Abstract
An investigation is conducted to study the flow and heat transfer on stagnation point over an exponentially stretching/shrinking cylinder filled with nanofluid in the presence of slip at the boundary. By using the appropriate exponential similarity transformation, the governing equations are converted into nonlinear ordinary differential equations and then solved computationally using bvp4c in Matlab software. The results of skin friction coefficient, heat transfer coefficient, velocity and temperature profiles on slip parameter, curvature parameter, nanoparticles as well as nanoparticle volume fraction parameter are presented graphically. The presence of slip and curvature parameters cause the region of dual solutions to expand and at once enhance the heat transfer rate at the surface but somehow the heat transfer rate at the surface decreases rapidly when cylinder is shrunk. The aim of this paper is to investigate the effect of slip parameter on nanofluid as well as on the stretching/shrinking surface. The new findings of the effects of skin friction and heat transfer coefficient on different nanoparticles and nanoparticle volume fraction were discussed. Since there are dual solutions in the flow characteristics, we carry out a stability analysis to verify which solution is in a stable state and can be realized physically.
1. Introduction
The applications of nanofluid are numerous, including heat exchanges, automotive cooling applications, electronic cooling and in nano drug delivery. The significance of nanofluid is to enhance the thermal conductivity due to their nanometer size ( volume fraction). Based on previous works (see [1,2,3]) copper nanofluid has a higher thermal conductivity compared to alumina and titania. Instead of studying the boundary layer flow in a linear surface, Bhattacharyya [4] introduced the boundary layer flow in a nonlinear surface by proposed the similarity variables in exponential form. Many works on exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet were studied by considering the flow in the cylinder case, some effects (MHD and radiation) and also in other fluids (viscous and nanofluid) [5,6,7,8]. The occurrence of thermophoretic particle deposition in Casson nanofluid [9] and the effect of activation energy on the chemically reactive non-Newtonian nanofluid [10] are among the latest studies in nanofluid. Apart from that, the influence of thermal radiation, porous materials and chemical reaction in bio-convective flow of a magnetohydrodynamic Williamson nanoliquid over an inclined convectively heated stretchy plate was discussed in [11]. Studies on magnetohydrodynamics of natural convection in alumina water nanofluid and carbon nanotube nanofluid were performed by Benos and Sarris [12] and Benos et al. [13], respectively.
The applications of exponential variations in industrial processes can be found in annealing and thinning of copper wire, whereby the final product depends on the heat transfer rate at the stretching continuous surface and temperature distribution. Some relevant research on exponential surface immersed in various fluid has been carried out, such as in hybrid nanofluid, magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid and also micropolar nanofluid, see [14,15,16].
By obeying the no-slip condition at the boundary, some of the physical characteristics are not consistent into practical flow situations and hence the no-slip boundary condition is replaced by the partial slip boundary condition. Some of the investigations on partial slip can be referred to [17,18]. Recently, the study of the exponential stretching/shrinking surface in hybrid nanofluid with slip and heat generation was performed by Wahid et al. [19]. Apart from that, a study in hybrid nanofluid in the presence of slip and temperature jump effect over mixed convection flow was carried out by Khan and Rasheed [20]. The findings in [20] reveal an increment of slip parameter leads in reduction of the local skin friction coefficient, temperature and heat transfer rate. Meanwhile, a study on rotational nano liquid movement above a linearly stretching surface with the slip at the boundary was formulated by Hussain et al. [21]. There are numerous technological applications for slip at the boundary, such as the polishing of artificial heart valves and internal cavities.
The existence of dual or multiple solutions leads to performing the stability analysis in order to validate which solutions are in a stable state and are physically realizable. The pioneering of stability solutions was performed by Merkin et al. [22] and the implemented method successfully attracted interest among researchers [23,24,25]. The main objective of this paper is to extend the work by Merkin et al. [26] by considering the slip effect at the boundary immersed in copper water nanofluid while the stability analysis is performed by following Najib et al. [24].
As far as we are concerned, no such attempts have been made regarding this present study to figure out the flow behavior and heat transfer as the slip effect is present in the boundary layer of an exponentially stretching or shrinking sheet. Apart from that, we try to fill the gap caused by the lack of research that has been conducted regarding the effect of slip in exponential problem. Therefore, the governing equations, numerical analysis and figures have been introduced, analyzed and indicated in the next section.
2. Mathematical Modeling
Flow and heat transfer over an exponentially stretching/shrinking cylinder with radius R immersed in nanofluid of constant temperature , see Figure 1. The nanoparticles are assumed to have a uniform shape and size. Apart from that, it is assumed that both fluid phase and nanoparticles are in a state of thermal equilibrium and they flow at the same velocity. The thermophysical properties of the nanofluid are assumed to be constant except for the density variation in the buoyancy force, which is based on the Boussinesq approximation (see Tiwari and Das [27]).
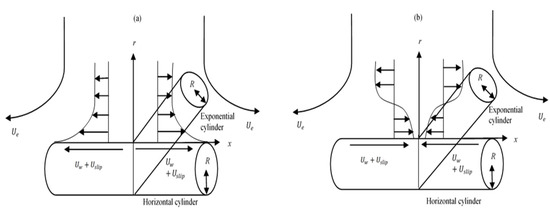
Figure 1.
Physical model and coordinate system of (a) stretching cylinder and (b) shrinking cylinder.
The free stream and stretching/shrinking velocity are assumed in the form and , respectively, where is stretching and is the shrinking constant, x is the cylinder coordinate and L is the characteristics length. The governing equations represent the mathematical model of the study, consisting of a continuity equation, a momentum equation and an energy equation together with the boundary condition. These mentioned equations were derived from the Navier–Stokes equations, (see Tiwari and Das [27]).
Hence, the governing equations are (see Bachok et al. [18] and Najib et al. [24])
where coordinates measured along the surface of the cylinder, x and in the radial direction, R correspond to velocity components and . T is the temperature in the boundary layer, is the kinematic viscosity coefficient and α is the thermal diffusivity. The initial and far field conditions are
is the effective thermal diffusivity of the nanofluid, is the dynamic viscosity of the nanofluid and is the density of the nanofluid, which are given in the table by Oztop and Abu-Nada [1].
The physical characteristics of the nanofluid are given by
where is the nanoparticle volume fraction, is the effective thermal conductivity of the nanofluid and is the specific heat at a constant pressure.
3. Steady-State Case
The exponential similarity variables of Equations (1)–(3), subject to initial and far field conditions (4), are
where η is the similarity variable, ψ is the stream function defined as and , which identically satisfies Equation (1). By defining η in this form, the boundary conditions at reduce to the boundary conditions at , which is more convenient for numerical computations. By using exponential similarity variables (6), the partial differential Equations (2)–(4) are reduced into ordinary differential equations as follows.
Then, the corresponding boundary conditions (4) become
Primes in the above equations denote differentiation with respect to η. refer to the Prandtl number and refers to the stretching/shrinking parameter. The dimensionless slip parameter, and the dimensionless curvature parameter,
where corresponding to stretching velocity and corresponding to shrinking velocity. The physical quantities of practical interest are the local skin friction coefficients and the local Nusselt number which are defined as
where is the skin friction or the shear stresses on the stretching/shrinking sheet, and is the heat flux from the surface of the plate, which are given by
Using (6) in (11) and (12), we obtain
where is the local Reynolds number (see Rao et al. [7] and Khan et al. [8]).
4. Stability Analysis
To carry out the stability analysis of the solutions, consider the unsteady Equations (2) and (3) and the new dimensionless time variable is introduced. The use of is associated with an initial value problem and is consistent with the question of which solution will be obtained in practice (physically realizable). The new exponential similarity variables (6) become
then Equations (2) and (3) are rewritten as
subject to the initial and far field conditions
To determine the stability of the solution and satisfying the boundary-value problem (15) and (16), we write
where unknown eigenvalue parameter,. and are small relative to and . Solutions of the eigenvalue problem (15)–(17) give an infinite set of eigenvalues ; if is negative, there is an initial growth of disturbances and the flow is unstable, but when is positive, there is an initial decay and the flow is stable. Substitute (18) into (15)–(17), then obtain
subject to the initial and far field conditions
The range of possible eigenvalues can be determined by relaxing a boundary condition either on or , see Harris et al. [28]. The condition as was relaxed in the present problem. For a fixed value of , the system (19) and (20) subject to (21) were solved along with the new initial condition .
5. Results and Discussion
The systems of ordinary differential Equations (7) and (8) together with respective initial and far field conditions (9) were solved computationally using bvp4c in MATLAB software. The verification of the numerical data was achieved by comparing the results obtained by Dzulkifli et al. [29]. From the verification process, the values of are all mutually agreed with those reported by [29], refer Table 1. Therefore, the authors guaranteed that the technique and results obtained in this study are all acceptable and valid.

Table 1.
Comparison of the values of and for various when and .
The skin friction coefficient and heat transfer coefficient for some values of slip parameter , curvature parameter , different nanoparticles as well as nanoparticle volume fraction are shown graphically in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. As for slip and curvature parameters, the range taken is between 0 and 0.4 while for nanoparticle volume fraction the range is 0 to 0.2. Basically, the range of the parameters were selected by following the previous research. The results reported that only single solution is found when is greater than −1 while dual solutions is obtained when cylinder is shrunken up to critical point and no solutions exist beyond the critical point . The figures indicate that the skin friction coefficient and heat transfer rate at the surface increased with an increment of slip and curvature parameter. However obvious observation can be seen where heat transfer rate is decreasing rapidly when the cylinder is shrunk because the boundary layer becomes thick as the rate of shrinking is increased. The presences of slip and curvature parameter cause the region of dual solution to expand. Physically, the increment of the slip parameter helps to reduce the contact area of the cylinder with the fluid and hence improves the velocity and temperature boundary layer thickness. Apart from that, the increment of curvature parameter leads to enlargement of the radius of the cylinder and therefore reduces the contact area between boundary layer and fluid. So, it enhances the velocity and temperature boundary layer thickness as well. The proof of dual nature solutions in Figure 2 is displayed in Figure 6 where we depict the dual velocity and temperature profiles for various value of slip parameter. All profiles satisfy the initial and far field condition (9) at once stating that the obtained numerical results are correct. Momentum and thermal boundary layer thickness for the second solution (dash line) is always thicker than the first solution (solid line).
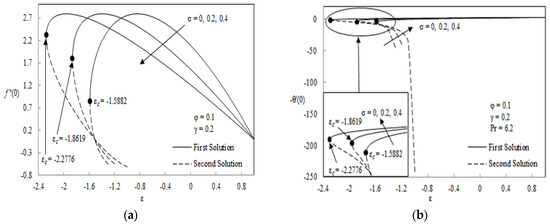
Figure 2.
Skin friction (a) and heat transfer coefficient (b) vs. for particular values of .
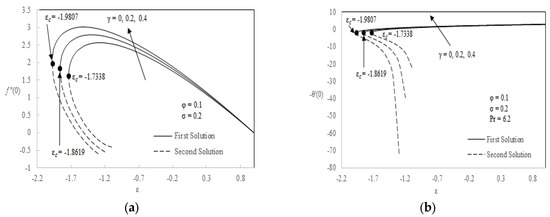
Figure 3.
Skin friction (a) and heat transfer coefficient (b) vs. for particular values of .
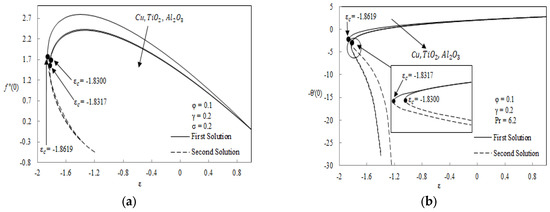
Figure 4.
Skin friction (a) and heat transfer coefficient (b) vs. for particular nanoparticles.
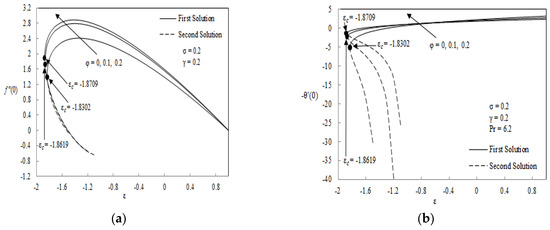
Figure 5.
Skin friction (a) and heat transfer coefficient (b) vs. for particular values of .
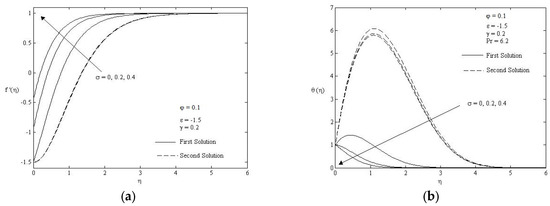
Figure 6.
Dual velocity (a) and temperature profile (b) for particular values of .
Figure 4 is plotted for different nanoparticles, namely and . According to thermophysical properties table in Oztop and Abu-Nada [1], it is obviously depicted that the thermal conductivity of is highest compared to and . Practically, this is due to Cu having a high melting point and moderate corrosion rate. This means that Cu is the most effective metal for minimalizing energy loss during heat transfer. These facts are supported by the finding in Figure 4 whereby the value of skin friction coefficient and heat transfer coefficient of is the highest among the other two nanoparticles. Besides that, the increment of the nanoparticle volume fraction caused an increase in the skin friction and heat transfer coefficient at the surface; see Figure 5. The increment of nanoparticles size enhances the collision between the particles as well as the thermal conductivity of the flow. Therefore, the velocity and the temperature of the fluid are increased, which leads to the reduction in boundary layer thickness as the size of nanoparticle increases; refer to Figure 7.
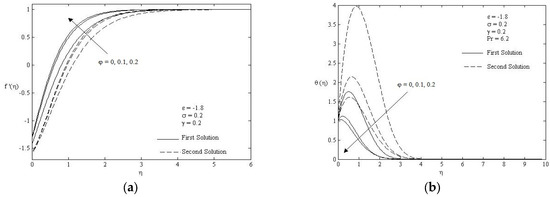
Figure 7.
Dual velocity (a) and temperature profile (b) for particular values of .
The existence of dual solutions led us to carry out a stability analysis to verify which solution is a stable solution and hence can be realized physically. The system of linear eigenvalue problems (19) and (20), along with a new boundary condition (21), was applied into the code (bvp4c) in order to get the smallest eigenvalues . The values of can be seen in Table 2, for which is approaching zero when the value of is nearer to the critical point . A positive value of corresponds to the first solution whereas a negative value of corresponds to the second solution. A negative value of indicates that there is initial growth of disturbance in the boundary layer separation and hence the solution is not stable and cannot be realized physically. On the contrary, a positive value of is expressed where there only a slight disturbance in the flow that does not interrupt the boundary layer separation, thus the first solution is stated as a stable solution and is physically realizable.

Table 2.
Smallest eigenvalues for several values of with different and for fixed .
6. Conclusions
The study considers the slip effect of flow behavior on stagnation point and heat transfer over an exponentially stretching/shrinking cylinder in nanofluid. The results reported that
- The increment of slip and curvature parameters lead to expansion in the range of the solutions.
- The skin friction coefficient decreased whereas the heat transfer coefficient increased as slip parameter increased.
- The increment of the curvature parameter caused the skin friction and heat transfer coefficient to increase.
- Cu has the highest skin friction coefficient and heat transfer coefficient.
- The larger nanoparticle volume fraction is required to increase the skin friction and heat transfer coefficient.
- The first solution is stated as a stable solution and is physically realizable, whereas the second solution is not.
7. Future Directions
The present study only focuses on the effect of slip parameter in stagnation point flow filled with nanofluid. Hence, it is worth mentioning that the following problems could be studied in the future.
- Constructing the mathematical model in different type of fluid such as hybrid nanofluid, micropolar fluid, etc.
- Constructing the mathematical model in an unsteady case when time variable is taken into consideration.
- Adding some other effects such as MHD, thermal radiation and viscous dissipation.
Author Contributions
N.N. and N.B. conceived and designed the research. N.N. performed the results. N.N. and N.B. analyzed the results. N.N., N.B., N.F.D. and I.P. contributed to the interpretation of the results. N.N. and N.B. wrote the manuscript and the Methods, while N.N., N.B., N.F.D. and I.P. contributed to the revisions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia (grant number 2022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
An express thankfulness to the Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia for the financial support. The authors also would like to thank the reviewers for their very good comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| Roman Letters | |||
| constant | Radius of cylinder | ||
| Alumina | Reynolds number | ||
| Stretching/shrinking constant | Local Reynolds number | ||
| Skin friction coefficient | Time | ||
| Specific heat at constant temperature | Constant fluid temperature | ||
| Copper | Fluid temperature of the ambient fluid | ||
| Heat capacitance of the nanofluid | Constant temperature rate | ||
| Thermal conductivity | Titania | ||
| Thermal conductivity of the nanofluid | axes | ||
| Characteristics length | Free stream velocity | ||
| Nusselt number | Stretching/shrinking velocity | ||
| Pr | Prandtl number | Slip velocity at the boundary | |
| Heat flux from the surface of the plate | Cartesian coordinate | ||
| Greek Symbols | |||
| Effective thermal diffusivity of the nanofluid | Dimensionless curvature parameter | ||
| Similarity variable | Dimensionless slip parameter | ||
| Stream function | Dimensionless time variable | ||
| Nanoparticle volume fraction | Skin friction or the shear stresses | ||
| Dimensionless temperature | Effective thermal conductivity of the nanofluid | ||
| Stretching/shrinking parameter | Dynamic viscosity of the nanofluid | ||
| Critical point of stretching/shrinking parameter | Kinematic viscosity coefficient | ||
| Eigenvalue parameter | Density of the nanofluid | ||
References
- Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulochana, C.; Sandeep, N. Stagnation point flow and heat transfer behavior of Cu–water nanofluid towards horizontal and exponentially stretching/shrinking cylinders. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleng, N.L.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet: Copper-Water. Math Comp. Meth. Sci Tech. 2014, 21, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, K. Boundary layer flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2011, 28, 074701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, N.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Ishak, A. Boundary layer stagnation point flow and heat transfer past a permeable exponentially shrinking cylinder. Int. J. Math. Models Meth. Appl. Sci. 2014, 8, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, S.; Singh, S.; Chaudhary, S. Thermal radation effects on MHD boundary layer flow over an exponentially stretching surface. Appl. Math. 2015, 6, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.A.; Vasumathi, G.; Mounica, J. Joule heating and thermal radiation effects on MHD boundary layer flow of a nanofluid over an exponentially stretching sheet in a porous medium. World J. Mech. 2015, 5, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.A.; Mustafa, M.; Hayat, T.; Sheikholesiami, M.; Alsaedi, A. Three-dimensional flow of nanofluid induced by an exponentially stretching sheet: An application to solar energy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankaralingappa, B.M.; Madhukesh, J.K.; Sarris, I.E.; Gireesha, B.J.; Prasannakumara, B.C. Influence of Thermophoretic Particle Deposition on the 3D Flow of Sodium Alginate-Based Casson Nanofluid over a Stretching Sheet. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punith Gowda, R.J.; Naveen Kumar, R.; Jyothi, A.M.; Prasannakumara, B.C.; Sarris, I.E. Impact of Binary Chemical Reaction and Activation Energy on Heat and Mass Transfer of Marangoni Driven Boundary Layer Flow of a Non-Newtonian Nanofluid. Processes 2021, 9, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, T.A.; Mabood, F.; Prasannakumara, B.C.; Sarris, I.E. Magneto-Bioconvection Flow of Williamson Nanofluid over an Inclined Plate with Gyrotactic Microorganisms and Entropy Generation. Fluids 2021, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, L.T.; Sarris, I.E. The interfacial nanolayer role on magnetohydrodynamic natural convection of an Al2O3-water nanofluid. Heat Transf. Eng. 2021, 42, 89–105. [Google Scholar]
- Benos, L.T.; Karvelas, E.G.; Sarris, I.E. Crucial effect of aggregations in CNT-water nanofluid magnetohydrodynamic natural convection. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2019, 11, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Mixed convection flow over an exponentially stretching/shrinking vertical surface in hybrid nanofluid. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Hussain, A.; Hassan, A.; Haider, Q.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Alqurashi, M.S.; Almaliki, A.H.; Abdussattar, A. Thermophoresis and Brownian Effect for Chemically Reacting Magneto-Hydrodynamic Nanofluid Flow across an Exponentially Stretching Sheet. Energies 2022, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, M.A.; Saaban, A. MHD micropolar nanofluid over an exponentially stretching/shrinking surface: Triple solution. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2019, 56, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Mat, N.A.A.; Arifin, N.M.; Nazar, R.; Bachok, N. Boundary layer stagnation point slip flow and heat transfer towards a shrinking/stretching cylinder over a permeable surface. Appl. Math. 2015, 6, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bachok, N.; Najib, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Senu, N. Stability of dual solutions in boundary layer flow and heat transfer on a moving plate in a copper-water nanofluid with slip effect. WSEAS Trans. Fluid Mech. 2016, 11, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wahid, N.S.; Arifin, N.M.; Khashi’ie, N.S.; Pop, I. Hybrid Nanofluid Slip Flow over an Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Permeable Sheet with Heat Generation. Mathematics 2021, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Rasheed, A. Slip velocity and temperature jump effects on molybdenum disulfide MoS2 and silicon oxide SiO2 hybrid nanofluid near irregular 3D surface. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Arshad, M.; Hassan, A.; Rehman, A.; Ahmad, H.; Baili, J.; Gia, T.N. Heat transport investigation of engine oil based rotating nanomaterial liquid flow in the existence of partial slip effect. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. J. Eng. Math. 1985, 20, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.S.; Arifin, N.M.; Bachok, N.; Mahiddin, N. Stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet: A stability analysis. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1739, 20023. [Google Scholar]
- Najib, N.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M. Stability of dual solutions in boundary layer flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking cylinder. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, N.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Senu, N. Boundary layer flow and heat transfer of nanofluids over a moving plate with partial slip and thermal convective boundary condition: Stability analysis. Int. J. Mech. 2017, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Merkin, J.H.; Najib, N.; Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially stretching/shrinking cylinder. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.J.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed Convection Boundary-Layer Flow Near the Stagnation Point on a Vertical Surface in a Porous Medium: Brinkman Model with Slip. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzulkifli, N.F.; Bachok, N.; Pop, I.; Yacob, N.A.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H. Unsteady stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponential stretching sheet in copper-water nanofluid with slip velocity effect. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1132, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).