Navigating the Complexity of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
2.1. Search Procedure
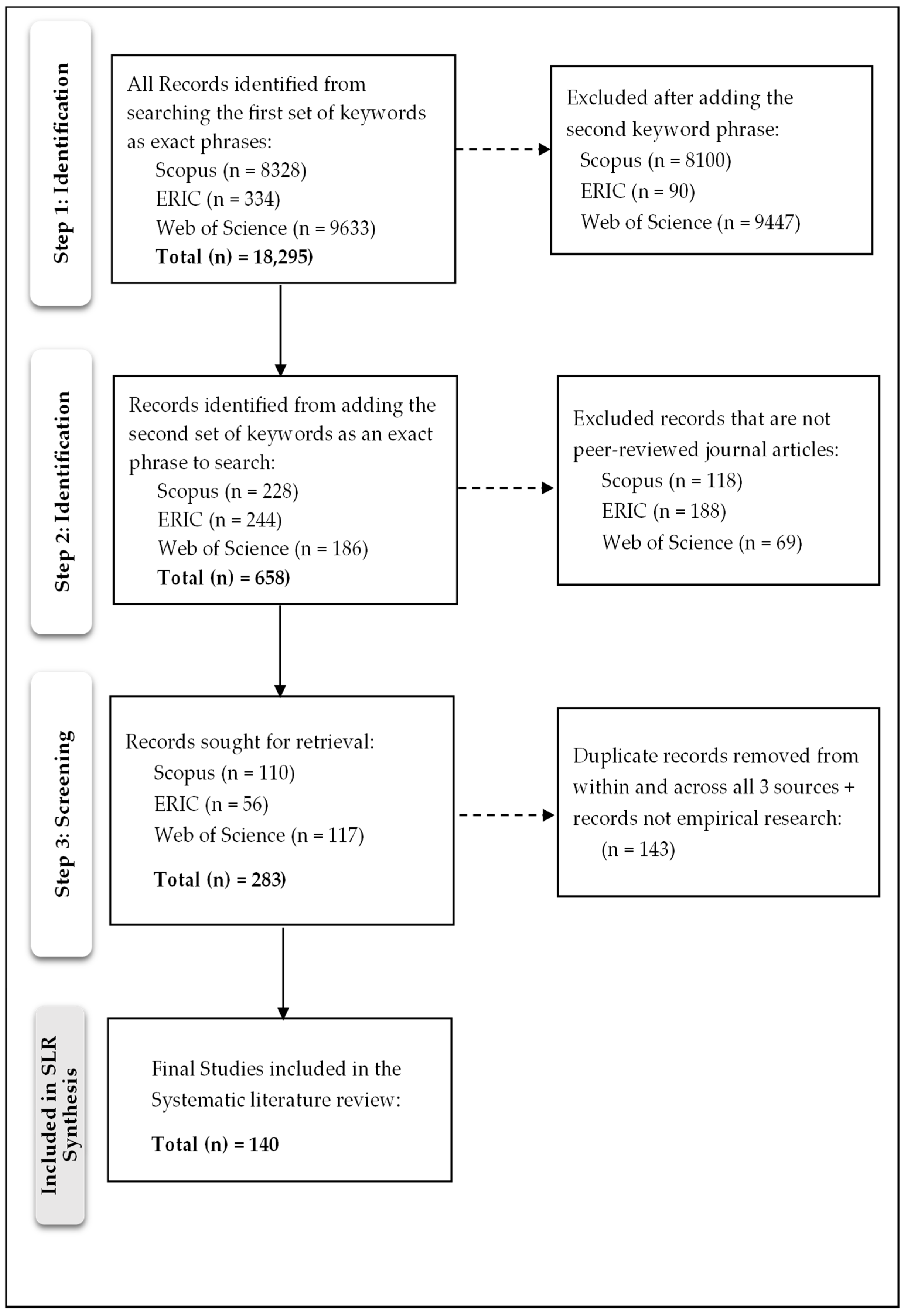
2.2. Search Steps and Article Selection
- Steps 1 and 2: Identification Phase
- Step 3: Screening Phase
- Step 4: Final Inclusion
3. Descriptive Analysis
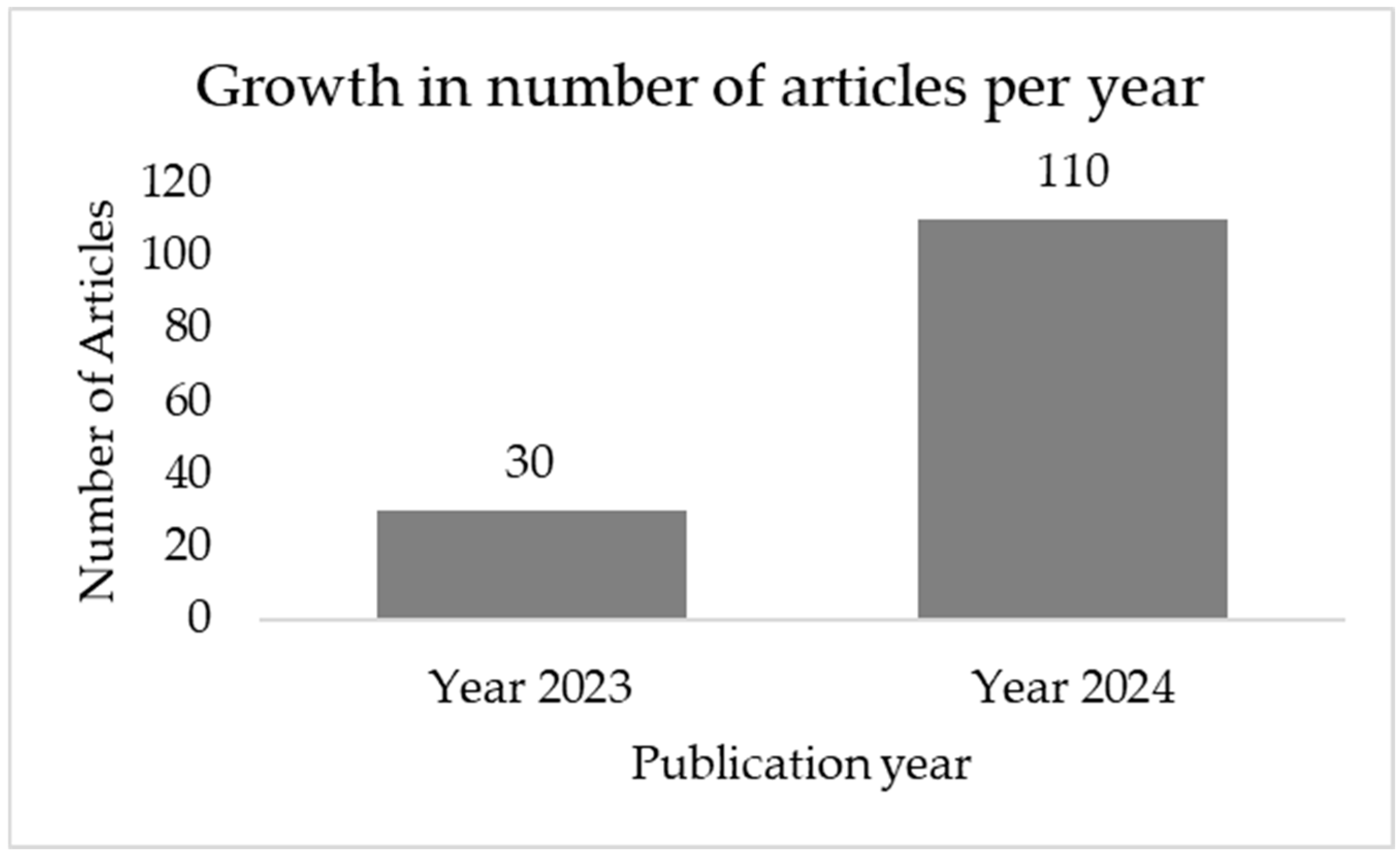
3.1. Number of Publications per Year
3.2. Influential Journals
3.3. Subject Areas
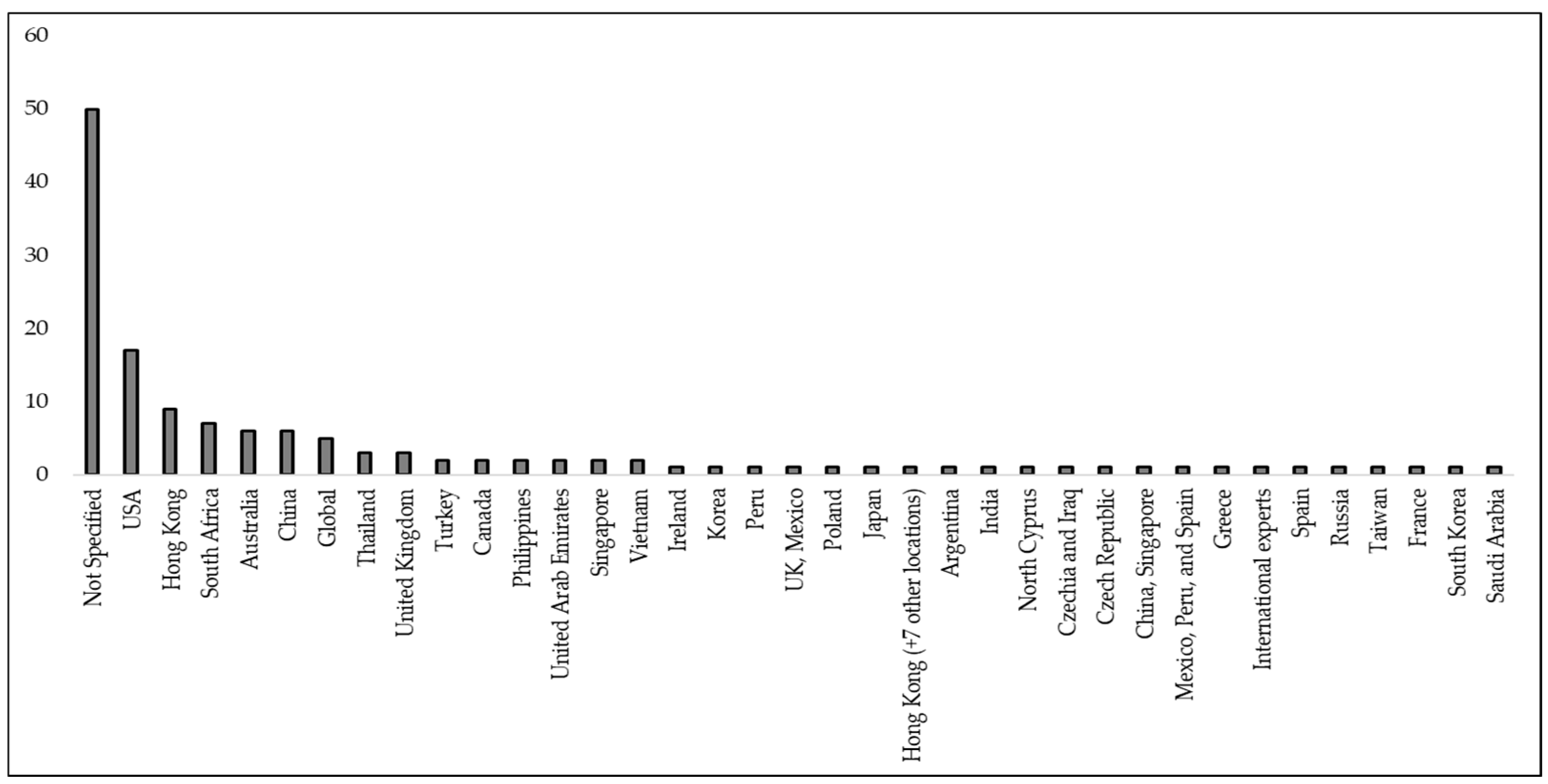
3.4. Country of Research Focus
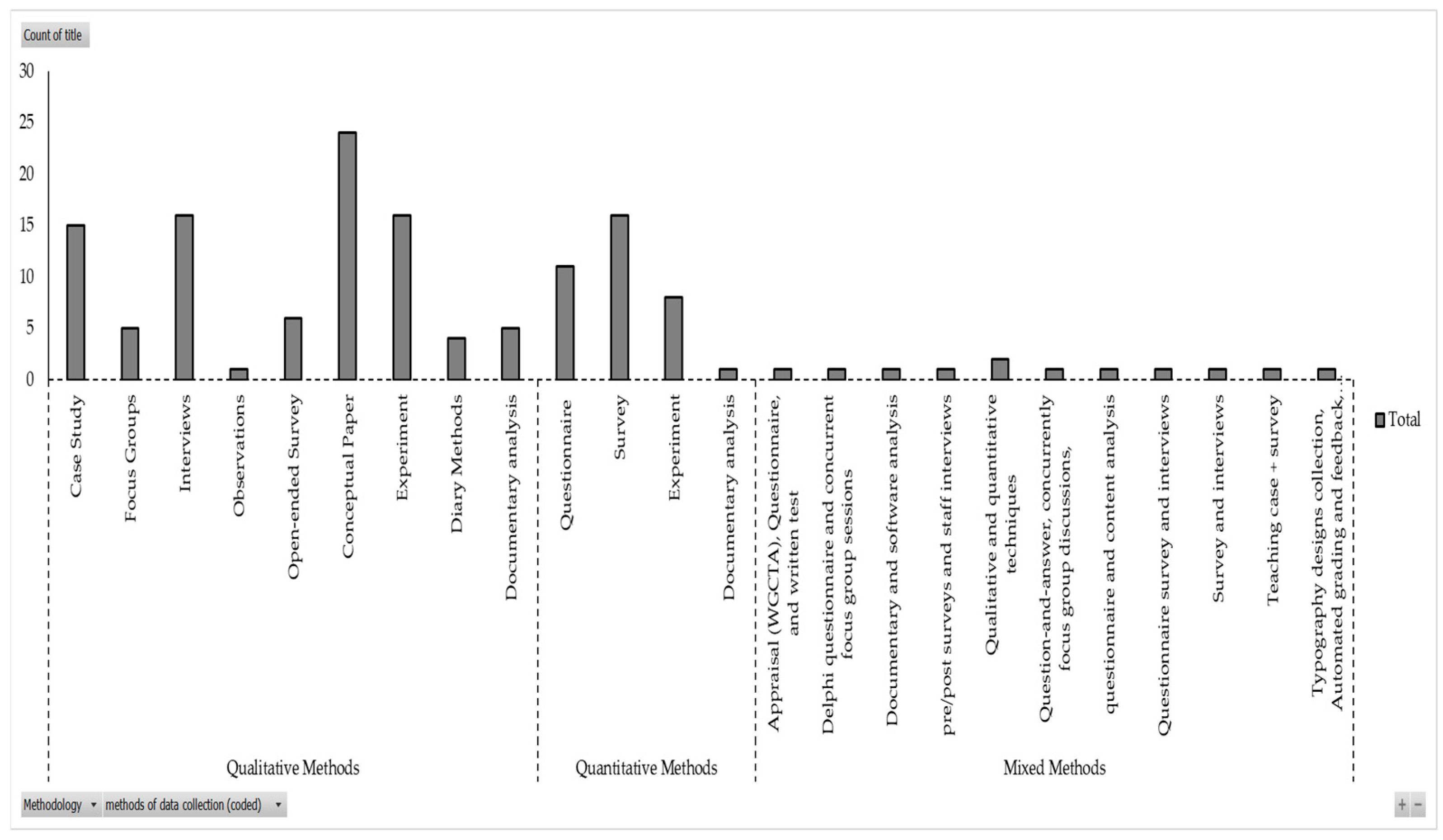
3.5. Frequently Used Research Methods
4. Thematic Analysis
4.1. Current Awareness of GAI
4.2. Perceptions of GAI in Higher Education
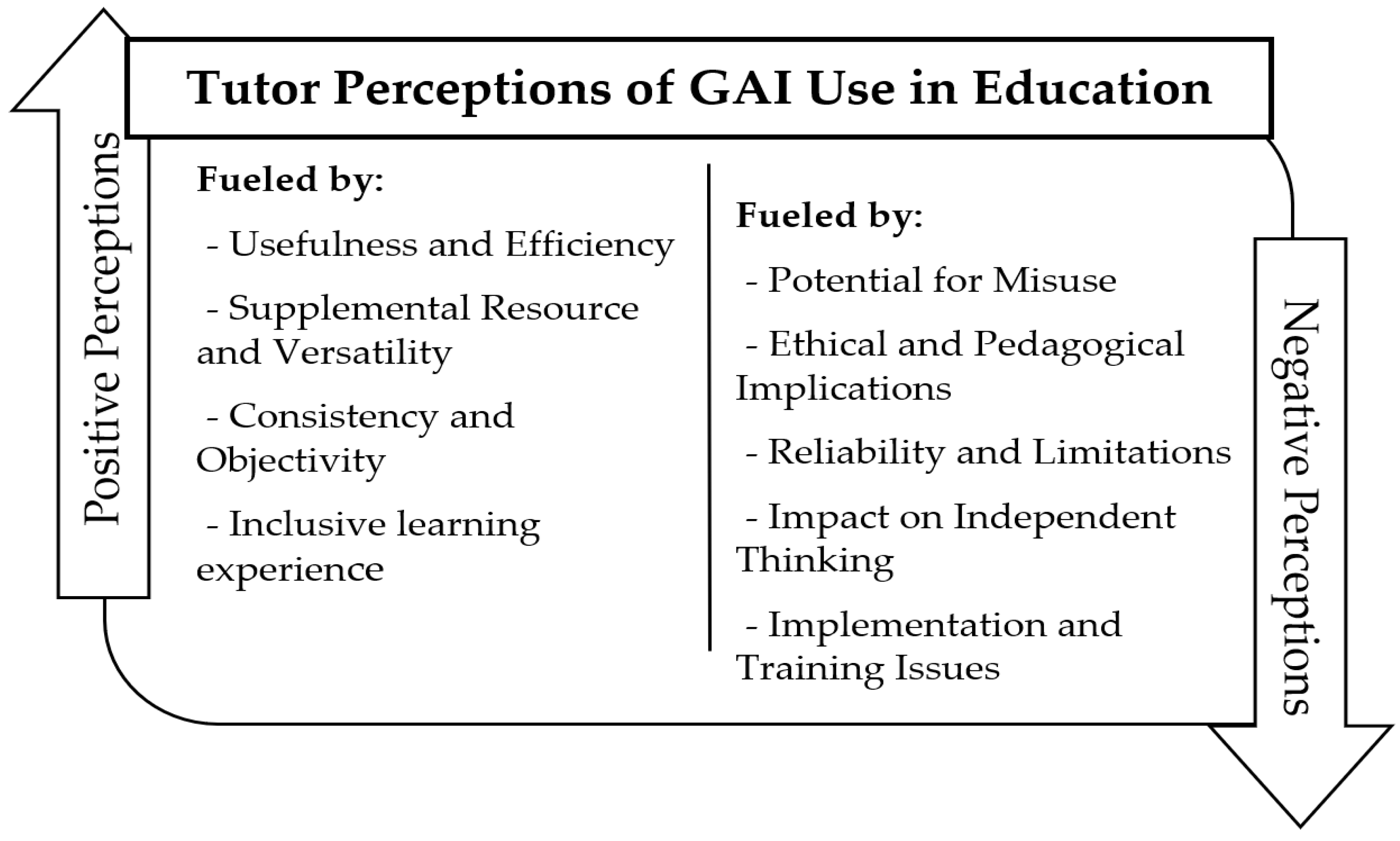
4.2.1. Tutors’ Perceptions
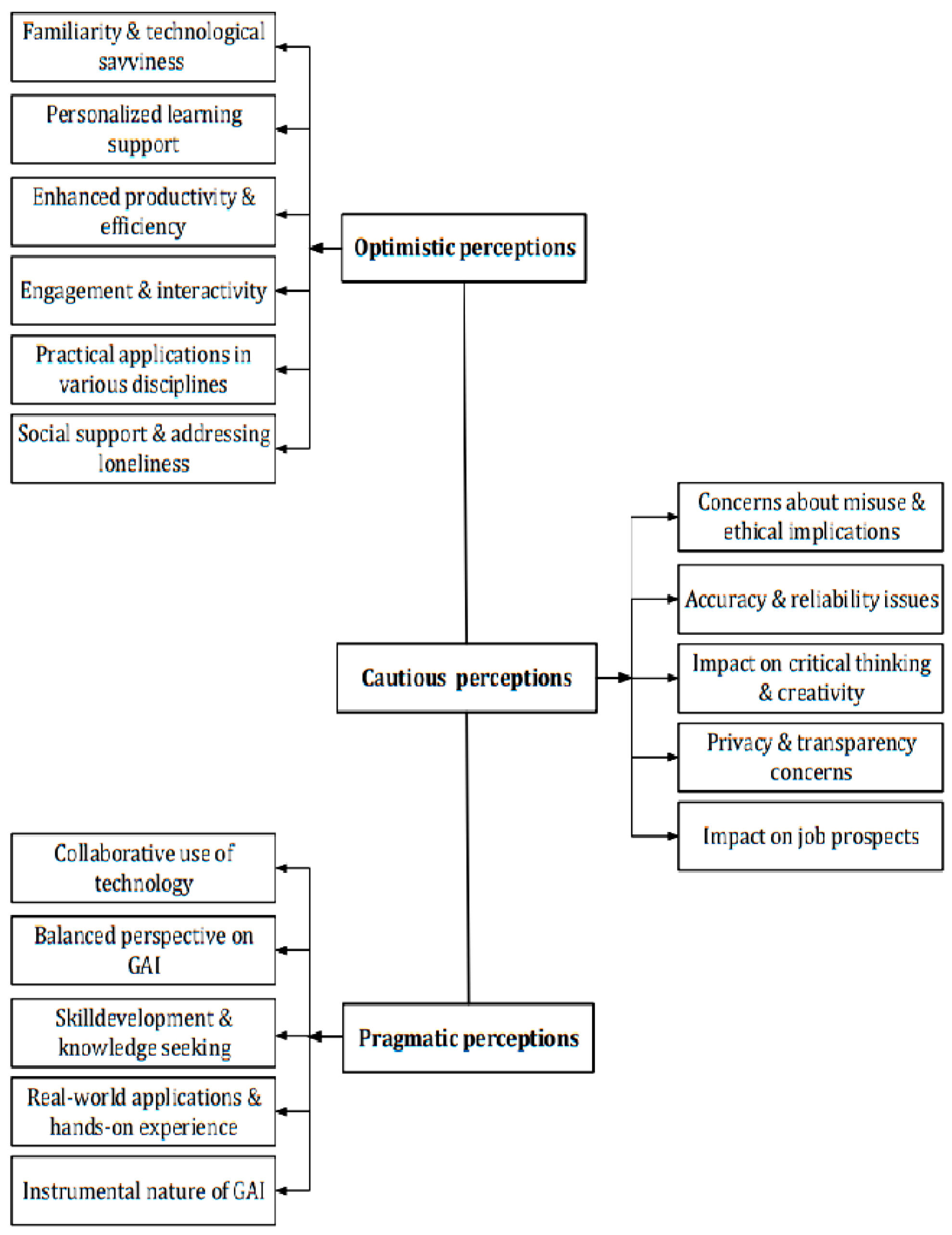
4.2.2. Students’ Perceptions
Student Optimistic Perceptions
Student Cautious Perceptions
Student Pragmatic Perceptions
4.2.3. Institutional Perceptions
4.3. Students’ Attitudinal Profiles and Academic Impact of GAI Use
4.4. Mechanisms for GAI Adoption: Drivers and Initial Barriers
4.5. Issues and Challenges of Implementing GAI
4.5.1. Accessibility and the Digital Divide
4.5.2. Institutional Support and Professional Development
4.5.3. Inclusivity and Cultural Representation
4.5.4. Academic Dishonesty: Integrity and Ethical Issues
4.5.5. Societal and Personal Impacts of Using GAI in Education
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Practical and Policy Implications of GAI in Education
5.2. Implications for Future Research: Understanding Unknown Unknowns
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almasre, M. (2024). Development and evaluation of a custom GPT for the assessment of students’ designs in a typography course. Education Sciences, 14(2), 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amofa, B., Oke, A., & Morrison, Z. (2023). Mapping the trends of sustainable supply chain management research: A bibliometric analysis of peer-reviewed articles. Frontiers in Sustainability, 4, 1129046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A., & Pack, A. (2023). Not quite eye to A.I.: Student and teacher perspectives on the use of generative artificial intelligence in the writing process. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1), 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3(2), 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. K. Y. (2023). A comprehensive AI policy education framework for university teaching and learning. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1), 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. K. Y., & Hu, W. (2023). Students’ voices on generative AI: Perceptions, benefits, and challenges in higher education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 20(1), 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C. K. Y., & Lee, K. K. W. (2023). The AI generation gap: Are Gen Z students more interested in adopting generative AI such as ChatGPT in teaching and learning than their Gen X and millennial generation teachers? Smart Learning Environments, 10(1), 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G., Brown, R., Willmers, M., & Held, M. (2024). Learning along the way: A case study on a pedagogically innovative approach to engage medical students in the creation of open educational resources using ChatGPT. Mousaion, 42(1), 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denyer, D., & Tranfield, D. (2009). Producing a systematic review. In D. A. Buchanan, & A. Bryman (Eds.), The Sage handbook of organizational research methods (pp. 671–689). Sage Publications Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Eager, B., & Brunton, R. (2023). Prompting higher education towards AI-augmented teaching and learning practice. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice, 20(5), 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M., & Haddaway, N. R. (2020). Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Research Synthesis Methods, 11(2), 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ironsi, C. S. (2023). Investigating the use of virtual reality to improve speaking skills: Insights from students and teachers. Smart Learning Environments, 10(1), 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackaria, P. M., Hajan, B. H., & Mastul, A. R. H. (2024). A Comparative analysis of the rating of college students’ essays by ChatGPT versus human raters. International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research, 23(2), 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jho, H., & Ha, M. (2024). Towards effective argumentation: Design and implementation of a generative AI-based evaluation and feedback system. Journal of Baltic Science Education, 23(2), 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan-Rakowski, R., Grotewold, K., Hartwick, P., & Papin, K. (2023). Generative AI and teachers’ perspectives on its implementation in education. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 34(2), 313–338. Available online: https://www.learntechlib.org/primary/p/222363/ (accessed on 10 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A., Sullivan, M., & Strampel, K. (2023). Generative artificial intelligence: University student awareness, experience, and confidence in use across disciplines. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice, 20(6), 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, B., Pikhart, M., & Al-Obaydi, L. H. (2024). Exploring the potential of ChatGPT for foreign language education at the university level. Frontiers in Psychology, 15, 1269319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A. V. Y., Tan, S. C., & Teo, C. L. (2023). Designs and practices using generative AI for sustainable student discourse and knowledge creation. Smart Learning Environments, 10(1), 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B., Kou, X., & Bonk, C. J. (2023). Embracing the disrupted language teaching and learning field: Analyzing YouTube content creation related to ChatGPT. Languages, 8(3), 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J., Wang, L., Luo, J., Yan, Y., & Fan, C. (2023). The relationship between student interaction with generative artificial intelligence and learning achievement: Serial mediating roles of self-efficacy and cognitive engagement. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1285392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Blanco, B., Álvarez-Ramos, E., Alejaldre-Biel, L., & Parrado-Collantes, M. (2024). Vademecum of artificial intelligence tools applied to the teaching of languages. Journal of Technology and Science Education, 14(1), 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M. Y., Tlili, A., Lampropoulos, G., Huang, R., Jandrić, P., Zhao, J., Salha, S., Xu, L., Panda, S., López-Pernas, S., & Saqr, M. (2024). A systematic review of literature reviews on artificial intelligence in education (AIED): A roadmap to a future research agenda. Smart Learning Environments, 11(1), 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, A., & Fernandes, F. A. P. (2020). Innovations in teaching and learning: Exploring the perceptions of the education sector on the 4th industrial revolution (4IR). Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(2), 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osobajo, O. A., & Oke, A. (2022). Exploring learning for on-campus students transitioning to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: Perceptions of students in the higher education. Education Sciences, 12(11), 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. The BMJ, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, V., Sureda, P., Corica, A., Schiaffino, S., & Godoy, D. (2024). Can generative AI solve geometry problems? Strengths and weaknesses of LLMs for geometric reasoning in Spanish. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 8(5), 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, I. (2023). The rise of generative AI and enculturating AI writing in postsecondary education. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 6, 1259407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T., Nguyen, B., Ha, S., & Ngoc, T. N. (2023). Digital transformation in engineering education: Exploring the potential of AI-assisted learning. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 39(5), 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, J., Tan, S., & Tan, S. (2023). ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching, 6(1), 342–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Navarro, D. E., Vilalta-Perdomo, E., Michel-Villarreal, R., & Montesinos, L. (2024). Using generative artificial intelligence tools to explain and enhance experiential learning for authentic assessment. Education Sciences, 14(1), 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, I., Kasai, H., Shikino, K., Araki, N., Takahashi, Z., Onodera, M., Kimura, Y., Tsukamoto, T., Yamauchi, K., Asahina, M., Ito, S., & Kawakami, E. (2023). Developing medical education curriculum reform strategies to address the impact of generative AI: Qualitative study. JMIR Medical Education, 9, e53466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M. (2023). Maintaining the integrity of the South African university: The impact of ChatGPT on plagiarism and scholarly writing. South African Journal of Higher Education, 37(5), 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šedlbauer, J., Činčera, J., Slavík, M., & Hartlová, A. (2024). Students’ reflections on their experience with ChatGPT. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 40(4), 1347–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thararattanasuwan, K., & Prachagool, V. (2024). Exploring perspectives of teacher students toward generative AI technologies. International Education Studies, 17(5), 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, G., & du Plessis, E. (2023). ChatGPT and generative AI: Possibilities for its contribution to lesson planning, critical thinking and openness in teacher education. Education Sciences, 13(10), 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wyk, M. M. (2024). Is ChatGPT an opportunity or a threat? Preventive strategies employed by academics related to a GenAI-based LLM at a faculty of education. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching, 7(1), 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Li, L., Tan, S. C., Yang, L., & Lei, J. (2023). Preparing for AI-enhanced education: Conceptualizing and empirically examining teachers’ AI readiness. Computers in Human Behavior, 146, 107798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., Luo, J., Yang, M., Yang, R., & Chen, J. (2024). From surface to deep learning approaches with Generative AI in higher education: An analytical framework of student agency. Studies in Higher Education, 49, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| Search Sources | Databases: Scopus, EBSCOhost’s ERIC database, Web of Science |
| Inclusion Criteria | Publication Focus: Generative AI in educational settings |
| Article Type: Peer-reviewed articles (to ensure quality and credibility) | |
| Language and Publication Year: No restrictions | |
| Geographical Scope: Included studies from all geographical regions | |
| Exclusions | Reviews, conference papers, books, book chapters, opinion pieces, editorials, and letters |
| Keywords Used | Phrases: “generative artificial intelligence” OR “generative AI” AND “teaching and learning” |
| Search Areas: Article titles, abstracts, and keywords | |
| Purpose: Ensure relevance to the intersection of generative AI and educational practices |
| Attributes | Receptive Students | Resistive Students |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Attitude | Positive and engaged; view GAI as beneficial for academic performance (Chan & Hu, 2023; Klimova et al., 2024). | Sceptical and cautious about the utility of GAI (Chan & Hu, 2023; Yang et al., 2024). |
| Willingness to Use | Willing to integrate GAI into studies and future work, with high expectations for its capabilities (Chan & Hu, 2023). | Limited interaction and superficial use due to dissatisfaction with the quality and relevance (Yang et al., 2024). |
| Engagement with Activities | Find AI-generated activities engaging and motivating, particularly in language learning contexts (Lee et al., 2023). | Exhibit scepticism and avoid further exploration of the tool due to concerns about its practical utility (Rudolph et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). |
| Interaction Experience | Describe interactions with GAI as fun, rewarding, and fast; view AI as a collaborator (Šedlbauer et al., 2024). | Limited and superficial interaction with GenAI, expressing dissatisfaction (Yang et al., 2024). |
| Confidence in Use | Confidence in using GenAI increases with experience (Kelly et al., 2023). | Concerned about accuracy and transparency, leading to lower confidence (Chan & Hu, 2023). |
| Learning Outcomes | A significant positive relationship between interaction with GAI and learning achievement is mediated by self-efficacy and cognitive engagement (Liang et al., 2023). | The educational value of GAI is doubtful, and it is a concern that it may undermine university education (Chan & Hu, 2023). |
| Ethical and Accuracy Concerns | Less concerned about ethical issues, confident in ethical use with experience (Kelly et al., 2023). Unthinkingly integrating GAI content into tasks raises ethical concerns (Yang et al., 2024). | Significant concerns about plagiarism, accuracy, transparency, and ethical implications (Chan & Hu, 2023). |
| Disciplinary Variations | Higher awareness and confidence in using GAI, especially in science and engineering disciplines (Kelly et al., 2023). | Lower awareness and confidence, particularly in healthcare disciplines (Kelly et al., 2023). |
| Motivations | Reference Authors |
|---|---|
| Personalised Learning and Tailored Assistance | (Chan & Hu, 2023; Chan & Lee, 2023) |
| Enhancing Language Learning and Communication Skills | (Ironsi, 2023; Klimova et al., 2024; Lee et al., 2023; Mateos-Blanco et al., 2024) |
| Enhancing Critical Thinking and Cognitive Engagement | (Lee et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2023; Šedlbauer et al., 2024) |
| Practical Applications | (Pham et al., 2023) |
| Meeting Modern Student Expectations | (Chan & Lee, 2023) |
| Extensive Media Coverage | (Kaplan-Rakowski et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024) |
| Barriers | Reference Authors |
| Lack of Awareness and Training | (Barrett & Pack, 2023; Kaplan-Rakowski et al., 2023) |
| Accuracy and Reliability | (Chan & Lee, 2023; Klimova et al., 2024; Parra et al., 2024; van den Berg & du Plessis, 2023) |
| Socio-Cultural Shock, Ethical Issues, Biases in Outputs, and Privacy Issues | (Chan & Hu, 2023; Pedersen, 2023; Van Wyk, 2024) |
| Impact on Learning and Critical Thinking | (Chan & Hu, 2023; Liang et al., 2023; Shimizu et al., 2023) |
| Domain | Illustrative Research Questions |
|---|---|
| Skill formation | How does sustained GAI use shape teamwork, communication, and creative thinking? |
| Tutor roles | In what ways can AI augment rather than displace the affective and ethical dimensions of teaching? |
| Detection and integrity | Which algorithmic and pedagogical methods best identify undisclosed AI assistance? |
| Model bias and reliability | How can training data diversity reduce hallucinations and linguistic bias? |
| Labour-market outcomes | What is the longitudinal relationship between student GAI proficiency and employability? |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amofa, B.; Kamudyariwa, X.B.; Fernandes, F.A.P.; Osobajo, O.A.; Jeremiah, F.; Oke, A. Navigating the Complexity of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070826
Amofa B, Kamudyariwa XB, Fernandes FAP, Osobajo OA, Jeremiah F, Oke A. Navigating the Complexity of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(7):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070826
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmofa, Birago, Xebiso Blessing Kamudyariwa, Fatima Araujo Pereira Fernandes, Oluyomi Abayomi Osobajo, Faith Jeremiah, and Adekunle Oke. 2025. "Navigating the Complexity of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review" Education Sciences 15, no. 7: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070826
APA StyleAmofa, B., Kamudyariwa, X. B., Fernandes, F. A. P., Osobajo, O. A., Jeremiah, F., & Oke, A. (2025). Navigating the Complexity of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review. Education Sciences, 15(7), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15070826











