Impact of Post-Translational Modifications of Crop Proteins under Abiotic Stress
Abstract
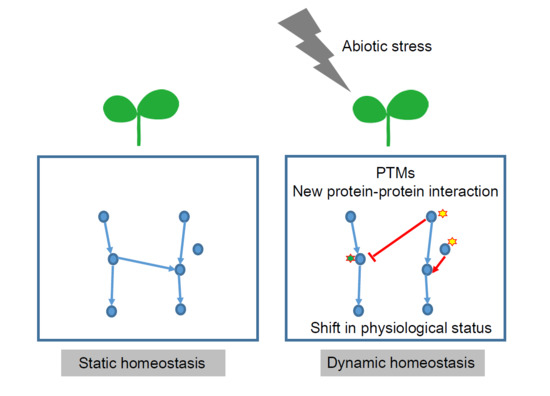
:1. Introduction
2. Techniques for Detection of Post-Translational Modifications in Crops
2.1. Difference Gel Electrophoresis and Gel-Free Approaches
2.2. Lectin Blot
2.3. Enrichment of Post-Translational Modifications
3. Systems for Post-Translational Modifications in Crops under Abiotic Stress
3.1. Phosphorylation
3.2. Glycosylation
3.3. Acetylation
3.4. Succinylation
3.5. Other PTMs
4. Post-Translational Modifications of Crop-Proteins
4.1. Histone
4.2. Tubulin
5. Post-Translational Modifications of Soybean Proteins under Flooding Stress
5.1. Phosphorylation in Nucleus
5.2. Glycosylation in Endoplasmic Reticulum
5.3. Ubiquitination in Cytosol
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mittler, R. Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizumi, T.; Luo, J.J.; Challinor, A.J.; Sakurai, G.; Yokozawa, M.; Sakuma, H.; Brown, M.E.; Yamagata, T. Impacts of El Niño Southern Oscillation on the global yields of major crops. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Ravindran, P.; Kumar, P.P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, L.; Zhao, F.; Li, R.; Xiao, H. Cross-talk modulation between ABA and ethylene by transcription factor SlZFP2 during fruit development and ripening in tomato. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Komatsu, S. Quantitative proteomics of nuclear phosphoproteins in the root tip of soybean during the initial stages of flooding stress. J. Proteom. 2015, 119, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagawa, Y.; Komatsu, S. Ubiquitin/proteasome-mediated proteolysis is involved in the response to flooding stress in soybean roots, independent of oxygen limitation. Plant Sci. 2012, 185–186, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Peng, X.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.L. A comprehensive catalog of the lysine-acetylation targets in rice (Oryza sativa) based on proteomic analyses. J. Proteom. 2016, 138, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Food Organization. Expert Paper: How to Feed the World in 2050; World Food Organization: Roma, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fita, A.; Rodríguez-Burruezo, A.; Boscaiu, M.; Prohens, J.; Vicente, O. Breeding and domesticating crops adapted to drought and salinity: A new paradigm for increasing food production. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, K.; Saito, T.; Ohyanagi, H.; Okumura, J.; Ishige, K.; Suzuki, H.; Nakamura, T.; Komatsu, S. Loss of variation of state detected in soybean metabolic and human myelomonocytic leukaemia cell transcriptional networks under external stimuli. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.J.; Retkute, R.; Preston, S.P.; Jensen, O.E.; Pound, M.P.; Pridmore, T.P.; Murchie, E.H. The 4-dimensional plant: Effects of wind-induced canopy movement on light fluctuations and photosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, K.J.; Miklavcic, S.J. Modeling root zone effects on preferred pathways for the passive transport of ions and water in plant roots. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, Y.; Hirakawa, H.; Ueno, M.; Matsui, K.; Katsube-Tanaka, T.; Yang, S.J.; Aii, J.; Sato, S.; Mori, M. Assembly of the draft genome of buckwheat and its applications in identifying agronomically useful genes. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, O.; Trösch, J.; Fenske, R.; Taylor, N.L.; Milla, A.H. Mapping the Triticum aestivum proteome. Plant J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, N.; Nanjo, Y.; Sawada, H.; Kohno, Y.; Komatsu, S. Ozone stress-induced proteomic changes in leaf total soluble and chloroplast proteins of soybean reveal that carbon allocation is involved in adaptation in the early developmental stage. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2605–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.; Cho, M.H.; Hahn, B.S.; Lim, H.; Kwon, Y.K.; Hahn, T.R.; Bhoo, S.H. Proteomic identification of rhythmic proteins in rice seedlings. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Murphy, T.B.; Watson, R.W. digeR: A graphical user interface R package for analyzing 2D-DIGE data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3033–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.S.; Richard, N.; Dias, J.P.; Rodrigues, P.M. Data visualization and feature selection methods in gel-based proteomics. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colignon, B.; Raes, M.; Dieu, M.; Delaive, E.; Mauro, S. Evaluation of three-dimensional gel electrophoresis to improve quantitative profiling of complex proteomes. Proteomics 2013, 13, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Tougou, M.; Nanjo, Y. Proteomic Techniques and Management of Flooding Tolerance in Soybean. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3768–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matros, A.; Kaspar, S.; Witzel, K.; Mock, H.P. Recent progress in liquid chromatography-based separation and label-free quantitative plant proteomics. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthes, A.; Köhl, K.; Schulze, W.X. SILAC and alternatives in studying cellular proteomes of plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1188, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schütz, W.; Hausmann, N.; Krug, K.; Hampp, R.; Macek, B. Extending SILAC to proteomics of plant cell lines. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, A.M.; Agudelo-Romero, P.; Silva, M.S.; Ali, K.; Sousa, L.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Grimplet, J.; Martinez-Zapater, J.M.; Verpoorte, R.; et al. Transcript and metabolite analysis in Trincadeira cultivar reveals novel information regarding the dynamics of grape ripening. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Tai, F.; Li, C.; Hu, X. The difference of physiological and proteomic changes in maize leaves adaptation to drought, heat, and combined both stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar-Schoenefeld, S.; Merx, K.; Jozefowicz, A.M.; Hartmann, A.; Seiffert, U.; Weschke, W.; Matros, A.; Mock, H.P. Label-free proteome profiling reveals developmental-dependent patterns in young barley grains. J. Proteom. 2016, 143, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minogue, C.E.; Hebert, A.S.; Rensvold, J.W.; Westphall, M.S.; Pagliarini, D.J.; Coon, J.J. Multiplexed quantification for data-independent acquisition. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2570–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Han, C.; Nanjo, Y.; Altaf-Un-Nahar, M.; Wang, K.; He, D.; Yang, P. Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis of abscisic acid effect in early-stage soybean under flooding. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 4769–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Oh, M.; Sakata, K.; Komatsu, S. Gel-free/label-free proteomic analysis of root tip of soybean over time under flooding and drought stresses. J. Proteom. 2016, 130, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Komatsu, S. Gel-free/label-free proteomic analysis of endoplasmic reticulum proteins in soybean root tips under flooding and drought stresses. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2211–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Henquet, M.G.; Mentink, R.A.; van Dijk, A.J.; Cordewener, J.H.; Bosch, D.; America, A.H.; van der Krol, A.R. N-glycoproteomics in plants: Perspectives and challenges. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-May, E.; Kim, S.J.; Brandizzi, F.; Rose, J.K. The secreted plant N-glycoproteome and associated secretory pathways. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madera, M.; Mann, B.; Mechref, Y.; Novotny, M.V. Efficacy of glycoprotein enrichment by microscale lectin affinity chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 2722–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuno, A.; Uchiyama, N.; Koseki-Kuno, S.; Ebe, Y.; Takashima, S.; Yamada, M.; Hirabayashi, J. Evanescent-field fluorescence-assisted lectin microarray: A new strategy for glycan profiling. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateno, H.; Onuma, Y.; Ito, Y.; Hiemori, K.; Aiki, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Higuchi, K.; Fukuda, M.; Warashina, M.; Honda, S.; et al. A medium hyperglycosylated podocalyxin enables noninvasive and quantitative detection of tumorigenic human pluripotent stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yin, X.; Sakata, K.; Yang, P.; Komatsu, S. Proteomic analysis of phosphoproteins in the rice nucleus during the early stage of seed germination. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2884–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batalha, I.L.; Lowe, C.R.; Roque, A.C. Platforms for enrichment of phosphorylated proteins and peptides in proteomics. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thingholm, T.E.; Jensen, O.N.; Robinson, P.J.; Larsen, M.R. SIMAC (sequential elution from IMAC), a phosphoproteomics strategy for the rapid separation of monophosphorylated from multiply phosphorylated peptides. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2008, 7, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallamilli, B.R.; Edelmann, M.J.; Zhong, X.; Tan, F.; Mujahid, H.; Zhang, J.; Nanduri, B.; Peng, Z. Global analysis of lysine acetylation suggests the involvement of protein acetylation in diverse biological processes in rice (Oryza sativa). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalá, C.; Howe, K.J.; Hucko, S.; Rose, J.K.; Thannhauser, T.W. Towards characterization of the glycoproteome of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit using Concanavalin A lectin affinity chromatography and LC-MALDI-MS/MS analysis. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Kang, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.L. Comprehensive profiling of the rice ubiquitome reveals the significance of lysine ubiquitination in young leaves. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camejo, D.; Romero-Puertas Mdel, C.; Rodríguez-Serrano, M.; Sandalio, L.M.; Lázaro, J.J.; Jiménez, A.; Sevilla, F. Salinity-induced changes in S-nitrosylation of pea mitochondrial proteins. J. Proteom. 2013, 79, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.I.; Uhrigshardt, H.; O’Meally, R.N.; Cole, R.N.; van Eyk, J.E. Identification and quantification of S-nitrosylation by cysteine reactive tandem mass tag switch assay. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.K.; Rao, S.; Mishra, L.K.; Sharma, M.; Pandey, G.K. Plant stress responses mediated by CBL-CIPK phosphorylation network. Enzymes 2016, 40, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.W.; Zhu, G.R.; Zhu, D.; Bian, Y.W.; Liang, X.N.; Cheng, Z.W.; Deng, X.; Yan, Y.M. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic analysis reveals the response and defense mechanism in leaves of diploid wheat T. monococcum under salt stress and recovery. J. Proteom. 2016, 143, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zörb, C.; Schmitt, S.; Mühling, K.H. Proteomic changes in maize roots after short-term adjustment to saline growth conditions. Proteomics 2010, 10, 4441–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Li, J.; Koh, J.; Dufresne, C.; Yang, N.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Duong, B.V.; Chen, S.; Li, H. Quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics of sugar beet monosomic addition line M14 in response to salt stress. J. Proteom. 2016, 143, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Lv, D.; Ge, P.; Bian, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Yan, Y. Phosphoproteome analysis reveals new drought response and defense mechanisms of seedling leaves in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Proteom. 2014, 109, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Subba, P.; Gayali, S.; Barua, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, N. Nuclear phosphoproteome of developing chickpea seedlings (Cicer arietinum L.) and protein-kinase interaction network. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Q.; Gao, Z.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Mei, Y.C.; Zhao, B.G.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.B.; Wang, B.C. The proteome and phosphoproteome of maize pollen uncovers fertility candidate proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yue, H.; Feng, K.; Deng, P.; Song, W.; Nie, X. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expressional profiles of mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) gene family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genom. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Pan, S. Maize protein phosphatase gene family: Identification and molecular characterization. BMC Genom. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Giri, J.; Kapoor, S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Pandey, G.K. Protein phosphatase complement in rice: Genome-wide identification and transcriptional analysis under abiotic stress conditions and reproductive development. BMC Genom. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fordham-Skelton, A.P.; Chilley, P.; Lumbreras, V.; Reignoux, S.; Fenton, T.R.; Dahm, C.C.; Pages, M.; Gatehouse, J.A. A novel higher plant protein tyrosine phosphatase interacts with SNF1-related protein kinases via a KIS (kinase interaction sequence) domain. Plant J. 2002, 29, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Myo, T.; Ma, W.; Lan, D.; Qi, T.; Guo, J.; Song, P.; Guo, J.; Kang, Z. TaTypA, a ribosome-binding GTPase protein, positively regulates wheat resistance to the stripe rustfungus. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, P.; Wang, P.; Su, J.; Lai, H.; Li, S.; Feng, D.; Wang, J.; et al. OsPFA-DSP1, a rice protein tyrosine phosphatase, negatively regulates drought stress responses in transgenic tobacco and rice plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocal-Lobo, M.; Ibañez, C.; Acebo, P.; Ramos, A.; Perez-Solis, E.; Collada, C.; Casado, R.; Aragoncillo, C.; Allona, I. Identification of a homolog of Arabidopsis DSP4 (SEX4) in chestnut: Its induction and accumulation in stem amyloplasts during winter or in response to the cold. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakagami, H.; Sugiyama, N.; Mochida, K.; Daudi, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Toyoda, T.; Ishihama, Y.; Shirasu, K. Large-scale comparative phosphoproteomics identifies conserved phosphorylation sites in plants. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimsrud, P.A.; den Os, D.; Wenger, C.D.; Swaney, D.L.; Schwartz, D.; Sussman, M.R.; Ané, J.M.; Coon, J.J. Large-scale phosphoprotein analysis in Medicago truncatula roots provides insight into in vivo kinase activity in legumes. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieśla, A.; Mituła, F.; Misztal, L.; Fedorowicz-Strońska, O.; Janicka, S.; Tajdel-Zielińska, M.; Marczak, M.; Janicki, M.; Ludwików, A.; Sadowski, J. A role for barley calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK2a in the response to drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, B.J.; Yu, X.X.; Wang, D.; Zu, S.H.; Xue, H.W.; Lin, W.H. Functional characterization of GmBZL2 (AtBZR1 like gene) reveals the conserved BR signaling regulation in Glycine max. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.B. Beyond lectins: The calnexin/calreticulin chaperone system of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, P.A.; Carpinetti, P.A.; Freitas, P.P.; Santos, E.G.; Camargos, L.F.; Oliveira, I.H.; Silva, J.C.; Carvalho, H.H.; Dal-Bianco, M.; Soares-Ramos, J.R.; et al. Functional and regulatory conservation of the soybean ER stress-induced DCD/NRP-mediated cell death signaling in plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Liu, X.X.; Yang, W.W.; Zhao, C.M.; Liu, J. Enhanced salt tolerance in tomato plants constitutively expressing heat-shock protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schussler, E.E.; Longstreth, D.J. Changes in cell structure during the formation of root aerenchyma in SAGITTARIA LANCIFOLIA (Alismataceae). Am. J. Bot. 2000, 87, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, S.; Matsuda, S.; Funabiki, A.; Furukawa, J.; Yamauchi, T.; Tokuji, Y.; Nakazono, M.; Shinohara, Y.; Takamure, I.; Kato, K. The rice RCN11 gene encodes β1,2-xylosyltransferase and is required for plant responses to abiotic stresses and phytohormones. Plant Sci. 2015, 236, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmoko, R.; Yoo, J.Y.; Ko, K.S.; Ramasamy, N.K.; Hwang, B.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, K.J.; Oh, D.B.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. N-glycan containing a core α1,3-fucose residue is required for basipetal auxin transport and gravitropic response in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2016, 212, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mega, T. Glucose trimming of N-glycan in endoplasmic reticulum is indispensable for the growth of Raphanus sativus seedling (kaiware radish). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.R.; Tabb, D.L.; Ching, T.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Sakharov, I.Y.; Li, Q.X. Site-specific N-glycosylation characterization of windmill palm tree peroxidase using novel tools for analysis of plant glycopeptide mass spectrometry data. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2026–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, L.; Liang, W.; Mu, P.; Wang, S.; Lin, Q. Comprehensive profiling of lysine acetylproteome analysis reveals diverse functions of lysine acetylation in common wheat. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Hammond, C.L.; Swatek, K.N.; Johnston, M.L.; Thelen, J.J.; Miernyk, J.A. Initial description of the developing soybean seed protein Lys-Nε-acetylome. J. Proteom. 2014, 96, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Deschamps, T.; Hiraga, S.; Kato, M.; Chiba, M.; Hashiguchi, A.; Tougou, M.; Shimamura, S.; Yasue, H. Characterization of a novel flooding stress-responsive alcohol dehydrogenase expressed in soybean roots. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 77, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Hu, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhou, D.X. The rice NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase OsSRT1 targets preferentially to stress- and metabolism-related genes and transposable elements. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, M.; Xie, Z.; Dai, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y. Identification of lysine succinylation as a new post-translational modification. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Damaris, R.N.; Yi, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, P. Global proteome analyses of lysine acetylation and succinylation reveal the widespread involvement of both modification in metabolism in the embryo of germinating rice seed. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, S.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, G.; Cao, H.; Yuan, L.; Yan, Y. First comprehensive proteome analyses of lysine acetylation and succinylation in seedling leaves of Brachypodium distachyon L. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Wu, F. Proteome-wide identification of lysine succinylation in the proteins of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindermayr, C.; Saalbach, G.; Durner, J. Proteomic identification of S-nitrosylated proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 37, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowra, U.; Yanase, E.; Koyama, H.; Panda, S.K. Aluminium-induced excessive ROS causes cellular damage and metabolic shifts in black gram Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper. Protoplasma 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehrawat, A.; Deswal, R. Sub-proteome S-nitrosylation analysis in Brassica juncea hints at the regulation of Brassicaceae specific as well as other vital metabolic pathway(s) by nitric oxide and suggests post-translational modifications cross-talk. Nitric Oxide 2014, 43, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Liu, X.; Singh, P.; Cui, Y.; Zimmerli, L.; Wu, K. Chromatin modifications and remodeling in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; You, Q.; Pan, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, X.E.; Wu, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhang, W. Histone modifications facilitate the coexpression of bidirectional promoters in rice. BMC Genom. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, P.; Schubert, V.; Fuková, I.; Manning, J.E.; Houben, A.; Macas, J. Epigenetic histone marks of extended meta-polycentric centromeres of Lathyrus and Pisum chromosomes. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanei, M.; Pickering, R.; Fuchs, J.; Banaei Moghaddam, A.M.; Dziurlikowska, A.; Houben, A. Interspecific hybrids of Hordeum marinum ssp. marinum × H. bulbosum are mitotically stable and reveal no gross alterations in chromatin properties. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2010, 129, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahrez, W.; Arellano, M.S.; Moreno-Romero, J.; Nakamura, M.; Shu, H.; Nanni, P.; Köhler, C.; Gruissem, W.; Hennig, L. H3K36ac is anevolutionary conserved plant histone modification that marks active genes. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sanz, H.; Moreno-Romero, J.; Solís, M.T.; Köhler, C.; Risueño, M.C.; Testillano, P.S. Changes in histone methylation and acetylation during microspore reprogramming to embryogenesis occur concomitantly with BnHKMT and BnHAT expression and are associated with cell totipotency, proliferation, and differentiation in Brassica napus. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 143, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiese Cigliano, R.; Sanseverino, W.; Cremona, G.; Ercolano, M.R.; Conicella, C.; Consiglio, F.M. Genome-wide analysis of histone modifiers in tomato: Gaining an insight into their developmental roles. BMC Genom. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wen, H.; Gao, F.; Ma, N.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. Histone acetylation is involved in gibberellin-regulated sodCp gene expression in maize aleurone layers. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yan, S.; Zhao, L.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, F.; Wang, P.; Hou, H.; Li, L. Histone acetylation associated up-regulation of the cell wall related genes is involved in salt stress induced maize root swelling. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, L.; Widmer, A. Environmental heat and salt stress induce transgenerational phenotypic changes in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Virlouvet, L.; Liu, N.; Riethoven, J.J.; Fromm, M.; Avramova, Z. Dehydration stress memory genes of Zea mays; comparison with Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasteneys, G.O. Progress in understanding the role of microtubules in plant cells. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaris, R.N.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Murage, H.; Yang, P. A proteomic analysis of salt stress response in seedlings of two African rice cultivars. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Xu, H.H.; Wang, W.Q.; Li, N.; Wang, W.P.; Møller, I.M.; Song, S.Q. A proteomic analysis of rice seed germination as affected by high temperature and ABA treatment. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 154, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hara, T.; Hamada, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Takeda, S.; Hattori, T. α-tubulin is rapidly phosphorylated in response to hyperosmotic stress in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.F.; Lloyd, C.W. Gibberellic acid stabilises microtubules in maize suspension cells to cold and stimulates acetylation of α-tubulin. FEBS Lett. 1999, 443, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vignani, R.; Scali, M.; Sensi, E.; Cresti, M. Post-translational modifications of α-tubulin in Zea mays L. are highly tissue specific. Planta 2004, 218, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gzyl, J.; Chmielowska-Bąk, J.; Przymusiński, R.; Gwóźdź, E.A. Cadmium affects microtubule organization and post-translational modifications of tubulin in seedlings of soybean (Glycine max L.). Front Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Y.; Jantasuriyarat, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Tang, S.; Park, C.H.; Wang, X.; et al. The SINA E3 ligase OsDIS1 negatively regulates drought response in rice. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, S.; Pytela, J.; Hotta, T.; Kato, T.; Hamada, T.; Akamatsu, R.; Ishida, Y.; Kutsuna, N.; Hasezawa, S.; Nomura, Y.; et al. An atypical tubulin kinase mediates stress-induced microtubule depolymerization in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckett, D.M.; Lloyd, C.W. Gibberellic acid-induced microtubule reorientation in dwarf peas is accompanied by rapid modification of an α-tubulin isotype. Plant J. 1994, 5, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjo, Y.; Skultety, L.; Ashraf, Y.; Komatsu, S. Comparative proteomic analysis of early-stage soybean seedlings responses to flooding by using gel and gel-free techniques. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3989–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjo, Y.; Skultety, L.; Uváčková, L.; Klubicová, K.; Hajduch, M.; Komatsu, S. Mass spectrometry-based analysis of proteomic changes in the root tips of flooded soybean seedlings. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.W.; Nanjo, Y.; Komatsu, S. Identification of nuclear proteins in soybean under flooding stress using proteomic technique. Protein Pept. Lett. 2014, 21, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Nishimura, M.; Hajika, M.; Komatsu, S. Quantitative proteomics reveals the flooding-tolerance mechanism in mutant and abscisic acid-treated soybean. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2008–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.; Komatsu, S. Quantitative proteomics reveals the effect of protein glycosylation in soybean root under flooding stress. Front Plant Sci. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nishizawa, K.; Nanjo, Y.; Furukawa, K. Comparative proteomics analysis of differentially expressed proteins in soybean cell wall during flooding stress. Amino Acids. 2010, 39, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.N.; Komatsu, S. Proteomic analysis of soybean root including hypocotyl during recovery from drought stress. J. Proteom. 2016, 144, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilova, T.; Lukasheva, E.; Brauch, D.; Greifenhagen, U.; Paudel, G.; Tarakhovskaya, E.; Frolova, N.; Mittasch, J.; Balcke, G.U.; Tissier, A.; et al. A snapshot of the plant glycatedproteome: Structural, functional and mechanistic aspects. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7621–7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T. Physiological roles of plant post-golgi transport pathways in membrane trafficking. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.M.; Balch, W.E. Modeling general proteostasis: Proteome balance in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirhindi, G.; Mir, M.A.; Abd-Allah, E.F.; Ahmad, P.; Gucel, S. Jasmonic acid modulates the physio-biochemical attributes, antioxidant enzyme activity, and gene expression in Glycine max under nickel toxicity. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Cui, X.; Lin, S.; Gan, S.; Xing, H.; Dou, D. GmCYP82A3, a soybean cytochrome P450 family gene involved in the jasmonic acid and ethylene signaling pathway, enhances plant resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arraes, F.B.; Beneventi, M.A.; Lisei de Sa, M.E.; Paixao, J.F.; Albuquerque, E.V.; Marin, S.R.; Purgatto, E.; Nepomuceno, A.L.; Grossi-de-Sa, M.F. Implications of ethylene biosynthesis and signaling in soybean drought stress tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Sakata, K.; Komatsu, S. Phosphoproteomics reveals the effect of ethylene in soybean root under flooding stress. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 5618–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Joshi, D.; Yadav, P.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhatt, T.K. Role of ubiquitin-mediated degradation system in plant biology. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukao, T.; Yeung, E.; Bailey-Serres, J. The submergence tolerance gene SUB1A delays leaf senescence under prolonged darkness through hormonal regulation in rice. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1795–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; To, T.K.; Ishida, J.; Morosawa, T.; Kawashima, M.; Matsui, A.; Toyoda, T.; Kimura, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Seki, M. Alterations of lysine modifications on the histone H3 N-tail under drought stress conditions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hashiguchi, A.; Komatsu, S. Impact of Post-Translational Modifications of Crop Proteins under Abiotic Stress. Proteomes 2016, 4, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040042
Hashiguchi A, Komatsu S. Impact of Post-Translational Modifications of Crop Proteins under Abiotic Stress. Proteomes. 2016; 4(4):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleHashiguchi, Akiko, and Setsuko Komatsu. 2016. "Impact of Post-Translational Modifications of Crop Proteins under Abiotic Stress" Proteomes 4, no. 4: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040042
APA StyleHashiguchi, A., & Komatsu, S. (2016). Impact of Post-Translational Modifications of Crop Proteins under Abiotic Stress. Proteomes, 4(4), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes4040042