Generative AI-Enhanced Virtual Reality Simulation for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Mixed-Methods Analysis of Usability and Instructional Utility for Course Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Virtual Reality Simulation in Teacher Education
2.2. GenAI-Enhanced Teacher Simulation
2.3. Instructional Design and Usability: A Dual-Theoretical Lens Using CTML and Gagné’s Nine Events of Instruction
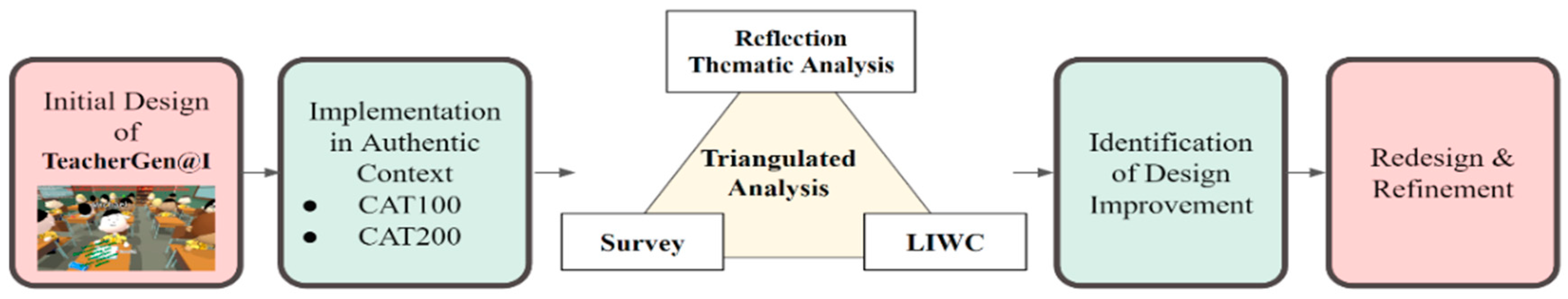
3. Methods
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Research Context and Participants
3.3. Data Collection and Instruments
3.4. Data Analysis
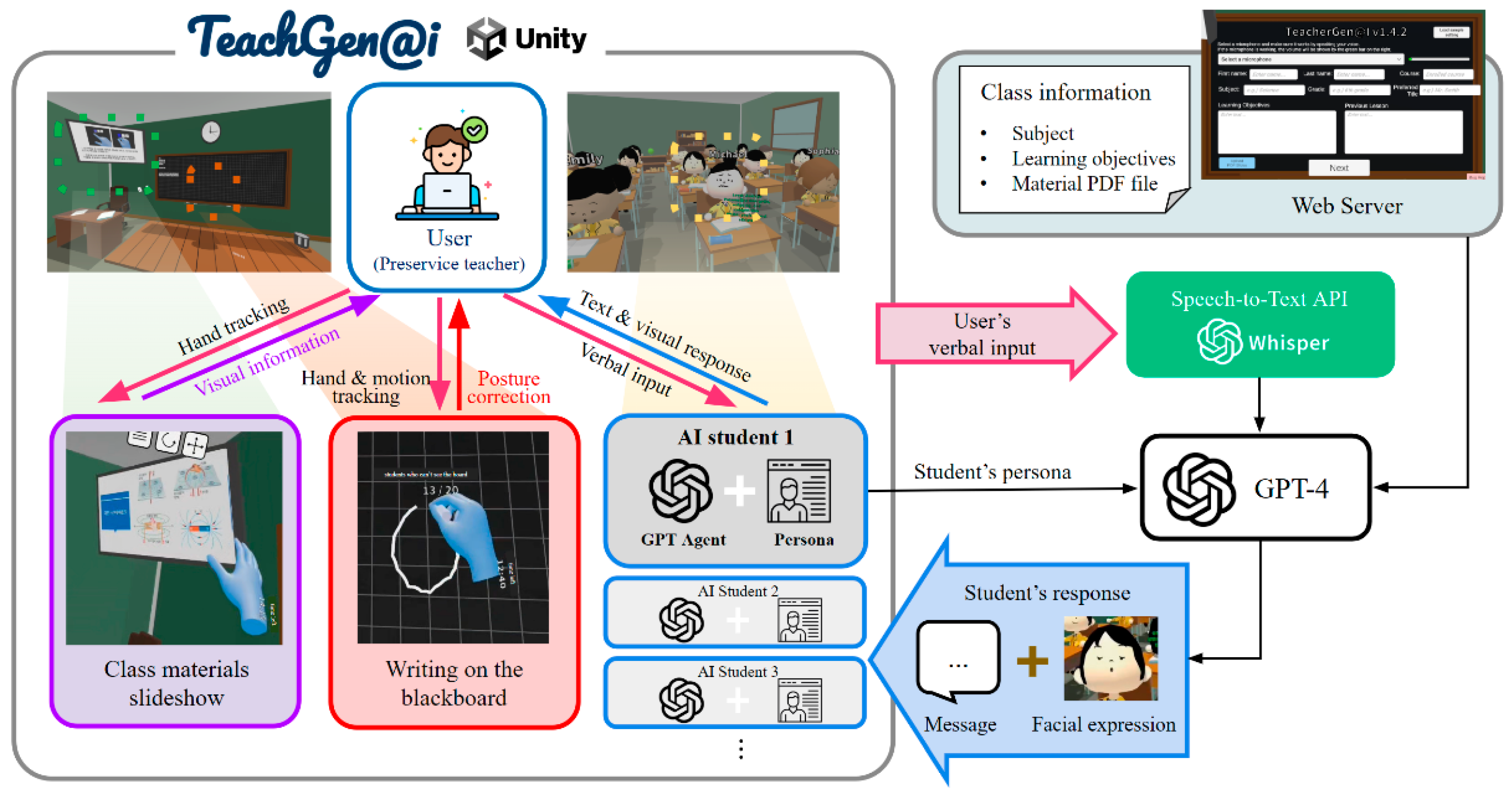
3.5. Learning Environment: TeacherGen@i
4. Results
4.1. RQ1: Identification of Technical and Usability Challenges Through Multimedia Design Principles
4.1.1. Usability Evaluation—Graduate Pilot Study
4.1.2. Usability Evaluation—Undergraduate Main Study
4.1.3. Multimedia Design Principle Evaluation
4.1.4. Severity-Frequency Analysis and Design Response
4.2. RQ2: Pre-Service Teachers’ Perceptions of Instructional Utility and Readiness for Classroom Teaching
4.2.1. Authentic Interaction and Adaptive Teaching Practice
4.2.2. Structured Scaffolding and Confidence Building
4.2.3. Multimodal Communication Development
4.2.4. Areas of Future Refinement
5. Discussion
5.1. RQ1: Identification of Technical and Usability Challenges Through Multimedia Design Principles
5.1.1. Multimedia Principles as Diagnostic Frameworks
5.1.2. Contextual Limitations in Immersive Environment Design
5.2. RQ2: Pre-Service Teachers’ Perceptions of Instructional Utility and Readiness for Classroom Teaching
Exploring Instructional Utility as Perceived by Pre-Service Teachers
6. Conclusions, Limitation, and Future Research
6.1. Limitation and Future Research
6.2. Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baceviciute, S., Lucas, G., Terkildsen, T., & Makransky, G. (2022). Investigating the redundancy principle in immersive virtual reality environments: An eye-tracking and EEG study. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 38(1), 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, N. U., & Boone, W. J. (2015). Exploring the impact of TeachME™ lab virtual classroom teaching simulation on early childhood education majors’ self-efficacy beliefs. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 26(3), 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, A., Holdheide, L., Brownell, M., & Foley, A. M. (2016). Learning to teach: Practice-based preparation in teacher education (Special issues brief). Center on Great Teachers and Leaders. [Google Scholar]
- Bommasani, R., Lin, K., Narayan, S., & Le, Q. V. (2021). On the opportunities and risks of foundation models [CRFM Technical Report FM-TR-2021-1]. Stanford Center for Research on Foundation Models. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J. (1996). SUS—A quick and dirty usability scale. In Usability evaluation in industry. Taylor and Francis. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, G. W., Kim, S. H., Lee, D., & Moon, J. (2024). Utilizing generative AI for instructional design: Exploring strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. TechTrends, 68(4), 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R. C., & Mayer, R. E. (2016). E-learning and the science of instruction: Proven guidelines for consumers and designers of multimedia learning (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, P., Donlon, E., Farrell, R., Campbell, A., Roulston, S., Taggart, S., & Brown, M. (2023). Virtual and augmented reality and pre-service teachers: Makers from muggles? Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 39(3), 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J. W. (2021). A concise introduction to mixed methods research. SAGE. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C. P., Ke, F., Pan, Y., Moon, J., & Liu, Z. (2024). Effects of artificial intelligence-powered virtual agents on learning outcomes in computer-based simulations: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 36(1), 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgarno, B., Gregory, S., Knox, V., & Reiners, T. (2016). Practising teaching using virtual classroom role plays. Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 41(1), 126–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalinger, T., Thomas, K. B., Stansberry, S., & Xiu, Y. (2020). A mixed reality simulation offers strategic practice for pre-service teachers. Computers & Education, 144, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling-Hammond, L. (2017). Teacher education around the world: What can we learn from international practice? European Journal of Teacher Education, 40(3), 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawley, L., & Dede, C. (2013). Situated learning in virtual worlds and immersive simulations. In J. M. Spector, M. D. Merrill, J. Elen, & M. J. Bishop (Eds.), Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (pp. 723–734). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M. R., & Lignugaris/Kraft, B. (2017). Meaningful practice: Generalizing foundation teaching skills from TLE TeachLivE™ to the classroom. Teacher Education and Special Education, 40(1), 26–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieker, L., Hughes, C., & Hynes, M. (2023). The past, the present, and the future of the evolution of mixed reality in teacher education. Education Sciences, 13(11), 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieker, L. A., Rodriguez, J. A., Lignugaris/Kraft, B., Hynes, M. C., & Hughes, C. E. (2014). The potential of simulated environments in teacher education: Current and future possibilities. Teacher Education and Special Education, 37(1), 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docter, M. W., De Vries, T. N. D., Nguyen, H. D., & van Keulen, H. (2024). A proof-of-concept of an integrated VR and AI application to develop classroom management competencies in teachers in training. Education Sciences, 14(5), 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M. C., Robinson, S. A., & Ertl, B. (2024). AI-based avatars are changing the way we learn and teach: Benefits and challenges. Frontiers in Education, 9, 1416307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, R. M., Wager, W. W., Golas, K. C., & Keller, J. M. (2005). Principles of instructional design (5th ed.). Thomson/Wadsworth. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, P., Hammerness, K., & McDonald, M. (2009). Redefining teaching, re-imagining teacher education. Teachers and Teaching: Theory and Practice, 15(2), 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, H., Fegely, A., Warriner, G., & Mckenzie, M. (2024). The teaching methods classroom meets virtual reality: Insights for pre-service teaching methods instructors. TechTrends, 68, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartstein, A. J., Verkuyl, M., Zimney, K., Yockey, J., & Berg-Poppe, P. (2022). Virtual reality instructional design in orthopedic physical therapy education: A mixed-methods usability test. Simulation & Gaming, 53(2), 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A. T., Straub, C. L., Dieker, L. A., Hughes, C. E., & Hynes, M. C. (2013). Ludic learning: Exploration of TLE TeachLivE™ and effective teacher training. International Journal of Gaming and Computer-Mediated Simulations (IJGCMS), 5(2), 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixon, E., & So, H. J. (2009). Technology’s role in field experiences for preservice teacher training. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 12(4), 294–304. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y., Richter, E., Kleickmann, T., & Richter, D. (2023). Virtual reality in teacher education from 2010 to 2020. In Bildung für eine digitale Zukunft (pp. 399–441). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J., Hong, S., Eom, T., & Lim, C. (2024, June 10–14). Enhancing pre-service teachers’ competence with a generative artificial intelligence-enhanced virtual reality simulation. 4th International Society of the Learning Sciences (pp. 24–27), New York, NY, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y., Lee, Y., Byun, G., & Moon, J. (2024). Navigating the creation of immersive learning environments in roblox: Integrating generative AI for enhanced simulation-based learning. Immersive Learning Research-Practitioner, 1(1), 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Glenberg, M. C. (2018). Immersive VR and education: Embodied design principles that include the body in cognition. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 5(5), 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D., & Ireland, A. (2016). Enhancing teacher education with simulations. TechTrends, 60, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F., & Xu, X. (2020). Virtual reality simulation-based learning of teaching with alternative perspectives taking. British Journal of Educational Technology, 51(6), 2544–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanović, V., Joksimović, S., Mirriahi, N., Blaine, E., Gašević, D., Siemens, G., & Dawson, S. (2018, March 5–9). Understand students’ self-reflections through learning analytics. 8th International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge (LAK18) (pp. 389–398), Sydney, NSW, Australia. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S., & Ahn, T. (2021). Pre-service teachers’ learning experience of using a virtual practicum simulation with AI learners. Multimedia-Assisted Language Learning, 24(4), 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U., Jeong, Y., Koh, J., Byun, G., Lee, Y., Lee, H., Eun, S., Moon, J., Lim, C., & Kim, H. (2024). I see you: Teacher analytics with GPT-4 vision-powered observational assessment. Smart Learning Environments, 11(1), 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U., Koh, J., Jeong, Y., & Lee, S. (2023, December 15). Generative agent for teacher training: Designing educational problem-solving simulations with LLM-based agents for pre-service teachers. NeurIPS Workshop on Generative AI for Education, New Orleans, LA, USA. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J., Lee, U., Koh, J., Jeong, Y., Lee, Y., Byun, G., Jung, H., Jang, Y., Lee, S., & Moon, J. (2025). Development and implementation of a generative artificial intelligence-enhanced simulation to enhance problem-solving skills for pre-service teachers. Computers & Education, 232, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T., Lin, Y., Wang, T., Yeh, S., & Kalyuga, S. (2021). Studying the effect of redundancy in a virtual reality classroom. Educational Technology Research and Development, 69, 1183–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, S. K. (2015). How do virtual world experiences bring about learning? A critical review of theories. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 31(1), 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R. E. (2024). The past, present, and future of the cognitive theory of multimedia learning. Educational Psychology Review, 36(1), 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, S., & Reeves, T. C. (2018). Conducting educational design research (2nd ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J., Lee, U., Koh, J., Jeong, Y., Lee, Y., Byun, G., & Lim, J. (2025). Generative artificial intelligence in educational game design: Nuanced challenges, design implications, and future research. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 30, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, T., Samuelsson, M., Hansson, P., Efmova, E., & Bachelder, S. (2025). AI versus human feedback in mixed reality simulations: Comparing LLM and expert mentoring in preservice teacher education on controversial issues. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parong, J., & Mayer, R. E. (2018). Learning science in immersive virtual reality. Journal of Educational Psychology, 110(6), 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southgate, E., Smith, S. P., Cividino, C., Saxby, S., Kilham, J., Eather, G., Scevak, J., Summerville, D., Buchanan, R., & Bergin, C. (2019). Embedding immersive virtual reality in classrooms: Ethical, organisational and educational lessons in bridging research and practice. International Journal of Child-Computer Interaction, 19, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiell, M., Markowski, M., Jameson, J., Essex, R., & Ade-Ojo, G. (2022). A systematic scoping review and textual narrative synthesis of physical and mixed-reality simulation in pre-service teacher training. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 38(3), 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, H., van den Beemt, A., & den Brok, P. (2019). Using 360-degree videos in teacher education: Effects on teacher self-efficacy, instructional skills, and classroom management. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 35(5), 635–647. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R. K. (2018). Case study research and applications: Design and methods (6th ed.). SAGE. [Google Scholar]
- Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education–where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16(1), 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J., Pan, Q., Zhang, D., Meng, B., & Hwang, G. J. (2024). Effects of virtual reality based microteaching training on pre-service teachers’ teaching skills from a multi-dimensional perspective. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 62(3), 655–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N., Ke, F., Dai, C. P., Southerland, S. A., & Yuan, X. (2025). Seeking to support preservice teachers’ responsive teaching: Leveraging artificial intelligence-supported virtual simulation. British Journal of Educational Technology, 56(3), 1148–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Zhang-Li, D., Yu, J., & Zhou, H. (2025, April 29–May 4). Simulating classroom education with LLM-empowered agents. 2025 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (pp. 10364–10379), Albuquerque, NM, USA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L., Jiang, F., Gu, X., & Li, Y. (2025). Teaching via LLM-enhanced simulations: Authenticity and barriers to suspension of disbelief. The Internet and Higher Education, 65, 100990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ease of Use | Usefulness | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usage Ease | Task Clarity | Speed | Content Amount | Text Clarity | Text Readability | Technical Reliability | Objective Alignment | |
| M (SD) | 3.17 (1.38) | 3.33 (1.14) | 3.56 (1.10) | 3.78 (1.17) | 3.56 (1.38) | 3.78 (1.35) | 2.28 (1.45) | 3.06 (1.06) |
| Usefulness | ||||||||
| Goal Support | User Motivation | Realistic Scenarios | Familiar Terminology | Broad Suitability | Class Preparation | Teacher Confidence | Future Use | |
| M (SD) | 3.17 (1.10) | 3.06 (1.06) | 3.56 (1.20) | 3.61 (1.20) | 3.39 (1.46) | 3.56 (1.25) | 3.56 (1.20) | 2.89 (1.23) |
| Design Principle | Well-Reflected Multimedia Elements | Elements Needing Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Coherence |
|
|
| Signaling |
|
|
| Redundancy |
|
|
| Spatial Contiguity |
|
|
| Temporal Contiguity |
|
|
| Segmenting |
|
|
| Pre-training |
|
|
| Modality |
|
|
| Personalization |
|
|
| Key Theme | Participant Perception | Detailed Description | LIWC Validation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authentic Interaction and Adaptive Teaching Practice |
|
|
|
| Scaffolding and Confidence Building |
|
|
|
| Multimodal Communication Development |
|
|
|
| Areas for Future Improvement |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.; Moon, J.; Eom, T.; Awoyemi, I.D.; Hwang, J. Generative AI-Enhanced Virtual Reality Simulation for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Mixed-Methods Analysis of Usability and Instructional Utility for Course Integration. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15080997
Hong S, Moon J, Eom T, Awoyemi ID, Hwang J. Generative AI-Enhanced Virtual Reality Simulation for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Mixed-Methods Analysis of Usability and Instructional Utility for Course Integration. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(8):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15080997
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sumin, Jewoong Moon, Taeyeon Eom, Idowu David Awoyemi, and Juno Hwang. 2025. "Generative AI-Enhanced Virtual Reality Simulation for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Mixed-Methods Analysis of Usability and Instructional Utility for Course Integration" Education Sciences 15, no. 8: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15080997
APA StyleHong, S., Moon, J., Eom, T., Awoyemi, I. D., & Hwang, J. (2025). Generative AI-Enhanced Virtual Reality Simulation for Pre-Service Teacher Education: A Mixed-Methods Analysis of Usability and Instructional Utility for Course Integration. Education Sciences, 15(8), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15080997








