Development and State of the Art of Entrepreneurship Education: A Bibliometric Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review of Entrepreneurship Education
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
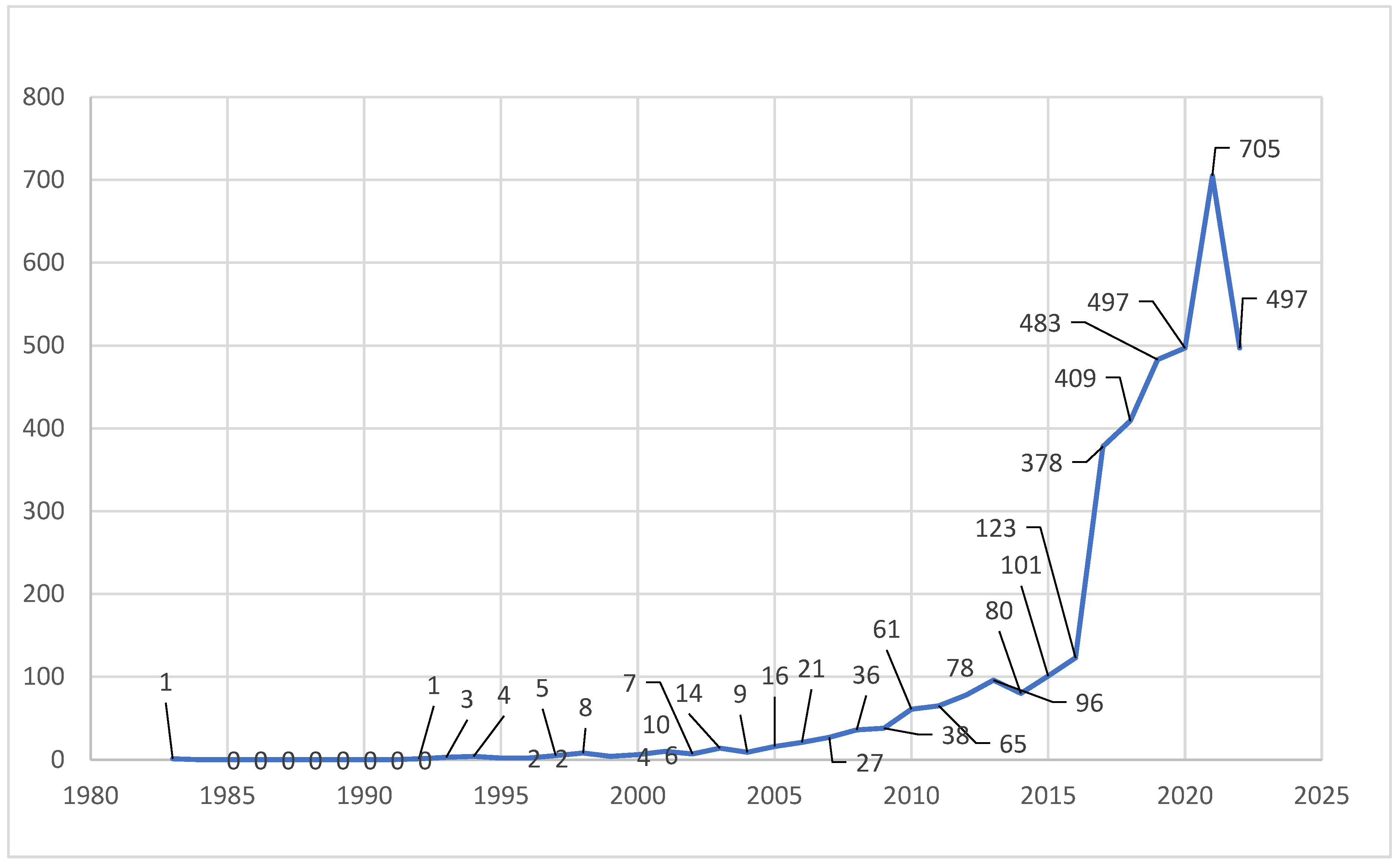
4.1. General Characteristic Features of EE Related Literature
4.2. Sources
4.3. Geographic Structure of the Research
4.4. Epistemological Analysis of the Knowledge Base Development of EE
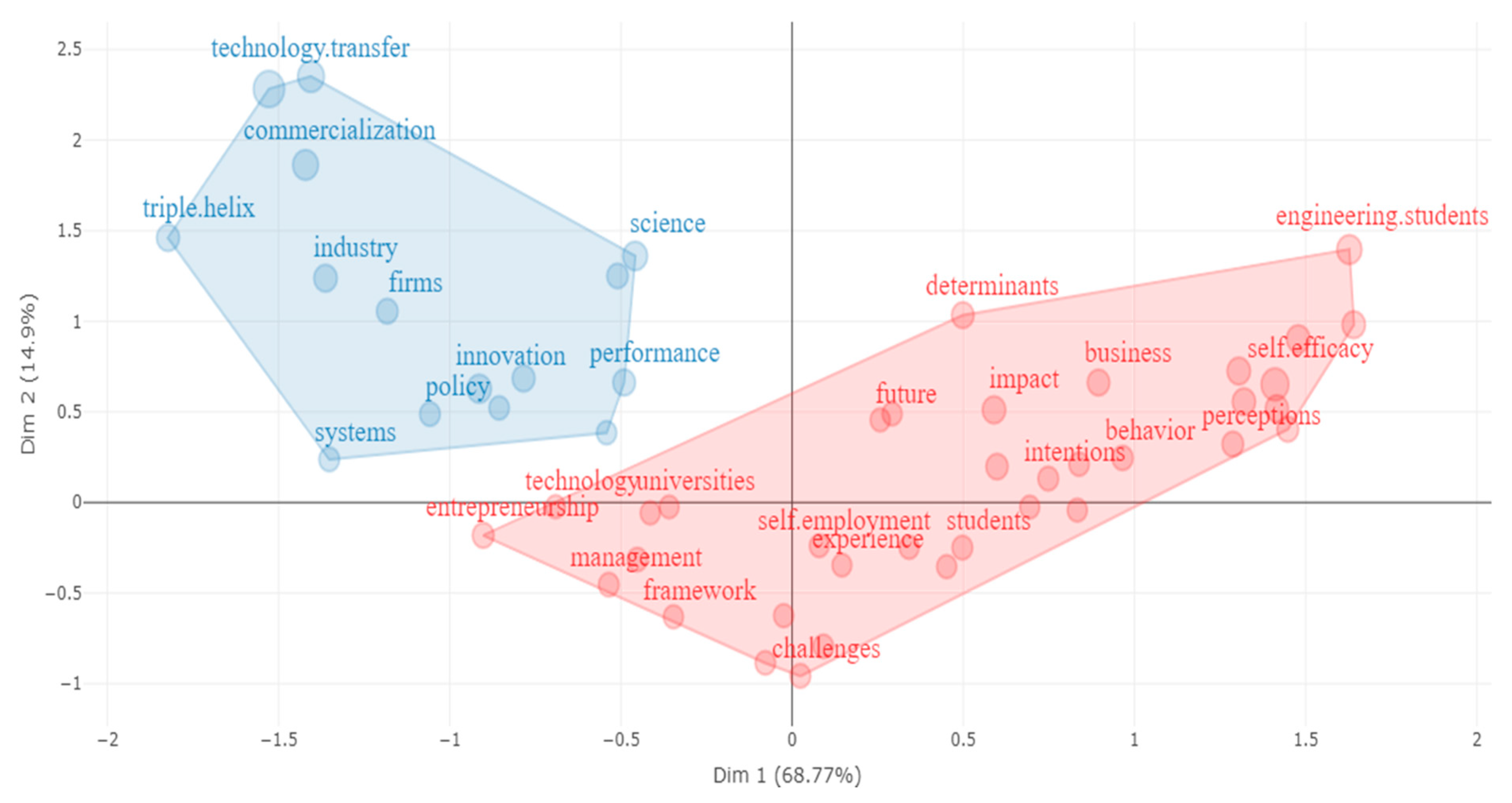
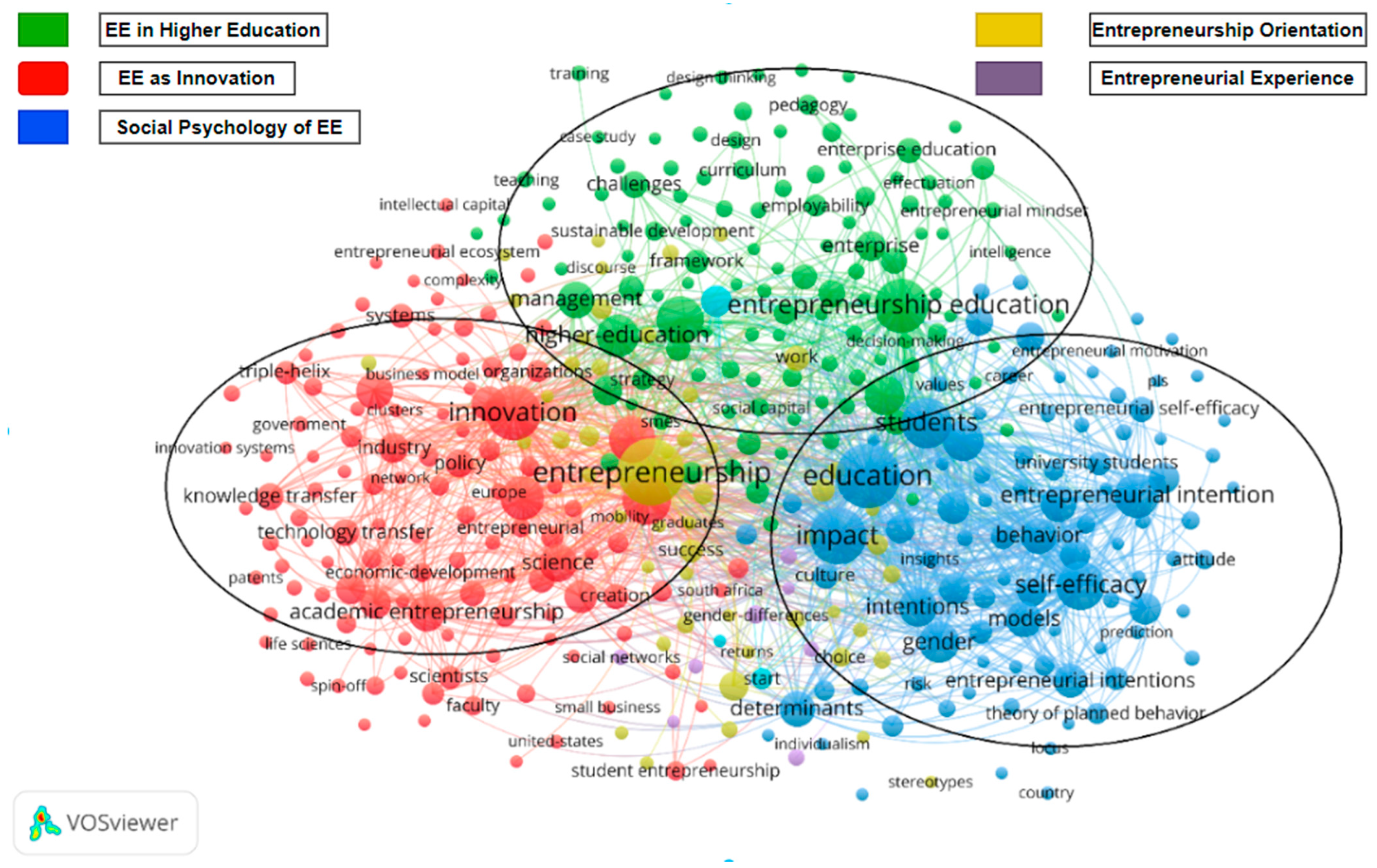
4.5. Conceptual Structure of EE Research
4.5.1. Application of the Conceptual Structure Map Method
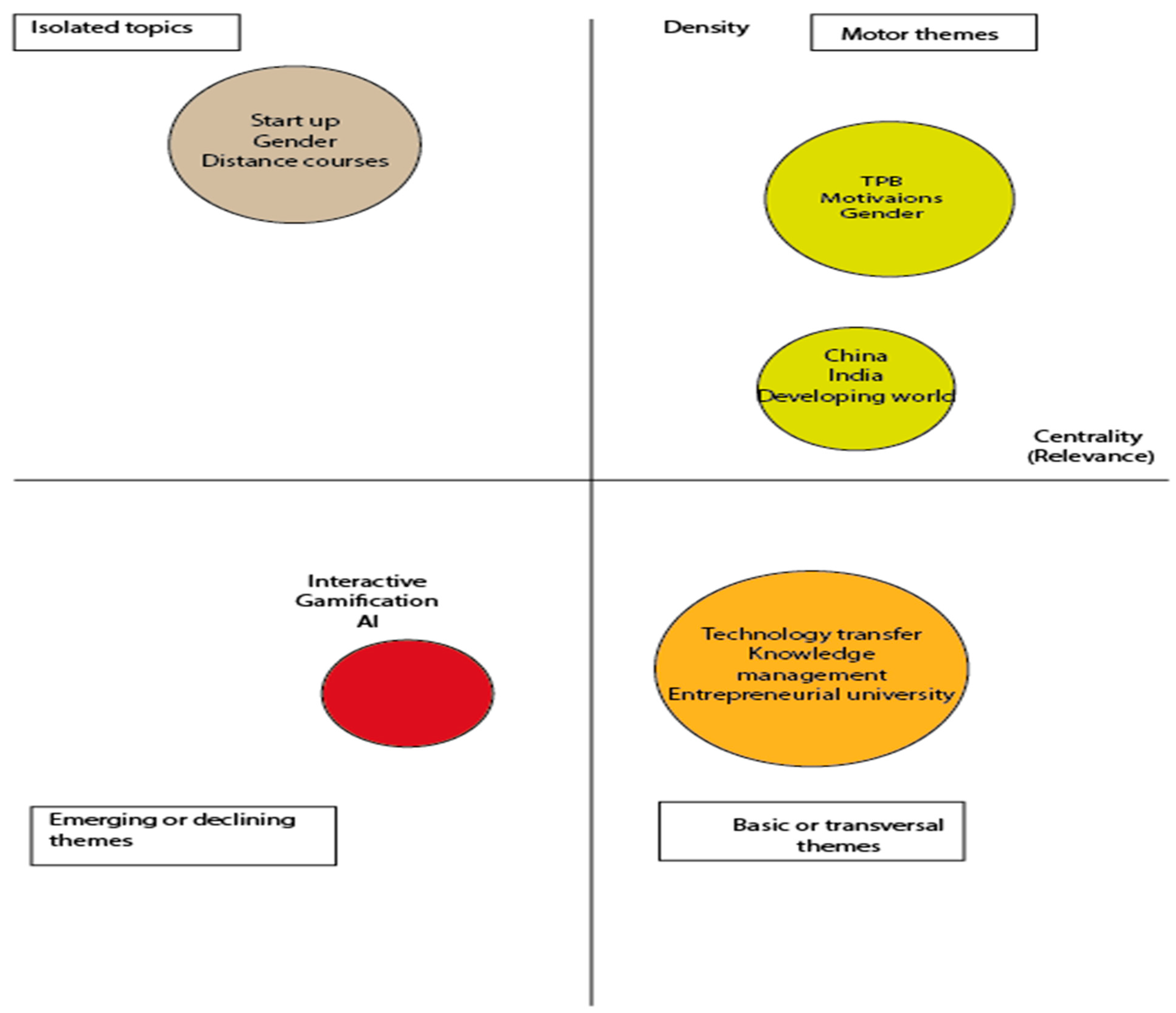
4.5.2. Application of Science Mapping in EE Research
5. Conclusions, Implications, and Limitations
- A rapid development can be seen in number of EE-related publications.
- There is a high level of diversity in the topics of publications applying a diverse methodological base (e.g., sociology, social psychology, organizational sciences, etc.)
- There is extending international collaboration between different countries.
- The academic level research of EE becomes increasingly democratic because new countries have appeared on the list as the most productive.
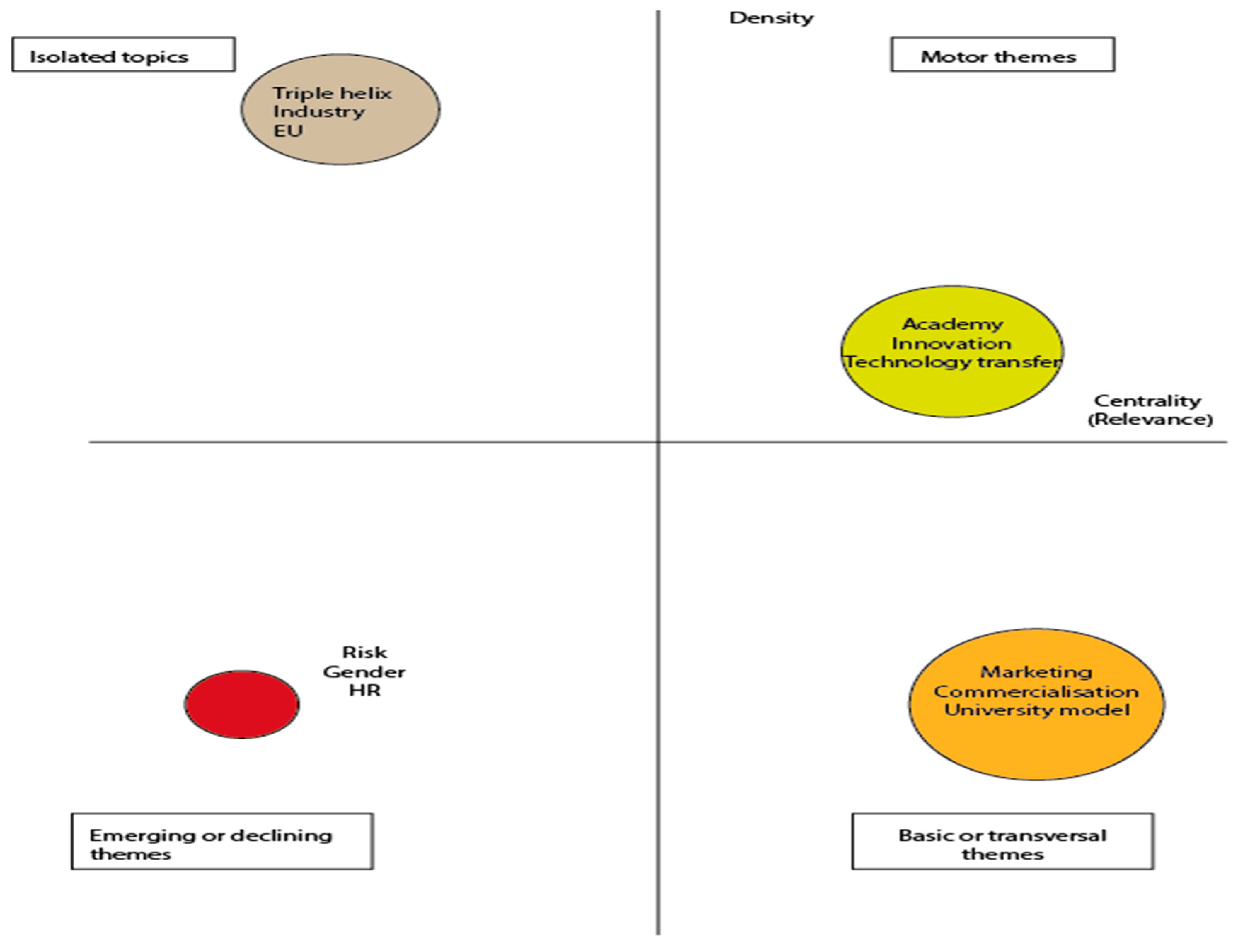
- EE was considered a relatively new direction of research, and this explains the application of innovation theory and the triple helix model in the first segment of the research.
- Meanwhile, the COVID-19 crisis and the rapid development of AI and new innovative methods of teaching, integrating distance learning, internet-based education, and enhancing learners’ involvement via gamification have brought to light the significance of some relatively novel topics. Researchers might consider concentrating their attention in the future on such emerging themes in EE research.
- Most of the publications focus on the sphere of higher education. However, EE would be highly important in the case of elementary, vocational, and secondary schools, because in the developing world, a considerable number of these schools prepare for such types of profession, where entrepreneurship is a very important component of daily activity (e.g., in the service sector).
- To evaluate the possibilities of further development, the researchers applied the triple helix method (Figure 9). According to this approach, the possible limit of academy–business and society cooperation are determined by an A-B-C triangle, but some parts of this triangle are interesting for just two and not three parties. The best, trilateral possibilities of cooperation are in the E-F-G triangle. In this sphere, a win-win situation can be achieved for all parties; this is why the promotion of such types of cooperation and collaboration is highly desirable. Shane and Venkataraman noted that the possibilities of the creation of innovative products [54] that are interesting for the industry are shown in the E-G-F triangular area.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zavodska, A.; Sramova, V.; Konecny, V. Developing Entrepreneurship Education: Case of the University of Zilina. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Learning Technology for Education Challenges (LTEC)-How Technologies Help us to Learn to Meet Future Learning, LTEC 2019, Zamora, Spain, 15–18 July 2019; Volume 1011, pp. 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashantham, S.; Eranova, M.; Couper, C. Globalization, entrepreneurship and paradox thinking. Asia Pacific J. Manag. 2018, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Sanchez, A.; Rio-Rama, M.D.; Alvarez-Garcia, J.; Garcia-Velez, D.F. Mapping of scientific coverage on education for Entrepreneurship in Higher Education. J. Enterp. Communities-People Places Glob. Econ. 2019, 13, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sha, Y.; Wang, J.; An, L.; Chen, T.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L. How Entrepreneurship Education at Universities Influences Entrepreneurial Intention: Mediating Effect Based on Entrepreneurial Competence. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 655868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Chandran, V.G.R.; Klobas, J.E.; Linan, F.; Kokkalis, P. Entrepreneurship education programmes: How learning, inspiration and resources affect intentions for new venture creation in a developing economy. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2020, 18, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashari, H.; Abbas, I.; Abdul-talib, A.N.; Mohd Zamani, S.N. Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Development Goals: A Multigroup Analysis of the Moderating Effects of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Intention. Sustainability 2022, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawang, W.; Sa’at, N.H.; Mamat, I. Development of Human Capital: A Case Study of the Program Tunas Niaga in Terengganu. Akademika 2022, 92, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.C. The Impact of an Entrepreneurship Education Program on Entrepreneurial Competencies and Intention. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2013, 51, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, R.; Quinto, I.; Thomas, A. The impact of higher education on entrepreneurial intention and human capital. J. Intellect. Cap. 2018, 19, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayob, A.H. Entrepreneurship education, institutions and student entrepreneurship: A cross-country analysis. Comp. J. Comp. Int. Educ. 2021, 51, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozahem, N.A.; Adlouni, R.O. Using Entrepreneurial Self-Efficacy as an Indirect Measure of Entrepreneurial Education. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2021, 19, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukesh, H.V.; Pillai, K.R.; Mamman, J. Action-embedded pedagogy in entrepreneurship education: An experimental enquiry. Stud. High. Educ. 2020, 45, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahn, D.; Poblete, C. Contextualizing the knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship: The Chilean paradox. Entrep. Reg. Dev. 2023, 35, 209–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagebakken, G.; Reimers, C.; Solstad, E. Entrepreneurship Education as a Strategy to Build Regional Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrichs, K. Dealing with Critical Incidents in the Postformation Phase: Design and Evaluation of an Entrepreneurship Education Course. Vocat. Learn. 2016, 9, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Bell, R. Behavioural entrepreneurial mindset: How entrepreneurial education activity impacts entrepreneurial intention and behaviour. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2022, 20, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamboulis, Y.; Barlas, A. Entrepreneurship education impact on student attitudes. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2014, 12, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, S.; Chau, K.Y.; Yu, L. The Influence of Undergraduate Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Intention: Evidence From Universities in China’s Pearl River Delta. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 732659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorz, M.; Mueller, S.; Volery, T. Entrepreneurship Education: A Systematic Review of the Methods in Impact Studies. J. Enterp. Cult. 2013, 21, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideout, E.C.; Gray, D.O. Does entrepreneurship education really work? A review and methodological critique of the empirical literature on the effects of university-based entrepreneurship education. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2013, 51, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, F.; Gangi, Y. Entrepreneurship education: A systematic literature review of curricula contents and teaching methods. Cogent Bus. Manag. 2015, 2, 1052034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, A.; Ferreira, J.J.; Marques, C. Entrepreneurship education and training as facilitators of regional development: A systematic literature review. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2018, 25, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. The past, present and future of research on Chinese entrepreneurship education: A bibliometric analysis based on CSSCI journal articles. Educ. Sci. Theory Pract. 2018, 18, 1255–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellnhofer, K. Toward a taxonomy of entrepreneurship education research literature: A bibliometric mapping and visualization. Educ. Res. Rev. 2019, 27, 28–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.A.; Fleury, A.L.; De Carvalho, M.M. Contemporary trends in engineering entrepreneurship education. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2019, 35, 824–841. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, G.; Iturralde, T.; Maseda, A. Conceptual structure and perspectives on entrepreneurship education research: A bibliometric review. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2019, 25, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, G.; Gabrielsson, J. A systematic literature review of the evolution of pedagogy in entrepreneurial education research. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2020, 26, 829–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N.; Lv, X. A bibliometric analysis on the landscape of entrepreneurship education in higher education (2001–2020). Entrep. Educ. 2021, 4, 375–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nájera-Sánchez, J.J.; Pérez-Pérez, C.; González-Torres, T. Exploring the knowledge structure of entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurial intention. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2022, 19, 563–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyomi, A.; Bayoumi, K.; El Din, N.S.; Abuhassna, H.; Abdullah Ali, E. Bibliometric Analysis of Entrepreneurship Education Research from 2012 to 2022. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2022, 12, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banha, F.; Coelho, L.S.; Flores, A. Entrepreneurship Education: A Systematic Literature Review and Identification of an Existing Gap in the Field. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiberius, V.; Weyland, M. Entrepreneurship education or entrepreneurship education? A bibliometric analysis. J. Furth. High. Educ. 2023, 47, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, A.; Suresh, M. Twenty years of entrepreneurship education: A bibliometric analysis. Entrep. Educ. 2023, 6, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Marc, W. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Martín, A.; Orduna-Malea, E.; Thelwall, M.; Delgado López-Cózar, E. Google Scholar, Web of Science, and Scopus: A systematic comparison of citations in 252 subject categories. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 1160–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M. Google Scholar to overshadow them all? Comparing the sizes of 12 academic search engines and bibliographic databases. Scientometrics 2019, 118, 177–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, C.; Codina, L.; Guerrero-Solé, F.; Lopezosa, C. Ranking by Relevance and Citation Counts, a Comparative Study: Google Scholar, Microsoft Academic, WoS and Scopus. Futur. Internet 2019, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadegani, A.A.; Salehi, H.; Yunus, M.M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ebrahim, N.A. A Comparison between Two Main Academic Literature Collections: Web of Science and Scopus Databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervis, H. Bibliometric analysis using bibliometrix an R package. J. Scientometr. Res. 2019, 8, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. CitNetExplorer: A new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. J. Informetr. 2014, 8, 802–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.H.; Lei, S.; Ali, M.; Doronin, D.; Hussain, S.T. Prosumption: Bibliometric analysis using HistCite and VOSviewer. Kybernetes 2020, 49, 1020–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Herrera, A.G.; Cobo, M.J.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F.; Bailon-Moreno, R.; Jimenez-Contreras, E. Visualization and Evolution of the Scientific Structure of Fuzzy Sets Research in Spain. Inf. Res. An Int. Electron. J. 2009, 14, 421. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Ren, H.; Yao, F.; Zou, C. Data-driven selection of the number of change-points via error rate control. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2021, 118, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- README. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/mcp/readme/README.html (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Xavier, L. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions—Entrepreneurship “2020 Action Plan”—Reigniting the Entrepreneurial Spirit in Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, R.A.K.; Chung, K.H. Patterns of Research Output and Author Concentration in the Economics Literature. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1991, 73, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodin, R.; Apriyani, E. Analysis of obsolescence and productivity of authors using lotka law on the journal of entrepreneurship in 2015–2019. Publ. Libr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensman, S.J.; Smolinsky, L.J. Lotka’s inverse square law of scientific productivity: Its methods and statistics. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formann, A.K.; Morris, R.J. The Newcomb-Benford Law in Its Relation to Some Common Distributions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, G.; Linan, F.; Fayolle, A.; Krueger, N.; Walmsley, A. The impact of entrepreneurship education in higher education. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2017, 16, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapero, A.; Sokol, L. The Social Dimensions of Entrepreneurship; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1982; Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=1497759 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Shane, S.; Venkataraman, S. The Promise of Enterpreneurship as a Field of Research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2000, 25, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzkowitz, H.; Leydesdorff, L. The dynamics of innovation: From National Systems and “Mode 2” to a Triple Helix of university–industry–government relations. Res. Policy 2000, 29, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senellart, M. (Ed.) The Birth of Biopolitics: Lectures at the Collège de France, 1978–1979; Palgrave MacMillan: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Forliano, C.; De Bernardi, P.; Yahiaoui, D. Entrepreneurial universities: A bibliometric analysis within the business and management domains. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 165, 120522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sources | Scope of the Review | Sample Articles | Time Period | Types of Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | The focus of this review is to identify methodological flaws in existing studies of the impact of entrepreneurship education and to provide recommendations for future research. | 39 | No time limit–2013 | Systematic literature review |
| [20] | This study presents a thorough literature review and critical analysis of empirical studies on entrepreneurship education (EE) in higher education. This study seeks to discover if EE helps start enterprises. | 12 | 1997–2011 | Systematic literature review |
| [21] | This study reviews the literature extensively to investigate widespread effective methods of teaching entrepreneurship at the university level. Curriculum and instructional practices are evaluated in light of recommendations from studies on entrepreneurial education. | 97 | 2005–2014 | Systematic literature review |
| [22] | The scope of this study is to organize and integrate the previous literature in the field of entrepreneurship education and training focussing on regional development. | 383 | 1973–2016 | Comprehensive review |
| [23] | This review examines 1134 CSSCI articles on Chinese entrepreneurship education from the past to the present. | 1134 | 1990–2017 | Bibliometric analysis |
| [24] | The focus of this study is to examine and classify EE research literature in order to provide a taxonomical scheme for use in future studies. | 1773 | 1975–2014 | Bibliometric analysis |
| [25] | This study reviews engineering student entrepreneurship education. | 324 | 2001–2017 | Comprehensive review |
| [26] | This literature review analyses 325 scholarly articles on entrepreneurship education (EE). The paper examines how EE research changed from an economic growth strategy to an academic pursuit. It highlights the shift from teachers to students in education. | 325 | 1987–2017 | Bibliometric review |
| [27] | The goal of this paper is to provide light on the development of pedagogy in studies of entrepreneurial education over the past few decades. | 395 | 1980–2018 | Systematic literature review |
| [28] | This review focusses on entrepreneurship education in higher education. | 581 | 201–2020 | Bibliometric analysis |
| [29] | The focus of this study is on entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurship intention. One potential strategy for encouraging this entrepreneurial mindset is participation in an entrepreneurial education program. | 298 | 2010–2020 | Bibliometric analysis |
| [30] | The purpose of this study is to shed light on the development and current state of research in the discipline and to point the way towards promising new avenues of research. | 615 | 2012–2021 | Bibliometric analysis |
| [31] | The scope of the review in this study is to investigate the decision-making processes associated with the implementation of education for entrepreneurship (EE) programs in schools and the integration of this topic into the policy-making process. | 19 | No time limit–2022 | Systematic literature review |
| [32] | The scope of this study is to organize and integrate the previous literature in the field of entrepreneurship education (EE). The researchers aim to address the broad, complex, and fragmented nature of the research field by conducting co-citation analysis. | 680 | 1977–2021 | Bibliometric analysis |
| [33] | The purpose of this research is to determine which factors in higher education contribute to individuals developing an interest in and plan to pursue a career in entrepreneurship. | 2185 | 2002–2022 | Bibliometric analysis |
| Our paper | Focussing on entrepreneurial education (EE), this study uses bibliometric analysis, science mapping, and ontological and epistemological inquiry to unravel its historical development and predict its future directions. | 3787 | 1983–2022 | Comprehensive bibliometric review |
| Description | Results |
|---|---|
| Timespan | 1983:2022 |
| Sources (journals, books, etc.) | 1154 |
| Documents | 3787 |
| Annual Growth Rate % | 17.26 |
| Document average age | 4.11 |
| Average citations per doc | 13.56 |
| References | 125,184 |
| Keywords Plus (ID) | 2897 |
| Author’s keywords (DE) | 8106 |
| Authors | 8778 |
| Authors of single-authored docs | 622 |
| Single-authored docs | 666 |
| Co-Authors per Doc | 2.89 |
| International co-authorships % | 26.06 |
| 1983–2009 | 2010–2016 | 2017–2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of Journal | Articles | Name of Journal | Articles | Name of Journal | Articles |
| Higher Education | 14 | Journal of Technology Transfer | 28 | Frontiers in Psychology | 157 |
| Technovation | 12 | International Journal of Engineering Education | 20 | Sustainability | 147 |
| International Journal of Engineering Education | 10 | Journal of Small Business Management | 15 | Education and Training | 113 |
| Journal of Business Venturing | 8 | International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal | 13 | Industry and Higher Education | 67 |
| Research Policy | 7 | International journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research | 13 | International Journal of Management Education | 56 |
| Entrepreneurship and Regional Development | 6 | Research Policy | 13 | Studies in Higher education | 49 |
| African Journal of Business Management | 4 | Small Business Economics | 13 | Journal of Technology transfer | 44 |
| Transformations in Business & Economics | 4 | Entrepreneurship and Regional Development | 12 | International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research | 42 |
| Journal of Higher Education | 3 | African Journal of Business Management | 11 | Entrepreneurship and Sustainability Issues | 28 |
| Journal of Technology Transfer | 3 | Studies in Higher Education | 10 | Higher Education Skills and Work-based Learning | 28 |
| Zone | Number of Journals | Ratio of Number of Journals to the Core Journals |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 28 | 1 |
| 2nd | 218 | 7.8 |
| 3rd | 1154 | 41.2 |
| First Period (1983–2009) | Second Period (2010–2016) | Third Period (2017–2022) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Share of Papers | Country | Share of Papers | Country | Share of Papers |
| US | 32.4 | US | 24 | CN | 13.5 |
| UK | 17.4 | UK | 11.4 | US | 9.6 |
| CA | 4.2 | ES | 8.1 | UK | 7.1 |
| AU | 3.3 | DE | 3.6 | ES | 6.7 |
| DE | 2.8 | AU | 3.5 | IT | 4.3 |
| CH | 2.3 | CA | 3.1 | DE | 2.9 |
| ES | 2.3 | CN | 3.1 | MY | 2.7 |
| IL | 1.9 | IT | 3.1 | PT | 2.4 |
| IT | 1.9 | SW | 3 | ZA | 2.4 |
| PO | 1.9 | NL | 2.8 | AU | 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talukder, S.C.; Lakner, Z.; Temesi, Á. Development and State of the Art of Entrepreneurship Education: A Bibliometric Review. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030295
Talukder SC, Lakner Z, Temesi Á. Development and State of the Art of Entrepreneurship Education: A Bibliometric Review. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(3):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030295
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalukder, Saurav Chandra, Zoltán Lakner, and Ágoston Temesi. 2024. "Development and State of the Art of Entrepreneurship Education: A Bibliometric Review" Education Sciences 14, no. 3: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030295
APA StyleTalukder, S. C., Lakner, Z., & Temesi, Á. (2024). Development and State of the Art of Entrepreneurship Education: A Bibliometric Review. Education Sciences, 14(3), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030295









