Standard Flow Multiplexed Proteomics (SFloMPro)—An Accessible Alternative to NanoFlow Based Shotgun Proteomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Cell Culture
2.2. High pH Reversed Phase Fractionation
2.3. NanoLC Separation
2.4. Standard-Flow HPLC Separation and Ionization Conditions
2.5. Mass Spectrometer Conditions
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
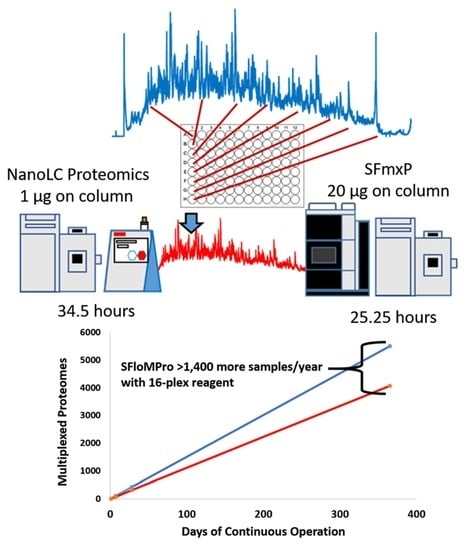
3.1. Total Instrument Acquisition Time
3.2. Peptide and Protein Identifications
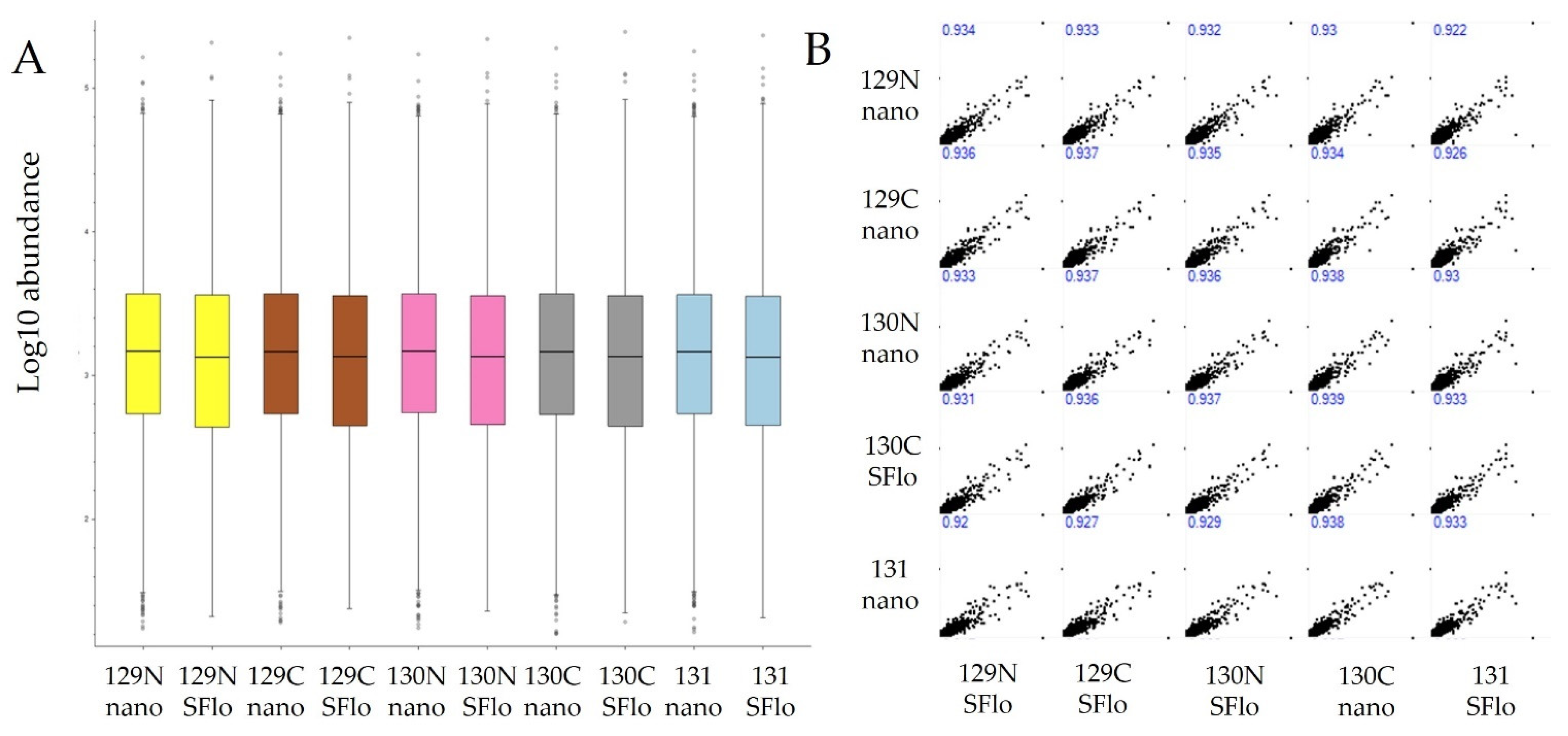
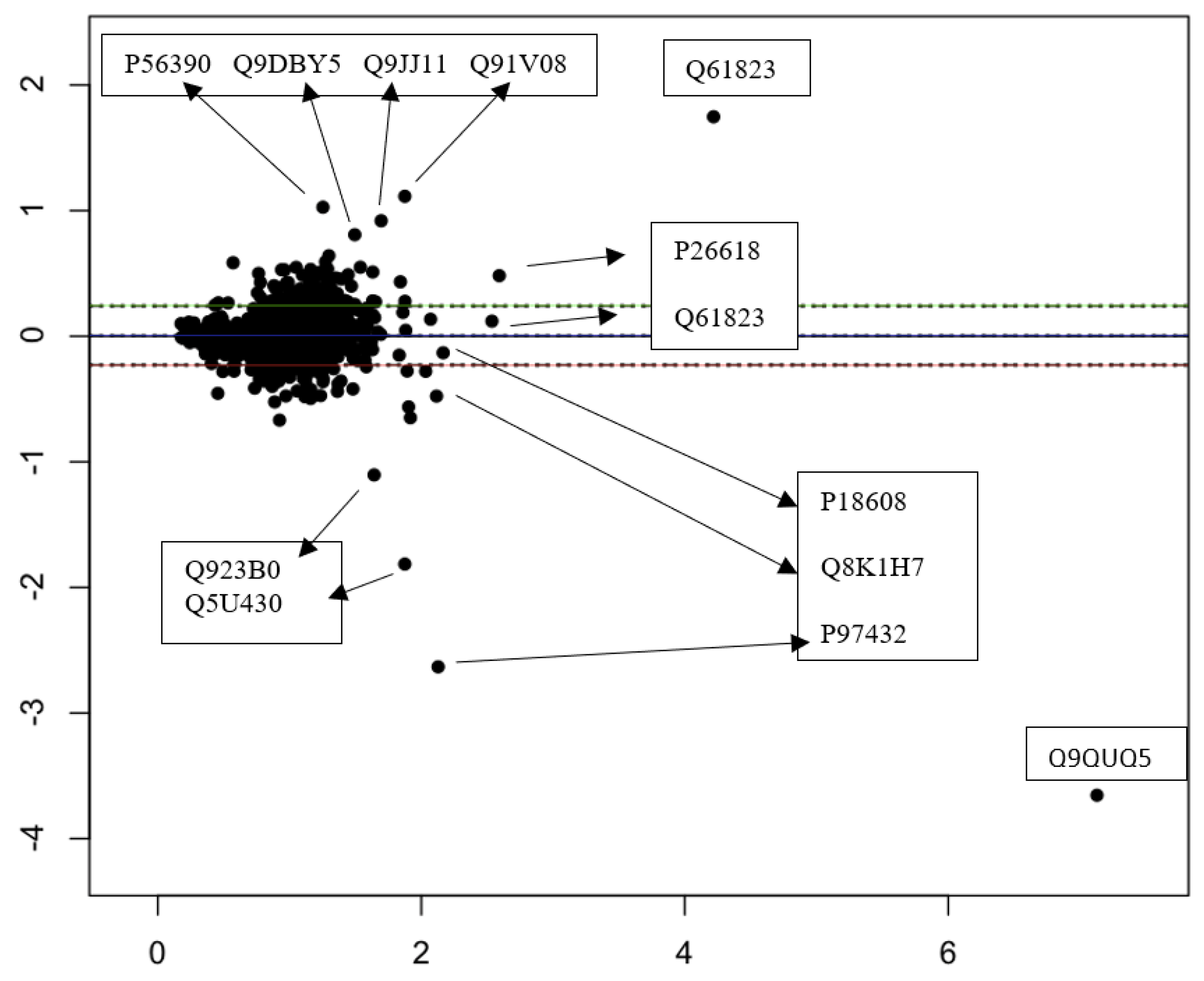
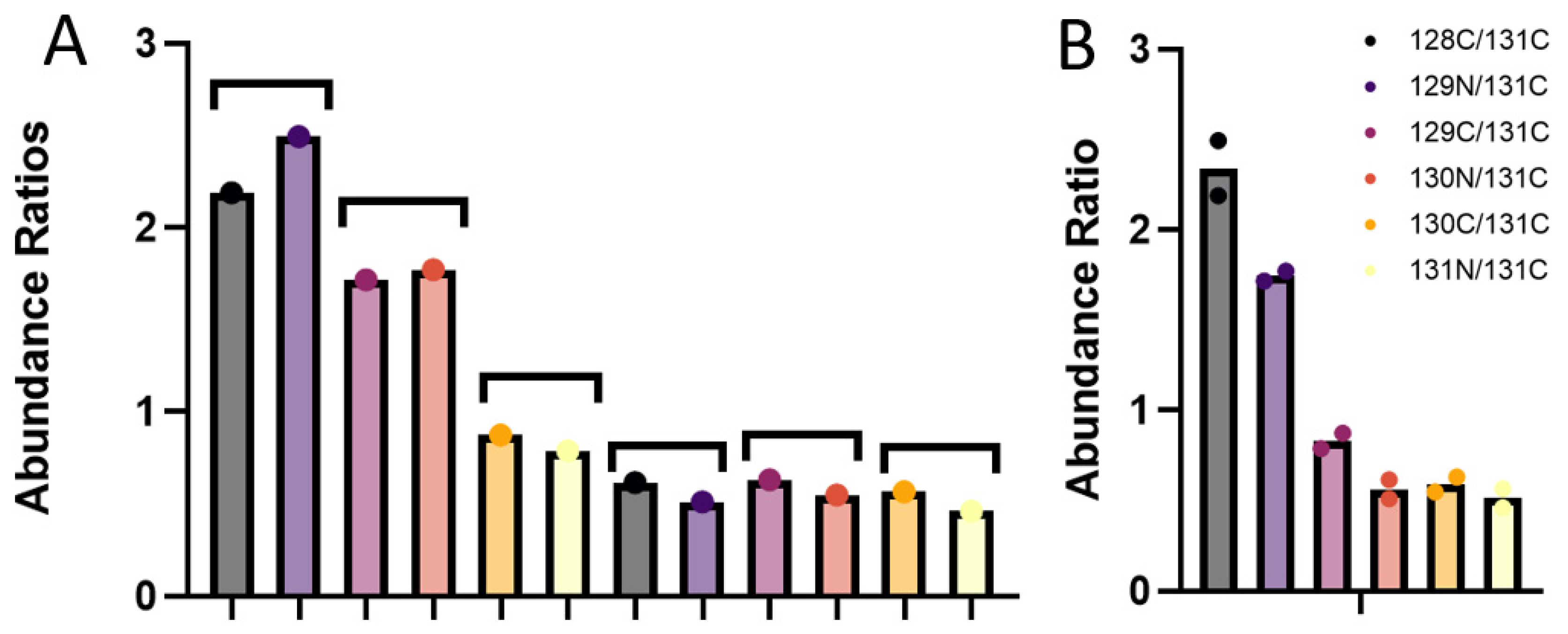
3.3. Quantitative Comparisons
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millikin, R.J.; Solntsev, S.K.; Shortreed, M.R.; Smith, L.M. Ultrafast Peptide Label-Free Quantification with FlashLFQ. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Neuhauser, N.; Michalski, A.; Scheltema, R.A.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Andromeda: A peptide search engine integrated into the MaxQuant environment. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisser, H.; Nahnsen, S.; Grossmann, J.; Nilse, L.; Quandt, A.; Brauer, H.; Sturm, M.; Kenar, E.; Kohlbacher, O.; Aebersold, R.; et al. An automated pipeline for high-throughput label-free quantitative proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 1628–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfer, V.; Pichler, P.; Stranzl, T.; Stadlmann, J.; Taus, T.; Winkler, S.; Mechtler, K. MS Amanda, a universal identification algorithm optimized for high accuracy tandem mass spectra. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3679–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fonslow, B.R.; Shan, B.; Baek, M.C.; Yates, J.R. Protein analysis by shotgun/bottom-up proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2343–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenčo, J.; Vajrychová, M.; Pimková, K.; Prokšová, M.; Benková, M.; Klimentová, J.; Tambor, V.; Soukup, O. Conventional-Flow Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Exploratory Bottom-Up Proteomic Analyses. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5381–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellors, J.S.; Gorbounov, V.; Ramsey, R.S.; Ramsey, J.M. Fully integrated glass microfluidic device for performing high-efficiency capillary electrophoresis and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6881–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, R.T.; Searle, B.C.; Llovet, A.; Villén, J. Plug-and-play analysis of the human phosphoproteome by targeted high-resolution mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Shen, S.; Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Nie, L.; Tu, C.; Wang, X.; Orsburn, B.; Wang, J.; Qu, J. An IonStar Experimental Strategy for MS1 Ion Current-Based Quantification Using Ultrahigh-Field Orbitrap: Reproducible, In-Depth, and Accurate Protein Measurement in Large Cohorts. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 2445–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammers, K.; Cole, R.N.; Tiengwe, C.; Ruczinski, I. Detecting Significant Changes in Protein Abundance. EuPA Open Proteom. 2015, 7, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarrete-Perea, J.; Yu, Q.; Gygi, S.P.; Paulo, J.A. Streamlined Tandem Mass Tag (SL-TMT) Protocol: An Efficient Strategy for Quantitative (Phospho)proteome Profiling Using Tandem Mass Tag-Synchronous Precursor Selection-MS3. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecha, J.; Satpathy, S.; Kanashova, T.; Avanessian, S.C.; Kane, M.H.; Clauser, K.R.; Mertins, P.; Carr, S.A.; Kuster, B. TMT labeling for the masses: A robust and cost-efficient, in-solution labeling approach. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, S.; Wang, X.; Orsburn, B.C.; Qu, J. How could IonStar challenge the current status quo of quantitative proteomics in large sample cohorts? Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hebert, A.S.; Westphall, M.S.; Qu, Y.; Coon, J.J.; Dovichi, N.J. Production of over 27,000 Peptide and Nearly 4400 Protein Identifications by Single-Shot Capillary-Zone Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry via Combination of a Very-Low-Electroosmosis Coated Capillary, a Third-Generation Electrokinetically-Pumped Sheath-Fl. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, R.; Li, Y.; MacCoss, M.J.; Dovichi, N.J. Capillary electrophoresis with Orbitrap-Velos mass spectrometry detection. Talanta 2012, 88, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vowinckel, J.; Zelezniak, A.; Bruderer, R.; Mülleder, M.; Reiter, L.; Ralser, M. Cost-effective generation of precise label-free quantitative proteomes in high-throughput by microLC and data-independent acquisition. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bian, Y.; Zheng, R.; Bayer, F.P.; Wong, C.; Chang, Y.C.; Meng, C.; Zolg, D.P.; Reinecke, M.; Zecha, J.; Wiechmann, S.; et al. Robust, reproducible and quantitative analysis of thousands of proteomes by micro-flow LC–MS/MS. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Niño, S.M.G.; Smith-Moritz, A.M.; Chan, L.J.G.; Adams, P.D.; Heazlewood, J.L.; Petzold, C.J. Standard flow liquid chromatography for shotgun proteomics in bioenergy research. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpen, P.B.; Hockberger, P.E.; Meyn, S.M.; Nicklin, C.; Tabarini, D.; Auger, J.A. Metrics for success: Strategies for enabling core facility performance and assessing outcomes. J. Biomol. Tech. 2016, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelstrup, C.D.; Bekker-Jensen, D.B.; Arrey, T.N.; Hogrebe, A.; Harder, A.; Olsen, J.V. Performance Evaluation of the Q Exactive HF-X for Shotgun Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bache, N.; Geyer, P.E.; Bekker-Jensen, D.B.; Hoerning, O.; Falkenby, L.; Treit, P.V.; Doll, S.; Paron, I.; Müller, J.B.; Meier, F.; et al. A novel LC system embeds analytes in pre-formed gradients for rapid, ultra-robust proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Van Beek, T.A.; Zuilhof, H.; Chen, B. Hyphenation of optimized microfluidic sample preparation with nano liquid chromatography for faster and greener alkaloid analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 797, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsburn, B.C. Proteome Discoverer—A Community Enhanced Data Processing Suite for Protein Informatics. Proteomes 2021, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, F.-X. Protein Inference by Assembling Peptides Identified from Tandem Mass Spectra. Curr. Bioinform. 2009, 4, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Costa, C.; Martínez-Bartolomé, S.; McClatchy, D.; Yates, J.R. Improving Proteomics Data Reproducibility with a Dual-Search Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1697–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayoun, K.; Gaillard, J.-C.; Pible, O.; Alpha-Bazin, B.; Armengaud, J. High-throughput proteotyping of bacterial isolates by double barrel chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on microplate paramagnetic beads and phylopeptidomics. J. Proteom. 2020, 226, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Shen, S.; Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Nie, L.; Tu, C.; Wang, X.; Poulsen, D.J.; Orsburn, B.C.; Wang, J.; et al. IonStar enables high-precision, low-missing-data proteomics quantification in large biological cohorts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4767–E4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekker-Jensen, D.B.; Martínez-Val, A.; Steigerwald, S.; Rüther, P.; Fort, K.L.; Arrey, T.N.; Harder, A.; Makarov, A.; Olsen, J.V. A compact quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometer with FAIMS interface improves proteome coverage in short LC gradients. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eliuk, S.; Makarov, A. Evolution of Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry Instrumentation. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2015, 8, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcaíno, J.A.; Deutsch, E.W.; Wang, R.; Csordas, A.; Reisinger, F.; Ríos, D.; Dianes, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Farrah, T.; Bandeira, N.; et al. ProteomeXchange provides globally coordinated proteomics data submission and dissemination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
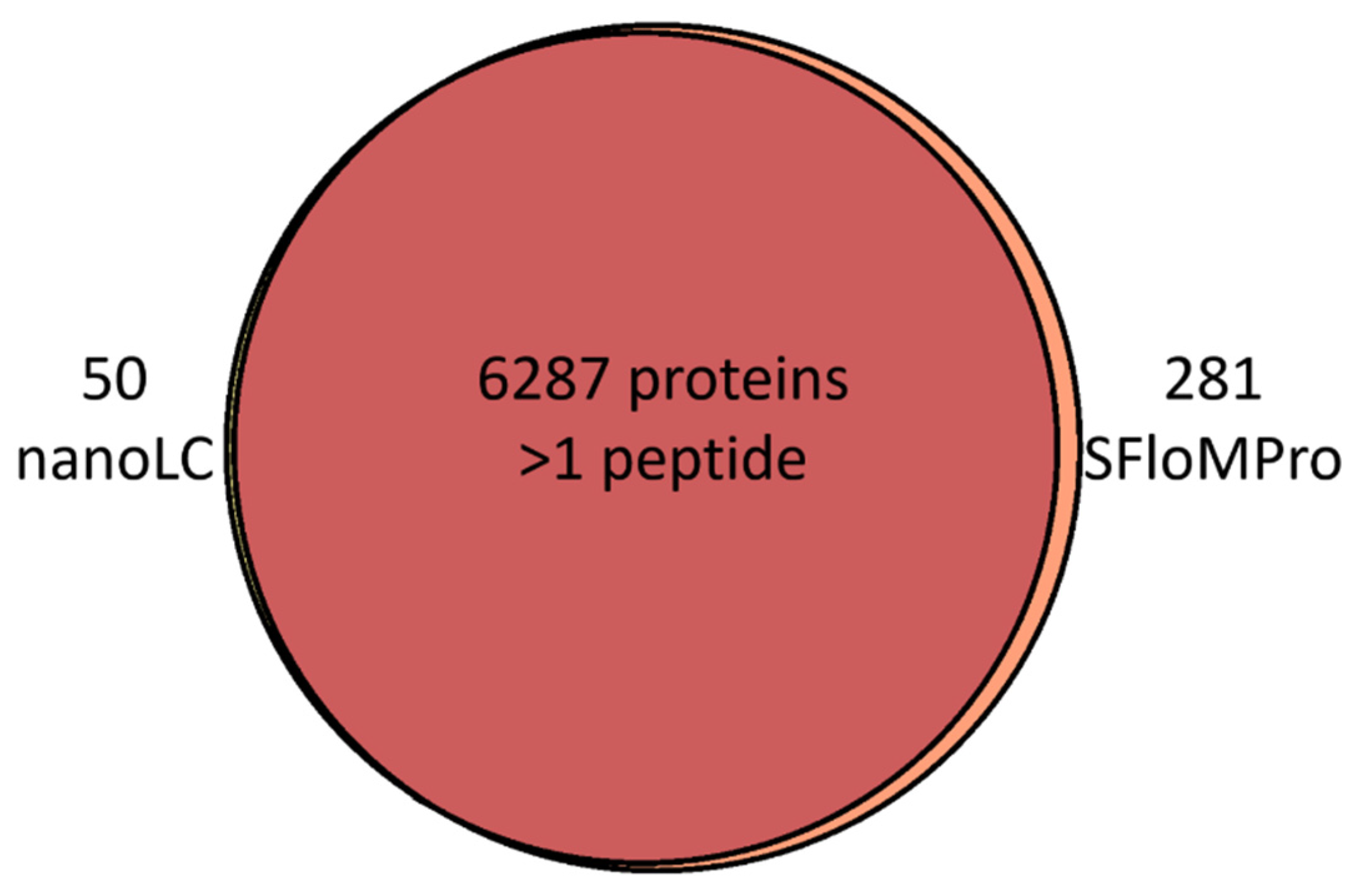
| Experiment | MS/MS Spectra | PSMs | Peptides | Proteins | Total Run Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NanoLC | 488,715 | 137,460 | 65,295 | 7685 | 34.50 |
| SFloMPro | 359,253 | 107,552 | 74,160 | 8086 | 25.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orsburn, B.C.; Miller, S.D.; Jenkins, C.J. Standard Flow Multiplexed Proteomics (SFloMPro)—An Accessible Alternative to NanoFlow Based Shotgun Proteomics. Proteomes 2022, 10, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes10010003
Orsburn BC, Miller SD, Jenkins CJ. Standard Flow Multiplexed Proteomics (SFloMPro)—An Accessible Alternative to NanoFlow Based Shotgun Proteomics. Proteomes. 2022; 10(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes10010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrsburn, Benjamin C., Sierra D. Miller, and Conor J. Jenkins. 2022. "Standard Flow Multiplexed Proteomics (SFloMPro)—An Accessible Alternative to NanoFlow Based Shotgun Proteomics" Proteomes 10, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes10010003
APA StyleOrsburn, B. C., Miller, S. D., & Jenkins, C. J. (2022). Standard Flow Multiplexed Proteomics (SFloMPro)—An Accessible Alternative to NanoFlow Based Shotgun Proteomics. Proteomes, 10(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proteomes10010003