Abstract
Continuing medical education (CME) and continuing education (CE) provide frameworks for assimilating and disseminating new advancements and are mainstays of clinicians’ professional development and accreditation. However, traditional CME/CE approaches may be challenged in providing opportunities for integrated and interprofessional learning and helping clinicians effectively translate innovations into individual practice. This Commentary describes the reflective learning approach, including its integration into CME/CE and how it can support interprofessional education. Also identified are barriers to reflective and interprofessional learning implementation and CME/CE access. The Commentary provides insights based on point-of-care reflection data and outlines considerations in trialing the use of an artificial intelligence (AI)-driven digital platform for reflective learning. Further, the Commentary describes how the AI-driven digital platform may help overcome barriers to reflective learning and interprofessional education and support equitable CME/CE program access.
1. Introduction
The continued proliferation of scientific and clinical developments can be overwhelming for healthcare professionals and lead to a gap between evidence-based information and clinical practices [1]. In the last year alone, the annual number of total MedlineR citations published has approached nearly 1.4 million [2]. Continuing medical education (CME) and continuing education (CE) provide frameworks for assimilating and disseminating new advancements and are mainstays of clinicians’ professional development and accreditation. An important question: are they providing opportunities for integrated and interprofessional learning and helping clinicians effectively translate innovations into practice?
In recent decades the learning approaches employed in CME/CE have continued to evolve, in part spurred by reports such as the 2010 Lifelong Learning in Medicine and Nursing Final Conference Report that advocated “decreasing the focus on the didactic lecture as the primary format for CE; increasing awareness of practice-based learning; heightening attentiveness to the importance of CE as a tool to improve competency and performance in the academic health center; developing interprofessional education; and instilling lifelong learning skills” [3]. Such active and more integrated learning approaches can help break through the ubiquity of available medical information to help clinicians access new knowledge and apply it in the context of practice change [4].
One active and integrated learning approach being used in CME/CE is reflective learning. Reflection is important for professional competence [5] and lifelong learning [6]. Reflection can enhance interprofessional education as well [7]. Yet while there are benefits to reflective learning, there can be barriers to its implementation too [8,9], including the distractions of technology and multi-tasking in today’s fast-paced environment, which may limit opportunities for constructive internal reflection [10]. For example, there is evidence that performing more than one task at a time can impair the ability to be introspective [11]. In addition, individual clinicians can face barriers as they seek to identify and obtain CME/CE opportunities, and such barriers can involve issues related to access, equity, and inclusion [12,13].
This Commentary describes reflective learning and how it has been used in CME/CE and interprofessional education. In addition, barriers to reflective and interprofessional learning implementation and CME/CE access are identified. Also highlighted are insights from point-of-care reflections and considerations in trialing the use of an artificial intelligence (AI)-driven digital platform for reflective learning. Finally, the Commentary outlines how the AI-driven digital platform may help overcome reflective learning and interprofessional education barriers and support equitable CME/CE program access.
2. The Reflective Learning Approach
As a metacognitive process, reflection supports lifelong learning and is critical for personal and professional growth and building therapeutic relationships [14]. Reflective practice has become widespread in the knowledge advancement of multiple professions in healthcare and can lead to improved patient care and health outcomes [15].
Reflection is not a new education strategy. Nearly a century ago, Dewey advocated for the need to reflect as part of the education process, believing that reflecting on one’s own practice required courage and open-mindedness [16]. The reflective learning approach in CME/CE is also not unique. In 1997, Brigley et al. identified that “continuing professional development grounded in principles of reflective practice is more effective than traditional CME in sustaining relevance, coherence, and progression of professional learning” [17]. Yet progress in integrating reflective learning in CME/CE has been slow. A 2010 report on Redesigning Continuing Education in Health Professions from the Institute of Medicine documented that lectures and conference sessions were the most commonly used CE methods [18], and even today, active learning strategies like reflective learning are still not as frequent in CME as a lecture [19].
2.1. Reflection and Professional Accreditation
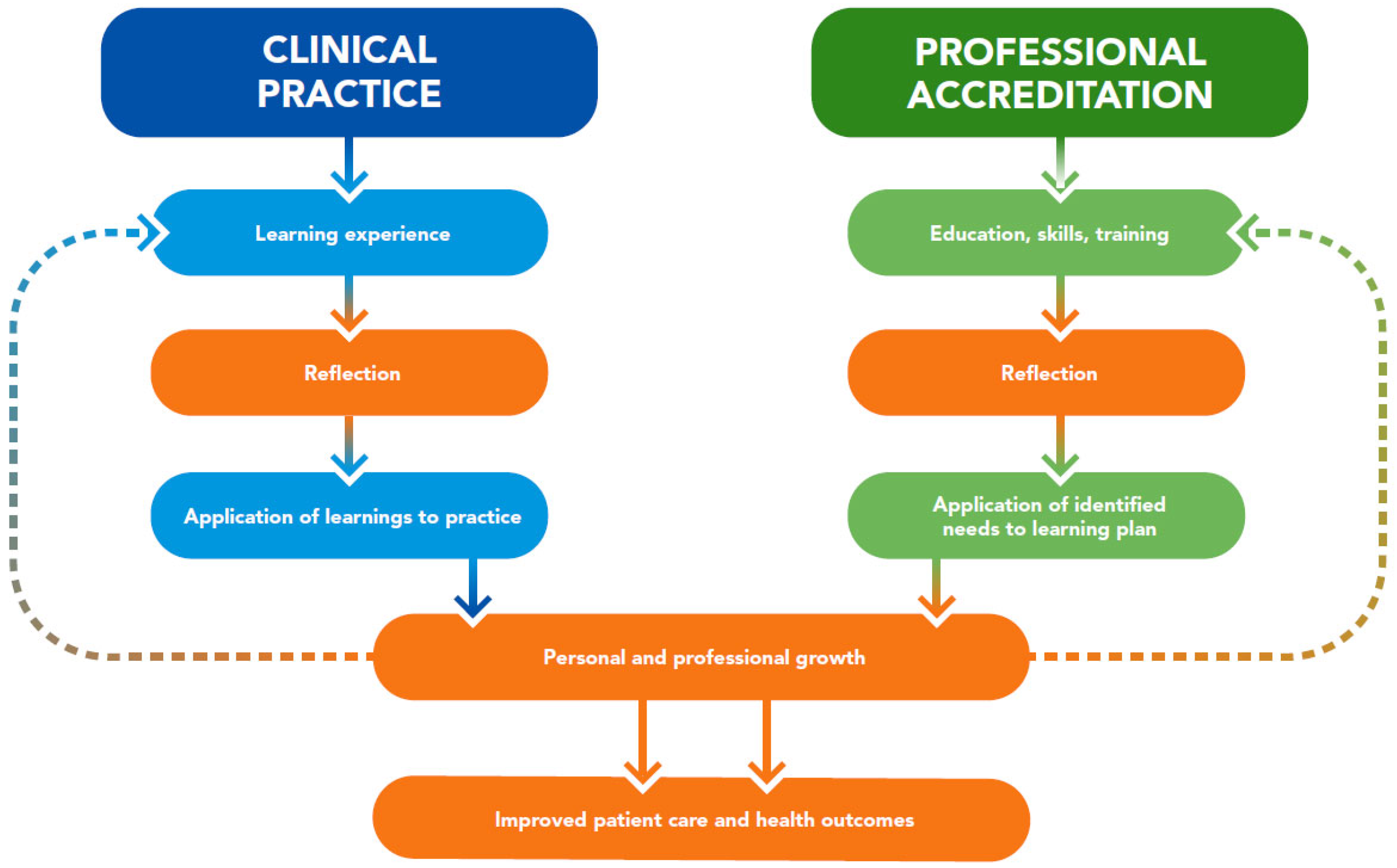
Continuing education and professional development have evolved over the years as learners have taken more control of their career paths [20], and reflection has become integral to professional development in multiple ways. Professional organizations of healthcare governance have recommendations and requirements related to reflection [6]. Indeed, reflection is a core component of continuing professional development (CPD) for healthcare accrediting groups like the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education [21]. Reflective learning is also included as an evidence-based educational intervention in CME toolkits in medicine [22] and CE guides in nursing [23]. Reflection is integral to the self-assessments that are foundational for professional development portfolios, including those of nutrition and dietetic professionals [24]. In addition, some position statements note the importance of reflection for continuously improving patient care, such as those from the Accreditation Council on Graduate Medical Education [25] and the American Association of Medical Colleges [26]. Taken together, reflection in clinical practice and in professional accreditation aligns for the shared purpose of improving patient care and health outcomes (Figure 1).
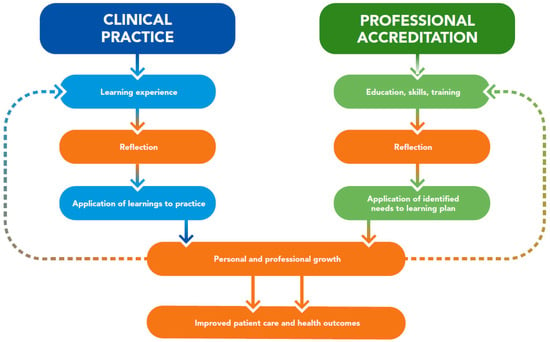
Figure 1.
Reflection in clinical practice and professional accreditation aligns to improve patient care and health outcomes.
2.2. Reflection Research
The research base supporting reflective learning is extensive and multiple models of reflection have been described [16,27,28,29,30,31,32]. While there is not a consistent definition of reflection and individual healthcare disciplines may have slightly different views of its role [33], reflective practice models typically describe reflection as starting with need awareness or practice disruption and are based on the premise that examining an experience builds knowledge and may help guide future practice [5].
One limitation of traditional education approaches is that they tend to be focused on updating the practitioner’s clinical knowledge [34] and thus may be less sensitive to the needs of the individual [35]. In contrast, reflection enhances personal development through self-awareness [36], and reflective learners assume responsibility for their own learning [34]. Such learner involvement is foundational to adult education, which is why reflecting supports the andragogical model of establishing the purpose of an activity and its application in real life [37].
Many studies and reviews have explored reflection in healthcare education. As an example, a reflective practice in healthcare education umbrella review (that included CE) documented over 500 reflective practice publications annually from 2011–2015 [38]. The authors concluded there appeared to be a positive association between reflection and different learning outcomes. Further, they reported reflective techniques were associated with multiple positive results, such as deep learning, understanding, and satisfaction [38]. Lowe et al. reported that when clinicians described learning without reflection, the learners believed there was less effect on their clinical practice. [39] Such views are in line with “surface learning,” which is described by Moon as occurring when learning only lasts through the end of an education course [40].
The importance of reflection in healthcare practice and workplace learning has also been considered. Miraglia and Asselin, in an integrative review on reflection as an educational strategy in nursing professional development, found many articles explored a reflective component in an educational program but without teaching about reflection or how to reflect on clinical experiences. They concluded it may be assumed reflection is an intuitive process, but practitioners would likely benefit from education on the reflection process [41]. Similarly, Cole identified that physiotherapists could find it difficult to employ reflective practice as a learning activity, yet Cole emphasized that for improved care, it is essential for practitioners to make the connection between reflection and action [42]. Koshy et al. also argued a practitioner’s contemplation of what will be performed differently in the future is the most critical stage in reflecting [43]. Purposeful reflection can provide a framework to facilitate this professional learning. In examining the critical role of reflection in work-based learning, Helyer explained that purposeful reflection provides a structure for making sense of learning so concepts and theories become rooted in practice [44].
2.3. Reflection Applications and Benefits
There are a number of different ways clinicians can reflect, from journal writing and discussions to the use of technology and other approaches [45]. In addition, there are different perspectives from which clinicians can reflect, such as individual, team, and societal perspectives [8]. Reflection is a method of quantifying meaningful qualitative feedback for further learning opportunities. Multiple benefits of reflective practice have been identified, including that reflection:
- “Increases learning from an experience or situation
- Promotes deep rather than superficial learning
- Identifies personal and professional strengths and weaknesses
- Identifies educational needs
- Results in the acquisition of new knowledge and skills
- Facilitates practitioners to understand their own beliefs, attitudes, and values
- Encourages self-motivated and self-directed learning
- Acts as a source of feedback and
- Improves personal and clinical confidence” [9].
Reflection can also help facilitate problem-solving, which may help practitioners use a more logical approach in seeking solutions. Importantly, reflection can help practitioners celebrate and highlight the good things that they perform, which can have “special virtue at those times when things feel bleak” [42]. In the education research literature, reflection is often “nested in multifaceted educational programs” [41], which may make identification of its specific benefits more challenging. However, there is evidence that, as an educational strategy, reflection allows practitioners the opportunity to explore personal biases, leading to transformed understandings and, subsequently, transformed practice. When reflection occurs at a group level, there is the potential for enhanced teamwork and impact on organizational-level practice [41].
2.4. Reflection and Interprofessional Continuing Education
Reflection can enhance interprofessional education [7]. Interprofessional continuing education is when “two or more professions learn about, from, and with each other to enable effective collaboration and improve health outcomes” [46]. Interprofessional education has evolved as a vital part of both healthcare quality and safety because of its potential to promote collaboration and communication, which can benefit health outcomes [47]. Similarly, there is also evidence that healthcare professionals’ engagement in interprofessional continuing education can improve patient and system outcomes [48]. It is not surprising, then, that leaders and employers are increasingly asking for educational strategies that will support interprofessional teamwork within their institutions [47].
Interprofessional literature on reflection frequently identifies reflection to be important for effective teamwork education as well as clinical practice [49,50]. However, it can be challenging to apply reflection’s theoretical dimensions to learning contexts and experiences like interprofessional education. Therefore, methods for encouraging and structuring reflection, as well as furthering its research application, are needed to effectively promote the use of reflection in interprofessional education [51].
2.5. Barriers to Reflective and Interprofessional Learning and CME/CE Implementation
Reflection can also face other barriers to integration into CME/CE, including those related to learners’ time, motivation, lack of understanding of the reflective process, discomfort in challenging/evaluating their own practice, uncertainty about which experiences/problems to reflect on, and lack of peer support [8,9].
Further, from diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) perspectives, clinicians may now be finding it more difficult to follow up on the self-reflections and pledges to change practices that they committed to through their engagement in DEI CME/CE. A strategic objective of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education is to “facilitate understanding that incorporating the issues of DEI into all aspects of accredited education will benefit healthcare professionals and the patients they serve” [52]. When significant as well as deep racial and ethnic injustices in the US became evident in 2020, through disproportionately greater death rates from COVID-19 and high-profile police-related deaths, some clinical leaders took direct action. For example, the Organization of Nurse Leaders published a Nurse’s Pledge to Champion Diversity, Equity, and Inclusivity [53]. Yet several years later, across industries, DEI roles are diminishing at a faster rate than non-DEI roles [54]. It may be that without DEI roles in clinical institutions, there are fewer programmatic resources for DEI education, and these limitations may be compounded by systemic barriers because of turnover in CPD planners, lack of administrative support and continuity in program planning, and challenges with the application of accreditation and quality standards.
There are potential barriers to interprofessional learning implementation, too, such as:
- Systemic barriers related to insufficient participation incentives and promotion;
- Behavioral barriers related to hierarchical issues between participating professions and differing attitudes on the relevance of interprofessional continuing education;
- Methodological barriers related to limited quality assurance measures (curricula/standardized evaluation) and faculty experience with interprofessional continuing education;
- Attitudinal barriers related to the role, relevance, and effectiveness of interprofessional continuing education as an education strategy [55].
For some professions, such as nursing, CE is “now readily recognized and implemented within the workplace versus outside of work hours” [56], which can help support learner access. However, in general, there can be multiple barriers to learners accessing CME/CE, including expense, time [57,58,59], and equity and inclusion in the development as well as delivery of education [12]. Historically physicians and nurses have preferred traditional instructional methods for CME, which may have been a barrier to CME/CE innovation [60,61]. Recently though, physicians have reported they would like to more frequently obtain CME for their patient-focused and self-directed learning as well as for their activities related to quality improvement and interprofessional education [62].
3. Use of an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Driven Digital Platform for Reflective Learning
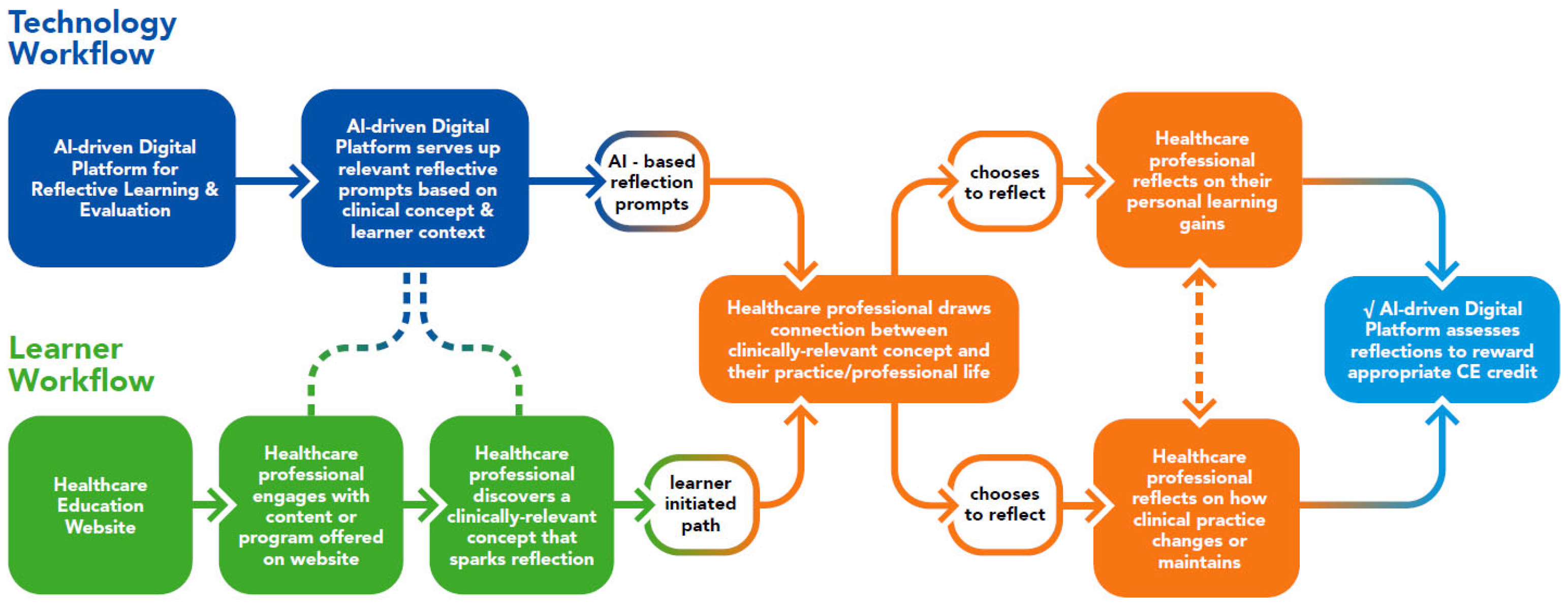
As outlined above, reflective learning can help healthcare professionals determine how evidence-based innovations can be applied in their clinical practices and can also support interprofessional education. To leverage this, an existing AI-driven digital platform for reflective learning was trialed through a current healthcare education website in December 2022. A diagram outlining the technology and learner workflows of this pilot trial is provided in Figure 2.
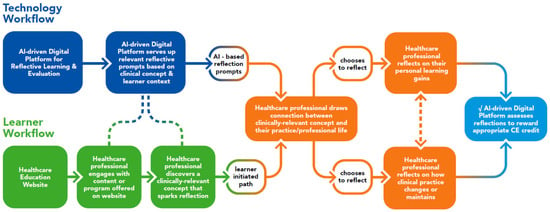
Figure 2.
Pathway trialed for an AI-driven platform for reflective learning CME/CE via a healthcare education website.
In the pilot trial, 16 unique healthcare professional learners self-selected to engage with various education modalities (infographics, podcast episodes, and video lessons) from a healthcare education website. The education modalities were tied to nutrition-focused topics, such as telehealth nutrition counseling, infant health and development, and care for patients with cancer. Learners responded to contextual prompts on concepts from each modality; based on anonymized data from the AI platform, learners provided a total of 43 written self-reflections, typing an average of 26 words per reflection, with the longest self-reflection totaling 75 words. The AI platform detected that 45% of learners would change future behaviors and/or apply new knowledge to their clinical practice, while 55% of learners provided deeper clinical and personal insights. Based on the pilot trial, several important considerations were identified for selecting an AI-driven digital platform for reflective learning through a healthcare education website. These considerations are described in more detail below.
First is the consideration that the opportunities for reflective learning can occur in various contexts and are not limited to a traditional classroom or lecture-based approach. Articles, podcasts, virtual meetings, and other encounters can all spark learning, particularly if there is an opportunity for clinicians to consider through reflection what the learning means for them as practitioners. Thus, the mechanism for reflective learning offered through a healthcare education website needs to be adaptable to the learning context. Digital platforms have the advantages of being learner-directed and asynchronous [60], fitting the need for adaptability and providing an opportunity for learning that can be faster, easier, and more self-directed.
A second consideration is the different types of clinicians and learners who may be engaged and how the learning experiences would be relevant and credible for them. As discussed earlier in this paper, reflection is an integral and recognized component for continuous professional development across healthcare practices [6] and can be beneficial for interprofessional education [7]. The goal is to trigger clinicians (whether physicians, physician associates, nurses, dietitians, or others) to think about how to connect the dots (individually or as a team) from engaging in learning opportunities to delivering improved care while at the same time receiving CME/CE credit. A digital platform for reflective learning offered through a healthcare education website needs to align with co-learning at the point of care and provide an accredited pathway for approval of a clinician’s reflection for CME/CE.
A third consideration for integrating a digital platform is to safeguard that the reflections are meaningful (i.e., not simple one-word responses) and can provide a source of data to gain insights into the experiences, encounters, and evidence-based clinical information driving real-world practice change. Such data can benefit interprofessional education development and help support clinician learning communities. For example, when teams come together in a common setting to watch a recorded program, peer support and co-learning can be fostered. When they reflect individually on the program, their reflections provide opportunities for understanding the application of education offerings. Using an AI-driven digital platform can be a practical way to help achieve these goals. The digital platform provides convenient access to educational offerings that can help support clinician learning communities. AI helps verify that learners’ reflections are not nonsensical responses and, thus, are appropriate for awarding CME/CE credit. Incorporating AI technology also provides the opportunity to anonymize and consolidate learners’ reflections to help identify trends.
A fourth consideration for integrating a digital platform through a healthcare education website is how it can help address barriers to reflective and interprofessional learning implementation and to learners accessing CME/CE. Digital education can be more inclusive of people and ideas [62], and using an AI-driven digital platform may help overcome common barriers and support equitable access to CME/CE programs (Table 1).

Table 1.
Opportunities for an AI-driven digital platform to help overcome common barriers to reflective learning, interprofessional education, and CME/CE access.
4. Conclusions
As lifelong learners, today’s clinicians are actively seeking ways to translate learning and information into practice. Reflective learning is an evidence-based education strategy that can be included in CME/CE to benefit lifelong learning and enhance interprofessional education. An AI-driven digital platform for reflective learning can provide a virtual backbone for integrated learning that can empower clinicians to take their point-of-care learnings and draw connections to their work. Such a platform can provide data to help better understand the needs of co-learning communities. Further, access to the platform through a health education website may help those healthcare settings challenged by limited time and resources to invest in education because the platform can provide a framework for overcoming barriers and supporting equitable CME/CE program access. In this way, the platform can help facilitate new concepts and ideas to become more meaningful for care delivery and to improve the practices of a broad and diverse range of clinicians.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S., K.N. and M.B.A.; writing and reviewing, B.C., S.D., P.A.L., N.S., K.N. and M.B.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This manuscript received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Data was abstracted from learners who had given informed consent, through the AI-driven digital platform, for the anonymized use of their reflections.
Data Availability Statement
All information available from the anonymized data has been included in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
B.C. is a partner at Miami Anesthesia Services, consultant at SCAD Ventures, and partner at CMEfy and Adaptrack; NS is a partner at SCAD Ventures, CMEfy, and Adaptrack; K.N. is an employee at SCAD Ventures, CMEfy, and Adaptrack; M.B.A. is an employee and shareholder of Abbott. S.D. and P.A.L. have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Davis, D. Continuing Education in the Health Professions: Research and Practice Considerations. Presented at the Meeting of the Advisory Committee on Interdisciplinary, Community-Based Linkages (ACICBL), Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011; Available online: https://www.hrsa.gov/sites/default/files/hrsa/advisory-committees/community-based-linkages/reports/eleventh-2011.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- National Library of Medicine. Citations Added to Medline by Fiscal Year. 2022. Available online: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/stats/cit_added.html (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Association of American Medical Colleges and the American Association of Colleges of Nursing. Lifelong Learning in Medicine and Nursing Final Conference Report. 2010. Available online: http://media01.commpartners.com/acme_eo2_docs/Lifelong_Learning_in_Medicine_and_Nursing.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Ramani, S.; McMahon, G.T.; Armstrong, E.G. Continuing professional development to foster behavior change: From principles to practice in health professions education. Med. Teach. 2019, 41, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.; Gordon, J.; MacLeod, A. Reflection and reflective practice in health professions education: A systematic review. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 2009, 14, 595–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.S.; Roberts, C. Contextualised reflective competence: A new learning model promoting reflective practice for clinical training. BMC Med. Educ. 2022, 22, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarezadeh, Y.; Pearson, P.; Dickinson, C. A model for using reflection to enhance interprofessional education. Int. J. Educ. 2009, 1, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayatilleke, N.; Mackie, A. Reflection as part of continuous professional development for public health professionals: A literature review. J. Public Health 2013, 35, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S. Embracing reflective practice. Educ. Prim. Care 2012, 23, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immordino-Yang, M.H.; Christodoulou, J.A.; Singh, V. Rest is no idleness: Implications of the brain’s default mode for human development and education. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2012, 7, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, B.; Lau, H. Manipulation of working memory contents selectively impairs metacognitive sensitivity in a concurrent visual discrimination task. Neurosci. Conscious 2015, 2015, niv002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agic, B.; Fruitman, H.; Maharaj, A.; Taylor, J.; Ashraf, A.; Henderson, J.; Ronda, N.; McKenzie, K.; Soklaridis, S.; Sockalingam, S. Advancing curriculum development and design in health professions education: A health equity and inclusion framework for education programs. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 2022, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.; Manley, K. Contemporary challenges of nursing CCPD: Time to change the model to meet citizens’ needs. Nurs. Open 2022, 9, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandars, J. The use of reflection in medical education. AMEE Guide No. 44. Med. Teach. 2009, 31, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.M.; Metersky, K. Reflective practice in nursing: A concept analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Knowl. 2022, 33, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, J. How We Think: A Restatement of the Relation of Reflective Thinking to the Educative Process; D.C. Heath & Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- Brigley, S.; Young, Y.; Littlejohns, P.; McEwen, J. Continuing education for medical professionals: A reflective model. Postgrad. Med. J. 1997, 73, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Committee on Planning a Continuing Health Care Professional Education Institute; Board on Health Care Services; Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Redesigning Continuing Education in the Health Professions; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/12704/redesigning-continuing-education-in-the-health-professions (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Bucklin, B.A.; Asdigian, N.L.; Hawkins, J.L.; Klein, U. Making it stick: Use of active learning strategies in continuing medical education. BMC Med. Educ. 2021, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinners, J.; Dickerson, P. 2019 Continuing education and professional development: Important milestones. J. Contin. Educ. Nurs. 2019, 50, 534–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Council for Pharmacy Education. Guidance on Continuing Professional Development (CPD) for the Profession of Pharmacy. January 2015. Available online: https://www.acpe-accredit.org/pdf/CPDGuidance%20ProfessionPharmacyJan2015.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- American Council for Continuing Medical Education, Society for Academic Continuing Medical Education. CE Educator’s Toolkit, Evidence-Based Design and Implementation Strategies for Effective Continuing Education. 2022. Available online: https://accme.org/sites/default/files/2023-02/985_20230124_ce_educators_toolkit.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- American Nurses Credentialing Center. Writing to the ANCC NCPD Accreditation Criteria, Self-Learning Guide. 2021. Available online: https://www.nursingworld.org/~4b0217/globalassets/docs/ancc/manuals/ancc-2784-ncpd-writing-to-the-ancc-criteria-final-v-1.0-9.27.21.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Commission on Dietetic Registration. Professional Development Portfolio Guide with Essential Practice Competencies. 2023. Available online: https://admin.cdrnet.org/vault/2459/web/CDR_PDP_Guide_cycles_ending_2028_50_.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Swing, S.R. The ACGME outcome project: Retrospective and prospective. Med. Teach. 2007, 29, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Core Entrustable Professional Activities for Entering Residency: Toolkits for the 13 Core EPAs-Abridged; Association of American Medical Colleges: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.aamc.org/media/20211/download (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Schon, D. The Reflective Practitioner. How Professionals Think in Action; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Schon, D. Educating the Reflective Practitioner; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Boud, D.; Keogh, R.; Walker, D. Reflection: Turning Experience into Learning; Routledge: London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Mezirow, J. Transformative Dimensions of Adult Learning; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hatton, N.; Smith, D. Reflection in teacher education: Towards definition and implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 1995, 11, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.A. A Handbook of Reflective and Experiential Learning; Routledge: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mantzourani, E.; Desselle, S.; Le, J.; Lonie, J.M.; Lucas, C. The role of reflective practice in healthcare professions: Next steps for pharmacy education and practice. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2019, 15, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.; Radloff, A. Enhancing reflective practice through online learning: Impact of clinical practice. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2008, 4, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M. Learning through reflective practice: A professional approach to effective continuing professional development among healthcare professionals. Res. Post-Compuls. Educ. 2000, 5, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, A.H. Private thoughts in public spheres: Issues in reflection and reflective practices in nursing. J. Adv. Nurs. 2001, 36, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, M.S. The Adult Learner: A Neglected Species, 4th ed.; Gulf Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Fragkos, K.C. Reflective practice in healthcare education: An umbrella review. Educ. Sci. 2016, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.; Rappolt, S.; Jaglal, S.; Macdonald, G. The role of reflection in implementing learning from continuing education into practice. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 2007, 27, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.A. Using reflective learning to improve the impact of short courses and workshops. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 2004, 24, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, R.; Asselin, M.E. Reflection as an educational strategy in nursing professional development. J. Nurses Prof. Dev. 2015, 3, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M. Reflection in healthcare practice: Why is it useful and how might it be done? Work. Based Learn. Prim. Care 2005, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Koshy, K.; Limb, C.; Gundogan, B.; Whithurst, K.; Jafree, D.J. Reflective practice in health care and how to reflect effectively. Int. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 2, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helyer, R. Learning through reflection: The critical role of reflection in work-based learning (WBL). J. Work.-Appl. Manag. 2015, 7, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chreitien, K.; Goldman, E.; Faselis, C. The reflective writing class blog: Using technology to promote reflection and professional development. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2008, 23, 2066–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Framework for Action on Interprofessional Education & Collaborative Practice. September 2010. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/framework-for-action-on-interprofessional-education-collaborative-practice (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Regnier, K.; Chappell, K.; Travlos, D.V. The role and rise of interprofessional continuing education. J. Med. Regul. 2019, 105, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, S.; Fletcher, S.; Barr, H.; Birch, I.; Boet, S.; Davies, N.; McFadyen, A.; Rivera, J.; Kitto, S. A BEME systematic review of the effects of interprofessional education: BEME Guide No. 39. Med. Teach. 2016, 38, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, H.; Koppel, I.; Reeves, S.; Hammick, M.; Freeth, D. Effective Interprofessional Education: Argument, Assumption, and Evidence; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- D’Eon, M. A blueprint for interprofessional learning. Med. Teach. 2004, 26, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, P.G. Reflecting on reflection in interprofessional education: Implications for theory and practice. J. Interprof. Care 2009, 23, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Resources. Available online: https://www.accme.org/diversity-equity-inclusion-resources (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Conroy, C.A.; DuBois, S.; Hudson-Jinks, T.; Mombrun, C.; Raymond, N.; Waddell, A.; Oberlies, A.S. Taking a stand: Developing a nurse’s pledge to champion diversity, equity, and inclusivity. Nurse Lead. 2021, 19, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayas, R.; Aceves, P.; Rawlings, D. Cutting Costs at the Expense of Diversity. 7 February 2023. Revelio Labs. Available online: https://www.reveliolabs.com/news/social/cutting-costs-at-the-expense-of-diversity/ (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Altin, S.V.; Tebest, R.; Kautz-Freimuth, S.; Redaelli, M.; Stock, S. Barriers in the implementation of interprofessional continuing education programs—A qualitative study from Germany. BMC Med. Educ. 2014, 13, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, P.; Graebe, J. Nursing continuing professional development—A paradigm shift. J. Contin. Educ. Nurs. 2020, 51, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlambo, M.; Silen, C.; McGarth, C. Lifelong learning and nurses’ continuing professional development, a metasynthesis of the literature. BMC Nurs. 2021, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, M.O.; Blanshan, A.S.; Huneke, K.M.; Thomas, B.L.B.; Cook, D.A. Barriers to identifying and obtaining CME: A national survey of physicians, nurse practitioners and physician assistants. BMC Med. Educ. 2021, 21, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.A.; Price, D.W.; Wittich, C.M.; West, C.P.; Blachman, M.J. Factors influencing physicians’ selection of continuous professional development activities: A cross-specialty national survey. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 2017, 37, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, E.A.; Girard, D.E.; Wessel, K.; Becker, T.M.; Choi, D. Barriers to innovation in continuing medical education. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 2008, 28, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilcher, J.W.; Bedford, L. Willingness and preferences of nurses related to learning with technology. J. Nurses Prof. Dev. 2011, 27, E10–E16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.M.; Kaur, G.; Nematollahi, S.; Ambinder, D.; Shafer, K.; Sulistio, M.; Berlacher, K.; Goyal, A. Medical education in the digital era: A new paradigm for acquiring knowledge and building communities. JACC Adv. 2022, 1, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).