Abstract
The application-based flipped classroom (APP-FC) is an innovative teaching-learning model that has not been applied and assessed in basic medical curricula teaching in China. The aim of this investigation is to assess students’ perceptions to the APP-based flipped classroom (APP-FC) teaching model in an immunology course. The data of this study were collected from second-year medical students (n = 92) at Lanzhou University. One class (n = 50), as a control group, was offered lecture-based learning (LBL), while the other class (n = 42), as the APP-FC group, was given lecture-based instruction and the APP-FC teaching model during September–November 2017. Afterward, the perceptions of students on APP-FC teaching model were evaluated using questionnaires. Students responded that APP-FC improves their motivation (83%) and interest in learning immunology (81%), as well as their self-directed learning skills (81%). Compared to the traditional lecture-based instruction, the APP-FC noticeably improved students’ motivation in learning (P = 0.011), self-directed learn skills (P = 0.001), memory abilities (P = 0.009), and problem-solving abilities (P = 0.010). Most medical students’ scores (60%) in the final examination were more than 80 points after implementing an APP-FC model as compared to the control group (40%). The majority of students (70%) preferred the APP-FC teaching approach over traditional lecture-based pedagogy. The implementation of the APP-FC teaching model could improve students’ learning motivation, self-directed learn skills, and problem-solving abilities, which is a preferable teaching model for medical immunology courses in China.
1. Introduction
Immunology is one of the core medical curricula that form the basis for training and developing trustworthy clinicians in China [1]. It is also one of the bridging courses and offers a transition from basic medical knowledge to clinical medicine. The traditional lecture-based instruction and rote learning is still usually used in Chinese medical education [1,2]. However, traditional lecture-based mode can be considered as a teacher-centered instruction method, which contributes to passive learning in the classroom and allows almost no time to take the proactivity to ponder, comprehend, and develop problem-solving abilities [2,3]. Moreover, traditional lecture-based teaching lacks efficiency, as previous researchers reported that the average attention span of students in a classroom is only 10 to 20 min at the beginning of the class [4,5]. Conversely, active learning modes (i.e., which engage students in their own learning and provide opportunities for students to participate) are not only supported by learning theories but have also been shown to be helpful to long-lasting learning and the development of self-directed learning skills [2,6]. Thus, the most useful methods to enhance teaching efficiency is to boost the active learning of students, which requires medical students to actively concentrate their attention on learning materials, collaborating with other classmates, and participating in the class [7,8].
Our group has studied the implementation of problem-based learning modes that promote student-centered learning, such as patient-oriented problem-solving (POPS) and case-based learning (CBL), in medical immunology [2,9]. Problem-based learning requires students to work on ‘real-life’ scenarios, and can mobilize their enthusiasm for learning medical immunology as well as enhance students’ learning motivation and problem-solving skills in clinical practice [2,9]. As the problem-based learning mode is still a new pedagogy to many higher medical schools in China, some instructors and participating scholars still have doubts about its educational profits [2,9,10]. Owing to the long-term application of lecture-based teaching mode, the resources (e.g., experienced teachers, available references, and teaching space) for problem-based learning are insufficient in China [8,11]. In particular, because of the huge population in China, there are many students who enroll in medical schools every year. For example, the number of medical students who enrolled in medical schools reached 587 thousand in 2012, and continued to increase at the rate of about 15% each year [12]. Over the past decade, the teacher-student ratio decreased from 1:8 to 1:20 as the increase of staff failed to keep pace with the increase of students [12]. In order to promote medical students’ active learning, the teaching approach of the flipped classroom has gained much attention in Chinese higher medical education. Although previous research works presented that a flipped classroom promotes students’ initiative in learning clinical medicine subjects such as electrocardiogram, pharmacology, radiology, epidemiology, stomatology, respirology, cardiology, ophthalmology, and renal physiology [8,11,12,13,14], the overall effectiveness of this method in medical education is still being debated [4,14]. Some instructors indicated that this educational method is not suitable for specific subjects, such as neuroanatomy, which are characterized by abstract and memorization-heavy content [15]. One possible reason for this is that students need to spend too much time for preparation before and after the class [15]. Therefore, it is important to assess the effectiveness of the flipped classroom each time that it is used in a new setting. Recently, we investigated the effects of flipped classroom teaching activities for Chinese medical students in an immunology course.
Information and communication technology has become a critical component of teaching and learning in higher medical education [16]. A systematic review of 14 studies showed that social media tools promoted learner engagement, feedback, collaboration, and professional development, but were hampered by variable learner participation, technical issues, and privacy/security concerns [17,18]. Mobile phone applications (APP) have similar benefits with their inherent increased accessibility and higher interactivity, and could be useful in learning basic medical curricula innovatively. In order to attempt to use a course APP for medical students, the immunology APP was developed by the Department of Immunology, Lanzhou University. Because the limitations of APPs are well-known and include issues related to technical support, the course text, picture, and PowerPoint (PPT) were able to be directly opened and browsed on the phone without internet after the APP was installed. However, the network was needed for the students watching immunology video and searching literature. This mobile immunology APP provided a basic convenient platform to better access quality educational materials for students in the flipped classroom.
As early as 1996, an “inverted classroom” was first studied by Lage et al. [19], and a “classroom flipping” teaching model was subsequently proposed and developed by Wesley Baker [3]. Recently, the teaching mode of the flipped classroom has been accepted by an increasing number of higher medical schools [20]. Van Vliet et al. found that the pedagogy of flipped-class improved students’ metacognition, critical thinking, and collaborative strategies, which are important for reaching deep learning [20]. It is important for learners to have skills in metacognition because they are used to monitor and regulate reasoning, comprehension, and problem-solving, which are fundamental outcomes of medical curricula [21,22]. The flipped classroom model provides students with opportunities for collaborative learning and concept application through active processes [23]. In the model of the flipped classroom, learners are first exposed to educational content prior to formal class sessions via readings, teaching materials, or other electronic exercises that have been formally allocated for this purpose [6]. The flipped classroom may allow students to freely select the most appropriate way to obtain knowledge and also provides the option of transferring knowledge outside the classroom [3,21,22]. In a flipped classroom, the teacher asks students to read materials prepared in advance so that they can be more interactive in higher-order activities. This teaching model translates the passive acceptance knowledge in traditional didactic lectures into self-exploration by respecting the individual characteristics of cognitive learning [3,21,22]. However, the APP-based flipped classroom (APP-FC) is an innovative teaching-learning strategy that has not been implemented in teaching basic medical curricula in China. In this research, an attempt of the APP-FC teaching approach in an immunology course was presented to Chinese clinical medicine students and the perceptions of students to the APP-FC teaching approach were subsequently assessed using questionnaires.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information of the Course
At Lanzhou University, medical immunology is a required 2.5-credit hour course for all second-year medical students during the autumn semester in each academic year. In this course, a weekly teaching schedule included 4 h of traditional didactic lectures (total 44 h). The subjects of each chapter on this course were generally instructed by the instructors through traditional lecture-based teaching models. In this study, one of the chapters in medical immunology was chosen as the learning subject to be presented through the teaching procedure according to the APP-FC model. Subsequently, teaching activities based on the APP-FC model were performed and questionnaires were conducted to evaluate students’ perceptions of the APP-FC teaching pedagogy.
2.2. Research Participants
During October–November 2017, two classes were randomly selected from 15 classes of second-year medical students in this research. A total of 92 second-year medical students were recruited in the medical immunology course of this study. One class (n = 50) was offered the traditional lecture-based learning (LBL) as a control group, while the other class (n = 42) was delivered through traditional lecture-based learning and the APP-FC model as the APP-FC group. All students were enrolled in current research with a mandatory medical immunology course. Students in the APP-FC teaching model class were briefly introduced to the study aim and procedure, without any adverse effect on the grade of the medical immunology course.
2.3. Ethical Considerations
Before the study, an approval for the present study was achieved from the institutional ethics committee and curriculum development committee at the School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, in China. In the present study, the hypothesis was that all second-year medical students would have an optimistic and active attitude towards the immunology course in response to the APP-FC instructional strategy.
2.4. Materials of Research
In order to perform the APP-based flipped classroom, it was necessary to prepare the mobile immunology course APP. This APP was developed by the Department of Immunology, Lanzhou University. The immunology learning APP was free and available in the mobile system for Android. We prepared available iPADs for some students without mobile phones. The course APP was installed on the iPAD or mobile phone to allow the students learning medical immunology to access the APP in real time. This course APP included a syllabus, course content, exercises, PPT, and video content of medical immunology. The immunology syllabus, content, exercises, and PPT were able to be directly opened and browsed on the phone without internet after the APP was installed. However, the network was needed for students watching immunology videos and searching literature.
2.5. Curriculum Design and Management
Students in the control group were conventionally offered traditional lecture-based teaching activities. The flowchart of the APP-based flipped classroom is depicted in Figure 1. After 9 weeks of traditional teaching, a trial of the APP-FC teaching model was implemented in the class of the APP-FC group, lasting a total of 4 h. Before the flipped classroom, students were divided into 10 groups (four to five students per group) and asked to finish the pre-test and read the material from the course APP or watch the video lecture online, which was expected to take approximately 1 h. Related questions were recorded by a student for each group to be discussed in the classroom. After the flipped classroom, students were asked to review their lessons with the course APP for approximately 1 h. All of students, including LBL group and APP-FC group, were asked to finish the final examination (post-test) at the end of the course.

Figure 1.
Flowchart of the APP-based flipped class structure and settings.
In the APP-based flipped classroom, the teaching activities were divided into three phases. In the first phase of the APP-FC teaching, based on the assignments and the problems collected from each group during the students’ learning, teachers tried to explain and illuminate any problems that the students had. This phase lasted approximately 20 min. The next phase was an interactive discussion and communication between the students and teachers, and students were encouraged to analyze questions. The discussion and analysis questions on the phone APP were prepared by an instructor in advance. This phase lasted approximately 80 min. In the third phase, the teacher gave a brief lecture on learning focus and emphasized the difficult aspects of this chapter. This phase lasted approximately 20 min.
2.6. Evaluation Methods
The questionnaire for the present study was referenced to the findings of previous studies [2,9]. In brief, a survey paper on the APP-FC teaching model was implemented in the APP-FC group after the end of the class. The students’ responded to YES or NO questions regarding the APP-FC teaching model. A separate questionnaire was administered to students to evaluate the capability perceptions of the APP-FC teaching model. According to the syllabus of the immunology course, each item on the questionnaire was responded to using a five-point Likert scale, ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree. Students gave a score according to their perceptions from 5 (strongly agreeing) to 1 (strongly disagree), and the total scores of students were calculated. All students completed the questionnaires anonymously to evaluate their perceptions of the APP-FC teaching model in this research.
2.7. Data Analysis
The independent samples t test was used to compare the test scores of two groups and the Pearson’s Chi-Square test was used to compare the percentages of high scores (marks ≥ 80) of the two groups. The scores of capability perception based on the APP-FC teaching model and conventional lecture-based teaching were compared using independent samples t test. All statistical analyses were performed in SPSS 19.0 for Windows software (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05. All data are reported as means ± SD.
3. Results
Out of a total of 92 medical students, there were no statistical differences in mean age, gender proportion, or final scores in anatomy, cellular biology, or histology and embryology courses between the groups in Table 1. None of the students withdrew from the classes, and all students completed the pre-test and final examination. The average scores achieved in the pre-test and final examination are shown in Figure 2. The pre-test (t = 0.78, P = 0.43) and final examination (t = 1.42, P = 0.16) scores showed that there were no statistical differences between the two groups. However, 25 students (25/42 = 60%) in the APP-FC group achieved final examination scores higher than 80 points, while this was the case for 20 students (20/50 = 40%) in the LBL control group. The high test score percentage (marks ≥ 80 points) of the APP-FC group was significantly higher than that of the LBL group (P = 0.049).

Table 1.
Baseline students characteristics (n = 92).
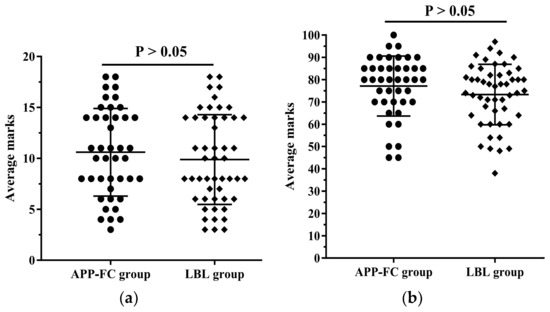
Figure 2.
Comparison of medical students average scores. (a) The average scores obtained in the pre-test (mean ± SD); (b) The average scores obtained in the final examination (mean ± SD).
Questionnaire feedback results gained from 42 medical students in the APP-FC group are shown in Table 2. Perceptions regarding the APP-FC teaching strategy included a negative response from 30% of students, and a positive response from 70% of students. Students responded that APP-FC may improve their intrinsic motivation (83%) and interest in learning immunology (81%), as well as their self-directed learning skills (81%), problem-solving skills (79%), and benefits in terms of long-term memory (74%). There were 86% students responded that they can easily browse lessons with the APP according to their own situation at any time. Furthermore, 71–74% students responded that the APP-FC teaching strategy may be feasible for the current educational environment and be worthy of promotion in China.

Table 2.
Students’ responses to the APP-FC teaching model (n = 42).
The average perception scores in the APP-FC teaching model and traditional didactic instruction were 33.05 ± 4.38 and 29.54 ± 5.33 in Table 3, respectively. Our results showed a significant difference in the capability perceptions of medical students regarding the APP-FC teaching model and lecture-based instruction (t = 3.28, P = 0.002). In particular, there were significant differences in students’ perceptions scores on learning motivation (t = 2.60, P = 0.011), self-directed learning abilities (t = 6.49, P = 0.001), problem-solving abilities (t = 2.65, P = 0.010), and recall abilities of basic knowledge (t = 2.68, P = 0.009) between APP-FC and traditional lecture-based instruction.

Table 3.
Capability perception scores based on the APP-FC teaching model and lecture-based instruction (mean ± SD) (n = 42).
4. Discussion
In a traditional lecture-based classroom, students are used to a passive, didactic lecture environment and are merely recipients of teachers’ knowledge [2]. As a consequence, the extent of students’ curiosity and motivation greatly depends on the quality of conventional teacher-centered performances. This study was firstly designed to evaluate the perceptions of second-year medical students regarding the APP-based flipped classroom (APP-FC) teaching model in an immunology course in China. The mobile devices and relevant APPs could improve the student knowledge of a subject, giving them additional resources and materials to complement their skills [24]. The mobile learning APP is a useful teaching tool that may deliver knowledge in a convenient and easy manner [16,25,26]. The previous survey results presented that medical students preferred to use mobile phone APPs in learning clinical medicine courses such as psychiatry, prosthodontics, and so on for improving their knowledge and test-taking [16,18,25,26]. Deshpande et al. found that 94% of students felt that mobile learning APPs should be regularly used along with conventional teaching methods, and represent an effective way to improve clinical reasoning skills [16,25]. In this study, 86% of students responded that they can easily browse lessons with this APP according to their own situation any time and that their workload of study was not increased during the flipped classroom stage (71%). The overall responses indicated that the APP-FC model produces significant, meaningful gains in both intrinsic motivation and overall ability.
Previous studies revealed that the teaching model of the flipped classroom notably enabled students to acquire knowledge, since the learning efficiency of the inverted classroom was more enhanced than that of the lecture-based instruction method [3,20,27]. The first documented use of the flipped classroom in teaching medical students was published in 2012 by Prober et al. [28]. Many medical instructors have since introduced elements of the flipped classroom into their teaching activities [28]. In this study, an attempt of the APP-FC teaching approach was first implemented in an immunology course in China. The results showed that 70% of students agreed that the APP-FC provides an approach of self-directed learning and helps in learning the immunology course. The APP-FC provides students with the opportunity to exchange information and discuss problems with each other. The data of this study showed that the teaching model of the APP-FC helps to strengthen students’ interest in learning immunology and improves problem-solving skills without an increase in workload, presenting a potentially desirable method of pedagogy that is feasible for the current Chinese educational environment and basic medical curricula.
Most studies reported that the flipped classroom is a powerful educational method that enhances medical students’ engagement, active learning, self-directed learn skills, and problem-solving skills [5,21,22,23,28,29,30]. The findings of the present investigation are consistent with previous research reporting on the effect of the flipped classroom for medical students in clinical medicine courses. Compared with traditional lecture-based teaching-learning, there was a significant increase of perception scores regarding the motivation of learning (P = 0.011), self-directed learn skills (P = 0.001), clinical problem-solving abilities (P = 0.010), and memory abilities (P = 0.009) with the APP-FC teaching model. The APP-FC teaching model permits medical students to discuss together in a group, search information from the internet and/or APP resources conveniently, and finally solve problems in the field of medical immunology [2,10]. Meanwhile, a meaningful difference in the final examination performance (marks ≥ 80) was observed, indicating that the APP-FC teaching model could help students in mastering immunology knowledge. The APP-FC teaching model encourages students to freely choose the most appropriate method to obtain knowledge as well as to actively acquire knowledge and independently develop solutions for problem-solving. Consequently, the introduction of the APP-FC instructional model would not only help students to obtain essential knowledge conveniently in an immunology course, but also boost their learning motivation and skills of problem-solving, which is an alternative teaching approach for immunology courses in China.
When we interpret the findings in this study, there are several limitations that must be considered. The first limitation is that we did not consider the learning styles of students, such as interactive or passive, and attitude toward the medical immunology course. The second limitation in this study is that the sample size was not large enough. Only 92 second-year medical students were involved in the study of our university. The final limitation is that the conclusions drawn from a single trial in this research may be ameliorated by more trials and a longer time study in China.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Teaching Research Project of Lanzhou University in China (2017185; 2017193; 2017197).
Author Contributions
Xingming Ma conceived and designed the research, performed experiments and made substantial contribution to the writing of the article. Yanping Luo designed the research, made substantial contribution to the writing of the article. Lifeng Zhang designed the research, analyzed the data of the article. Jingqiu Wang collected and analyzed the data of the article. Yaling Liang, Hongjuan Yu and Yufeng Wu prepared learning materials and collected the data of the article. Jiying Tan conceived and designed the research of the article. Mingqiang Cao prepared learning materials of the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Cao, M.; Wu, Y.; Tan, J.; Liang, Y. Establishment of the experimental education system of medical immunology for undergraduate students. Chin. J. Med. Educ. Res. 2016, 15, 394–396. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Y. A perceptions assessment of patient-oriented problem-solving teaching strategy for medical immunology course in Chinese students. J. Balt. Sci. Educ. 2016, 15, 706–711. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.; Xiang, L.-R.; Yue, R.-Z.; Zeng, J.; Wan, X.-H.; Zuo, C. Friend or foe? Flipped classroom for undergraduate electrocardiogram learning: A randomized controlled study. BMC Med. Educ. 2017, 17, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, L.; Yi, Z.; Chuan, C.; Wei, W.; Tingting, C.; Tao, L.; Yonghao, L.; Bingqian, L.; Yu, L.; Lin, L.; et al. Facing the challenges in ophthalmology clerkship teaching: Is flipped classroom the answer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174829. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart, J.; Rutherford, R.J. Medical student concentration during lectures. Lancet 1978, 2, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sait, M.S.; Siddiqui, Z.; Ashraf, Y. Advances in medical education and practice: Student perceptions of the flipped classroom. Adv. Med. Educ. Pract. 2017, 8, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, S.; Eddy, S.L.; McDonough, M.; Smith, M.K.; Okoroafor, N.; Jordt, H.; Wenderoth, M.P. Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8410–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zuo, C.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhou, L.; Zou, Y.; Liang, D. Comparison between flipped classroom and lecture-based classroom in ophthalmology clerkship. Med. Educ. Online 2017, 22, 1395679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H.; Cao, M. Comparison of student perception and performance between case-based learning and lecture-based learning in a clinical laboratory immunology course. J. Lab. Med. 2016, 40, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Han, J.; Guo, S.; Wu, Y. A trial of patient-oriented problem-solving system for immunology teaching in china: A comparison with dialectic lectures. BMC Med. Educ. 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Lui, A.M.; Martinelli, S.M. A systematic review of the effectiveness of flipped classrooms in medical education. Med. Educ. 2017, 51, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Meng, Q. Study on the scale and structure of health professional education in Chinas’ colleges and universities from 1998 to 2012. Chin. J. Med. Edu. Res. 2016, 15, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Tolks, D.; Schafer, C.; Raupach, T.; Kruse, L.; Sarikas, A.; Gerhardt-Szep, S.; Kllauer, G.; Lemos, M.; Fischer, M.R.; Eichner, B.; et al. An introduction to the inverted/flipped classroom model in education and advanced training in medicine and in the healthcare professions. GMS J. Med. Educ. 2016, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tune, J.D.; Sturek, M.; Basile, D.P. Flipped classroom model improves graduate student performance in cardiovascular, respiratory, and renal physiology. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2013, 37, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whillier, S.; Lystad, R.P. No differences in grades or level of satisfaction in a flipped classroom for neuroanatomy. J. Chiropr. Educ. 2015, 29, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, S.; Chahande, J.; Rathi, A. Mobile learning app: A novel method to teach clinical decision making in prosthodontics. Educ. Health (Abingdon) 2017, 30, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheston, C.C.; Flickinger, T.E.; Chisolm, M.S. Social media use in medical education: A systematic review. Acad. Med. 2013, 88, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Kolli, V. App use in psychiatric education: A medical student survey. Acad. Psychiatry 2016, 41, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lage, M.; Platt, G.; Treglia, M. Inverting the classroom: A gateway to creating an inclusive learning environment. J. Econ. Educ. 2000, 31, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van-Vliet, E.A.; Winnips, J.C.; Brouwer, N. Flipped-class pedagogy enhances student metacognition and collaborative-learning strategies in higher education but effect does not persist. CBE-Life Sci. Educ. 2015, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.S.; Castleberry, A.N.; Persky, A.M. Strategies for improving learner metacognition in health professional education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2017, 81, 78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Persky, A.M.; McLaughlin, J.E. The flipped classroom—From theory to practice in health professional education. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2017, 81, 118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.G., Jr.; Frazier, L.; Anderson, S.L.; Stanton, R.; Gillette, C.; Broedel-Zaugg, K.; Yingling, K. Comparison of pharmaceutical calculations learning outcomes achieved within a traditional lecture or flipped classroom andragogy. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2017, 81, 70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Briz-Ponce, L.; Juanes-Méndez, J.A.; García-Peñalvo, F.J.; Pereira, A. Effects of mobile learning in medical education: A counterfactual evaluation. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.W.; Tsang, T.; Cheow, E.; Ho, C.S.; Yeong, N.B.; Ho, R.C. Enabling psychiatrists to be mobile phone app developers: insights into app development methodologies. MIR mHealth uHealth 2014, 2, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeds, M.R.; Thrush, C.R.; Mizell, J.S.; Berry, K.S.; Bentley, F.R. Mobile spaced education for surgery rotation improves national board of medical examiners scores. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 201, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munson, A.; Pierce, R. Flipping content to improve student examination performance in a pharmacogenomics course. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2015, 79, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prober, C.G.; Heath, C. Lecture halls without lectures—A proposal for medical education. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1657–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, S.S.; Arain, F.M.; Enam, S.A. Flipped classroom instructional approach in undergraduate medical education. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgis, F.; Miller, J.P. Implementation of a “flipped classroom” for neurosurgery resident education. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 45, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).