A New Spike Membership Function for the Recognition and Processing of Spatiotemporal Spike Patterns: Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Related Works
2. Methods
2.1. Fuzzy Adaptive Neurons
2.2. Spike Activation Function Model
3. Models for the Processing of Spike-Time-Encoded Information and Pattern Recognition
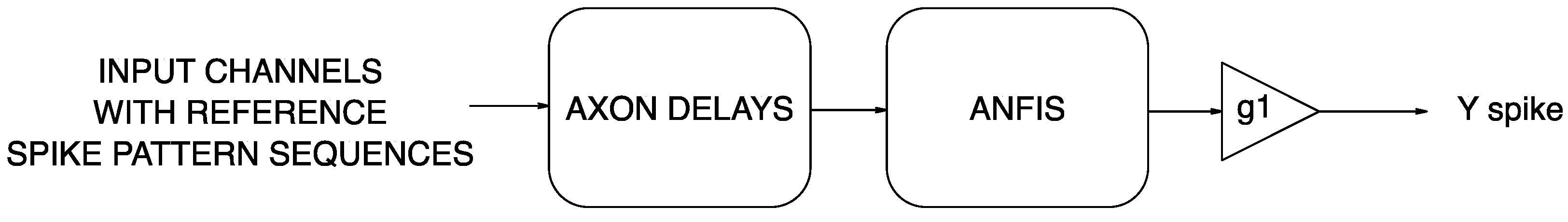
3.1. ANFIS Model
3.1.1. Algorithm
3.1.2. Adaptive Network Based Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS)
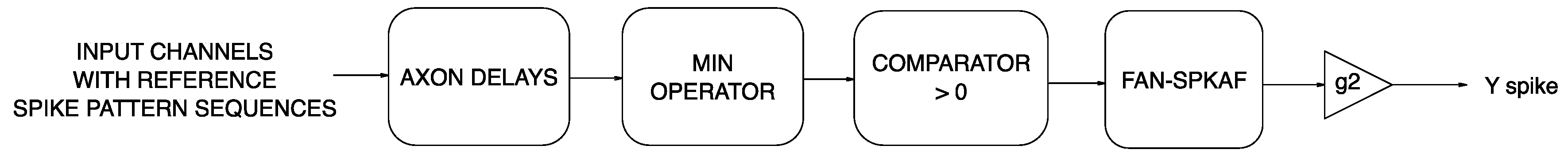
3.2. FAN-SPKAF Model
3.2.1. Algorithm
3.2.2. Fuzzy Adaptive Neuron with Spike Activation Function (FAN-SPKAF)
3.3. FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF Model for Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application
3.4. Augmented Spiking Neuron Model for Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application
3.5. Augmented FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF Model for Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application
4. Model Analysis
4.1. Nonlinear Systems Fuzzy Modeling
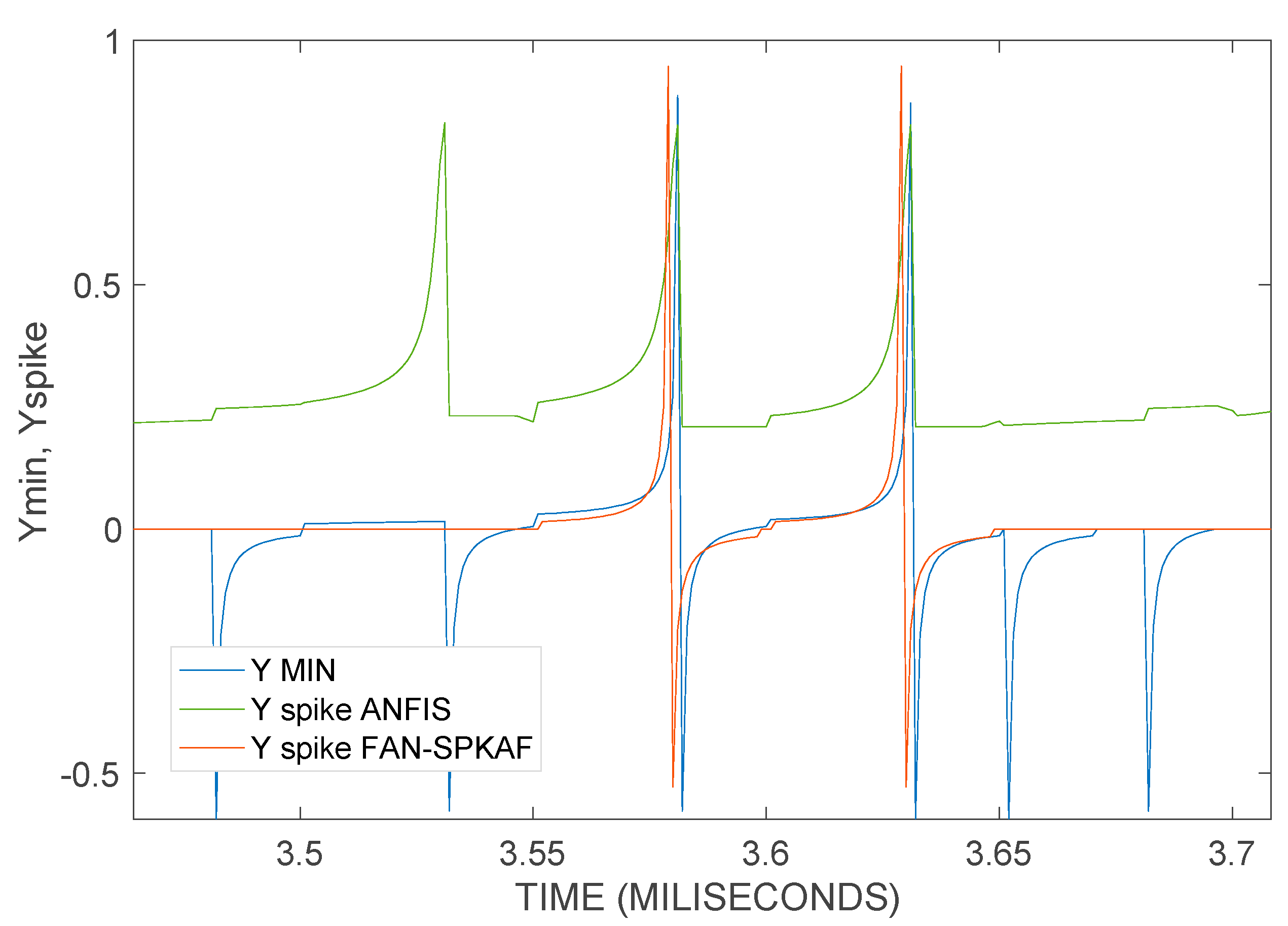
4.1.1. Analysis of ANFIS Model
4.1.2. Analysis of FAN-SPKAF model
4.1.3. Analysis of FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF Model
4.2. Fuzzy System Training
4.3. Stability Analysis
5. Results of the Simulation of the Fuzzy Systems
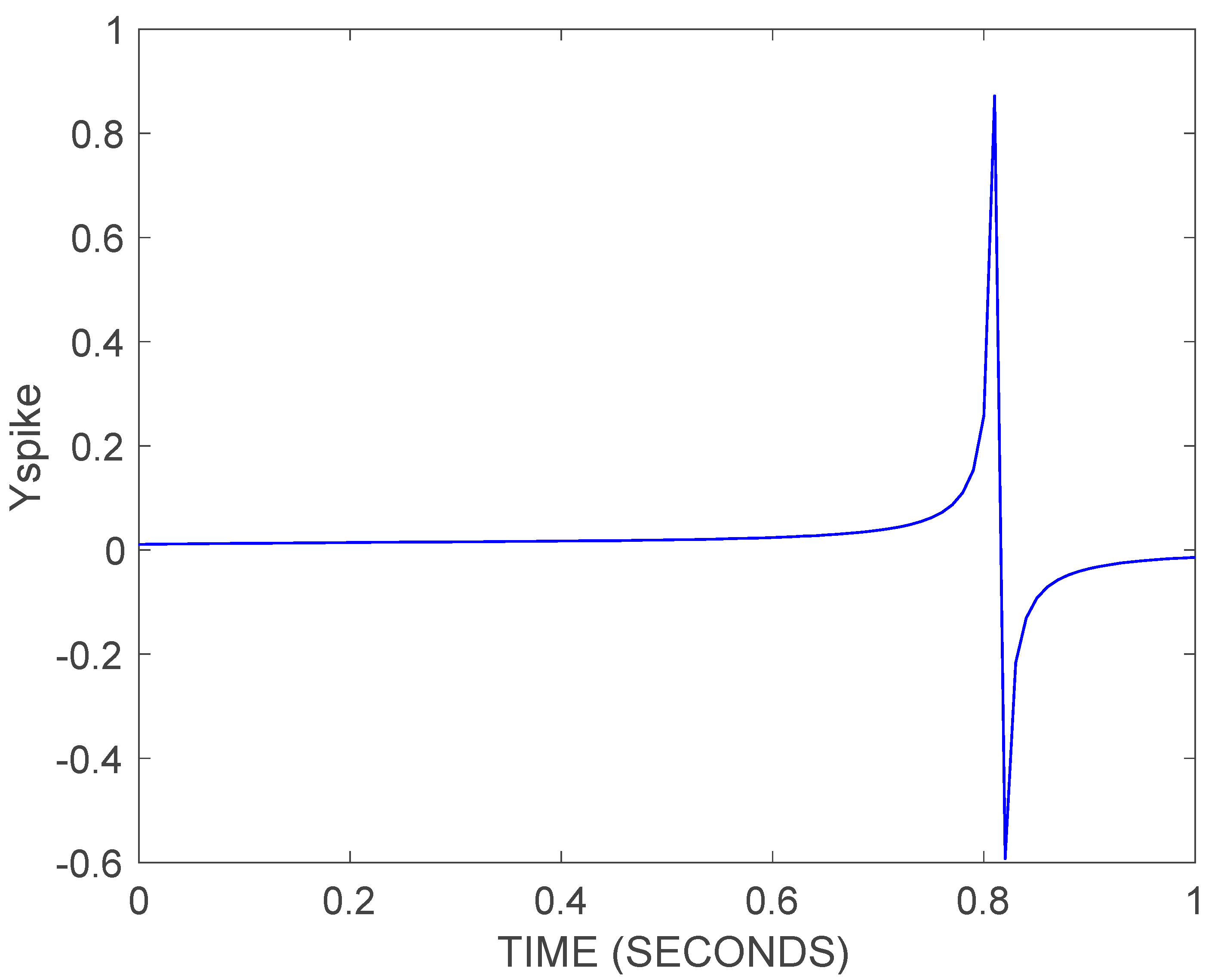
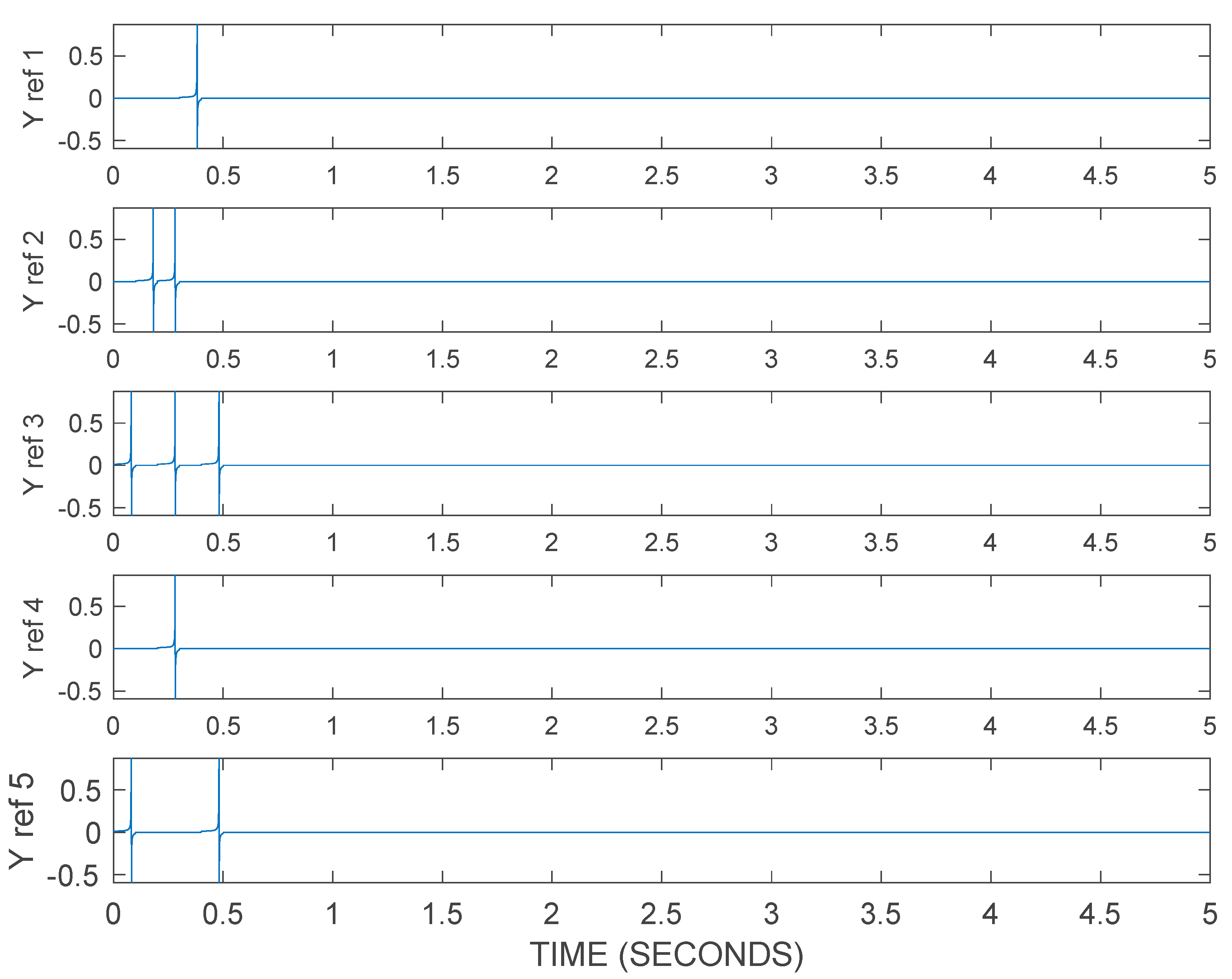
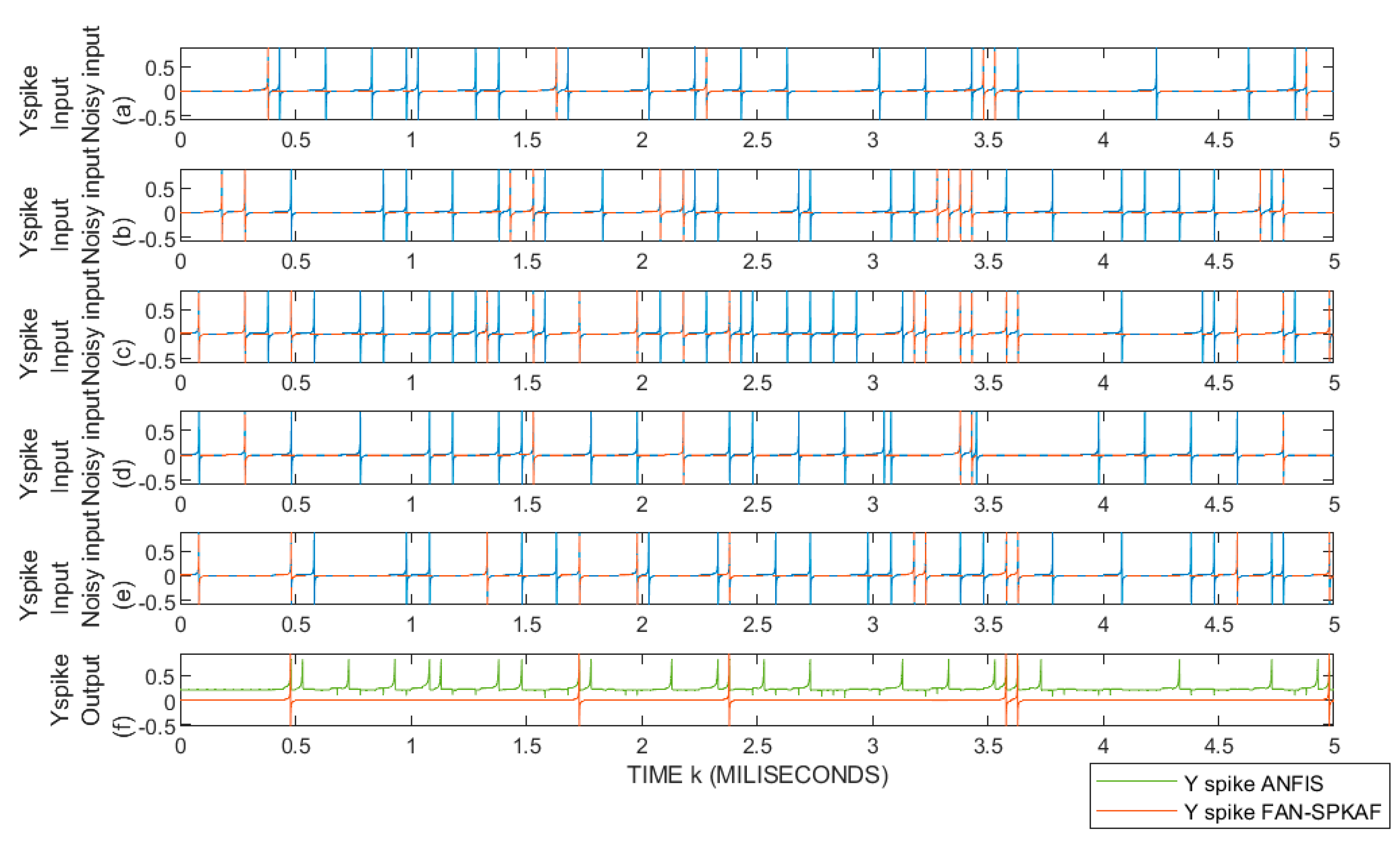
5.1. Recognition of Spatiotemporal Spike Patterns
- ○
- Weights [0,1],
- ○
- Learning factor, fixed value, .
- ○
- ○
- Weights [0,1],
- ○
- Learning factor, fixed value, .
- ○
- Threshold, fixed value, .
- ○
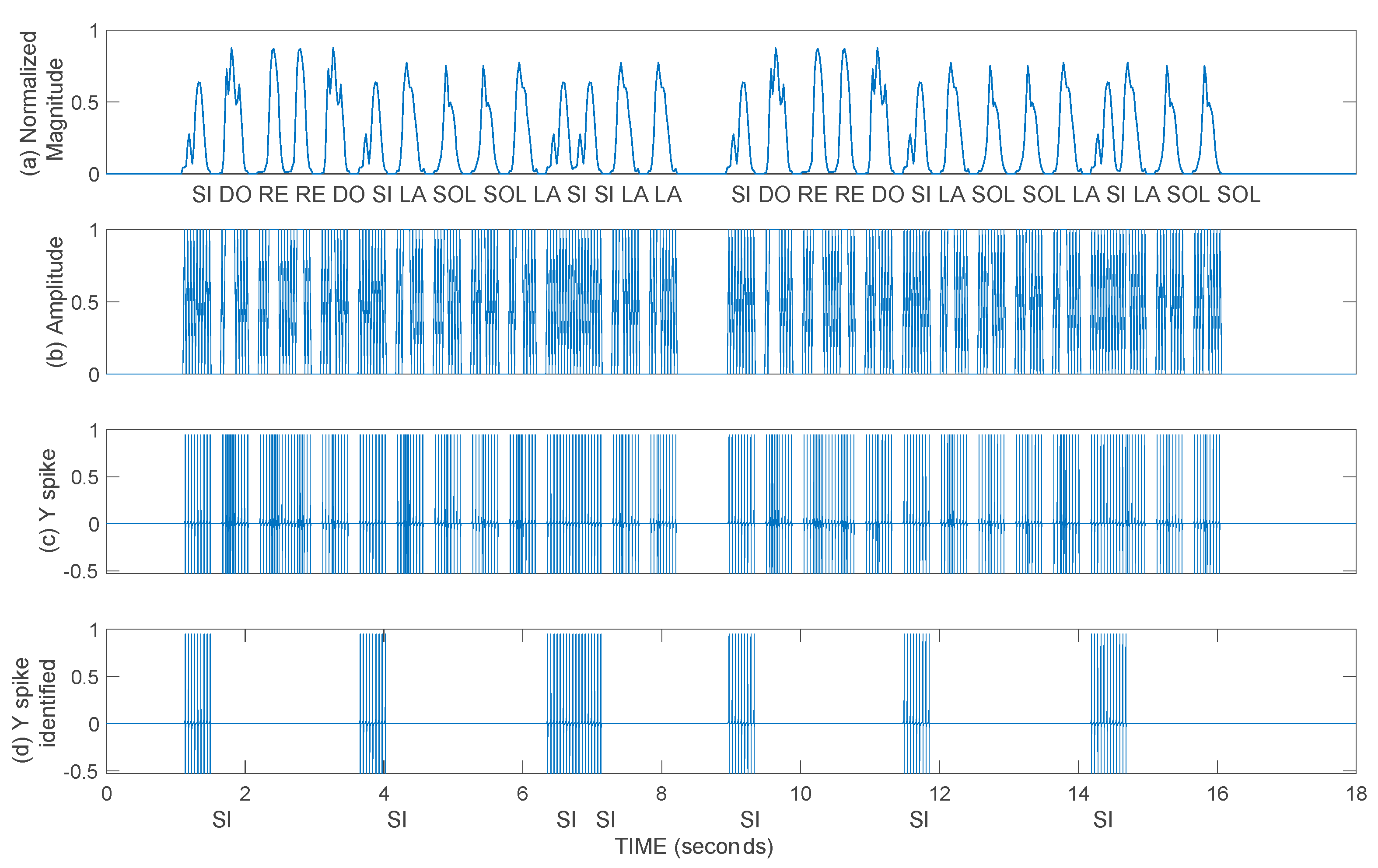
5.2. Syllable-Based Spike Pattern Speech Recognition
5.2.1. Results of the FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF Method
5.2.2. Results of the Augmented Spiking Neuron Model Method
5.2.3. Results of the Augmented FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF Method
5.3. MSE
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANFIS | adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system |
| FAN | fuzzy adaptive neuron |
| FAN-SPKAF | fuzzy adaptive neuron with spike activation function |
| FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF | fuzzy adaptive neuron–step activation function–spike activation function |
| LIF | leaky integrate-and-fire |
| MSE | mean squared error |
| NARMA | nonlinear autoregressive-moving average |
| Nomenclature | |
| SAF | sigmoid activation function |
| SNN | spiking neural networks |
| SPKAF | spike activation function |
| STEPAF | step activation function |
| STFT | short-time Fourier transform |
| UAV | unmanned aerial vehicles |
| real numbers | |
| real numbers | |
| spike coefficient | |
| augmented constant | |
| unmodeled dynamic | |
| error of identification or modeling error | |
| modeling error | |
| modeling error | |
| modeling error | |
| nonlinear function | |
| learning factor, | |
| gain | |
| learning factor, | |
| learning rate, | |
| inputs of the nonlinear plant | |
| inputs of the unmodeled dynamic | |
| input | |
| time | |
| input spike time from the afferent | |
| time of the output spike | |
| time constant | |
| time constant of the synaptic currents | |
| number of or samples | |
| mean squared error | |
| number of synaptic afferents | |
| frequency index | |
| adaptive parameters | |
| target pattern | |
| constant parameter that normalizes the peak of the kernel to unity | |
| number of or samples | |
| number, | |
| firing threshold, | |
| with | |
| threshold | |
| synaptic weight | |
| synaptic weights, | |
| normalized firing strength | |
| weights, proposed fixed weights or | |
| weights of the proposed model | |
| weights of the unmodeled dynamic | |
| unknown weights to minimize unmodeled dynamic | |
| window sequence to select a finite-length (local) segment from and possibly to reduce the spectral leakage | |
| dendrite inputs | |
| sliding sequence | |
| output of the nonlinear plant | |
| output of the proposed model | |
| SAF | |
| SPKAF | |
| reference | |
| identified spikes voice pattern | |
| identified spikes voice pattern | |
| SPKAF, identified spikes voice pattern | |
| spikes voice pattern of the syllable or musical note SI of solfeggio in Spanish | |
| spikes voice pattern of the syllable or musical note SI of solfeggio in Spanish | |
| identified spikes voice pattern | |
| identified spikes voice pattern | |
| triangular signal with a peak amplitude of 0.1 with an added constant of 0.8 and period | |
| dendrite inputs |
References
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W.H. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952, 117, 500–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstner, W.; Kistler, W.M. Spiking Neuron Models; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; 480p, ISBN 978-0521890793. [Google Scholar]
- Izhikevich, E.M. Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2003, 14, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.M.E. Modeling the Spike Response for Adaptive Fuzzy Spiking Neurons with Application to a Fuzzy XOR. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2018, 115, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Theory of Fuzzy Sets. In Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Technology; Marcel Dekker: New York City, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.M.; Qi, J. On Fuzzy Neuron Models. In Fuzzy Logic for the Management of Uncertainty; Zadeh, L.A., Kacprzyk, J., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 479–491. ISBN 0-471-54799-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.M. Fuzzy logic, neural networks and virtual cognitive systems. In Second International Symposium on Uncertainty Modeling and Analysis; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.M.; Rao, D.H. On the principles of fuzzy neural networks. In Fuzzy Set Syst; Elsevier Science B. V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 61, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, A.; Pérez, J.L. A fuzzy Gupta integrator neuron model with spikes response and axonal delay. Adv. Artif. Intell. Eng. Cybern. 2002, 9, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.; Pérez-Silva, J.L.; Lara-Rosano, F. Electronic Implementation of a Fuzzy Neuron Model with a Gupta Integrator. JART 2011, 9, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Building logistic spiking neuron models using analytical approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 80443–80452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, N.; Nishida, K. The Role of Spiking Neurons for Visual Perception of a Partner Robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fuzzy Systems Sheraton Vancouver Wall Centre Hotel, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–21 July 2006; pp. 122–129, IEEE 0-7803-9489-5/06. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Tang, H.; Tan, K.C.; Li, H. Rapid feedforward computation by temporal encoding and learning with spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapson, J.C.; Cohen, G.K.; Afshar, S.; Stiefel, K.M.; Buskila, Y.; Wang, R.M.; Hamilton, T.J.; Schaik, A.V. Synthesis of neural networks for spatio-temporal spike pattern recognition and processing. Front. Neurosci. Neuromorphic Eng. 2013, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susi, G.; Toro, L.A.; Canuet, L.; López, M.E.; Maestú, F.; Mirasso, C.R.; Pereda, E.A. Neuro-Inspired System for Online Learning and Recognition of Parallel Spike Trains, Based on Spike Latency, and Heterosynaptic STDP. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Z.-G.; Tan, M.; Du, D.; Fei, M. A rapid spiking neural network approach with an application on hand gesture recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2019, 13, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, Y. A Curiosity-Based Learning Method for Spiking Neural Networks. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Sarwar, S.S.; Panda, P.; Srinivasan, G.; Roy, K. Enabling Spike-Based Backpropagation for Training Deep Neural Network Architectures. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimaila, N.K.V. Generation of Future Image Frames using Adaptive Network Based Fuzzy Inference System on Spatiotemporal Framework. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop (AIPR), Washington, DC, USA, 9–11 October 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasabov, N. Evolving Spiking Neural Networks and Neurogenetic Systems for Spatio- and Spectro- Temporal Data Modelling and Pattern Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, Advances in Computational Intelligence, LNCS 7311, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 10–15 June 2012; pp. 234–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Goh, S.K.; Tang, H.; Tan, K.C. Application of Precise-Spike-Driven Rule in Spiking Neural Networks for Optical Character Recognition. In Proceedings of the 18th Asia Pacific Symposium on Intelligent and Evolutionary Systems—Volume 2; Proceedings in Adaptation, Learning and Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhilipan, A.; Preethi, J. Pattern Recognition using Spiking Neural Networks with Temporal Encoding and Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sponsored 9th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Control (ISCO), Coimbatore, India, 9–10 January 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q. Spike-Event-Driven Deep Spiking Neural Network with Temporal Encoding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Song, S.; Ma, C.; Pan, L.; Tan, K.C. Synaptic Learning with Augmented Spikes. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bose, B.K. Evaluation of membership functions for fuzzy logic controlled induction motor drive. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2002 28th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society, IECON 02, Sevilla, Spain, 5–8 November 2002; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basterretxea, K.; Tarela, J.M.; Del Campo, I. Digital Gaussian membership function circuit for neuro-fuzzy hardware. Electron. Lett. 2006, 42, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Sang, S.; Lam, H.-K.; Zhang, J. A polynomial-membership-function approach for stability analysis of fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.M.E.; Yu, W. A novel learning algorithm for Fuzzy Adaptive Neural Networks: Application to the neuro-fuzzy design of control law for a PID controller. submitted.
- Mendoza, A.M.E.R.; Yu, W. Fuzzy Adaptive Control Law for Trajectory Tracking Based on a Fuzzy Adaptive Neural PID Controller of a Multi-rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.M.E.; Yu, W.; Li, X. A novel fuzzy system with adaptive neurons for earthquake modeling. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 101369–101376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.M.E.; Yu, W.; Li, X. Fuzzy Identification of Systems based on Adaptive Neurons. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 10767–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A. Study of the response of the connection of Fuzzy Adaptive Spiking Neurons with self-synapse in each single neuron. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), Mexico City, Mexico, 9–11 November 2014; pp. 1–6, ISBN 978-1-4799-6228-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.; Covarrubias-Fabela, J.; Amezquita-Brooks, L.; Hernández-Alcantara, D. Parameter Identification using Fuzzy Neurons: Application to Drones and Induction Motors. DYNA 2018, 93, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Mendoza, A.M.E.; Covarrubias-Fabela, J.R.; Amezquita-Brooks, L.A.; Garcia-Salazar, O.; Yu, W. Fuzzy Adaptive Neurons applied to the identification of parameters and trajectory tracking control of a multi-rotor Unmanned Aerial Vehicle based on experimental aerodynamic data. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2020, 100, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, J.-I.; Nakatani, T.; Yoneyama, M. Speaker-Independent Word Recognition Using Fuzzy Pattern Matching. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1989, 32, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.S.; Ghoshal, J. Approximate reasoning approach to pattern recognition. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1996, 77, 125–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasmeyer, G. The perceptual importance of selected voice quality parameters. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Munich, Germany, 21–24 April 1997; Volume 3, pp. 1615–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, J.A.; Qadir, G.; Abbass, H. Perception of syllables pitch contour in Sindhi language. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Engineering, Dalian, China, 24–27 September 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, R.; Takashima, R.; Takiguchi, T.; Ariki, Y. Individuality-preserving voice conversion for articulation disorders based on non-negative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 8037–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chleboun, J. A new membership function approach to uncertain functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2020, 387, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Brooks, L.A.; Hernández-Alcántara, D.; Santana-Delgado, C.; Covarrubias-Fabela, J.R.; García-Salazar, O.; Ramírez-Mendoza, A.M.E. Improved model for micro-UAV propulsion systems: Characterization and applications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 2174–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, W.; Lara-Rosano, F. Dynamic Knowledge Inference and Learning under Adaptive Fuzzy Petri Net Framework. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2000, 30, 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Li, X. Fuzzy identification using fuzzy neural networks with stable learning algorithms. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2004, 12, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Santiago, A.; Azucena, A.D.P.; Gómez-Zea, J.M.; Jesús-Magaña, J.A.; Valdez-Ramos, M.D.L.L.; Sosa-Silva, E.; Falcón-Pérez, F. Adaptive Model IoT for Monitoring in Data Centers. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 5622–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Deformable Convolutional Networks for Efficient Mixed-Type Wafer Defect Pattern Recognition. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2020, 33, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lele, A.; Fang, Y.; Ting, J.; Raychowdhury, A. An End-to-End Spiking Neural Network Platform for Edge Robotics: From Event-Cameras to Central Pattern Generation. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022, 14, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mendoza, A.M.E.; Yu, W. Simplified model of the propulsion system for a PVTOL with a disturbance and estimate of power efficiency. DYNA 2022, 97, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, F.; Cervantes-Rojas, J.S.; Valdovinos, J.M.; Sandre-Hernández, O.; Salazar, S.; Romero, H. Dynamic Neural Network-Based Adaptive Tracking Control for an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Subject to Modeling and Parametric Uncertainties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steccanella, L.; Bloisi, D.D.; Castellini, A.; Farinelli, A. Waterline and obstacle detection in images from low-cost autonomous boats for environmental monitoring. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2020, 124, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergies, S.; Su, S.-F.; Elsisi, M. Model Predictive Paradigm with Low Computational Burden Based on Dandelion Optimizer for Autonomous Vehicle Considering Vision System Uncertainty. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, T.K.N.; Tay, Y.W.D.; Lim, J.H.; Tan, M.J.; Wong, T.N.; Li, K.H.H. Concrete 3D Printing: Process Parameters for Process Control, Monitoring and Diagnosis in Automation and Construction. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, E.; Virtanen, T.; Nurminen, J.; Gabbouj, M. Voice Conversion Using Partial Least Squares Regression. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 18, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, E.; Silén, H.; Virtanen, T.; Gabbouj, M. Voice Conversion Using Dynamic Kernel Partial Least Squares Regression. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2012, 20, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



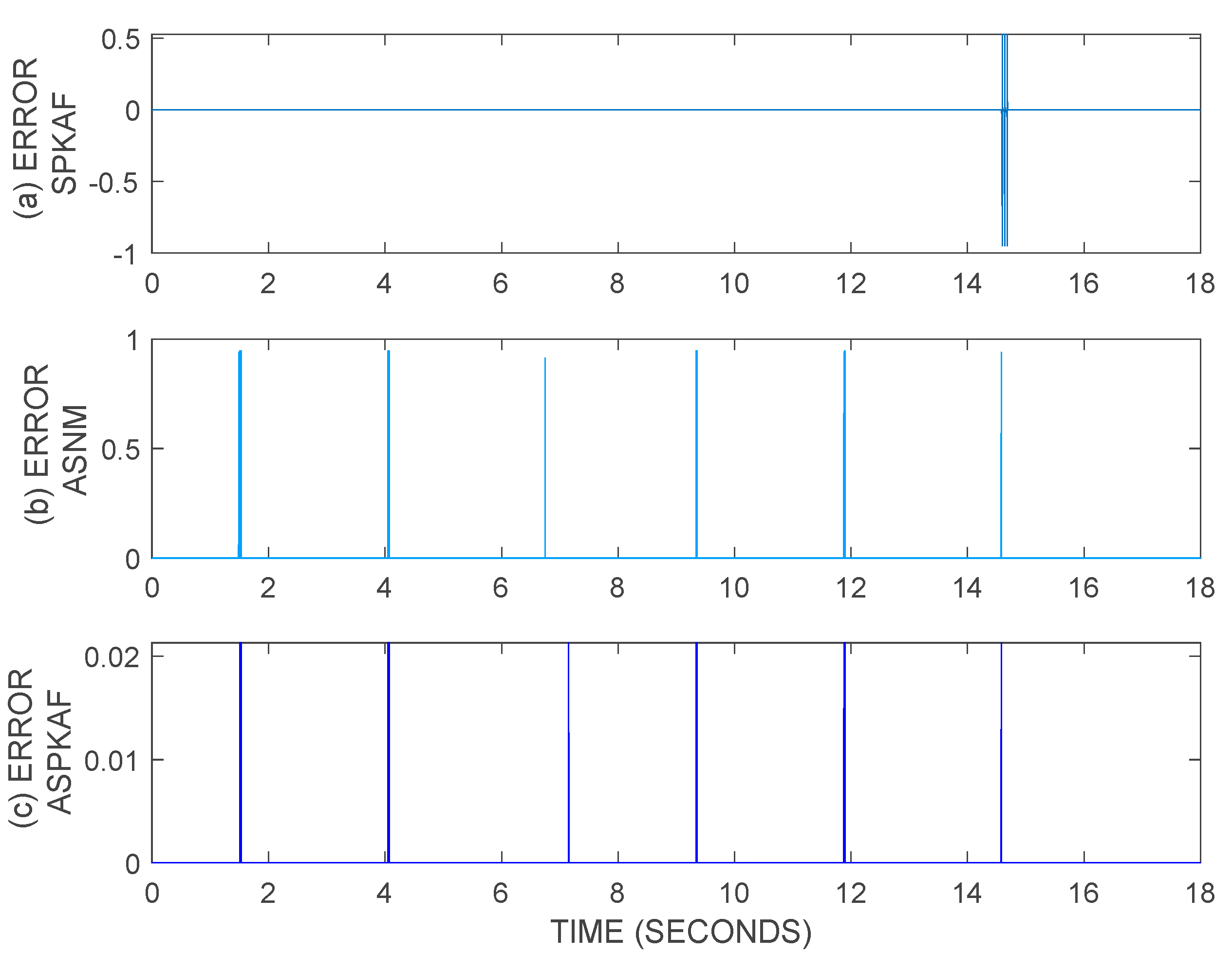
| MODEL | MSE | Precision (%) |
|---|---|---|
| FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF | 1.0823 × 10−4 | 99.99 |
| Augmented Spiking Neuron Model | 3.6915 × 10−4 | 99.96 |
| Augmented FAN-STEPAF-SPKAF | 1.6543 × 10−7 | 99.999983457 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez-Mendoza, A.M.E.; Yu, W.; Li, X. A New Spike Membership Function for the Recognition and Processing of Spatiotemporal Spike Patterns: Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112525
Ramírez-Mendoza AME, Yu W, Li X. A New Spike Membership Function for the Recognition and Processing of Spatiotemporal Spike Patterns: Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application. Mathematics. 2023; 11(11):2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112525
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez-Mendoza, Abigail María Elena, Wen Yu, and Xiaoou Li. 2023. "A New Spike Membership Function for the Recognition and Processing of Spatiotemporal Spike Patterns: Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application" Mathematics 11, no. 11: 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112525
APA StyleRamírez-Mendoza, A. M. E., Yu, W., & Li, X. (2023). A New Spike Membership Function for the Recognition and Processing of Spatiotemporal Spike Patterns: Syllable-Based Speech Recognition Application. Mathematics, 11(11), 2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112525








