these are defined as , . And let be the demand for the i-th type household appliances on the i-th type production lines in this area. The company always wishes to try every means to satisfy every requirement in the region and avoid a vacancy. Therefore, , where . Similarly, in the realistic economic activities, the demand in the future is generally uncertain.
In this problem, we assume the variables above are all Z fuzzy numbers. Under the background of actual enterprise research, expert interviews and simulations, do not have precisely defined constraints. If the decision maker in the company sets to be the confidence level to meet the requirements of the i-th category components, we will obtain the chance constraints as follows
We suppose that the margin provided by each i-th category of machines is for , and the sum of profits is . Profits are distributed by the enterprise based on the sales of the final products, which are generally influenced by rivals, seasons and other uncertain factors. In this case, we define the profits as the form of Z fuzzy number variables in the following example, with the maximum objective expected value of the sum profits, which is written as
Therefore, we design an integral programming model for the investment production problem, which is
Let , and be a series of independent regular LR fuzzy intervals whose credibility distribution is , and separately, where . As follows, on the basis of Theorem 10, it is possible to convert the model from Model (16) into the following conclusive form.
where the problem can be simply solved using .
On the basis of the established Model (17) and the fuzzy interval data catalogued in Table 2, it is possible to obtain the exampled linear programming model as follows

Table 2.
Parameters and values for the procurement planning problems.
In this model, it is important to transform Z-numbers data into regular LR-fuzzy-numbers first, which helps to simplify the calculation. Using the converting method given by Kang et al. [2], we first convert each Z-parameter into LR fuzzy numbers and use them in the regular LR fuzzy programming model in [26], easily obtaining the programming model described above.
Using , the total optimal margin is 8476.8, while the final solution is
It is notable that the conventional approaches struggle to solve this problem with both the Z-numbers parameters and LR fuzzy intervals, but the fuzzy simulation is possible. Since there are three types of fuzzy numbers listed, which are Z-numbers, Gaussian fuzzy numbers and Cauchy fuzzy numbers, the multiplication has increased significantly in the programming model. Meanwhile, Models (16) and (17) are shown, and idea about transformation revealed that the achievement of deterministic form makes it easy for us to solve the fuzzy programming using classical methods related to the framework of fuzzy programming with Z-number parameters.
4.2. Optimal Portfolio Problem
In this section, we think about the portfolio selection. A portfolio is any collection of financial assets, like stocks and bonds, which may be executed by individuals or managements. The relevant notations are given in Table 3 which helps with clearer comprehension.

Table 3.
Notations.
First, we make an assumption of p stocks with their Z fuzzy number returns , where , and each portfolio is , where expresses the ratio people invested in stock i on aggregate. Generally, is given as where is the closing value for now, is the closing value in the following year, and is the dividend in the following year. Interestingly, and in the future are obviously unclear for now. If they are estimated to be fuzzy numbers, then is known to be a fuzzy variable. Moreover, when facing the portfolios , the total return is
is also a fuzzy variable. Moreover, if the investor is willing to achieve the maximization of total return, the following fuzzy linear programming model is proposed.
As for fuzzy identities of Z-numbers, it is hard to perform calculations that directly bypass genetic algorithms. Therefore, inspired by the expected value model in Model (12), we are able to measure the investment returns from the expected value, that the function can be depicted as
We set the price of invested amount restrictions for the p stocks, and the total amount of funds for investment planning is . Because represents the ratio of investment, the total amount of stocks purchased should be provided as m. Then, the total amount restriction about portfolio is depicted as
Additionally, Samuelson (1970) stated that almost all investors would like to choose the portfolio with a relatively larger tendency, meaning that there are more possibilities to acquire a larger payment than the expected value. In order to minimize the risk that investment brought, the total investment sum is supposed to constrain the maximum investment amount that can restrict over-capitalization to a great extent. Based on this analysis, we establish the multi-objective credibility linear programming model.
where is the amount invested in each stock, m is the total amount of shares purchased and is the investment sum.
In order to explain this clearly, we establish the example below using an explicit value. First, we assume there are four stocks, and each of their Z fuzzy number returns is shown in the following Table 4.

Table 4.
Four Z-number stock returns.
Learning from Kang et al. [2], we use the converting factor and refer to Theorem 5, based on which it is simple for us to figure out the expected value for each Z-numbers from the defined formulas of mean value in Table 4, which are listed to be combined with the invested amounts in the following Table 5.

Table 5.
Expected value and invested amount of four Z-number stock.
According to the data, we substitute the above values into the equation that has established the maximum expected model as follows:
where we set the total investment amount 200,000 experienced from the former research, and the number of stocks purchased restricted in .
Using , the final optimal portfolio is
with the maximum expected value of 3.9274.
5. Conclusions
The Z-number is mainly applied based on the description of conformity between objective natural phenomenon and subjective consciousness, which affects both the vagueness of information and the level of human belief about certain occasions. Thus, Z-numbers hold great confidence and reliability when portraying realistic issues compared with normal fuzzy numbers. Many researchers have made great contributions to the converting and arithmetic methods referencing Z-numbers since their introduction. However, there i limited research on the Z-number linear programming models using this method; on the contrary, many researchers have made efforts in intelligent algorithms-based programming which bring great complexity to the calculation. The explicit solution problem has yet to be resolved.
In this case, our model had successfully solve this problem and fill the gap in the Z-number application field. We combined Z fuzzy numbers with a linear programming model, which can easily create explicit results using our method with , instead of using intelligent algorithms. Thus, compared with the former fuzzy model, our model can provide an explicit solution when facing maximum expected value linear programming models, in which a smaller error provides great benefits in industrial engineering or decision making. Secondly, it is much easier to put into use and comprehend with fewer calculation difficulties, leading to faster decision making and resource allocation.
This paper was split into two parts. First, we explored the Z-number theoretical preparation using the method of transform reliability B of Z-numbers into the weight on its restrictions A ending to be an LR fuzzy interval. Next, we discussed the Z-number linear programming, especially for the trapezoidal Z-numbers which have been widely used in many fields.
In order to start the work on modeling, the practical theory of Z-numbers must be investigated. To insert the definition of credibility measure, inverse distribution function, operational law and expected value of Z-numbers, we used the converted factor calculated from the reliability of Z-numbers. After transforming reliability into the weight of its restriction, it is possible to convert classical Z-numbers into LR fuzzy intervals with a variety of wonderful identities. And then we succeeded in deriving Z-numbers based on the properties of LR fuzzy intervals.
Meanwhile, learning from the LR fuzzy linear programming, we established one of the most traditional linear programming models, the maximum expected model, for Z-numbers as a paradigm, using the theoretical preparation. Since the model is maturely applied in LR fuzzy intervals, what we focus on first and foremost is to transform Z-numbers into classical trapezoidal LR fuzzy intervals using set converting factors which help to a great extent in our models. Using the basic properties and measurements of Z-numbers, we translate the model into Z-number form, which contain Z-numbers as parameters, and then the crisp equivalent is formed. In addition, in order to explain the accessibility of these models, we provide several explicit examples for explanation, which include a supplier selection problem and an optimal portfolio problem. In order to solve the specific Z-number linear programming models, we use as a tool that is much simpler than intelligent algorithms.
This article also has some unavoidable limitations. At first, we only set the maximum expected programming models as a paradigm; others like Maximum Regret Model and Entropy Optimization Model were not deduced here, despite having a similar calculation process to our models.
This will be explored by future researchers. Next, in our explicit Z-number programming examples, trapezoidal forms of Z-numbers are put into use. Other forms like triangular distribution or Gaussian distribution are not applied in this section owing to the restrictions of time and energy, which need to be further investigated in future work. Additionally, in order to express the practicability, we have presented two examples for our expected value linear programming model, which are a supplier selection problem and an optimal portfolio problem. However, two examples are limited when it comes to explaining the model clearly. If possible, in the following work, more application problems of our model can be solved, such as risk investment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y.; formal analysis, M.Y. and B.Z.; investigation, M.Y.; methodology, B.Z.; software, B.Z. and C.W.; visualization, C.W.; supervision, M.Y.; validation, M.Y., B.Z., J.C. and C.W.; writing—original draft, M.Y. and J.C.; writing—review and editing, M.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the editors and anonymous referees for their kindly review and helpful comments. In addition, the authors would like to thank Jian Zhou and Mingxuan Zhao for their assistance and support. Any remaining errors are ours.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare that we have no relevant or material financial interests that relate to the research described in this paper. The manuscript has neither been published before, nor has it been submitted for consideration for publication in another journal.
Appendix A
Definition A1
(Zadeh [17]). In a given domain , the fuzzy number ϕ whose membership function is defined as
where and .
Definition A2
(Liu et al. [18]). When the shape function of an LR fuzzy interval ξ, defined as L for left and R for right, is continuous on the domains , combined with the condition that it strictly decreases on the domains , then the LR fuzzy interval is said to be a regular one.
Definition A3
(Dubois and Prade [27]). A fuzzy interval ξ distributed in universal real set is regulated to be an LR fuzzy interval on the condition of the shaping functions, where L represents the left one and R the right one, and the numerical range is , . Thus, its membership function is
where and as real numbers are named as the lower and upper modal value of ξ, a and b are named as the left and right scales separately. In more simpler terms, we denote the fuzzy interval ξ as .
References
- Zadeh, L.A. A Note on Z-numbers. Inf. Sci. 2011, 181, 2923–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y. A method of converting Z-number to classical fuzzy number. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2012, 9, 703–709. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, R.; Pal, S.K.; Pal, J.K. A decade of the Z-numbers. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 2800–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, R.A.; Alizadeh, A.V.; Huseynov, O.H. The arithmetic of discrete Z-numbers. Inf. Sci. 2015, 290, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, R.A.; Huseynov, O.H.; Zeinalova, L.M. The arithmetic of continuous Z-numbers. Inf. Sci. 2016, 373, 441–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, R.A.; Pedrycz, W.; Huseynov, O.H. Functions defined on a set of Z-numbers. Inf. Sci. 2018, 423, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Xie, C.; Luo, Y.; Tang, Y. Ranking Z-numbers with an improved ranking method for generalized fuzzy numbers. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 32, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Deng, Y.; Sadiq, R. Total utility of Z-number. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 703–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, R.A.; Alizadeh, A.V.; Huseynov, O.H.; Jabbarova, K.I. Z-number based linear programming. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2015, 30, 563–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasankhani, F.; Daneshian, B.; Allahviranloo, T.; Khiyabani, F. A new method for solving linear programming problems using Z-numbers’ ranking. Math. Sci. 2023, 17, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Gao, M.; Goh, M.; Xiao, X. Green supplier selection mechanism based on information environment of Z-numbers. Cogn. Comput. 2023, 15, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y. Decision making using Z-numbers under uncertain environment. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2012, 8, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar]
- Bakar, A.S.A.; Gegov, A. Multi-layer decision methodology for ranking Z-numbers. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2015, 8, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku Khalif, K.; Gegov, A.; Abu Bakar, A. Hybrid fuzzy MCDM model for Z-numbers using intuitive vectorial centroid. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 33, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, R.R.; Mraiziq, D.A.T.; Huseynov, O.H. Expected Utility Based Decision Making under Z-Information and Its Application. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2015, 2015, 364512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Hu, C.; Guo, S.; Yu, J. Z-Number-Based Quantitative Expression of Activity Information in Uncertain Project Scheduling. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Pantelous, A.A.; Zhou, J.; Ji, P. On fuzzy simulations for expected values of functions of fuzzy numbers and intervals. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1978, 1, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. A Theory of Approximate Reasoning, Mathematical Frontiers of the Social and Policy Sciences; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1979; pp. 69–129. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y. Expected value of fuzzy variable and fuzzy expected value models. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2002, 10, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Theory and Practice of Uncertain Programming; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 57–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J. An extensive operational law for monotone functions of LR fuzzy intervals with applications to fuzzy optimization. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 11381–11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H. A theoretical extension on the operational law for monotone functions of uncertain variables. Soft Comput. 2016, 20, 4363–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Iwamura, K. Chance-constrained programming with fuzzy parameters. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1994, 94, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, K. Fuzzy arithmetic on LR fuzzy numbers with applications to fuzzy programming. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 30, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Fuzzy real algebra: Some results. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1979, 1, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).