Automatic Morphological Processing in Middle School Students with and without Word Reading Difficulties
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Morphological Processing
1.2. Morphological Ability and Students with Word Reading Difficulties
1.3. Automaticity
1.4. The Present Study
- Does the performance decrement for masking differ for morphologically complex words and morphologically simple words? If students are using morphological structure to read words, they should show a smaller decrement for morphologically complex words than morphologically simple words matched on other factors.
- Is the masking decrement moderated by group (i.e., students with WRD vs. proficient word readers)? If students with word reading difficulties rely more on morphological structure to automatically read words, there should be an interaction between morphological status, masking, and reading ability group.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Assessments
2.3. Experimental Measures
2.4. Inter-Rater Reliability and Procedural Fidelity
2.5. Analyses
3. Results
3.1. RQ1: The Effect of Morphological Status on Masked and Unmasked Performance
3.2. RQ2: Differences in Students With and Without WRD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Syllables | Picture | Say | Verify | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | S | C | S | C | S | C | S |
| applause | altar | accordion | appetite | addition | agenda | actor | bargain |
| arrival | cantaloupe | angelic | calendar | agency | artifact | allergic | broccoli |
| botanist | captain | armor | canyon | brownie | babble | anxiety | burrow |
| burglarize | chimpanzee | artist | caravan | buzzer | biscuit | authorize | cadet |
| contagious | clever | athletic | carnival | careful | campaign | boredom | cannon |
| continent | college | baggage | casserole | childhood | cardigan | bravery | carousel |
| cottage | confetti | bracelet | collar | clueless | catapult | cheerful | cellar |
| disastrous | embarrass | cashier | corridor | dangerous | challenge | chilly | chipmunk |
| eagerness | formula | cavalry | crocodile | dentistry | cinnamon | classify | clarinet |
| eyeful | funeral | cavity | curtain | devilish | citizen | clerical | custom |
| greedy | gallon | circular | daisy | edible | concrete | closet | eclipse |
| harden | hurdle | cooler | dinosaur | entrance | connect | colorful | emerald |
| leakage | legend | cutlery | flamingo | erosion | elephant | contestant | faucet |
| lonely | lettuce | dinner | garden | favorite | garlic | emotion | gargoyle |
| merciful | minister | dynamite | guitar | heroic | habitat | eruption | horizon |
| nursery | molasses | explorer | helmet | infancy | indigo | explosion | insect |
| objection | moustache | ferocious | honey | metallic | magazine | famous | kangaroo |
| opposite | mussel | flatten | hospital | mighty | magnet | gorgeous | leprechaun |
| outer | obnoxious | freezer | hurricane | numeral | mannequin | justice | magenta |
| pacify | occupy | golden | iguana | parental | monkey | listener | mistletoe |
| package | orchestra | kingdom | kitchen | passable | nourish | moisture | ocean |
| parchment | pamphlet | lemonade | leopard | porous | papyrus | musical | ordinance |
| piglet | papaya | lioness | mandolin | pressure | peculiar | novelist | ornament |
| piracy | parliament | magician | mountain | reporter | pheasant | outage | pedestal |
| reflection | pigeon | motorist | neighbor | retirement | porcelain | passage | potato |
| rivalry | prohibit | mouthful | nozzle | rotation | progress | persuasion | privilege |
| runner | revenue | pavement | octopus | rotten | rally | poetic | protocol |
| servant | rhythm | physician | paradise | roughly | restaurant | precedent | proton |
| seventh | salon | pianist | pelican | scary | retina | raider | python |
| silence | scribble | prisoner | pilgrim | sparkle | ribbon | robber | rabies |
| snowy | serpent | referee | porridge | spiral | somersault | seasonal | reckon |
| stroller | signature | sculptor | pyramid | splatter | sparrow | shortage | sarcasm |
| tablet | silhouette | skater | science | suspicion | specimen | smelly | sergeant |
| terminal | stomach | student | spatula | tolerant | statistic | therapist | sinister |
| threaten | throttle | sweater | sprinkle | tourist | sugar | venomous | skeleton |
| traumatic | torment | tambourine | surgeon | urgent | tribute | vicious | squirrel |
| tropical | turtle | thirsty | terrain | usage | umbrella | weaken | thesaurus |
| typical | vehicle | victory | thermostat | wilderness | walrus | widen | ventricle |
| verbal | vinegar | windy | vitamin | wishful | whistle | wooden | village |
| visitor | volcano | wizard | weasel | wringer | wrangle | worthy | villain |
| Task | SS | df | MS | F | p | η2p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAY | ||||||
| Masking | 1.007 | 1 | 1.007 | 119.345 | <0.001 | 0.605 |
| Morphological Status | 0.179 | 1 | 0.179 | 57.676 | <0.001 | 0.425 |
| Difficulty | 0.960 | 1 | 0.960 | 49.106 | <0.001 | 0.386 |
| Masking Morphological Status | 0.264 | 1 | 0.264 | 53.772 | <0.001 | 0.408 |
| Morphological Status Difficulty | 0.025 | 1 | 0.025 | 8.005 | 0.006 | 0.093 |
| Masking Morphological Status Difficulty | 0.048 | 1 | 0.048 | 9.826 | 0.002 | 0.112 |
| SYLLABLES | ||||||
| Masking | 0.572 | 1 | 0.572 | 66.167 | <0.001 | 0.459 |
| Morphological Status | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.004 | 0.953 | 0 |
| Difficulty | 0.386 | 1 | 0.386 | 14.5 | <0.001 | 0.157 |
| Masking Morphological Status | 0.003 | 1 | 0.003 | 1.165 | 0.284 | 0.015 |
| Morphological Status Difficulty | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.246 | 0.621 | 0.003 |
| Masking Morphological Status Difficulty | 0.002 | 1 | 0.002 | 0.64 | 0.426 | 0.008 |
| PICTURE | ||||||
| Masking | 0.222 | 1 | 0.222 | 148.727 | <0.001 | 0.656 |
| Morphological Status | 0.006 | 1 | 0.006 | 5.541 | 0.021 | 0.066 |
| Difficulty | 0.127 | 1 | 0.127 | 34.4 | <0.001 | 0.306 |
| Masking Morphological Status | 0.005 | 1 | 0.005 | 4.015 | 0.049 | 0.049 |
| Morphological Status Difficulty | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.641 | 0.426 | 0.008 |
| Masking MorphologicalStatus Difficulty | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.006 | 0.939 | 0 |
| VERIFY | ||||||
| Masking | 0.218 | 1 | 0.218 | 48.906 | <0.001 | 0.385 |
| Morphological Status | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.058 | 0.811 | 0.001 |
| Difficulty | 0.013 | 1 | 0.0123 | 0.994 | 0.322 | 0.013 |
| Masking Morphological Status | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0.246 | 0.622 | 0.003 |
| Morphological Status Difficulty | 0.003 | 1 | 0.003 | 1.612 | 0.208 | 0.020 |
| Masking Morphological Status Difficulty | 0.002 | 1 | 0.002 | 1.017 | 0.316 | 0.013 |
References
- National Governors Association Center for Best Practices & Council of Chief State School Officers. Key Shifts in English Language Arts. 2010. Available online: http://www.thecorestandards.org/other-resources/key-shifts-in-english-language-arts/ (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Hiebert, E.H.; Goodwin, A.P.; Cervetti, G.N. Core vocabulary: Its morphological content and presence in exemplar texts. Read. Res. Q. 2018, 53, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Education Statistics [NCES]. The Nation’s Report Card: National Achievement-Level Results; National Center for Education Statistics, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.nationsreportcard.gov/ (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Pyle, N.; Vaughn, S. Remediating reading difficulties in a response to intervention model with secondary students. Psychol. Sch. 2012, 49, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cirino, P.T.; Romain, M.A.; Barth, A.E.; Tolar, T.D.; Fletcher, J.M.; Vaughn, S. Reading skill components and impairments in middle school struggling readers. Read. Writ. 2013, 26, 1059–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, M.F.; Brasseur, I.F.; Deshler, D.D.; Catts, H.W.; Marquis, J.G.; Mark, C.A.; Stribling, J.W. What is the reading component skill profile of adolescent struggling readers in urban schools? Learn. Disabil. Q. 2009, 32, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur-Hock, I.F.; Hock, M.F.; Kieffer, M.J.; Biancarosa, G.; Deshler, D.D. Adolescent struggling readers in urban schools: Results of a Latent Class Analysis. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2011, 21, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglin, J.M.; Miller, G.A.; Wakefield, P.C. Vocabulary development: A morphological analysis. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child Dev. 1993, 58, i+iii+v-vi+1–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, W.E.; Anderson, R.C. How Many Words Are There in Printed School English? Read. Res. Q. 1984, 19, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.B.; Gutlohn, L.; van Dijk, W. Morpheme frequency in academic words: Identifying high-utility morphemes for instruction. Lit. Res. Instr. 2019, 58, 184–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, W.E.; Anderson, R.C.; Schommer, M. Morphological families in the internal lexicon. Read. Res. Q. 1989, 24, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moats, L.C.; Smith, C. Derivational morphology: Why it should be included in language assessment and instruction. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 1992, 23, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nippold, M.A.; Sun, L. Knowledge of morphologically complex words: A developmental study of older children and young adolescents. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2008, 39, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastle, K. The place of morphology in learning to read in English. Cortex 2019, 116, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, A.P.; Cho, S.-J. Unraveling vocabulary learning: Reader and item-level predictors of vocabulary learning within comprehension instruction for fifth and sixth graders. Sci. Stud. Read. 2016, 20, 490–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, A.P.; Petscher, Y.; Carlisle, J.F.; Mitchell, A.M. Exploring the dimensionality of morphological knowledge for adolescent readers: Dimensionality of morphological knowledge. J. Res. Read. 2017, 40, 91–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutchen, D.; Logan, B. Inside incidental word learning: Children’s strategic use of morphological information to infer word meanings. Read. Res. Q. 2011, 46, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, A.; Nagy, W. The acquisition of English derivational morphology. J. Mem. Lang. 1989, 28, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, E.; Currie, N.K.; Tong, S.X.; Cain, K. The relations between morphological awareness and reading comprehension in beginner readers to young adolescents. J. Res. Read. 2021, 44, 110–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, M.J.; Lesaux, N.K. Direct and Indirect Roles of Morphological Awareness in the English Reading Comprehension of Native English, Spanish, Filipino, and Vietnamese Speakers: Roles of Morphological Awareness. Lang. Learn. 2012, 62, 1170–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, C.P.; Daley, S.G.; Xu, Y.; Graham, S.; Li, Z.; Hall, T.E. Shared knowledge between reading and writing among middle school adolescent readers. Elem. Sch. J. 2020, 120, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltheart, M.; Rastle, K.; Perry, C.; Langdon, R.; Ziegler, J. DRC: A dual route cascaded model of visual word recognition and reading aloud. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 53, 204–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harm, M.W.; Seidenberg, M.S. Computing the meanings of words in reading: Cooperative division of labor between visual and phonological processes. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 111, 662–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastle, K.; Davis, M.H. Morphological decomposition based on the analysis of orthography. Lang. Cogn. Process. 2008, 23, 942–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelonkiewicz, J.R.; Ktori, M.; Crepaldi, D. Morphemes as letter chunks: Discovering affixes through visual regularities. J. Mem. Lang. 2020, 115, 104152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, W.E.; Carlisle, J.F.; Goodwin, A.P. Morphological knowledge and literacy acquisition. J. Learn. Disabil. 2014, 47, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastle, K.; Davis, M.H.; New, B. The broth in my brother’s brothel: Morpho-orthographic segmentation in visual word recognition. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2004, 11, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehri, L.C. Learning to read words: Theory, findings, and issues. Sci. Stud. Read. 2005, 9, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, E.D.; Perfetti, C.A. Morphology in word identification: A word-experience model that accounts for morpheme frequency effects. Sci. Stud. Read. 2003, 7, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shachar, M.; Dougherty, R.F.; Deutsch, G.K.; Wandell, B.A. The development of cortical sensitivity to visual word forms. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, J.F.; Stone, C.A. Exploring the role of morphemes in word reading. Read. Res. Q. 2005, 40, 428–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, N.; Rastle, K.; Ricketts, J. Morphological effects in visual word recognition: Children, adolescents, and adults. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2018, 44, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, S.H.; Whalen, R.; Kirby, J.R. Do children see the danger in dangerous? Grade 4, 6, and 8 children’s reading of morphologically complex words. Appl. Psycholinguist. 2011, 32, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutchen, D.; Logan, B.; Biangardi-Orpe, U. Making meaning: Children’s sensitivity to morphological information during word reading. Read. Res. Q. 2009, 44, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalis, S.; Colé, P.; Sopo, D. Morphological awareness in developmental dyslexia. Ann. Dyslexia 2004, 54, 114–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, J.F.; Katz, L.A. Effects of word and morpheme familiarity on reading of derived words. Read. Writ. 2006, 19, 669–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.E.; Liberman, I.Y. The role of phonology and orthography in morphological awareness. In Morphological Aspects of Language Processing; Feldman, L.B., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 157–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tsesmeli, S.N.; Seymour, P.H.K. Derivational morphology and spelling in dyslexia. Read. Writ. 2006, 19, 587–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, L.S. Morphological awareness skills of English language learners and children with dyslexia. Top. Lang. Disord. 2008, 28, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, A. Knowledge of suffixed words: A comparison of reading disabled and nondisabled readers. Ann. Dyslexia 1997, 47, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.K.; Goodwin, A.P.; Compton, D.L.; Kearns, D.M. Multisyllabic word reading as a moderator of morphological awareness and reading comprehension. J. Learn. Disabil. 2014, 47, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.J.; Carroll, J.M. Early predictors of phonological and morphological awareness and the link with reading: Evidence from children with different patterns of early deficit. Appl. Psycholinguist. 2015, 36, 509–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, W.; Berninger, V.W.; Abbott, R.D. Contributions of morphology beyond phonology to literacy outcomes of upper elementary and middle-school students. J. Educ. Psychol. 2006, 98, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, J.; Pring, L. The processing of inflectional morphology: A comparison of children with and without dyslexia. Read. Writ. Interdiscip. J. 2004, 17, 567–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, A.P.; Petscher, Y.; Tock, J. Morphological supports: Investigating differences in how morphological knowledge supports reading comprehension for middle school students with limited reading vocabulary. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2020, 51, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breadmore, H.L.; Carroll, J.M. Effects of orthographic, morphological and semantic overlap on short-term memory for words in typical and atypical development. Sci. Stud. Read. 2016, 20, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quémart, P.; Casalis, S. Visual processing of derivational morphology in children with developmental dyslexia: Insights from masked priming. Appl. Psycholinguist. 2015, 36, 345–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, S.H.; Parrila, R.; Kirby, J.R. A review of the evidence on morphological processing in dyslexics and poor readers: A strength or weakness. In The SAGE Handbook of Dyslexia; SAGE Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 212–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbro, C.; Arnbak, E. The role of morpheme recognition and morphological awareness in dyslexia. Ann. Dyslexia 1996, 46, 209–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.; Lo, S. Is morphological priming stronger for transparent than opaque words? It depends on individual differences in spelling and vocabulary. J. Mem. Lang. 2013, 68, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, C. Reading ability: Lexical quality to comprehension. Sci. Stud. Read. 2007, 11, 357–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, S.J. The method of repeated readings. Read. Teach. 1979, 32, 403–408. [Google Scholar]
- Förster, J.; Higgins, E.T.; Bianco, A.T. Speed/accuracy decisions in task performance: Built-in trade-off or separate strategic concerns? Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2003, 90, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrila, R.; Kirby, J.R.; McQuarrie, L. Articulation rate, naming speed, verbal short-term memory, and phonological awareness: Longitudinal predictors of early reading development? Sci. Stud. Read. 2004, 8, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roembke, T.C.; Hazeltine, E.; Reed, D.K.; McMurray, B. Automaticity of word recognition is a unique predictor of reading fluency in middle-school students. J. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 118, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roembke, T.C.; Hazeltine, E.; Reed, D.K.; McMurray, B. Automaticity as an independent trait in predicting reading outcomes in middle-school. Dev. Psychol. 2021, 57, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitmeyer, B.G.; Ogmen, H. Recent models and findings in visual backward masking: A comparison, review, and update. Percept. Psychophys. 2000, 62, 1572–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanovich, K.E. Toward an interactive-compensatory model of individual differences in the development of reading fluency. Read. Res. Q. 1980, 16, 32–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, R.W. Woodcock Reading Mastery Tests, 3rd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lesaux, N.K.; Harris, J.R. An investigation of comprehension processes among adolescent English learners with reading difficulties. Top. Lang. Disord. 2017, 37, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, S.; Gersten, R.; Dimino, J.; Taylor, M.J.; Newman-Gonchar, R.; Krowka, S.; Kieffer, M.J.; McKeown, M.; Reed, D.; Sanchez, M.; et al. Providing Reading Interventions for Students in Grades 4–9 (WWC 2022007); National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance (NCEE), Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics. WebCelex [Web Application. 2001. Available online: http://celex.mpi.nl/ (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi, Version 2.3 [Computer Software]. 2022. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Singmann, H. Afex: Analysis of Factorial Experiments. [R Package]. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=afex (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. [R Package]. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Tukey, J.W. The Problem of Multiple Comparisons; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1953; Unpublished manuscript. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Some statistical issues in psychological research. In Handbook of Clinical Psychology; Wolman, B.B., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1965; pp. 95–121. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analyses for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Crosson, A.C.; Lei, P.-W.; Cheng, W.; McKeown, M.G. The curious role of morphological family size in language minority learners’ problem solving of unfamiliar words. Sci. Stud. Read. 2020, 24, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Morphological awareness and reading comprehension: Differential mediation mechanisms in native English speakers, fluent English learners, and limited English learners. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2020, 199, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, J.A.; Branum-Martin, L.; Sun, C.; Lee-James, R. The impact of dialect density on the growth of language and reading in African American Children. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2018, 49, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.R.; Deacon, S.H.; Bowers, P.N.; Izenberg, L.; Wade-Woolley, L.; Parrila, R. Children’s morphological awareness and reading ability. Read. Writ. 2012, 25, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastle, K.; Tyler, L.K.; Marslen-Wilson, W. New evidence for morphological errors in deep dyslexia. Brain Lang. 2006, 97, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, F.; Bailey, K.G.; Ferraro, V. Good-enough representations in language comprehension. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2002, 11, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
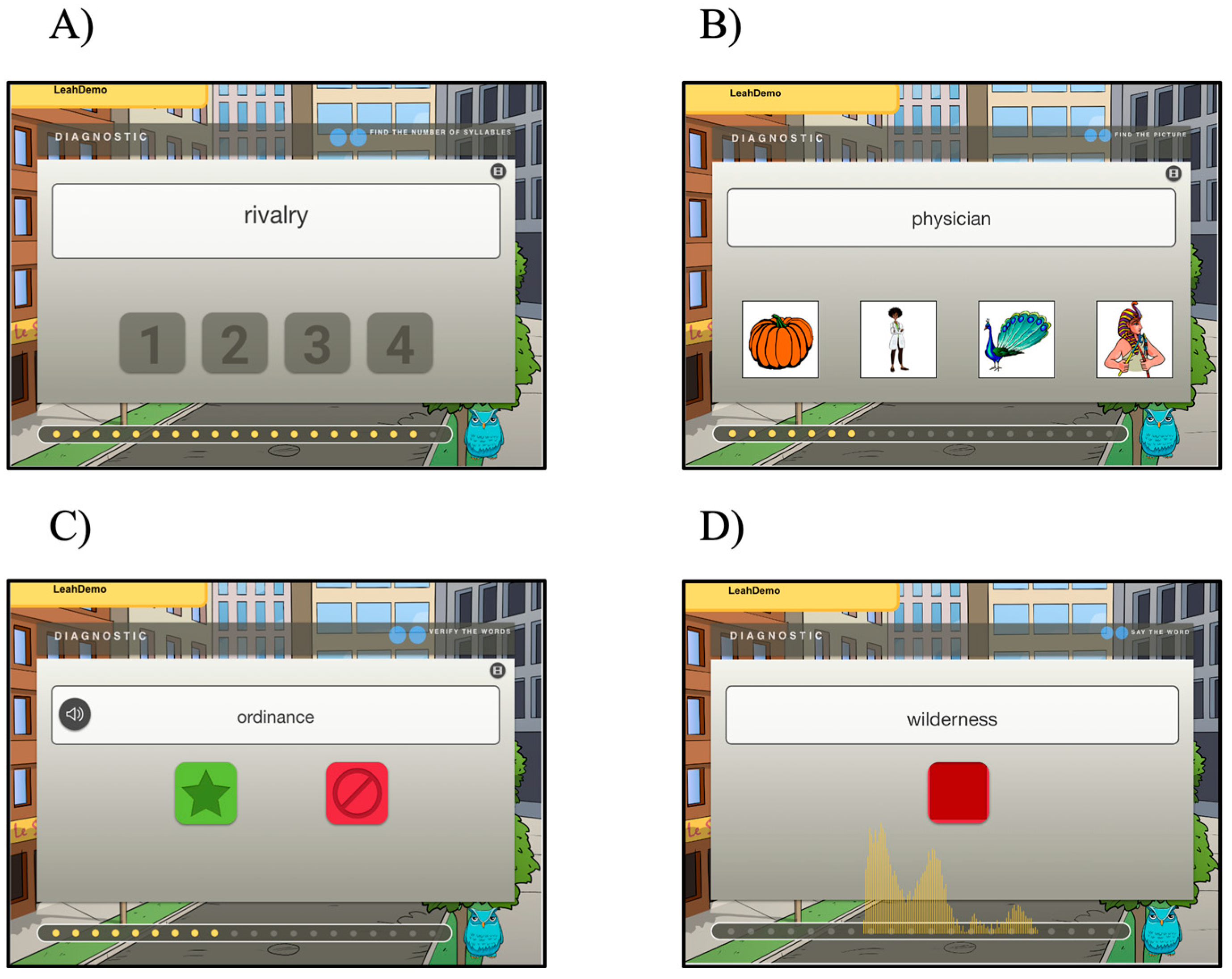



| Task | Response | Pathway(s) Targeted |
|---|---|---|
| Count the Number of Syllables | Written target word presented. Participant clicks on the correct number of syllables in the word. | O → P → S |
| Find the Picture | Written target word presented. Participant clicks on picture that best represents target. | O → S |
| Say the Word | Written target word presented. Participant says the word aloud and clicks on a button when finished. | O → P → S O → S |
| Verify the Word | Spoken and written target word presented. Participant clicks green or red button to indicate whether the stimuli matched. | O → P → S O → S |
| Property | Syllables | Picture | Say | Verify | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | S | C | S | C | S | C | S | |
| Length | 7.40 | 7.38 | 7.25 | 7.25 | 7.35 | 7.35 | 7.3 | 7.28 |
| Syllables | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 2.50 |
| Log Frequency | 7.59 | 7.79 | 7.59 | 7.88 | 7.92 | 7.83 | 7.66 | 7.42 |
| Orthographic Neighborhood | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.43 |
| Masked | Unmasked | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex | Simple | Complex | Simple | |
| Full Sample | ||||
| Say | 0.87 (0.13) | 0.78 (0.15) | 0.93 (0.07) | 0.93 (0.08) |
| Syllables | 0.86 (0.12) | 0.86 (0.12) | 0.94 (0.09) | 0.94 (0.09) |
| Picture | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.94 (0.06) | 0.98 (0.03) | 0.99 (0.02) |
| Verify | 0.93 (0.07) | 0.93 (0.08) | 0.98 (0.06) | 0.99 (0.07) |
| Proficient Word Readers | ||||
| Say | 0.91 (0.1) | 0.84 (0.10) | 0.95 (0.05) | 0.96 (0.07) |
| Syllables | 0.89 (0.09) | 0.90 (0.11) | 0.96 (0.08) | 0.96 (0.09) |
| Picture | 0.96 (0.04) | 0.96 (0.04) | 0.98 (0.03) | 0.99 (0.03) |
| Verify | 0.94 (0.07) | 0.95 (0.08) | 0.98 (0.06) | 0.99 (0.09) |
| Students with WRD | ||||
| Say | 0.80 (0.16) | 0.64 (0.13) | 0.87 (0.08) | 0.88 (0.09) |
| Syllables | 0.79 (0.14) | 0.91 (0.12) | 0.92 (0.11) | 0.90 (0.10) |
| Picture | 0.89 (0.08) | 0.89 (0.08) | 0.97 (0.04) | 0.99 (0.03) |
| Verify | 0.92 (0.08) | 0.91 (0.09) | 0.99 (0.04) | 0.99 (0.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zimmermann, L.M.; Rodgers, D.B.; McMurray, B. Automatic Morphological Processing in Middle School Students with and without Word Reading Difficulties. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080849
Zimmermann LM, Rodgers DB, McMurray B. Automatic Morphological Processing in Middle School Students with and without Word Reading Difficulties. Education Sciences. 2024; 14(8):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080849
Chicago/Turabian StyleZimmermann, Leah M., Derek B. Rodgers, and Bob McMurray. 2024. "Automatic Morphological Processing in Middle School Students with and without Word Reading Difficulties" Education Sciences 14, no. 8: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080849
APA StyleZimmermann, L. M., Rodgers, D. B., & McMurray, B. (2024). Automatic Morphological Processing in Middle School Students with and without Word Reading Difficulties. Education Sciences, 14(8), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14080849







