Instructional Designers’ Integration of Generative Artificial Intelligence into Their Professional Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
Instructional Design and GenAI
- How have instructional designers been integrating GenAI into their professional practice since the launch of ChatGPT?
- What factors have been affecting instructional designers’ integration of GenAI into their professional practice?
2. Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Instruments
2.3.1. Demographic Survey
2.3.2. Semi-Structured Interviews
2.4. Procedures
2.4.1. Data Collection
2.4.2. Data Analysis
2.5. Trustworthiness
3. Results
3.1. Instructional Designers’ Integration of GenAI into Their Professional Practice
3.1.1. Nikki
3.1.2. Taylor
3.1.3. Elvin
3.1.4. Cameron
3.1.5. Jordan
3.1.6. Riley
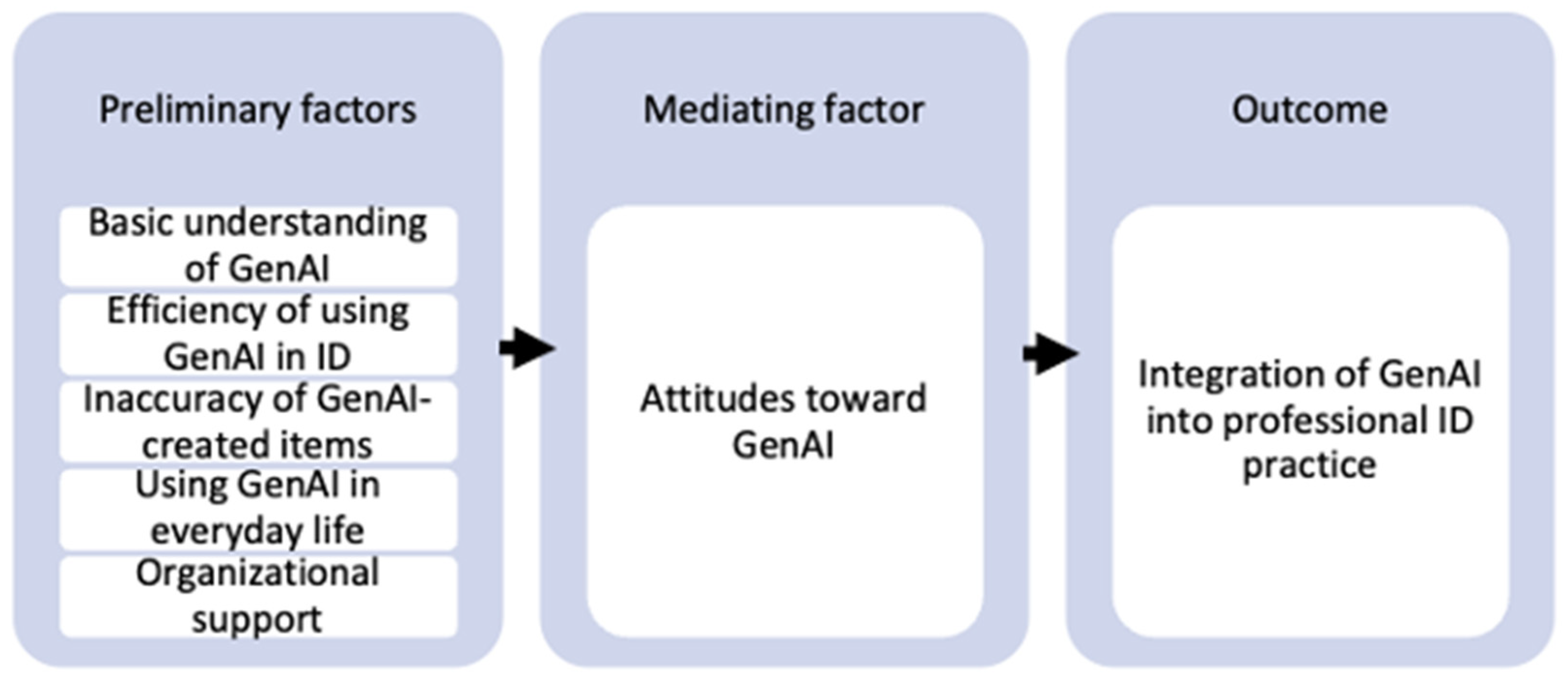
3.2. Factors Affecting Instructional Designers’ Integration of GenAI into Their Professional Practice
3.2.1. Nikki’s Attitudes
3.2.2. Taylor’s Attitudes
3.2.3. Elvin’s Attitudes
3.2.4. Cameron’s Attitudes
3.2.5. Jordan’s Attitudes
3.2.6. Riley’s Attitudes
3.3. Cross-Case Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADDIE | Analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| GenAI | Generative artificial intelligence |
| ID | Instructional design |
| IDer | Instructional designer |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
Appendix A. Demographic Survey
- Name and surname
- Age
- Gender
- Years of experience as an instructional designer
- Years of experience related to instructional design (please indicate the relationship)
- Are you currently working as an instructional designer (please indicate your current position or when you worked as an instructional designer)?
- Highest terminal degree
- Field of study in which the highest terminal degree was earned
- Contact email
Appendix B. Semi-Structured Interview Questions
- For instructional designers with more than 5 years of experience who started to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice:
- ○
- What is your background in instructional design?
- ○
- In what ways do you think AI has been impacting our lives?
- ○
- What do you think AI is?
- ○
- You indicated that you have started to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into your professional practice. Can you give us more details about it? How have you done it so far?
- ○
- Why did you start integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice?
- ○
- Can you provide any concrete examples of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice? For instance, any assessment items or content pieces?
- ○
- Would there be any pros and cons of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice?
- ○
- In what other ways are you planning to integrate or in what other ways do you think artificial intelligence and machine learning can be integrated into your professional practice?
- ○
- How has your employer’s approach to the use of AI in the workplace?
- ○
- How do you think your degrees or training has prepared you for technologies like AI?
- ○
- What phase of ADDIE do you think AI will impact the most?
- For instructional designers with 5 or less than 5 years of experience who started to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice:
- ○
- What is your background in instructional design?
- ○
- In what ways do you think AI has been impacting our lives?
- ○
- What do you think AI is?
- ○
- You indicated that you have started to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into your professional practice. Can you give us more details about it? How have you done it so far?
- ○
- Why did you start integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice?
- ○
- Can you provide any concrete examples of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice? For instance, any assessment items or content pieces?
- ○
- Would there be any pros and cons of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice?
- ○
- In what other ways are you planning to integrate or in what other ways do you think artificial intelligence and machine learning can be integrated into your professional practice?
- ○
- How has your employer’s approach to the use of AI in the workplace?
- ○
- How do you think your degrees or training has prepared you for technologies like AI?
- ○
- What phase of ADDIE do you think AI will impact the most?
- For instructional designers with more than 5 years of experience who are planning to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice or who would like to provide hypothetical insights:
- ○
- What is your background in instructional design?
- ○
- In what ways do you think AI has been impacting our lives?
- ○
- What do you think AI is?
- ○
- How are you planning to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice? Or How do you think instructional designers would integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice?
- ○
- Why are you planning to integrate artificial intelligence into your professional practice? Or Why do you think instructional designers would integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice?
- ○
- Are you planning to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning to create certain items such as assessments or content pieces? Can you provide any concrete examples? Or What outcomes/products do you think can be achieved by integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into professional instructional design practice?
- ○
- Would there be any pros and cons of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice?
- ○
- In what other ways are you planning to integrate or in what other ways do you think artificial intelligence and machine learning can be integrated into your professional practice?
- ○
- How has your employer’s approach to the use of AI in the workplace?
- ○
- How do you think your degrees or training has prepared you for technologies like AI?
- ○
- What phase of ADDIE do you think AI will impact the most?
- For instructional designers with 5 or less than 5 years of experience who are planning to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice or who would like to provide hypothetical insights:
- ○
- What is your background in instructional design?
- ○
- In what ways do you think AI has been impacting our lives?
- ○
- What do you think AI is?
- ○
- How are you planning to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice? Or How do you think instructional designers would integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice?
- ○
- Why are you planning to integrate artificial intelligence into your professional practice? Or Why do you think instructional designers would integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning into their professional practice?
- ○
- Are you planning to integrate artificial intelligence and machine learning to create certain items such as assessments or content pieces? Can you provide any concrete examples? Or What outcomes/products do you think can be achieved by integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into professional instructional design practice?
- ○
- Would there be any pros and cons of integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into your professional practice?
- ○
- In what other ways are you planning to integrate or in what other ways do you think artificial intelligence and machine learning can be integrated into your professional practice?
- ○
- How has your employer’s approach to the use of AI in the workplace?
- ○
- How do you think your degrees or training has prepared you for technologies like AI?
- ○
- What phase of ADDIE do you think AI will impact the most?
References
- Aboalela, R. A. (2023). ChatGPT for generating questions and assessments based on accreditations. arXiv, arXiv:2312.00047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahroun, Z., Anane, C., Ahmed, V., & Zacca, A. (2023). Transforming education: A comprehensive review of generative artificial intelligence in educational settings through bibliometric and content Analysis. Sustainability, 15, 12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A., & Pack, A. (2023). Not quite eye to A.I.: Student and teacher perspectives on the use of generative artificial intelligence in the writing process. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(59). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binhammad, M. H. Y., Othman, A., Abduljadayel, L., Al Mheiri, H., Alkaabi, M., & Almarri, M. (2024). Investigating how generative AI can create personalized learning materials tailored to individual student needs. Creative Education, 15, 1499–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolick, A., & da Silva, R. (2024). Exploring artificial intelligence tools and their potential impact to instructional design workflows and organizational systems. TechTrends, 68, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buolamwini, J., & Gebru, T. (2018). Gender shades: Intersectional accuracy disparities in commercial gender classification. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, 81, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chassignol, M., Khoroshavin, A., Klimova, A., & Bilyatdinova, A. (2018). Artificial intelligence trends in education: A narrative overview. Procedia Computer Science, 136, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., Chen, P., & Lin, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in education: A review. IEEE Access, 8, 75264–75278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’ng, L. K. (2023). How AI makes its mark on instructional design. Asian Journal of Distance Education, 18(2), 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, H., David, P., & Ross, A. (2023). Trust in AI and its role in the acceptance of AI technologies. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 39(9), 1727–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches (4th ed.). Sage. [Google Scholar]
- DaCosta, B., & Kinsell, C. (2024). Investigating media selection through ChatGPT: An exploratory study on generative artificial intelligence in the aid of instructional design. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 12, 187–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, D., Shanmugapriya, I., Choudhary, R. K., Patil, S. S., Singh, A., & Lotlikar, S. (2023). An empirical study on the impact of artificial intelligence in education with reference to teaching and learning. Asian and Pacific Economic Review, 16(1), 1350–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, W., Carey, L., & Carey, J. O. (2022). The systematic design of instruction (9th. ed.). Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Egara, F. O., & Mosimege, M. (2024). Exploring the integration of artificial intelligence-based ChatGPT into mathematics instruction: Perceptions, challenges, and implications for educators. Education Sciences, 14(7), 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, J., Pack, A., & Barrett, A. (2023). AI-generated feedback on writing: Insights into efficacy and ENL student preference. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(57). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, C., Caddell, C., Godwin, S., & Myers, B. (2024, May 20–22). Automating analysis for efficient and effective learning solutions. MODSIM World, Norfolk, VA, USA. Available online: https://modsimworld.org/papers/2024/MODSIM_2024_paper_32.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Gligorea, I., Cioca, M., Oancea, R., Gorski, A. T., Gorski, H., & Tudorache, P. (2023). Adaptive learning using artificial intelligence in e-learning: A literature review. Education Sciences, 13(12), 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, G., Bunce, A., & Johnson, L. (2006). How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods, 18(1), 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, C. B., & Kirschner, P. A. (2024). Innovation of instructional design and assessment in the age of generative artificial intelligence. TechTrends, 68, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssani, M. S., Aboutajeddine, A., Toughrai, I., & Ibrahimi, A. (2024). Development of a design course for medical curriculum: Using design thinking as an instructional design method empowered by constructive alignment and generative AI. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 52, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-L., Liu, Y.-C., & Dong, M.-Q. (2024). Incorporating AIGC into design ideation: A study on self-efficacy and learning experience acceptance under higher-order thinking. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 52, 101508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G. J., Xie, H., Wah, B. W., & Gasevic, D. (2020). Vision, challenges, roles and research issues of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasowitz, A. (1998). Tools for automating instructional design (ERIC digest, EDO-IR-1998-1). Available online: http://www.ericit.org/digests/EDO-IR-1998-01.shtml (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Katiyar, N., Awasthi, V. K., Pratap, R., Mishra, K., Shukla, N., Singh, R., & Tiwari, M. (2024). AI-driven personalized learning systems: Enhancing educational effectiveness. Educational Administration: Theory and Practice, 30(5), 11514–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T., Shane, S., Reid, M., Matsuo, Y., & Iwasawa, Y. (2023). Large language models are zero-shot reasoners. arXiv, arXiv:2205.11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krushinskaia, K., Elen, J., & Raes, A. (2024). Effects of generative artificial intelligence on instructional design outcomes and the mediating role of pre-service teachers’ prior knowledge of different types of instructional design tasks. In A. M. Olney, I.-A. Chounta, Z. Liu, O. C. Santos, & I. I. Bittencourt (Eds.), AIED 2024 workshops, CCIS 2151 (pp. 395–400). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., Gunn, A., Rose, R., Pollard, R., Johnson, M., & Ritzhaupt, D. (2024). The role of instructional designers in the integration of generative artificial intelligence in online and blended learning in higher education. Online Learning, 28(3), 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J., Li, T., Jenkin, M., Liu, S., & Dudek, G. (2024). Hallucination detection and hallucination mitigation: An investigation. arXiv, arXiv:2401.08358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T., Muljana, P. S., Ren, X., & Young, D. (2025). Exploring instructional designers’ utilization and perspectives on generative AI tools: A mixed methods study. Educational Technology Research and Development, 73, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, L. (2024, January 3–7). Automation or innovation? A generative AI and instructional design snapshot. The IAFOR International Conference of Education in Hawaii 2024 Official Conference Proceedings (pp. 187–194), Honolulu, HI, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H., Staudt Willet, K. B., Shi, H., Hur, J., He, D., & Kim, C. (2024). Initial discussions of ChatGPT in education-related subreddits. Journal of Research on Technology in Education. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, A., Gupta, S., Perrine, O., Reddy, R., Ershadi, S., & Remick, D. (2024). ChatGPT 3.5 fails to write appropriate multiple choice practice exam questions. Academic Pathology, 11(1), 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A., Ngo, H. N., Hong, Y., Dang, B., & Nguyen, B.-P. T. (2023). Ethical principles for artificial intelligence in education. Education and Information Technologies, 28, 4221–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B., Sonnefeld, N., Duruaku, F., Alonso, A., & Jentsch, F. (2024). A case study for using AI tools to develop training materials for high consequence industries. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, 68(1), 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B., Sonnefeld, N., Finkelstein, L., Alonso, A., Gomez, C., Duruaku, F., & Jentsch, F. (2023). Using AI tools to develop training materials for aviation: Ethical, technical, and practical concerns. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, 67(1), 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, Z.-F., Harun, M. H. M., Ishar, N. I. M., Mustapha, N. A., & Ismail, Z. (2024). Enhancing professional development and training through AI for personalized learning: A framework to engaging students. International Journal on e-Learning and Higher Education, 19(3), 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteng-Darko, C., Karki, R., Teye, E. Q., & Liu, L. (2024, March 25). Assessment of the quality of design of human-created and AI-based learning materials. Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference (pp. 841–846), Las Vegas, NV, USA. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/primary/p/224049/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Ouyang, F., & Zhang, L. (2024). AI-driven learning analytics applications and tools in computer-supported collaborative learning: A systematic review. Educational Reseach Review, 44, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S., Zhang, J. M., Harman, M., & Wang, M. (2023). LLM is like a box of chocolates: The non-determinism of ChatGPT in code generation. arXiv, arXiv:2308.02828. [Google Scholar]
- Pack, A., Barrett, A., & Escalante, J. (2024). Large language models and automated essay scoring of English language learner writing: Insights into validity and reliability. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 6, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, B., & Curry, J. H. (2023). Can ChatGPT pass graduate-level instructional design assignments? Potential implications of artificial intelligence in education and a call to action. TechTrends, 68, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popenici, S. A. D., & Kerr, S. (2017). Exploring the impact of artificial intelligence on teaching and learning in higher education. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quian, C. (2023). Research on human-centered design in college music education to improve student experience of artificial intelligence-based information systems. Journal of Information Systems Engineering and Management, 8(3), 2468–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezigalla, A. A. (2024). AI in medical education: Uses of AI in construction of type A MCQs. BMC Medical Education, 24, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, J. (2016). The coding manual for qualitative researchers (3rd ed.). Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Sallam, M. (2023). ChatGPT utility in healthcare education, research, and practice: Systematic review on the promising perspectives and valid concerns. Healthcare, 11(6), 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J., Moon, S., Cho, B., Hwang, S., & Choi, B. (2022). Extended technology acceptance model to explain the mechanism of modular construction adoption. Journal of Cleaner Production, 342, 130963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. L., & Ragan, T. J. (2005). Instructional design (3rd ed.). Wiley. [Google Scholar]
- Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research. Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Stake, R. E. (2006). Multiple case study analysis. Guildford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Szilas, J. W., & Emery, P. B. (2024, June 16–18). Can “smart import” create smart learning content? Learning in the Age of AI: Toward Imaginative Futures-EDEN Annual Conference Proceedings (pp. 37–38), Graz, Austria. [Google Scholar]
- Tennyson, R. D. (1984). Artificial intelligence methods in computer-based instructional design. Journal of Instructional Development, 7(3), 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennyson, R. D., & Barron, A. E. (1995). Automating instructional design: Computer-based development and delivery tools. Springer. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-642-57821-2 (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Thomas, G. (2011). A typology for the case study in social science following a review of definition, discourse, and structure. Qualitative Inquiry, 17(6), 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, V. (2023). The role of artificial intelligence (AII) in personalizing online learning. Journal of Online and Distance Learning, 3(1), 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, W. (1987). Instructional design and intelligent systems: Shifts in the designer’s decision-making role. Instructional Science, 16, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D., & Moss, S. H. (2024). Evaluating the impact of students’ generative AI use in educational contexts. Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning, 17(2), 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R. K. (2014). Case study research: Design and methods (5th ed.). Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R. K. (2018). Case study research and applications: Design and methods (6th ed.). Sage. [Google Scholar]
| Pseudonym | Position | Years of ID Experience | Years of Experience Related to ID | Highest Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nikki (Case 1) | IDer in a corporate | 6 | >20 years newspaper editor (online) | BA—journalism + grad certificate—ID |
| Taylor (Case 2) | Senior IDer in a corporate | 20 | 5 years—technical writing | training and performance improvement |
| Elvin (Case 3) | IDer in higher education | 5 | 5 years— K-12 teacher | PhD—learning, design, and technology |
| Cameron (Case 4) | Postdoc researcher | 12 (higher education + contract-based) | 4 years—outreach coordinator | Postdoc—learning, design, and technology |
| Jordan (Case 5) | IDer in a corporate | 3 | 5 years—onboarding new staff | EdD—learning design and performance technology |
| Riley (Case 6) | IDer in higher education | 10 | none | PhD—instructional systems technology |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozan, K.; Hur, J.; Kim, I.; Barrett, A. Instructional Designers’ Integration of Generative Artificial Intelligence into Their Professional Practice. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15091133
Kozan K, Hur J, Kim I, Barrett A. Instructional Designers’ Integration of Generative Artificial Intelligence into Their Professional Practice. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(9):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15091133
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozan, Kadir, Jaesung Hur, Idam Kim, and Alex Barrett. 2025. "Instructional Designers’ Integration of Generative Artificial Intelligence into Their Professional Practice" Education Sciences 15, no. 9: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15091133
APA StyleKozan, K., Hur, J., Kim, I., & Barrett, A. (2025). Instructional Designers’ Integration of Generative Artificial Intelligence into Their Professional Practice. Education Sciences, 15(9), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15091133






