Abstract
Cognitive stimulation during the first years of school is key to the comprehensive development of children, as it impacts functions such as attention, memory, and intelligence, and contributes to their academic performance and social adaptation. The present study aims to evaluate how the use of the abacus and physical exercise improve cognitive skills in children in the second year of primary school. This study is a randomized clinical trial with a total of 82 children, of which 58.50% were boys and 41.50% girls in the first cycle of primary education, divided into an experimental group that carried out a combined program of training with abacus and physical exercise and a control group. Selective attention and concentration were measured with the D2 test, memory with the Spanish adaptation of the Reynolds Intelligence Scale, differential perception with the Differential Perception Test (CARA-R), and general intelligence with the Raven Progressive Matrices Test. The intervention showed statistically significant improvements in attention (Cohen’s d = 0.55), concentration (Cohen’s d = 0.04), memory (Cohen’s d = 0.53), differential perception (Cohen’s d = 0.77), impulsivity control (Cohen’s d = 0.90), and general intelligence (Cohen’s d = 0.43) within the experimental group, as well as significant differences between the training and control groups in post-intervention assessments. The combination of physical exercise and abacus training effectively improves children’s cognitive development.
1. Introduction
Cognitive stimulation in the early years of schooling is a critical factor in the comprehensive development of children, impacting their ability to learn and adapt to academic and social environments. During this period, cognitive functions, such as attention, concentration, memory, differential perception, and intelligence, are in a phase of growth and plasticity, which allows appropriate interventions to generate positive long-term effects (Harvey, 2019). Current literature has widely explored the role of different tools and methodologies in children’s cognitive stimulation, especially highlighting the use of the abacus and physical exercise as effective and accessible practices (Lima-Silva et al., 2021; Peng & Rogier, 2020). These practices not only support the development of academic skills but also promote neuroplasticity and the development of executive functions, fundamental aspects for students’ academic performance and mental well-being.
The abacus, an ancient calculation tool, has been shown to be effective in stimulating mathematical skills in children, as it offers a sensory learning experience that connects abstract calculation with visual and motor processing (C. Wang et al., 2017). This type of multisensory learning can significantly improve children’s ability to perform mental calculations and develop spatial and concentration skills (Frank & Barner, 2012). Some studies have revealed that the constant use of the abacus strengthens areas of the brain related to numerical processing and working memory, which has a positive impact on students’ ability to solve complex problems and carry out tasks that require sustained concentration (Dong et al., 2016). Furthermore, it has been suggested that children who practice using the abacus develop greater creativity and cognitive flexibility when faced with calculation situations that stimulate alternative thinking and problem solving (C. Wang, 2020).
In parallel, scientific evidence supports the role of physical exercise in strengthening cognitive skills in children. Regular physical activity has been linked to improvements in executive function, attention, and memory due to its influence on neuroplasticity and neurogenesis (Best, 2010). Physical exercise contributes to better cerebral blood flow and to an increase in neurotrophic factors, which are essential for the growth and survival of neuronal cells, thus facilitating learning processes (Ratey & Loehr, 2011). Longitudinal studies have shown that children who participate in structured physical activities present superior performance in cognitive tasks that require concentration and working memory, skills that are particularly important in the school context (Ruhland & Lange, 2021; Diamond & Ling, 2016). Furthermore, physical activity has been associated with increased creativity and cognitive flexibility, key skills in problem solving and adapting to new challenges (Rominger et al., 2022).
The synergy between the use of the abacus and physical exercise as cognitive stimulation strategies is an area of growing interest in the field of education and developmental psychology. Both approaches offer benefits that, when combined, can enhance the effects on cognitive functions, providing a stronger foundation for learning in children in the first cycle of school (Y. Wang et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2011). Since the abacus focuses on specific calculation skills and mental processes and physical exercise improves executive function and general attention, the integration of both practices can provide a comprehensive framework for early cognitive development. This combination allows students to not only improve in specific academic areas but also develop fundamental skills for general learning and socio-emotional development (Li et al., 2016).
Attention and concentration are fundamental cognitive skills for effective learning, as they allow children to focus their minds on specific tasks, avoiding distractions and facilitating the acquisition of new knowledge. These processes are crucial in the context of primary education, where students must manage multiple stimuli and activities at the same time. The ability to maintain sustained attention and concentrate on a task improves content comprehension, problem solving, and overall academic performance (Huang et al., 2023). Furthermore, research has shown that the proper development of these skills favors self-regulation, allowing children to control their impulses and remain focused for long periods, which positively impacts their academic performance (Cuartas et al., 2022).
Memory, on the other hand, is essential for the acquisition and retention of information throughout the learning process. An efficient memory allows children to store and retrieve previously acquired knowledge, facilitating the integration of new ideas and the resolution of complex problems. During the first years of schooling, short- and long-term memory play a crucial role in the retention of key content, such as facts, vocabulary and mathematical concepts, which are necessary to develop more advanced skills in the future (Davidson et al., 2023). In addition, it has been proven that strengthening working memory, which allows information to be maintained and manipulated temporarily, has a direct impact on general academic performance and the ability of students to apply what they have learned in diverse contexts (Bergman Nutley & Söderqvist, 2017).
Differential perception, or the ability to distinguish between different sensory stimuli, is fundamental to children’s cognitive development. This skill allows students to improve their selective attention capacity and their accuracy in processing visual and auditory information. Differential perception is benefited by activities that stimulate the distinction of patterns, colors, and sounds, promoting greater precision in the interpretation of stimuli and improving performance in specific academic activities. Studies have shown that adequate development of differential perception is associated with improved reading and processing of mathematical operations, since children are able to better process symbols and spatial relationships (Anderson & Subrahmanyam, 2017; Föcker et al., 2022).
The concept of intelligence has been studied extensively in the educational context, and is considered a set of cognitive skills that include problem solving, logical thinking, and the ability to adapt to new contexts. According to recent research, intelligence in children can be enhanced through early cognitive interventions that include both motor activities and mental calculation exercises, since these practices promote neurogenesis and strengthen neural connections in key brain regions for learning (Goldberg, 2022; Clemente-Suárez et al., 2024). The development of intelligence in the early years of education is crucial, as it establishes a solid foundation for the acquisition of more complex skills and encourages cognitive flexibility and adaptability (Han et al., 2018).
In this context, the results of the present research have the potential to offer a novel and accessible approach to cognitive stimulation in the classroom, providing evidence on the benefits of integrating the abacus and physical exercise as complementary tools. Since the development of cognitive skills in childhood is a key predictor of academic success and psychological well-being in adult life, the identification of effective strategies in the early school years is essential for the design of educational programs that foster comprehensive and meaningful learning (Diamond, 2013). Based on this, the aim of the study is to evaluate how the use of the abacus and physical exercise as cognitive stimulation strategies can improve the cognitive abilities of second-year primary school children. In relation to this objective, the hypothesis of the study is that the use of the abacus and physical exercise as cognitive stimulation strategies can improve the cognitive skills of second-year primary school children.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design Study
This study is a randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of a combined abacus training and physical exercise program on the physical development of children in the first cycle of primary education. All participants’ legal guardians signed informed consent prior to the start of the study, which was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of the Middle Atlantic (CEI/01-013) and was carried out following the Declaration of Helsinki, good clinical practices, and all applicable laws and regulations.
2.2. Participants
Initially, 87 children in the first cycle of Primary Education were contacted, of whom 83 expressed their interest in participating and met the established criteria. The inclusion requirements were as follows: (i) school-aged children in the first cycle of Primary Education; (ii) students able to perform moderate physical activity without medical restrictions and who could handle the abacus; (iii) voluntary participation, with informed consent signed by parents or guardians. Exclusion criteria included the following: (i) children with health problems that prevented them from safely performing physical activity or using the abacus (for example, heart disease, severe respiratory problems, or motor disabilities that made physical activity difficult); (ii) students with severe cognitive or learning disabilities that significantly interfered with the use of the abacus or the possibility of benefiting from the intervention; (iii) children participating in other extracurricular programs focused on physical or cognitive training, in order to avoid interference from other interventions. Finally, a total of 82 children from the first cycle of Primary Education with an average age of 6.67 ± 1.02 years agreed to participate, of which 48 were boys (58.50%) and 34 were girls (41.50%) (Figure 1).
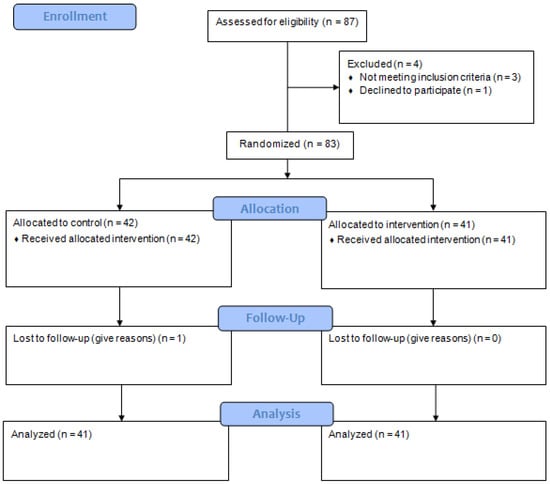
Figure 1.
Flowchart of participants in this process.
2.3. Outcomes
Data were collected pre- and post-intervention by an independent researcher, i.e., not involved in the design or implementation of the intervention. Sociodemographic information was collected from participants, including sex, age, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, height, weight, and body mass index (BMI). Height was measured using an Asimed T201-T4 stadiometer (New Delhi, India), and weight was recorded using a Tefal digital scale, accurate to 100 g up to 130 kg. From these data, BMI was calculated using the standard formula (weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared).
2.3.1. Selective Attention and Concentration
The D2 test, in its Spanish version (Seisdedos, 2012), assesses selective attention and concentration in the school context. The participant’s task is to carefully check, starting from left to right, what is written on each line and mark all the letters that have two small lines (two lower, two upper, or one lower and one upper) with a “d”. These elements are considered relevant. The other combinations (the “d” and the “p”, with and without lines) are known as irrelevant, and should not be marked. The participant has 20 s for each line. This test has demonstrated excellent reliability, with ranges between 0.90 and 0.97 for both Cronbach’s α and the test–retest, and has also shown convergent and divergent validity (Pawlowski, 2020).
2.3.2. Memory
To assess memory, a 1 min ad hoc test was used, based on the original ideas of the memory test included in the Spanish adaptation of the Reynolds Intelligence Scale [RIAS] (Santamaría-Fernández & Fernández-Pinto, 2013). A poster of 15 randomly selected Spanish playing cards was projected for 20 s on a 3 × 2 m screen. Immediately afterwards, participants had 40 s to record on a standardized sheet the greatest number of cards they remembered. The total number of correct answers was counted (range 0–15). Before the test, it was verified that all participants knew the structure and content of the 40 cards of the Spanish deck. This memory test has also been previously used in other recent research with a test–retest reliability (48 h, n = 21) of 0.919 (Ruiz-Ariza et al., 2018).
2.3.3. Difference Perception
The Differential Perception Test (CARA-R) (Thurstone & Yela, 2012) measures the ability to quickly and accurately appreciate differences and similarities in different sequential stimulation patterns. This test assesses attentional and perceptual skills through 60 graphic items composed of representative images of faces with basic features. The task carried out in this test is based on seeing which of the three faces has a different characteristic. The form of application can be individual or collective in a fairly short time, approximately 3 min. Through this test, we can obtain a measure of Differential Perception (PD) and, additionally, we can calculate the Impulsiveness Control Index (ICI) manifested in the impulsivity shown by the subjects during the task. This test has demonstrated high reliability (Cronbach’s α = 0.91), as well as convergent and divergent validity in the normative data sample (Ison & Carrada, 2012).
2.3.4. General Intelligence
To assess general intelligence, the Raven Progressive Matrices Test for children was used. This test consists of a series of incomplete geometric patterns that participants must complete by choosing the correct option from among several alternatives. The test primarily measures analogical and abstract reasoning, providing an accurate assessment of children’s general (non-verbal) intelligence, independent of linguistic or cultural influences. Results are interpreted based on the total number of correct answers, with a range varying according to the age group and educational level of participants. Before taking the test, all children are ensured to understand the dynamics of the test by introductory training with example exercises (Raven, 1957).
All questionnaires were given to participants before starting the intervention and after the end of the treatment period.
2.4. Intervention
Participants assigned to the experimental group engaged in a combined program that incorporated the use of the abacus alongside physical exercises. This 12-week intervention aimed to enhance both cognitive and physical abilities through twice-weekly, hour-long sessions divided into three distinct phases: (i) Warm-Up Phase (5 Minutes): The sessions began with a brief warm-up, featuring dynamic exercises to activate muscles and prepare participants for physical activity. During this phase, children reviewed the correct techniques for manipulating the abacus, focusing on specific finger movements: using the thumb to lift the beads, the index finger to lower them, and exclusively manipulating the top bead (representing five) with the index finger. Additionally, time was allocated to revisiting the calculations practiced in the previous session, ensuring continuity in learning. (ii) Main Phase (45 min): The central portion of each session integrated cognitive tasks with physical activities, fostering both mental and motor skill development. A step-by-step approach was adopted to teach abacus use: (a) Sessions 1–3: Introduction to the abacus, explaining its parts and bead values, followed by hands-on practice with single-digit addition and subtraction without formulas; (b) Sessions 4–5: Introduction to mental calculations for direct addition and subtraction, encouraging participants to visualize the abacus and mentally manipulate the beads; (c) Sessions 6–7: Exploration of “number friends” (complementary numbers that sum to a target, e.g., 1 + 4 = 5) to handle situations with insufficient beads for direct calculations; (d) Sessions 8–9: Application of “number friends” to subtraction scenarios with limited beads; (e) Sessions 10–11: Progression to two-digit addition and subtraction, employing two rows of the abacus; and (f) Sessions 12–14: Mastery of three-digit addition and subtraction using three rows. At the same time, physical exercises included motor games designed to improve coordination, balance, and strength. Each session included 2–3 motor games, ensuring variety and progression in difficulty. The games were selected based on their ability to promote active and cooperative learning, inspired by strategies used in playful teaching. Some of them were: (A) Coordination: (i) “Crazy traffic light”: children run or stop depending on the color indicated by the teacher, improving reaction speed; (ii) “Obstacle courses”: zigzag race between cones and jumps between hoops, promoting agility; (iii) “Number relay race”: children take turns running to a board where they must place a number to complete a mathematical operation; (B) Balance: (i) “Acrobat path”: Walk on lines drawn on the ground or ropes placed on the ground; (ii) “Mathematical statues”: upon hearing a number, children must remain motionless in a specific posture; (iii) “Number jump”: jumps between numbered marks on the floor according to the result of an operation with the abacus; and (C) Strength: (i) “Cooperative pull”: resistance games with ropes or elastic bands in teams; (ii) “Push and solve”: in pairs, children must gently push with the palms of their hands while mentally solving an operation; (iii) “Mathematical load”: Carry small sandbags while solving a simple calculation when reaching the goal. These games were conducted in a cooperative, engaging environment and linked to abacus learning. After completing each physical activity, children solved mathematical problems using the abacus, reinforcing both sets of skills and promoting a holistic learning experience. (iv) Correction Phase (10 min): In the final phase, exercises were reviewed to address any uncertainties and consolidate understanding. Group discussions were encouraged, allowing participants to reflect on their progress, share experiences, and celebrate achievements. Consistent communication was maintained with participants’ guardians to ensure adherence to the program’s activities, thereby maintaining the intervention’s integrity.
2.5. Procedure
To recruit participants, a school in eastern Andalusia was contacted. An initial meeting was organized with the legal guardians of the students, during which detailed information about the study was shared. Guardians were provided with both an information sheet and informed consent forms. Once the consent forms were signed and eligibility criteria verified, baseline data collection began. This involved administering all questionnaires to participants prior to the start of the intervention and repeating the process after the intervention concluded. Participants were then randomly assigned to one of two groups: (i) Experimental Group (EG): This group participated in a combined program incorporating abacus use and physical exercises, conducted in the school gymnasium during their Physical Education class (from 12:00 to 12:45 p.m.). (ii) Control Group (CG): This group followed their regular Physical Education curriculum without any additional program.
The group allocation process was blinded for participants, researchers, and teachers. It was carried out in a 1:1 ratio, using a computer-generated random number table. Assignments were determined using sealed, opaque, and numbered envelopes stored in an unsecured location. These envelopes were opened by an independent third party uninvolved in the study to ensure objectivity. The intervention sessions were delivered by the students’ teachers, who were trained in the program methodology during a two-week preparatory phase before the intervention commenced. Throughout the study, research team members supervised the sessions to ensure adherence to the planned activities. To monitor engagement and compliance, an attendance and observation log was maintained for each session. Any participant who failed to attend at least 80% of the scheduled sessions was excluded from the study, as insufficient attendance would jeopardize the reliability and validity of the findings.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Analysis of continuous and categorical variables based on study participation (CG vs. EG) was performed using Student’s t test and χ2 test, respectively. Before proceeding with the analysis, normality and homogeneity tests were performed (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test and Levene’s test, respectively). To investigate the effects of the intervention, a mixed analysis of variance (ANOVA) was carried out, considering the intervention (GE vs. CG) as the between-group factor and the assessment time (pre- and post-treatment) as the within-subject factor. Dependent variables included concentration, attention, memory, difference perception, and general intelligence, and specific assessments were carried out for each of them. Likewise, the possible interaction between treatment group and assessment time was examined. Cohen’s d was used to calculate the effect size between groups, where values of ≤0.2 indicated a small effect, 0.5 a moderate effect, and 0.8 a large effect. A threshold for statistical significance was set at a p value less than 0.05. Data analysis was performed using SPSS software, version 17.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
The mean age of the participants was 6.67 ± 1.02 years, of which 58.50% were boys and 41.50% were girls (Table 1). Every participant enrolled in the study maintained attendance above 80% of the scheduled sessions, ensuring their full participation and completion of the intervention program. Significant differences between CG and EG were not found in concentration, attention, memory, difference perception, or general intelligence in pre-measurements (all p > 0.05).

Table 1.
Preintervention sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of the participants as a whole and by group.
3.1. Selective Attention and Concentration
In the selective attention, statistically significant differences were observed between pre and post measurements in the training group (t(40) = −8.169, p = 0.000, with a medium Cohen’s d = 0.55), and statistically significant differences were found between both groups in the post-intervention measurement (t(80) = −2.084, p = 0.040, with a small Cohen’s d = 0.46). In the concentration, statistically significant differences were observed between pre and post measurements in the training group (t(40) =2.358, p = 0.023, with an insignificant Cohen’s d = 0.04), and statistically significant differences were found between both groups in the post-intervention measurement (t(80) = 4.273, p = 0.000, with a large Cohen’s d = 0.94) (Figure 2) (Table 2).

Figure 2.
Inter- and intragroup comparisons regarding concentration and selective attention. * p < 0.05. *** p < 0.001.

Table 2.
Effects of physical exercise and the abacus on cognitive capacities.
3.2. Memory
In the memory, statistically significant differences were observed between pre and post measurements in the training group (t(40) = −11.443, p = 0.000, with a medium Cohen’s d = 0.53), and statistically significant differences were found between both groups in the post-intervention measurement (t(80) = −3.555, p = 0.001, with a medium Cohen’s d = 0.79) (Figure 3) (Table 2).
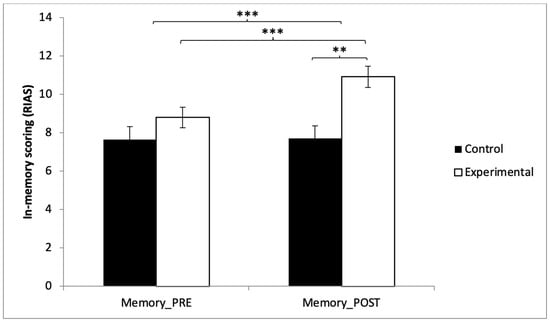
Figure 3.
Inter- and intragroup comparisons regarding memory. ** p < 0.01. *** p < 0.001.
3.3. Difference Perception and Impulsivity
In the difference perception, statistically significant differences were observed between pre and post measurements in the training group (t(40) = −4.607, p = 0.000, with a medium Cohen’s d = 0.77), and statistically significant differences were found between both groups in the post-intervention measurement (t(80) = 2.173, p = 0.033, with a small Cohen’s d = 0.48). In the Impulsivity Control Index, statistically significant differences were observed between pre and post measurements in the training group (t(40) = −12.892, p = 0.000, with a large Cohen’s d = 0.90), and statistically significant differences were found between both groups in the post-intervention measurement (t(80) = −2.059, p = 0.043, with a small Cohen’s d = 0.45) (Figure 4) (Table 2).

Figure 4.
Inter- and intragroup comparisons regarding difference perception and impulsivity control. * p < 0.05. ** p < 0.01. *** p < 0.001.
3.4. General Intelligence
In the general intelligence, statistically significant differences were observed between pre and post measurements in the training group (t(40) = −2.877, p = 0.006, with a small Cohen’s d = 0.43), and statistically significant differences were found between both groups in the post-intervention measurement (t(80) = −6.013, p = 0.000, with a large Cohen’s d = 1.33) (Figure 5) (Table 2).
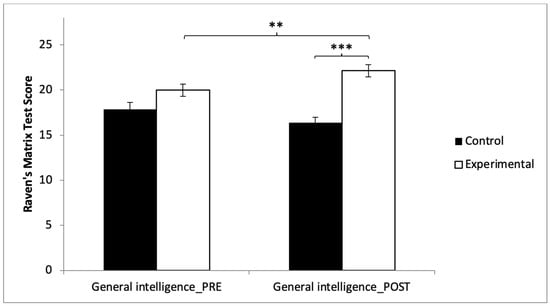
Figure 5.
Inter- and intragroup comparisons regarding general intelligence. ** p < 0.01. *** p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to analyse the effects of using the abacus and physical exercise in improving cognitive skills in second-grade children. The results showed significant improvements in attention, concentration, memory, differential perception, impulsivity control, and general intelligence in the group that carried out the intervention. The findings of this study underline the importance of combining physical exercise and the use of the abacus as effective tools for cognitive development in childhood. The results are in line with previous research highlighting the positive impact of these interventions on key cognitive functions such as attention, concentration, memory, linguistic reasoning speed, and mathematical calculation. These effects are best understood through a number of neurophysiological and cognitive mechanisms described in the scientific literature (Bherer et al., 2013; Mandolesi et al., 2018; Bidzan-Bluma & Lipowska, 2018).
Physical exercise has been shown to positively influence children’s attention and concentration. Several studies highlight that exercise contributes to the regulation of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine, both crucial for attention control (Mahindru et al., 2023). In addition, it has been observed that exercise stimulates activity in the prefrontal cortex, improving sustained attention and the ability to concentrate in academic contexts (Best, 2010; Budde et al., 2008). This coincides with research reporting that physically active children show better performance in attention and inhibitory control tasks (Latino & Tafuri, 2023; Ruhland & Lange, 2021). In the long term, these benefits can be maintained and prevent attention deficits in adolescence and adulthood, contributing to better academic and professional performance (Hillman et al., 2008).
Memory is another variable significantly influenced by both physical exercise and the use of the abacus. In the case of exercise, it has been proposed that the increase in neurotrophic factors such as BDNF contributes to neurogenesis in the hippocampus, a fundamental area for memory (Erickson et al., 2011; Voss et al., 2011). Research shows that regular exercise in children and adolescents is associated with better performance in tests of working memory and spatial memory (Hillman et al., 2009; Khan & Hillman, 2014). In the long term, these effects may translate into less memory loss in adulthood and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases (Schneider et al., 2020). On the other hand, the abacus improves memory through its focus on mental visualization, which facilitates the retention of information and the manipulation of numerical data (Kowatari et al., 2009; Frank & Barner, 2012). This has been supported by studies indicating that abacus training strengthens working memory by requiring mental representation of calculations and operations (Y. Wang et al., 2019).
Regarding linguistic reasoning speed, physical exercise also plays a relevant role by increasing neuronal processing speed, which facilitates fast and accurate reasoning (Pesce, 2012; Chang et al., 2013). Physical activity not only improves linguistic processing speed but also influences reading comprehension and verbal fluency, with possible variations depending on age or level of linguistic ability. In the long term, this can translate into greater cognitive efficiency in solving complex problems and improved learning in adulthood (Hillman et al., 2020). Although the abacus is more directly related to mathematical skills, its frequent use seems to have positive effects on other cognitive areas, such as general reasoning, by training mental processing speed (Barner et al., 2016). Furthermore, mental calculation training not only strengthens the speed of verbal decision-making, but can also contribute to the development of more efficient cognitive strategies. This finding is in line with studies indicating that training in calculation skills can be transferred to other cognitive functions (Takeuchi et al., 2011), as can other types of cognitive training that enhance language and verbal reasoning.
Differential perception also plays a crucial role in cognitive development. Physical exercise not only improves functions related to memory and attention but also fosters sensory perception and the ability to process external stimuli more efficiently. It has been shown that the activation of brain areas related to perception, such as the sensory cortex, is increased by physical activity, thus improving children’s ability to discriminate visual and auditory stimuli more effectively (Best, 2010). This improvement in perception can have direct implications for learning, especially in activities that require sensory discrimination and rapid decision making.
As for general intelligence, both physical exercise and the use of the abacus have been shown to contribute to the increase in general cognitive abilities. Exercise, by improving cerebral circulation and neuronal plasticity, has a positive impact on high-level cognitive functions, such as abstract reasoning and problem solving (Hillman et al., 2008). Similarly, the use of the abacus not only improves mathematical skills but also enhances the capacity for logical and abstract reasoning, central aspects of general intelligence (Y. Wang et al., 2019). Longitudinal studies suggest that the development of these skills in childhood is associated with greater academic and professional success in adulthood (Diamond & Ling, 2016).
The results of this study have important practical implications. Implementing school-based programs that combine physical exercise and cognitive training, such as the use of abacus, could improve academic performance in key areas such as mathematics and reading comprehension, while strengthening executive functions and attentional control (Schmidt et al., 2020). This combination of interventions is especially useful for children with attention problems and learning difficulties, who often benefit from improvements in their cognitive ability and self-confidence when participating in these programs (Chaddock-Heyman et al., 2014; Diamond & Lee, 2011). Furthermore, while previous studies have indicated that factors such as socioeconomic status can influence children’s cognitive development through access to educational resources, nutrition, and stress levels at home (Cuartas et al., 2022), the present study focused on evaluating the direct effects of a specific intervention in a controlled school setting. By randomly assigning participants, we sought to minimize potential biases related to differences in socioeconomic context. However, future research could analyze how variables such as family environment or parents’ educational level can influence the effectiveness of this type of intervention.
This study presents some limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, the sample of participants was relatively small and homogeneous, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Future studies need to include larger and more diverse samples to verify the validity of the results in different cultural and socioeconomic contexts. Second, the intervention period was short, so it cannot be determined whether the observed effects are maintained in the long term. Longitudinal studies could provide information on the durability of the cognitive benefits associated with physical exercise and abacus training. Finally, the study did not consider other variables that could influence the results, such as family support, school environment, and individual differences in emotional and motivational development, aspects that also affect cognitive performance (Scionti et al., 2020).
5. Conclusions
Both physical exercise and the use of the abacus are effective interventions to promote cognitive development in childhood. Evidence suggests that exercise improves the neurophysiological basis necessary for learning, while the abacus enhances specific cognitive skills, such as perception and reasoning. The joint implementation of both interventions could be a valuable strategy to maximize cognitive development in children. However, additional longitudinal studies are needed to assess the sustained effects of these interventions over time and determine whether their benefits can be maintained in the long term.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.d.C.C.-F. and V.L.; methodology, J.L.S.-M.; formal analysis, A.A.-A.; writing—original draft preparation, V.L. and J.L.S.-M.; writing—review and editing, M.d.C.C.-F. and A.A.-A.; supervision, A.A.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been partially supported by the R&D&I project (grant number: PID2022-137432OB-I00). Support was also received from the University Teacher Training Program of the Spanish Ministry [Reference: AP-2020-03217].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the University of the Middle Atlantic (CEI/01-013).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Anderson, D. R., & Subrahmanyam, K. (2017). Cognitive impacts of digital media workgroup. Digital screen media and cognitive development. Pediatrics, 140(Suppl. 2), S57–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barner, D., Alvarez, G., Sullivan, J., Brooks, N., Srinivasan, M., & Frank, M. C. (2016). Learning mathematics in a visuospatial format: A randomized, controlled trial of mental abacus instruction. Child Development, 87(4), 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman Nutley, S., & Söderqvist, S. (2017). How is working memory training likely to influence academic performance? Current evidence and methodological considerations. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J. R. (2010). Effects of physical activity on children’s executive function: Contributions of experimental research on aerobic exercise. Developmental Review, 30(4), 331–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bherer, L., Erickson, K. I., & Liu-Ambrose, T. (2013). A review of the effects of physical activity and exercise on cognitive and brain functions in older adults. Journal of Aging Research, 2013, 657508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidzan-Bluma, I., & Lipowska, M. (2018). Physical activity and cognitive functioning of children: A systematic review. International journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(4), 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, H., Voelcker-Rehage, C., Pietrabyk-Kendziorra, S., Ribeiro, P., & Tidow, G. (2008). Acute coordinative exercise improves attentional performance in adolescents. Neuroscience Letters, 441(3), 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddock-Heyman, L., Hillman, C. H., Cohen, N. J., & Kramer, A. F. (2014). The importance of physical activity and aerobic fitness for cognitive control and memory in children. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 79(4), 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y. K., Tsai, Y. J., Chen, T. T., & Hung, T. M. (2013). The impacts of coordinative exercise on executive function in kindergarten children: An ERP study. Experimental Brain Research, 225(2), 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. S., Wang, T. C., & Wang, C. N. (2011). Effect of mental abacus training on working memory for children. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Industrial Engineers, 28(6), 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V. J., Beltrán-Velasco, A. I., Herrero-Roldán, S., Rodriguez-Besteiro, S., Martínez-Guardado, I., Martín-Rodríguez, A., & Tornero-Aguilera, J. F. (2024). Digital device usage and childhood cognitive development: Exploring effects on cognitive abilities. Children, 11(11), 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuartas, J., Hanno, E., Lesaux, N. K., & Jones, S. M. (2022). Executive function, self-regulation skills, behaviors, and socioeconomic status in early childhood. PLoS ONE, 17(11), e0277013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, C., Shing, Y. L., McKay, C., Rafetseder, E., & Wijeakumar, S. (2023). The first year in formal schooling improves working memory and academic abilities. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 60, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A. (2013). Executive functions. Annual Review of Psychology, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A., & Lee, K. (2011). Interventions shown to aid executive function development in children 4 to 12 years old. Science, 333(6045), 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, A., & Ling, D. S. (2016). Conclusions about interventions, programs, and approaches for improving executive functions that appear justified and those that, despite much hype, do not. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 18, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S., Wang, C., Xie, Y., Hu, Y., Weng, J., & Chen, F. (2016). The impact of abacus training on working memory and underlying neural correlates in young adults. Neuroscience, 22, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K. I., Voss, M. W., Prakash, R. S., Basak, C., Szabo, A., Chaddock, L., Kim, J. S., Heo, S., Alves, H., White, S. M., & Wojcicki, T. R. (2011). Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(7), 3017–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föcker, J., Atkins, P., Vantzos, F. C., Wilhelm, M., Schenk, T., & Meyerhoff, H. S. (2022). Exploring the effectiveness of auditory, visual, and audio-visual sensory cues in a multiple object tracking environment. Attention, Perception & Psychophysics, 84(5), 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M. C., & Barner, D. (2012). Representing exact number visually using mental abacus. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 141(1), 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, H. (2022). Growing brains, nurturing minds-neuroscience as an educational tool to support students’ development as life-long learners. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K., Hadjipantelis, P. Z., Wang, J. L., Kramer, M. S., Yang, S., Martin, R. M., & Müller, H. G. (2018). Functional principal component analysis for identifying multivariate patterns and archetypes of growth, and their association with long-term cognitive development. PLoS ONE, 13(11), e0207073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, P. D. (2019). Domains of cognition and their assessment. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 21(3), 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, C. H., Erickson, K., & Kramer, A. (2008). Be smart, exercise your heart: Exercise effects on brain and cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9(1), 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, C. H., McDonald, K. M., & Logan, N. E. (2020). A review of the effects of physical activity on cognition and brain health across children and adolescence. Nestle Nutrition Institute Workshop Series, 95, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, C. H., Pontifex, M. B., Raine, L. B., Castelli, D. M., Hall, E. E., & Kramer, A. F. (2009). The effect of acute treadmill walking on cognitive control and academic achievement in preadolescent children. Neuroscience, 159(3), 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H., Li, R., & Zhang, J. (2023). A review of visual sustained attention: Neural mechanisms and computational models. PeerJ, 11, e15351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M. S., & Carrada, M. (2012). Tipificación argentina del Test de Percepción de Diferencias (CARAS). In T. Louis Leon, & Y. Mariano (Eds.), Test de Percepción de Diferencias Revisado (CARAS-R) (pp. 37–63). Tea Edition. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N. A., & Hillman, C. H. (2014). The relation of childhood physical activity and aerobic fitness to brain function and cognition: A review. Pediatric Exercise Science, 26(2), 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowatari, Y., Lee, S. H., Yamamura, H., Nagamori, Y., Levy, P., Yamane, S., & Yamamoto, M. (2009). Neural networks involved in artistic creativity. Human Brain Mapping, 30(5), 1678–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latino, F., & Tafuri, F. (2023). Physical activity and academic performance in school-age children: A systematic review. Sustainability, 15(8), 6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Chen, F., & Huang, W. (2016). Neural plasticity following abacus training in humans: A review and future directions. Neural Plasticity, 2016, 1213723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Silva, T. B., Barbosa, M. E. C., Zumkeller, M. G., Verga, C. E. R., Prata, P. L., Cardoso, N. P., de Moraes, L. C., & Brucki, S. M. D. (2021). Cognitive training using the abacus: A literature review study on the benefits for different age groups. Dementia & Neuropsychologia, 15(2), 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahindru, A., Patil, P., & Agrawal, V. (2023). Role of physical activity on mental health and well-being: A review. Cureus, 15(1), e33475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolesi, L., Polverino, A., Montuori, S., Foti, F., Ferraioli, G., Sorrentino, P., & Sorrentino, G. (2018). Effects of physical exercise on cognitive functioning and wellbeing: Biological and psychological benefits. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlowski, J. (2020). Test de atención d2: Consistencia interna, estabilidad temporal y evidencias de validez. Revista Costarricense de Psicología, 39(1), 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P., & Rogier, A. K. (2020). The development of academic achievement and cognitive abilities: A bidirectional perspective. Child Development Perspectives, 14(1), 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, C. (2012). Shifting the focus from quantitative to qualitative exercise characteristics in exercise and cognition research. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 34(6), 766–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratey, J. J., & Loehr, J. E. (2011). The positive impact of physical activity on cognition during adulthood: A review of underlying mechanisms, evidence and recommendations. Reviews in the Neurosciences, 22(2), 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, J. C. (1957). Test de matrices progresivas. Escala especial Buenos Aires. Paidós. [Google Scholar]
- Rominger, C., Schneider, M., Fink, A., Tran, U. S., Perchtold-Stefan, C. M., & Schwerdtfeger, A. R. (2022). Acute and chronic physical activity increases creative ideation performance: A systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis. Sports Med-Open, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhland, S., & Lange, K. W. (2021). Effect of classroom-based physical activity interventions on attention and on-task behavior in schoolchildren: A systematic review. Sports Medicine and Health Science, 3(3), 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ariza, A., Casuso, R. A., Suarez-Manzano, S., & Martínez-López, E. J. (2018). Effect of augmented reality game Pokémon GO on cognitive performance and emotional intelligence in adolescent youth. Computers & Education, 116, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría-Fernández, P., & Fernández-Pinto, I. (2013). Adaptación Española de RIAS. Reynolds intellectual assessment scales. TEA Ediciones. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M., Mavilidi, M. F., Singh, A., & Englert, C. (2020). Combining physical and cognitive training to improve kindergarten children’s executive functions: A cluster randomized controlled trial. Contemporaru Educational Psychology, 63, 101908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F., Horowitz, A., Lesch, K. P., & Dandekar, T. (2020). Delaying memory decline: Different options and emerging solutions. Translational Psychiatry, 10(1), 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scionti, N., Cavallero, M., Zogmaister, C., & Marzocchi, G. M. (2020). Is cognitive training effective for improving executive functions in preschoolers? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seisdedos, N. (2012). Adaptación Española D2, test de atención de brickenkamp. TEA Ediciones. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, H., Taki, Y., Hashizume, H., Sassa, Y., Nagase, T., Nouchi, R., & Kawashima, R. (2011). Effects of training of processing speed on neural systems. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(34), 12139–12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurstone, L. L., & Yela, M. (2012). CARAS-R. Test de percepción de diferencias-revisado. TEA Ediciones. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, M. W., Nagamatsu, L. S., Liu-Ambrose, T., & Kramer, A. F. (2011). Exercise, brain, and cognition across the life span. Journal of Applied Physiology, 111(5), 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. (2020). A review of the effects of abacus training on cognitive functions and neural systems in humans. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., Weng, J., Yao, Y., Dong, S., Liu, Y., & Chen, F. (2017). Effect of abacus training on executive function development and underlying neural correlates in Chinese children. Human Brain Mapping, 38(11), 5234–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Lu, C., & Chen, C. (2019). The effect of abacus-based mental calculation on the cognitive performance of elementary school students: A meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).