Critical Thinking in Reading Comprehension: Fine Tuning the Simple View of Reading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Executive Function
3. Critical Thinking
4. Belief Systems
5. Reading Comprehension
6. Conceptual Framework
7. The Present Study
8. Methods
8.1. Participants
8.2. Assessments
8.3. Encoding
8.4. Vocabulary
8.5. Reading Fluency
8.6. Critical Thinking
8.7. Listening Comprehension
8.8. Silent Reading Comprehension
8.9. Assessment Administration
9. Results
9.1. Research Question 1
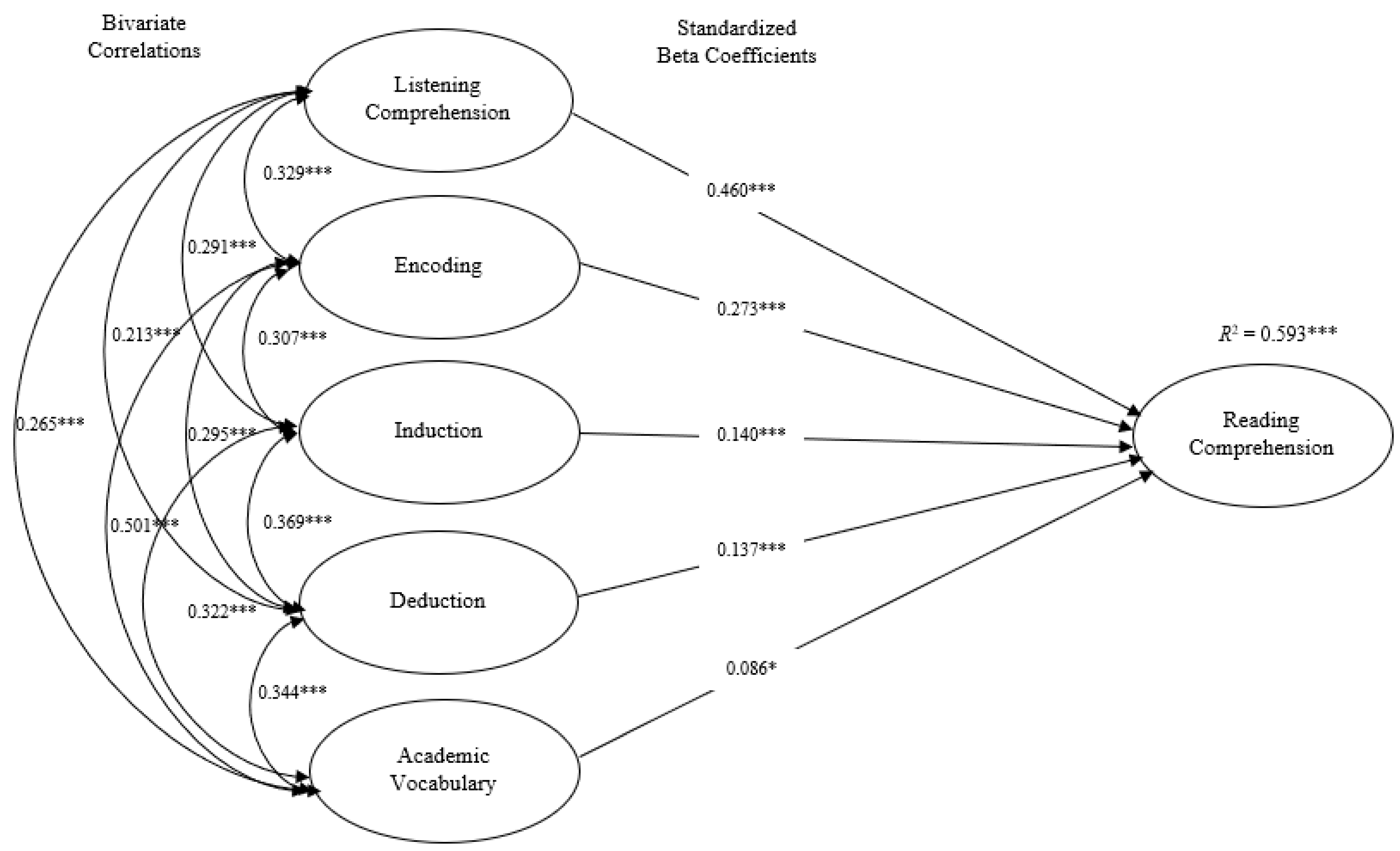
9.2. Research Question 2
9.3. Research Question 3
10. Discussion
11. Conclusions
11.1. Limitations
11.2. Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. The Future of Education and Skills: Education 2030. 2023. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/education/2030/E2030%20Position%20Paper%20.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2018).
- Peng, P.; Kievit, R.A. The Development of Academic Achievement and Cognitive Abilities: A Bidirectional Perspective. Child Dev. Perspect. 2020, 14, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, R.L.; Patton, J.; Murdoch, A. Early reading success and its relationship to reading achievement and reading volume: Replication of ‘10 years later’. Read. Writ. 2013, 27, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D. Thinking Fast and Slow; Farrer, Straus, and Giroux: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.S.B.T. Dual-Processing Accounts of Reasoning, Judgment, and Social Cognition. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.R.; Kuncel, N.R. Does College Teach Critical Thinking? A Meta-Analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 2016, 86, 431–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaksford, M.; Chater, N.; Hahn, U. Human reasoning and argumentation: The probabilistic approach. In Reasoning: Studies of Human Inference and Its Foundations; Adler, J., Rips, L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 383–413. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, A. Want to optimize executive functions and academic outcomes? In Minnesota Symposia on Child Psychology: Developing Cognitive Processes: Mechanisms, Implications, and Interventions; Zelazo, P.D., Sera, M.D., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 37, pp. 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.W.; Elder, L. Critical Thinking: The Nature of Critical and Creative Thought. J. Dev. Educ. 2006, 30, 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Baddeley, A.D.; Hitch, G.J. Developments in the concept of working memory. Neuropsychology 1994, 8, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.E.; Jonides, J. Storage and Executive Processes in the Frontal Lobes. Science 1999, 283, 1657–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelazo, P.D.; Mϋller, U. Executive function in typical and atypical development. In Blackwell Handbook of Childhood Cognitive Development; Goswami, U., Ed.; Blackwell Publisher: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 445–469. [Google Scholar]
- Lizarraga, M.L.S.d.A.; Baquedano, M.T.S.d.A.; Villanueva, O.A. Critical thinking, executive functions and their potential relationship. Think. Ski. Creativity 2012, 7, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.J.; Burgess, P.W. Executive function. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R110–R114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arum, R.; Roksa, J. Academically Adrift: Limited Learning on College Campuses; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, J.; Granato, L.; Spranca, M.; Teubal, E. Decision making biases in children and early adolescence: Exploratory studies. Merrill-Palmer Q. 1993, 39, 22–46. [Google Scholar]
- Erikson, M.G.; Erikson, D. Learning outcomes and critical thinking – good intentions in conflict. Stud. High. Educ. 2019, 44, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, D.F. Assessing the Effectiveness of Critical Thinking Instruction. J. Gen. Educ. 2001, 50, 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D.; Tversky, A. Subjective probability: A judgment of representativeness. Cogn. Psychol. 1972, 3, 430–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D. Connecting scientific and informal reasoning. Merrill-Palmer Q. 1993, 39, 74–103. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, D.N. Postprimary education has little impact on informal reasoning. J. Educ. Psychol. 1985, 77, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, R.H. A taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities. In Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and Practice; Baron, J., Sternberg, R., Eds.; Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bensley, D.A. Critical thinking and the rejection of unsubstantiated claims. In Critical Thinking in Psychology, 2nd ed.; Sternberg, R.J., Halpern, D.F., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 68–102. [Google Scholar]
- Facione, P. Critical Thinking: A Statement of Expert Consensus for Purposes of Educational Assessment and Instruction. Research Findings and Recommendations; American Philosophical Association: Newark, DE, USA, 1990; Available online: https://philarchive.org/archive/faccta (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Sternberg, R.J. Thinking Styles; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, R.J. Wisdom, Intelligence, and Creativity Synthesized; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pithers, R.T.; Soden, R. Critical Thinking in Education: A Review. Educ. Res. 2000, 42, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrami, P.C.; Bernard, R.M.; Borokhovski, E.; Wadem, A.; Surkes, M.A.; Tamim, R.; Zhang, D. Instructional interventions affecting critical thinking skills and dispositions: A stage 1 meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 2008, 78, 1102–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintsch, W. Comprehension: A Paradigm for Cognition; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, K.S.; McNamara, D.S. The multidimensional knowledge in text comprehension framework. Educ. Psychol. 2021, 56, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, D.S.; Magliano, J. Toward a comprehensive model of comprehension. Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 2009, 51, 297–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B. Critical Thinking—A Tangible Construct? Res. Matters A Camb. Assess. Publ. 2007, 3, 2–4. Available online: https://www.cambridgeassessment.org.uk/our-research/all-published-resources/research-matters/rm-03/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Klaczynski, P.A.; Gordon, H.D.; Fauth, J. Goal-oriented critical reasoning and individual differences in critical reasoning biases. J. Educ. Psychol. 1997, 89, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, R.; Stanovich, K.E. Cognitive ability, thinking dispositions, and instructional set as predictors of critical thinking. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2007, 17, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, W.B.; Parker, A.M.; Fischhoff, B. Individual differences in adult decision-making competence. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2007, 92, 938–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, D.F. Thought and Knowledge: An Introduction to Critical Thinking, 5th ed.; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M. Critical Thinking and the Disciplines Reconsidered. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2013, 32, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, M.C. Designing the knowledge integration environment. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2000, 22, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philley, J. Critical thinking concepts. Prof. Safety 2005, 50, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Haverty, L.A.; Koedinger, K.A.; Klahr, D.; Alibali, M.W. Solving inductive reasoning problems in mathematics. Not-so-trivial pursuit. Cogn. Sci. 2000, 24, 249–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R.J.; Sternberg, K. Cognitive Psychology; Wadsworth-Cengage: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Capó, B. The Development of Inductive Reasoning: Cross-sectional Assessments in an Educational Context. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 1997, 20, 609–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, U. Inductive and deductive reasoning. In Blackwell Handbook of Childhood Cognitive Development; Goswami, U., Ed.; Blackwell Publisher: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 282–302. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Laird, P.N. Deductive reasoning. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1999, 50, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J. Thinking and Deciding, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, R.J. Why schools should teach for wisdom: The balance theory of wisdom in educational settings. Educ. Psychol. 2001, 36, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.F.; Toplak, M.E.; Stanovich, K.E. Heuristics and biases as measures of critical thinking: Associations with cognitive ability and thinking dispositions. J. Educ. Psychol. 2008, 100, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassok, M.; Holyoak, K.J. Interdomain transfer between isomorphic topics in algebra and physics. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1989, 15, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bransford, J.D.; Stein, B.S. The Ideal Problem Solver, 2nd ed.; Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, M.T.H.; Feltovich, P.J.; Glaser, R. Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cogn. Sci. 1981, 5, 121–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.J.; Gibson, E.J. Perceptual learning: Differentiation or enrichment? Psychol. Rev. 1955, 62, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greeno, J.G.; Smith, D.R.; Moore, J.L. Transfer of situated learning. In Transfer on Trial: Intelligence, Cognition, and Instruction; Detterman, D.K., Sternberg, R.J., Eds.; Ablex: Norwood, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 99–167. [Google Scholar]
- Marton, F.; Booth, S. Learning and Awareness; Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (NRC); Committee on Developments in the Science of Learning with additional material from the Committee on Learning, Research and Educational Practice; Commission on Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition; Bransford, J.D., Brown, A.L., Cocking, R.R., Eds.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler, D. Cognitive Therapy: A Practical Guide; WW Norton and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.S.B.T.; Stanovich, K.W. Dual process theories of higher cognition: Advancing the debate. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 8, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanovich, K.E. What Intelligence Tests Miss: The Psychology of Rational Thought; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stanovich, K.E. Rationality and the Reflective Mind; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, S. Cognitive science and science education. Am. Psychol. 1986, 41, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardash, C.M.; Scholes, R.J. Effects of pre-existing beliefs, epistemological beliefs, and need for cognition on interpretation of controversial issues. J. Educ. Psychol. 1996, 88, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaczynski, P.A.; Gordon, D.H. Self-serving influences on adolescents’ evaluations of belief-relevant evidence. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 1996, 62, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanovich, K.E.; West, R.F. Reasoning independently of prior belief and individual differences in actively open-minded thinking. J. Educ. Psychol. 1997, 89, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Broek, P.; Lorch, R.F.; Linderholm, T.; Gustafson, M. The effects of readers’ goals on inference generation and memory for texts. Mem. Cogn. 2001, 29, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graesser, A.C.; Millis, K.K.; Zwann, R.A. Discourse comprehension. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 48, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, T.A.; Kintsch, W. Strategies of Discourse Comprehension; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 189–221. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, J.; Sternberg, R.J. Teaching Thinking Skills: Theory and Practice; Freeman: Dallas, TX, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, R.J.; Roediger, H.L., III; Halpern, D.F. (Eds.) Critical Thinking in Psychology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Perfetti, C.A.; Stafura, J. Word Knowledge in a Theory of Reading Comprehension. Sci. Stud. Read. 2013, 18, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, V.L.; Rupley, W.H. A structural equation model for reading comprehension based on background, phonemic, and strategy knowledge. Sci. Stud. Read. 1997, 1, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakido, I.N.; Ioanno, M.C.; Christodoulou, S.A. Reading argumentative texts: Comprehension and evaluation goals and outcomes. Read. Writ. 2017, 30, 1869–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, N.K.; Cartwright, K.B. The science of reading progresses: Communicating advances beyond the simple view of reading. Read. Res. Q. 2021, 56, S25–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.A.; Gough, P.B. The simple view of reading. Read. Writ. 1990, 2, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, D.M.; Al Ghanem, R. The role of semantic information in children’s word reading: Does meaning affect readers’ ability to say polysyllabic words aloud? J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 111, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendeou, P.; Savage, R.; Broek, P.v.D. Revisiting the simple view of reading. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2009, 79, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonigan, C.J.; Burgess, S.R.; Schatschneider, C. Examining the Simple View of Reading with Elementary School Children: Still Simple After All These Years. Remedial Spec. Educ. 2018, 39, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.M.; Brady, S.A. The effect of vocabulary knowledge on novel word identification. Ann. Dyslexia 2013, 63, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coté, N.; Goldman, S.R.; Saul, E.U. Students making sense of informational text: Relations between processing and representation. Discourse Process. 1998, 25, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, K.; Oakhill, J.V.; Barnes, M.A.; Bryant, P.E. Comprehension skill, inference-making ability, and their relation to knowledge. Mem. Cogn. 2001, 29, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretti, B.; Caldarola, N.; Tencatti, C.; Cornoldi, C. Improving reading comprehension in reading and listening settings: The effect of two training programmes focusing on metacognition and working memory. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 84, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbro, C.; Buch-Iversen, I. Activation of background knowledge for inference making: Effects on reading comprehension. Sci. Stud. Read. 2013, 17, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Barnes, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Swanson, H.L.; Dardick, W.; Tao, S. A meta-analysis on the relation between reading and working memory. Psychol. Bull. 2018, 144, 48–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, C.A. Reading ability: Lexical quality to comprehension. Sci. Stud. Read. 2007, 11, 357–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.I.; Paolieri, D.; Macizo, P.; Bajo, T. The role of working memory in inferential sentence comprehension. Cogn. Process. 2014, 15, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilip, C. Public–Private Partnership to Meet the Skills Challenges in India; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-94-007-5936-7. [Google Scholar]
- Banerji, R.; Chavan, M. Improving literacy and math instruction at scale in India’s primary schools: The case of Pratham’s Read India program. J. Educ. Chang. 2016, 17, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganske, K. Developmental Spelling Analysis: A Diagnostic Measure for Instruction and Research. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, USA, 1994, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Ehri, L.C. How English orthography influences phonological knowledge as children learn to read and spell. In Literacy and Language Analysis; Scales, R.J., Ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 21–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ganske, K. Word Journeys: Assessment-Guided Phonics, Spelling, and Vocabulary Instruction, 2nd ed.; Guildford: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, E.H.; Templeton, S. A developmental perspective of formal spelling instruction through alphabet, pattern, and meaning. Elem. Sch. J. 1986, 86, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, D.D.; Smith, G.S. Academic vocabulary and reading fluency: Unlikely bedfellows in the quest for textual meaning. Educ. Sci. 2018, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxhead, A. A new academic word list. TESOL Q. 2000, 34, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, D.D.; Rupley, W.S. Revisiting complex text instruction: A study of 11th-grade history students. Psychol. Sch. 2023, 60, 3633–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zutell, J.; Rasinski, T.V. Training teachers to attend to their students’ oral reading fluency. Theory Into Pract. 1991, 30, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S.; Paige, D.D. A Study of Reliability Across Multiple Raters When Using the NAEP and MDFS Rubrics to Measure Oral Reading Fluency. Read. Psychol. 2019, 40, 34–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, R.H.; Millman, J.; Tomko, T.N. Cornell Critical Thinking Test, 5th ed.; The Critical Thinking Company: North Bend, OR, USA, 2005; Available online: www.criticalthinking.com (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Carrow-Woolfolk, E. Oral and Written Language Scales-Second Edition (OWLS-II); Western Psychological Services: Torrance, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, V.L.; Widerholt, J.L.; Hammill, D.D. Test of Reading Comprehension, 4th ed.; Pro-Ed: Austin, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, P.T.; Romain, M.A.; Barth, A.E.; Tolar, T.D.; Fletcher, J.M.; Vaughn, S. Reading skill components and impairments in middle school struggling readers. Read. Writ. 2012, 26, 1059–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjetland, H.N.; Lervåg, A.; Lyster, S.-A.H.; Hagtvet, B.E.; Hulme, C.; Melby-Lervåg, M. Pathways to reading comprehension: A longitudinal study from 4 to 9 years of age. J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 111, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighe, E.L.; Schatschneider, C. A dominance analysis approach to determining predictor importance in third, seventh, and tenth grade reading comprehension skills. Read. Writ. 2013, 27, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, A. Executive Functions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, P.; Guare, R. Executive Skills in Children and Adolescents; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zelazo, P.D.; Blair, C.B.; Willoughby, M.T. Executive Function: Implications for Education (NCER, 2017-2020); National Center for Education Research, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Sabatini, J.; O’Reilly, T.; Weeks, J. Decoding and reading comprehension: A test of the decoding threshold hypothesis. J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 111, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbrouck, J.; Tindal, G. An Update to Compiled ORF Norms; Technical Report No. 1702; Behavioral Research and Teaching, University of Oregon: Eugene, OR, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ehri, L. Learning To Read and Learning to Spell: Two Sides of a Coin. Top. Lang. Disord. 2000, 20, 19–36. Available online: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=ovftd&NEWS=N&AN=00011363-200020030-00005 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- McGuinness, D. Early Reading Instruction: What Science Really Tells Us About How to Teach Reading; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Perfetti, C. Reading acquisition and beyond: Decoding includes cognition. Am. J. Educ. 1984, 93, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla-Martinez, J.; Kieffer, M.J.; Biancarosa, G.; Christodoulou, J.A.; Snow, C.E. Investigating English comprehension growth in adolescent language minority learners: Some insights from the simple view. Read. Writ. 2011, 24, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, S.A.; Whitehurst, G.J. Oral language and code-related precursors to reading: Evidence from a longitudinal structural model. Dev. Psychol. 2002, 38, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, W.; Townsend, D. Words as Tools: Learning Academic Vocabulary as Language Acquisition. Read. Res. Q. 2012, 47, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffee, J. Thinking Critically; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MS, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, S.R.; Freisner, D.; Khayum, M. Do reading skills courses help underprepared readers achieve academic success in college. J. Coll. Read. Learn. 2003, 33, 170–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, R.H. No One to Waste: A Report to Public Decision-Makers and Community College Leaders; Community College Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Oudenhoven, B. Remediation at the community college: Pressing issues, uncertain solutions. New Dir. Community Coll. 2002, 2002, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.; Teravainen-Goff, A. Children and Young People’s Reading in 2020: Findings from Our Annual Literacy Survey; National Literacy Trust: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. CCTTInduction | 1 | ||||||||||
| 2. CCTTDeduction | 0.369 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| 3. CCTTCredibility | 0.265 ** | 0.224 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| 4. CCTTAssumptions | 0.125 ** | 0.284 ** | 0.101 | 1 | |||||||
| 5. CCTTComposite | 0.746 ** | 0.714 ** | 0.650 ** | 0.454 ** | 1 | ||||||
| 6. Reading comprehension | 0.436 ** | 0.396 ** | 0.199 ** | 0.182 ** | 0.481 ** | 1 | |||||
| 7. Encoding | 0.307 ** | 0.295 ** | 0.163 ** | 0.065 | 0.339 ** | 0.551 ** | 1 | ||||
| 8. Accumaticity (WCPM) | 0.204 ** | 0.238 ** | 0.154 ** | 0.097 | 0.273 ** | 0.286 ** | 0.509 ** | 1 | |||
| 9. Prosody | 0.121 ** | 0.215 ** | 0.066 | 0.020 | 0.170 ** | 0.186 ** | 0.247 ** | 0.208 ** | 1 | ||
| 10. Academic vocabulary | 0.322 ** | 0.344 ** | 0.201 ** | 0.109 ** | 0.391 ** | 0.437 ** | 0.501 ** | 0.297 ** | 0.073 | 1 | |
| 11. Listening comprehension | 0.291 ** | 0.213 ** | 0.080 | 0.121 ** | 0.279 ** | 0.642 ** | 0.329 ** | 0.197 ** | 0.132 ** | 0.265 ** | 1 |
| Range (min–max) | 0–19 | 0–14 | 0–17 | 0–14 | 3–53 | 4–26 | 7–16 | 7–16 | 0–10 | 5–43 | 72–108 |
| Mean (sd) | 10.34 (3.19) | 6.79 (2.61) | 10.17 (2.87) | 3.34 (1.69) | 30.54 (6.87) | 15.27 (4.20) | 15.66 (3.25) | 126.62 (26.10) | 11.18 1.86 | 24.19 5.82 | 92.96 6.35 |
| Percentile Attainment | na | na | na | na | <4th grade | 9th | DC | 50th | na | 45th | 45th |
| Item | Factor Loading | Communalities |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.712 | 0.507 |
| 2 | 0.767 | 0.588 |
| 3 | 0.519 | 0.269 |
| 4 | 0.585 | 0.342 |
| % of variance extracted | 42.64 |
| Location | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meghalaya | Assam | West Bengal | Total | |
| Variable | Mean (sd) | Mean (sd) | Mean (sd) | Mean (sd) |
| Reading Comprehension | 11.85 (3.40) *** | 16.02 (3.97) | 16.51 (3.77) | 15.27 (4.20) |
| Critical Thinking Composite | 25.91 (5.23) *** | 32.33 (6.96) | 31.43 (6.44) | 30.54 (6.87) |
| Accumaticity (WCPM) | 110.33 (22.54) ***1 | 138.66 (25.32) ***2 | 123.88 (26.10) ***3 | 126.62 (26.10) |
| Prosody | 4.80 (1.11) ***4 | 5.32 (1.27) | 5.57 (1.07) | 5.30 (1.9) |
| Encoding | 12.31 (3.18) *** | 16.26 (2.41) | 17.02 (2.62) | 15.66 (3.25) |
| Academic Vocabulary | 19.30 (4.85) *** | 25.65 (5.38) | 25.58 (5.22) | 24.19 (5.82) |
| Listening Comprehension | 89.42 (6.54) *** | 94.16 (5.96) | 93.54 (6.34) | 92.86 (6.35) |
| 95% Confidence Interval | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE B | β | t | R2 | Lower | Upper | |
| Model 1 | 0.594 | ||||||
| Constant | −23.691 | 2.144 | −11.050 *** | −27.907 | −19.474 | ||
| Induction | 0.175 | 0.051 | 0.133 | 3.435 *** | 0.075 | 0.275 | |
| Credibility | 0.054 | 0.052 | 0.037 | 1.044 | −0.048 | 0.156 | |
| Deduction | 0.192 | 0.063 | 0.119 | 3.036 ** | 0.068 | 0.317 | |
| Assumptions | 0.117 | 0.088 | 0.047 | 1.335 | −0.055 | 0.289 | |
| Accumaticity | −0.009 | 0.006 | −0.053 | −1.324 | −0.021 | 0.004 | |
| Prosody | 0.149 | 0.134 | 0.042 | 1.109 | −0.115 | 0.412 | |
| Academic Vocabulary | 0.058 | 0.029 | 0.081 | 1.995 * | 0.001 | 0.116 | |
| Encoding | 0.366 | 0.059 | 0.283 | 6.198 *** | 0.250 | 0.482 | |
| Listening Comprehension | 0.302 | 0.024 | 0.457 | 12.441 *** | 0.254 | 0.350 | |
| Model 2 | 0.593 | ||||||
| Constant | −23.369 | 2.079 | −11.238 *** | −27.459 | −19.280 | ||
| Induction | 0.184 | 0.050 | 0.140 | 3.666 *** | 0.085 | 0.282 | |
| Deduction | 0.220 | 0.061 | 0.137 | 3.621 *** | 0.101 | 0.339 | |
| Academic Vocabulary | 0.062 | 0.029 | 0.086 | 2.108 * | 0.004 | 0.119 | |
| Encoding | 0.353 | 0.052 | 0.273 | 6.738 *** | 0.250 | 0.456 | |
| Listening Comprehension | 0.304 | 0.024 | 0.460 | 12.540 *** | 0.256 | 0.352 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paige, D.; Rupley, W.H.; Ziglari, L. Critical Thinking in Reading Comprehension: Fine Tuning the Simple View of Reading. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030225
Paige D, Rupley WH, Ziglari L. Critical Thinking in Reading Comprehension: Fine Tuning the Simple View of Reading. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(3):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030225
Chicago/Turabian StylePaige, David, William H. Rupley, and Leily Ziglari. 2024. "Critical Thinking in Reading Comprehension: Fine Tuning the Simple View of Reading" Education Sciences 14, no. 3: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030225
APA StylePaige, D., Rupley, W. H., & Ziglari, L. (2024). Critical Thinking in Reading Comprehension: Fine Tuning the Simple View of Reading. Education Sciences, 14(3), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14030225







