Phases and Activities of Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning in K-12: Findings from a Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Previous Research
2.1. Project-Based Learning (PjBL)
- Initiation: consists of defining the problem or purpose of the project, establishing objectives, scope, and resources, and exploring ideas. Management artifacts include resource lists, mind maps, project definition documents, and team-working agreements. Initial meetings and alignment workshops are also held to organize the team’s objectives, skills, and practices.
- Planning: Focuses on planning activities and tasks, identifying resources, and defining roles and responsibilities. Detailed plans are developed for project scope, schedules, budgets, and responsibility assignment matrices. Communication and resource acquisition are planned.
- Execution: The production and presentation of the project results and the fulfillment of the objectives are carried out. Final products include scale models, prototypes, solutions, services, and designs. The presentation of these products can be performed through exhibitions, contests, and portfolios, among others. Students usually act as project managers, ensuring that the objectives are met.
- Closing: Focuses on reviewing and reflecting on the project. It involves stakeholder feedback, the celebration of success, recognition, and self-reflection. Project success or failure, performance, and lessons learned are documented. Artifacts include project management evaluation rubrics. Performance is analyzed, lessons learned are refined, process standardization is assessed, and results are presented to all stakeholders.
2.2. Use of Digital Technologies in PjBL
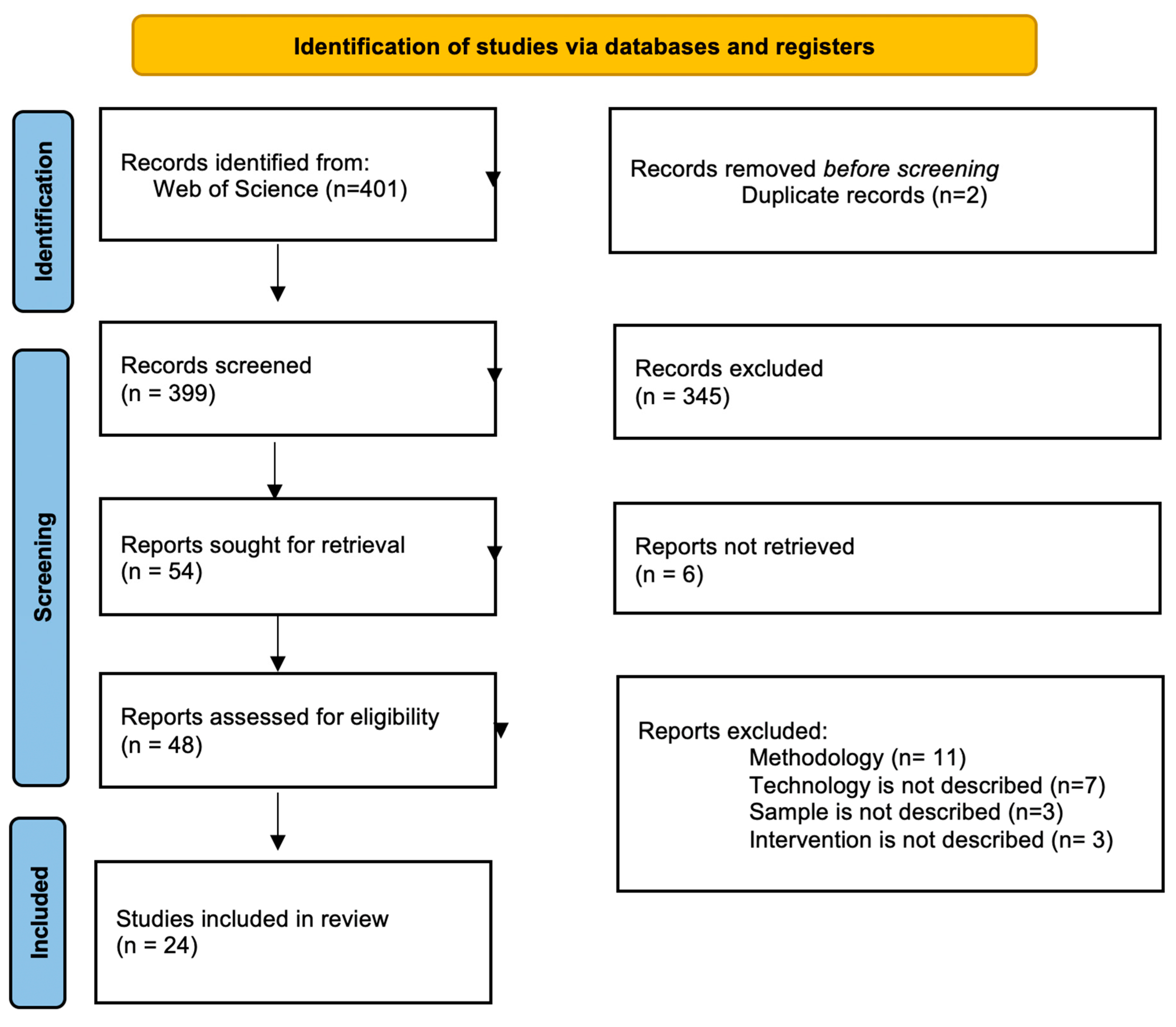
3. Methods
4. Results
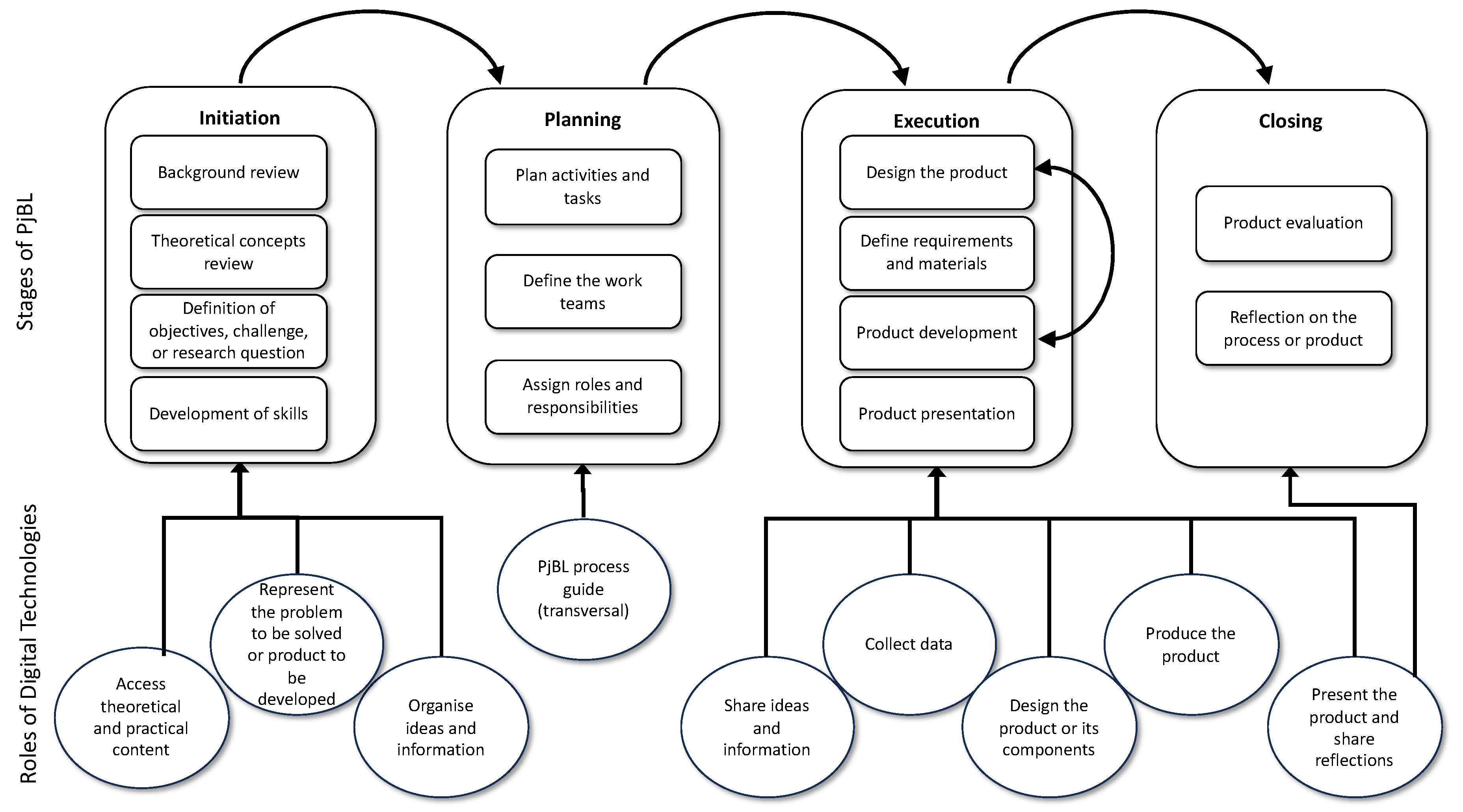
4.1. Phases of Project-Based Learning
4.1.1. Initiation
4.1.2. Planning
4.1.3. Execution
4.1.4. Closing Stage
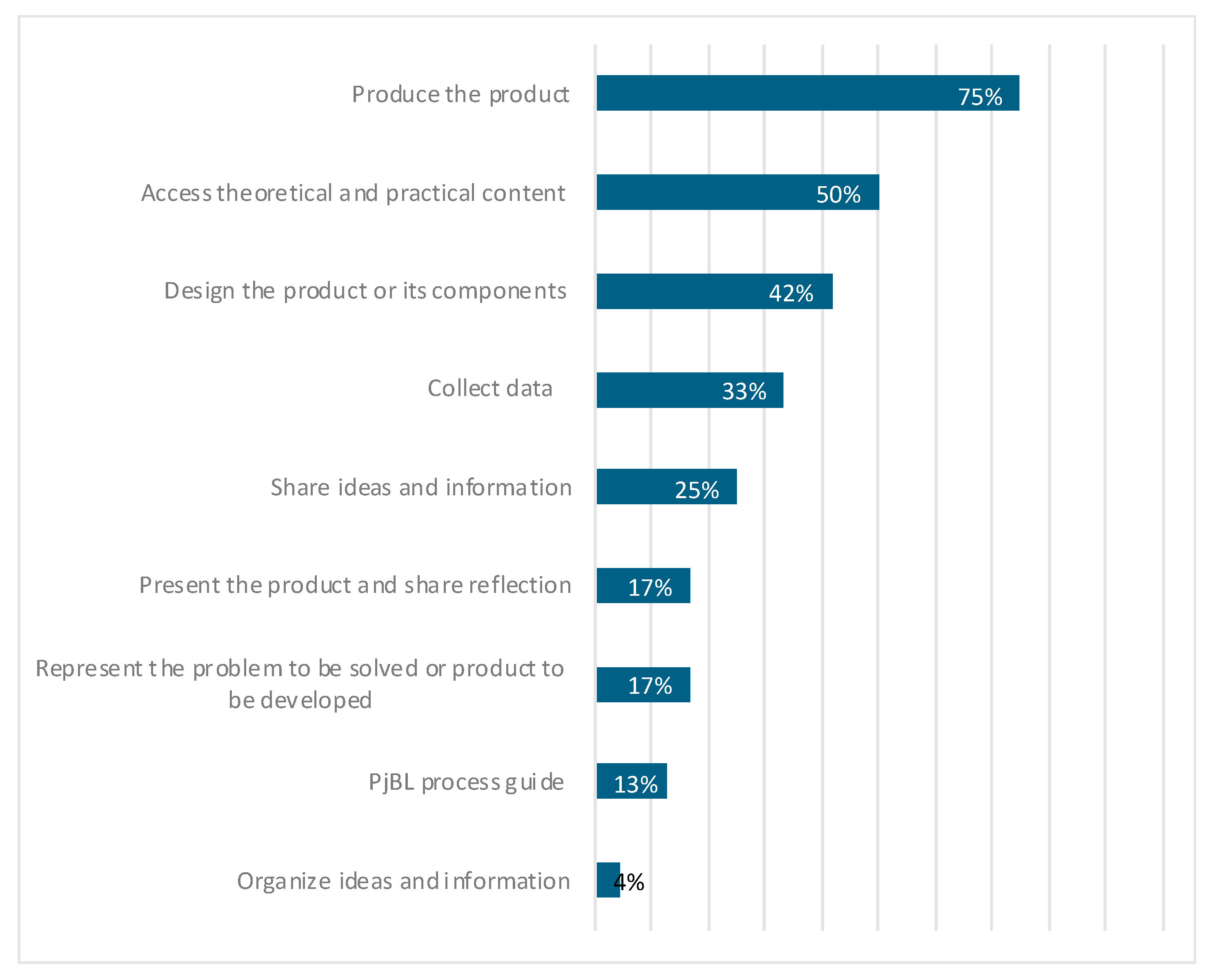
4.2. Roles of Digital Technologies in the Development of PjBL
4.2.1. Produce the Product
4.2.2. Access Theoretical and Practical Content
4.2.3. Design the Product or Its Components
4.2.4. Collect Data
4.2.5. Share Ideas and Information
4.2.6. Present the Product and Share Reflection
4.2.7. Represent the Problem to Be Solved or Product to Be Developed
4.2.8. PjBL Process Guide
4.2.9. Organize Ideas and Information
5. Discussion
5.1. PjBL Implementation Phases
5.2. Roles of Digital Technologies in PjBL
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PjBL | Project-Based Learning |
References
- Almulla, M. A. (2020). The effectiveness of the project-based learning (PBL) approach as a way to engage students in searning. SAGE Open, 10(3), 2158244020938702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alò, D., Castillo, A., Marín Vial, P., & Samaniego, H. (2020). Low-cost emerging technologies as a tool to support informal environmental education in children from vulnerable public schools of southern Chile. International Journal of Science Education, 42(4), 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebaum, L. R., Vitale, J. M., Gerard, E., & Linn, M. C. (2017). Comparing design constraints to support learning in technology-guided inquiry projects. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 20(4), 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, N. (2023). Exploring STEM integration: Assessing the effectiveness of an interdisciplinary informal program in fostering students’ performance and inspiration. Research in Science & Technological Education, 41(2), 675–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ábalos-Aguilera, F., Romero-Rodríguez, L. M., & Bernal Bravo, C. (2024). TIC, motivación y rendimiento académico en educación primaria. Education in the Knowledge Society (EKS), 25, e31799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchi, H., & Bell, R. (2008). The many levels of inquiry. Science and Children, 46(2), 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Belagra, M., & Draoui, B. (2018). Project-based learning and information and communication technology’s integration: Impacts on motivation. International Journal of Electrical Engineering & Education, 55(4), 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S. (2010). Project-based learning for the 21st century: Skills for the future. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 83(2), 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blampied, N., Buttrick, R., Jucan, G., Piney, C., Stevens, C., Violette, D., & Max Wideman, R. (2023). In search of project management principles. Project Management Journal, 54(6), 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, C. W., Vijayasarathy, L. R., & Roberts, N. (2020). Managing software development projects for success: Aligning plan- and agility-based approaches to project complexity and project dynamism. Project Management Journal, 51(3), 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C. C., & Chen, Y. K. (2022). Educational values and challenges of i-STEM project-based learning: A mixed-methods study with data-transformation design. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 976724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C. Y., Du, Z., Kuo, H. C., & Chang, C. C. (2023). Investigating the impact of design thinking-based STEAM PBL on students’ creativity and computational thinking. IEEE Transactions on Education, 66(6), 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H., & Yang, Y.-C. (2019). Revisiting the effects of project-based learning on students’ academic achievement: A meta-analysis investigating moderators. Educational Research Review, 26, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-C., & Yang, Y.-T. (2023). Impact of smart classrooms combined with student-centered pedagogies on rural students’ learning outcomes: Pedagogy and duration as moderator variables. Computers & Education, 207, 104911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, C., Magana, A. J., & Vieira, C. (2019). Investigating the affordances of a CAD enabled learning environment for promoting integrated STEM learning. Computers & Education, 129, 122–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle-Vergini, S., Eacersall, D., Dann, C., Ally, M., & Chakraborty, S. (2024). Teaching project management to primary school children: A scoping review. The Australian Educational Researcher, 51, 1035–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebm, C., del Pozo, C., Barbarello, A., Poli, G., & Brusa, S. (2024). Unleashing excellence: Using a project management approach to effectively implement a simulation curriculum to improve residents’ preparedness. BMC Medical Education, 24(1), 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, K. (2017). Real and relevant: A guide for service and project-based learning. Rowman & Littlefield. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, G., Tassari, G., Rocha, L., Santos, J. M. R. C. A., Ferreira, L. M. D. F., Ribeiro, P., & O’Sullivan, D. (2024). Overcoming the ‘use misfit’ of project management practices in collaborative research, development and innovation. Project Leadership and Society, 5, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R. M. (2016). Cooperative learning: Review of research and practice. Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 41(3), 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N. R., Page, M. J., Pritchard, C. C., & McGuinness, L. A. (2022). PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and open synthesis. Campbell Systematic Reviews, 18(2), e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanham, J., & Hendry, A. (2024). Timing matters: Unpacking the dynamics of project-based groups through exploring proxy efficacy and collective efficacy. International Journal of Educational Research, 126, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasni, A., Bousadra, F., Belletête, V., Benabdallah, A., Nicole, M.-C., & Dumais, N. (2016). Trends in research on project-based science and technology teaching and learning at K–12 levels: A systematic review. Studies in Science Education, 52(2), 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herczeg, M. (2024). The role of digital technologies and human-computer interaction for the future of education. i-com, 23(2), 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.-S., Chen, J.-C., Chen, J.-H., Zeng, Y.-T., & Chung, G.-H. (2022). An assessment of junior high school students’ knowledge, creativity, and hands-on performance using PBL via cognitive–affective interaction model to achieve STEAM. Sustainability, 14(9), 5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H. F., & Shannon, S. E. (2005). Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qualitative Health Research, 15(9), 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-C., Yang, Y.-F., Cheng, Y.-W., & Chen, N.-S. (2023). Integrating educational robot and low-cost self-made toys to enhance STEM learning performance for primary school students. Behaviour & Information Technology, 43(8), 1614–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G. J., Tu, N. T., & Wang, X. M. (2018). Creating interactive e-books through learning by design: The impacts of guided peer-feedback on students’ learning achievements and project outcomes in science courses. Educational Technology & Society, 21(1), 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kokotsaki, D., Menzies, V., & Wiggins, A. (2016). Project-based learning: A review of the literature. Improving Schools, 19(3), 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcik, J., Schneider, B., Miller, E. A., Chen, I. C., Bradford, L., Baker, Q., Bartz, K., Miller, C., Li, T., Codere, S., & Peek-Brown, D. (2022). Assessing the effect of project-based learning on science learning in elementary schools. American Educational Research Journal, 60(1), 70–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajcik, J. S., & Czerniak, C. (2018). Teaching science in elementary and middle school: A project-based learning approach (5th ed.). Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Krajcik, J. S., & Shin, N. (2022). Project-based learning. In R. K. Sawyer (Ed.), The Cambridge handbook of the learning sciences (3rd ed., pp. 72–92). Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larmer, J., Mergendoller, J., & Boss, S. (2015). Setting the standard for project based learning: A proven approach to rigorous classroom instruction. ASCD. Available online: https://www.perlego.com/book/3292581/setting-the-standard-for-project-based-learning-pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Li, M., Donnelly-Hermosillo, D. F., & Click, J. (2022). Comparing simulation sequencing in a chemistry online-supported project-based learning unit. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 31(1), 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S. J., Chou, Y. C., Shih, R. C., & Chung, C. C. (2017). A study of creativity in CaC2 steamship-derived STEM project-based learning. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics Science and Technology Education, 13(6), 2387–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. Y., Lo, C. C., & Syu, J. Y. (2022). Project-based learning oriented STEAM: The case of micro-bit paper-cutting lamp. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 32(5), 2553–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, R., Paz-Baruch, N., Grinshpan, N., Milman, A., Mevarech, Z., Levi, R., Shlomo, S., & Zion, M. (2023). Relationships between metacognition, creativity, and critical thinking in self-reported teaching performances in project-based learning settings. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 50, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markula, A., & Aksela, M. (2022). The key characteristics of project-based learning: How teachers implement projects in K-12 science education. Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research, 4(1), 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnewick, C. (2023). Student experiences of project-based learning in agile project management education. Project Leadership and Society, 4, 100096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N., Dong, Y., Roehrs, D., & Luan, L. (2023). Tackle implementation challenges in project-based learning: A survey study of PBL e-learning platforms. Educational Technology Research and Development, 71, 1179–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, A. D., & Hite, R. L. (2020). Enhancing student communication competencies in STEM using virtual global collaboration project based learning. Research in Science & Technological Education, 40(1), 76–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., & Moher, D. (2021). Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: Development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedaste, M., Mäeots, M., Siiman, L. A., de Jong, T., van Riesen, S. A. N., Kamp, E. T., Manoli, C. C., Zacharia, Z. C., & Tsourlidaki, E. (2015). Phases of inquiry-based learning: Definitions and the inquiry cycle. Educational Research Review, 14, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, J. W., & Hilton, M. L. (2012). Education for life and work: Developing transferable knowledge and skills in the 21st century. The National Academies Press. [Google Scholar]
- PMI. (2021). A guide to the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK guide) (7th ed.). Project Management Institute, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Project Management Institute. (2018). The standard for project management and a guide to the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK guide) (7th ed.). Project Management Institute. [Google Scholar]
- Queiruga-Dios, M.-Á., López-Iñesta, E., Diez-Ojeda, M., Sáiz-Manzanares, M.-C., & Vázquez-Dorrío, J.-B. (2021). Implementation of a STEAM project in compulsory secondary education that creates connections with the environment. Journal for the Study of Education and Development, Infancia y Aprendizaje, 44(4), 871–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, A., Suryani, N., Akhyar, M., & Sukarmin. (2020). Technology-integrated project-based learning for pre-service teacher education: A systematic literature review. Open Engineering, 10(1), 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Hidalgo, D., & Ortega-Sánchez, D. (2022). El aprendizaje basado en proyectos: Una revisión sistemática de la literatura (2015–2022). Human Review: International Humanities Review, 14(6), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, M., Farooqi, H., Ammar, M., Siby, N., Bhadra, J., Al-Thani, N. J., Sellami, A., Fatima, N., & Ahmad, Z. (2023). A meta-analysis to gauge the effectiveness of STEM informal project-based learning: Investigating the potential moderator variables. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 32, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sart, G. (2014). The effects of the development of metacognition on project-based learning. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 152, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesan, N. C., Mehta, S., Joshi, R., Ayyappan, C., Devi, M. P., Kumar, P., & Pawar, S. (2024). A new reflective thinking framework to improve project-based learning of undergraduate engineering students. In S. Khanra Jha, M. V. Shenoy, T. Bhattacharyya, & P. Seshaiyer (Eds.), Perspective and strategies on newage education and creative learning. Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Skjott Linneberg, M., & Korsgaard, S. (2019). Coding qualitative data: A synthesis guiding the novice. Qualitative Research Journal, 19(3), 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y. (2018). Improving primary students’ collaborative problem solving competency in project-based science learning with productive failure instructional design in a seamless learning environment. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66(4), 979–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukackė, V., Guerra, A. O. P. d. C., Ellinger, D., Carlos, V., Petronienė, S., Gaižiūnienė, L., Blanch, S., Marbà-Tallada, A., & Brose, A. (2022). Towards active evidence-based learning in engineering education: A systematic literature review of PBL, PjBL, and CBL. Sustainability, 14(21), 13955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallera, F. L., & Bodzin, A. M. (2020). Integrating STEM with AgLIT (agricultural literacy through innovative technology): The efficacy of a project-based curriculum for upper-primary students. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 18(3), 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls Pou, A., Canaleta, X., & Fonseca, D. (2022). Computational thinking and educational robotics integrated into project-based learning. Sensors, 22(10), 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videnovik, M., Vlahu-Gjorgievska, E., & Trajkovik, V. (2021). To code or not to code: Introducing coding in primary schools. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 29(5), 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H. (2020). Integrating games, e-books and AR techniques to support project-based science learning. Educational Technology & Society, 23(3), 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Westland, J. (2006). The project management life cycle: A complete step-by-step methodology for initiating, planning, executing & closing a project successfully. Kogan Page. [Google Scholar]
- Wijnia, L., Noordzij, G., Arends, L. R., Rikers, R. M. J. P., & Loyens, S. M. M. (2024). The Effects of problem-based, project-based, and case-based learning on students’ motivation: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 36(1), 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarni, E. W., Purwandari, E. P., & Raharjo, F. O. (2024). The effect of integrating STEAM and virtual reality using PjBL on scientific literacy in elementary schools. Education and Information Technologies, 29(18), 24991–25011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y., & Zhang, X. (2023). Research on the design and implementation of primary school STEM project based on VR coursewares. International Journal of Technology and Design Education, 34, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S., Morrow, D. A. L., Curtis, J., & Mitchell, S. (2021). Learning culture and computational thinking in a Spanish course: A development model. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 59(5), 844–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D., & Hwang, G.-J. (2023). Effects of interaction between peer assessment and problem-solving tendencies on students’ learning achievements and collaboration in mobile technology-supported project-based learning. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 61(1), 208–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., & Ma, Y. (2023). A study of the impact of project-based learning on student learning effects: A meta-analysis study [systematic review]. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1202728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Phase | Activity | Focus | Alò et al. (2020) | Applebaum et al. (2017) | Awad (2023) | C. C. Chang and Chen (2022) | C. Y. Chang et al. (2023) | Cheng and Yang (2023) | Dasgupta et al. (2019) | Hsiao et al. (2022) | Hu et al. (2023) | Hwang et al. (2018) | Li et al. (2022) | Lou et al. (2017) | Lu et al. (2022) | Owens and Hite (2020) | Queiruga-Dios et al. (2021) | Song (2018) | Vallera and Bodzin (2020) | Valls Pou et al. (2022) | Videnovik et al. (2021) | Wang (2020) | Winarni et al. (2024) | Xie and Zhang (2023) | Zha et al. (2021) | D. Zhang and Hwang (2023) | Total Focus | Total Activity | Total Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Background review | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 24 | |||||||||||||||
| Theoretical concepts review | Teachers | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 24 | ||||||||||
| Students | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Definition of objectives, challenge, or research question | Teachers | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 12 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Students | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Development of competencies | Tools | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 17 | |||||||||
| Project management | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Planning | Plan activities and tasks | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 14 | 21 | |||||||||||
| Define the work teams | Groups | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15 | 18 | |||||||||||
| Mixed | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Define roles and responsibilities | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Execution | Design the product | Design the product | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 13 | 24 | |||||||||||
| Define requirements and materials | Collect data | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 17 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Requirements | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Materials | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Product development | Models or prototypes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Iterative | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||||||||
| Components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Product presentation | Institution | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Support material | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trial | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Closing | Product evaluation | Teachers | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Peers | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mixed | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection on the process or product | Reflections | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 7 |
| Roles of Digital Technologies | Alò et al. (2020) | Applebaum et al. (2017) | Awad (2023) | C. C. Chang and Chen (2022) | C. Y. Chang et al. (2023) | Cheng and Yang (2023) | Dasgupta et al. (2019) | Hsiao et al. (2022) | Hu et al. (2023) | Hwang et al. (2018) | Li et al. (2022) | Lou et al. (2017) | Lu et al. (2022) | Owens and Hite (2020) | Queiruga-Dios et al. (2021) | Song (2018) | Vallera and Bodzin (2020) | Valls Pou et al. (2022) | Videnovik et al. (2021) | Wang (2020) | Winarni et al. (2024) | Xie and Zhang (2023) | Zha et al. (2021) | D. Zhang and Hwang (2023) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Produce the product | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 18 | ||||||
| Access theoretical and practical content | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||||
| Design the product or its components | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | ||||||||||||||
| Collect data | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Share ideas and information | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Present the product and share reflection | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Represent the problem to be solved or product to be developed | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| PjBL process guide | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Organize ideas and information | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hinostroza, J.E.; Armstrong-Gallegos, S.; Soto-Valenzuela, P.; Villafaena, M. Phases and Activities of Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning in K-12: Findings from a Systematic Literature Review. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081021
Hinostroza JE, Armstrong-Gallegos S, Soto-Valenzuela P, Villafaena M. Phases and Activities of Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning in K-12: Findings from a Systematic Literature Review. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(8):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081021
Chicago/Turabian StyleHinostroza, J. Enrique, Stephanie Armstrong-Gallegos, Paulina Soto-Valenzuela, and Mariana Villafaena. 2025. "Phases and Activities of Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning in K-12: Findings from a Systematic Literature Review" Education Sciences 15, no. 8: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081021
APA StyleHinostroza, J. E., Armstrong-Gallegos, S., Soto-Valenzuela, P., & Villafaena, M. (2025). Phases and Activities of Technology-Integrated Project-Based Learning in K-12: Findings from a Systematic Literature Review. Education Sciences, 15(8), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15081021






